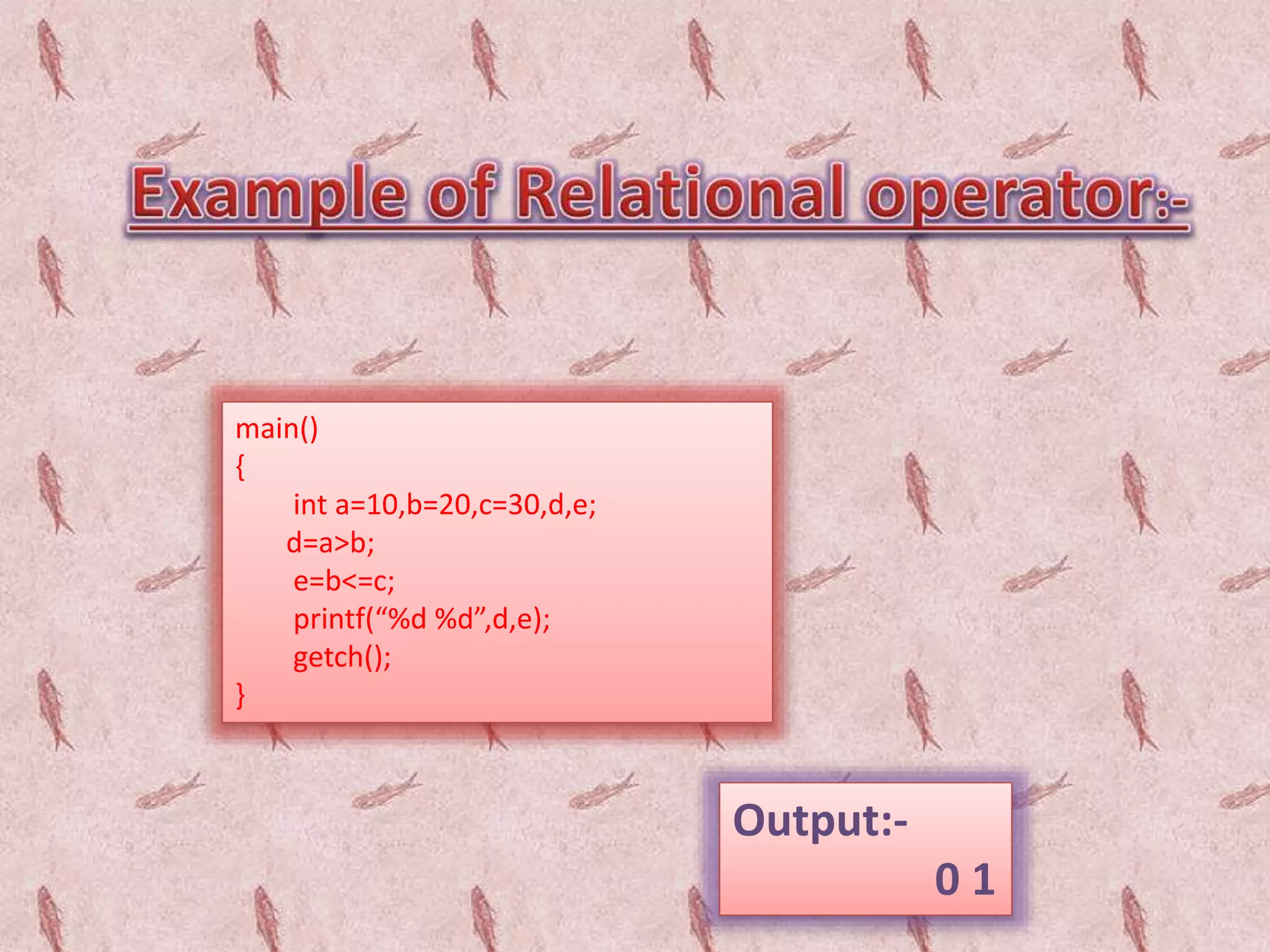
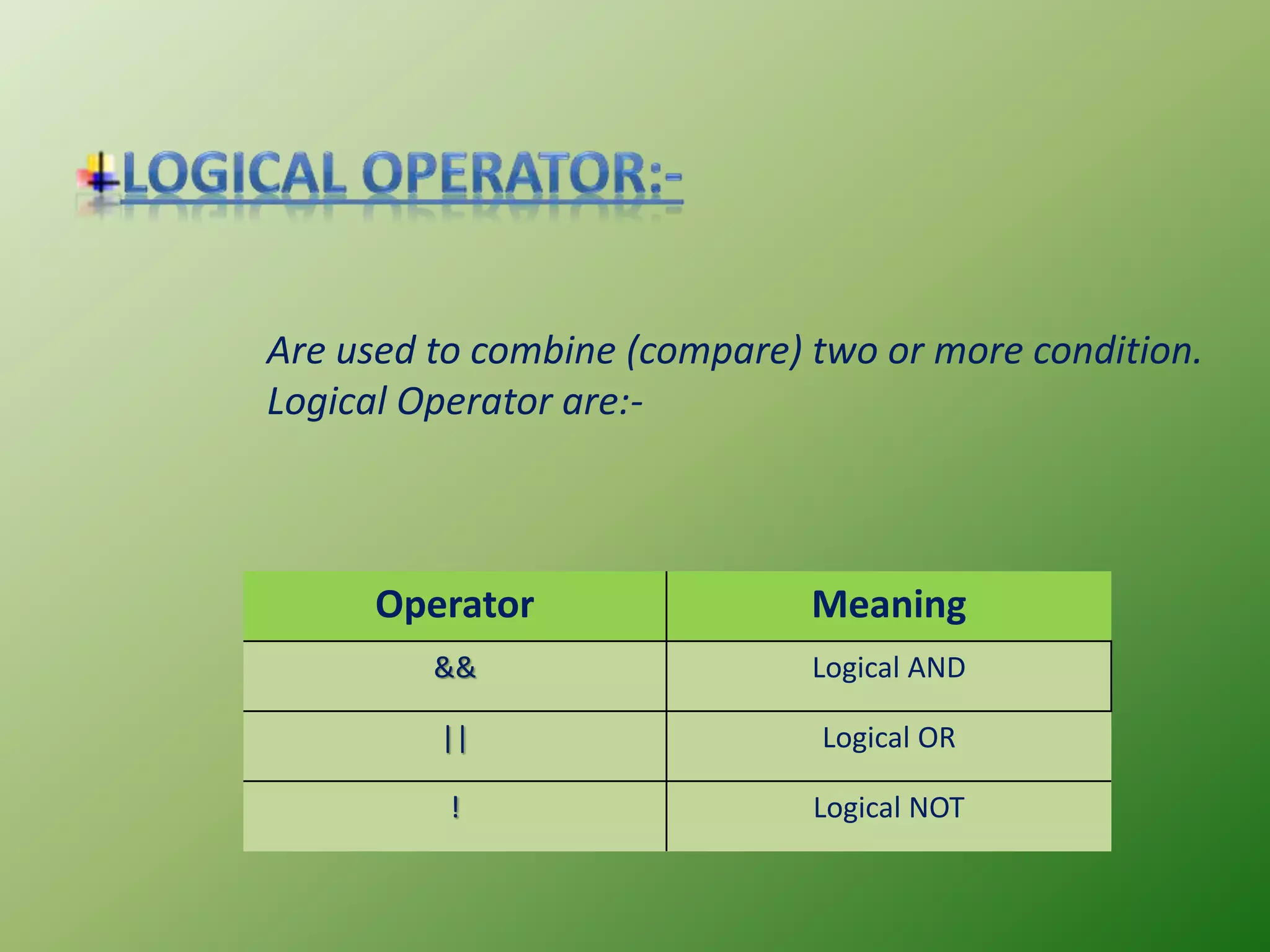
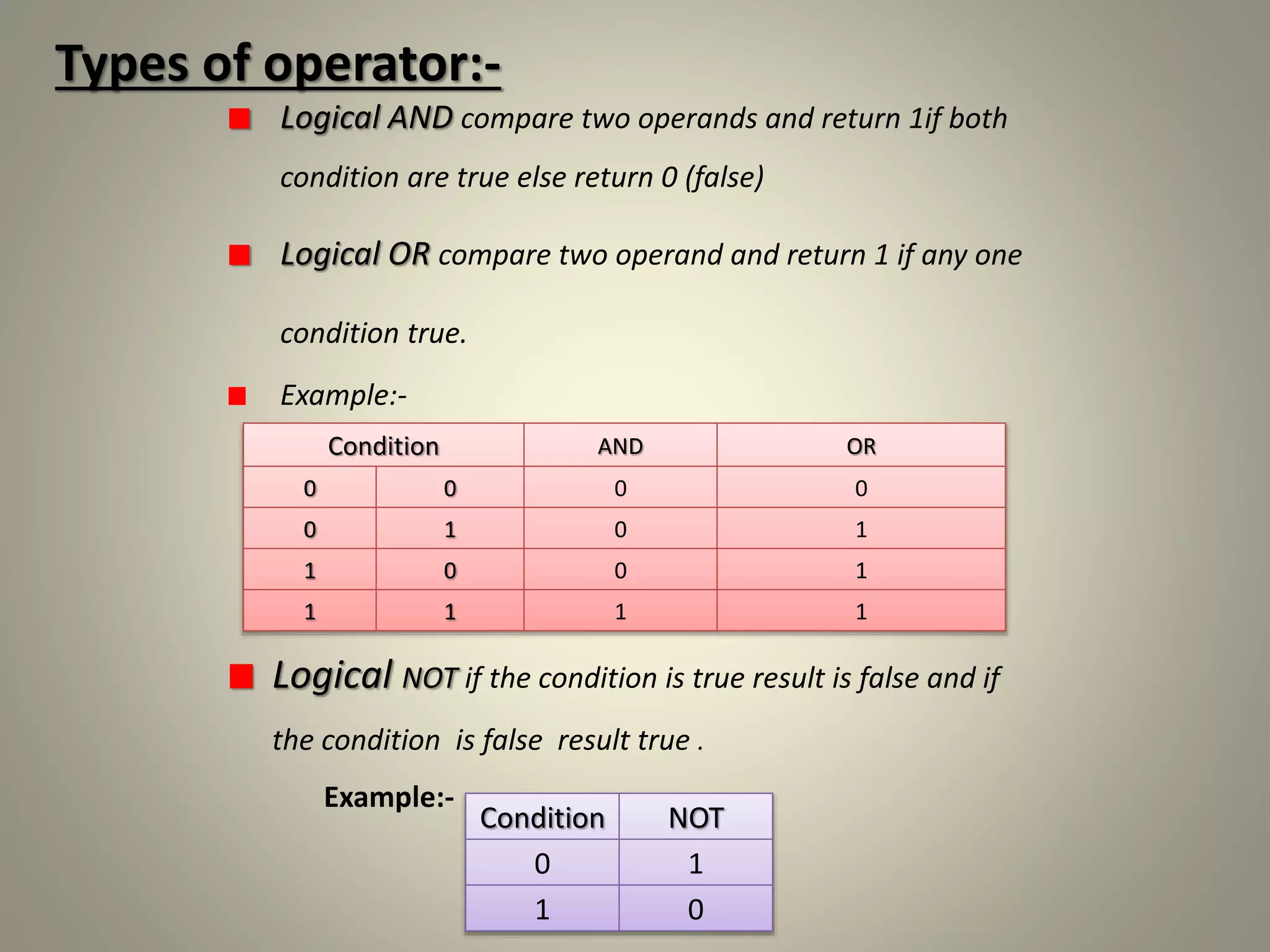
