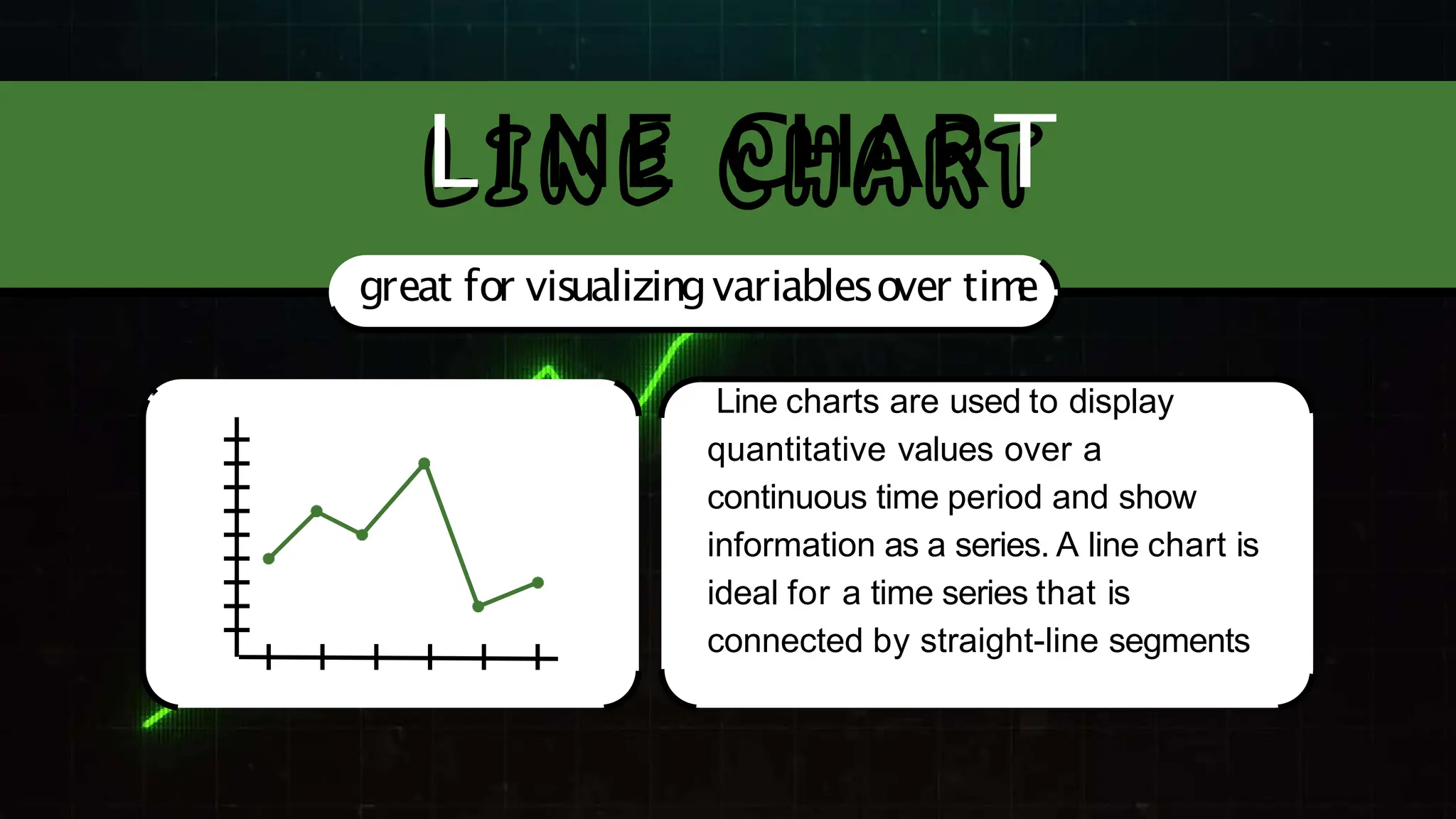
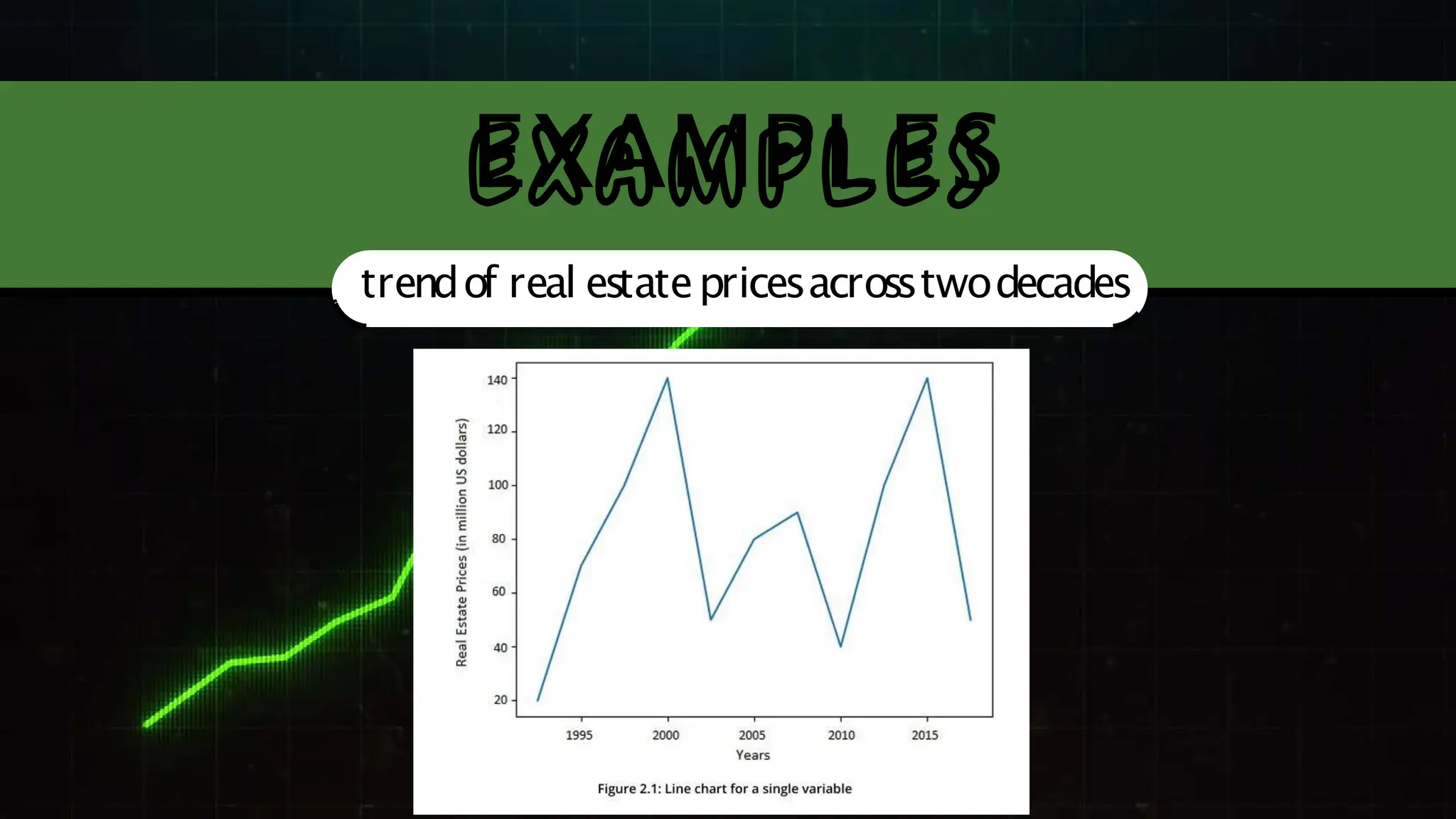
