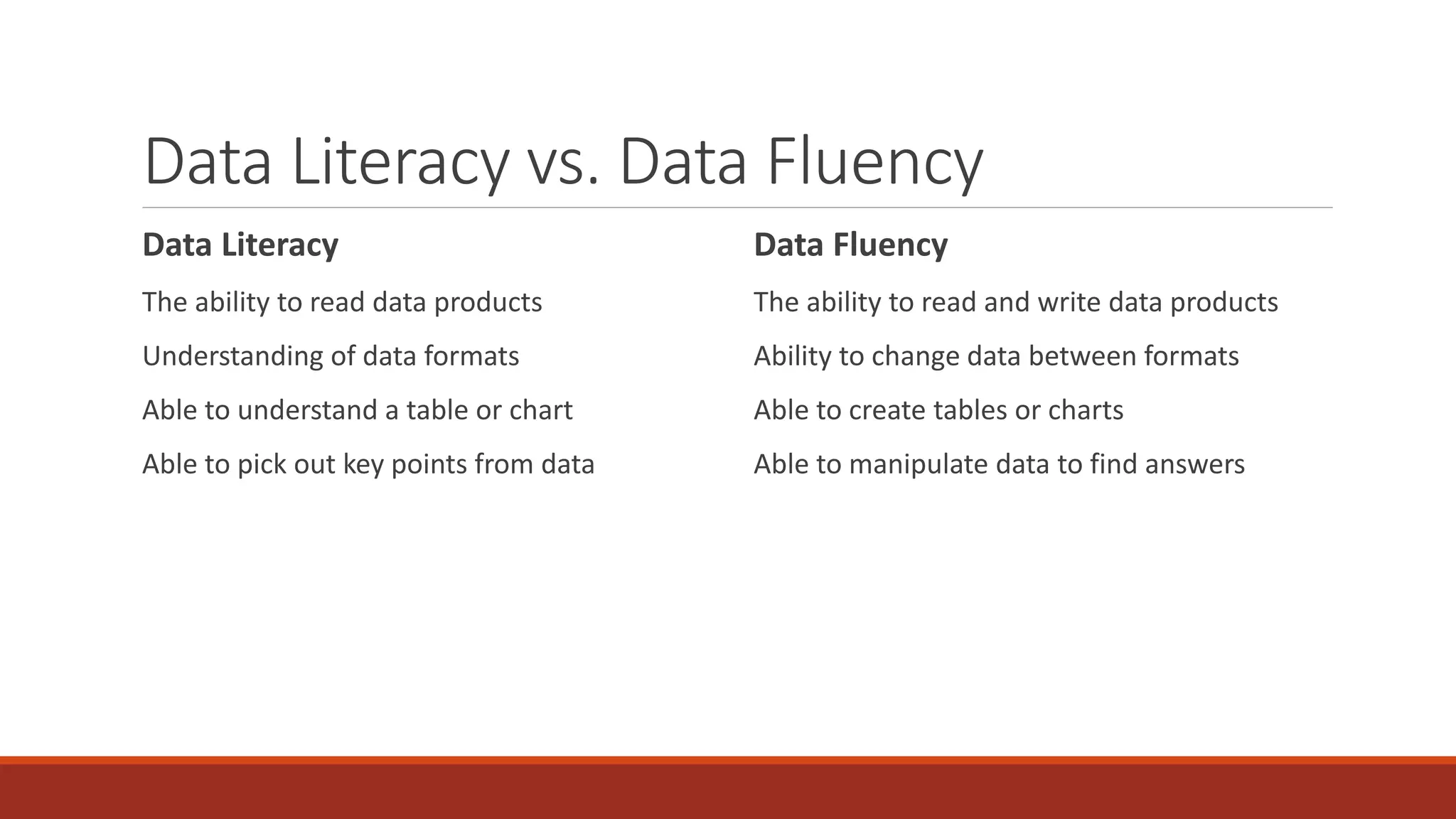
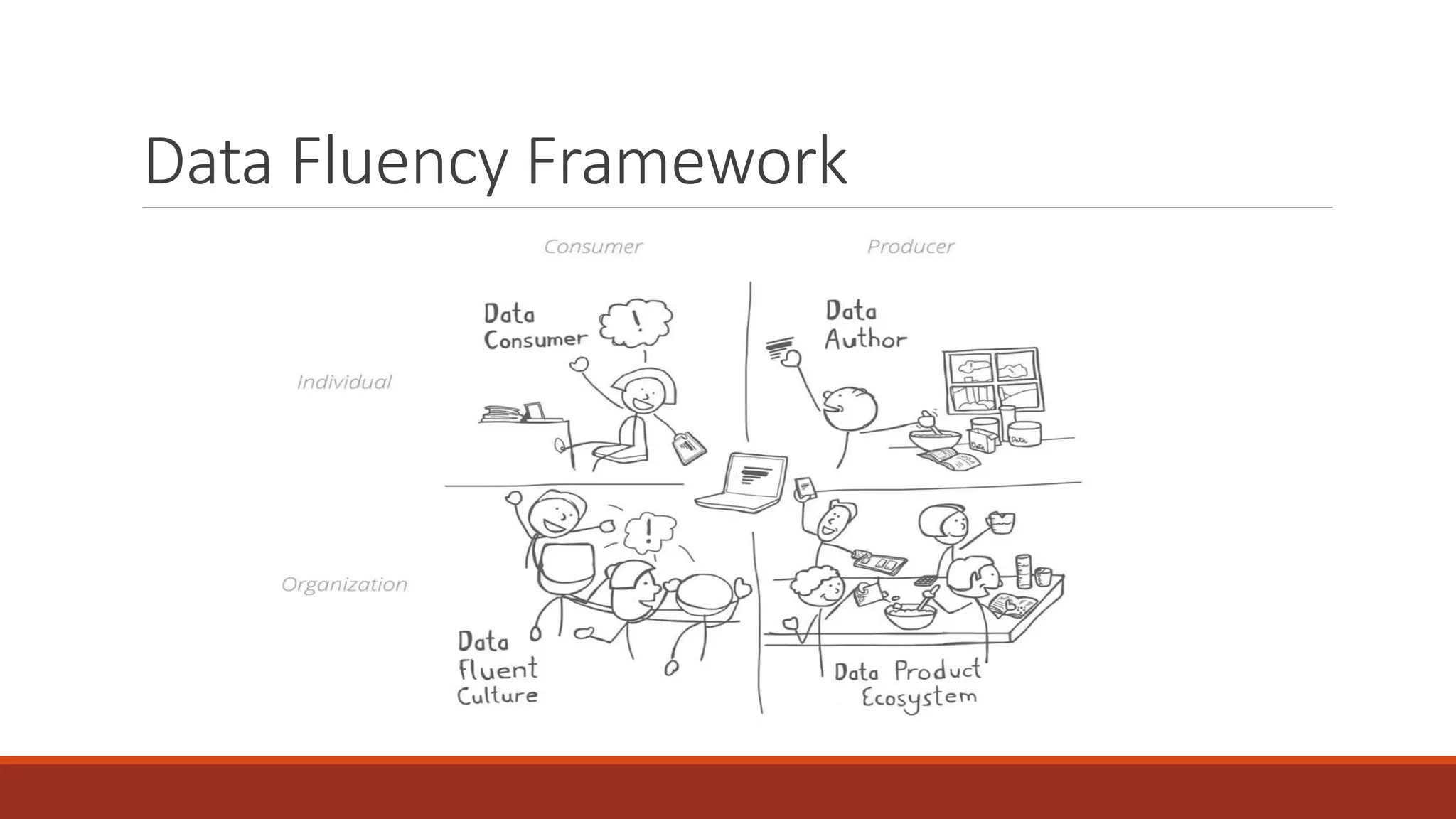
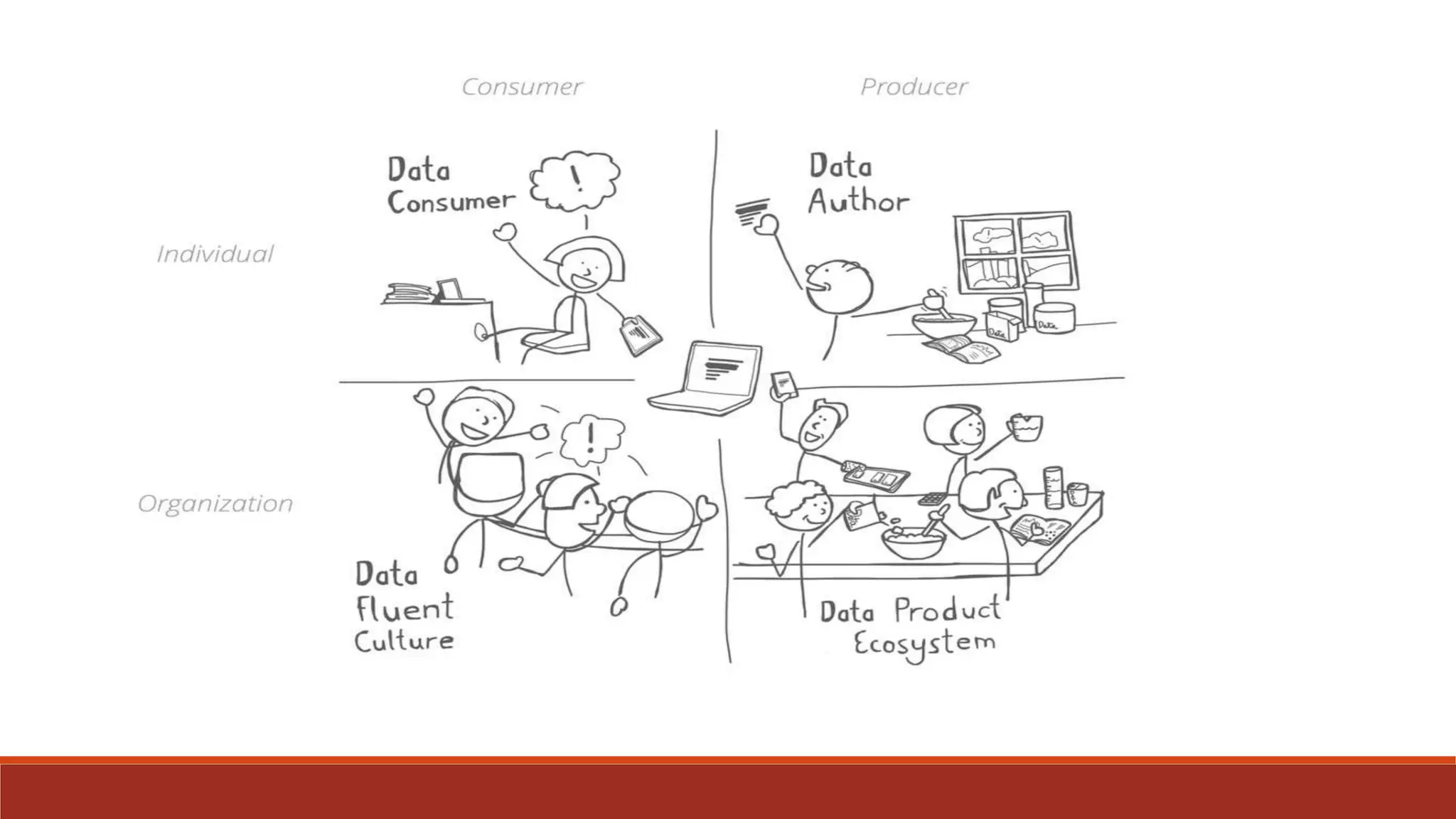
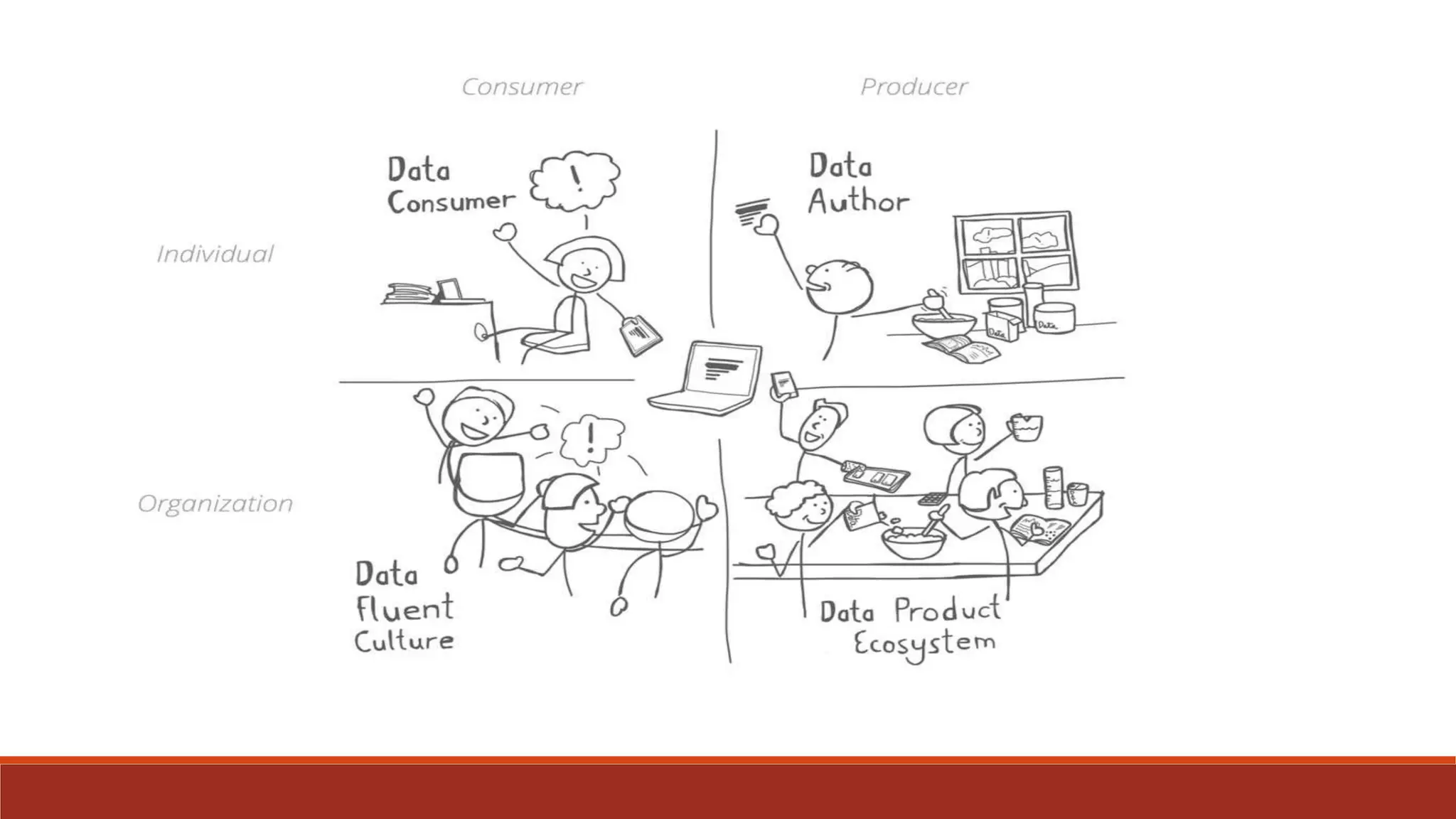
The document discusses the importance of data fluency in universities, distinguishing between data literacy and data fluency, and outlining a framework for effective data communication. It highlights common data problems, tools for data management, and emphasizes the need for a culture that supports data-driven decision-making. Additionally, it addresses data governance and provides resources for further learning and development in data communication skills.