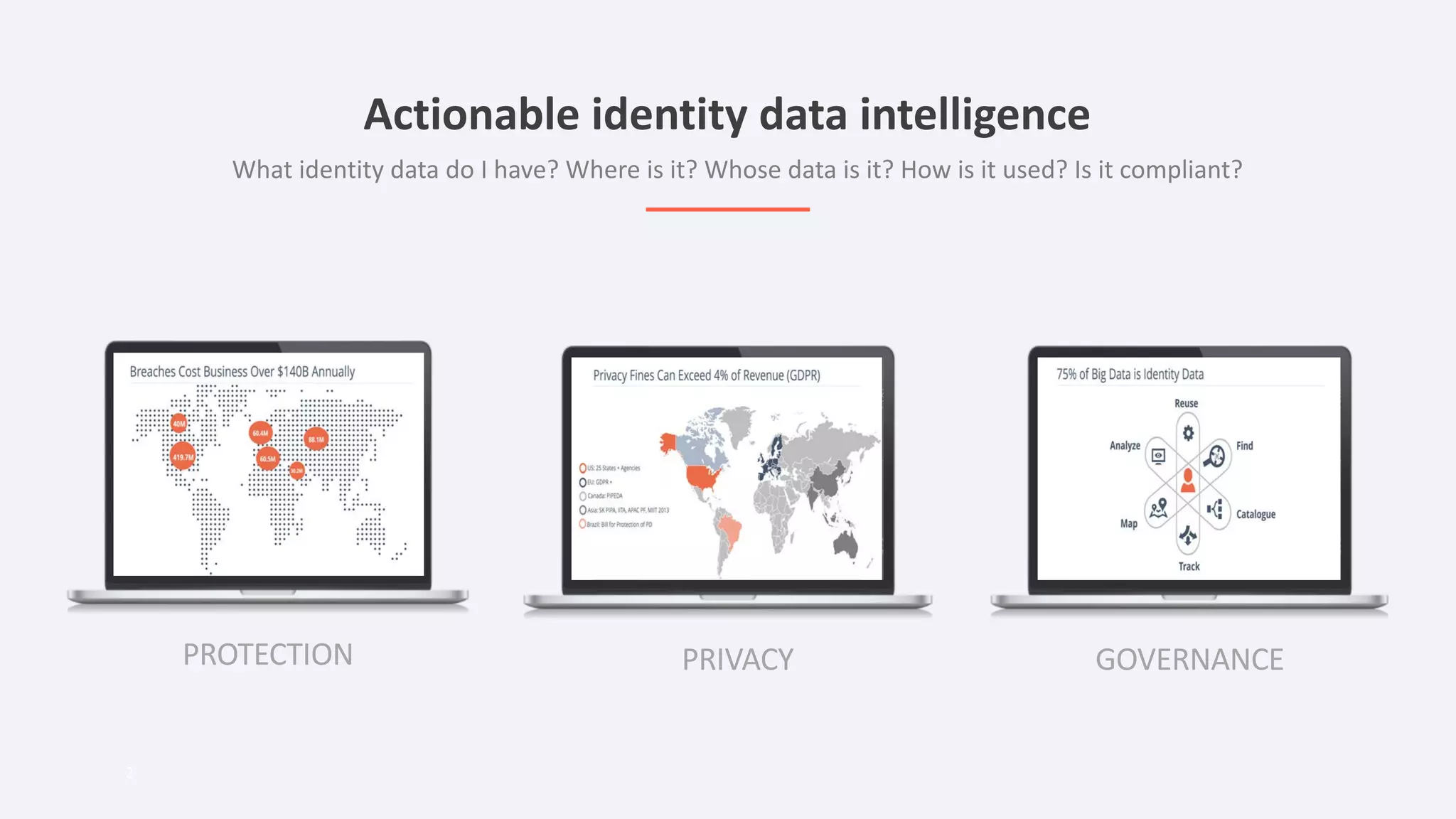
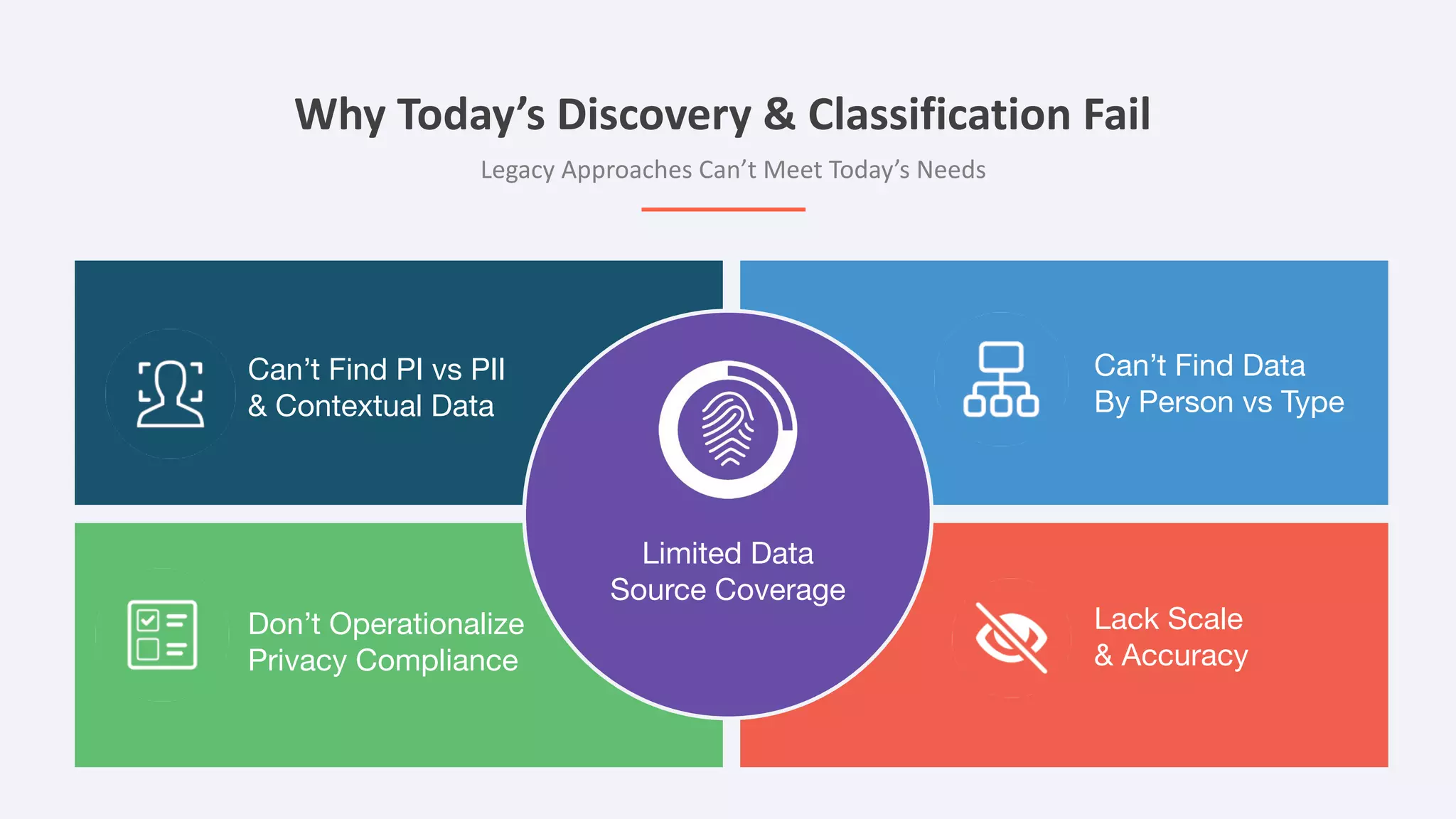
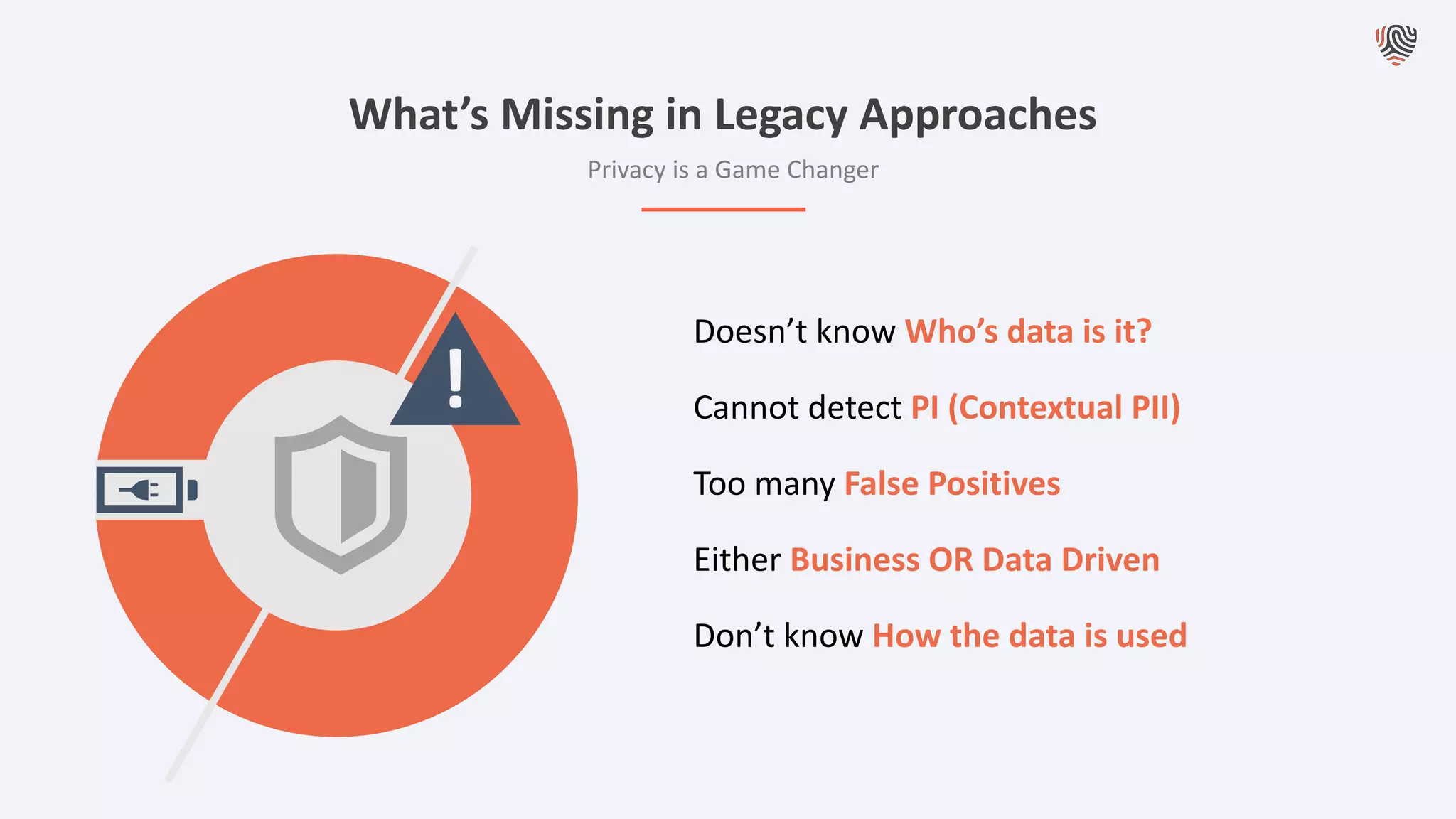
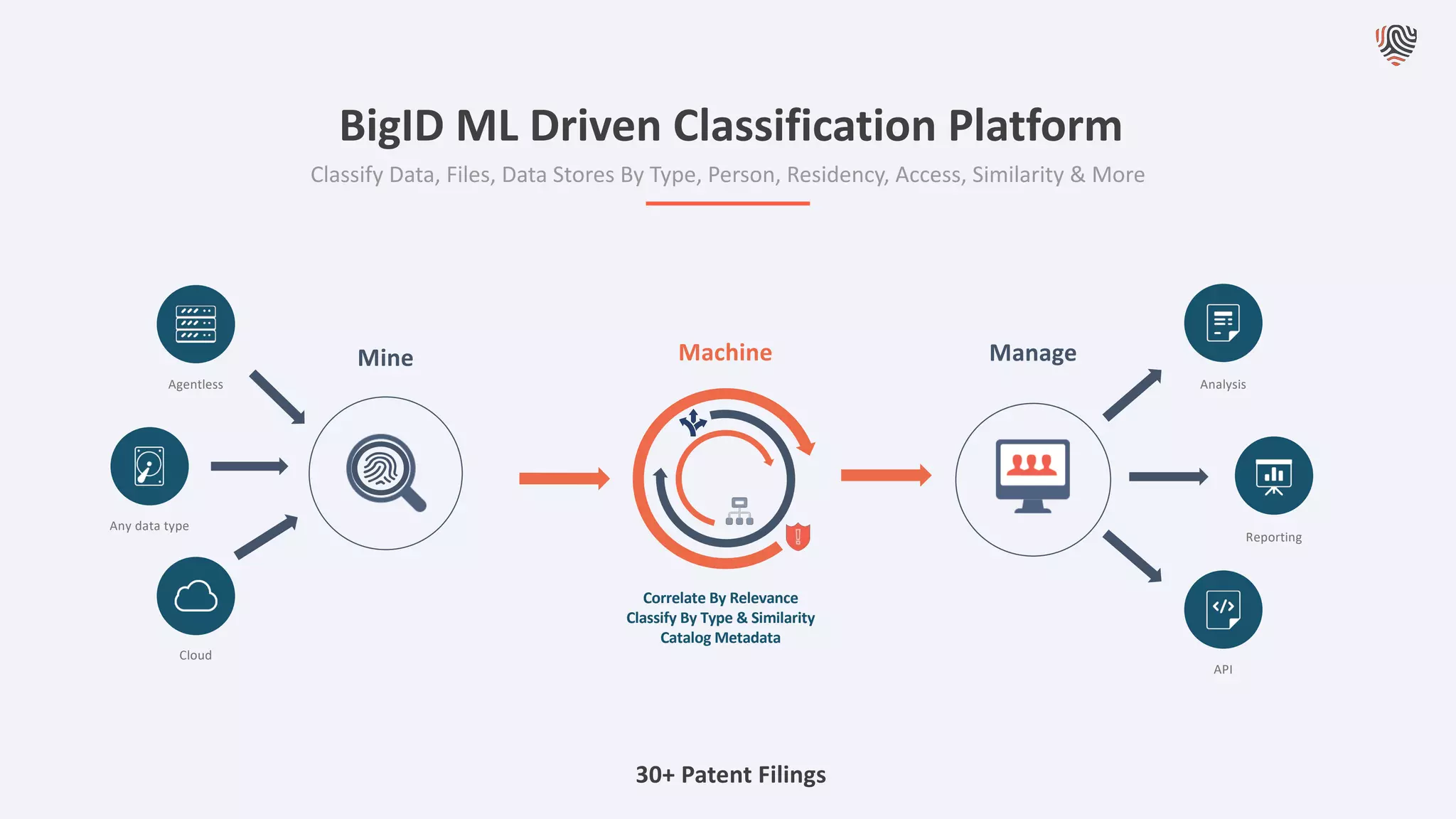