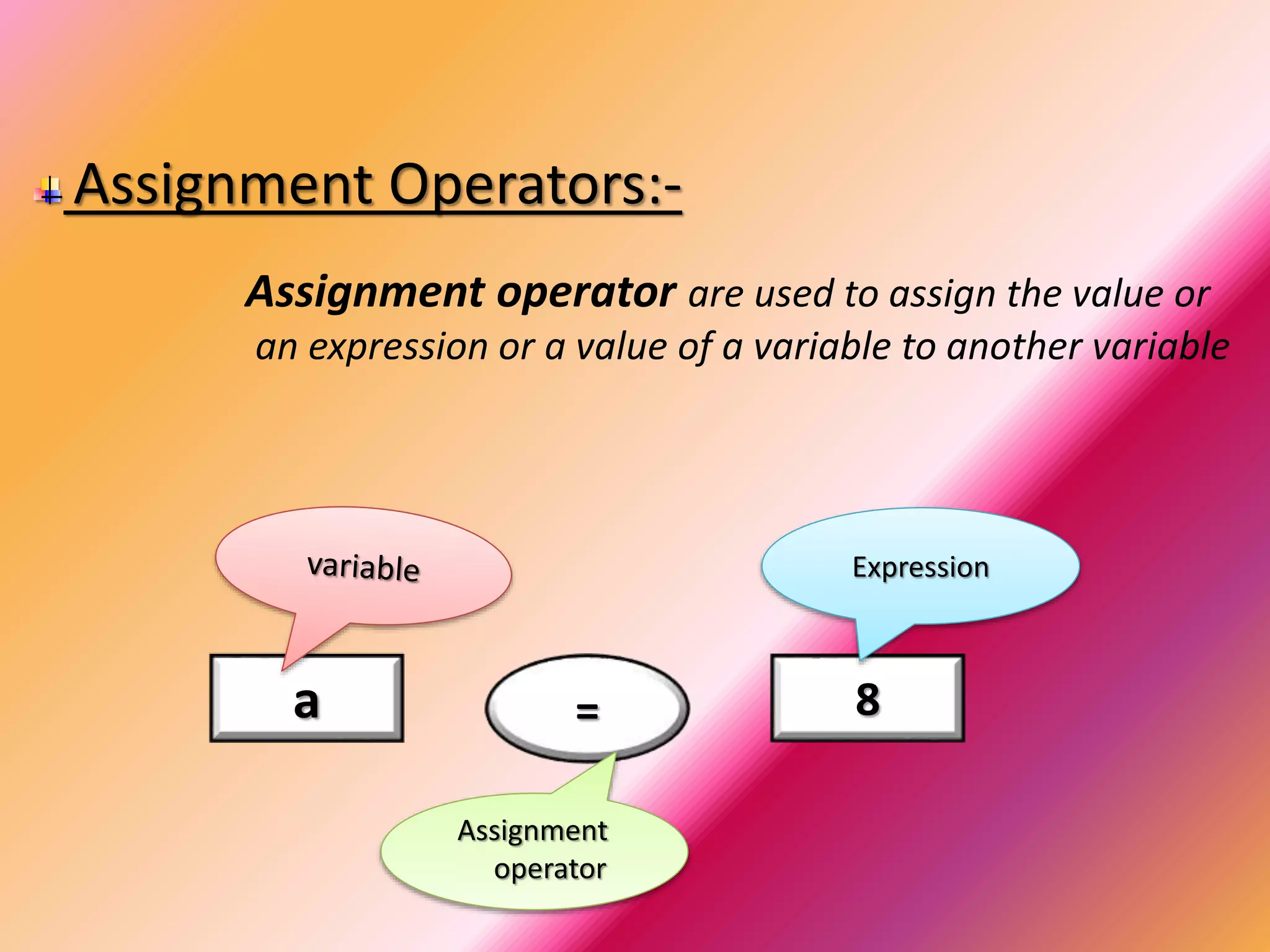
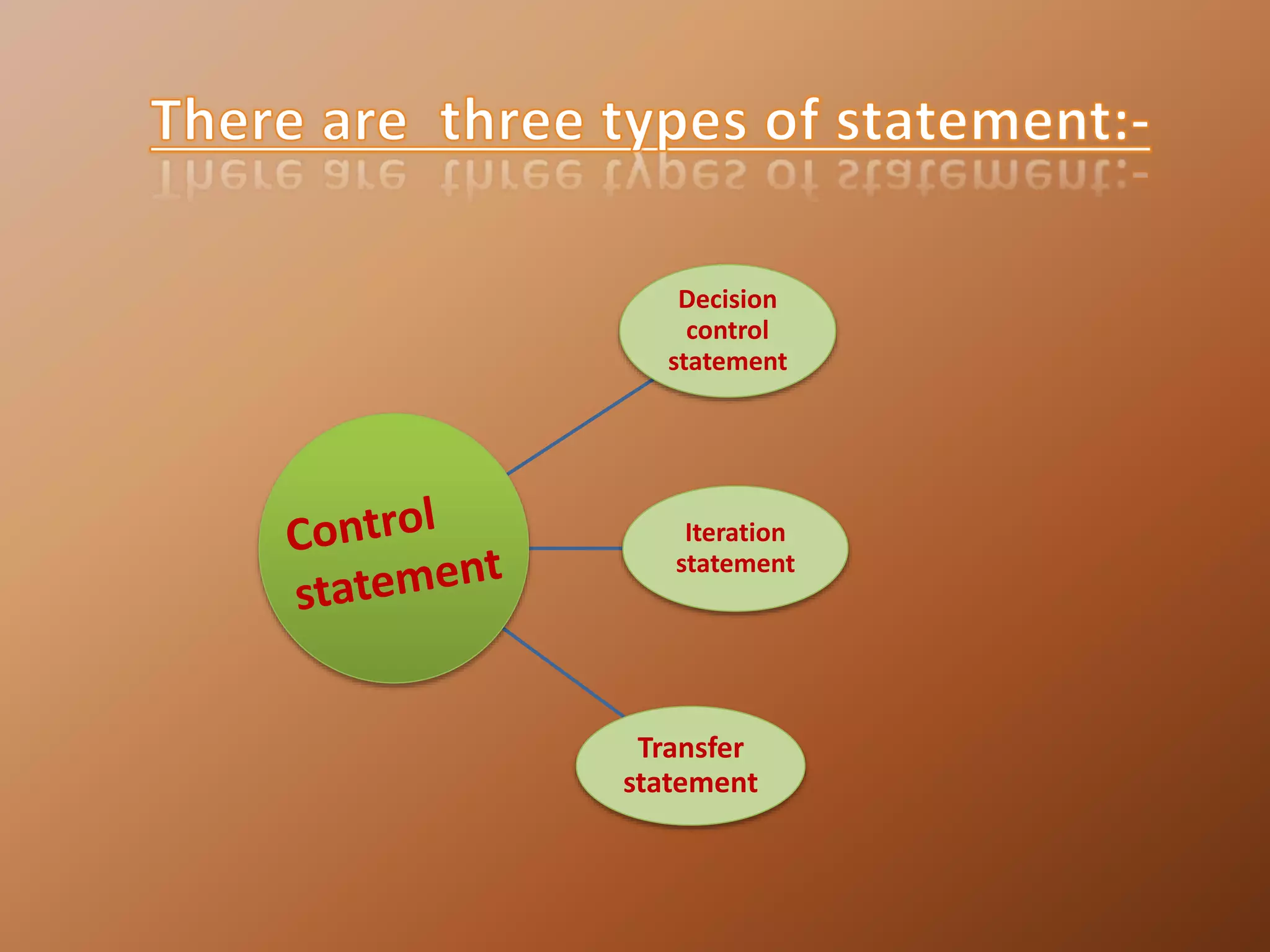
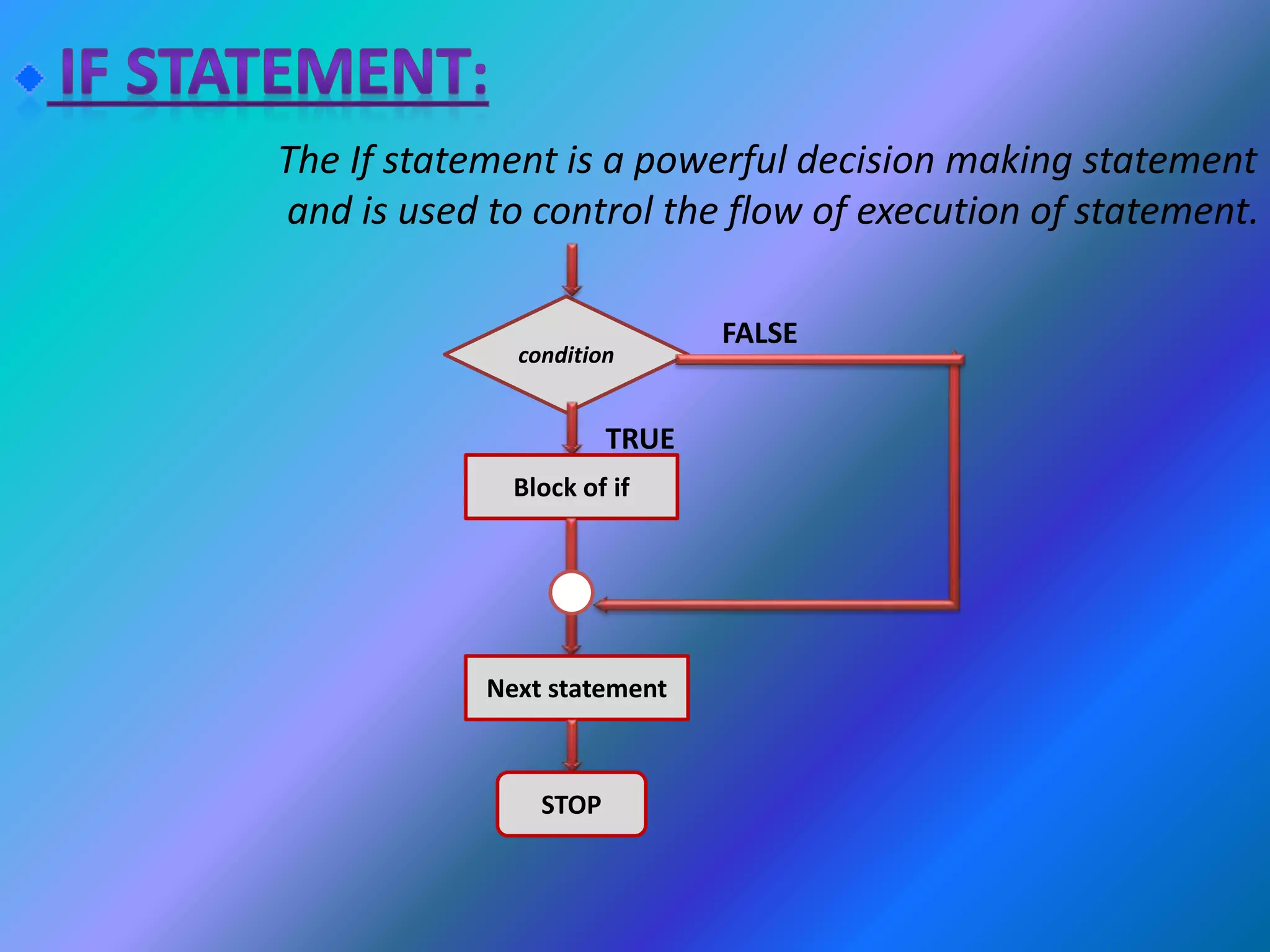
