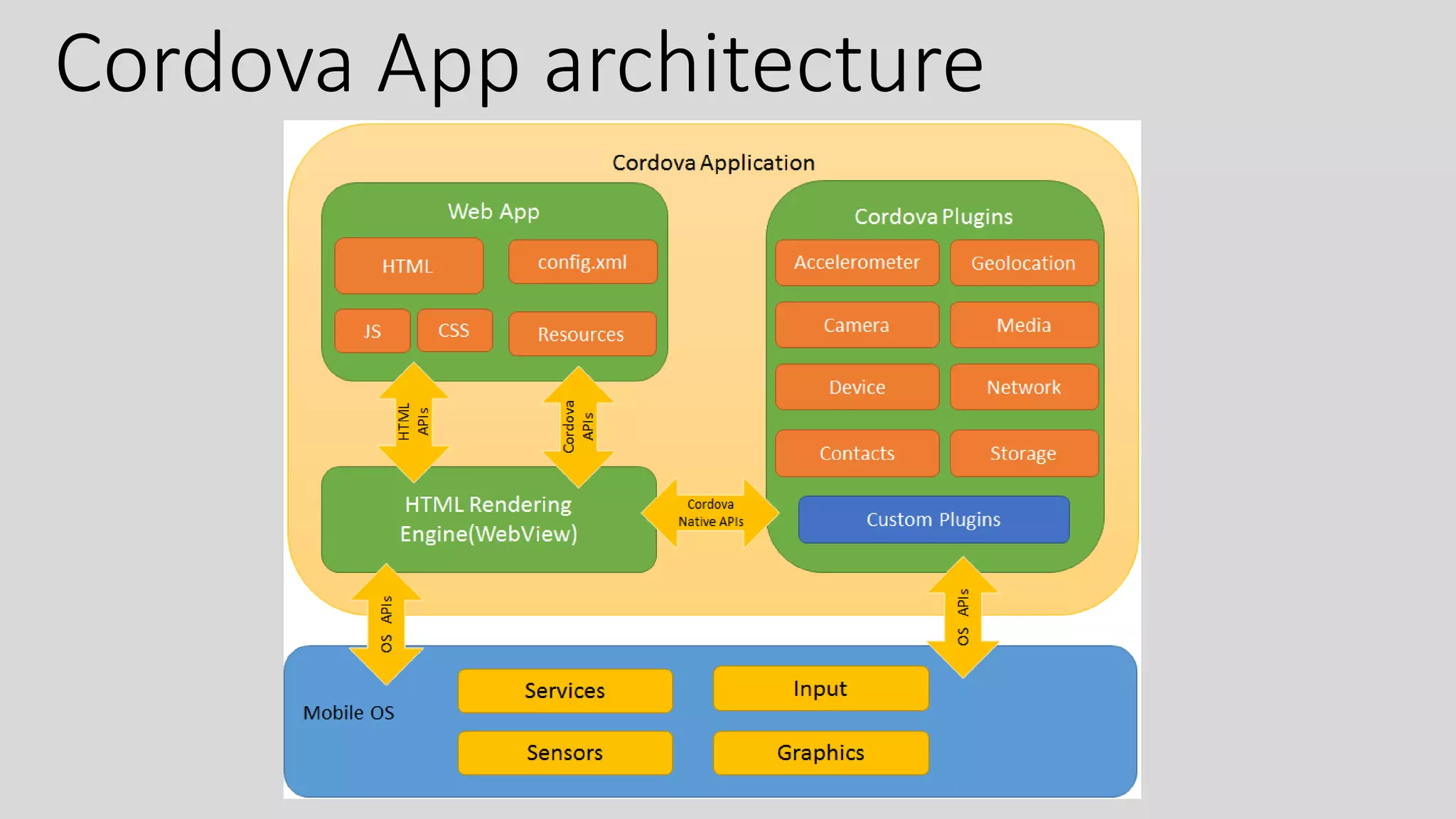
- Hybrid mobile apps are built using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript but wrapped in a native container using frameworks like Cordova or Apache Cordova. This allows them to work as native apps and access device capabilities.
