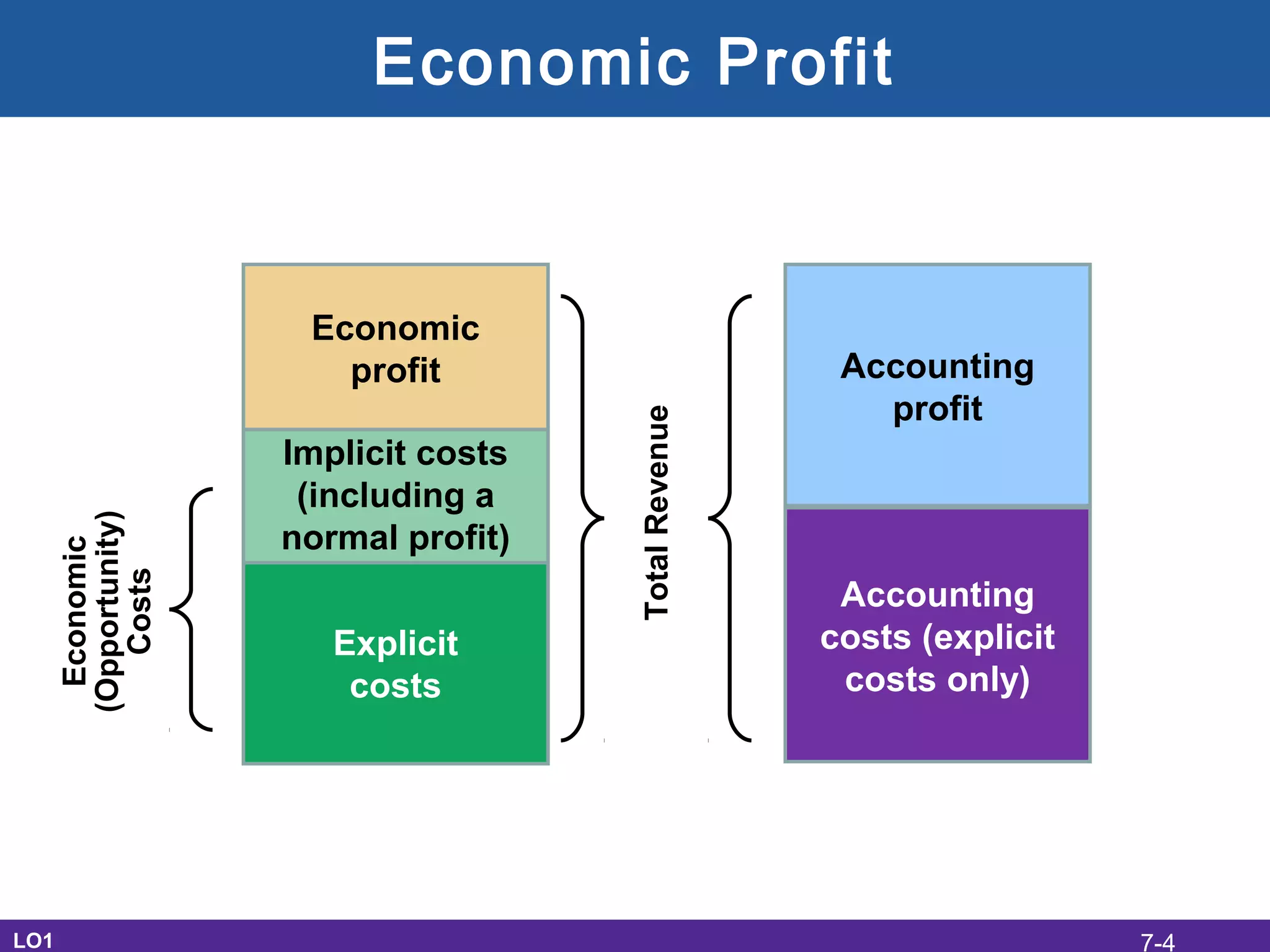
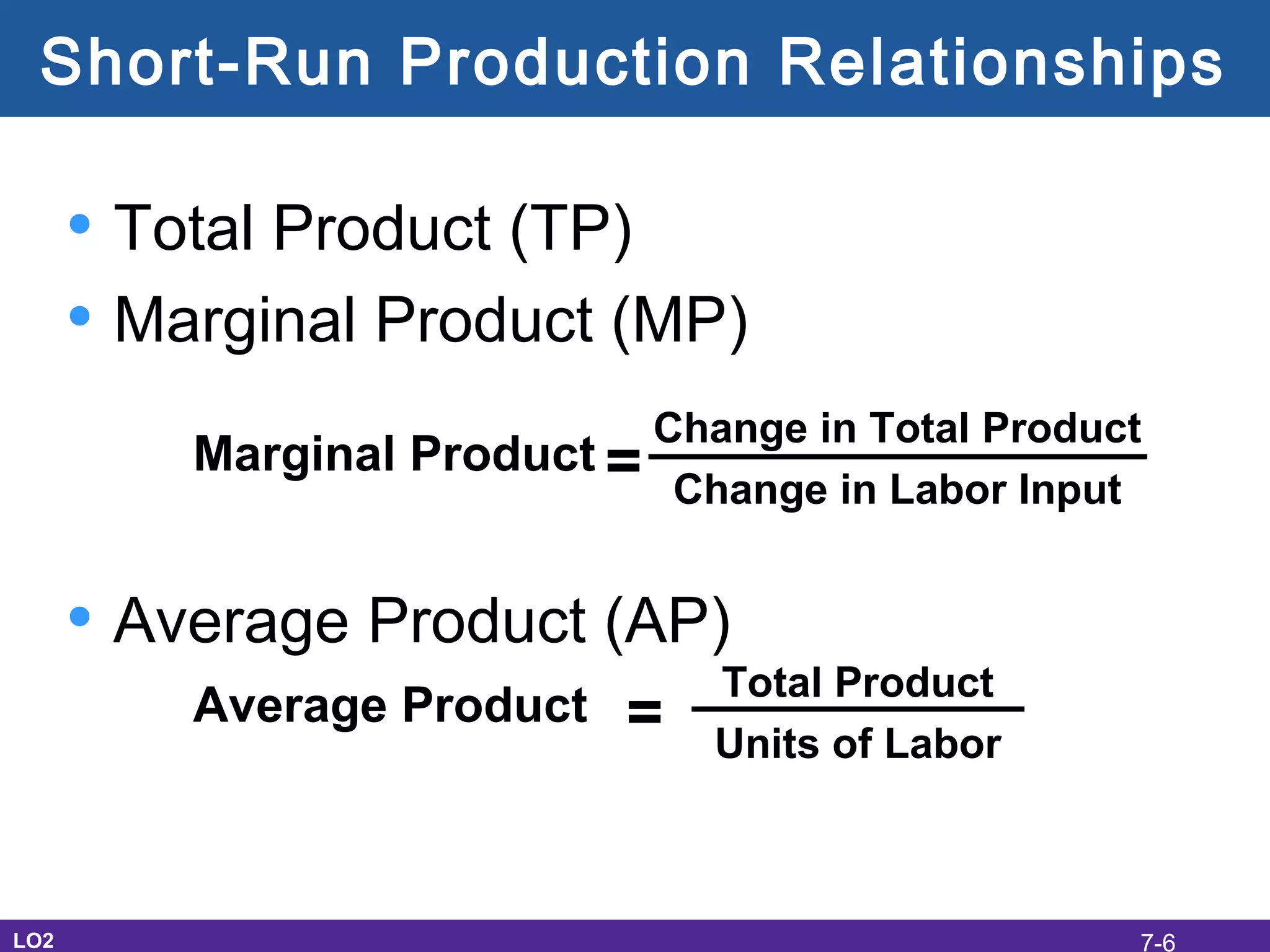
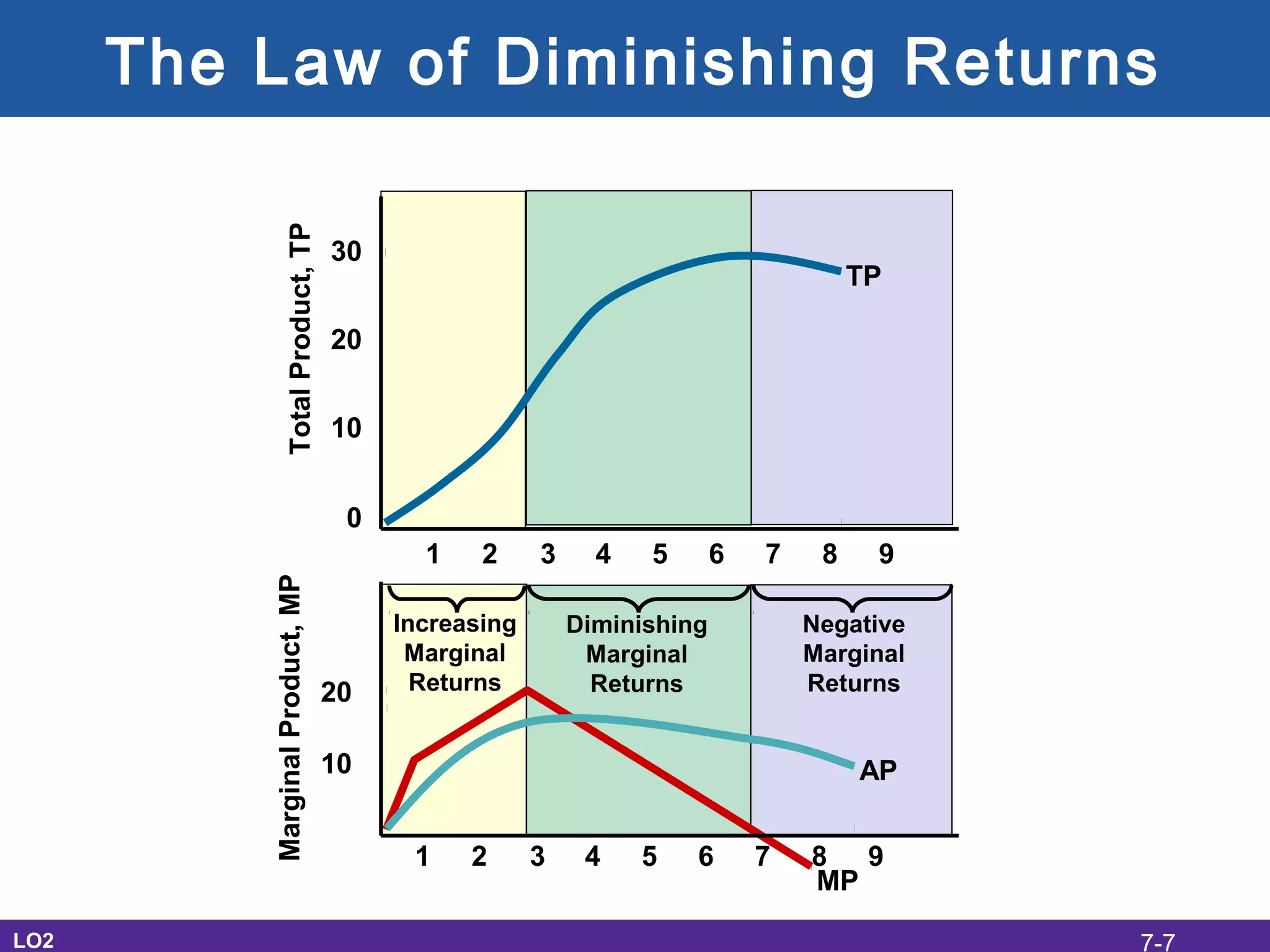
