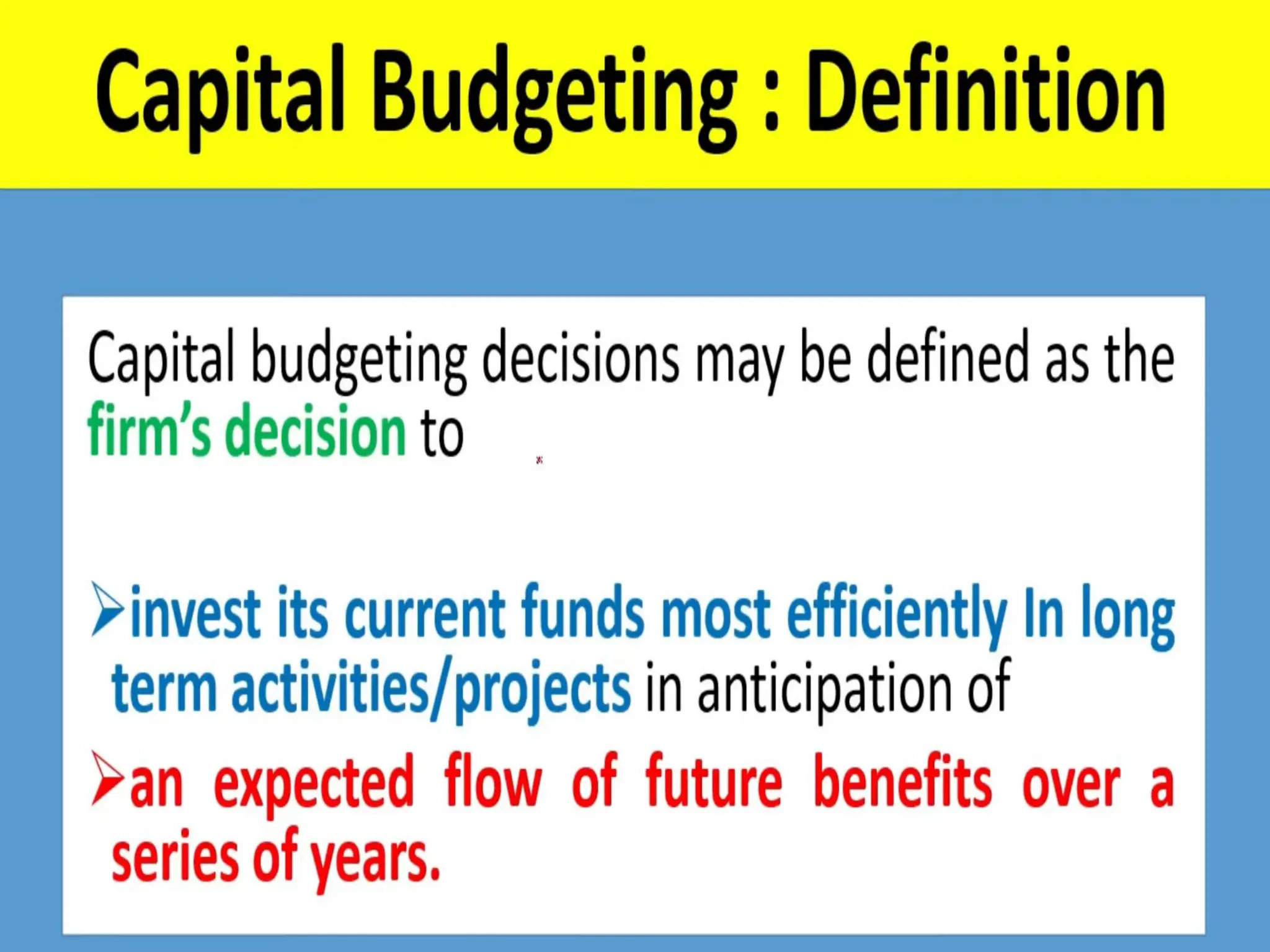