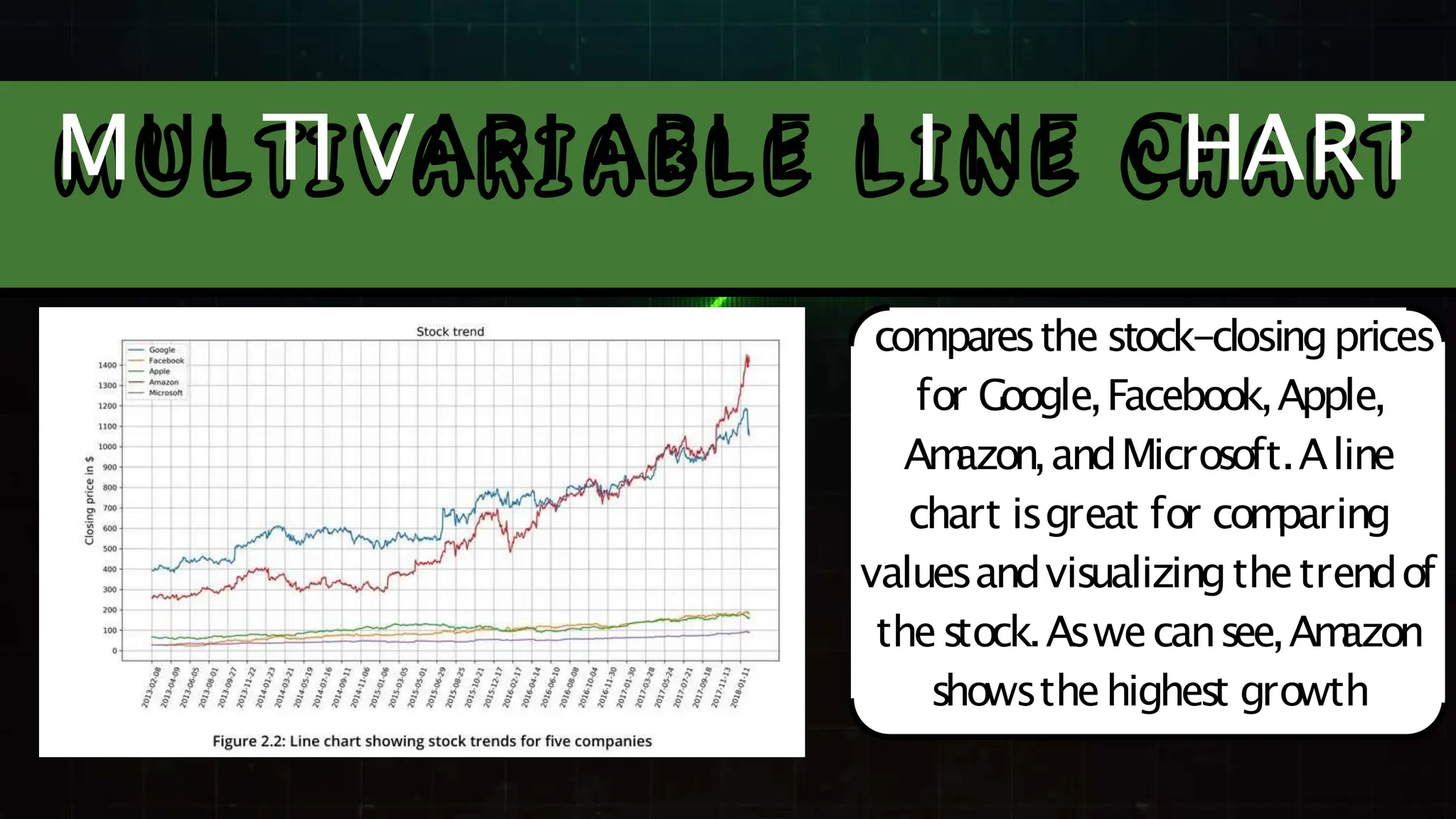
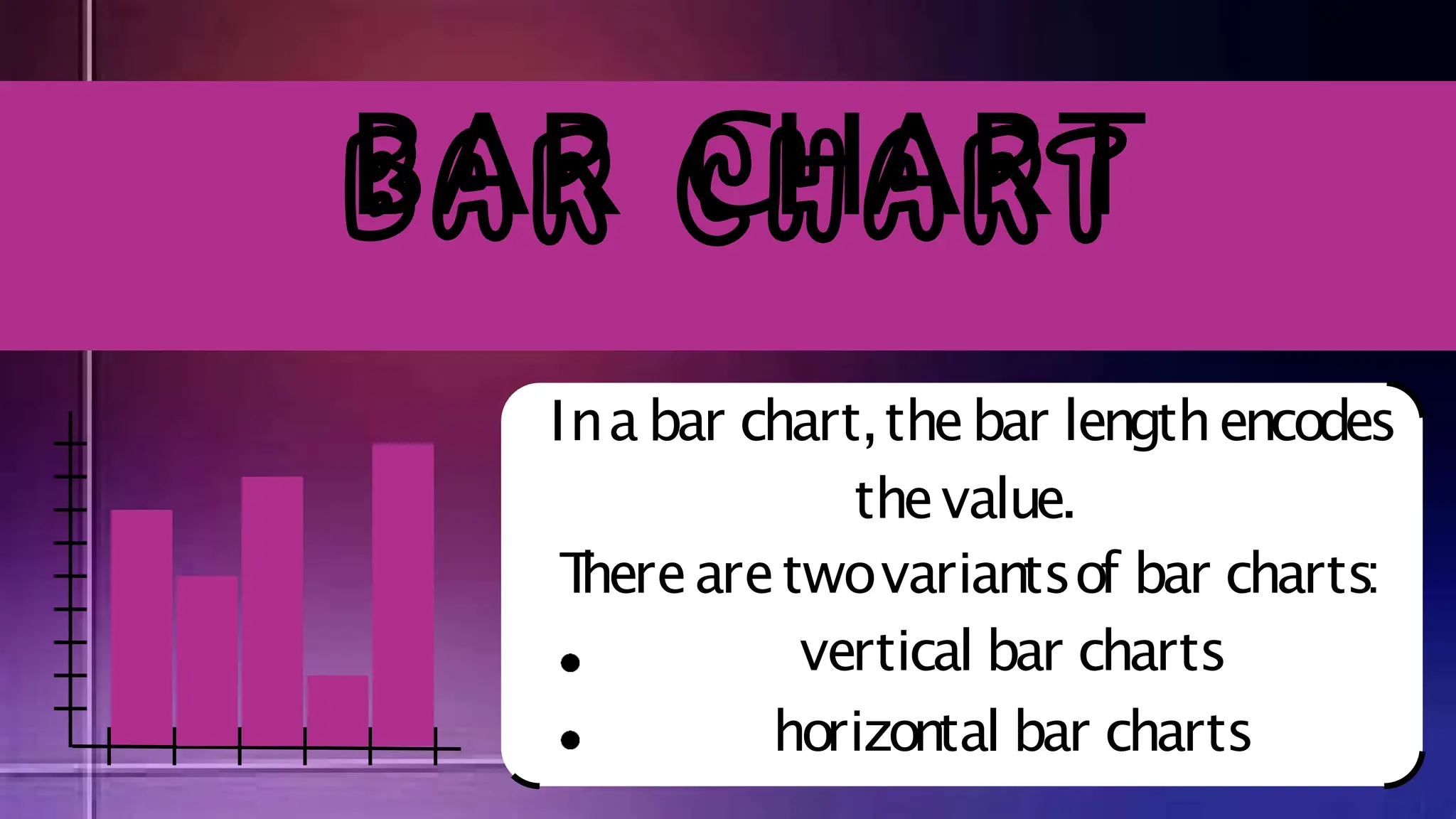
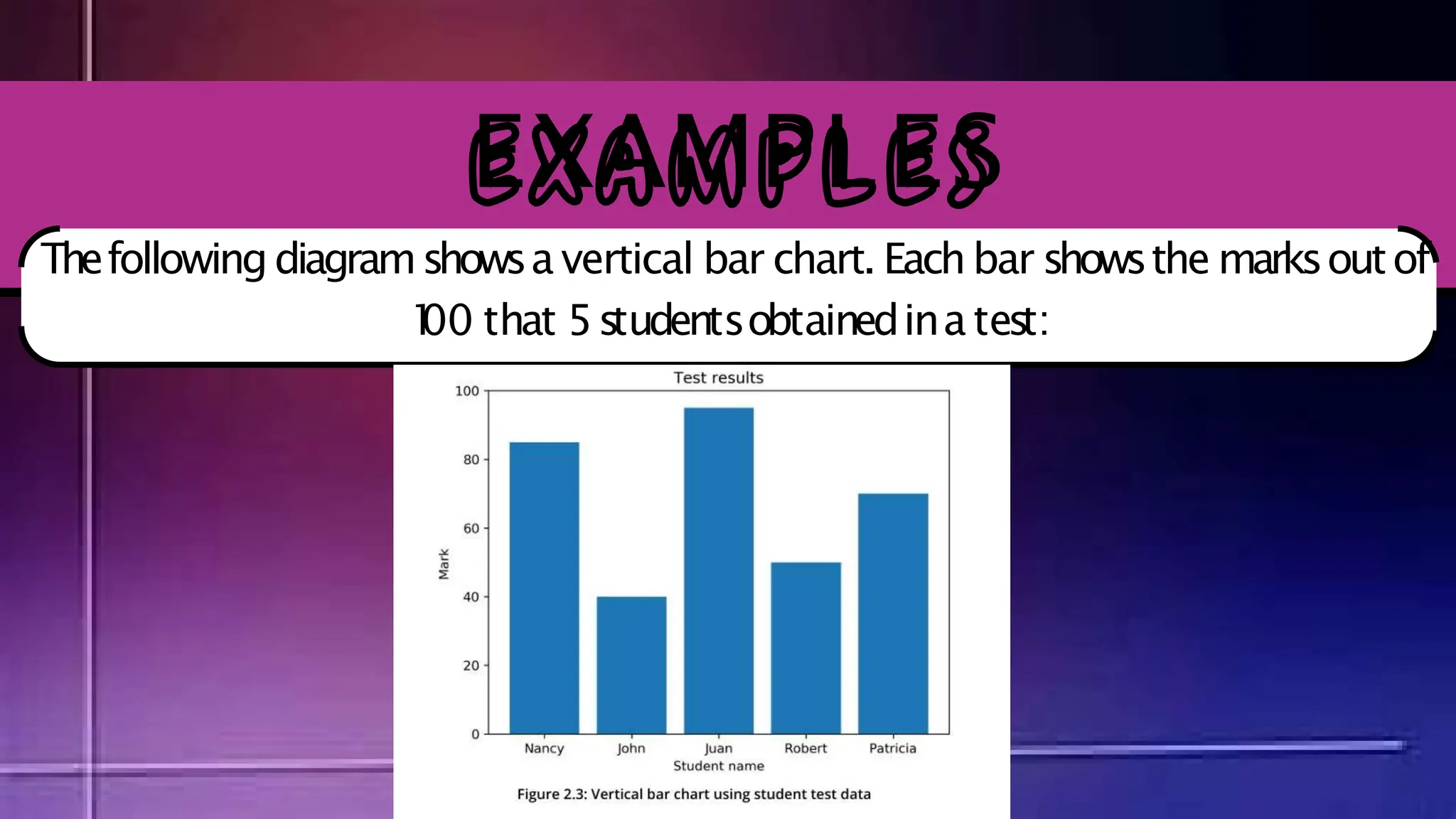
