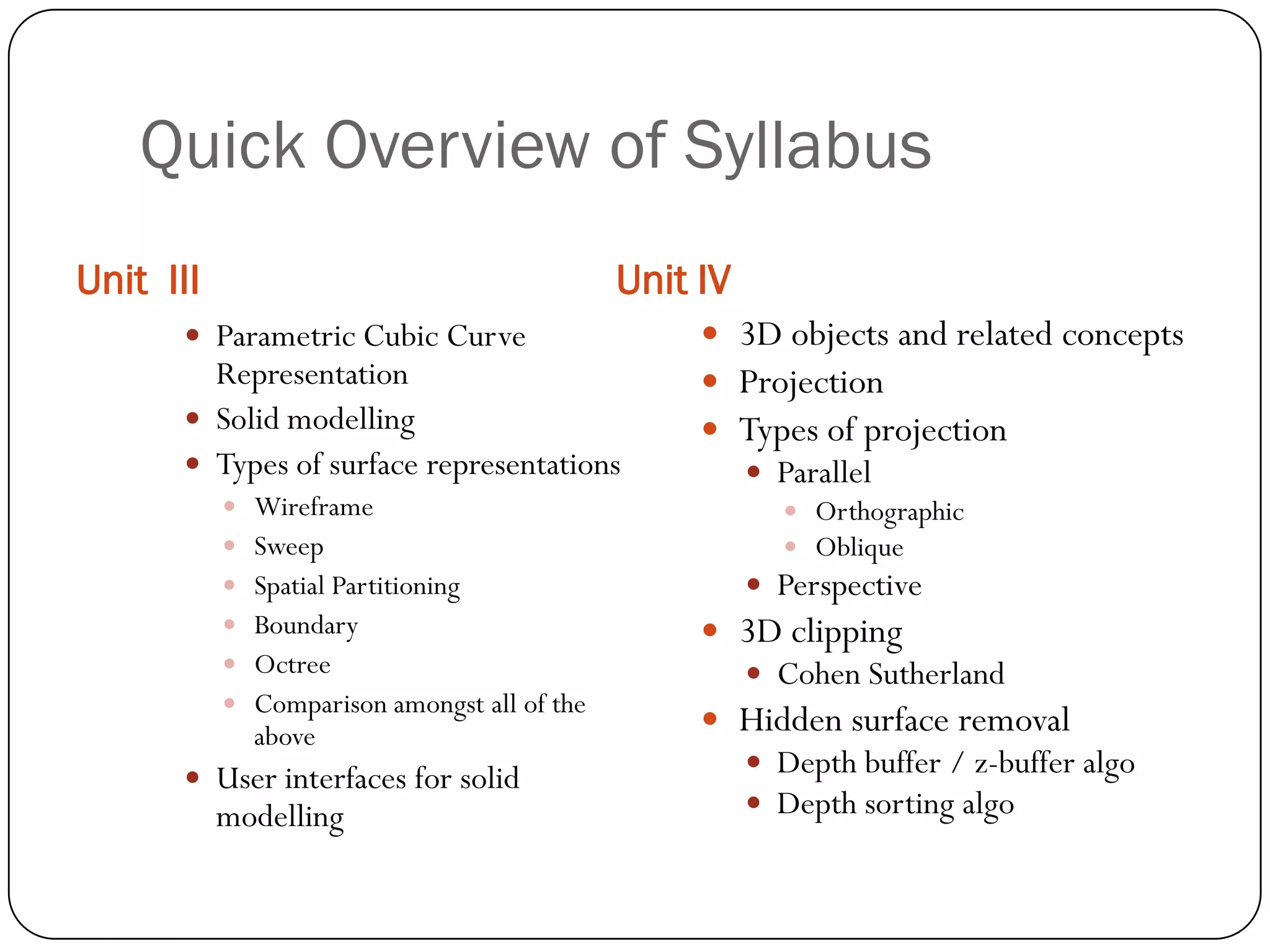
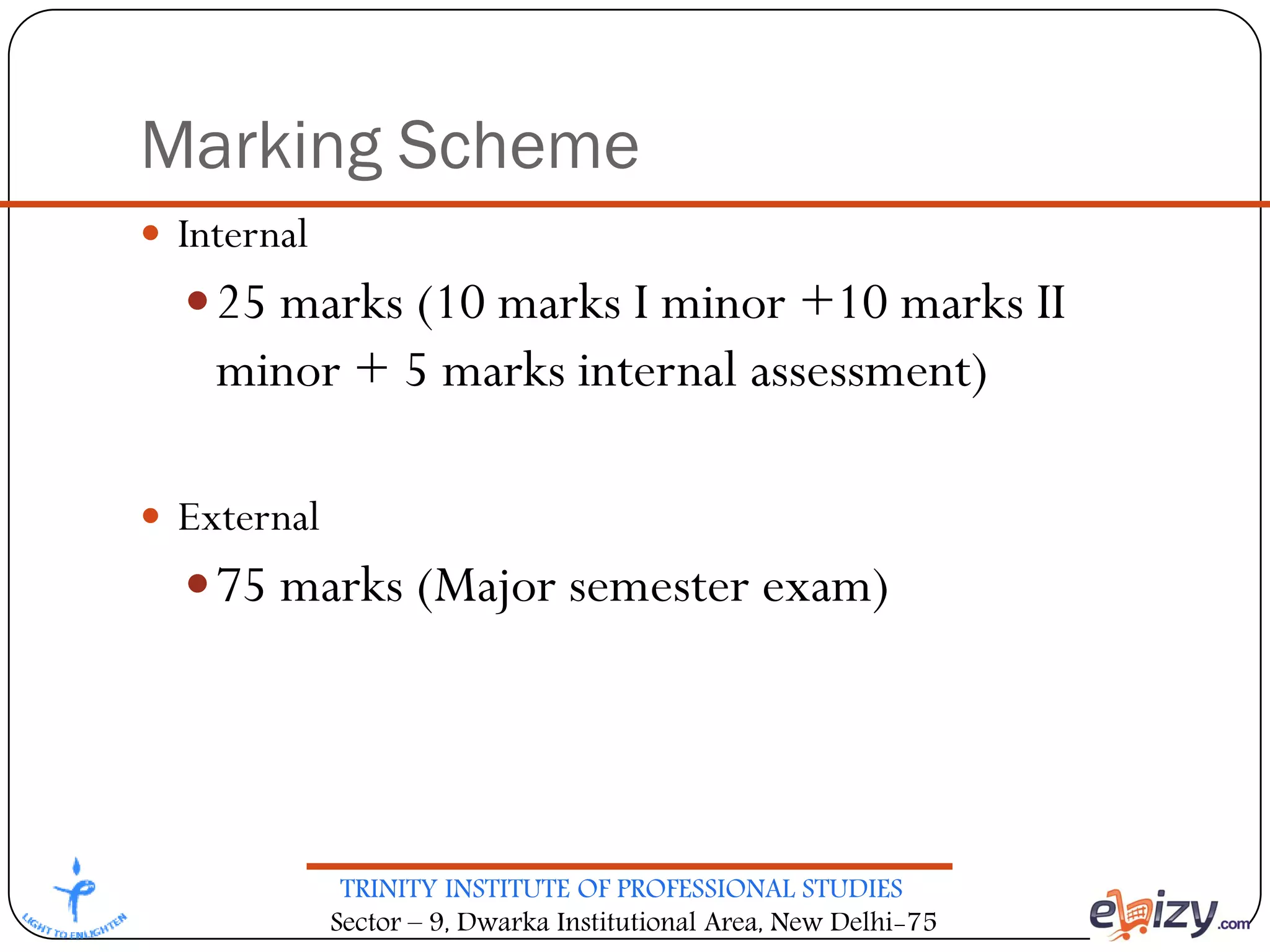
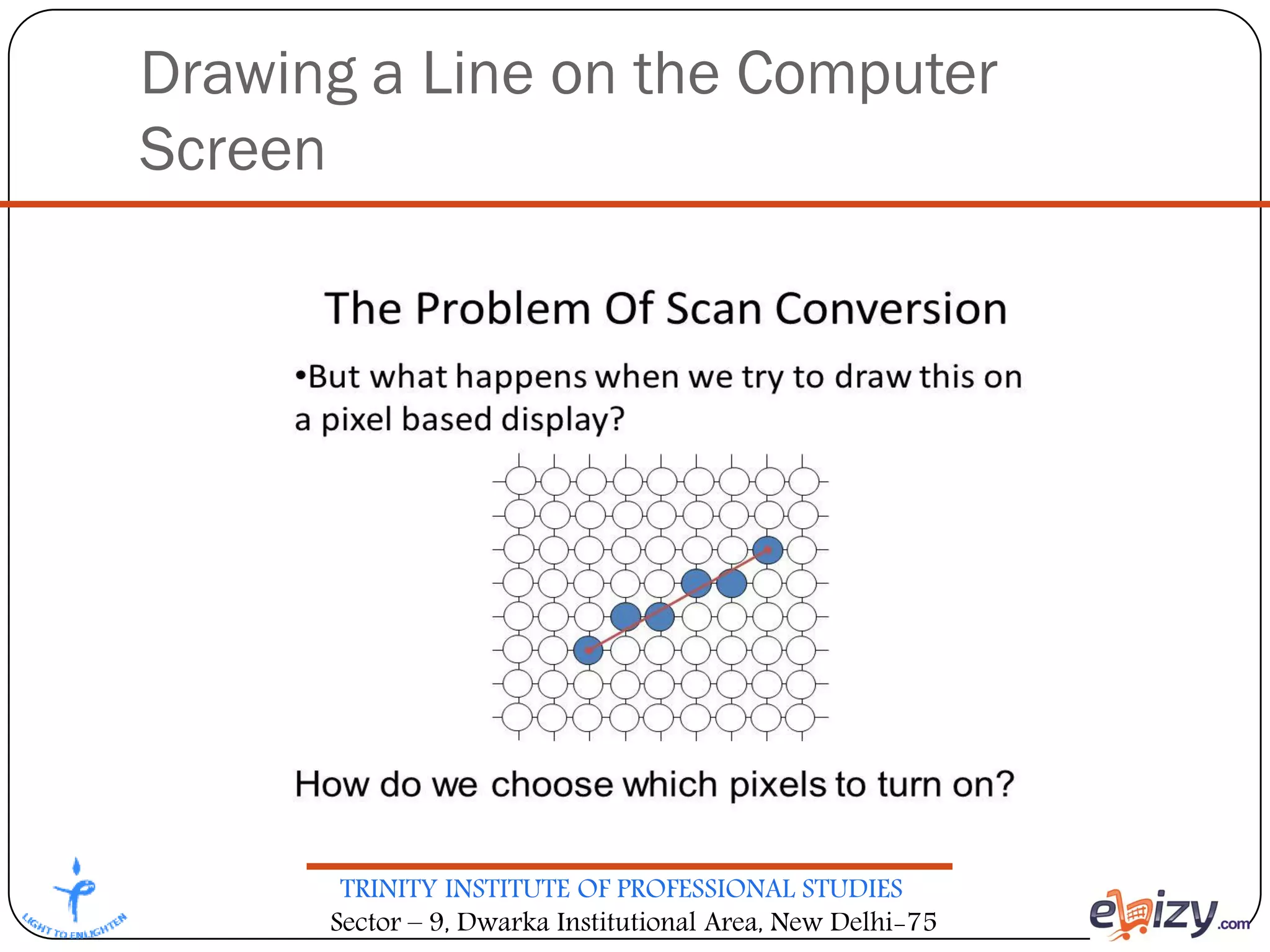
