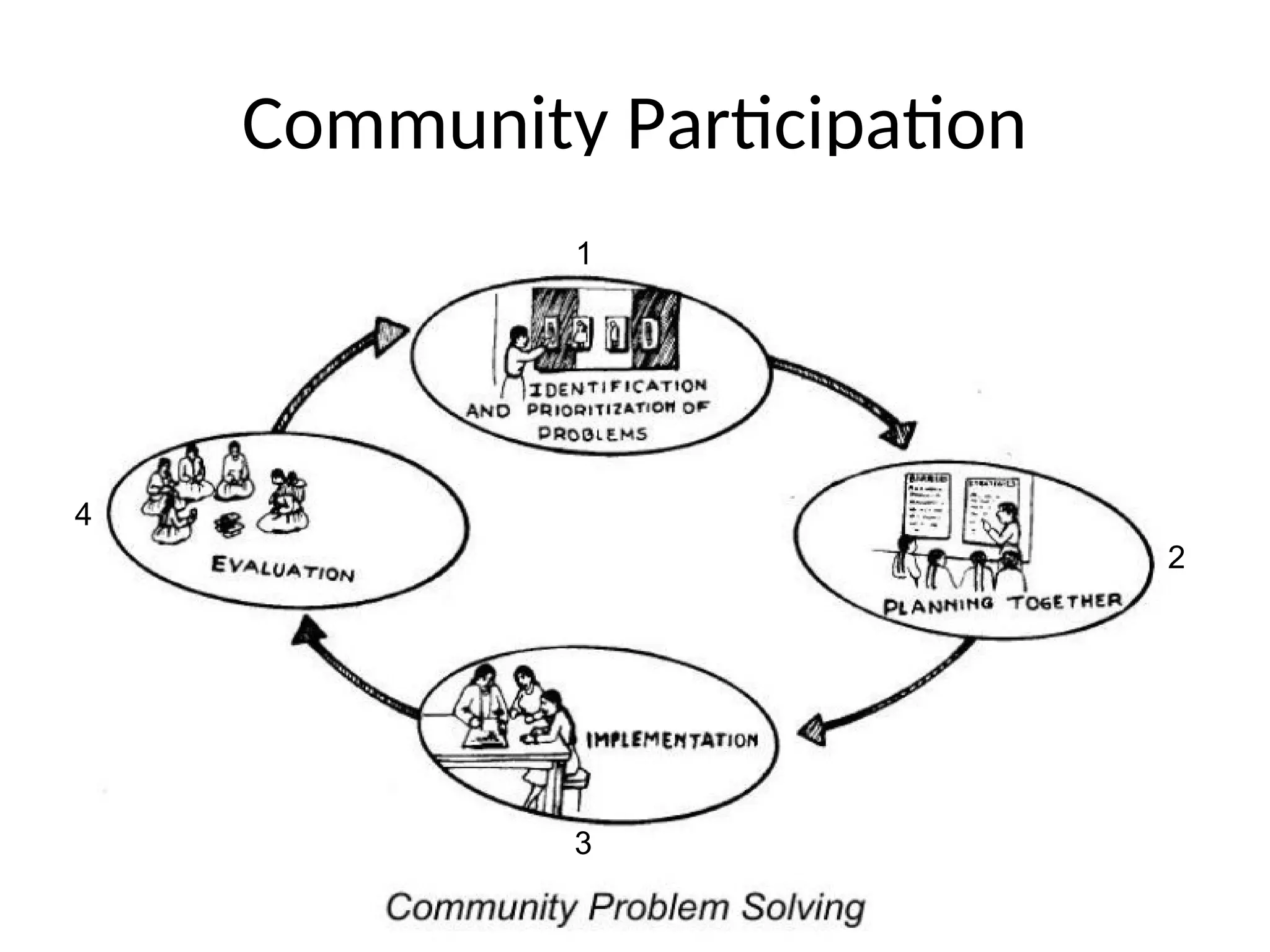
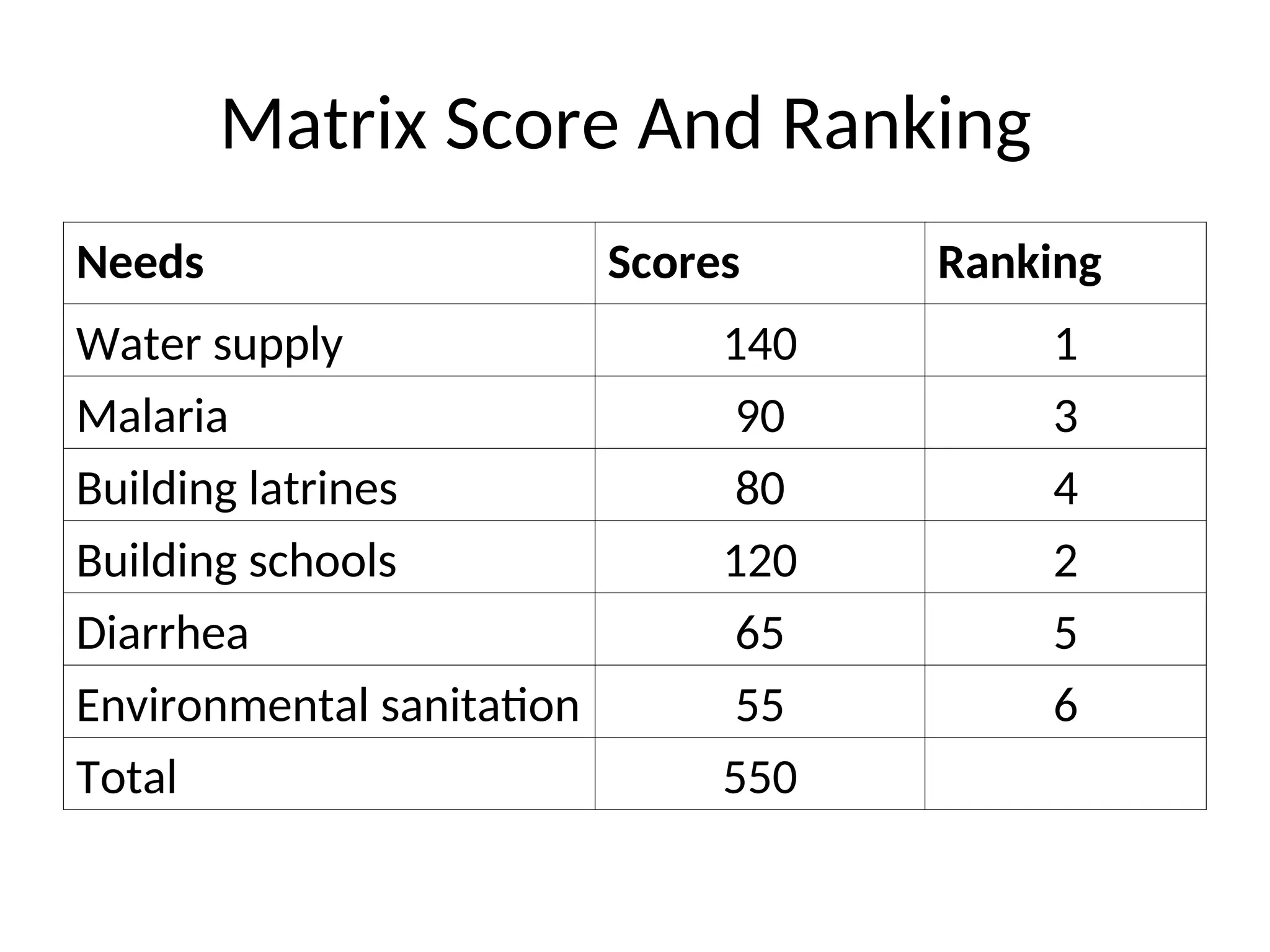
The document discusses the importance of community participation in health care, defining key terms and concepts like empowerment, mobilization, and community involvement. It outlines various types of participation, including manipulative, passive, and self-mobilization, and emphasizes the need for a bottom-up approach in program implementation to ensure community ownership and effectiveness. Challenges and factors influencing community participation are also highlighted, alongside methods for conducting participatory appraisals to enhance community engagement in health-related initiatives.