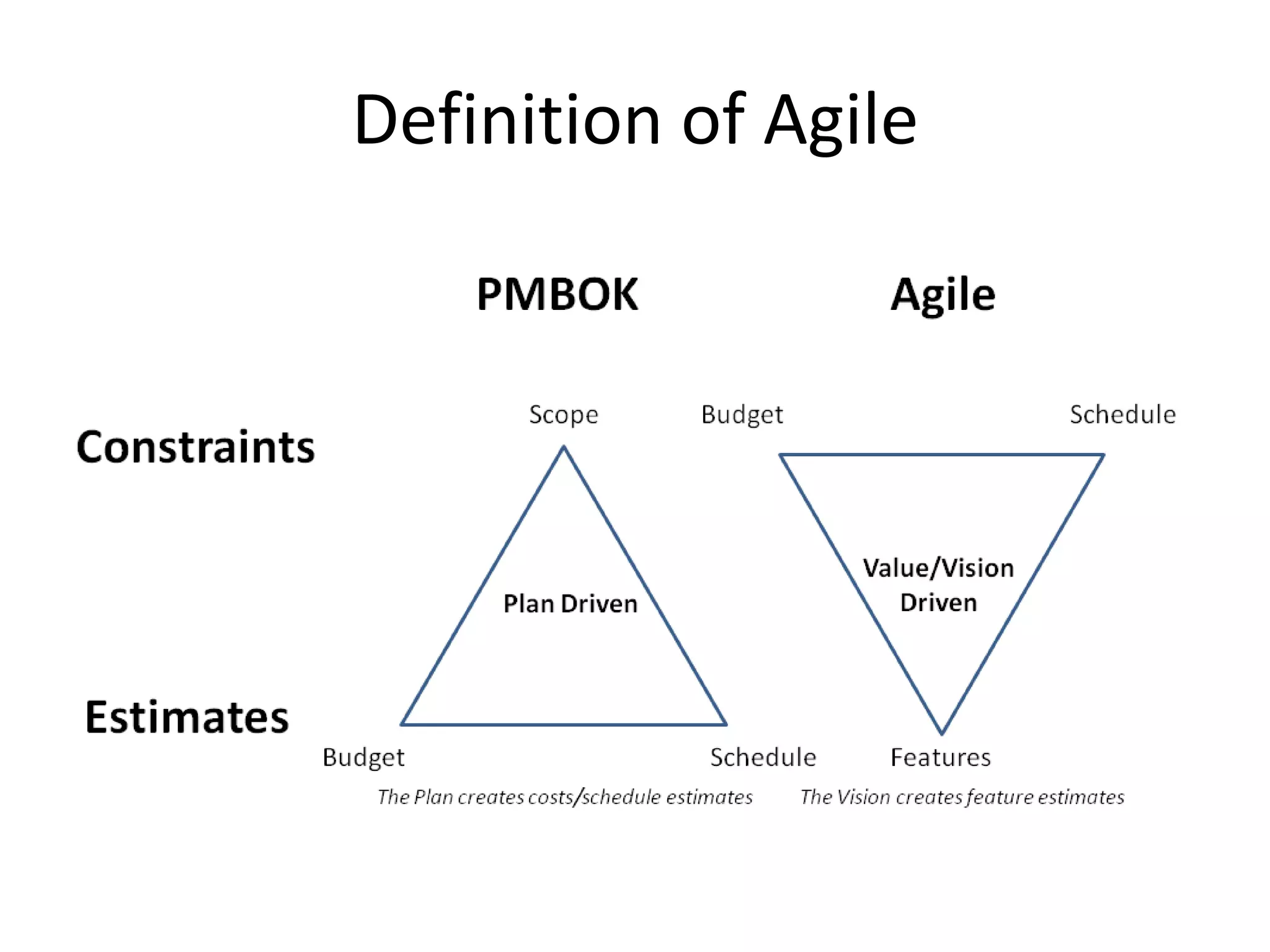
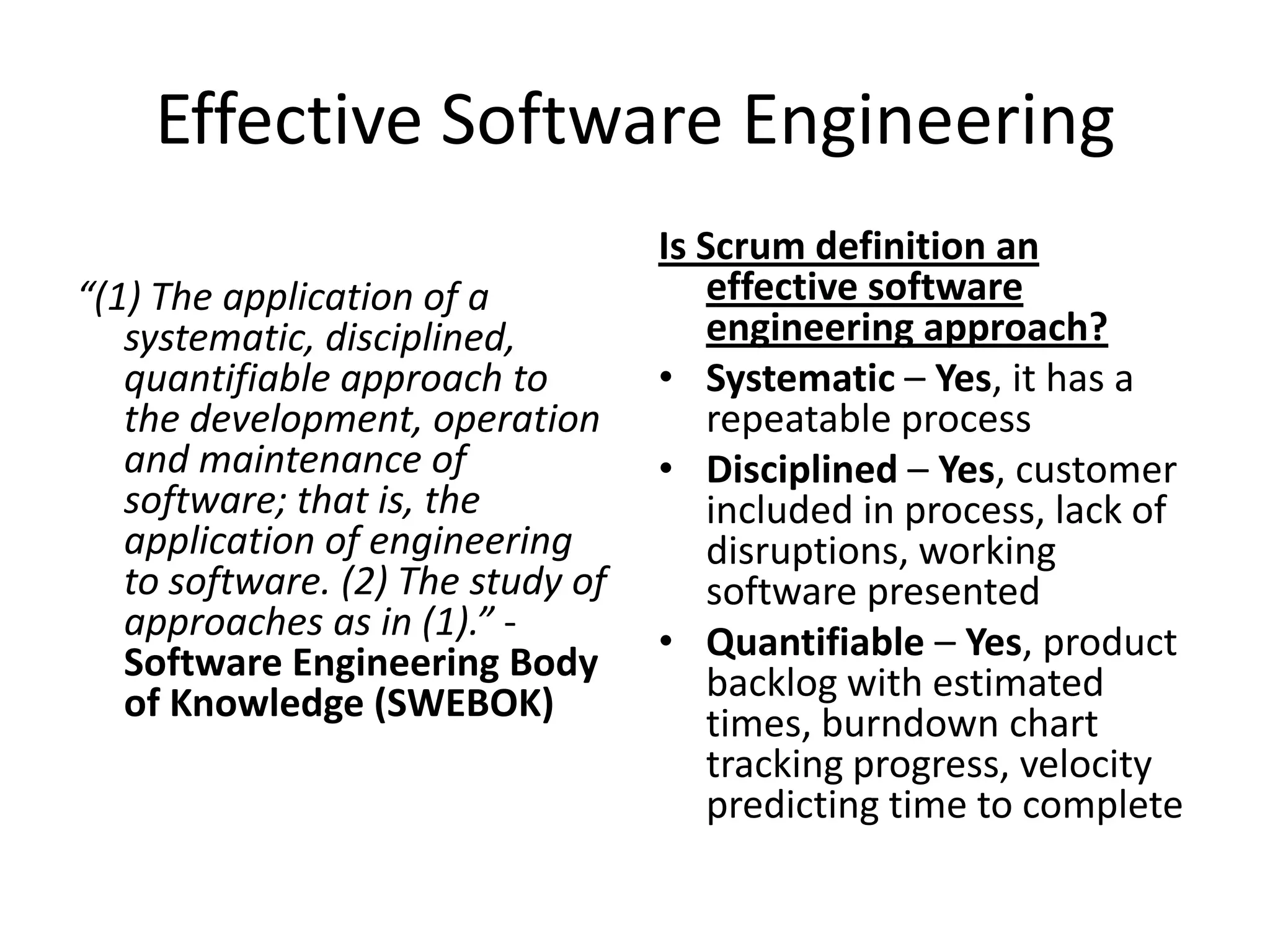
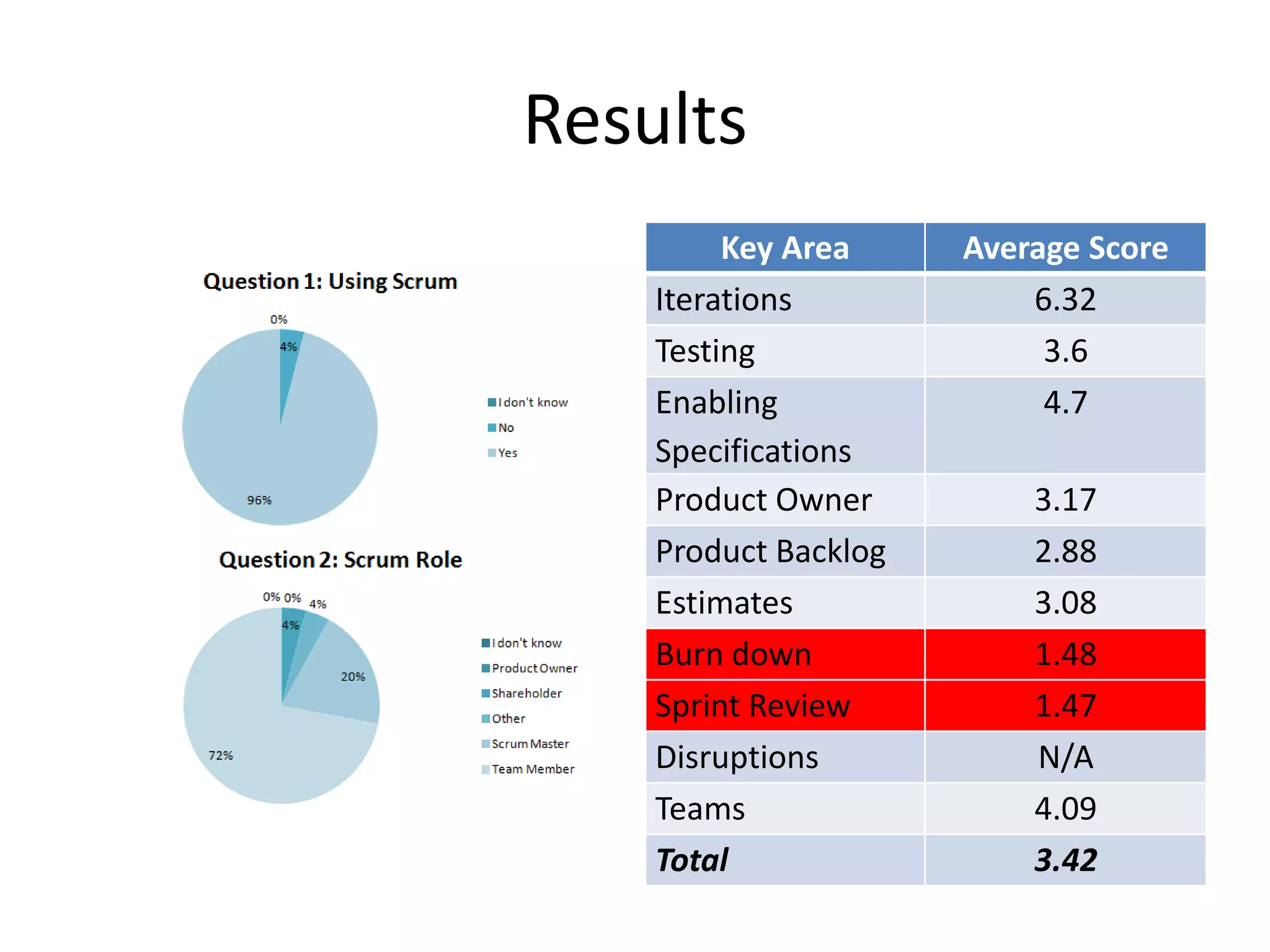
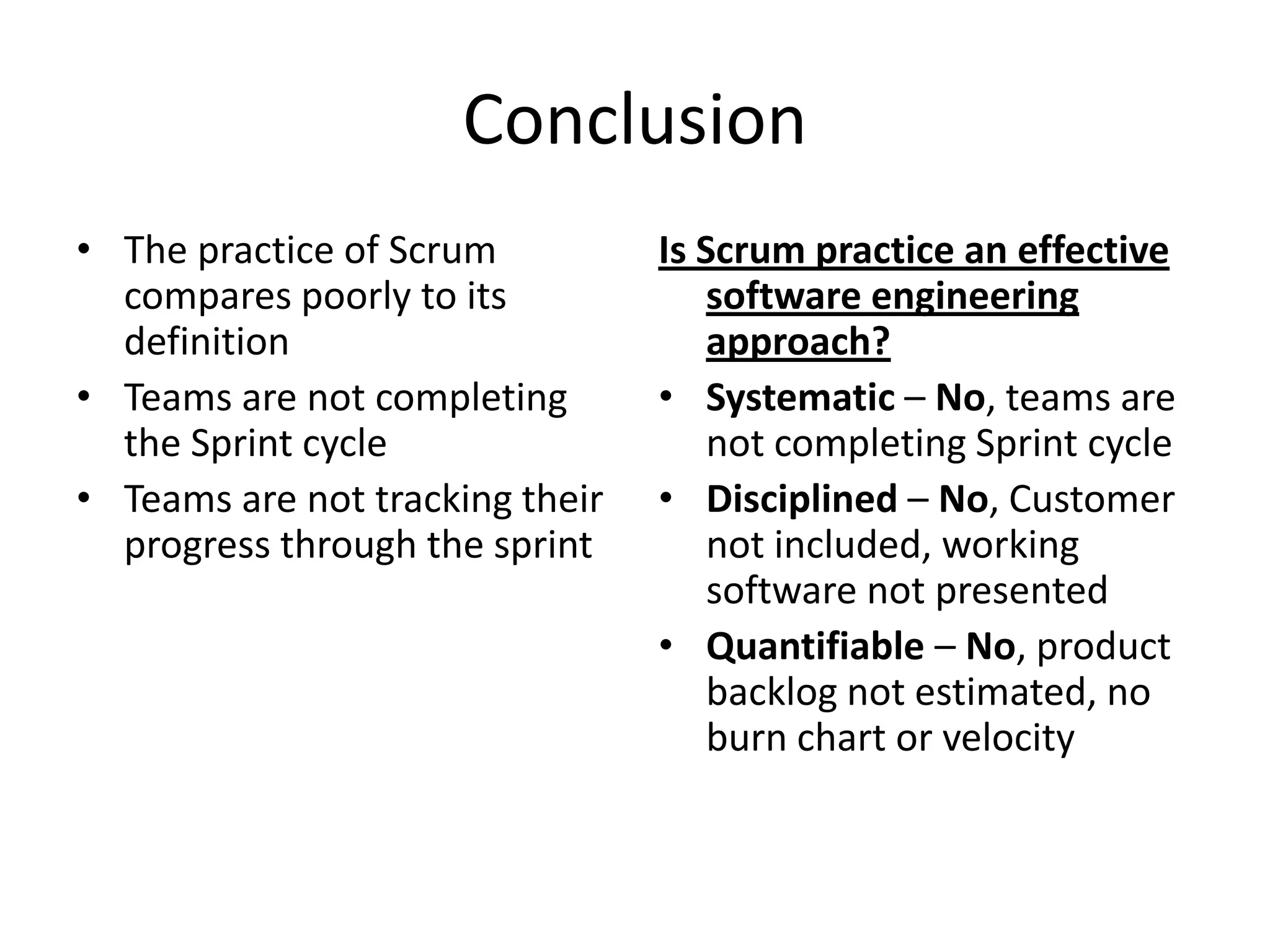
This document discusses the definition of Scrum versus its practice based on a study. It defines Scrum and Agile and outlines an agenda to discuss the research method, results, and conclusion. The results show that Scrum practice scores poorly compared to its definition in key areas like iterations, testing, product backlog, and burn down charts. The conclusion is that Scrum practice is not an effective software engineering approach as teams are not completing sprints and not tracking progress systematically as defined by Scrum.