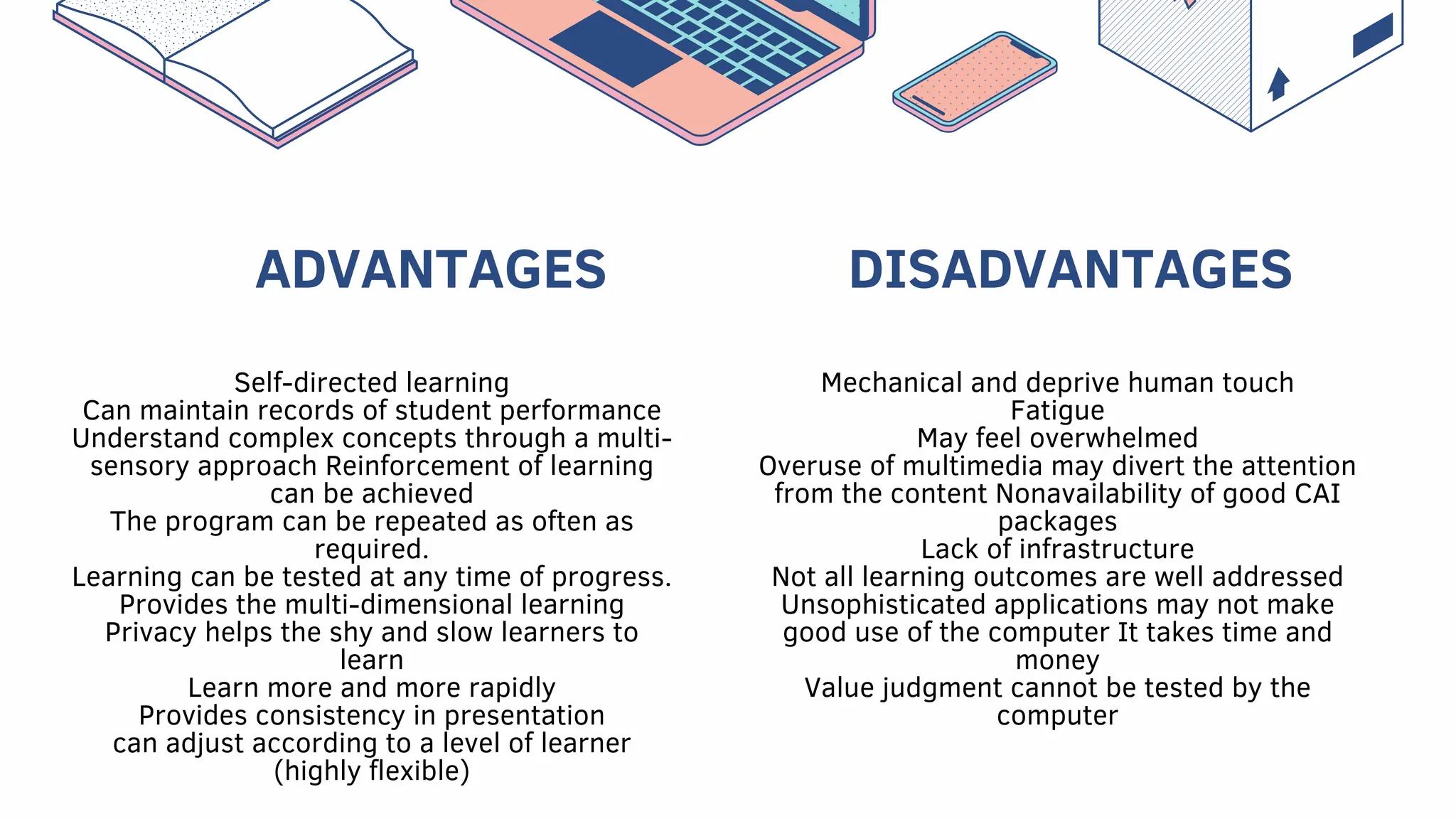
Computer Assisted Instruction (CAI) is an interactive strategy that uses computers for drills, tutorials, and simulations to enhance student learning. It offers various formats including informational instruction, drill and practice, tutorials, educational games, and problem-solving activities, allowing for self-directed learning and management of student performance. Advantages include personalized learning experiences and the ability to reinforce knowledge, while disadvantages include dependence on technology and potential distractions from content.