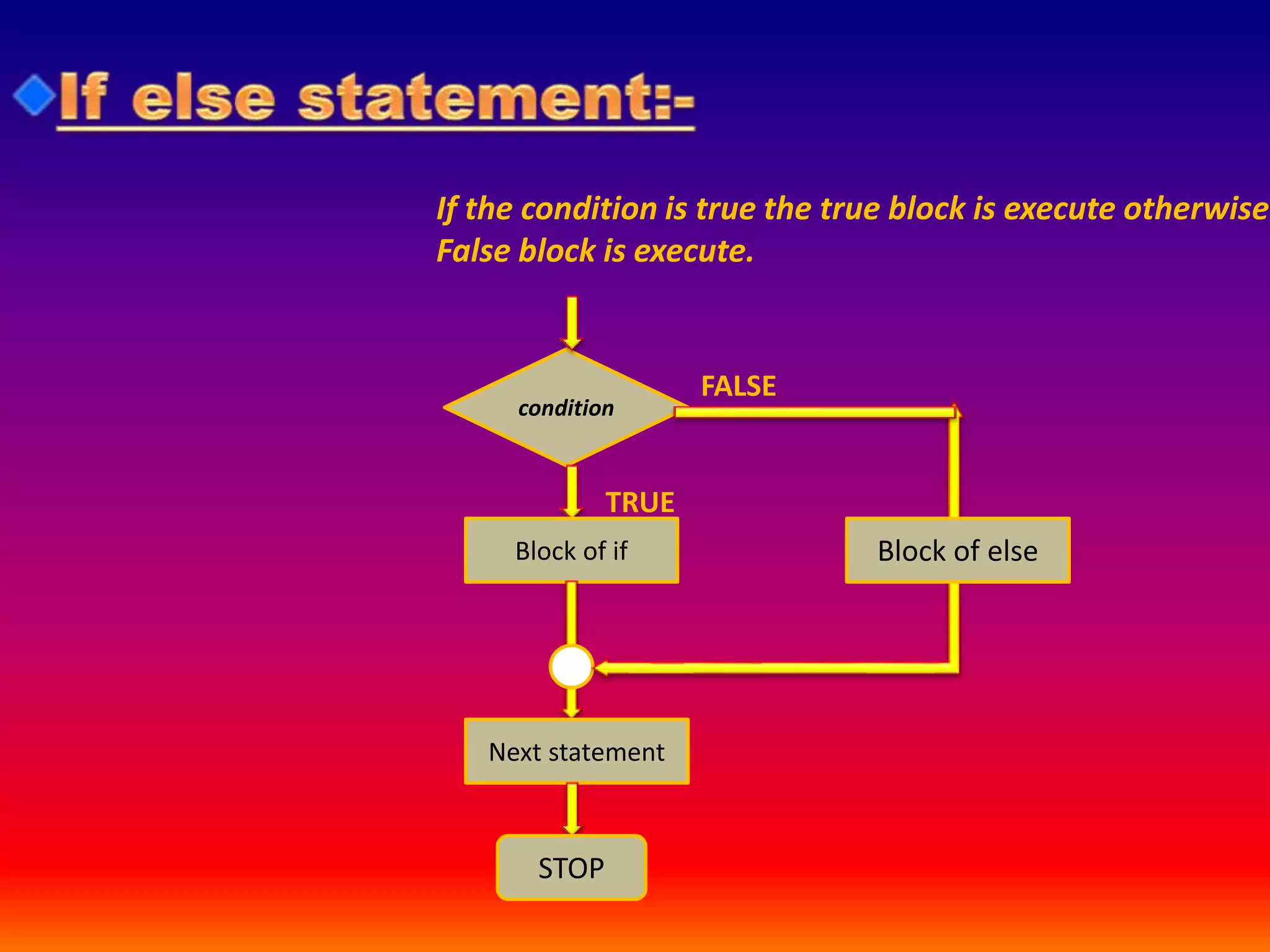
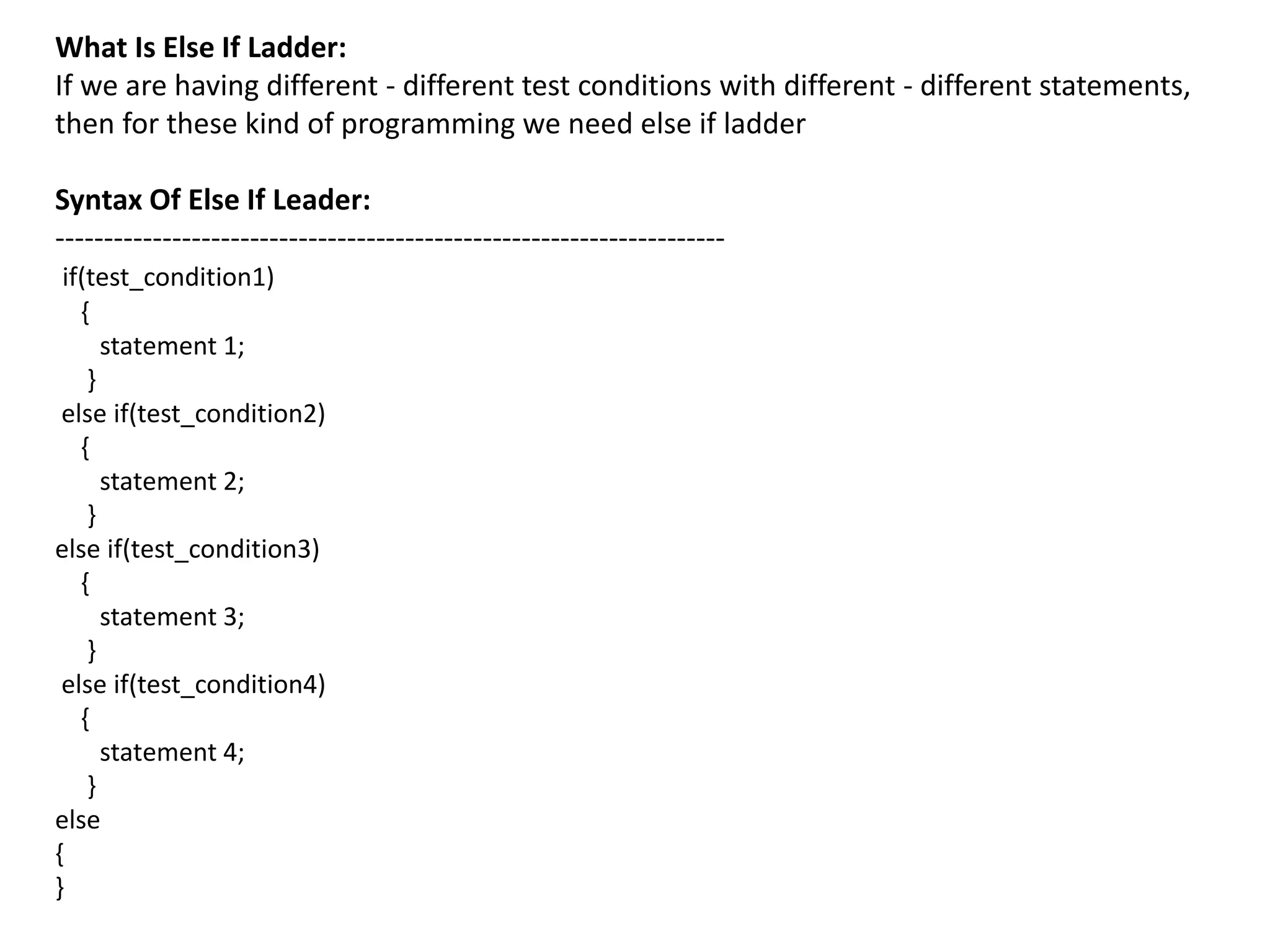
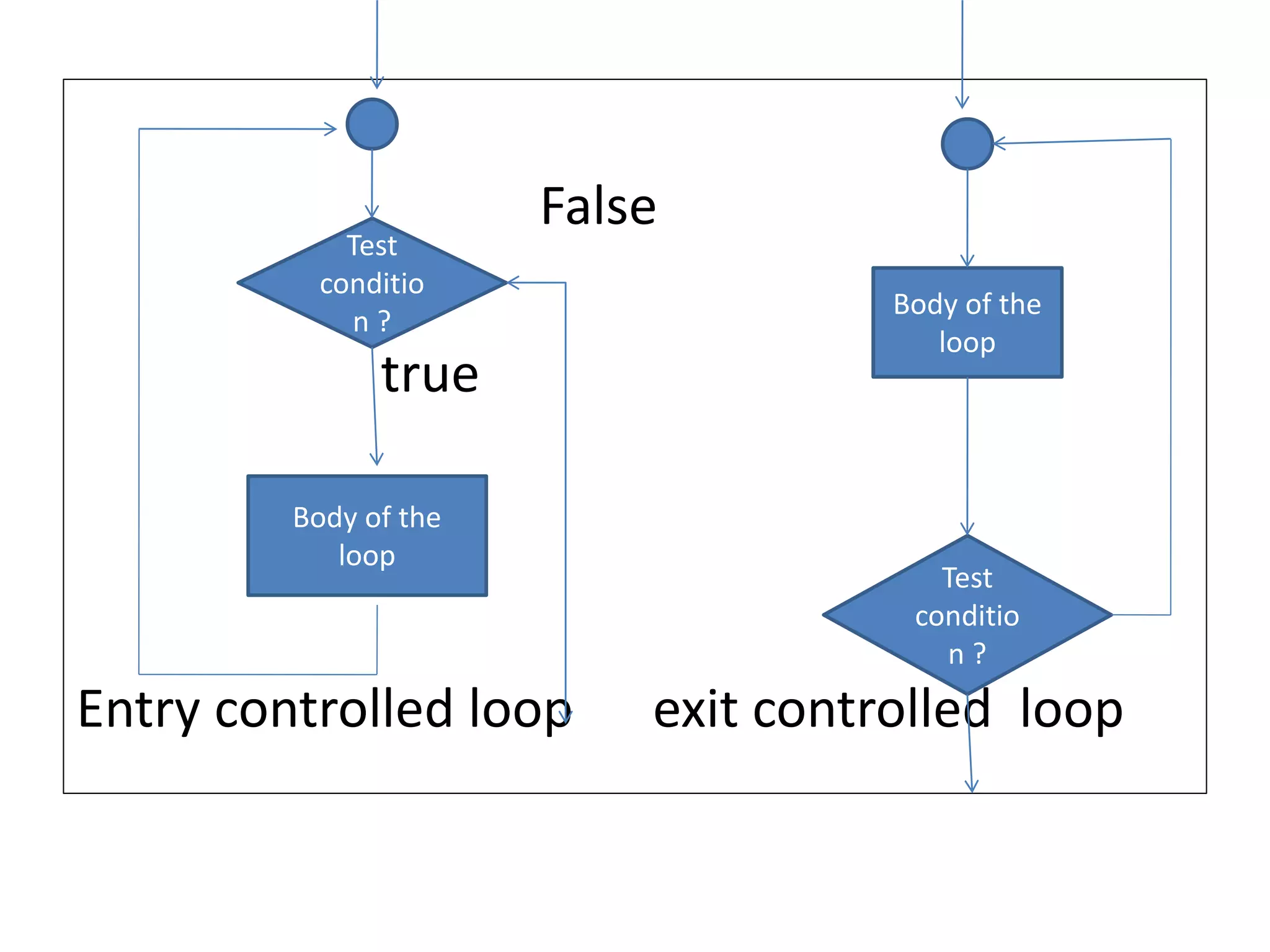
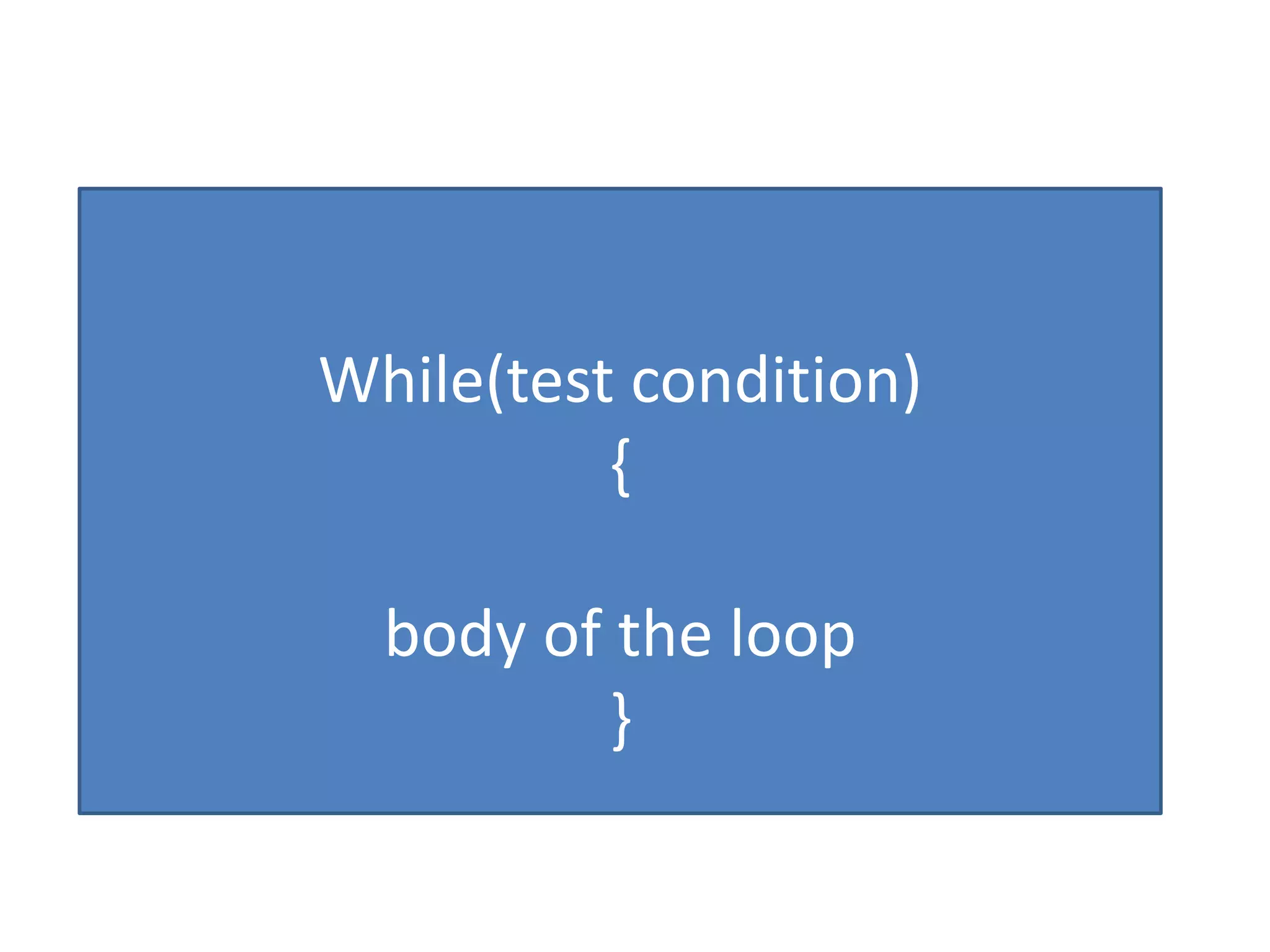
