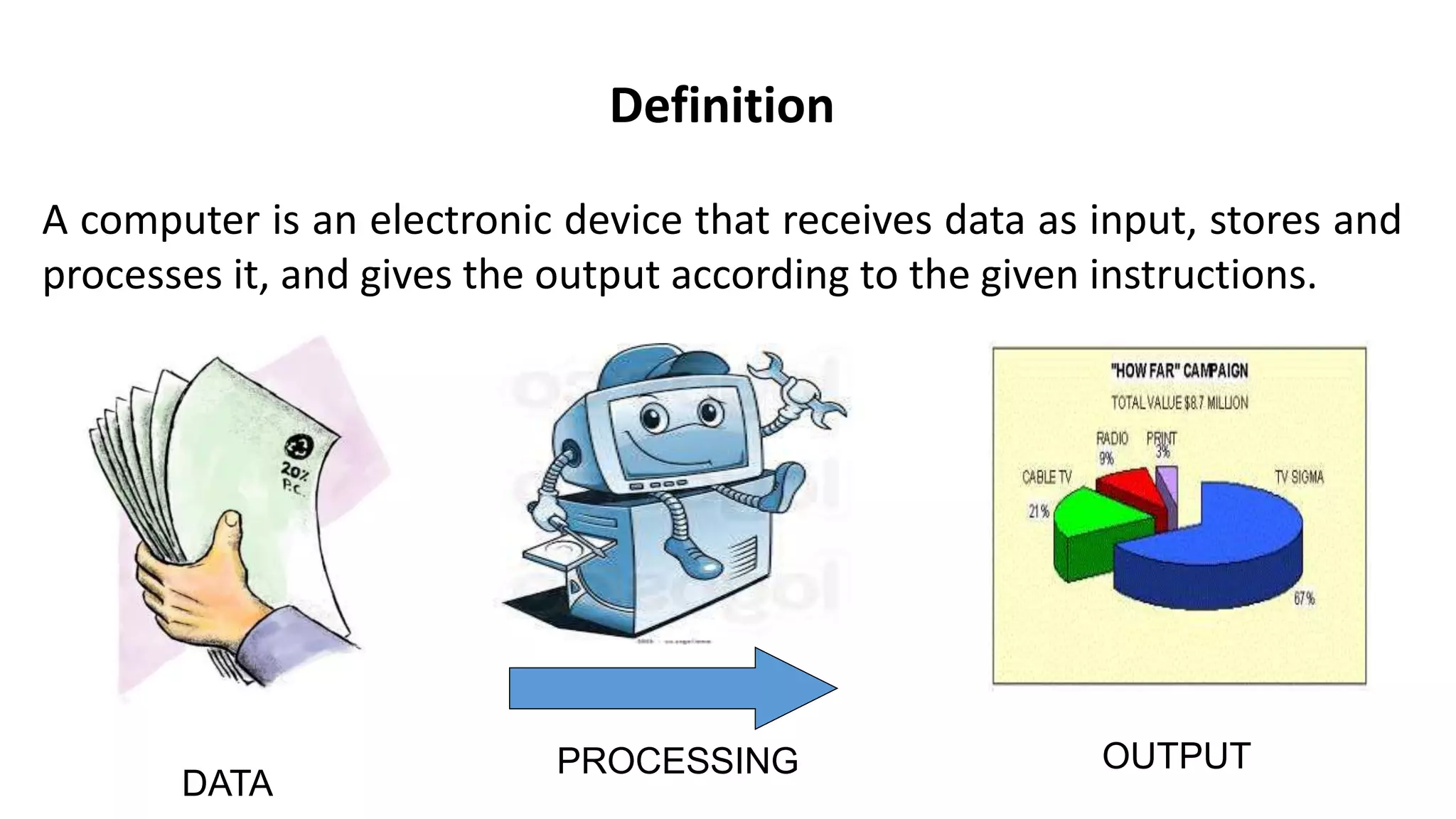
This document provides an overview of computer fundamentals, including:
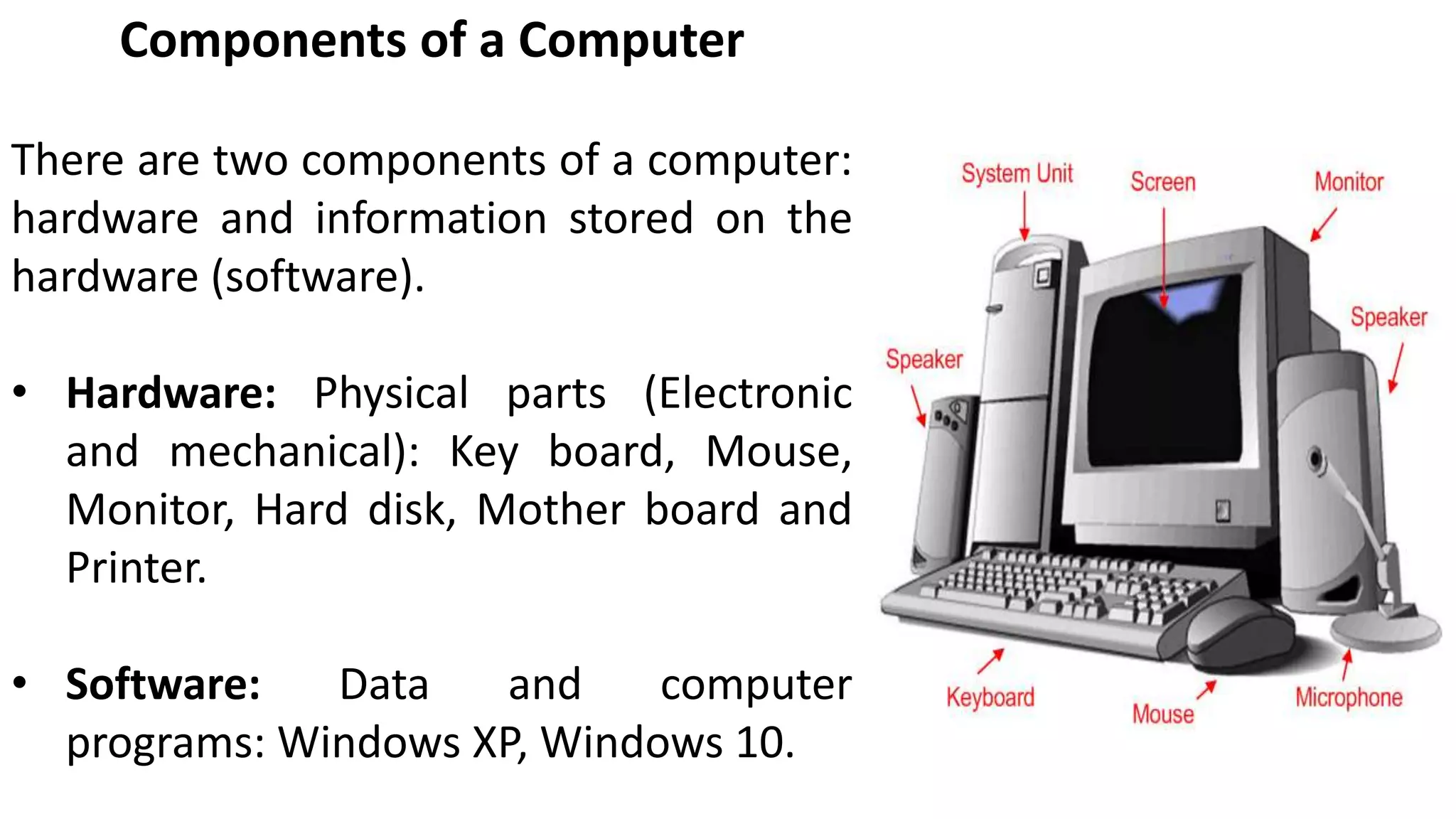
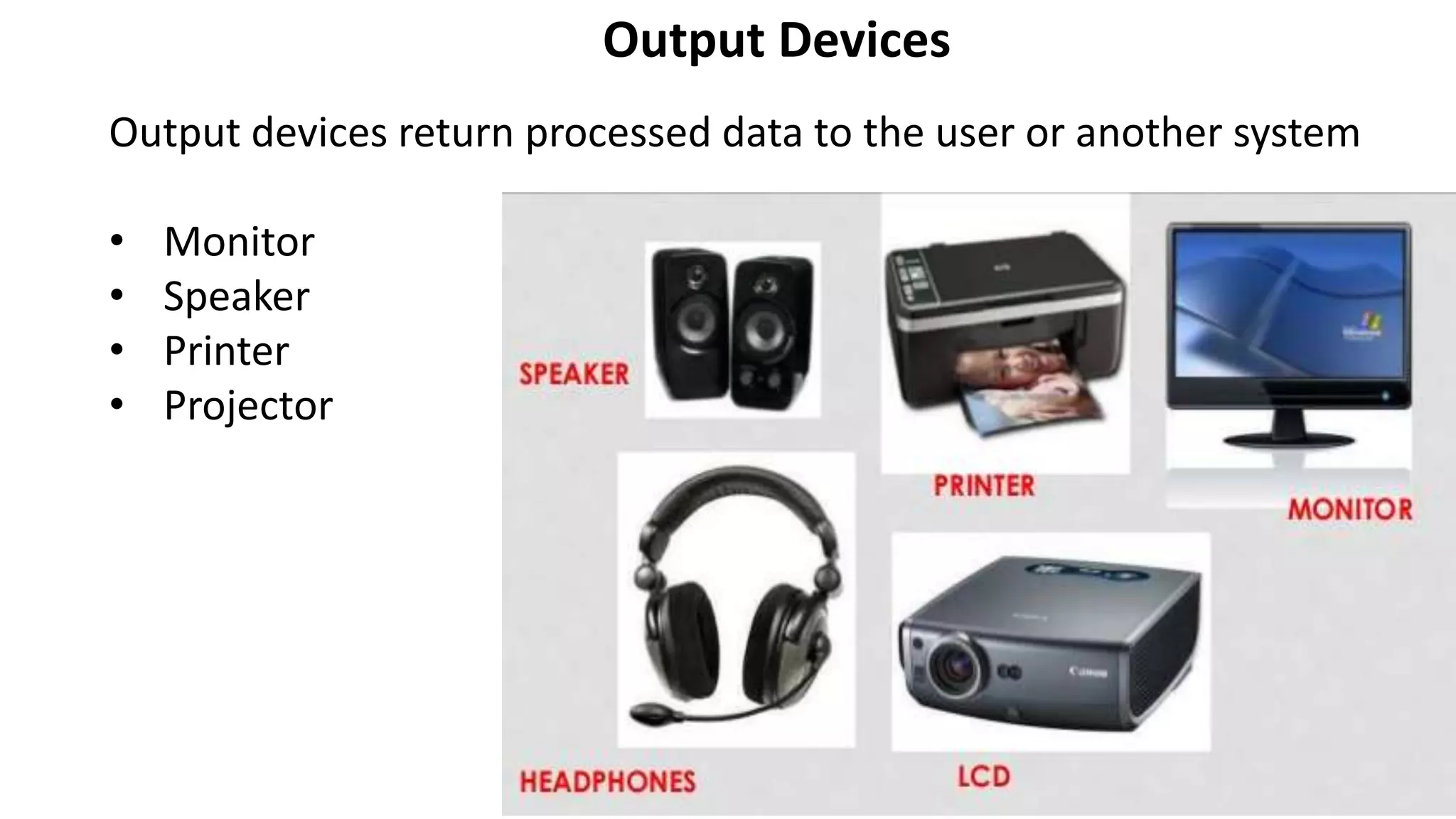
- The basic elements of a computer system including input/output devices, processing and storage components.