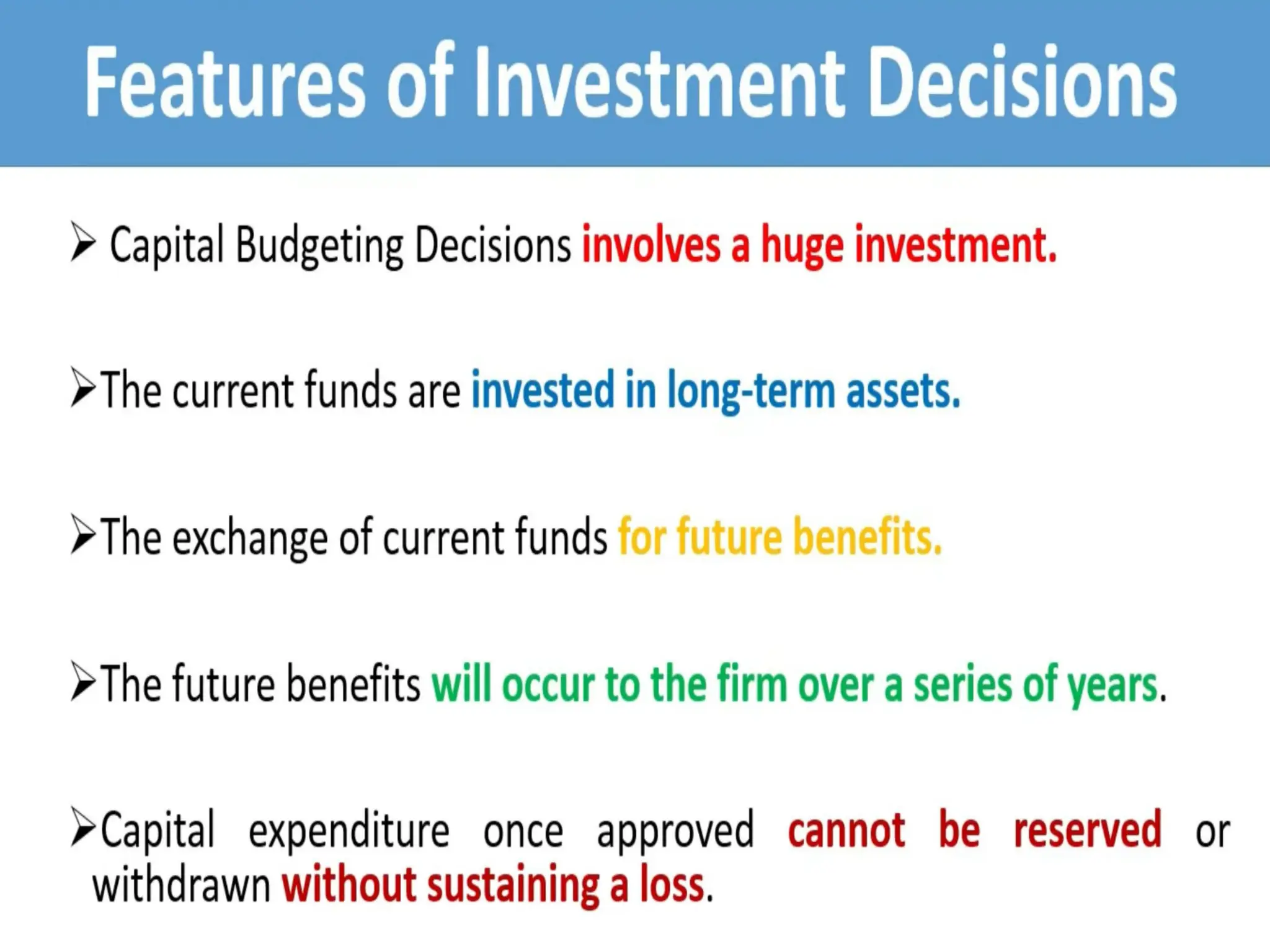