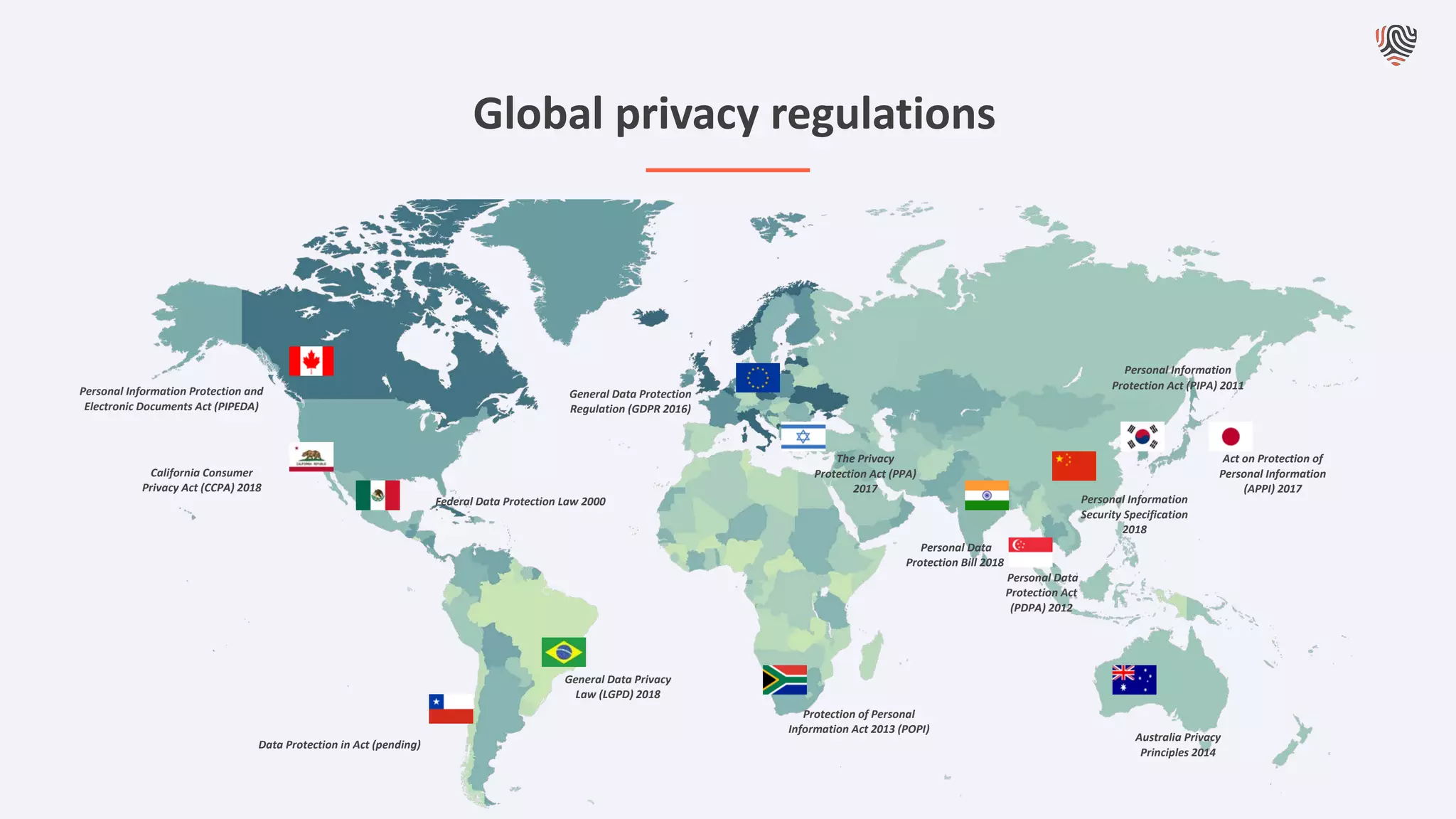
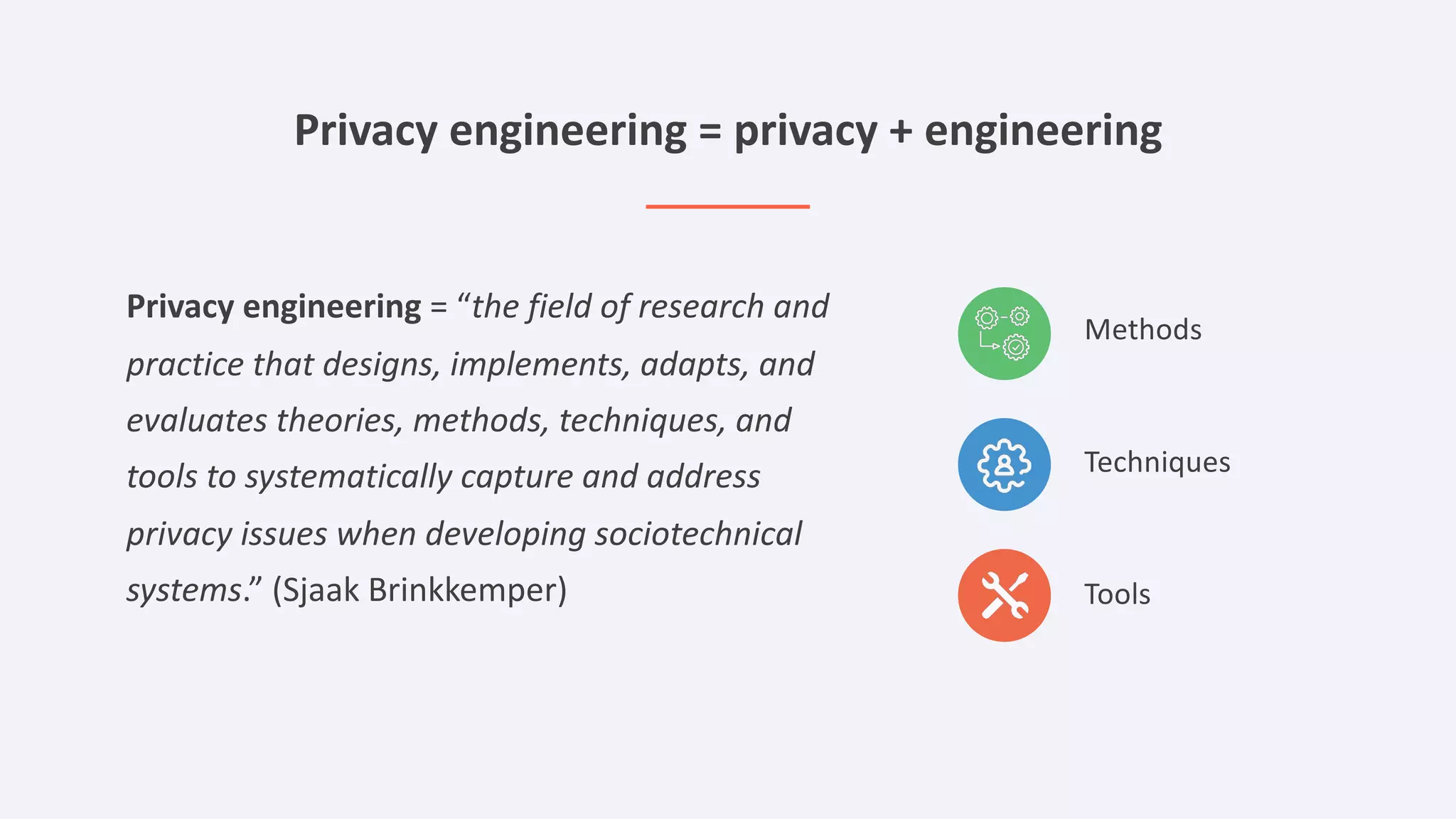
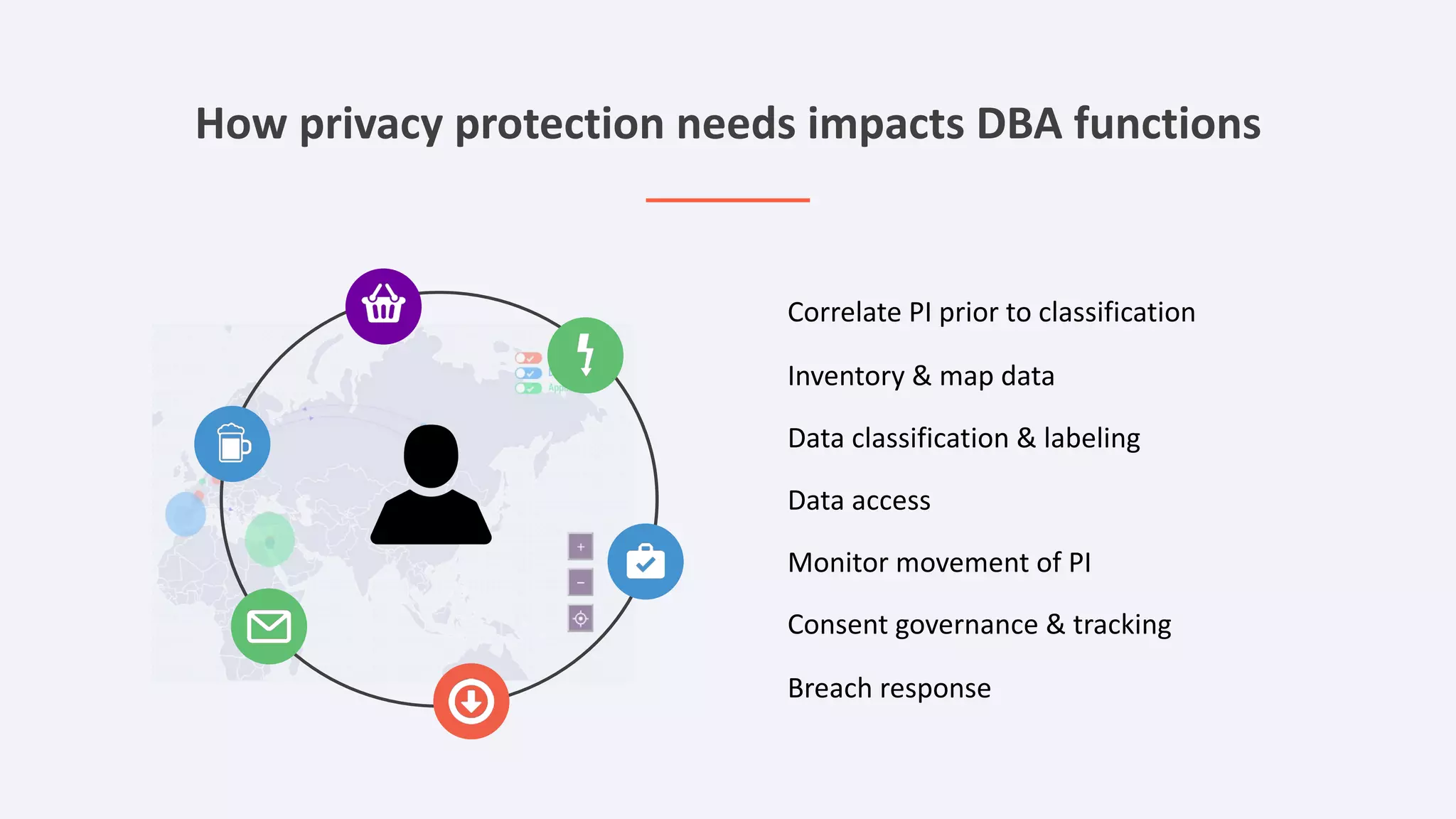