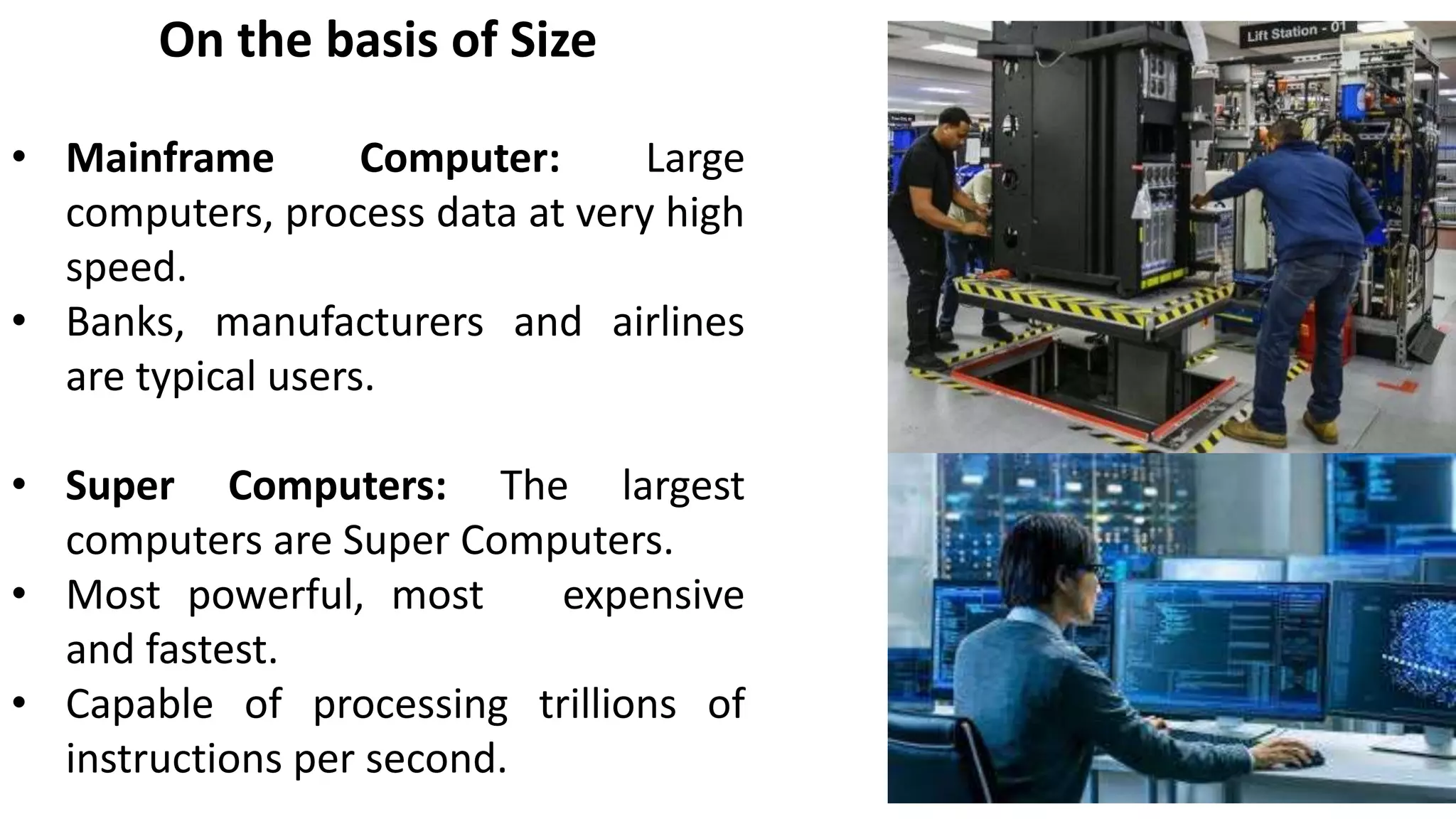
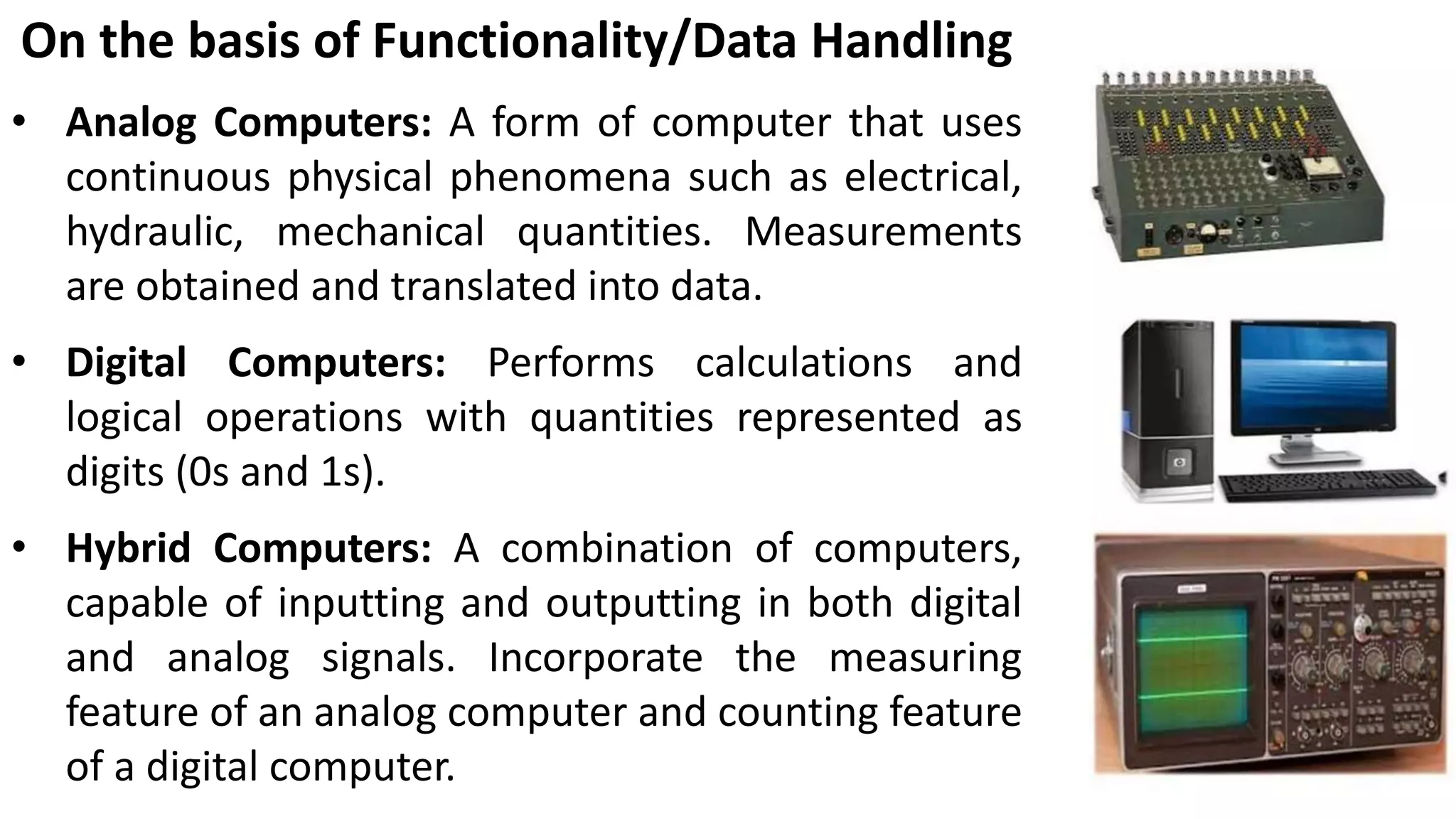
- Classifications of computers based on purpose, size, and data handling capabilities including general purpose, special purpose, microcomputers, mainframes, analog and digital computers.
