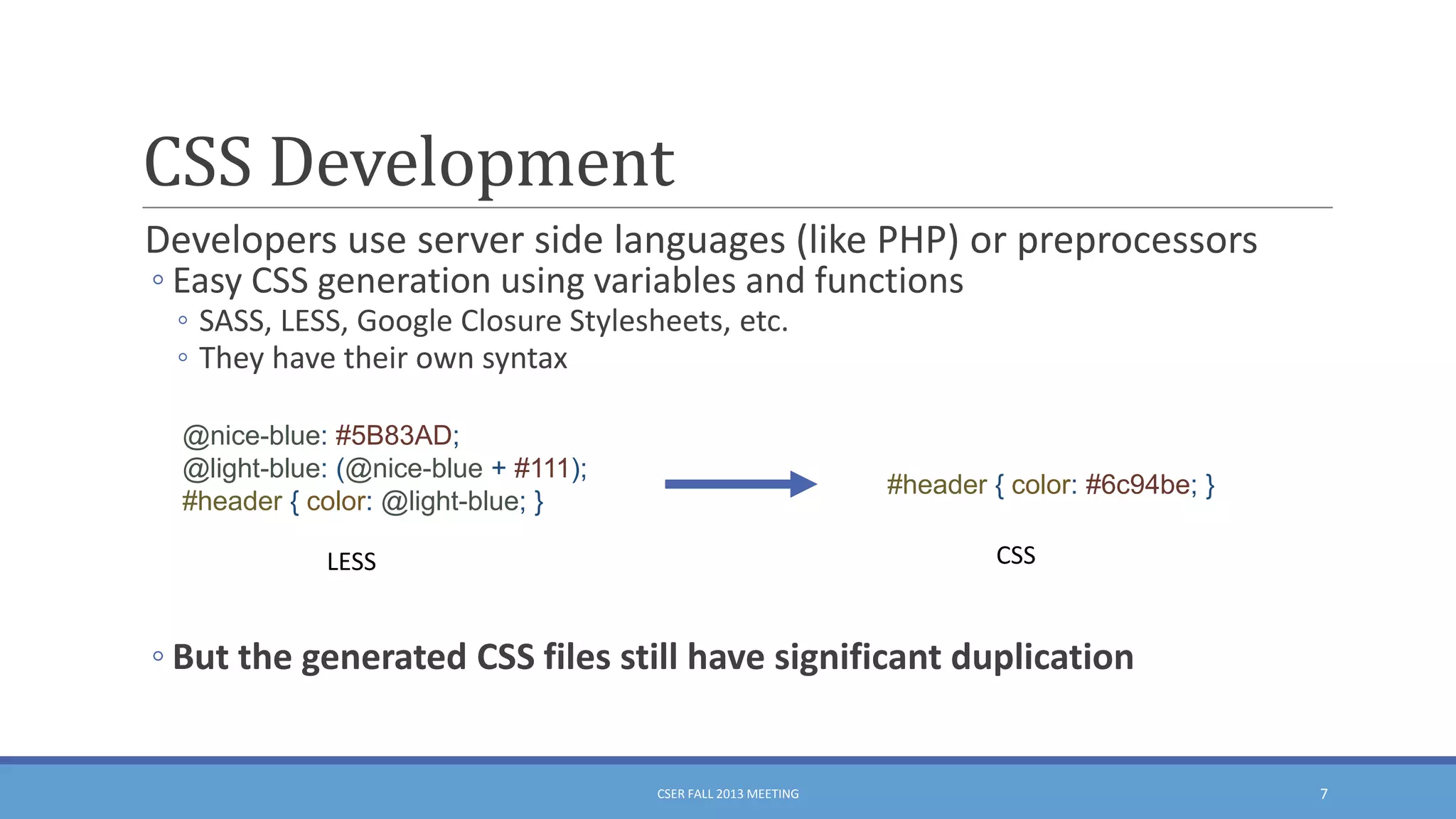
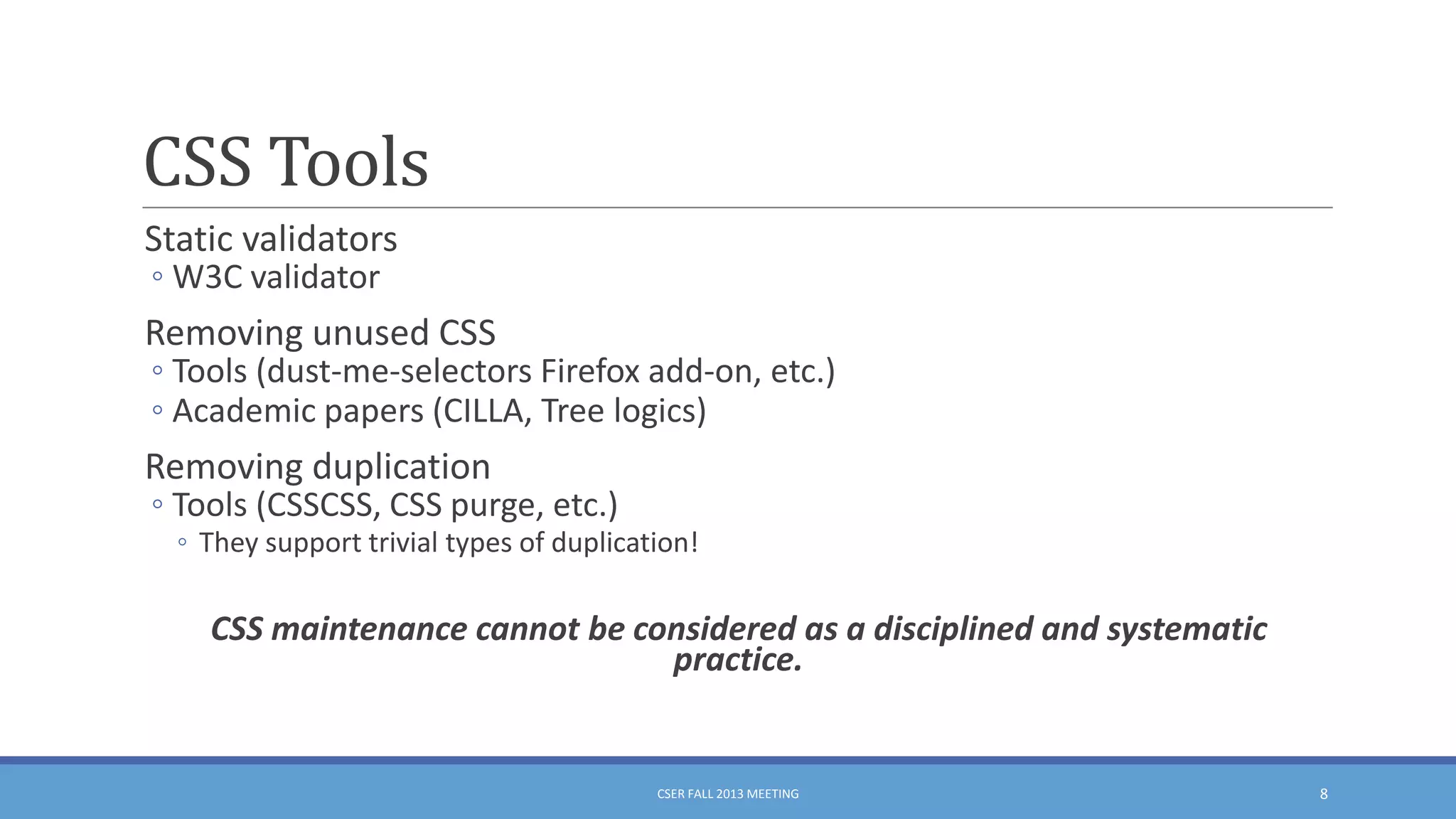
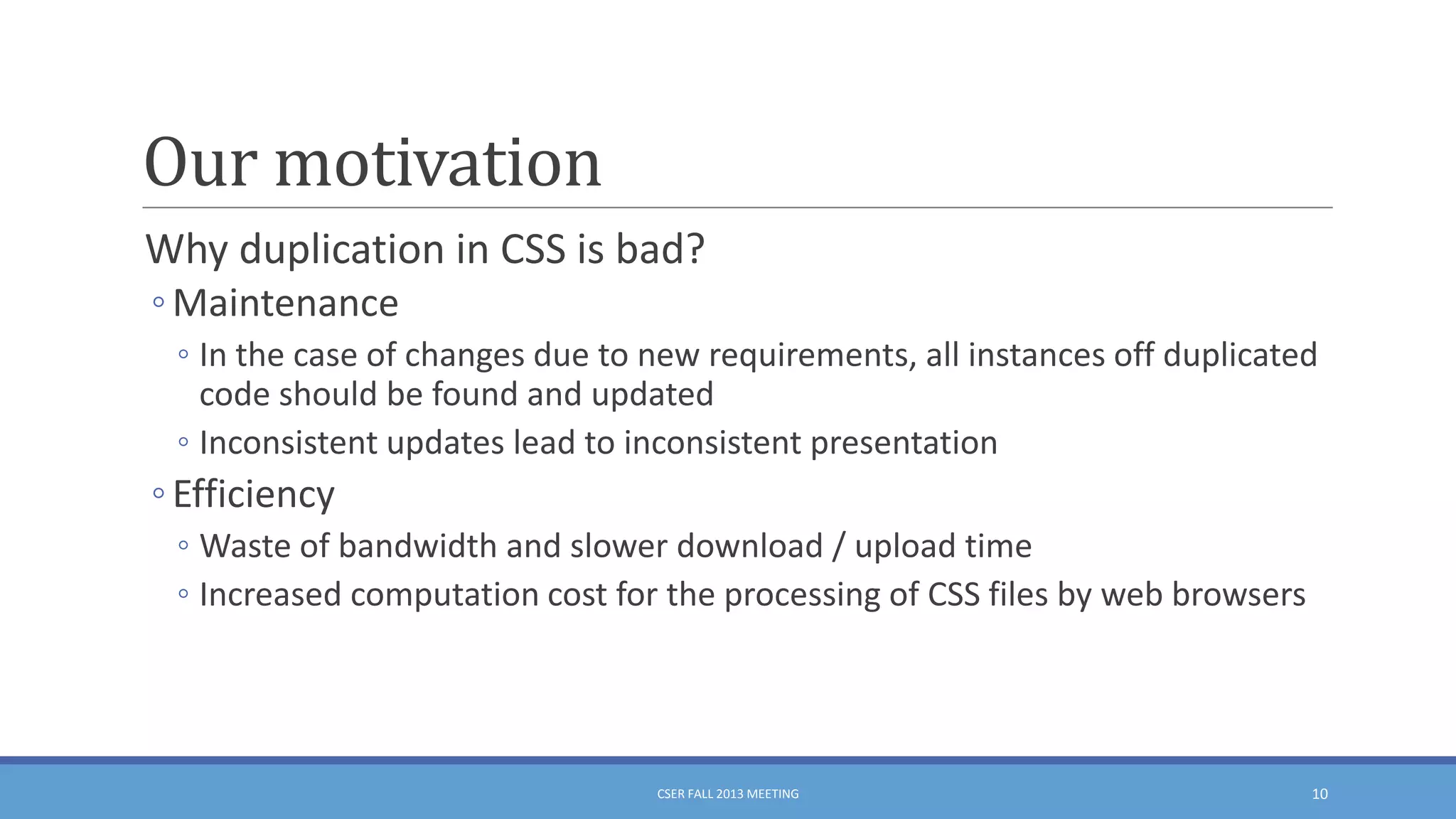
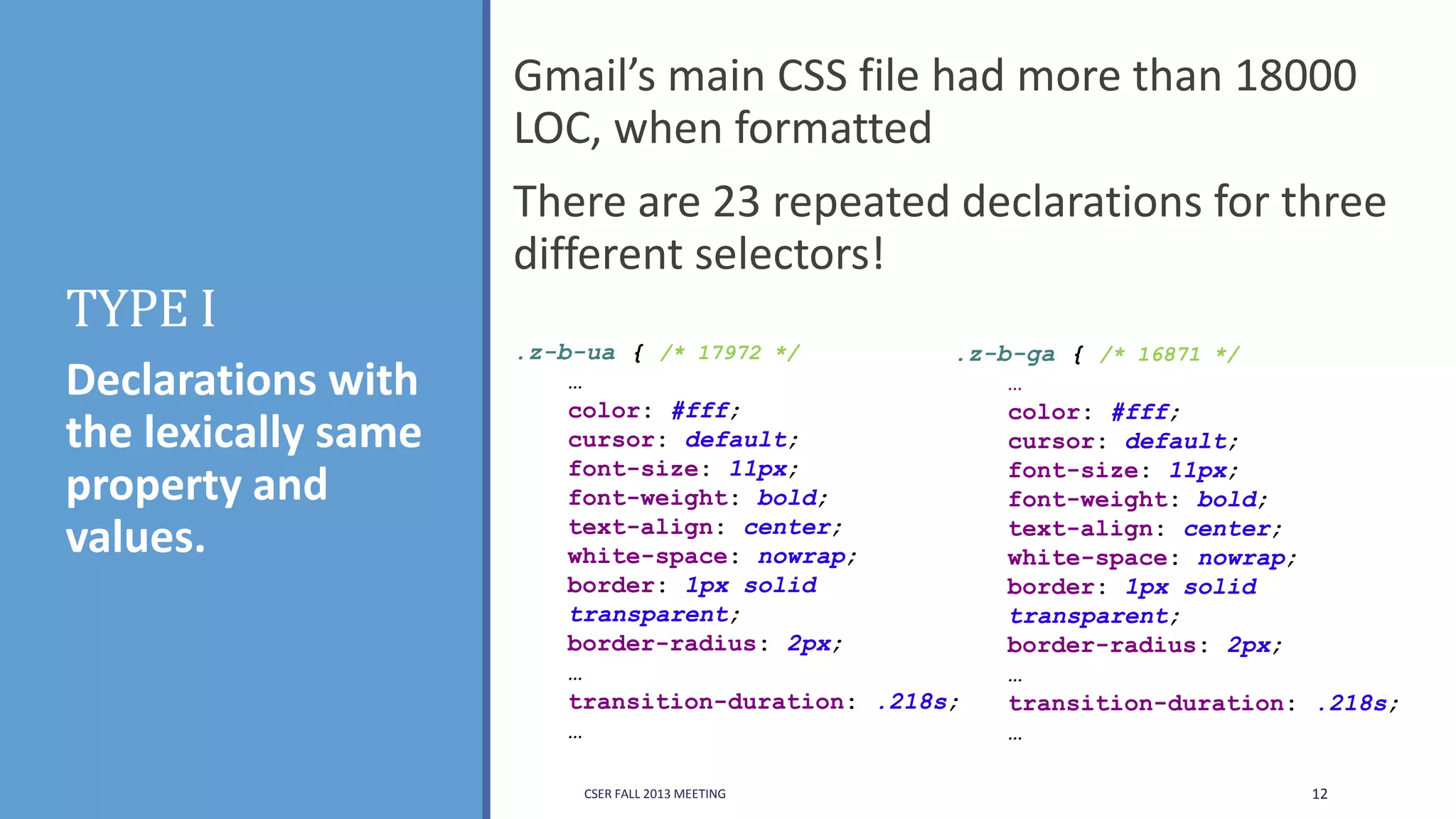
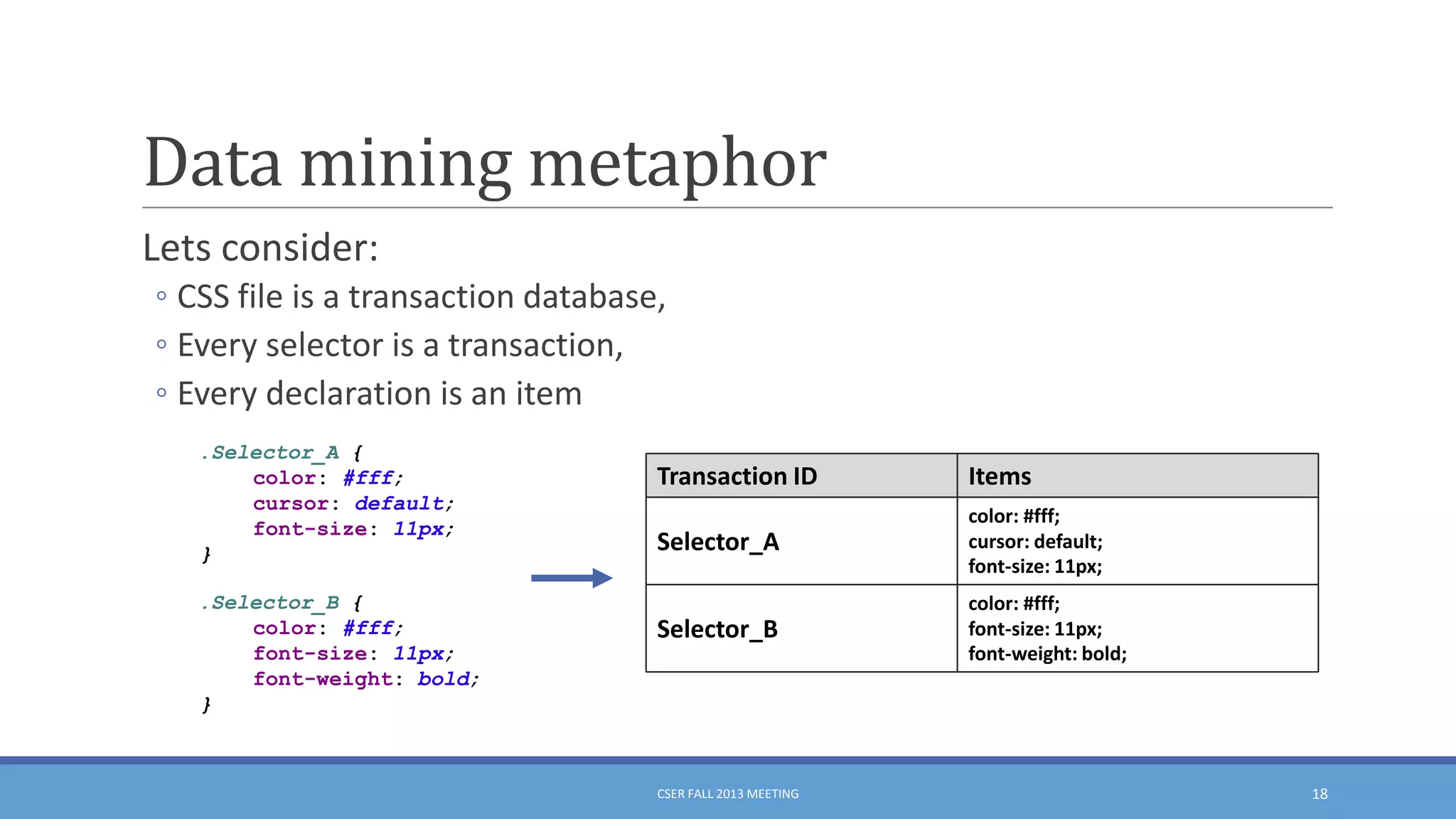
