This document describes the design and implementation of a fuzzy logic controller for DC motor speed control using a laptop computer. A tachometer is connected to the motor to provide feedback to the controller. The controller is implemented using a .NET class library developed by the author to allow students to easily design fuzzy logic systems. Experimental results show that the fuzzy logic controller is able to control the speed of the DC motor to follow a desired setpoint.
![Design and Implementation of Real Time
DC Motor Speed Control using Fuzzy Logic
Waleed Abd El-Meged El-Badry
Mechatronics Department
Faculty of Engineering, MUST
wbadry@must.edu.eg
3rd June, 2008
Abstract
In this paper, we try to implement a fuzzy logic controller (FLC) for DC motor
using Laptop, tower or industrial PC. The feedback is taken via tachometer
connected directly to motor of interest by coupling. Interfacing between PC and
DC Motor-Tachometer is done using NI USB 6008 and additional signal
conditioning circuitry. This system could assist students and novices to evaluate
rapidly Fuzzy Logic concepts and application using this low cost case study.
1. Introduction
Speed control of DC motors has been one of the crucial topics in Mechatronics
engineering, starting from simple Cartesian Robots, to giant industries such as
steel where maintaining motor speed of rollers affects drastically the shape of
rolled bars[1-2]. Due to non linearity of DC motors, designing control system
based on system identification is difficult and all system parameters are
approximated [2].
The heuristic knowledge based system, Fuzzy Logic proved to have the flexibility
of modelling nonlinear systems with fair or no knowledge of systems
identification. As the fuzzy logic core is based on “how people can do it”, many
legacy control systems are nowadays converted to be “fuzzy based systems” for
ease of maintenance and enhancement.
Fuzzy Logic Controllers can be practically implemented using several techniques,
using Microcontroller [3] where all fuzzy rules are placed by means of assembly
language, or a FL chip that is configurable using accompanying software, and
finally using PC where education mainly takes place in development process.
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fuzzypaper-110309172759-phpapp02/75/Design-and-Implementation-of-DC-Motor-Speed-Control-using-Fuzzy-Logic-1-2048.jpg)
![2. Motivation
Several reasons were beyond selection of this implementation, these are
summarised below:
Development of Class Library can be utilised by students to develop fuzzy
logic systems easily with any .NET language (C#, VB, C++, Delphi and COBOL).
This would enable many students whose skills are in one or more of the
