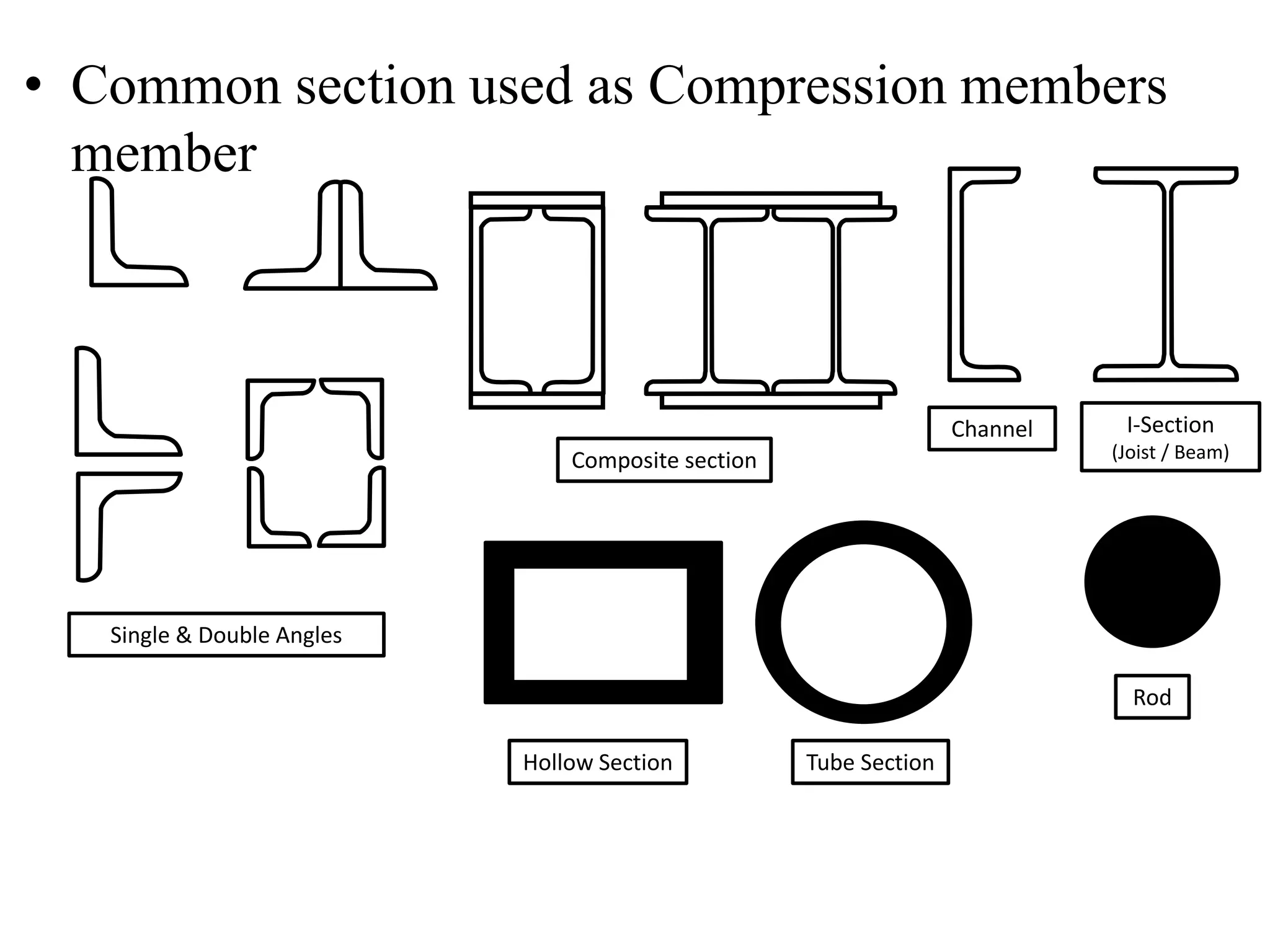
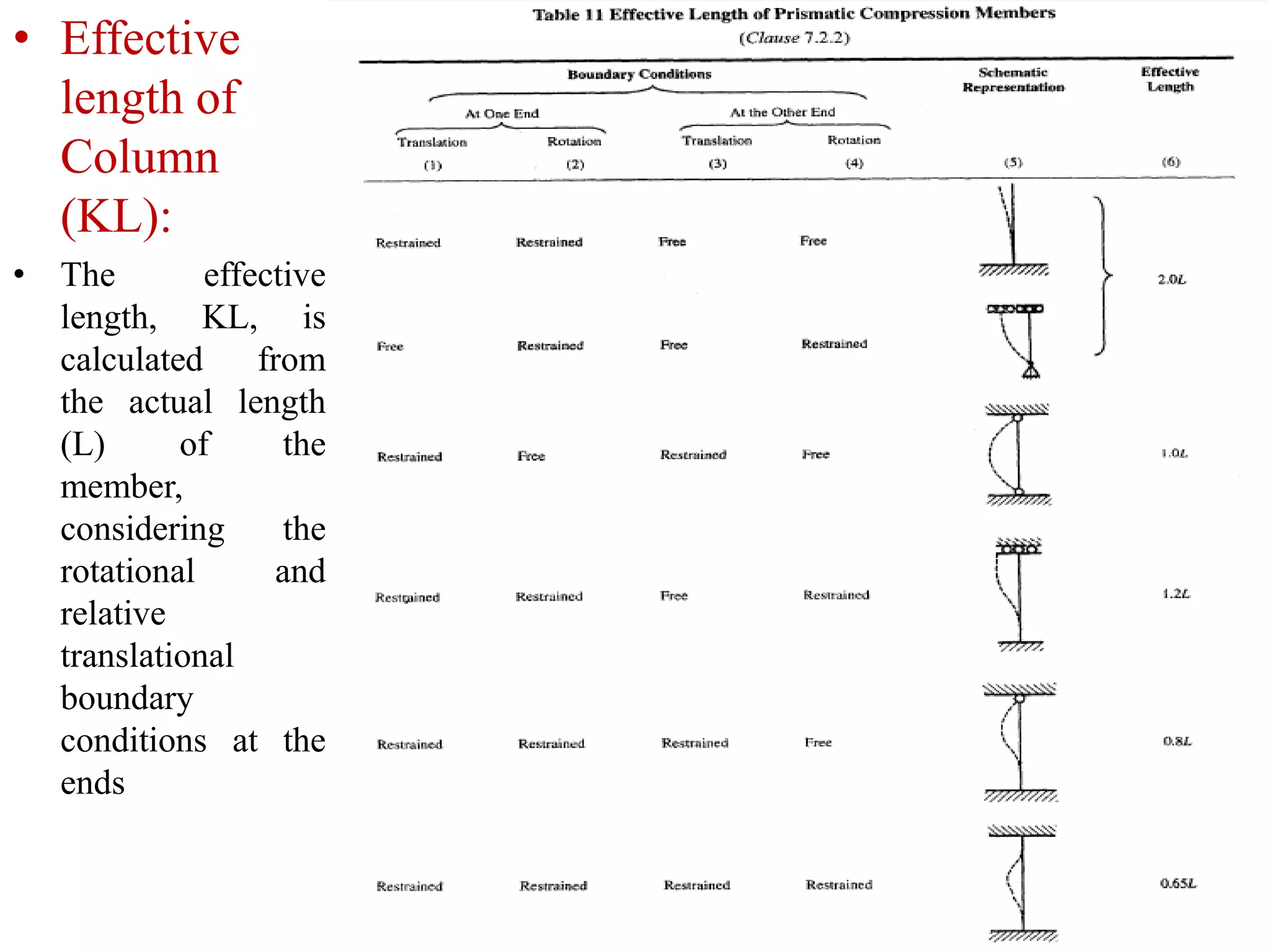
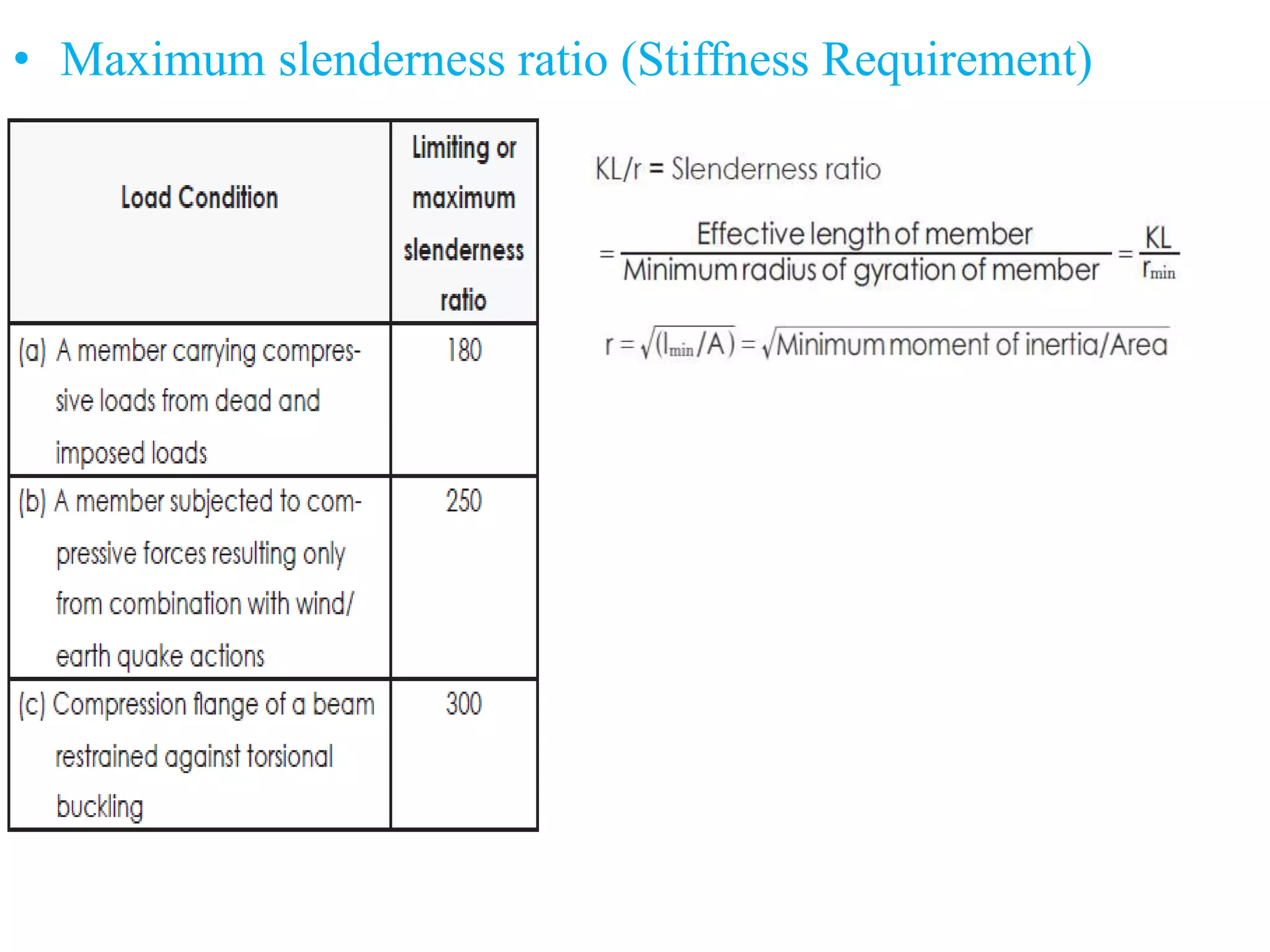