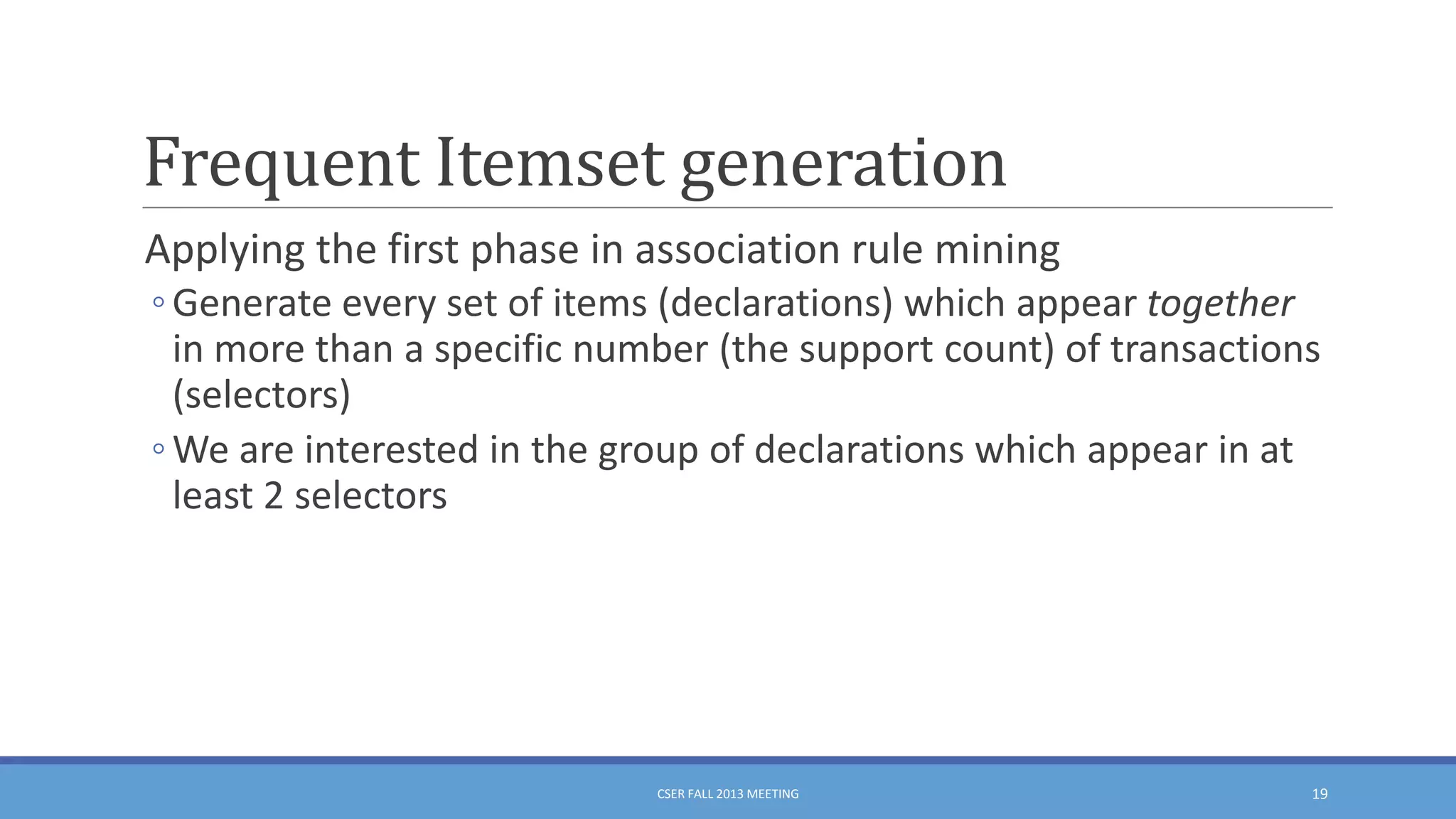
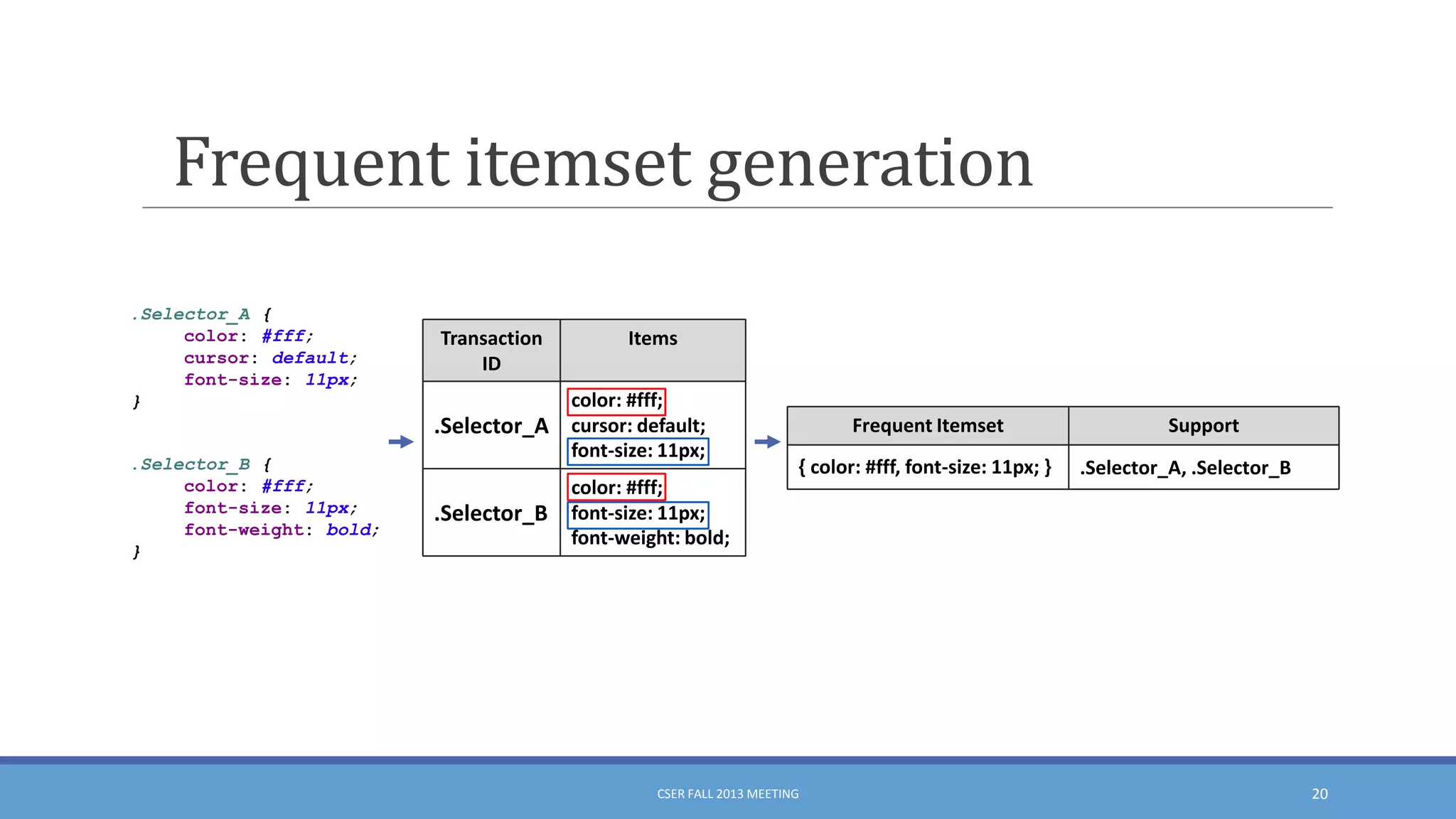
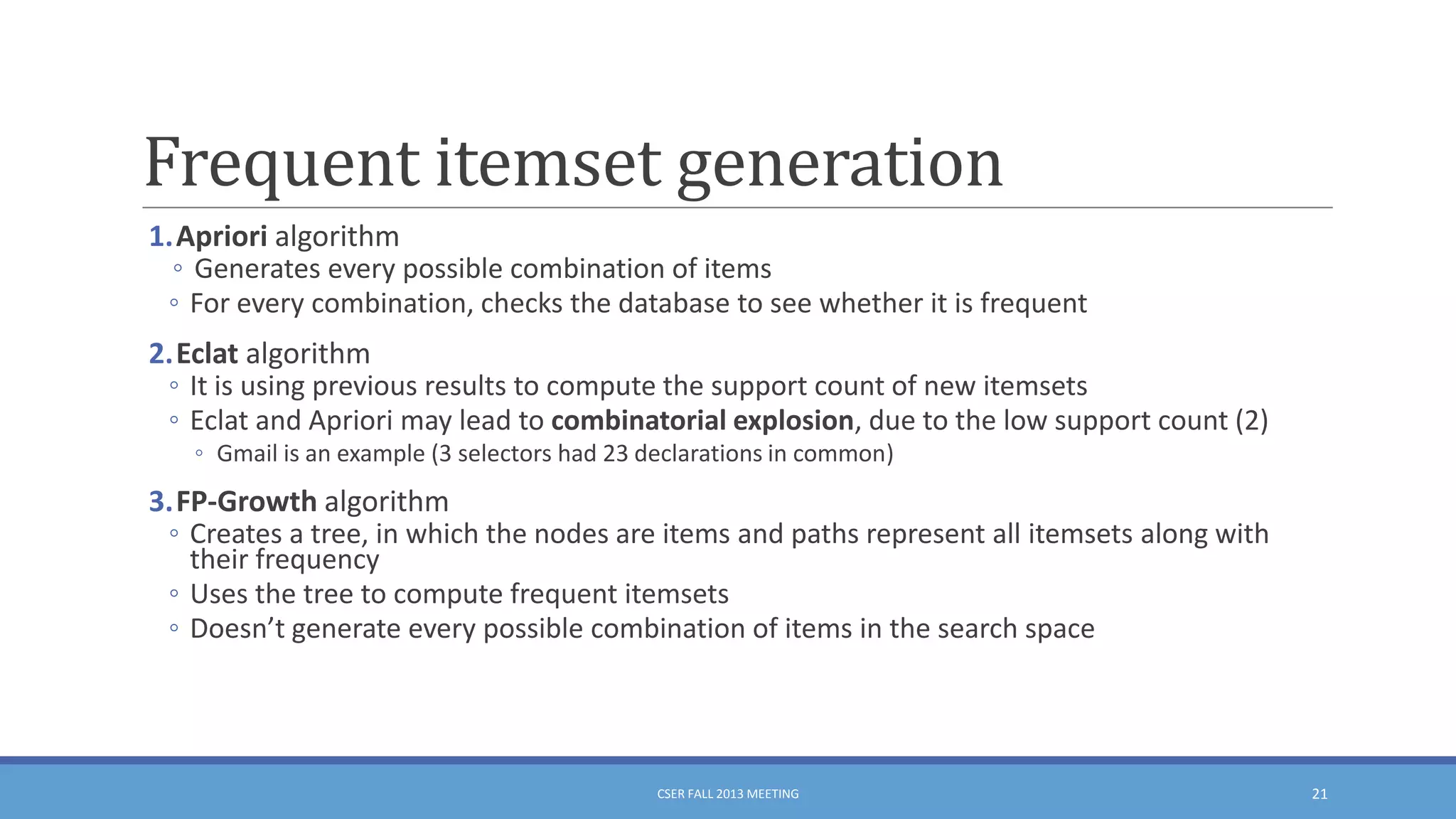
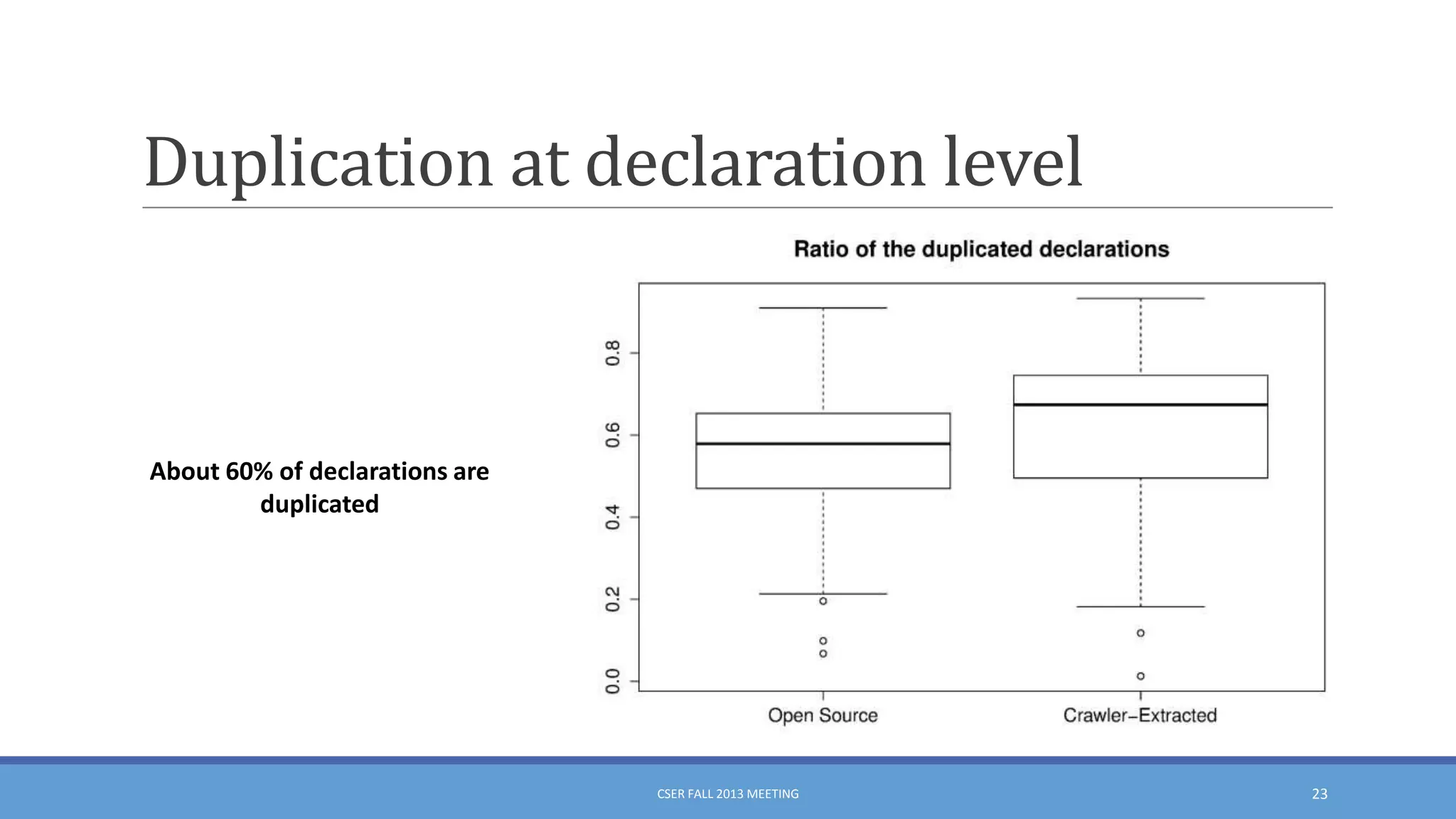
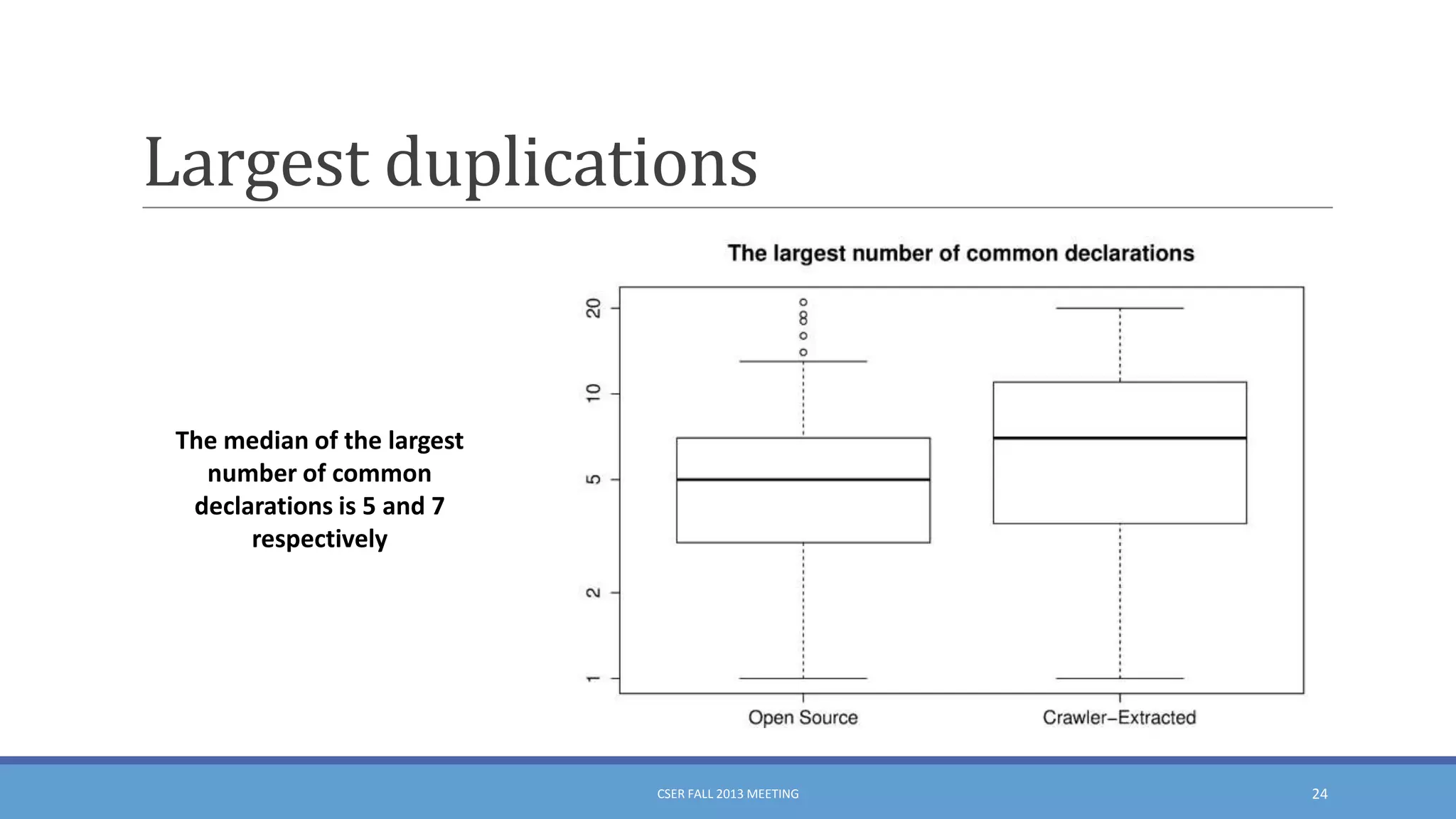