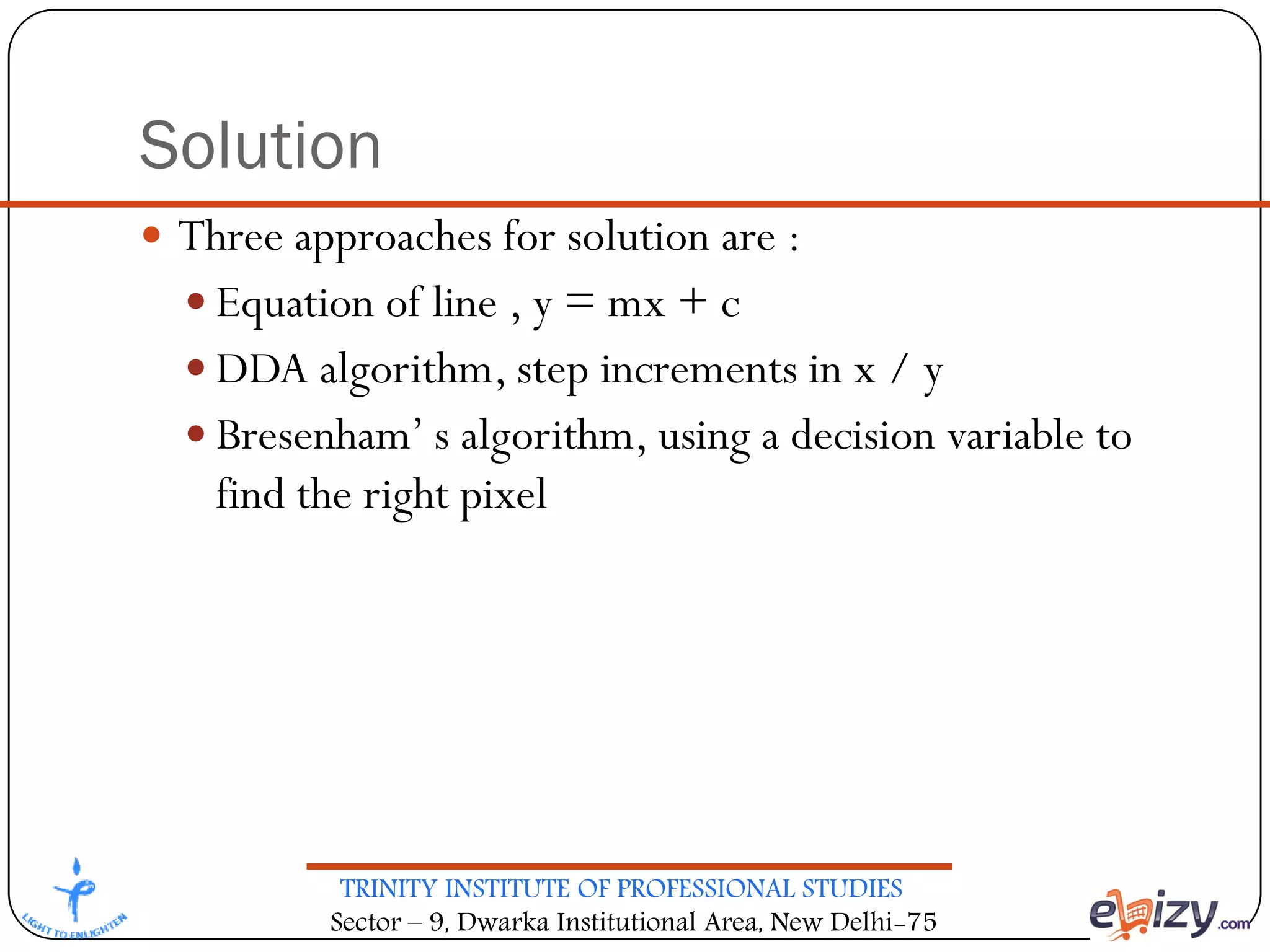
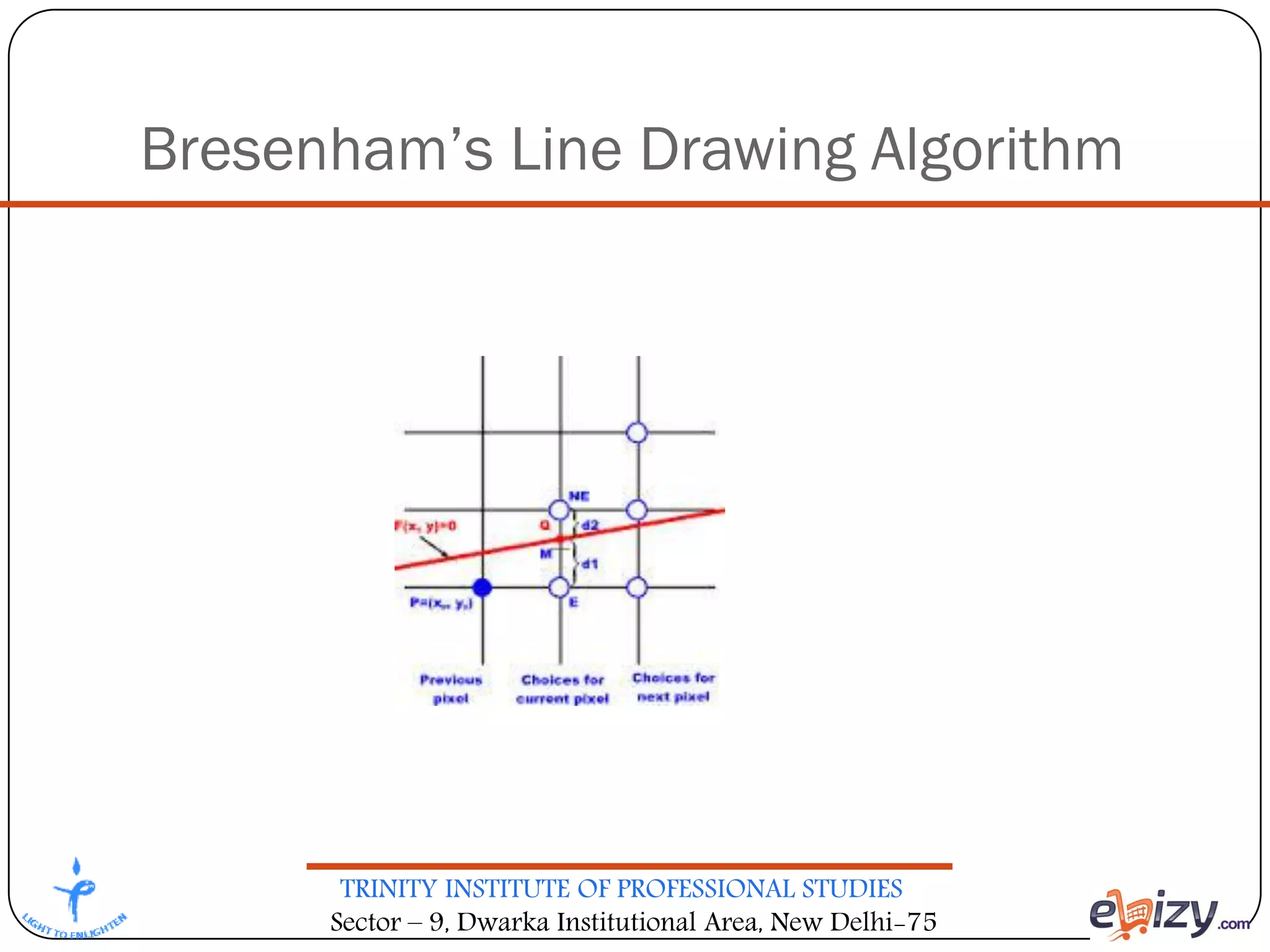
