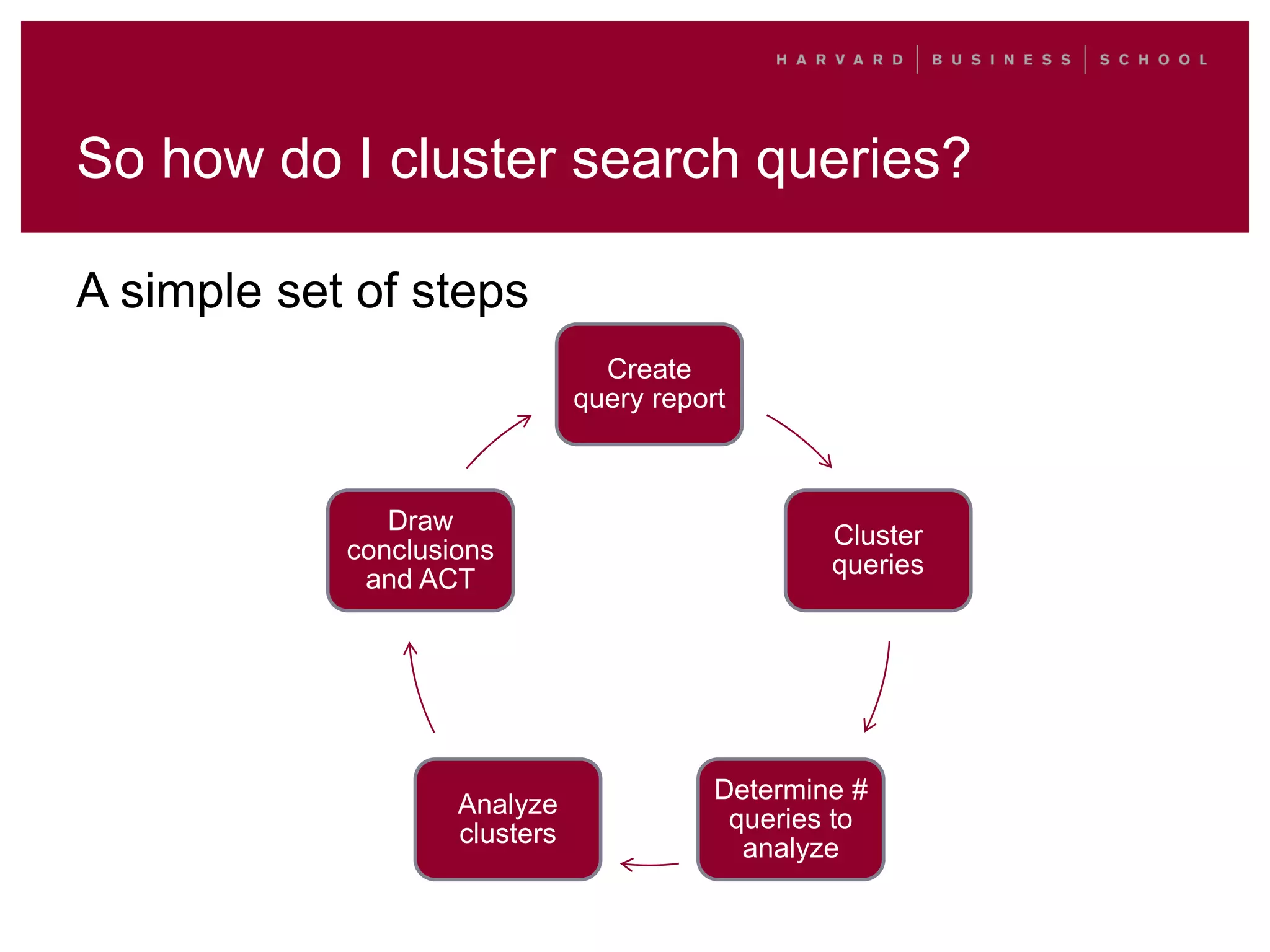
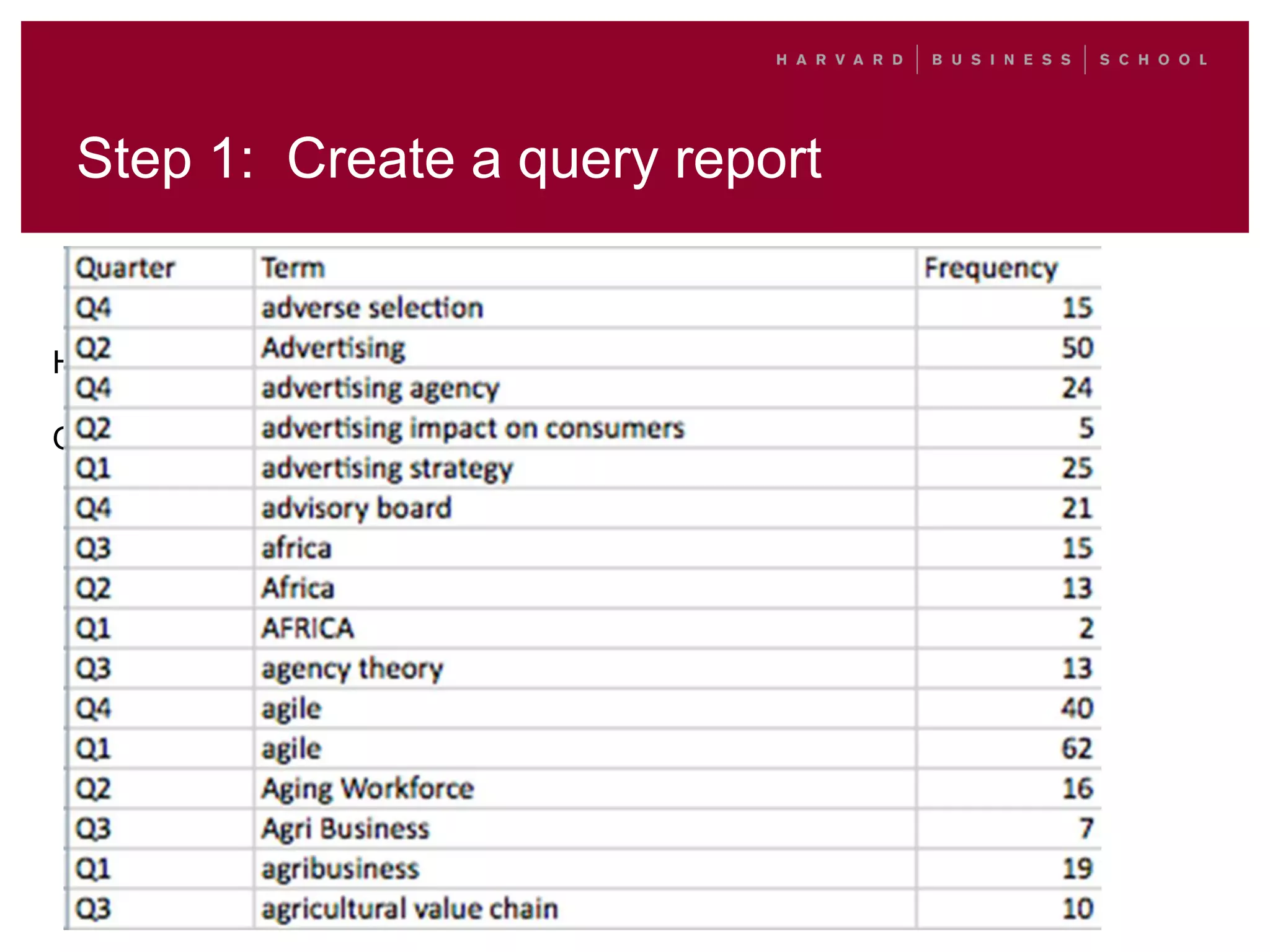
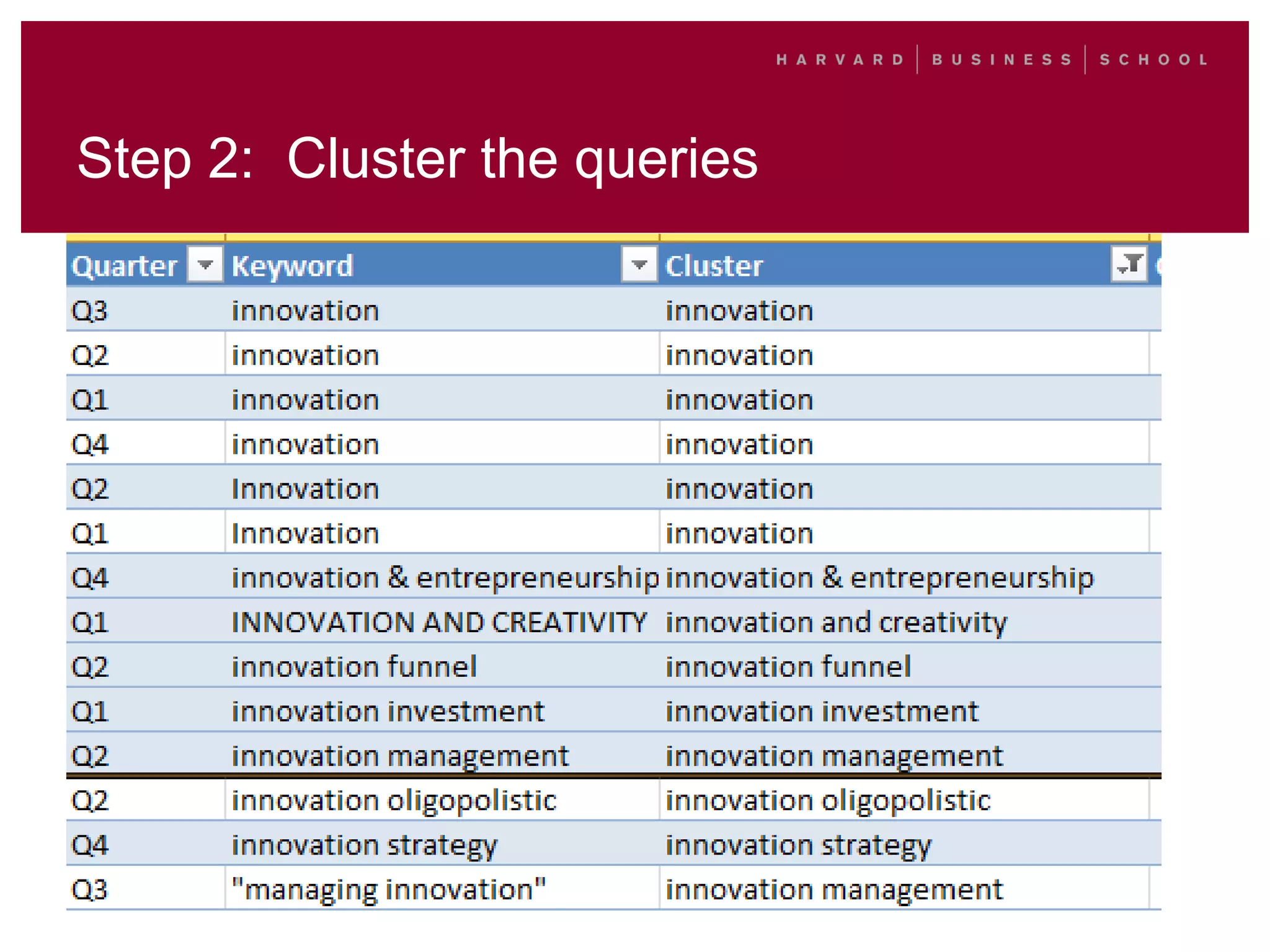