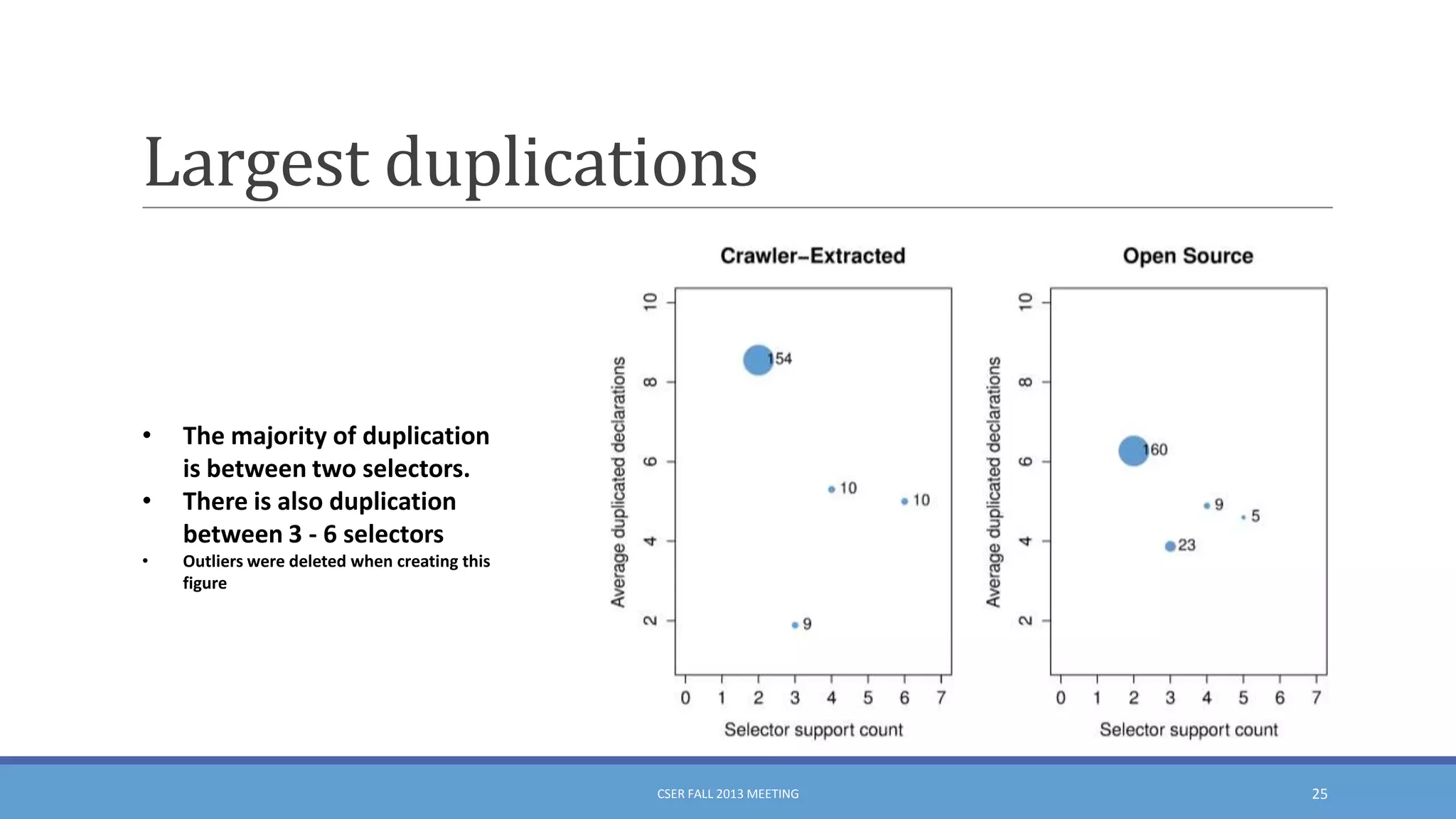
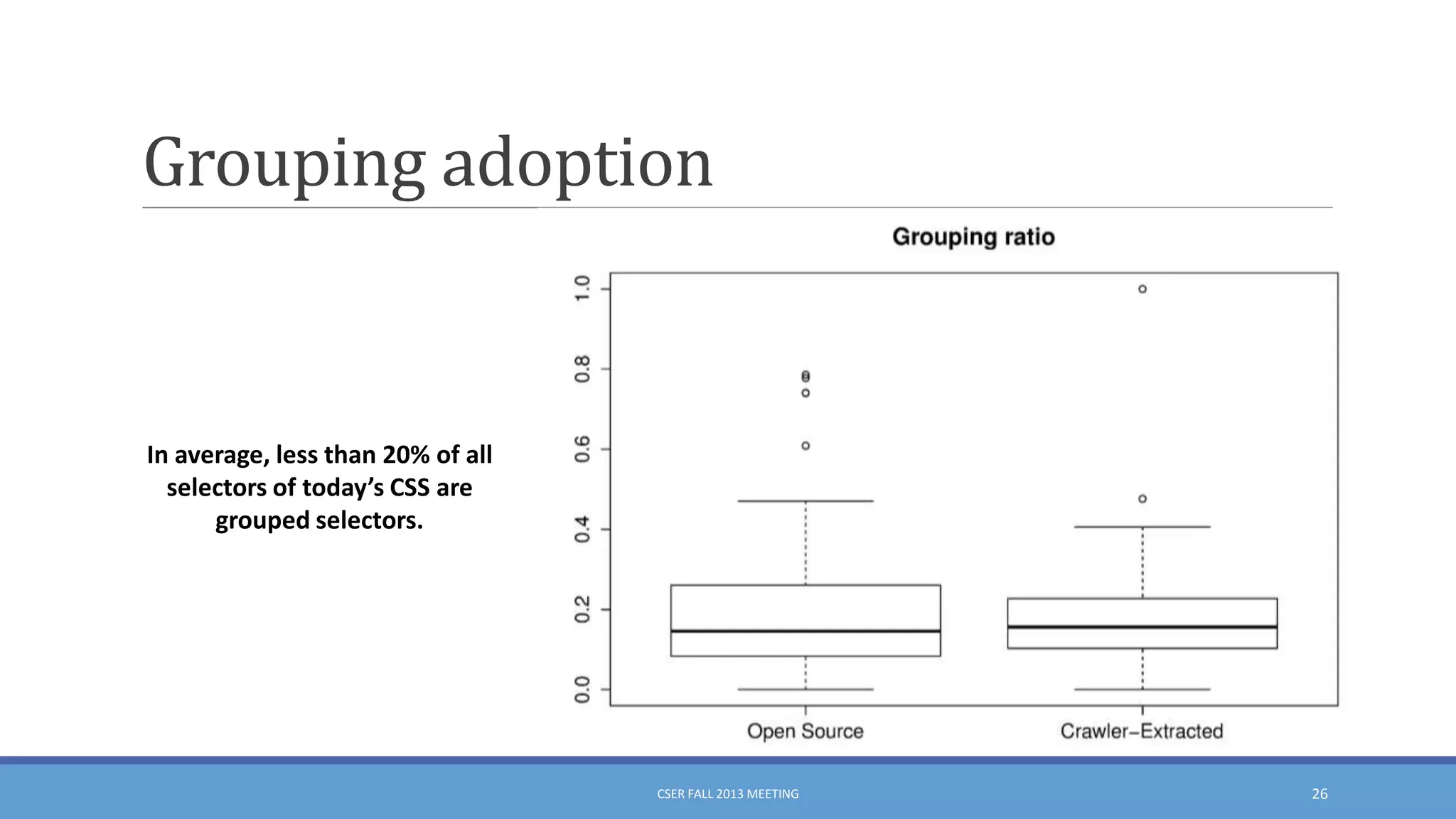
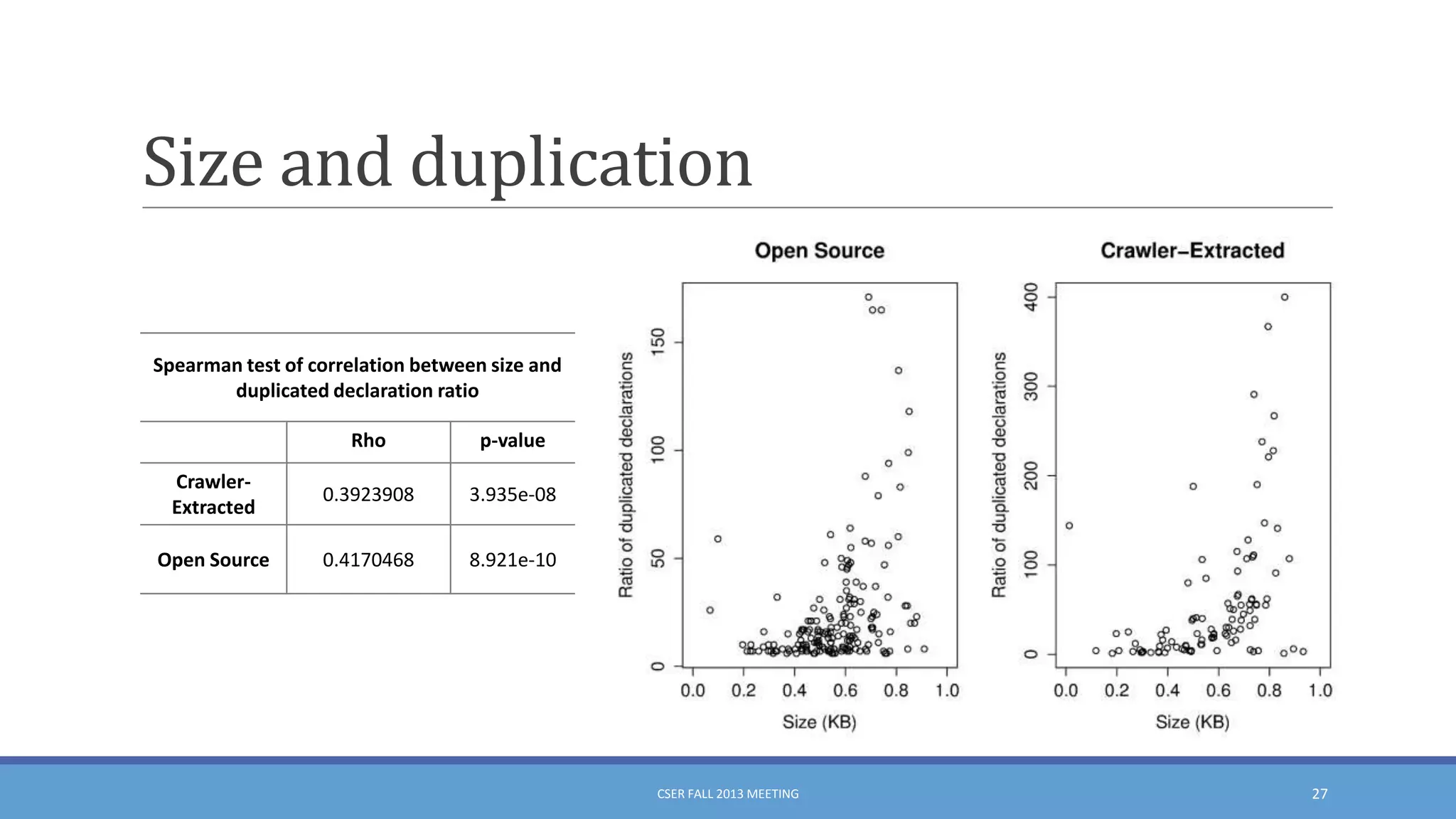
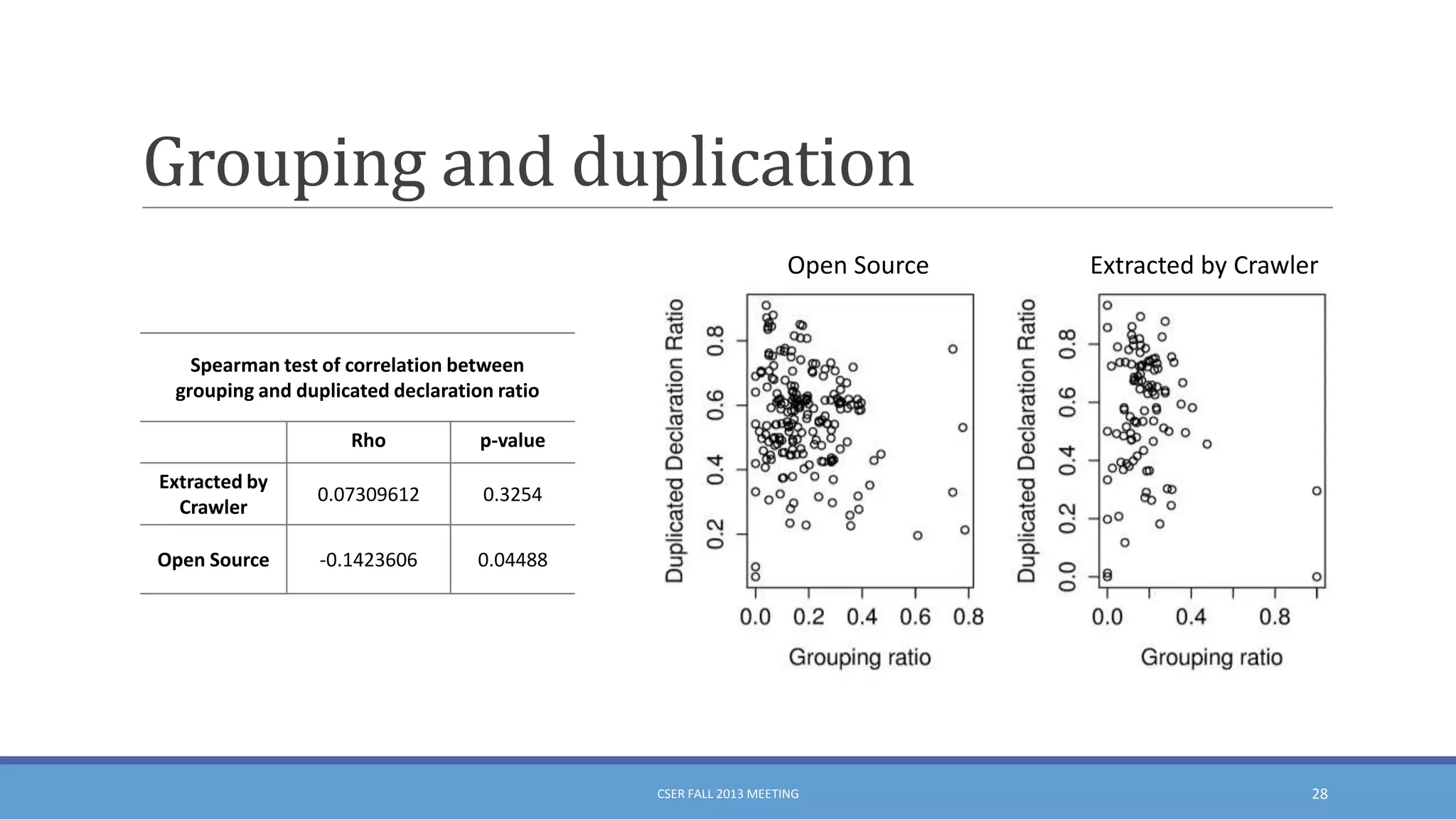
This document summarizes an empirical study on duplication in Cascading Style Sheets (CSS). It finds that about 60% of declarations are duplicated on average across CSS files from various websites. The study analyzes three types of duplication and detects duplication by parsing CSS into a model. It examines CSS files from open source projects and top websites, finding the largest duplications are typically between two selectors and involve five or more common declarations. While CSS size correlates with duplication, grouping adoption does not strongly correlate with reducing duplication. Future work is needed to refactor duplications and help migrate CSS to preprocessing languages.




![CSS is widely used…
90 percent of web developers use CSS [w3techs.com, Mozilla survey]
Large number of CSS contributors in open source world [ohloh.net]
100%
90%
80%
70%
60%
50%
40%
30%
20%
10%
0%
Mozilla survey results: What programming language do you use?
CSER FALL 2013 MEETING
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cser2013fall-140220183208-phpapp01/75/An-Empirical-Study-of-Duplication-in-Cascading-Style-Sheets-5-2048.jpg)