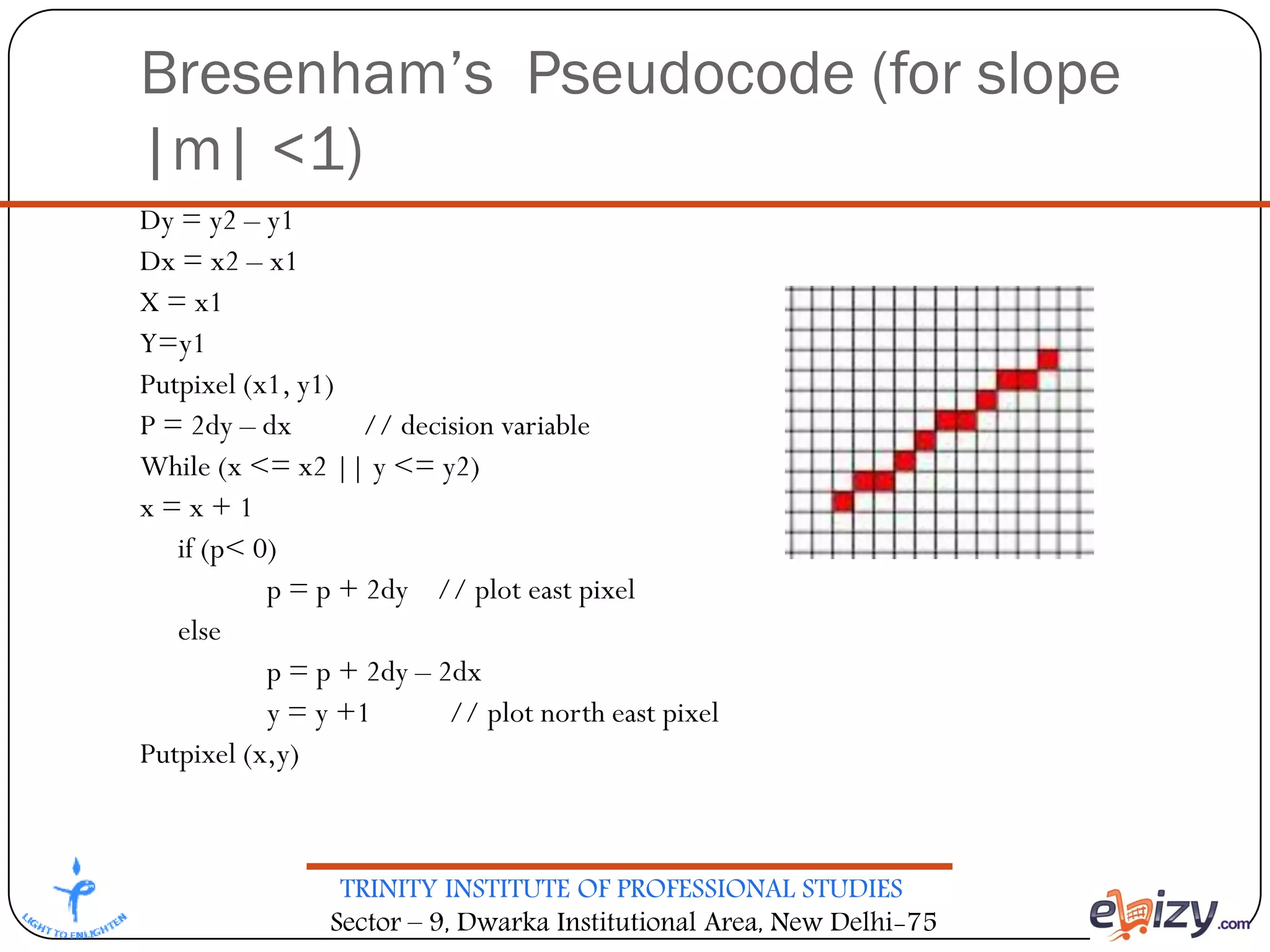
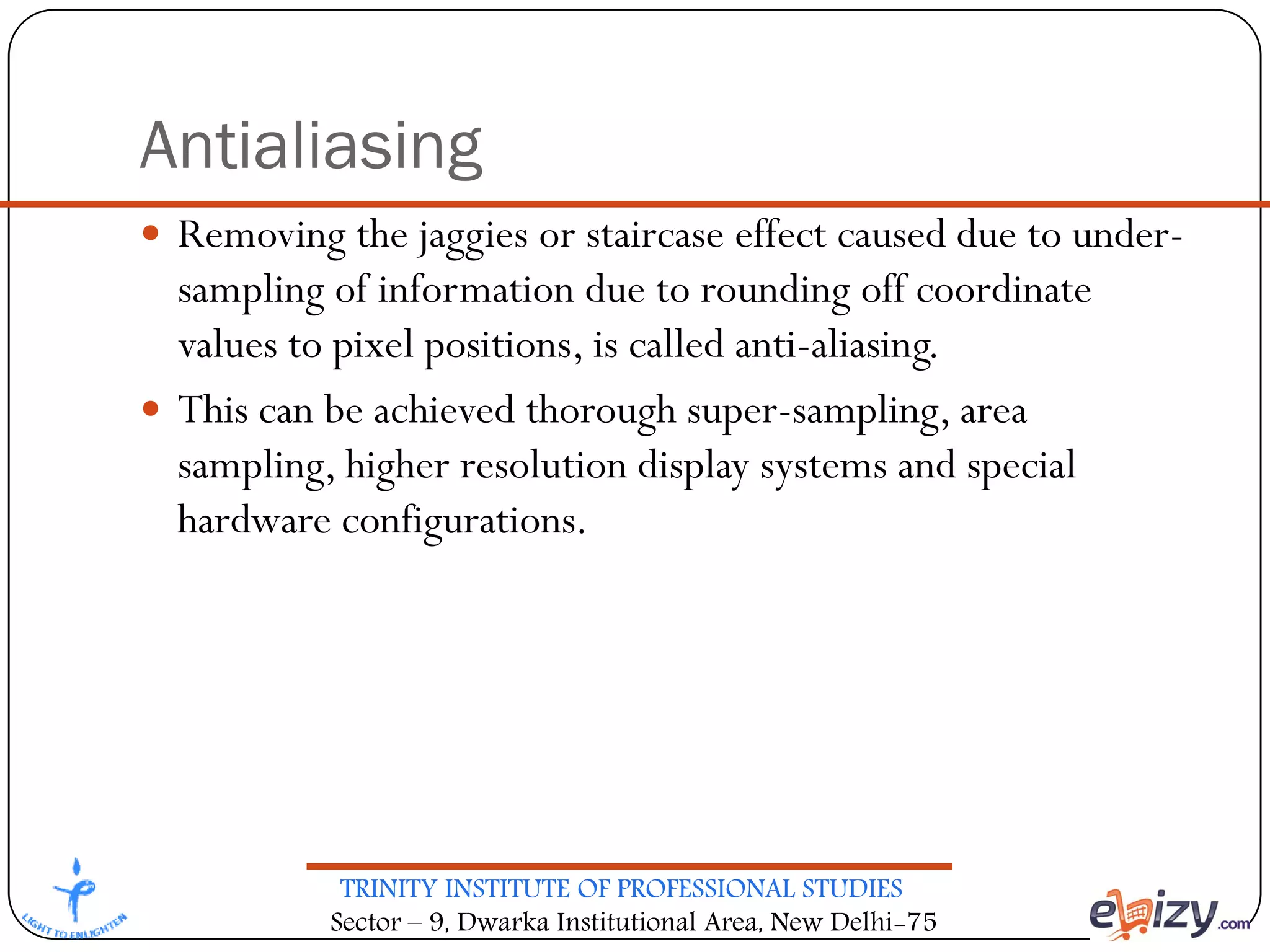
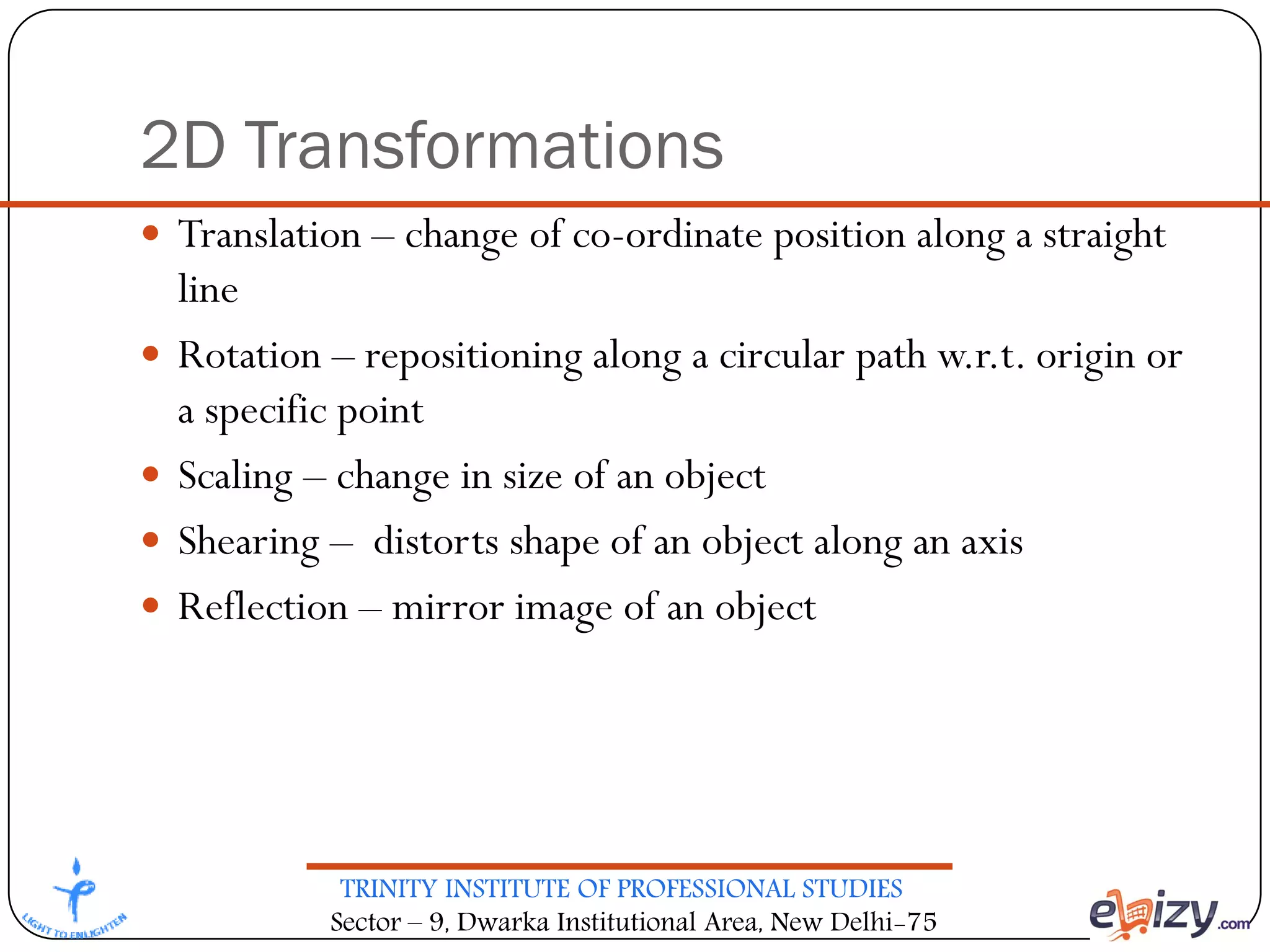