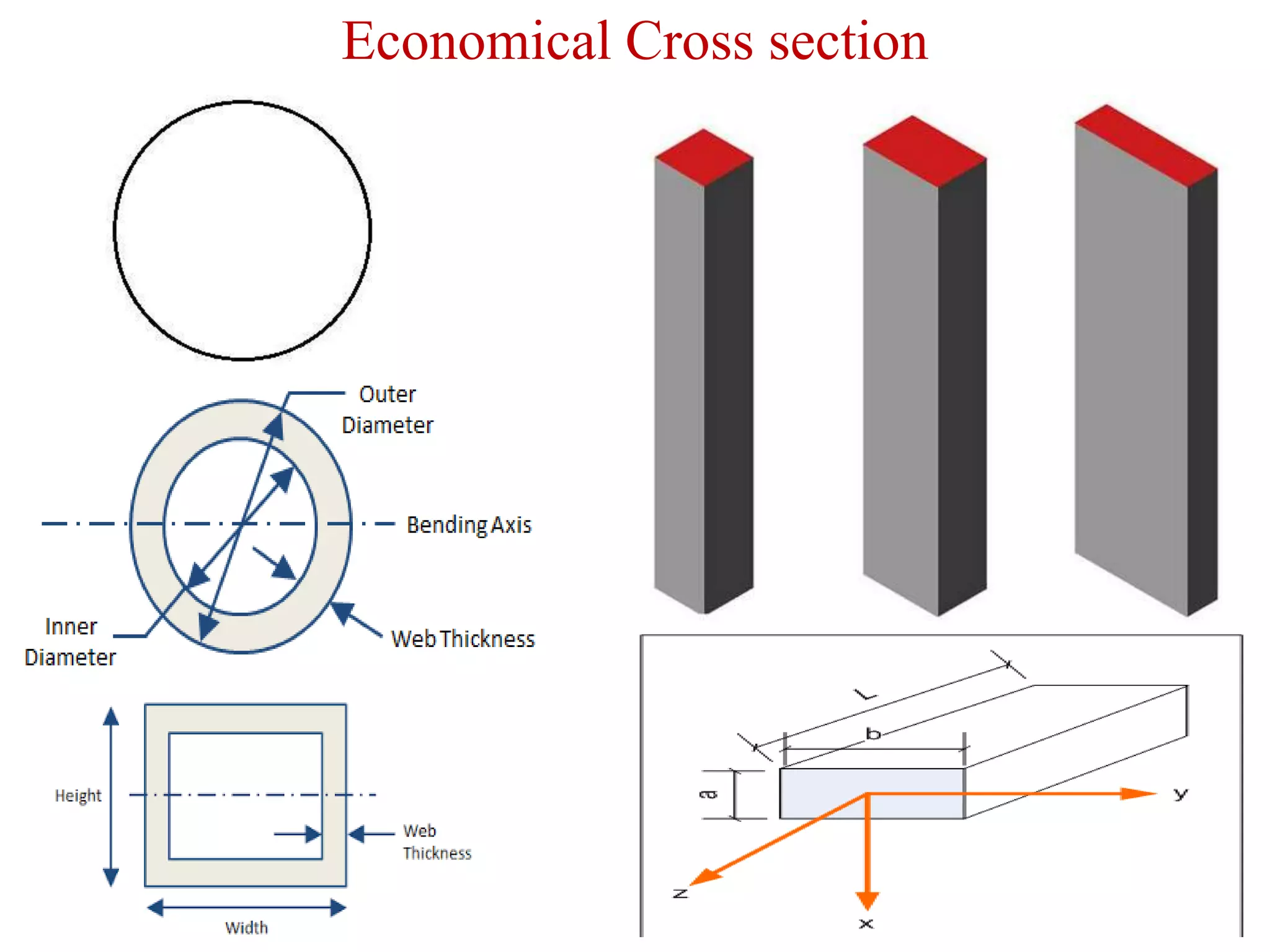
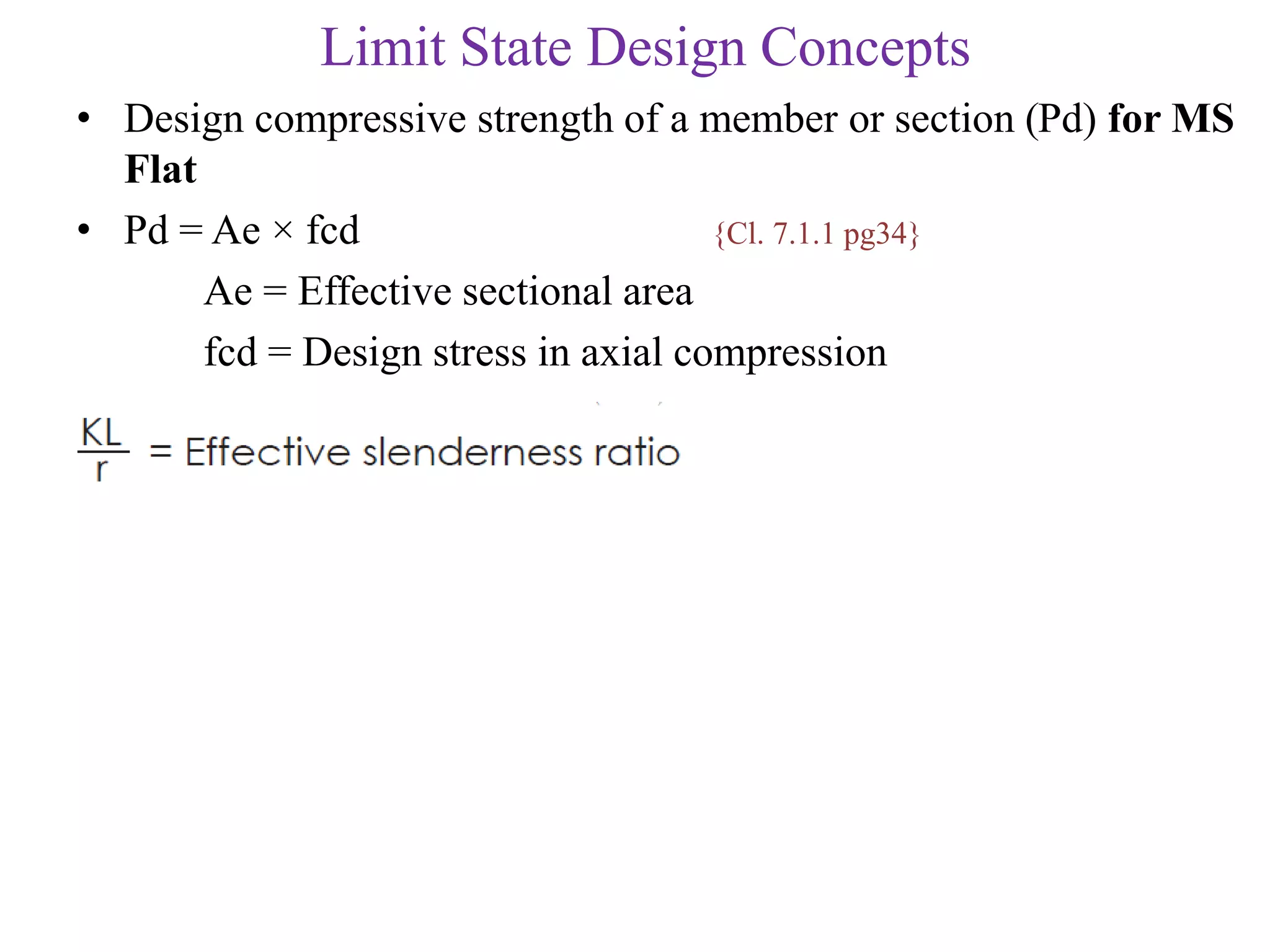
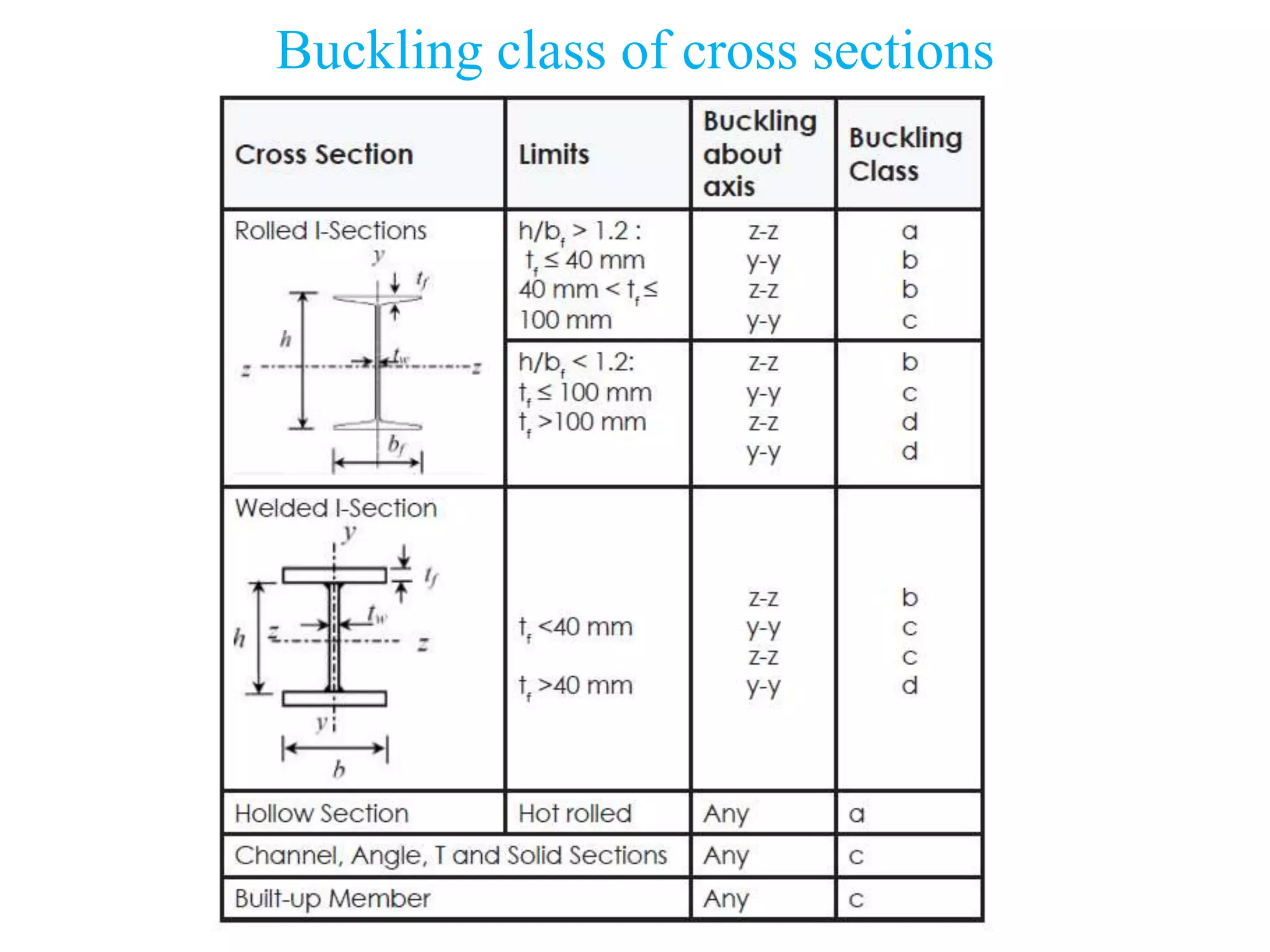