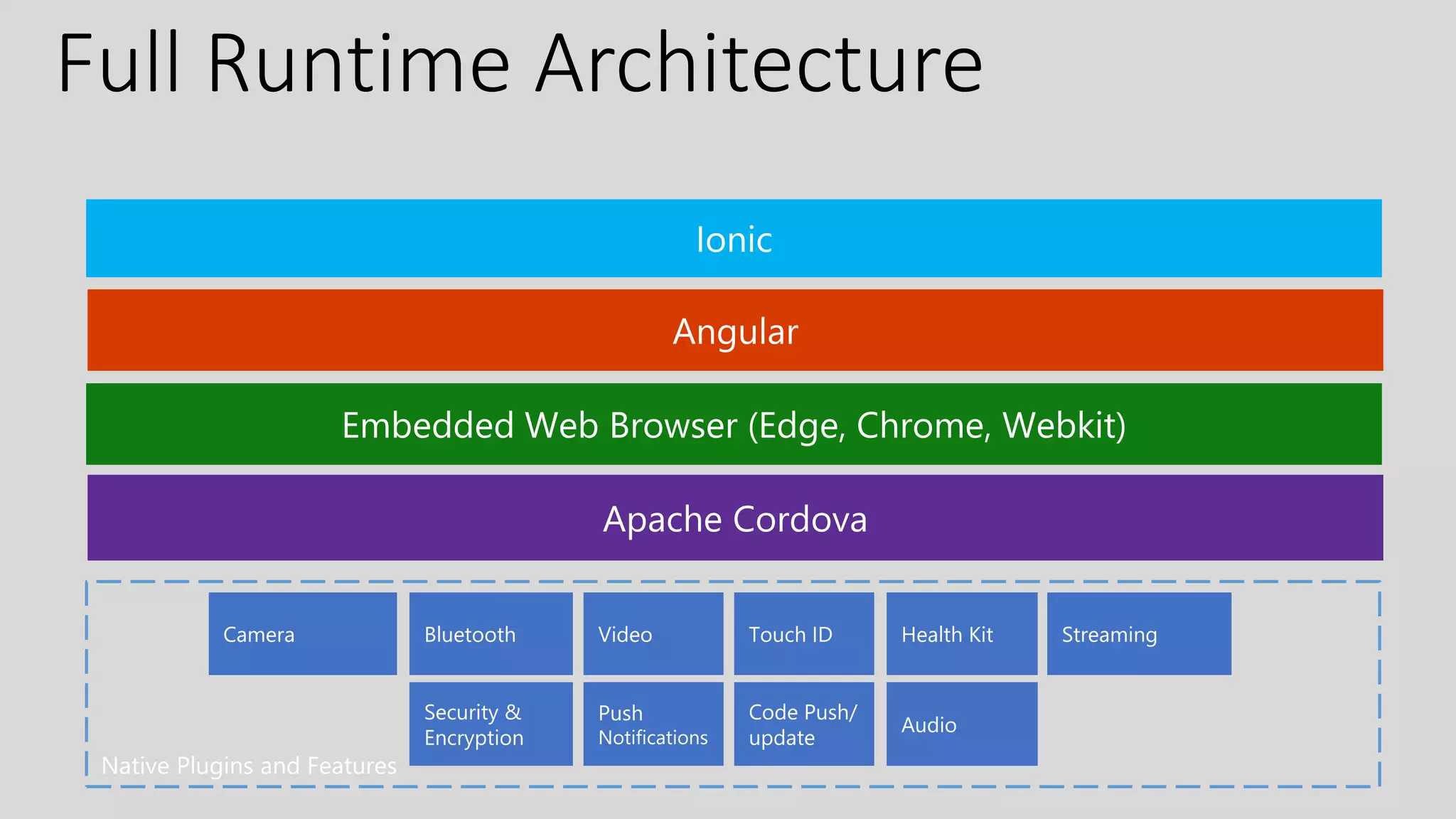
- Ionic is a popular framework for developing interactive hybrid mobile apps that uses Angular and supports mobile-specific components. Apps are developed using web technologies and published using Cordova.
- The architecture involves a client-side single page app interacting via RESTful services with a server-side backend for business logic and data storage. Cordova tools provide access to native device features.












![Env. to deploy Cordova apps
Common:
• NPM [v.^3.10]
• Node.js [v.^6]
• Cordova (npm install –g cordova) [v.6.4.0 - latest stable]
• Ionic (npm install –g ionic) [v.2.0 RC 2 - latest stable]
• Visual Studio 2013+
• Tools for Apache Cordova (extension for VS)
For deploy to Android:
• Java Development Kit (JDK) [v.8+]
• Android SDK Manager
• Hyper-V Manager
For deploy to iOS:
• Mac
• OS X [v.10+]
• Xcode [v.7+]
• iOS SDK [v.9+]
Another way it’s use Cloud Services (e.g., Ionic Cloud) with pre-built Docker containers for deploy on iOS or Android.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofx7iaftsdkehfrbsawt-signature-71ba2d4d67cd3167dcdc6a7c5ebfcb08fd52334af9a3bcb1cf6a8e3f0e4a5a6e-poli-161111100521/75/Developing-a-native-mobile-apps-using-Ionic-Cordova-15-2048.jpg)