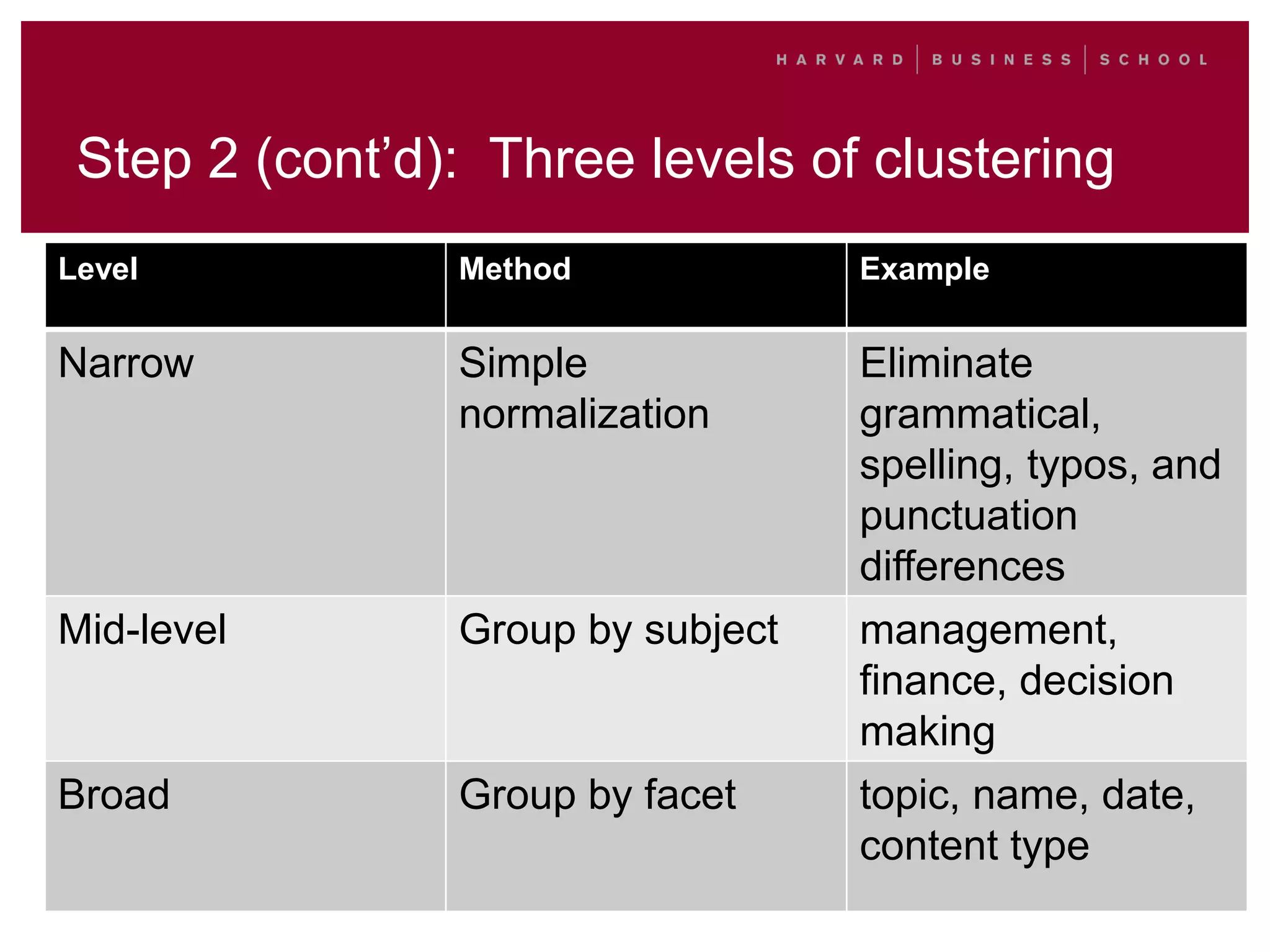
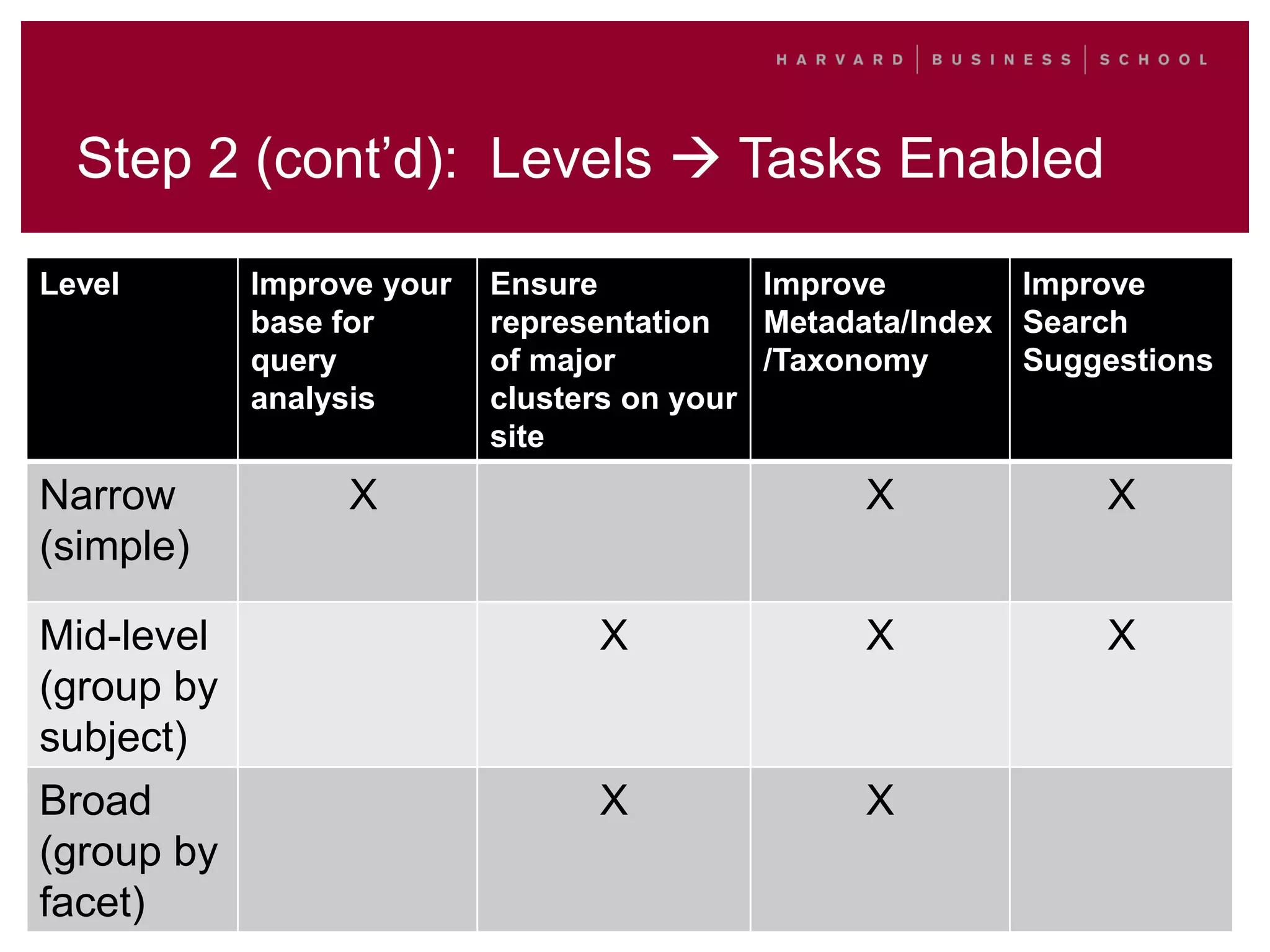
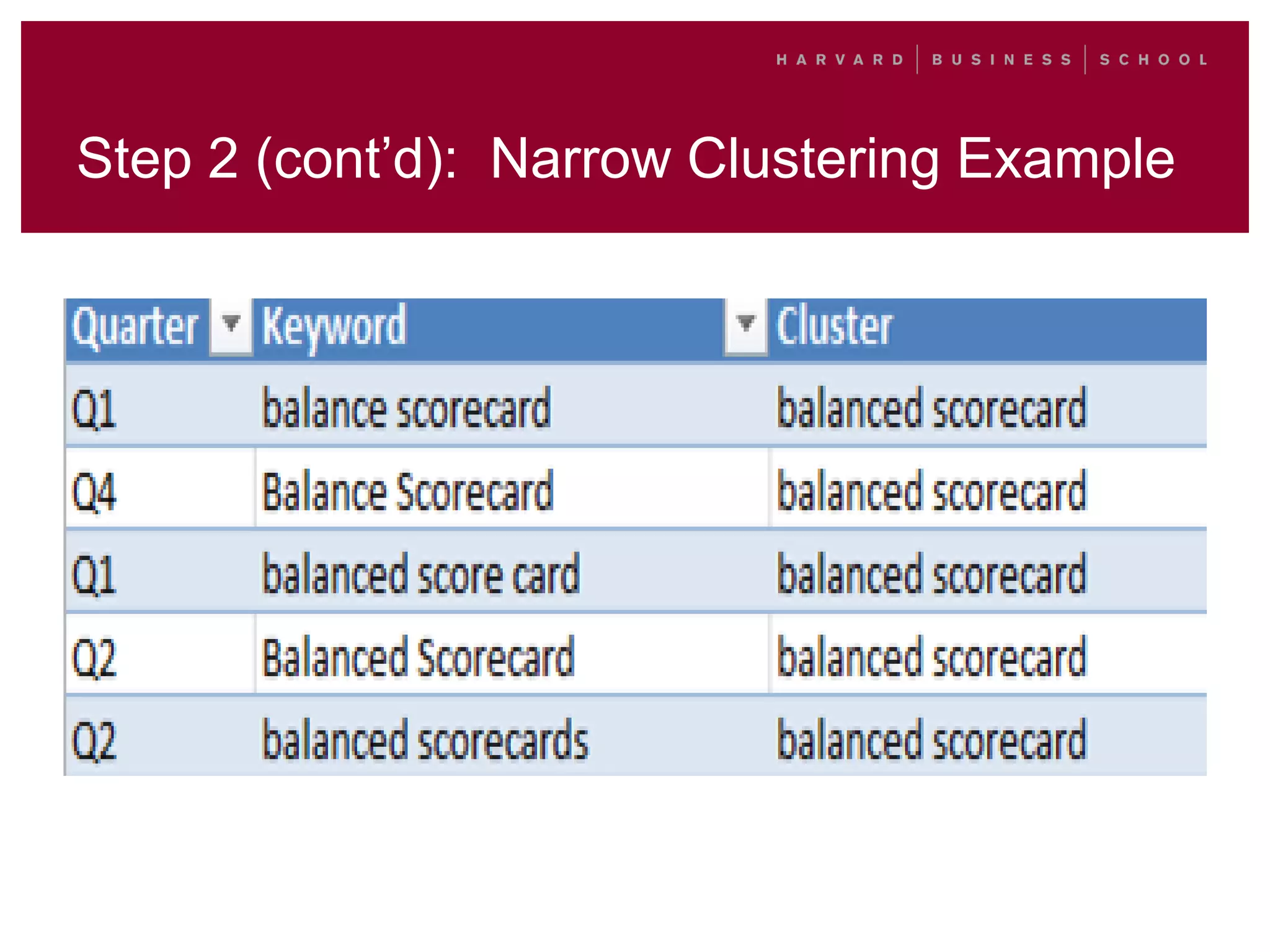
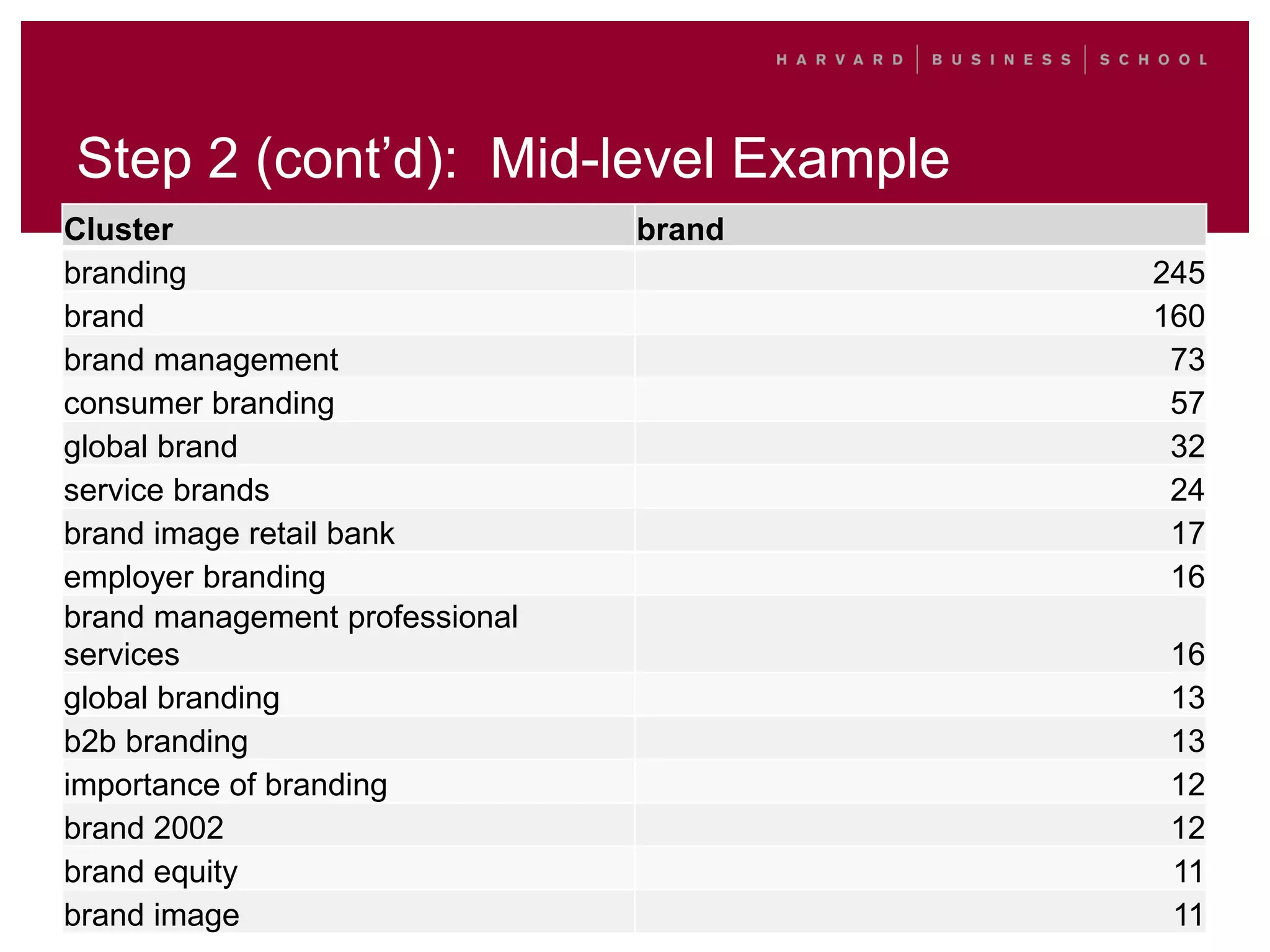