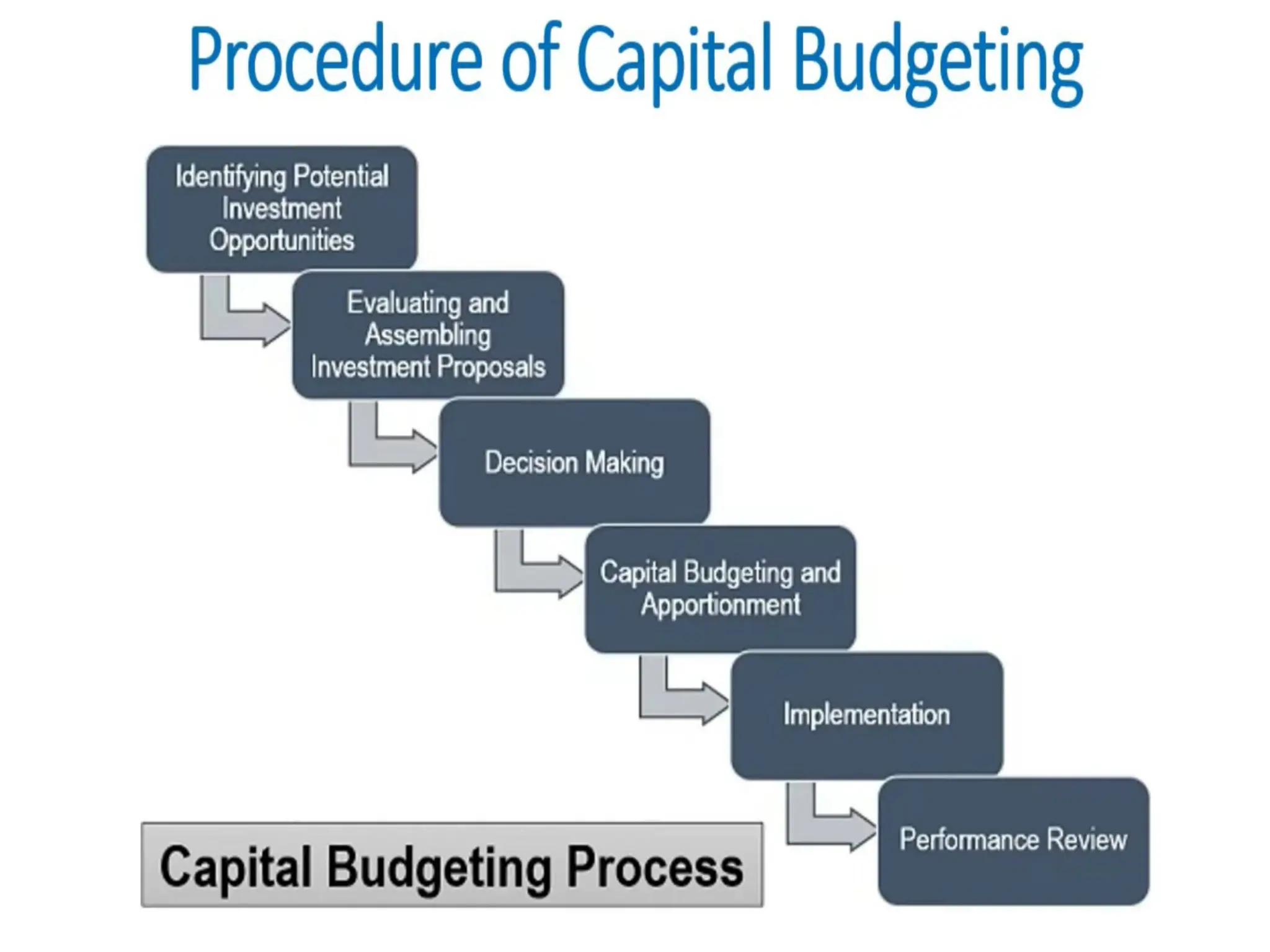