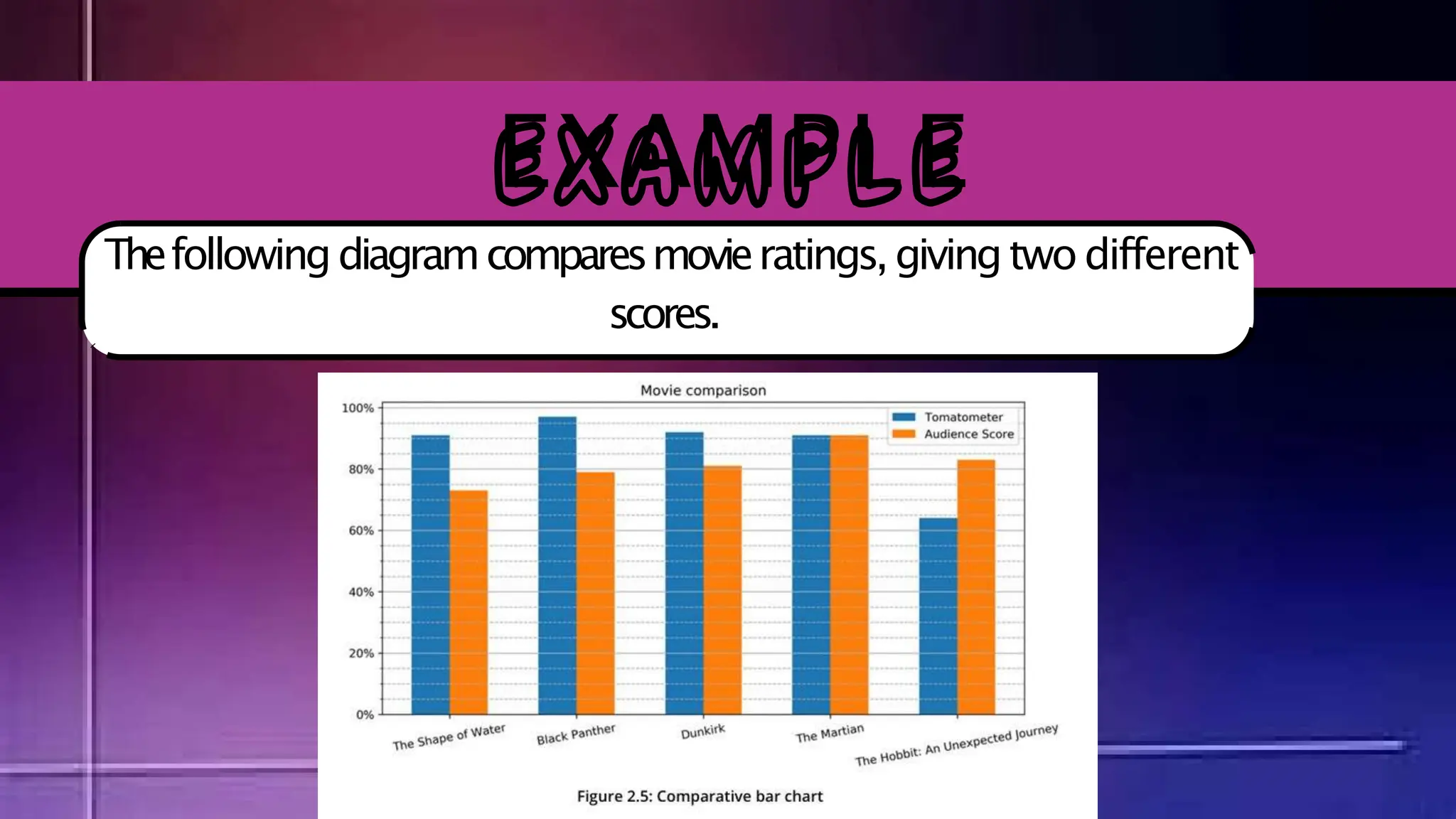
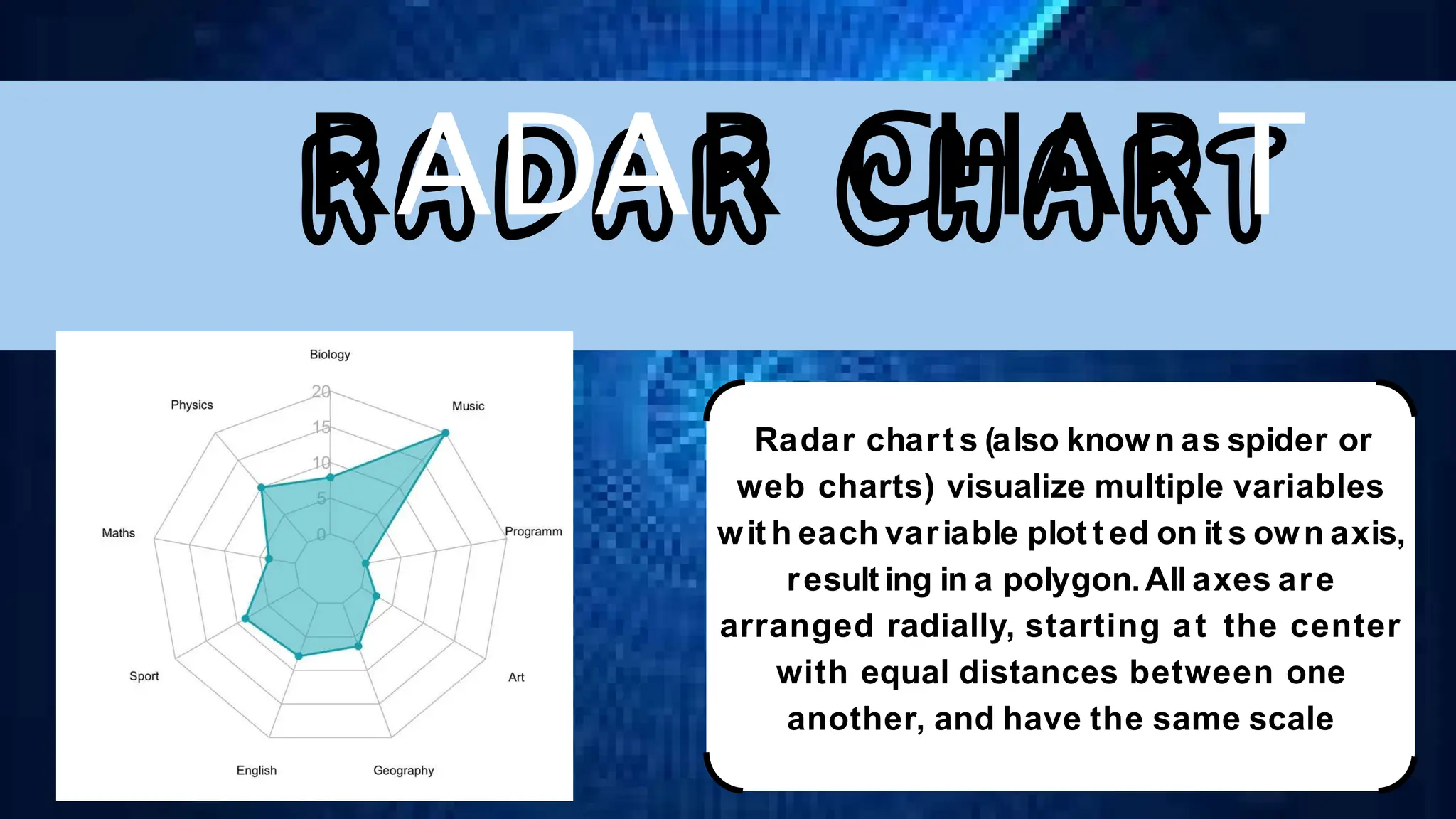