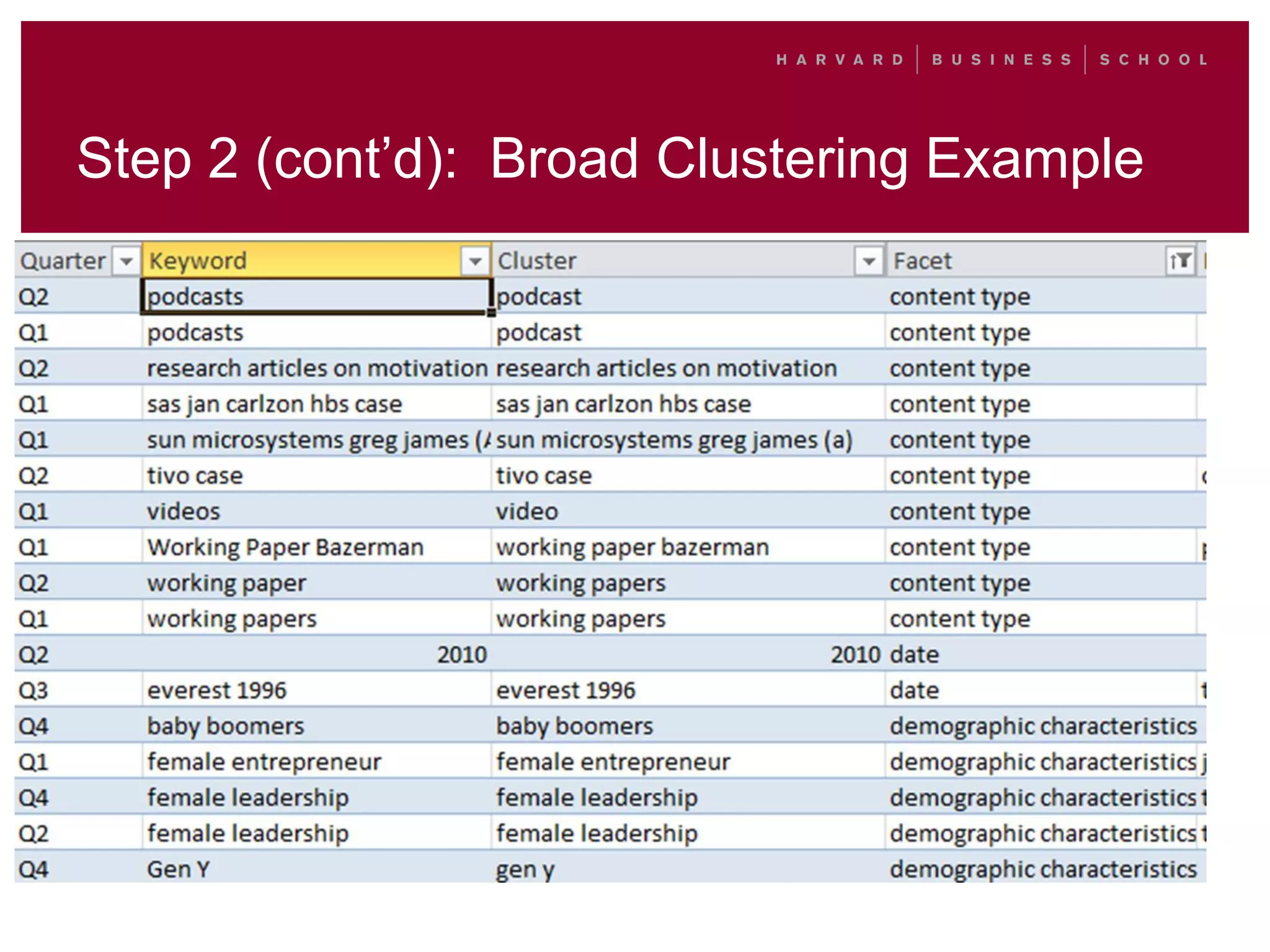
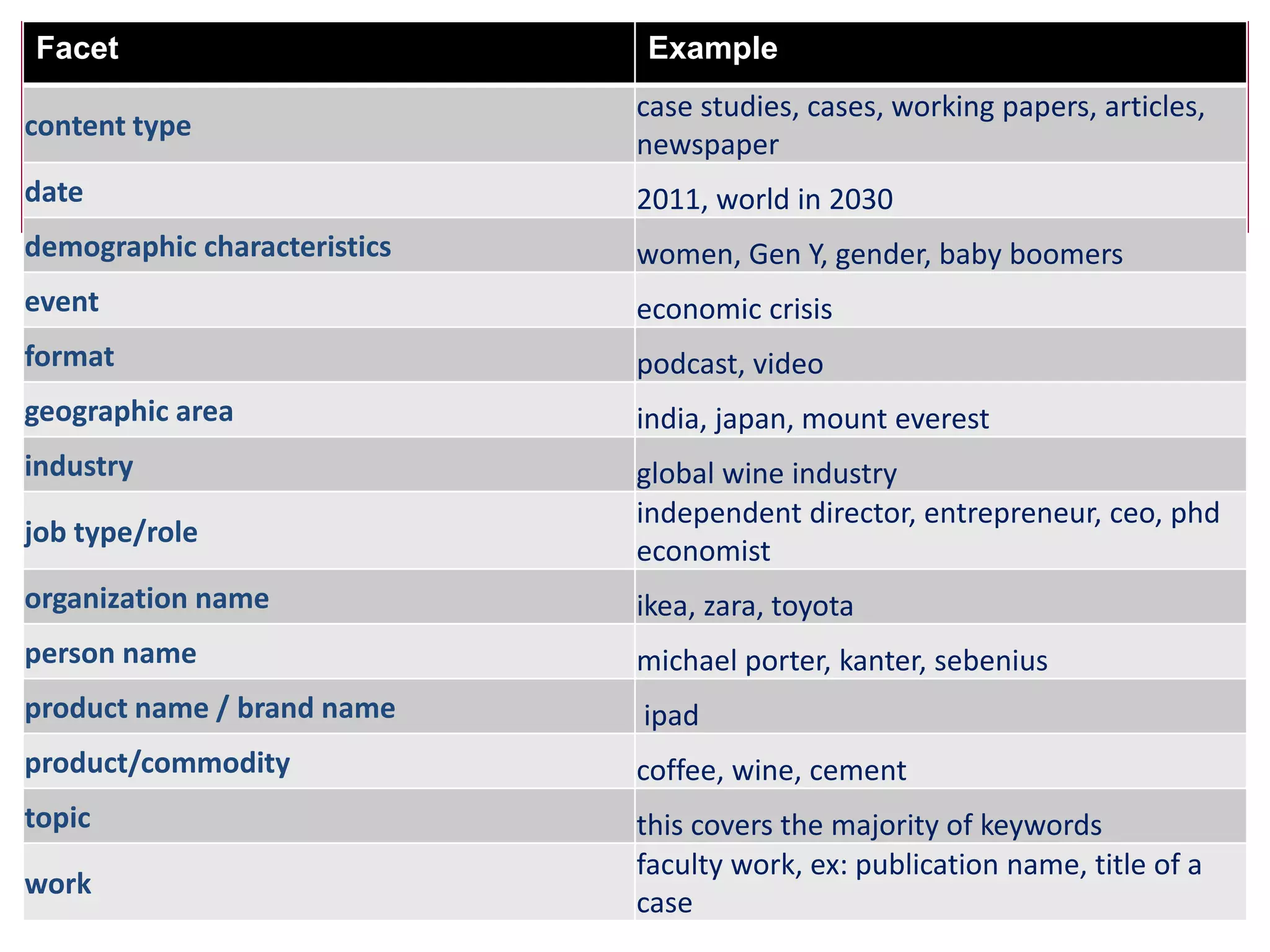
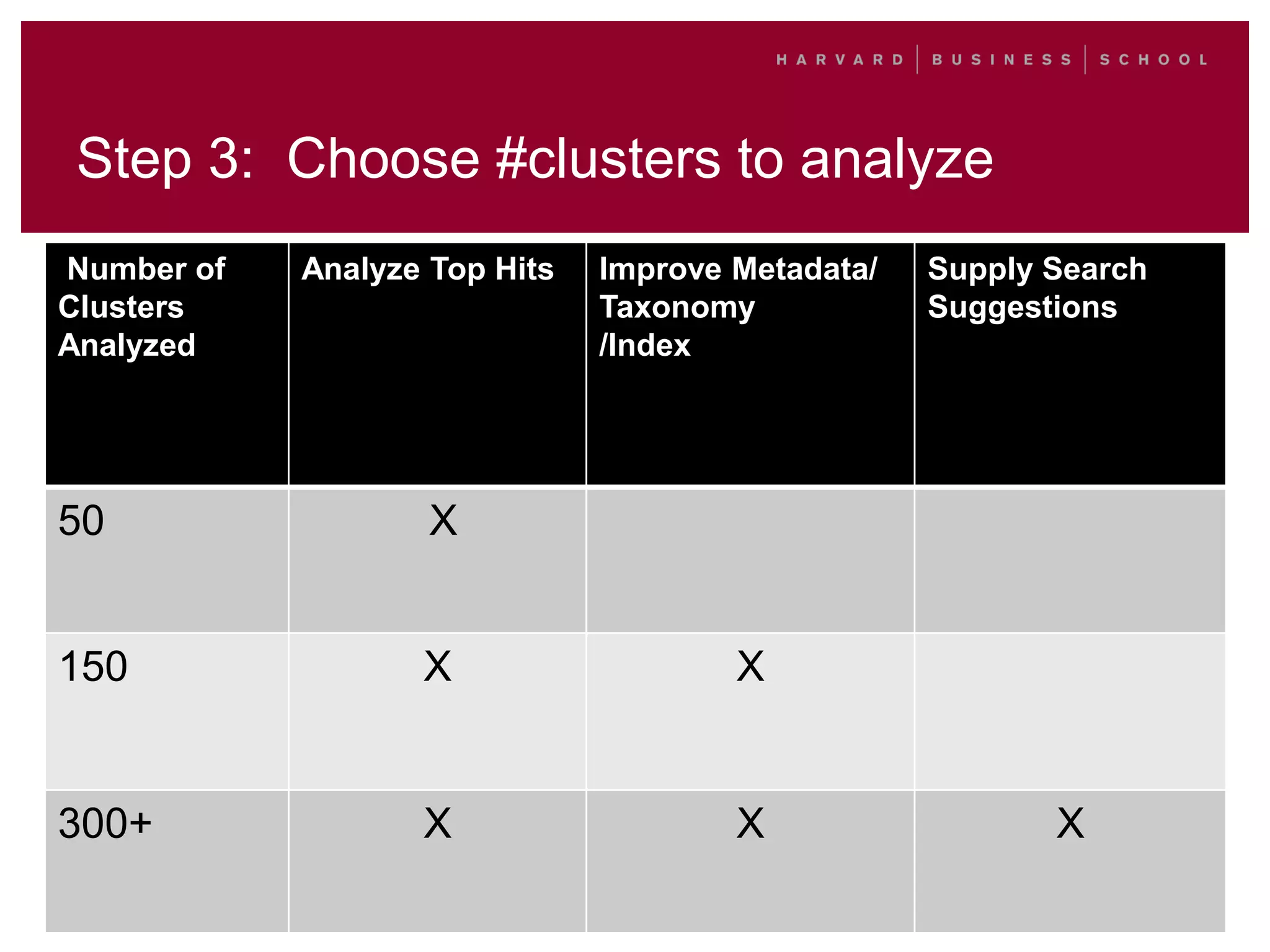