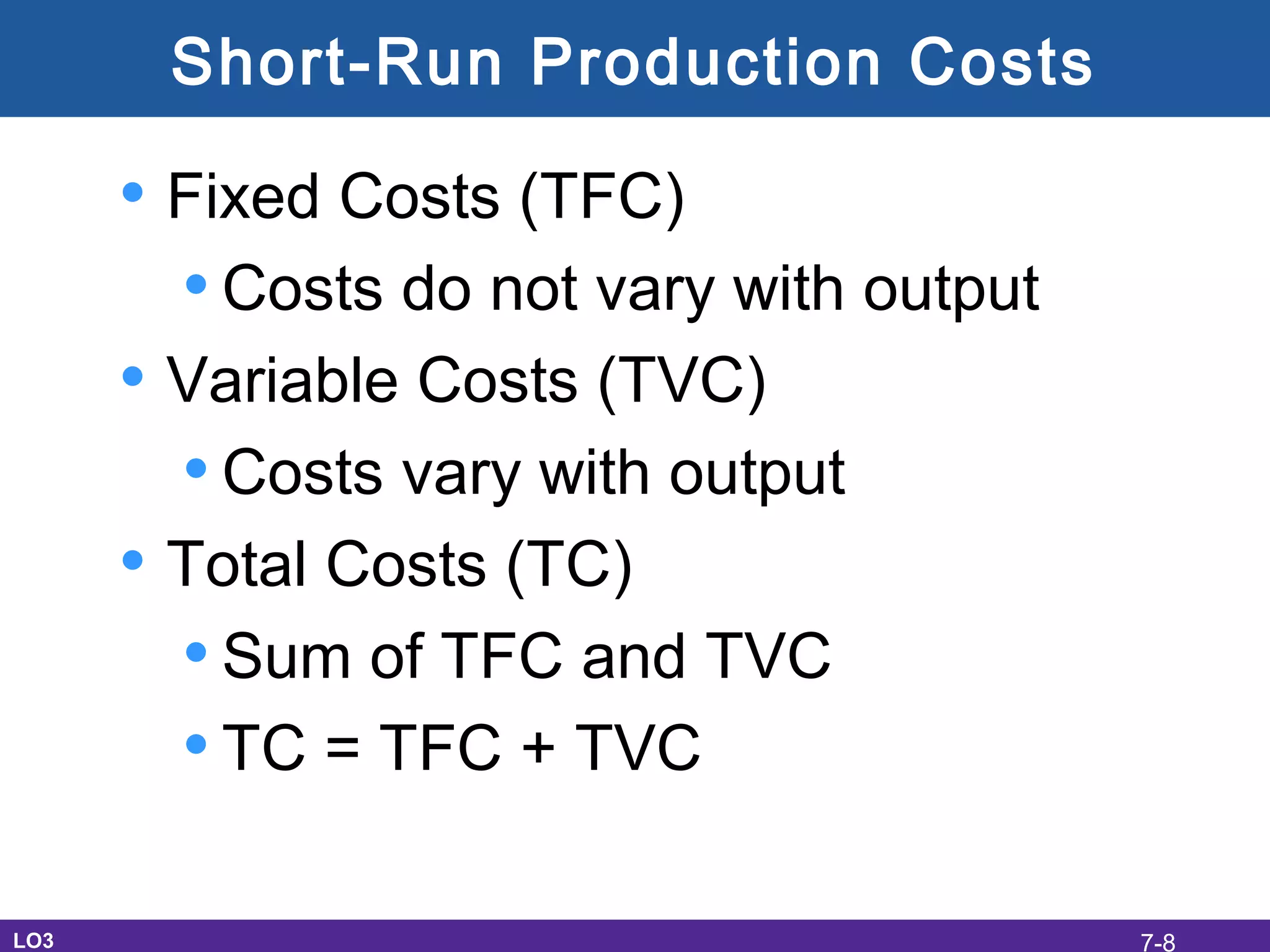
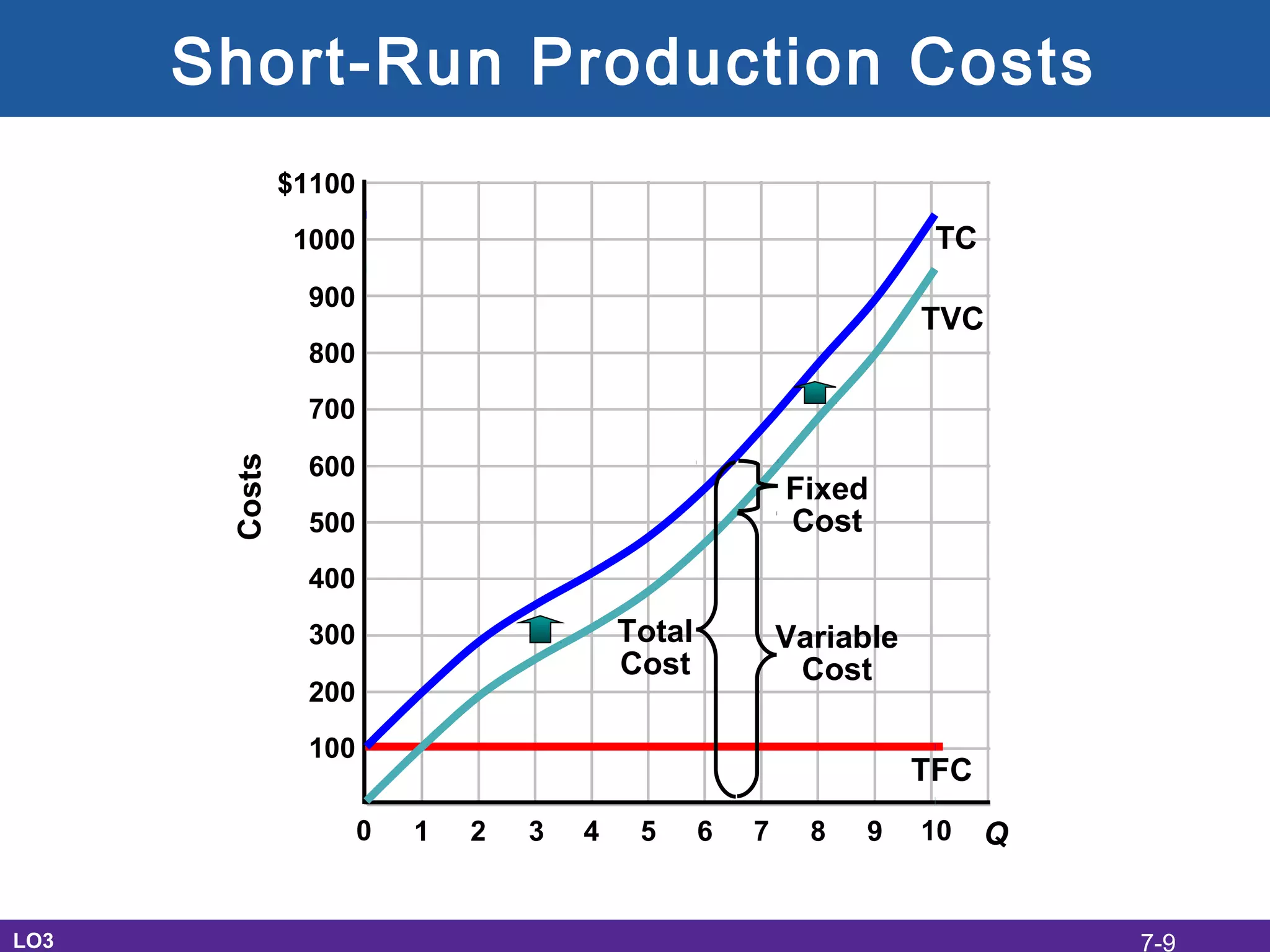
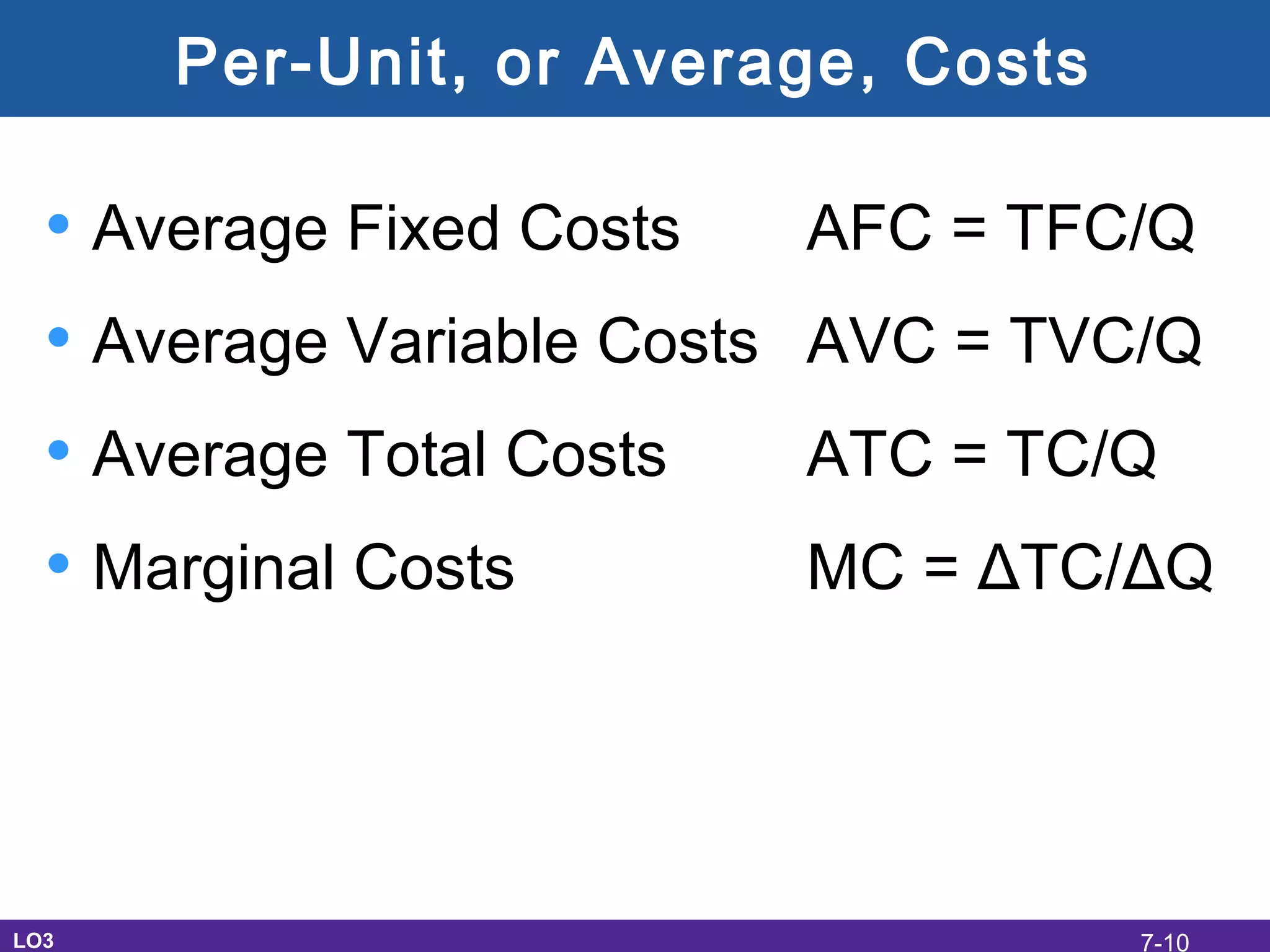
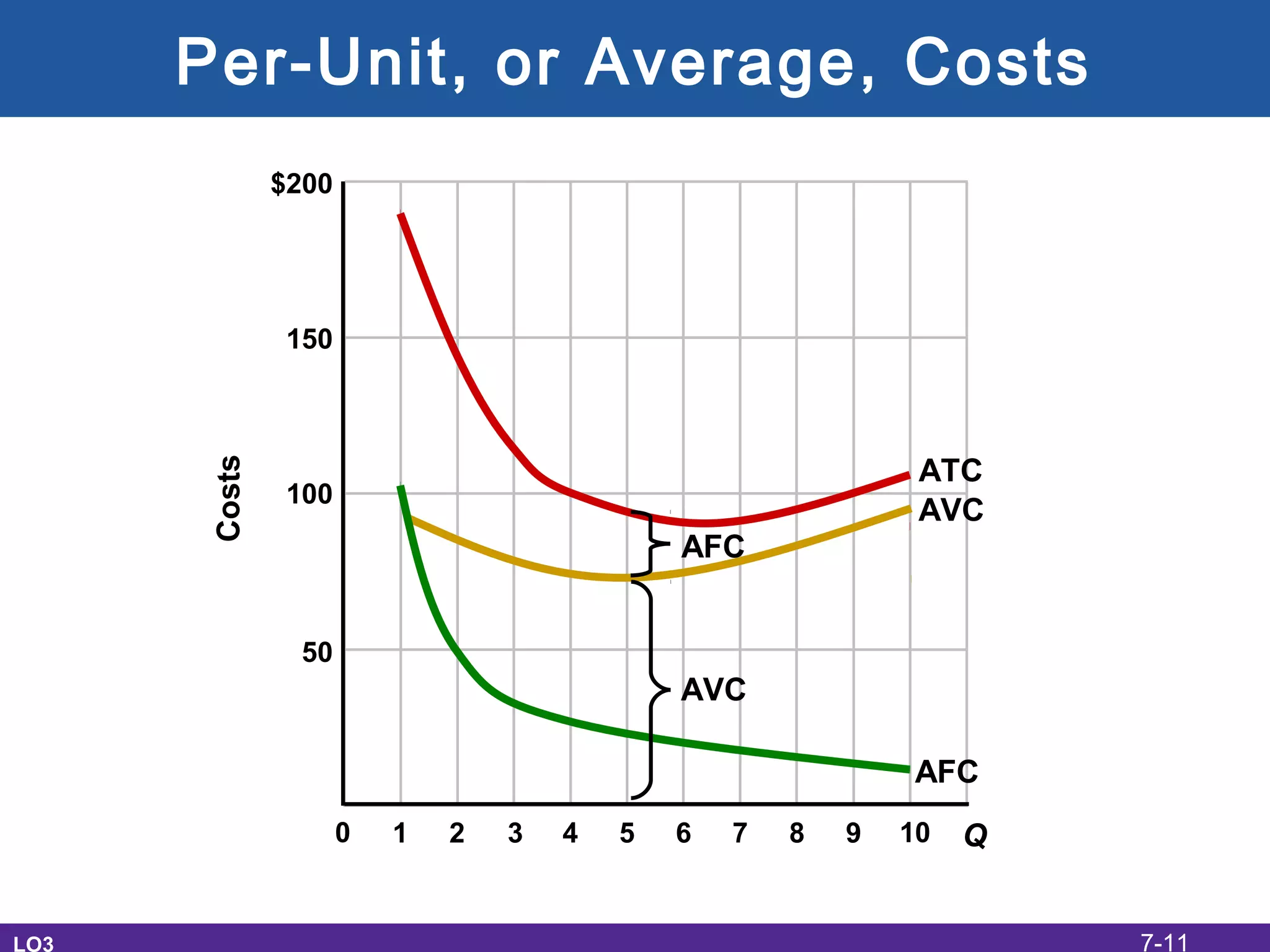