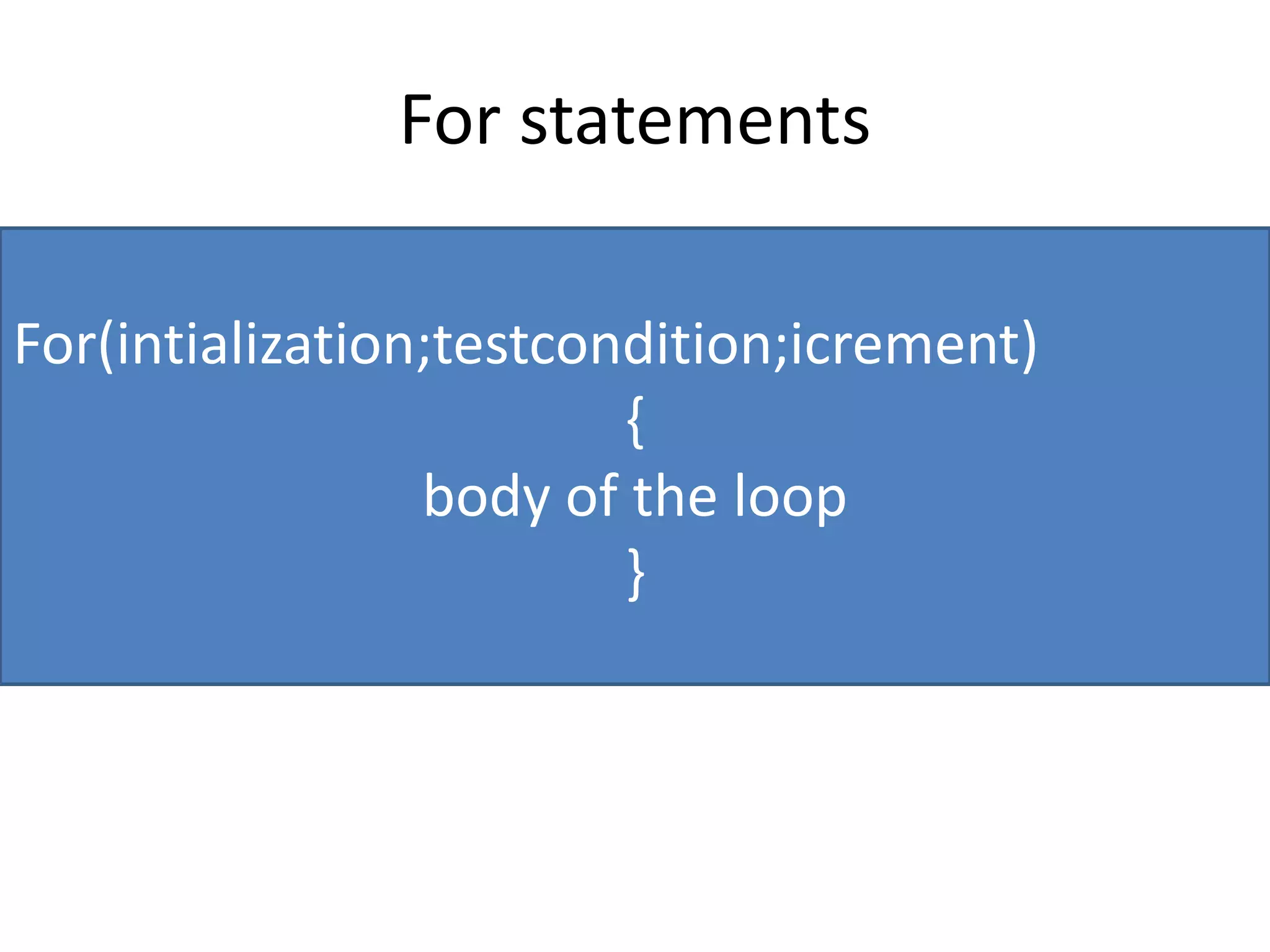
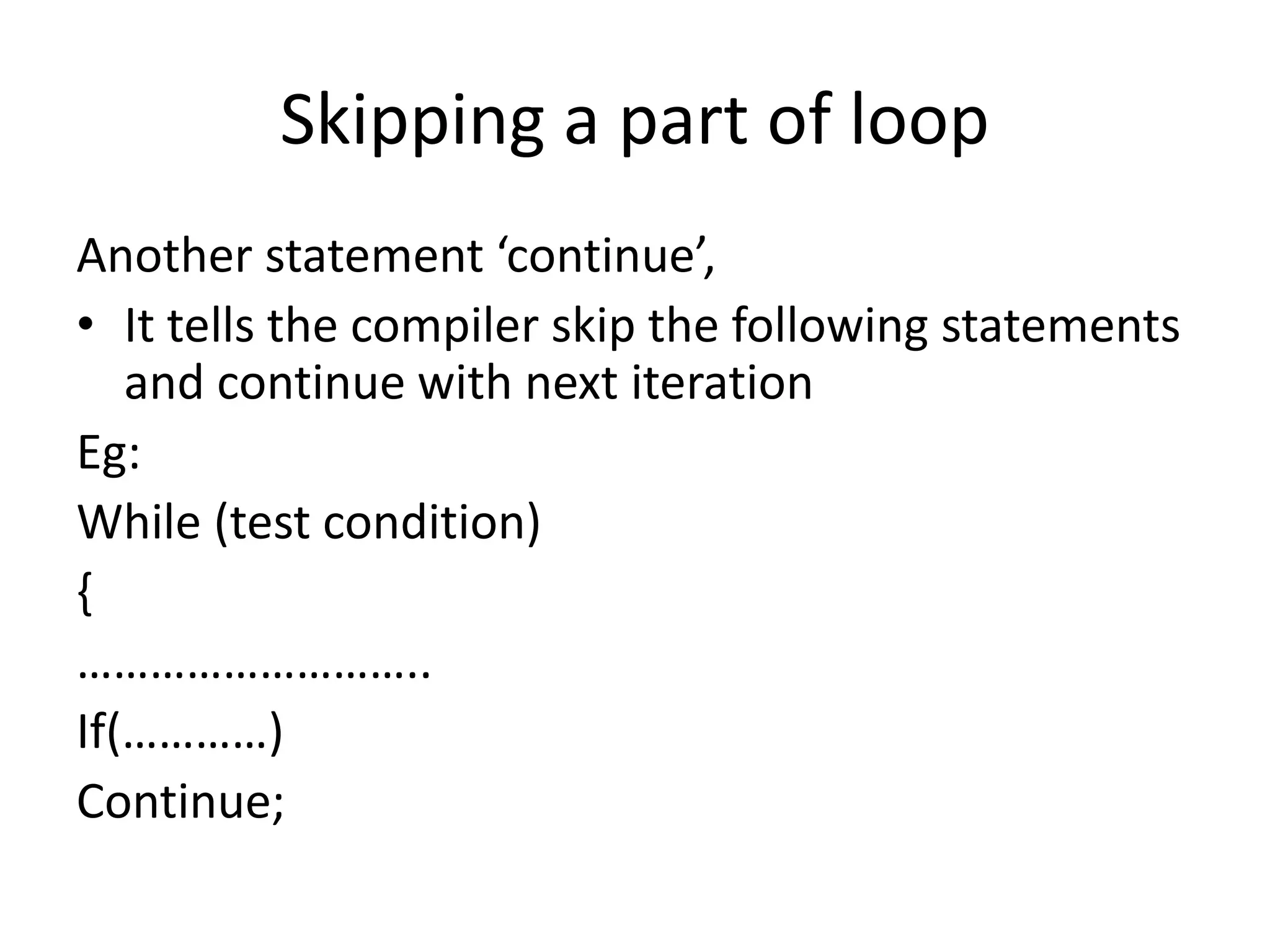
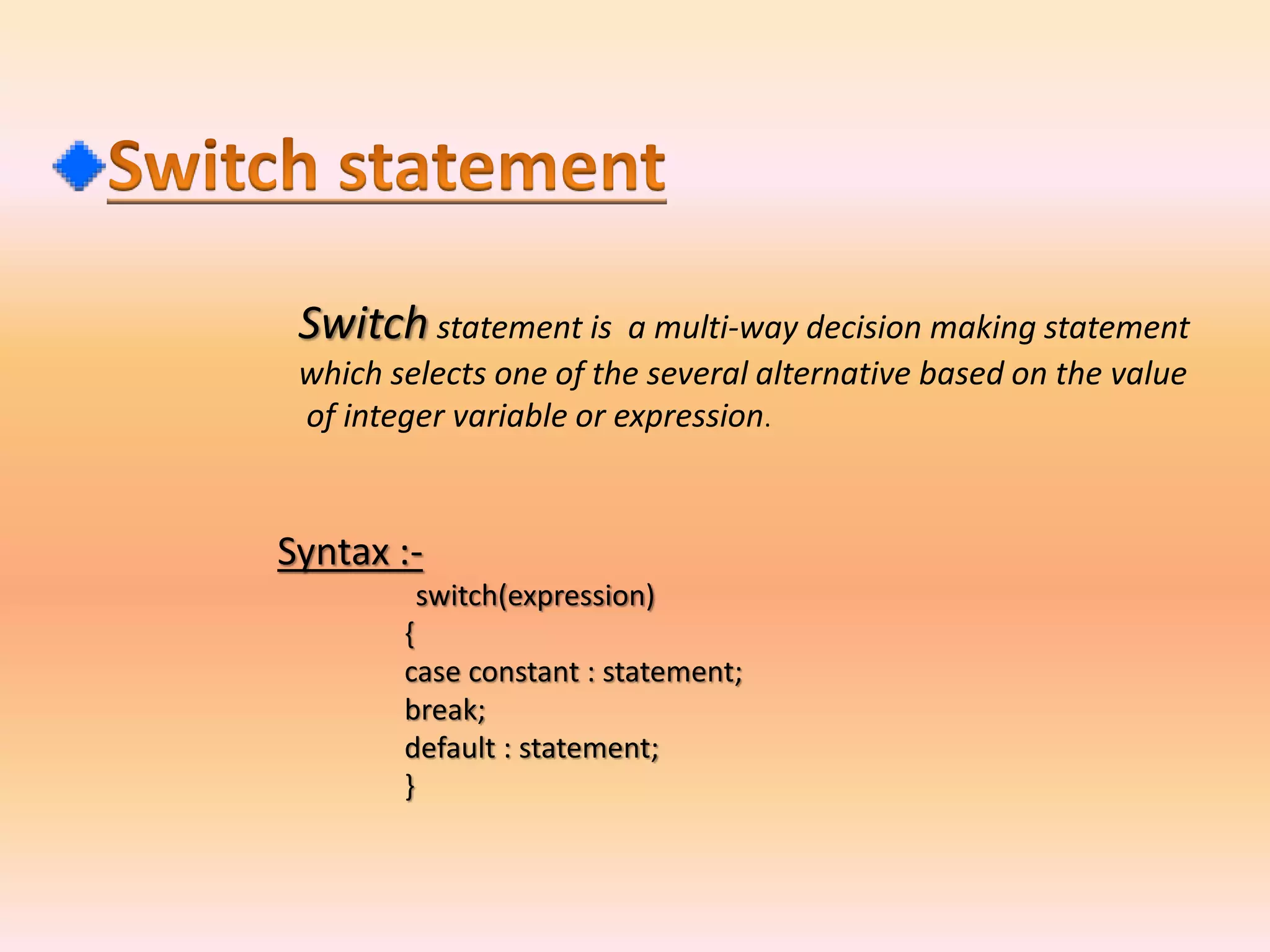