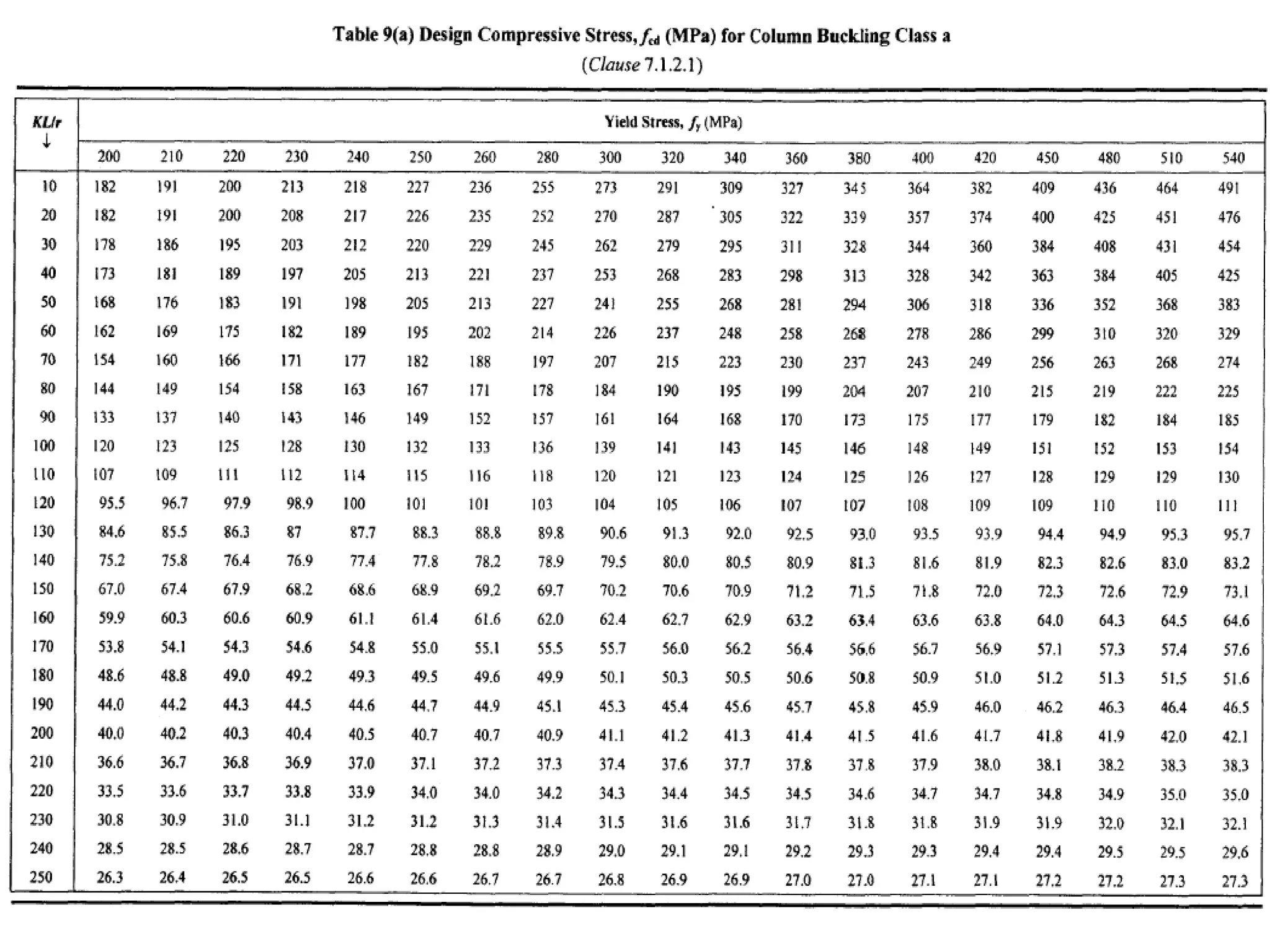
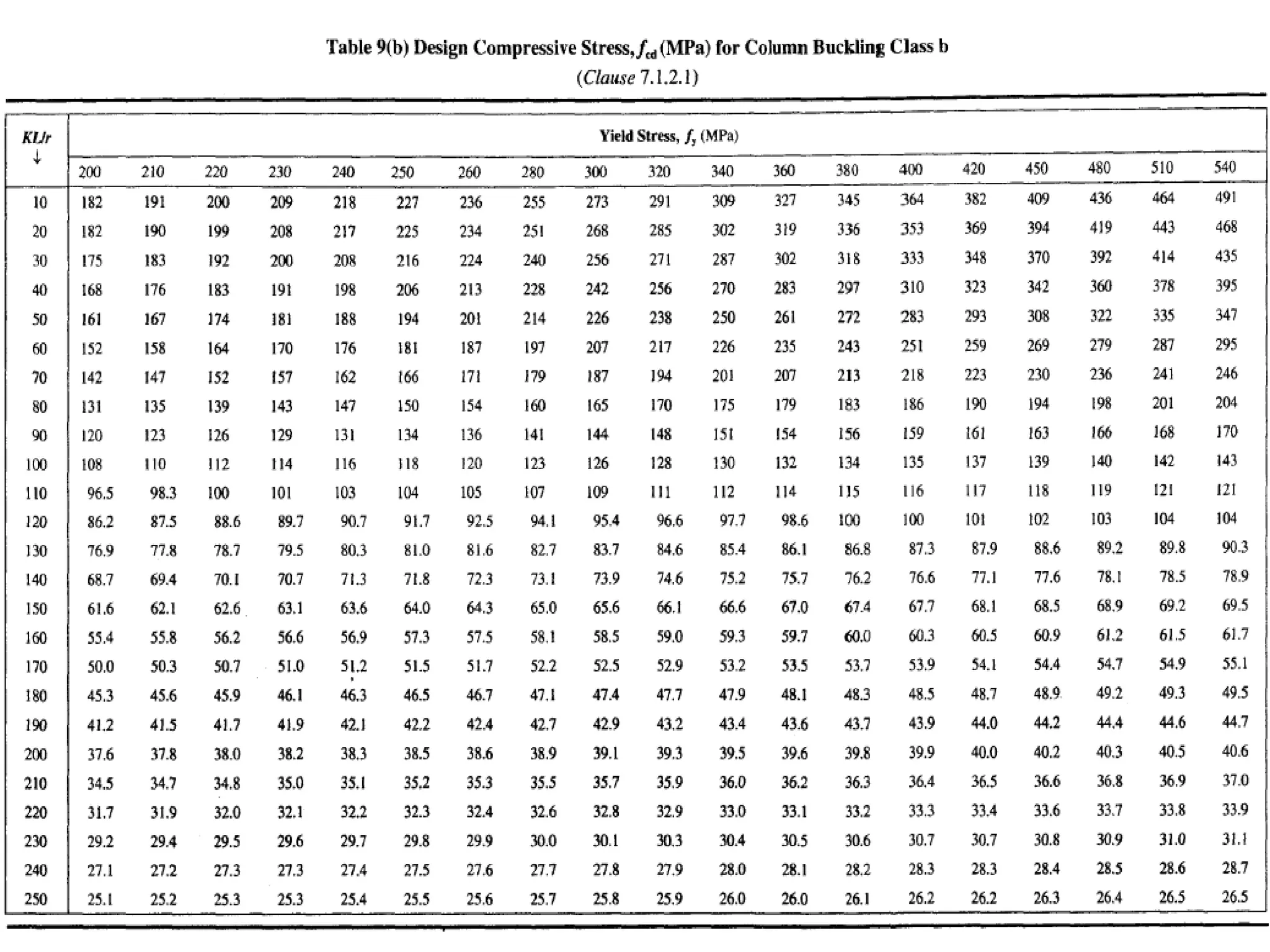
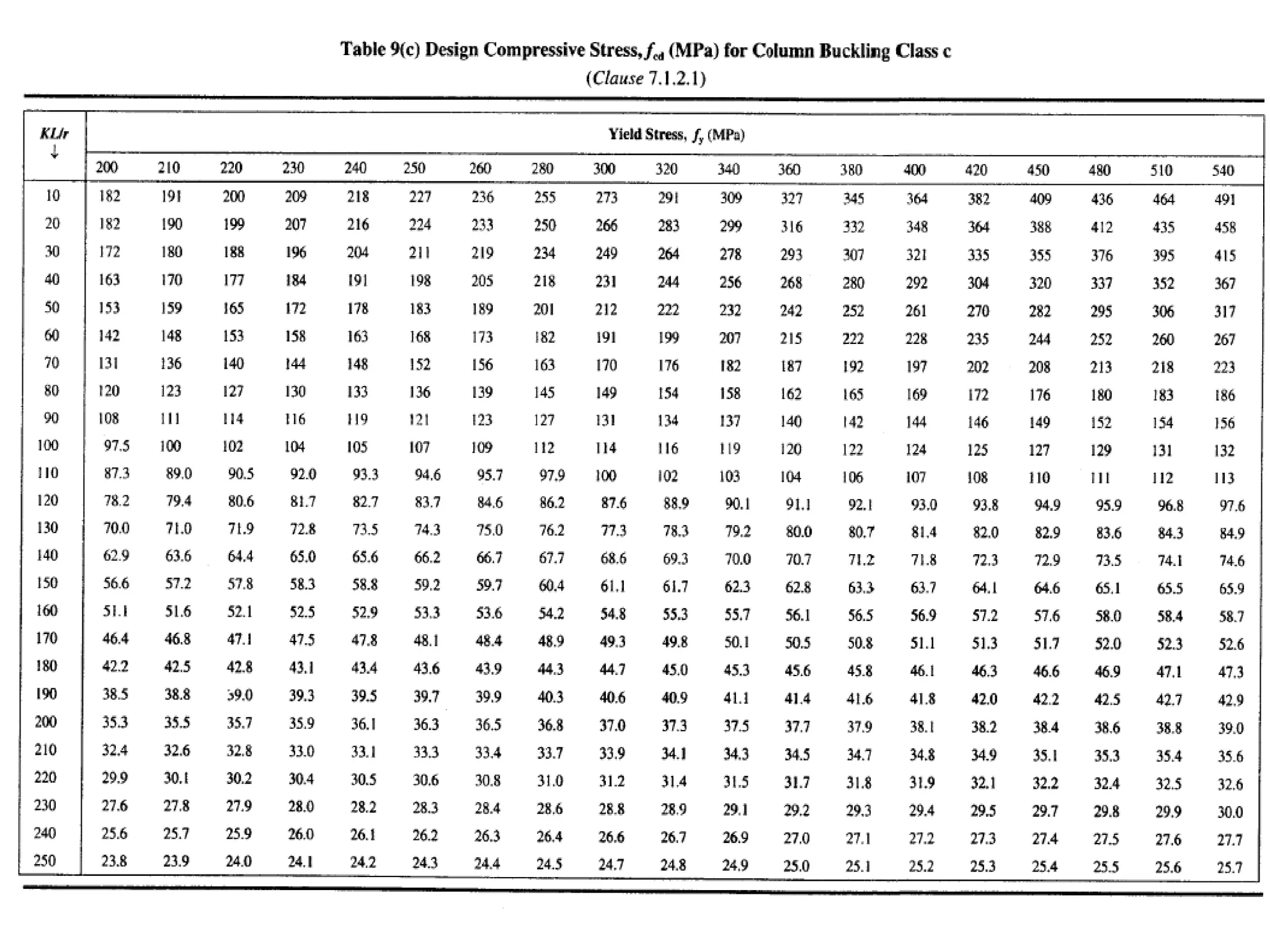