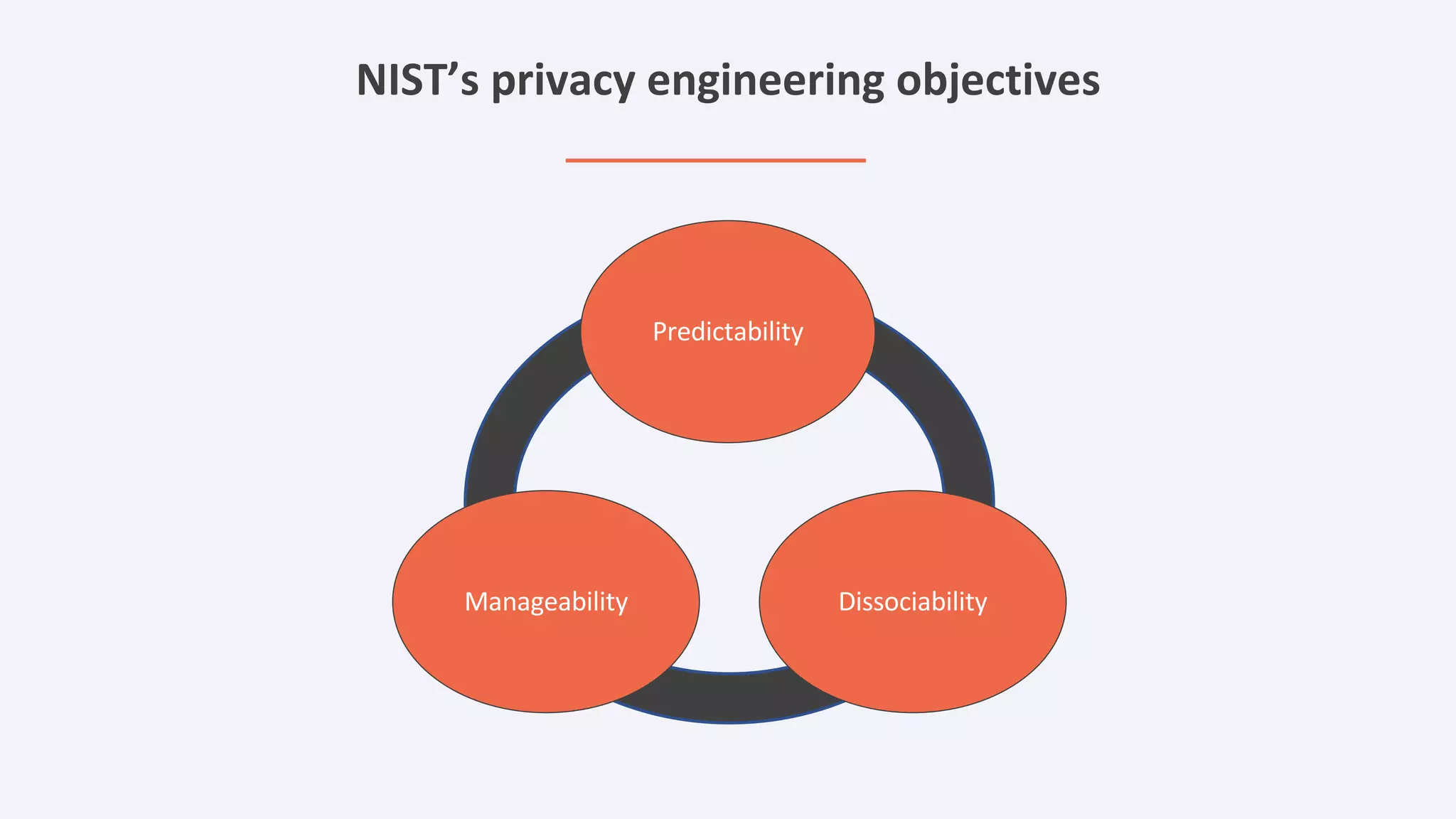
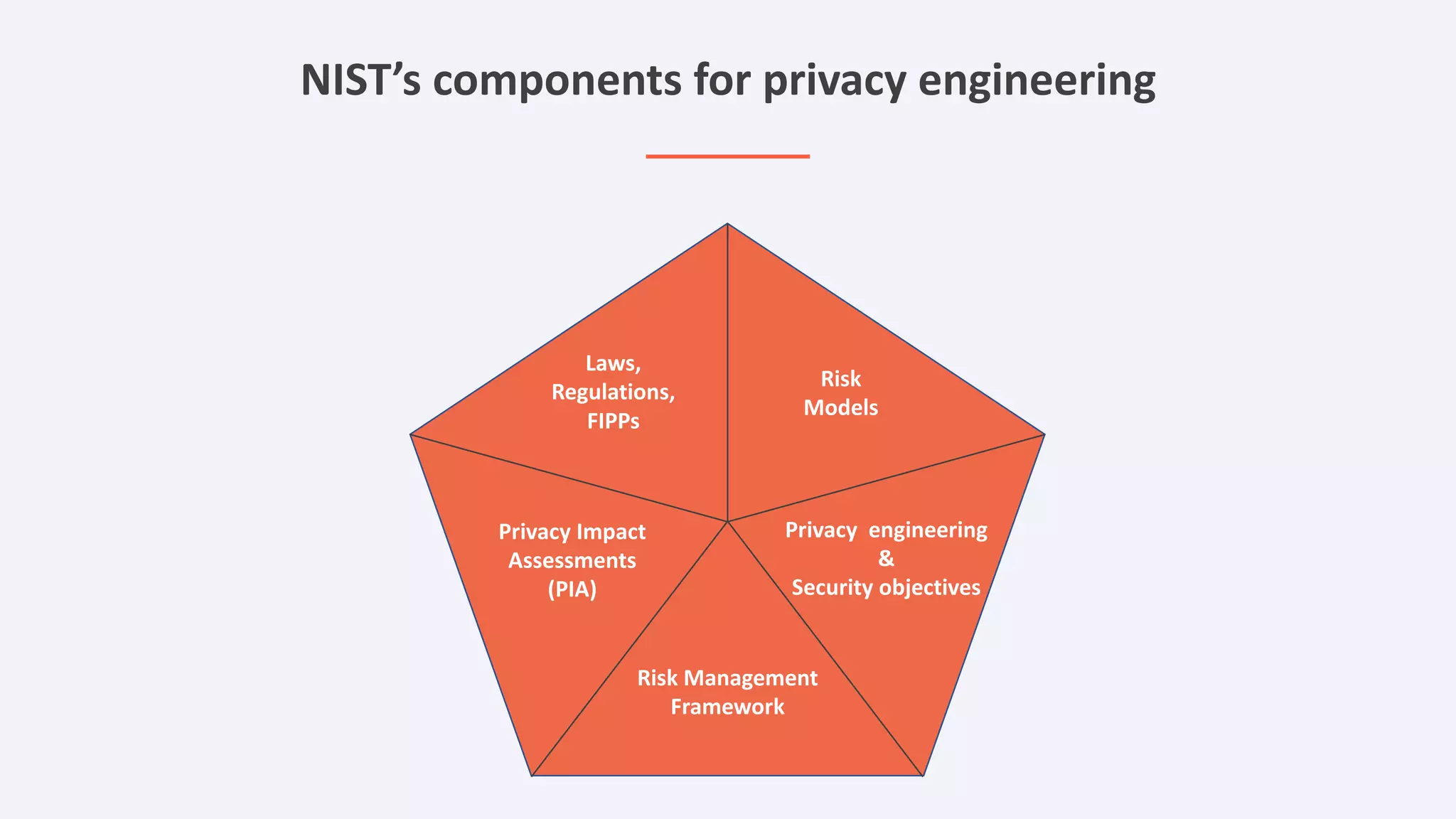
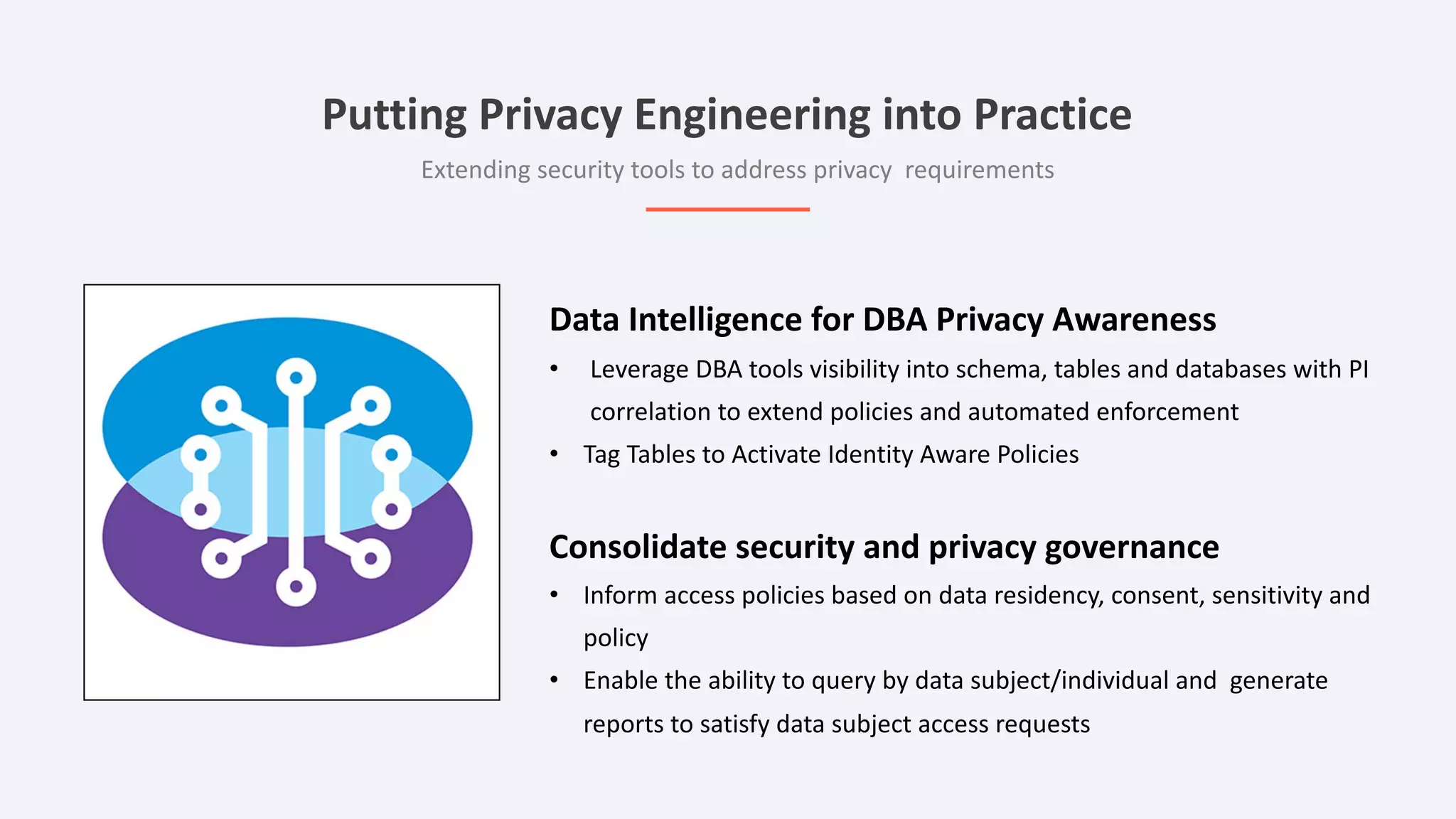
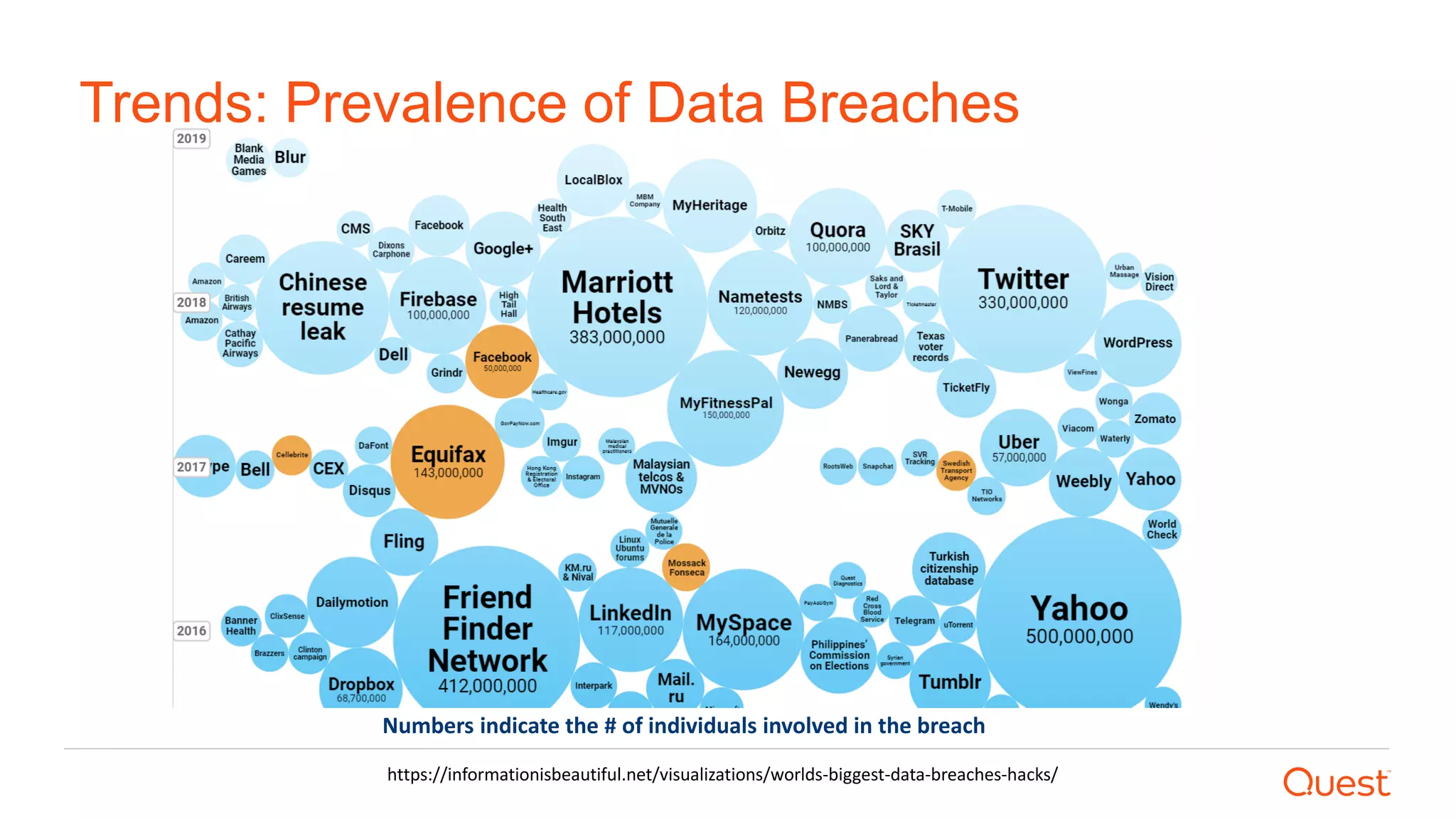