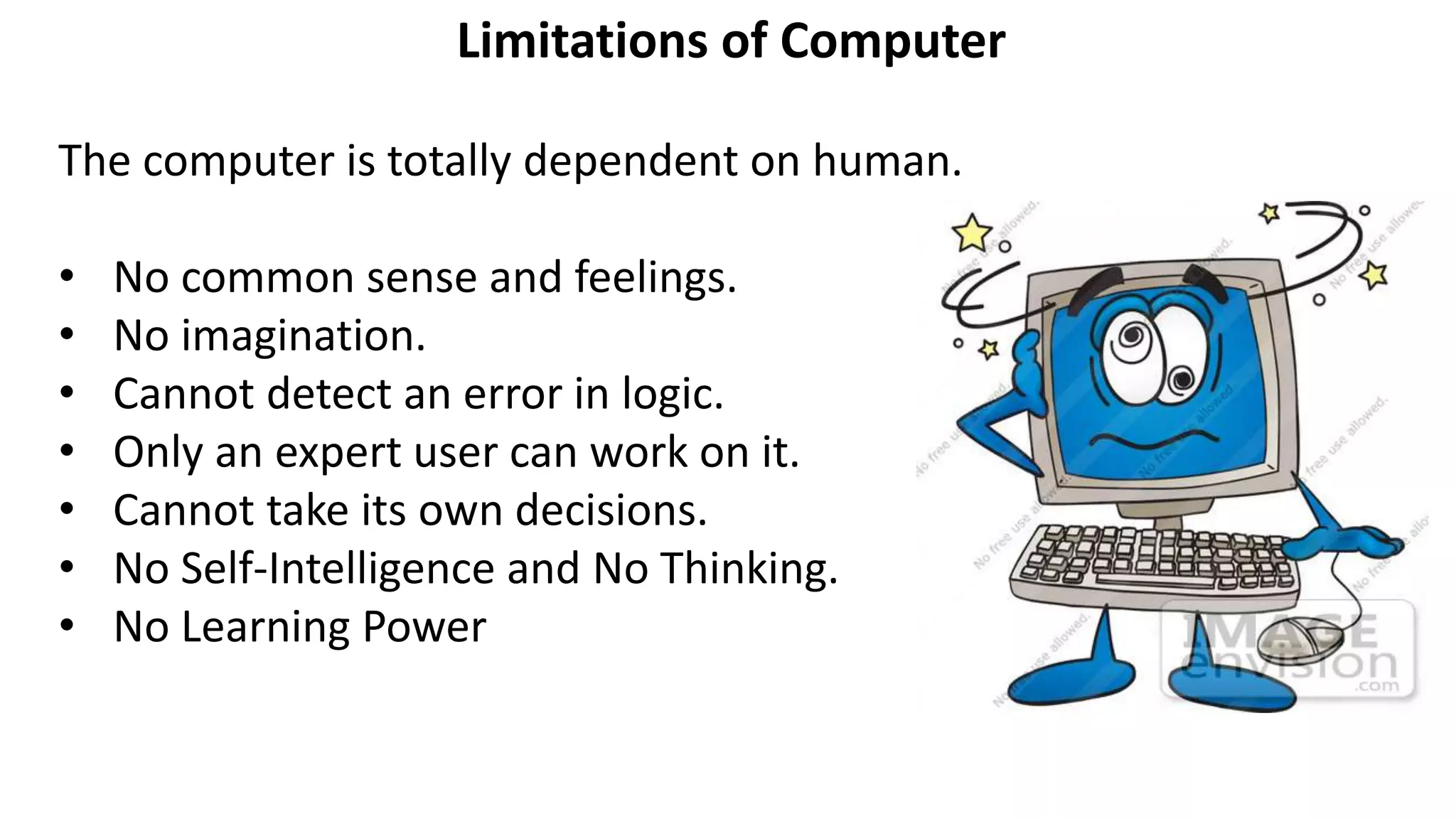
- Characteristics of computers such as speed, accuracy, reliability and storage capacity.