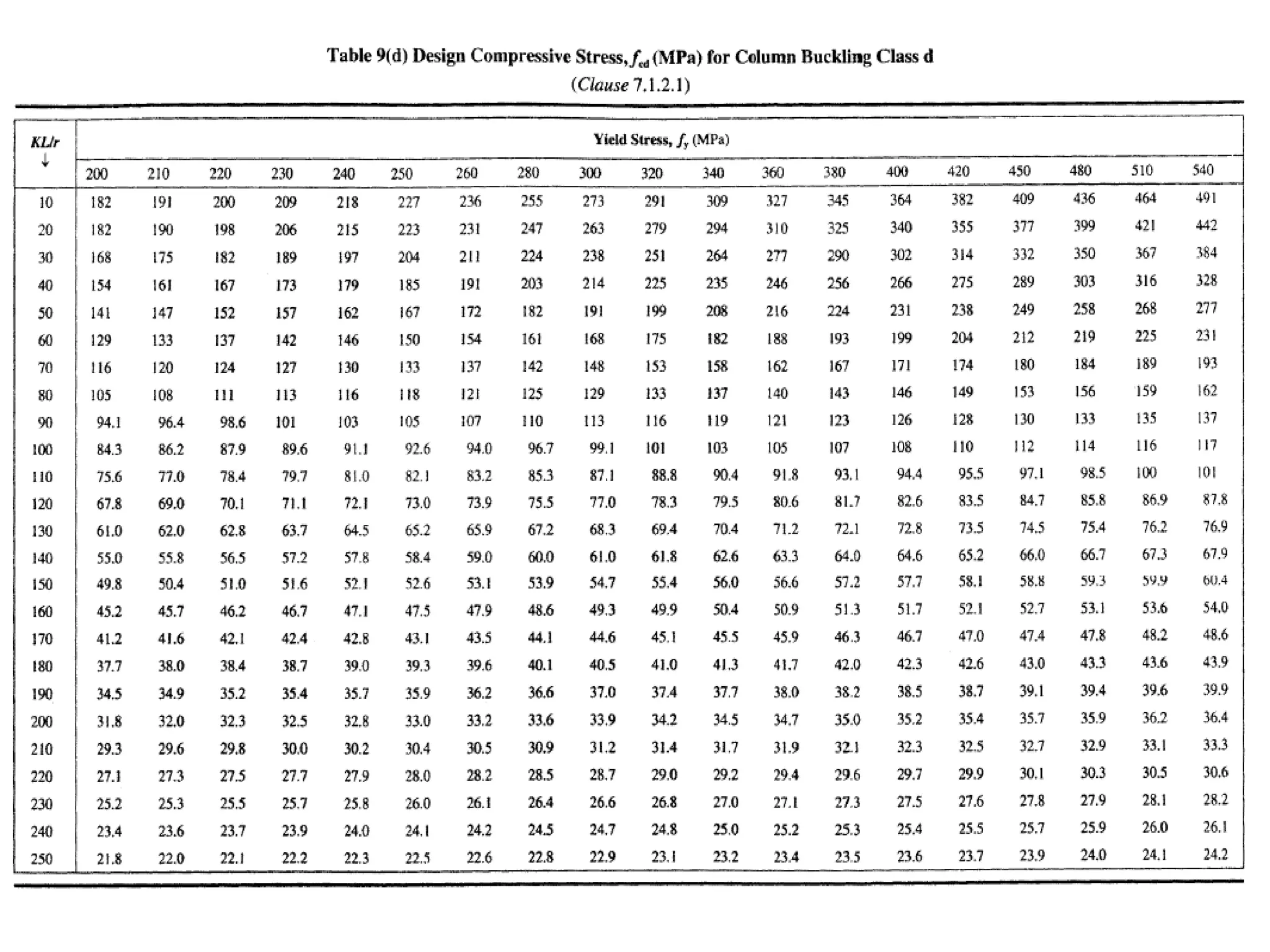
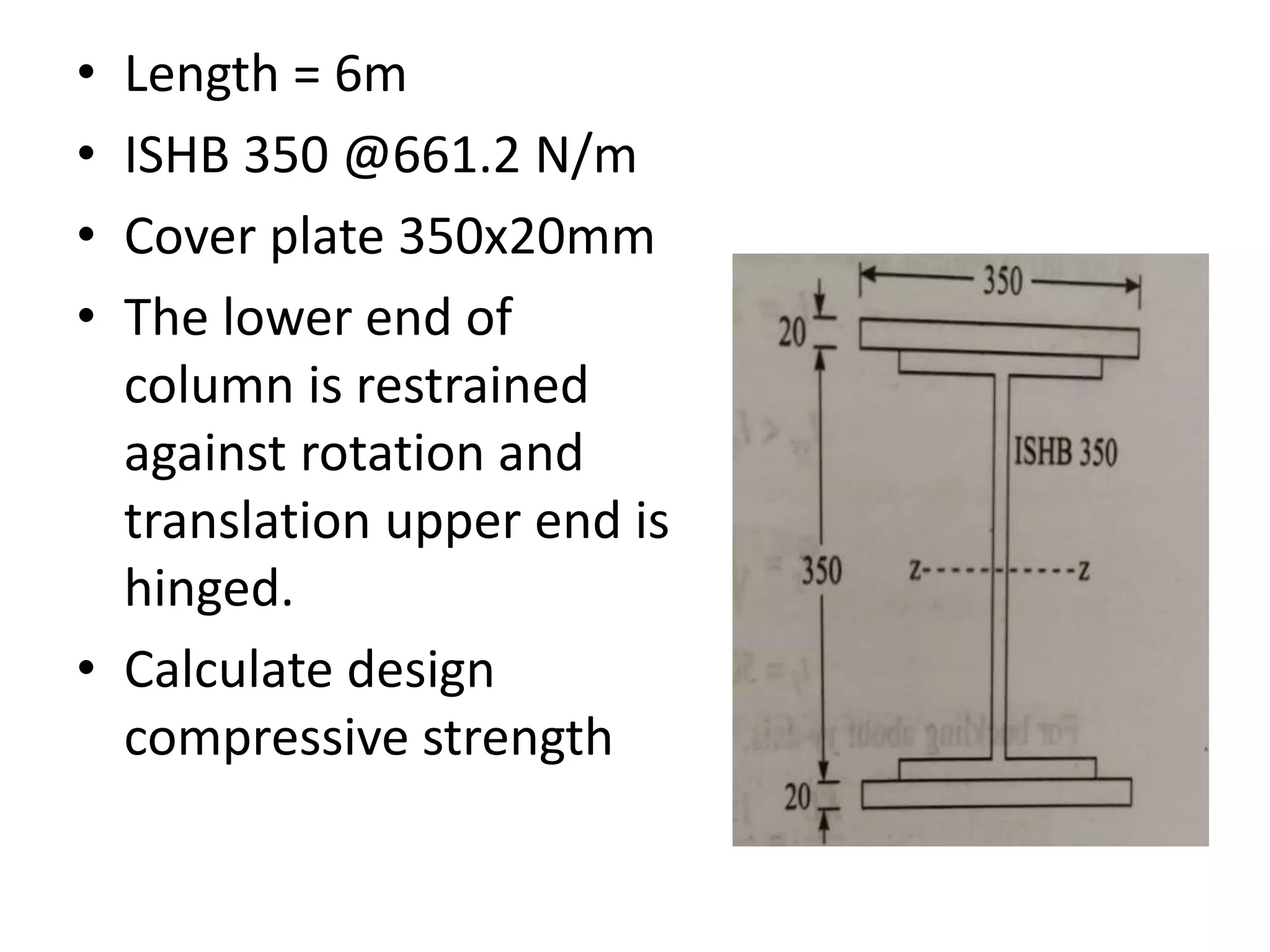
This document discusses compression members, which include columns, struts, stanchions, and posts. Common cross sections used for compression members are single and double angles, channels, I-sections, rods, composite sections, and tube sections. Compression members can fail due to crushing or buckling. Key terms in the design of compression members are effective length, slenderness ratio, and economical cross section. The document provides examples of calculating the effective length and design compressive strength of a column.