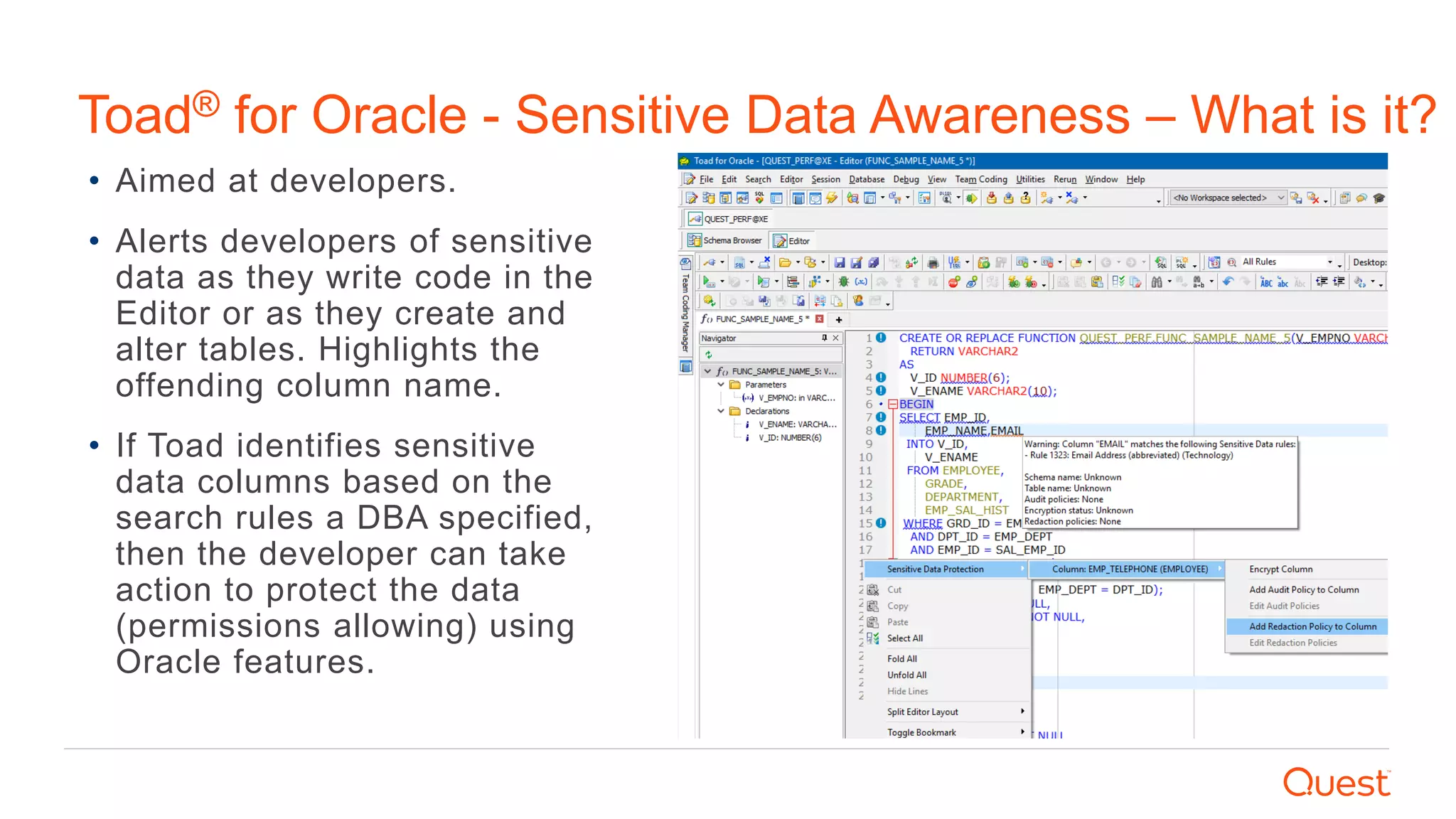
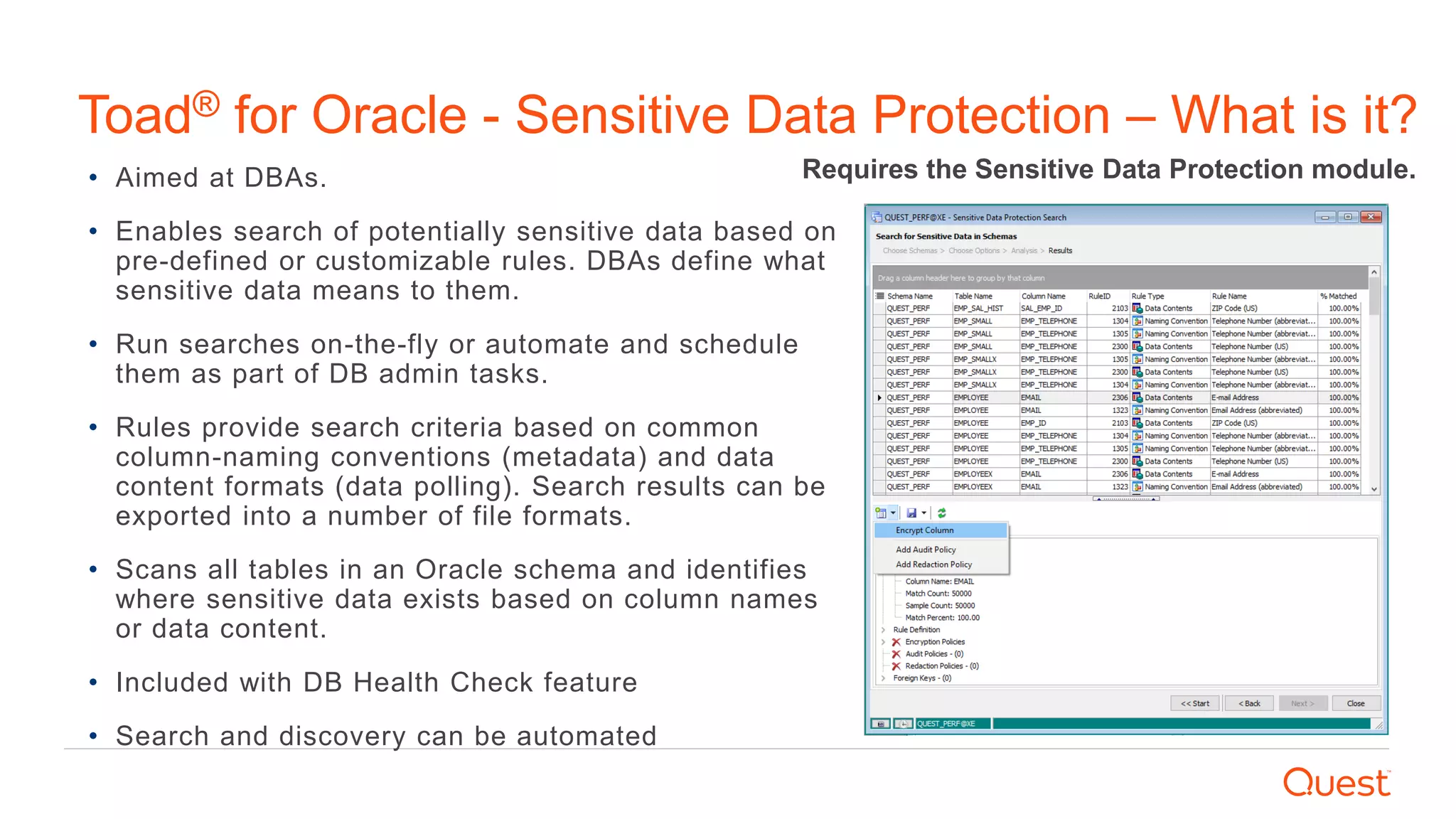
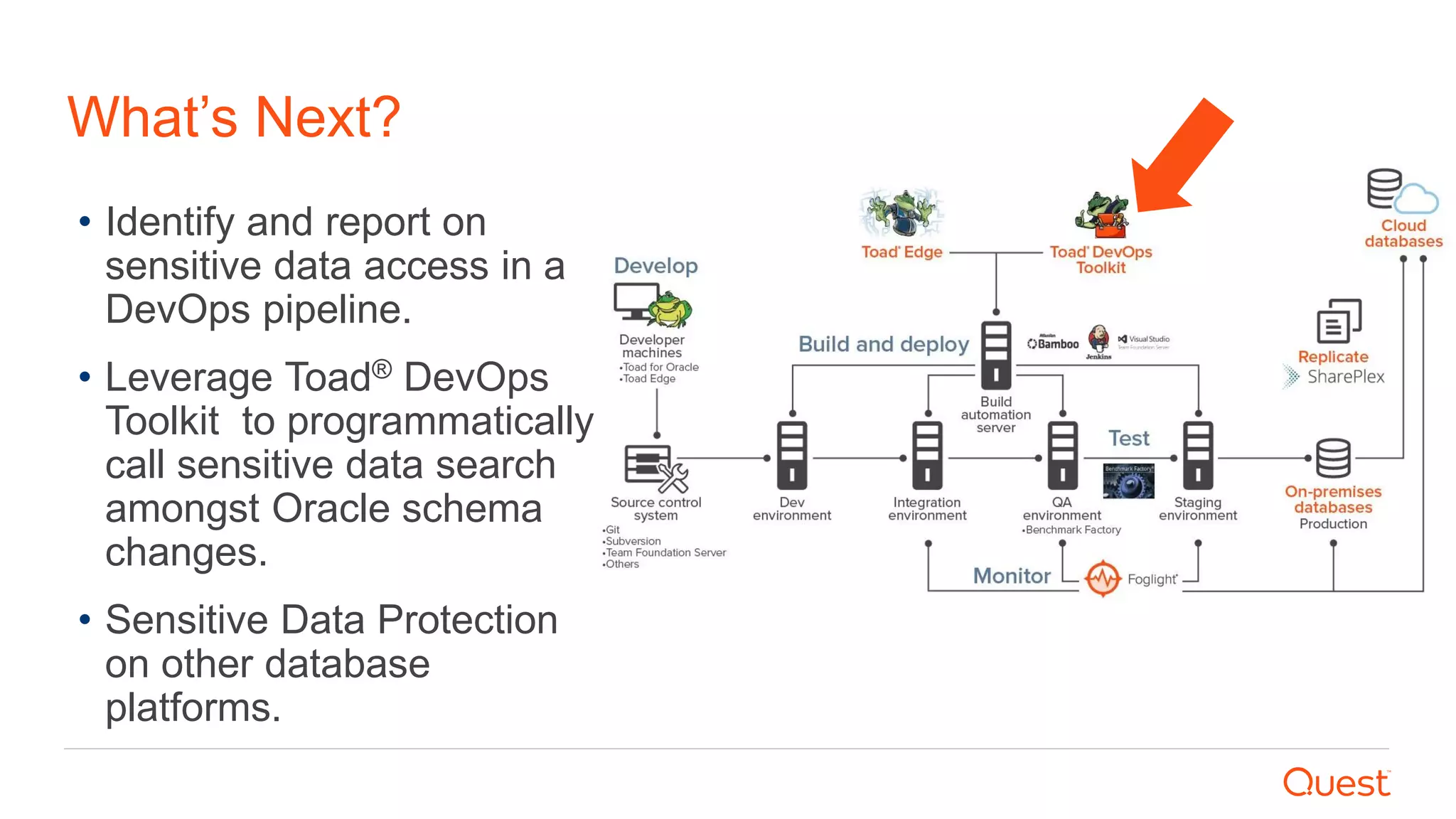
The document discusses the importance of data privacy and protection for DBAs, highlighting the challenges they face in identifying and managing sensitive data within their systems. It emphasizes the need for effective tools, such as Toad for Oracle, to automate sensitive data discovery and protection and mentions the evolving role of DBAs in the context of regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, CCPA). Additionally, it outlines the responsibilities of CTOs, CIOs, and data controllers in implementing data security strategies and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.