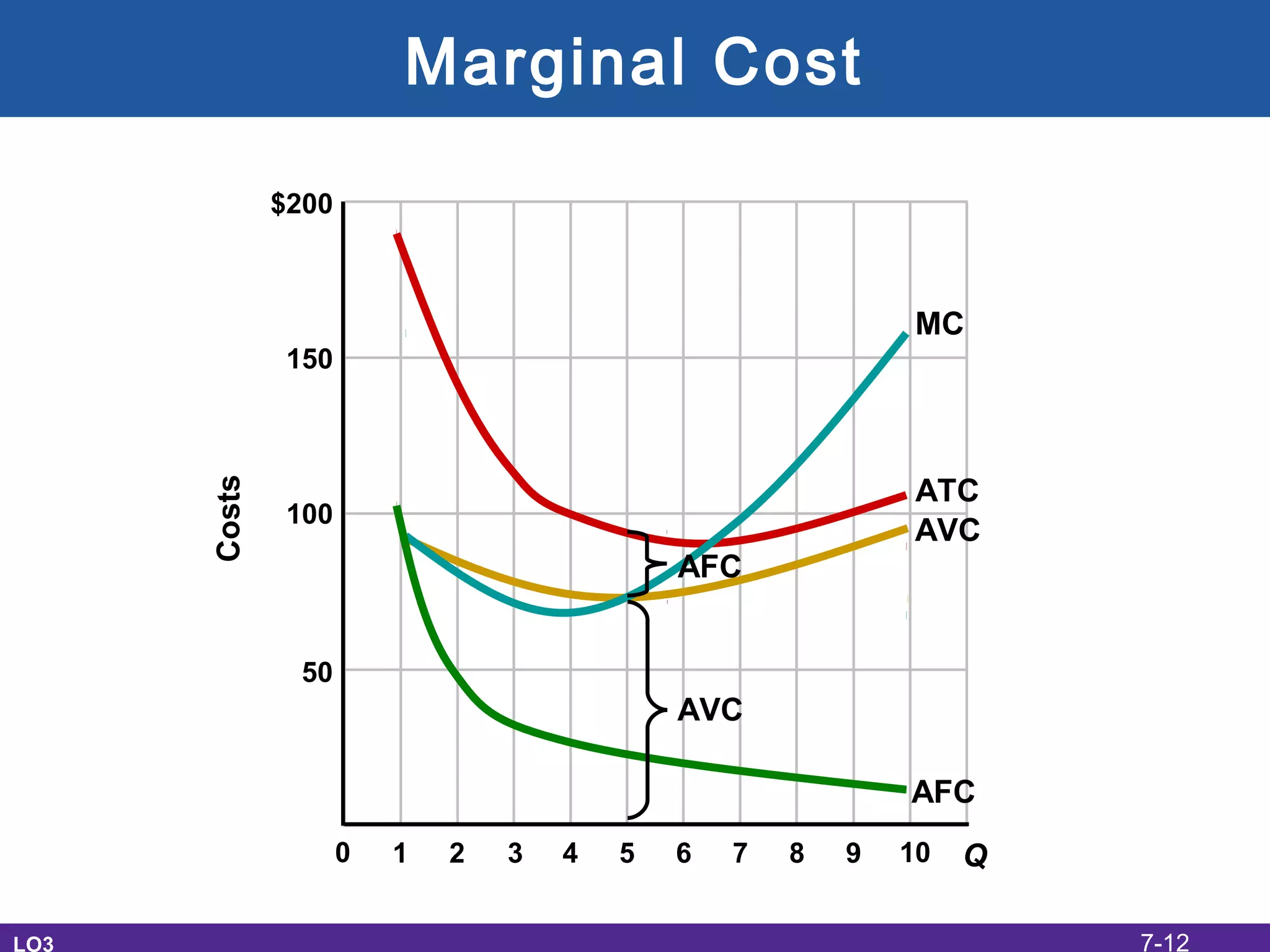
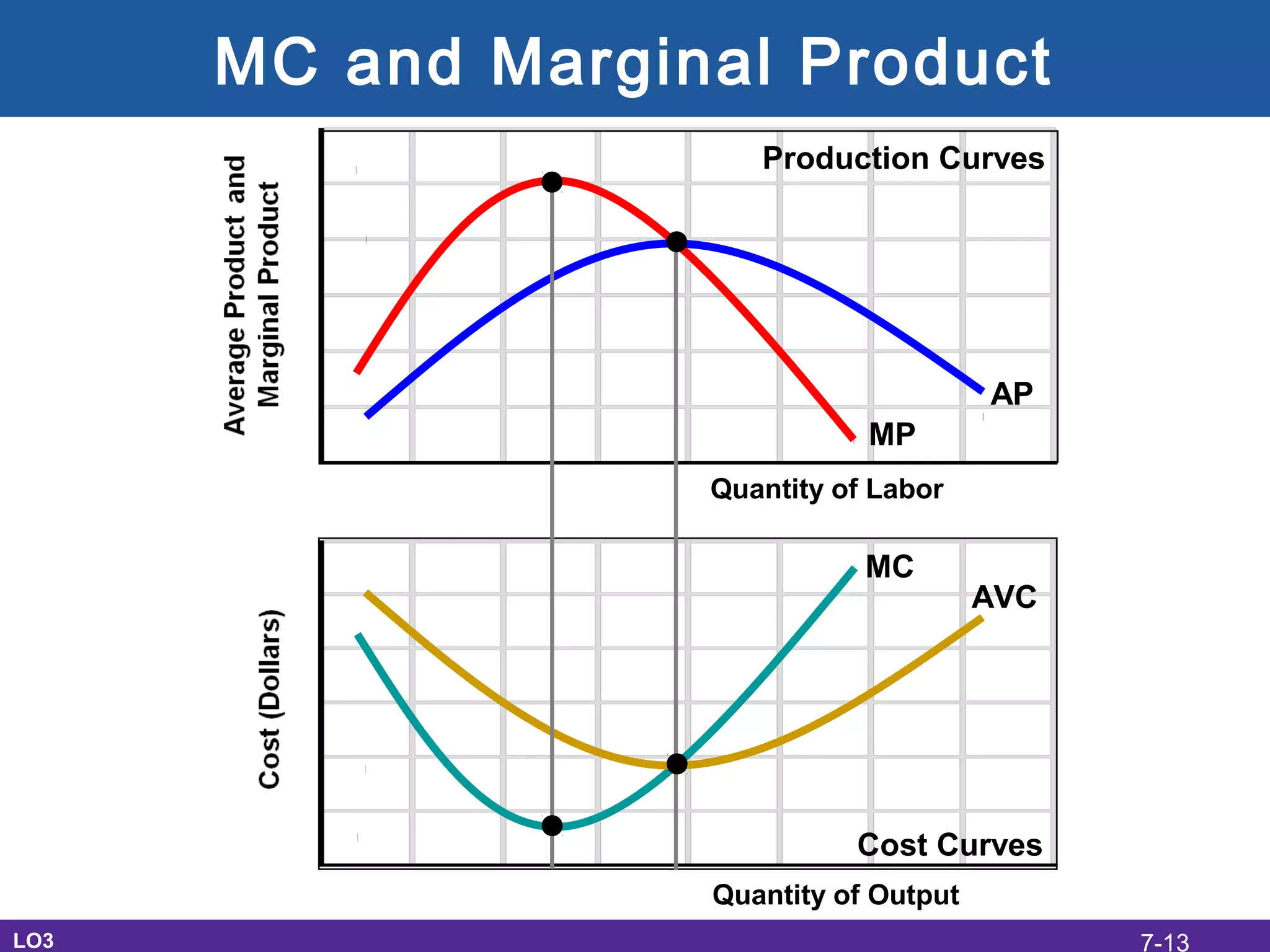
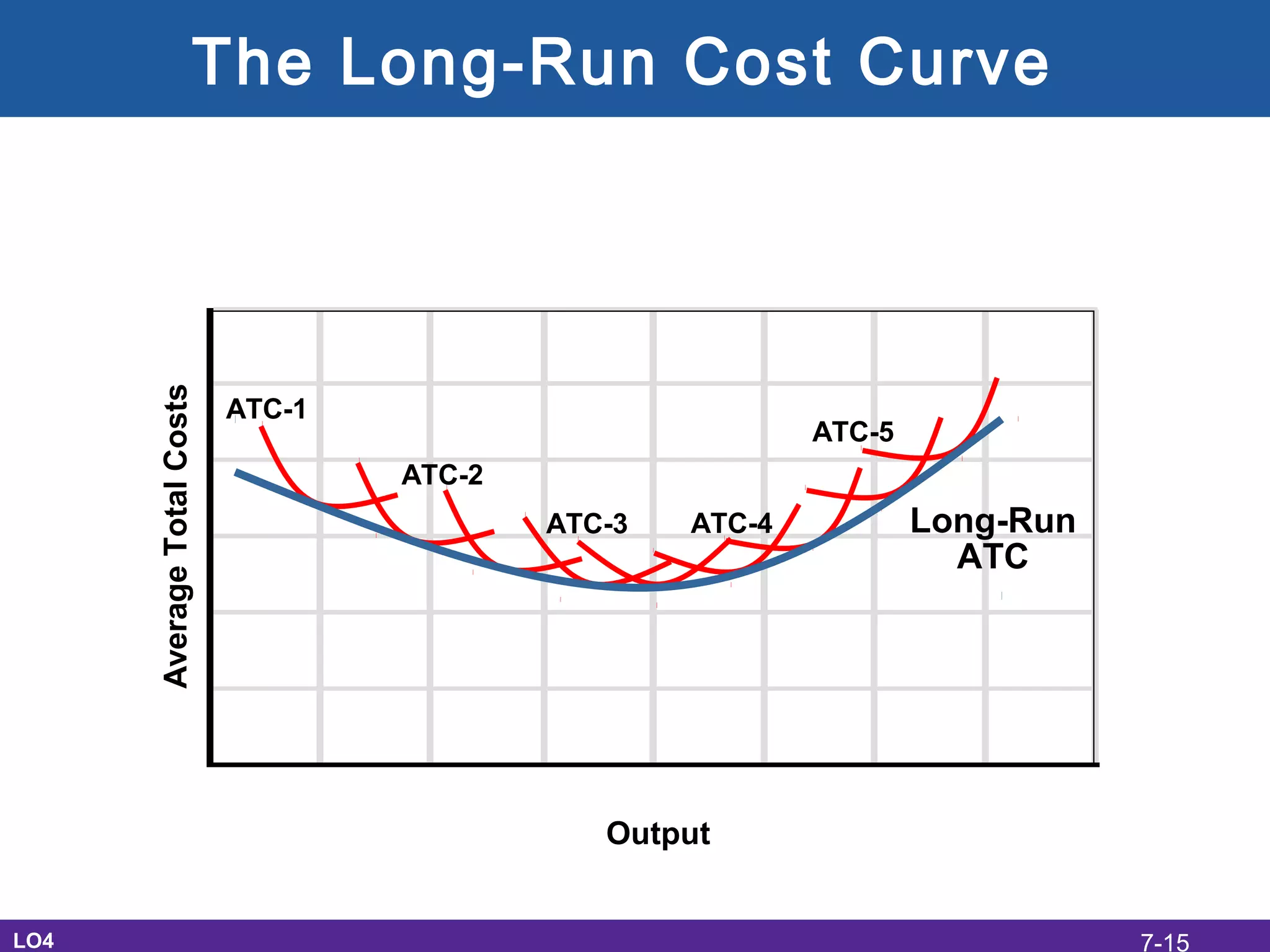