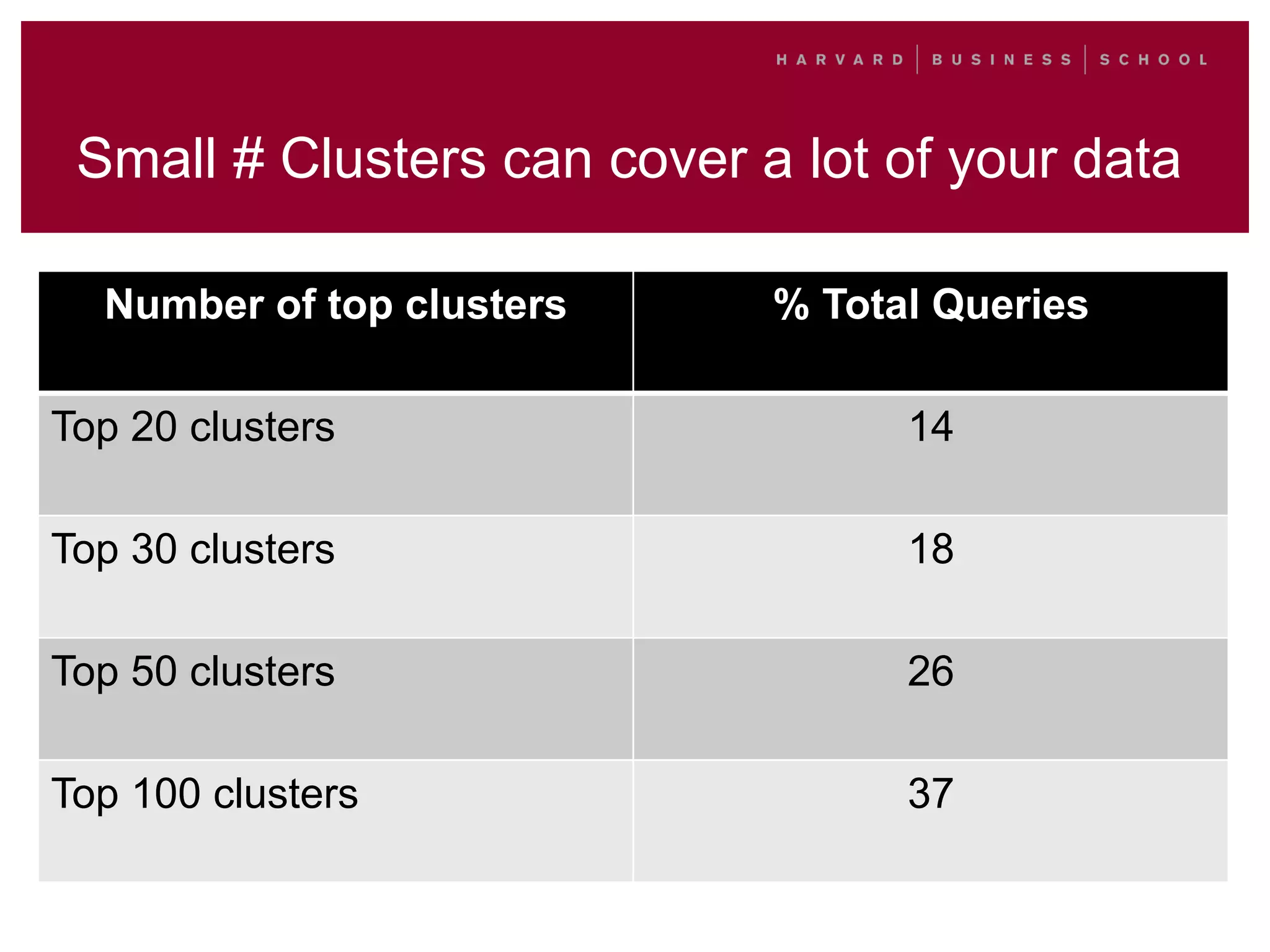
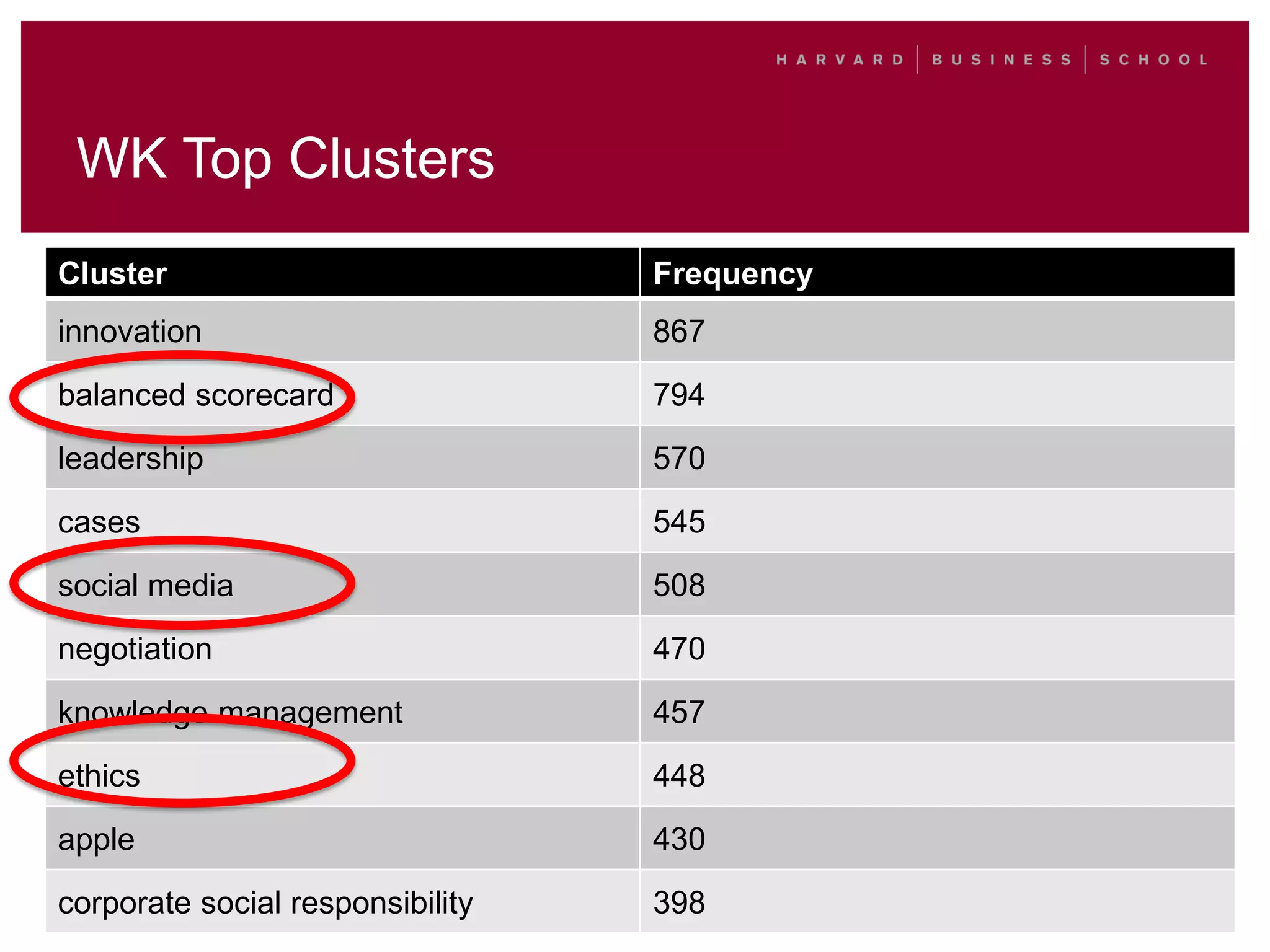
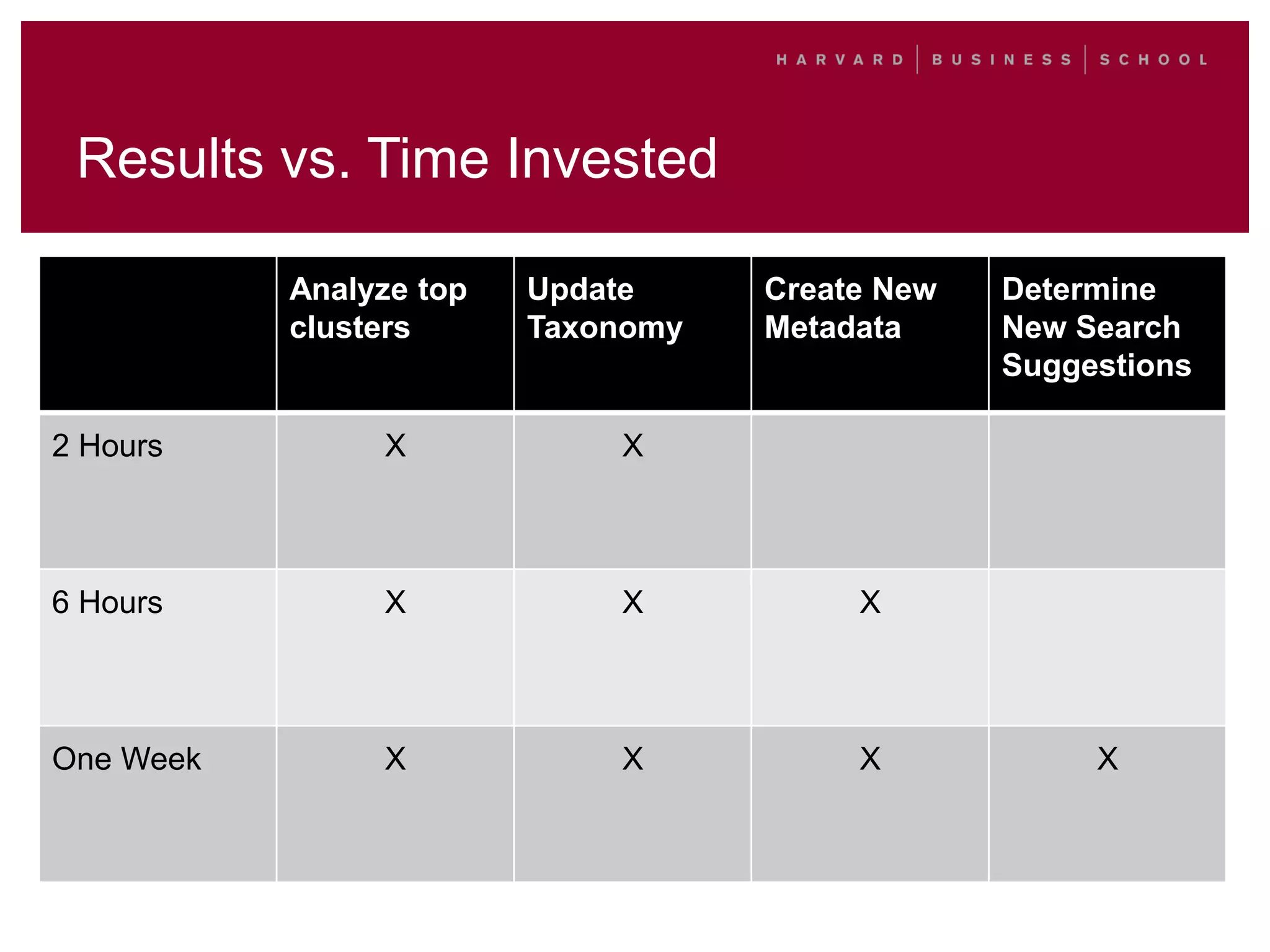
This document outlines a process for clustering search queries to improve search and navigation on a website. It involves creating a report of search queries from the site's search logs, clustering the queries into groups at different levels of specificity, analyzing the top clusters to identify areas for improvement, and taking action such as updating site navigation, taxonomy, metadata, and search suggestions based on insights from the clusters. The process is presented as repeatable, scalable, and capable of driving continuous incremental improvements to search with relatively low time investment.