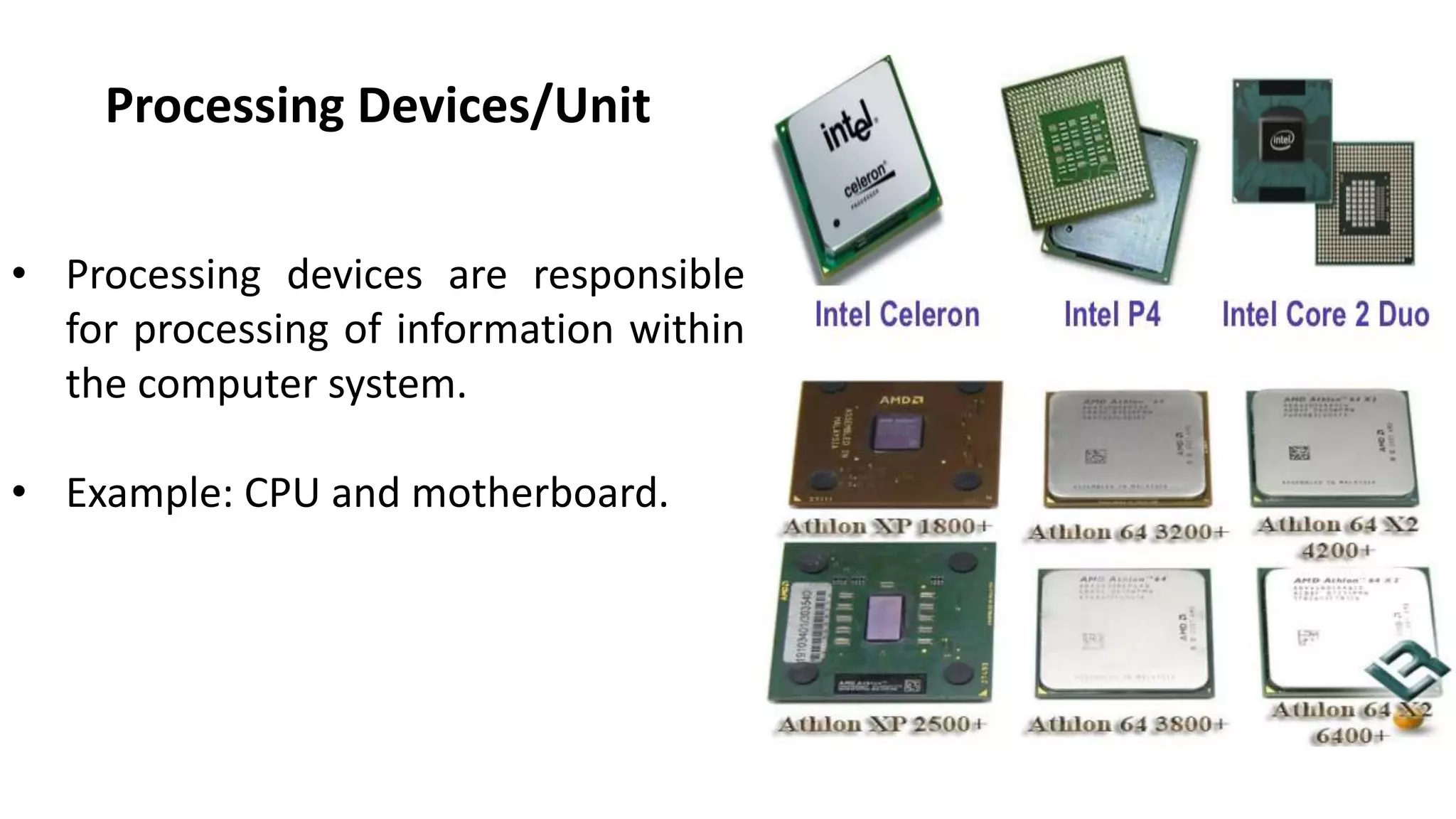
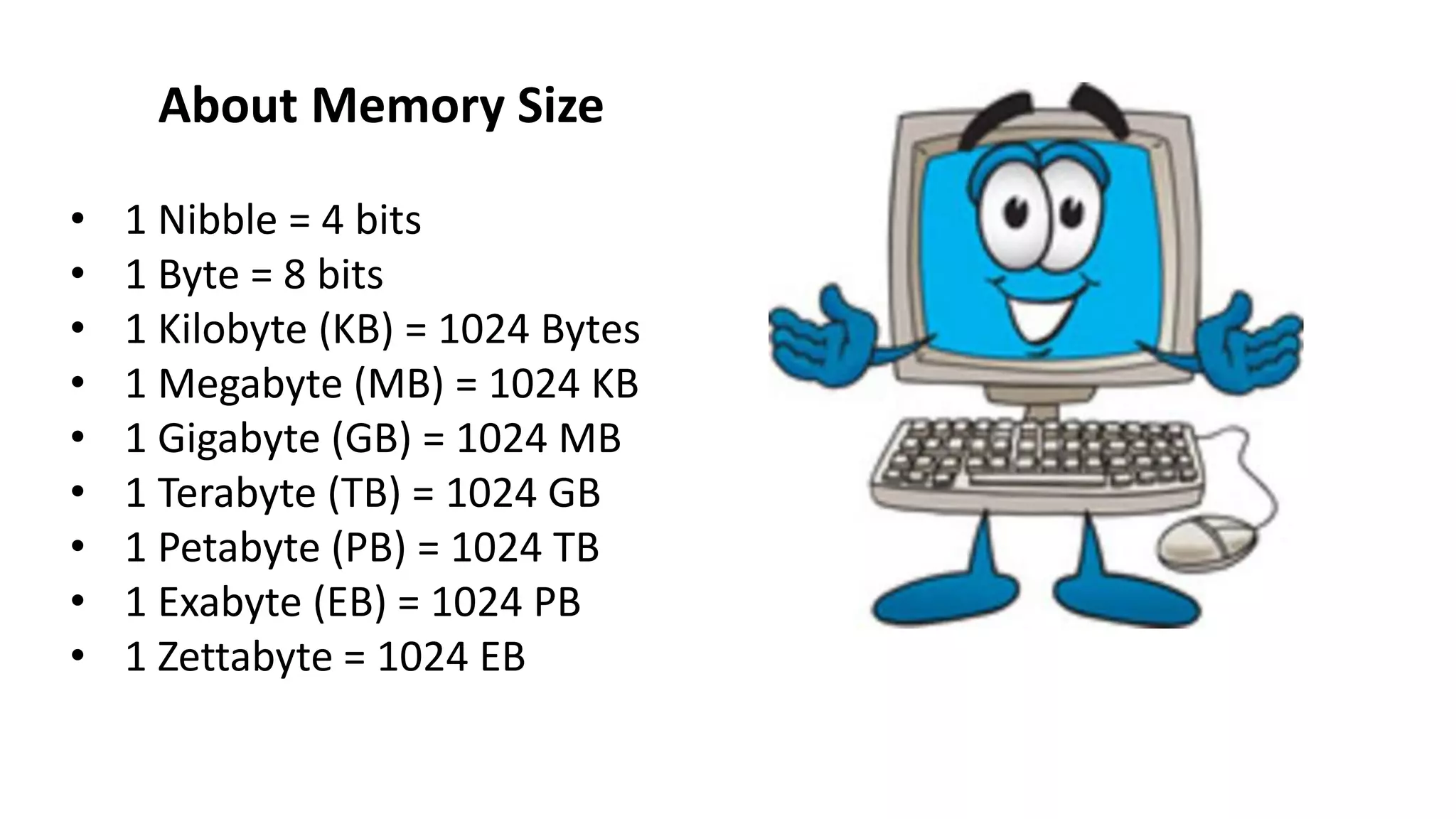
- Common input devices like keyboards and mice, processing components like CPUs, and storage devices including RAM, ROM, hard disks.