preceded languages rather than compulsory knowledge of MATLAB.
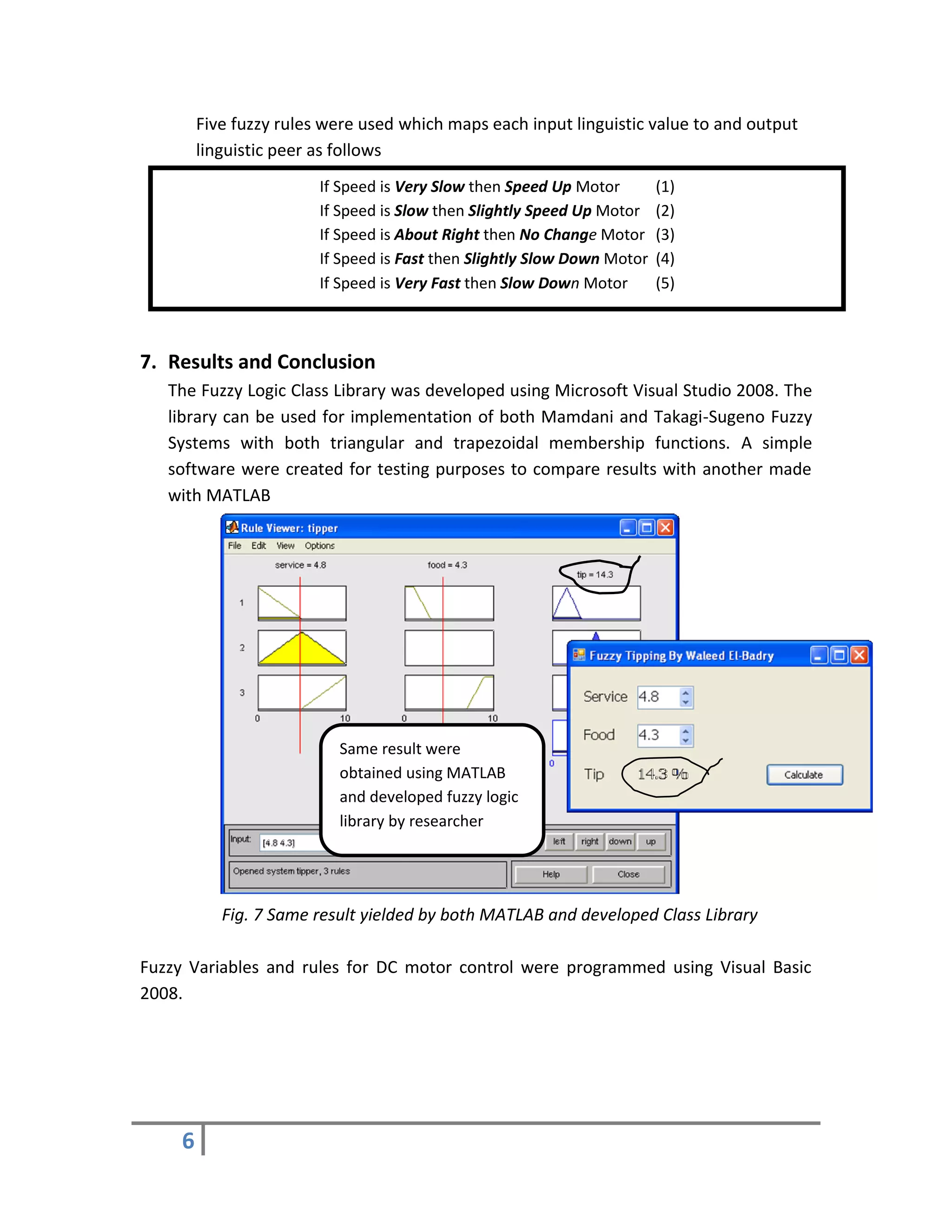
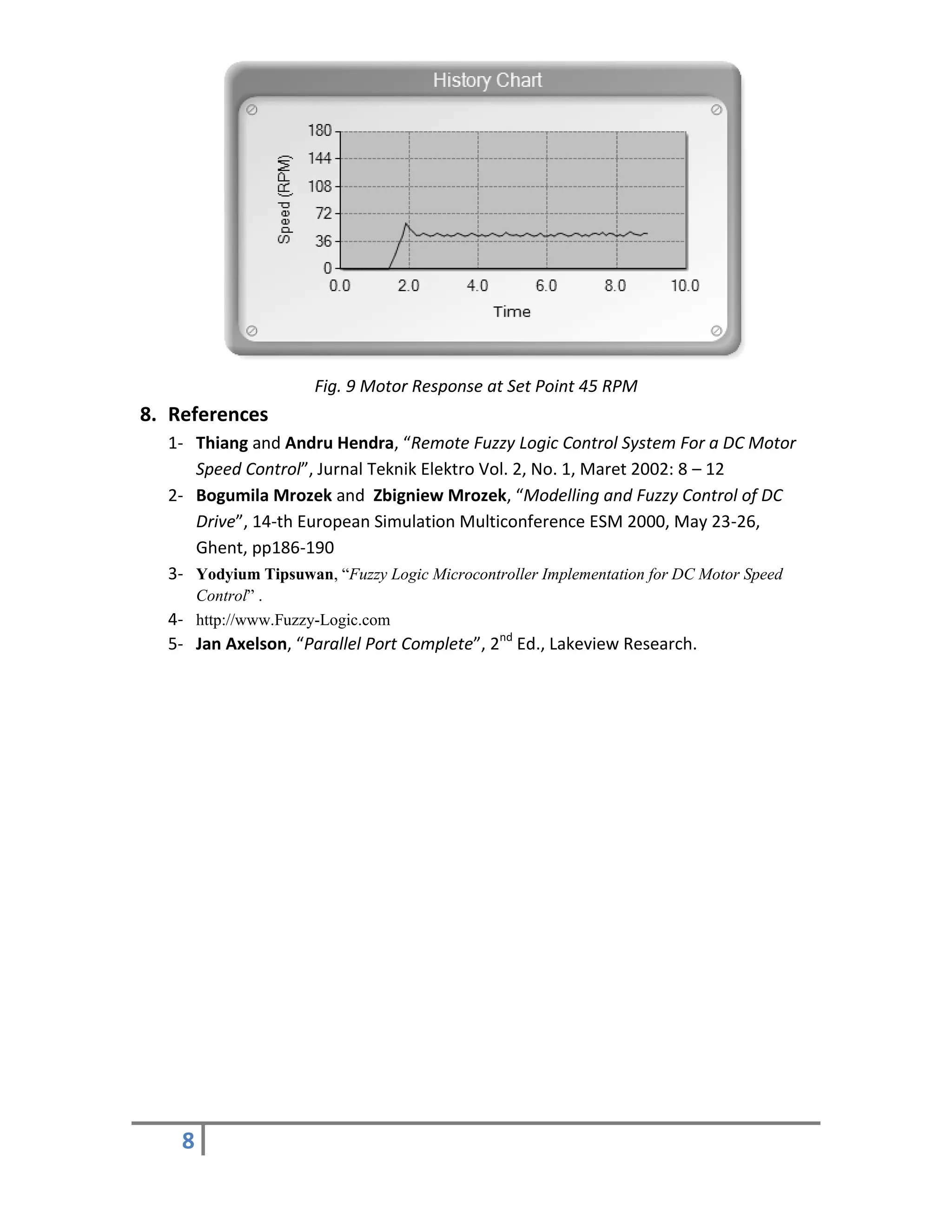
Implementing knowledge gained from “Fuzzy Logic” course tutored.
Studying the impact of fuzzy controller designed in real time environment.
3. Project Framework
DC motor speed control was inspired by an article entitled “Fuzzy Logic for Plain
Folks. Fig. 1 illustrates the proposed circuit connection [4].
Fig. 1 Proposed Circuit Connection
The proposed system can be summarised in the below block diagram
Knowledge Base
Fuzzification Fuzzy Rules Defuzzification
Computer
BJT Amplifier
Coupling
D/A M T A/D
Fig.2 DC Motor Speed Control Block Diagram
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fuzzypaper-110309172759-phpapp02/75/Design-and-Implementation-of-DC-Motor-Speed-Control-using-Fuzzy-Logic-2-2048.jpg)
![4. Project Setup
Two Identical DC motor were used to implement the project (one as DC motor and
the other works as tachometer), they are Toshiba 24V, 1.5A and Maximum of 180
RPM. Other parameters were obtained experimentally. The NI USB 6008 has built in
12 bits Analogue to Digital converter that can generate output voltage from 0- 5V
with maximum sourcing current of 150 mA. It also has a 0-10V, 12 bits Analogue to
Digital converter that were sufficient to measure the tachometer voltage directly.