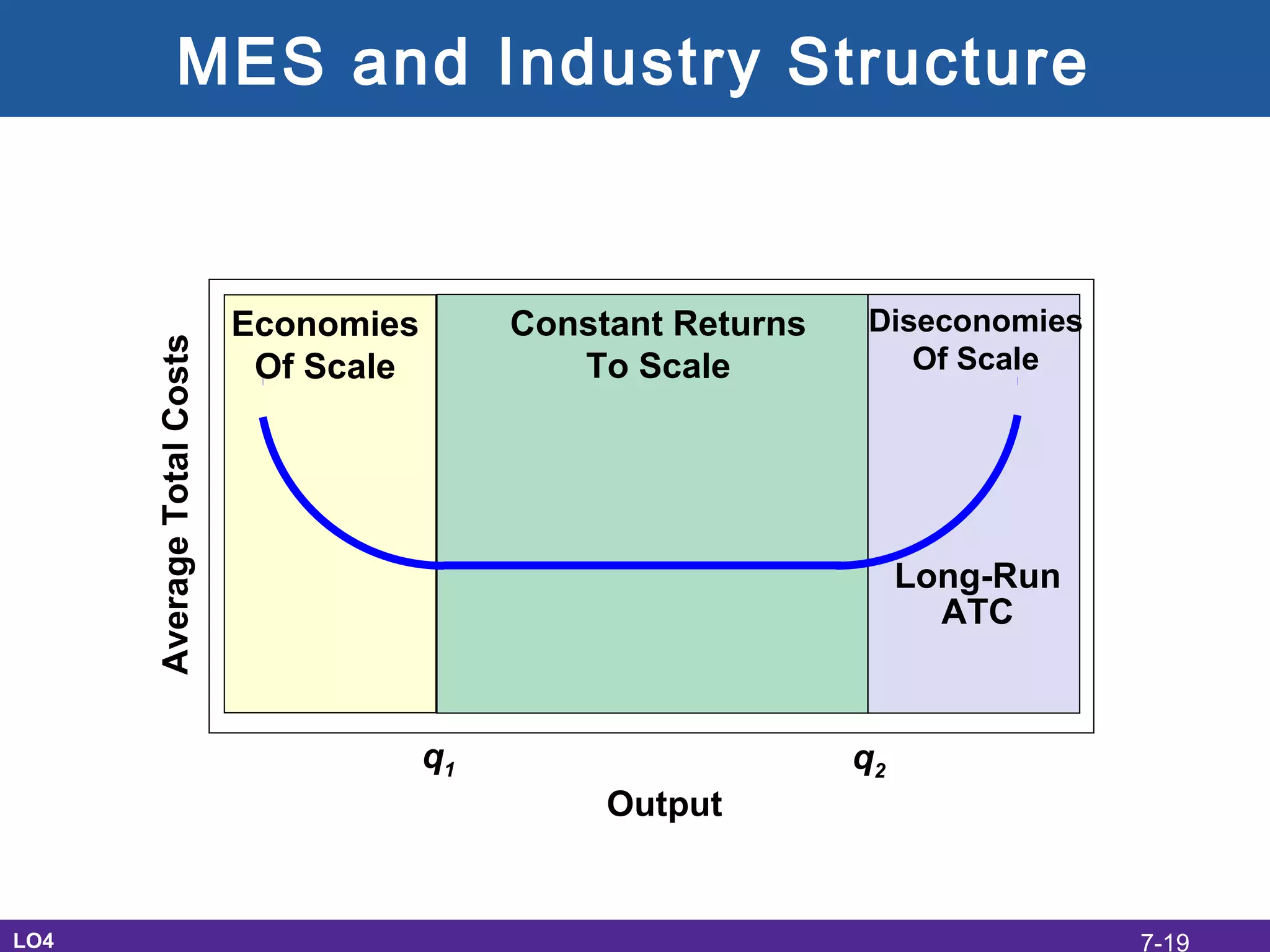
This document discusses the economic costs of production for businesses. It defines explicit costs as monetary payments and implicit costs as the value of the next best use of self-owned resources, which together make up total economic costs. Accounting profit only considers explicit costs, while economic profit subtracts both explicit and implicit costs from total revenue. The document also covers short-run and long-run production relationships, costs, and curves, explaining how costs change based on variable and fixed inputs over time. In the long run, all inputs are variable and economies and diseconomies of scale can impact average total costs.