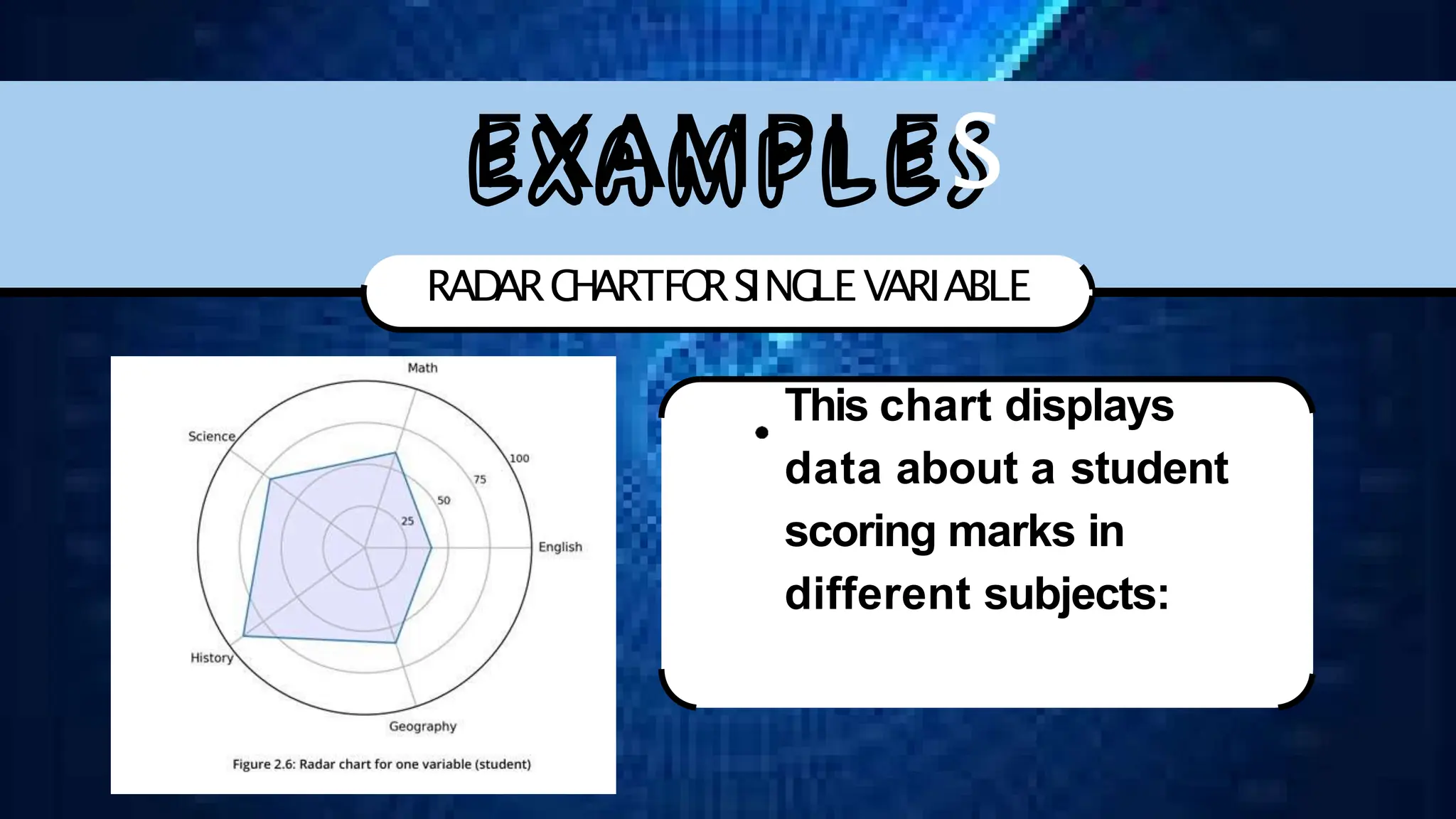
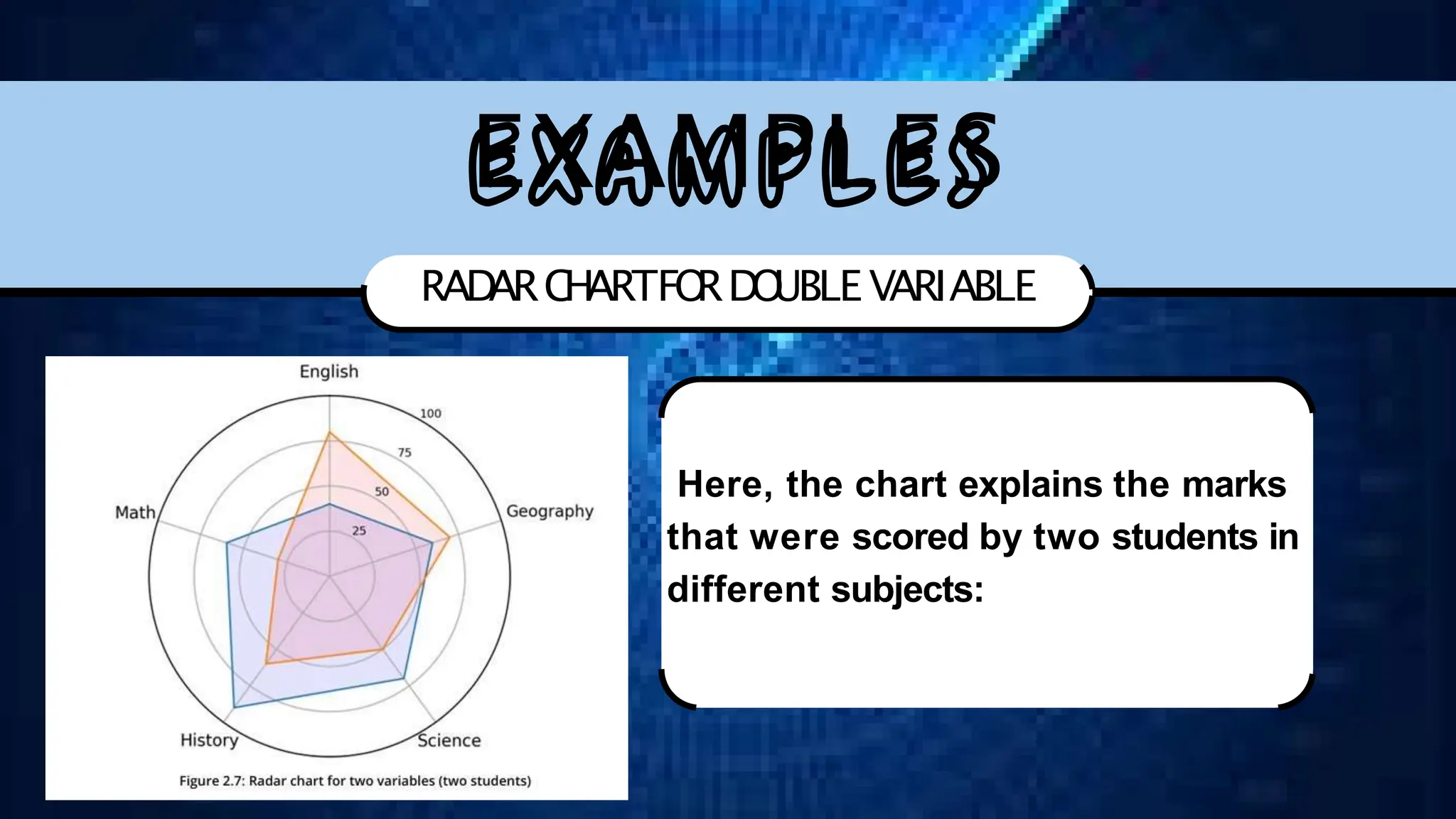
The document discusses various comparison plots, highlighting the use of line charts for visualizing trends over time and comparing multiple variables. It also explains the application and design practices for bar charts, including the importance of using appropriate scales and avoiding common mistakes. Additionally, it introduces radar charts for comparing multiple quantitative variables and emphasizes clarity in data presentation.