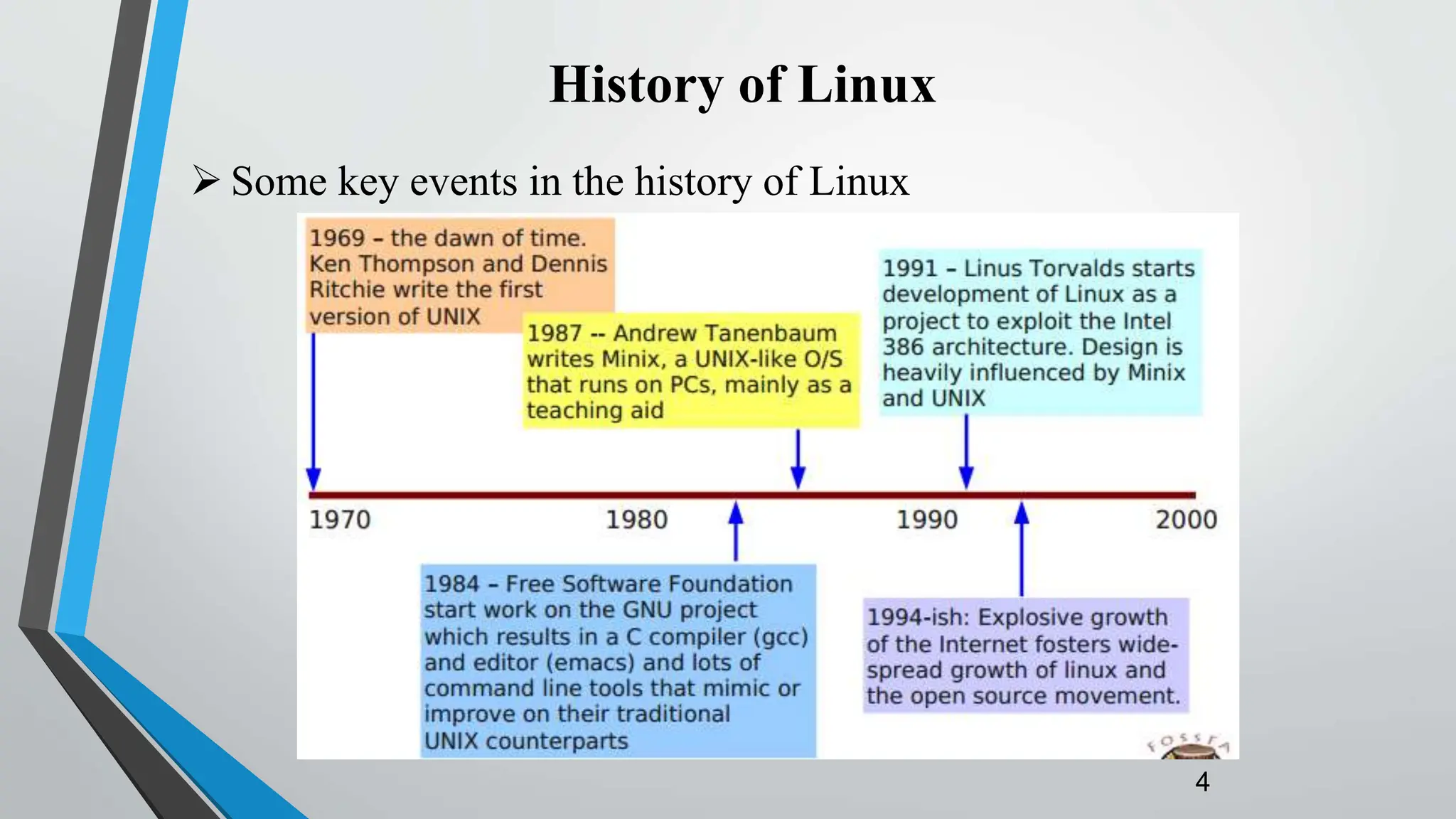
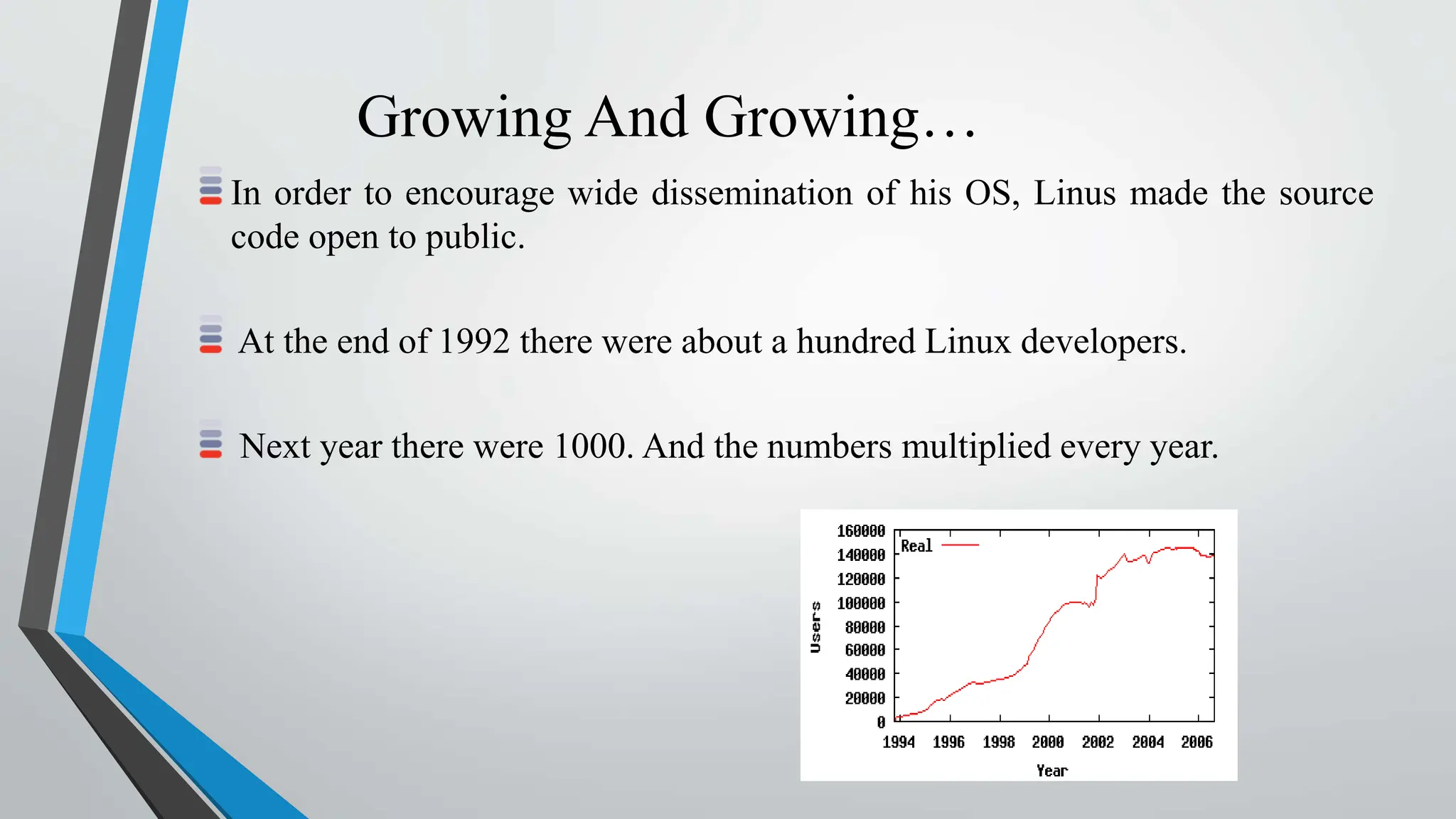
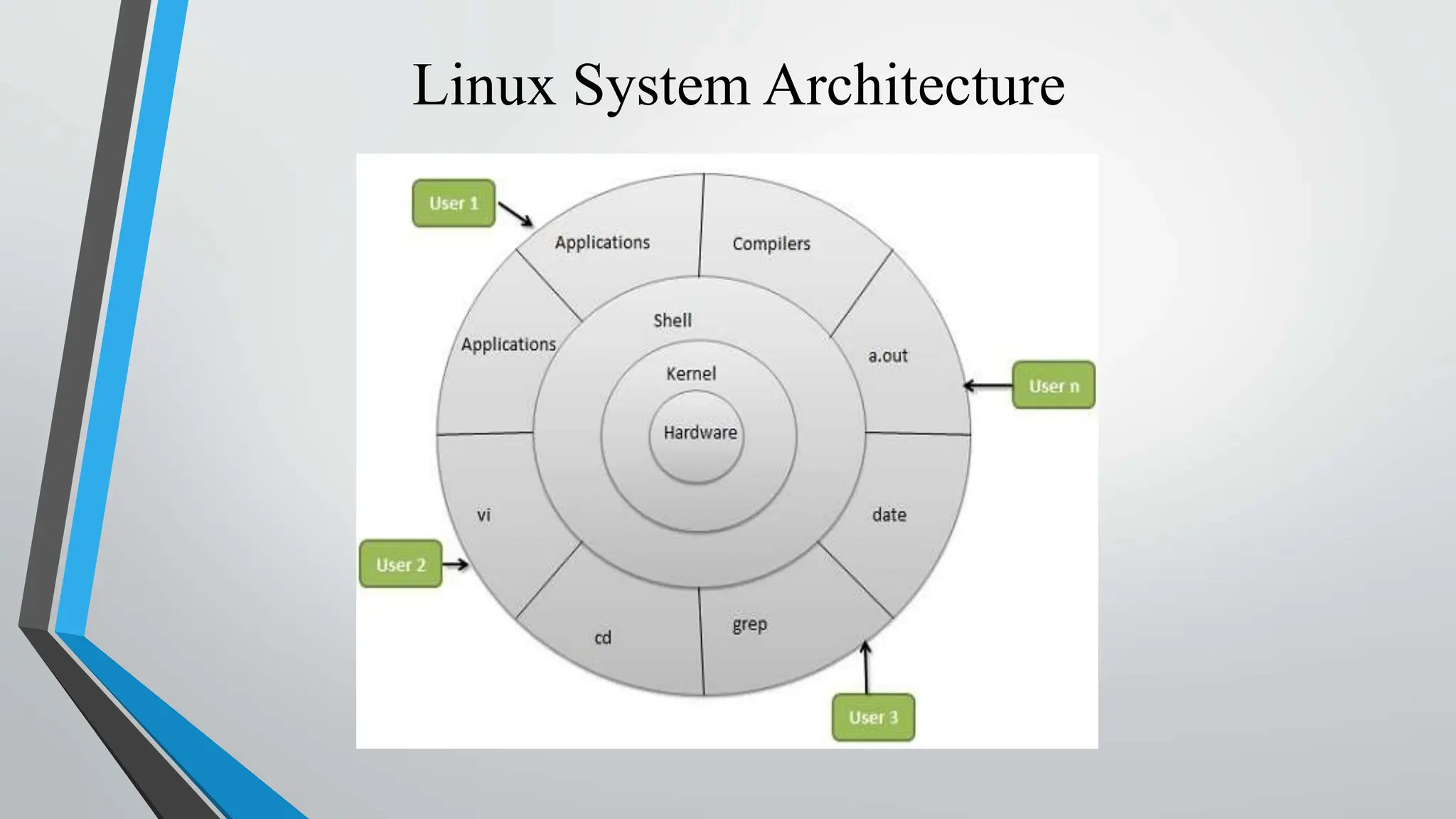
Linux is an open-source operating system kernel created by Linus Torvalds. It can run on a variety of systems including servers, desktops, embedded devices, and more. Since its initial release in 1991, the Linux kernel has grown significantly with contributions from thousands of programmers. It is free to use, modify, and distribute, driving its widespread adoption for servers, embedded systems, and as an alternative to other proprietary operating systems.