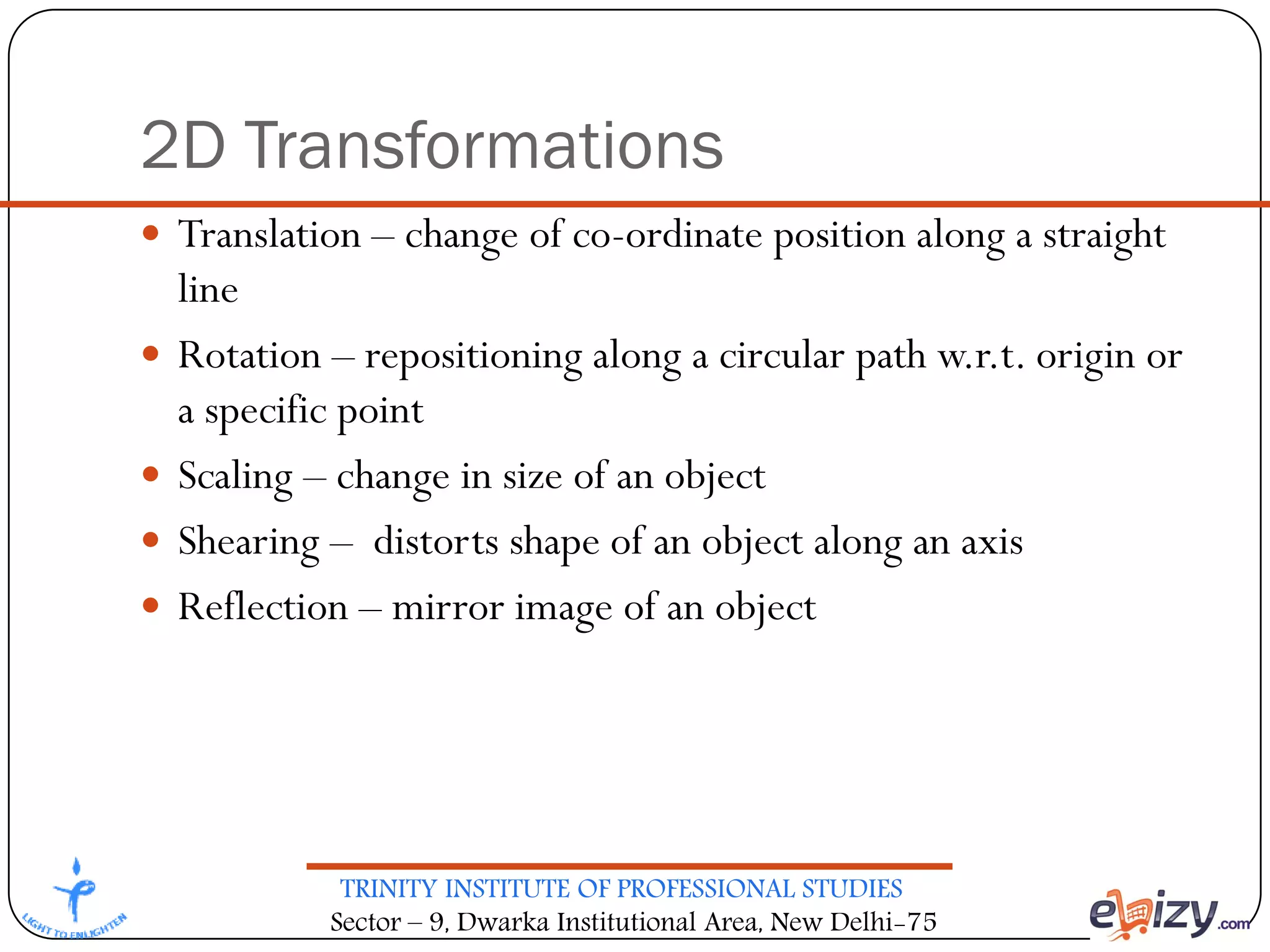
The document outlines the curriculum for a BCA course on computer graphics at Trinity Institute of Professional Studies, detailing topics like scan conversion algorithms, 2D and 3D transformations, and various graphics representations. It includes a breakdown of the marking scheme, textbooks, and references, as well as instructional strategies for answering exam questions. The course emphasizes raster graphics and algorithms such as DDA and Bresenham's for line drawing.