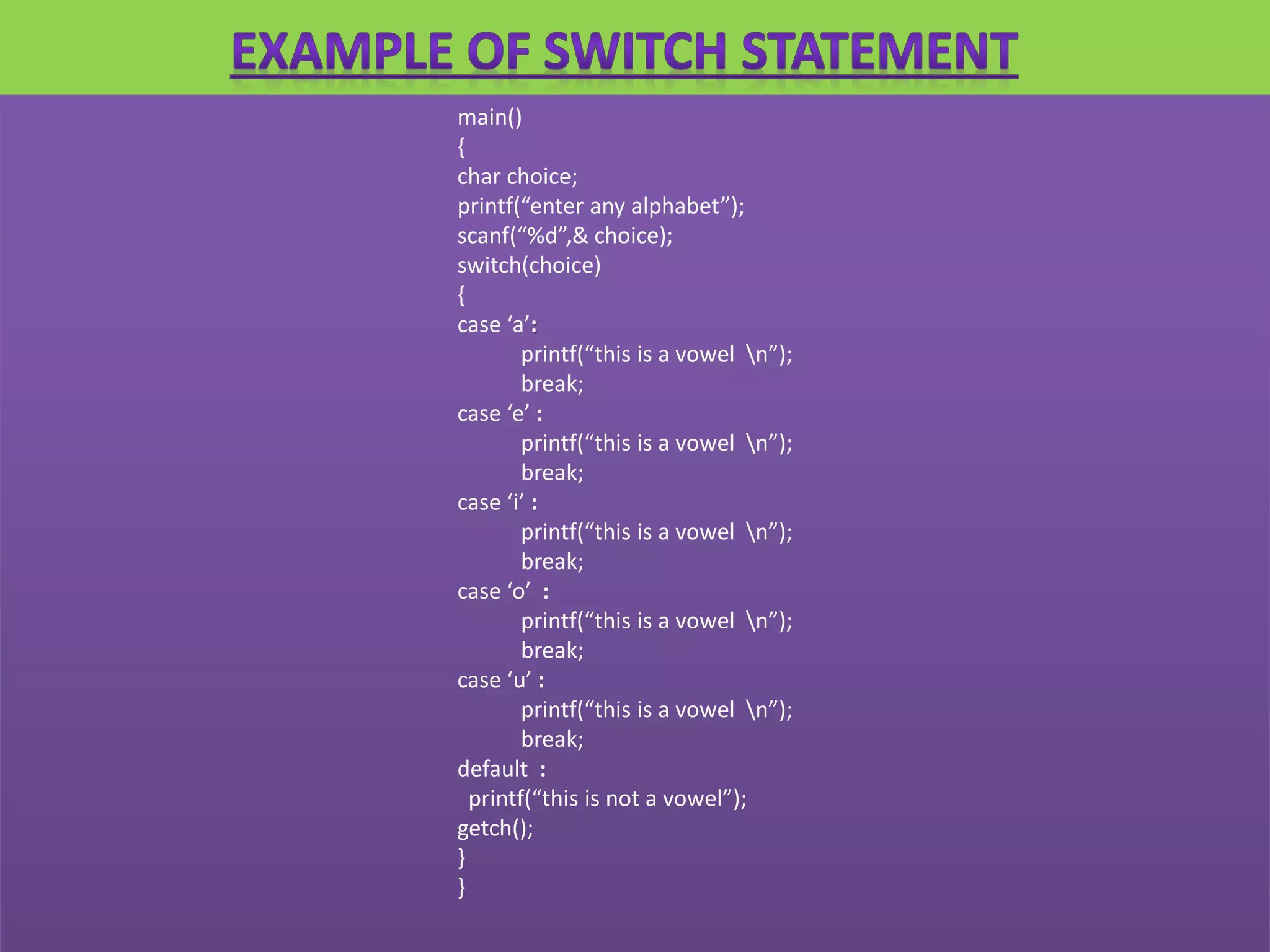
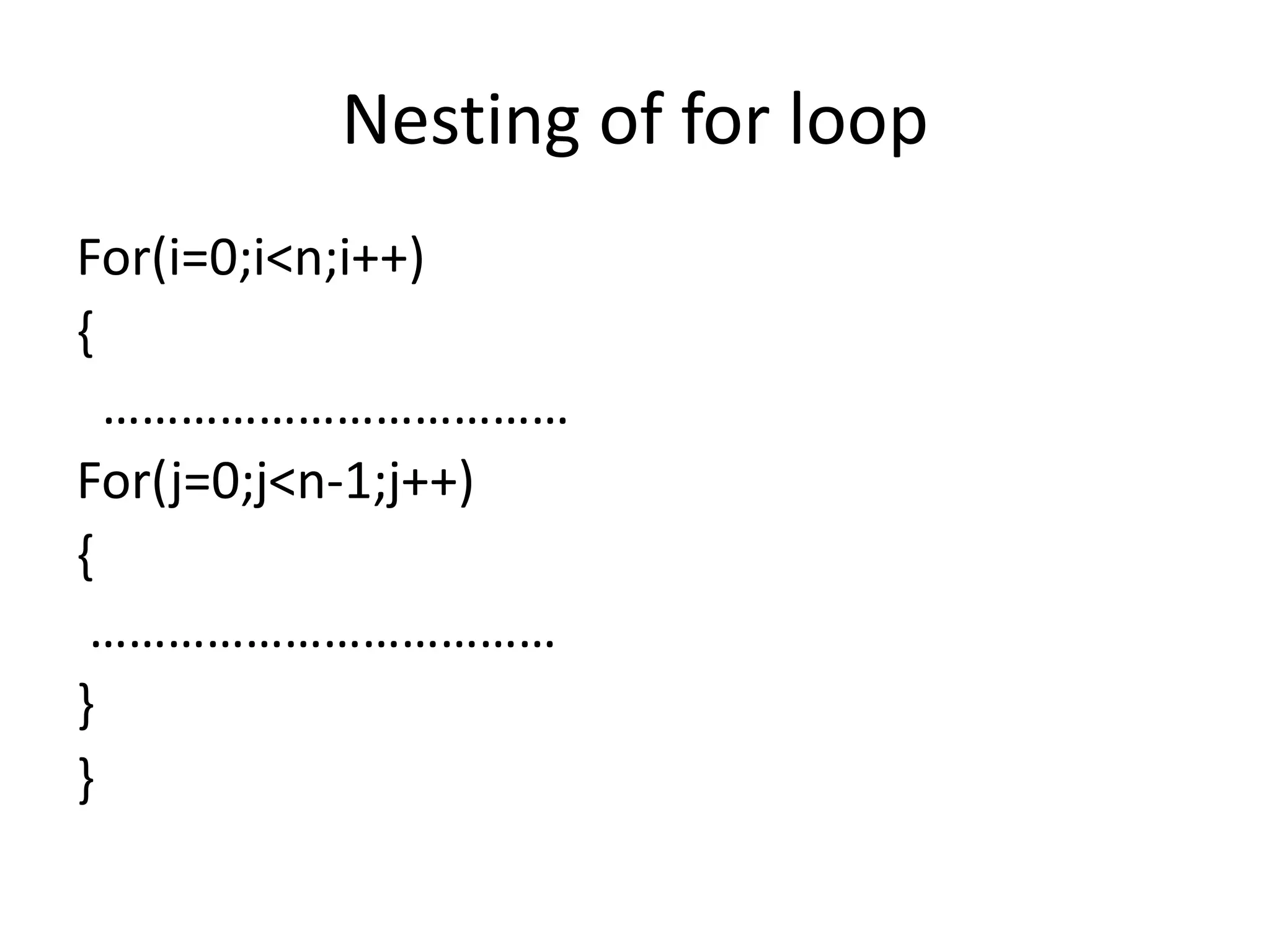Operator & control statements in C are used to perform operations and control program flow. Arithmetic operators (+, -, *, /, %) are used for mathematical calculations on integers and floating-point numbers. Relational operators (<, <=, >, >=, ==, !=) compare two operands. Logical operators (&&, ||, !) combine conditions. Control statements like if-else, switch, while, for, break, continue and goto alter program execution based on conditions.