Additional Circuit were used to accomplish two objectives, to start with, to amplify
the output analogue voltage generated from USB D/A from 0-5V into 0-12V, and
secondly, to supplement the DC Motor with current necessary that USB device can’t
afford. The figure shown illustrates how these problems were tackled by using
TIP41C NPN transistor with variable resistor for tuning [5]. Value of resistance were
evaluated experimentally
+12V
Fig. 3 Mapping 0-5V 150mA into
Q1
0-12V 2A Circuit 43%
TIP41
(Created Using Proteus VSM) From USB 6008
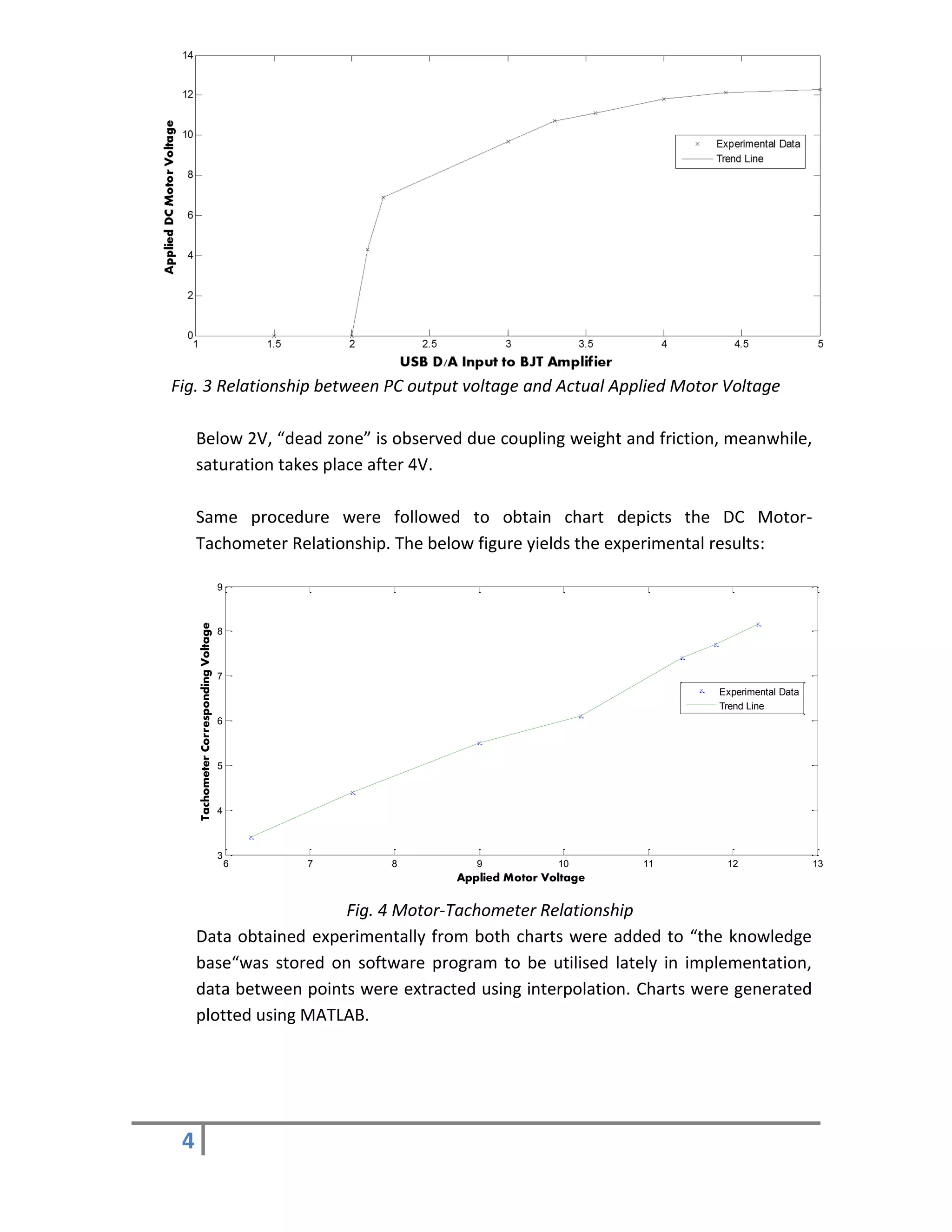
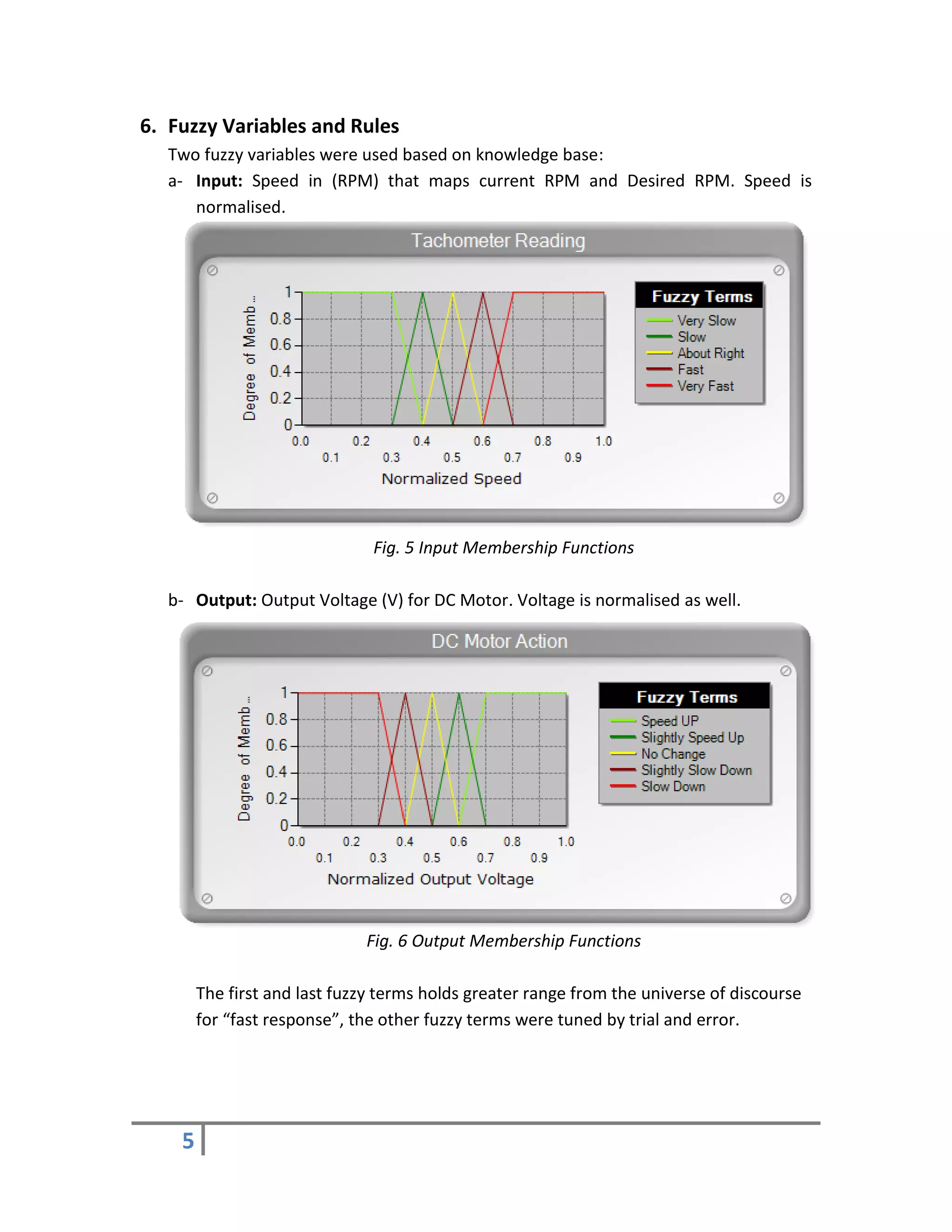
5. Experimental Work
Common-Emitter BJT amplifier described in preceded section has a nonlinear
relationship between Base Voltage (Vb) and Collector Voltage (Vc), the below chart
describes the relation between output USB analogue voltage (0-5V) from NI USB
6008 and Actual applied DC Motor voltage after amplification stage. The chart was
drawn by applying different voltages from USB Card and measuring the
corresponding applied voltage on DC motor simultaneously.
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fuzzypaper-110309172759-phpapp02/75/Design-and-Implementation-of-DC-Motor-Speed-Control-using-Fuzzy-Logic-3-2048.jpg)