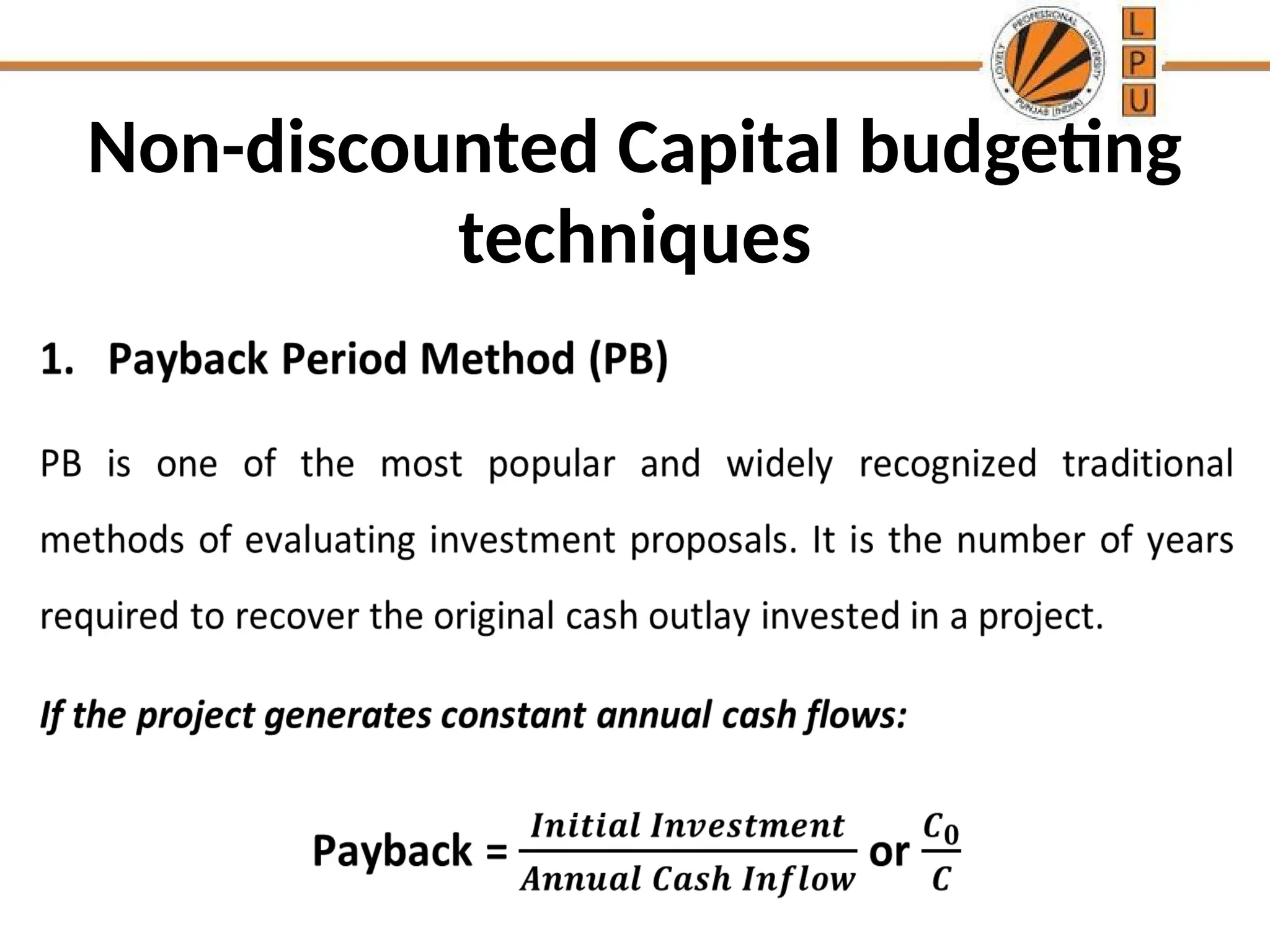
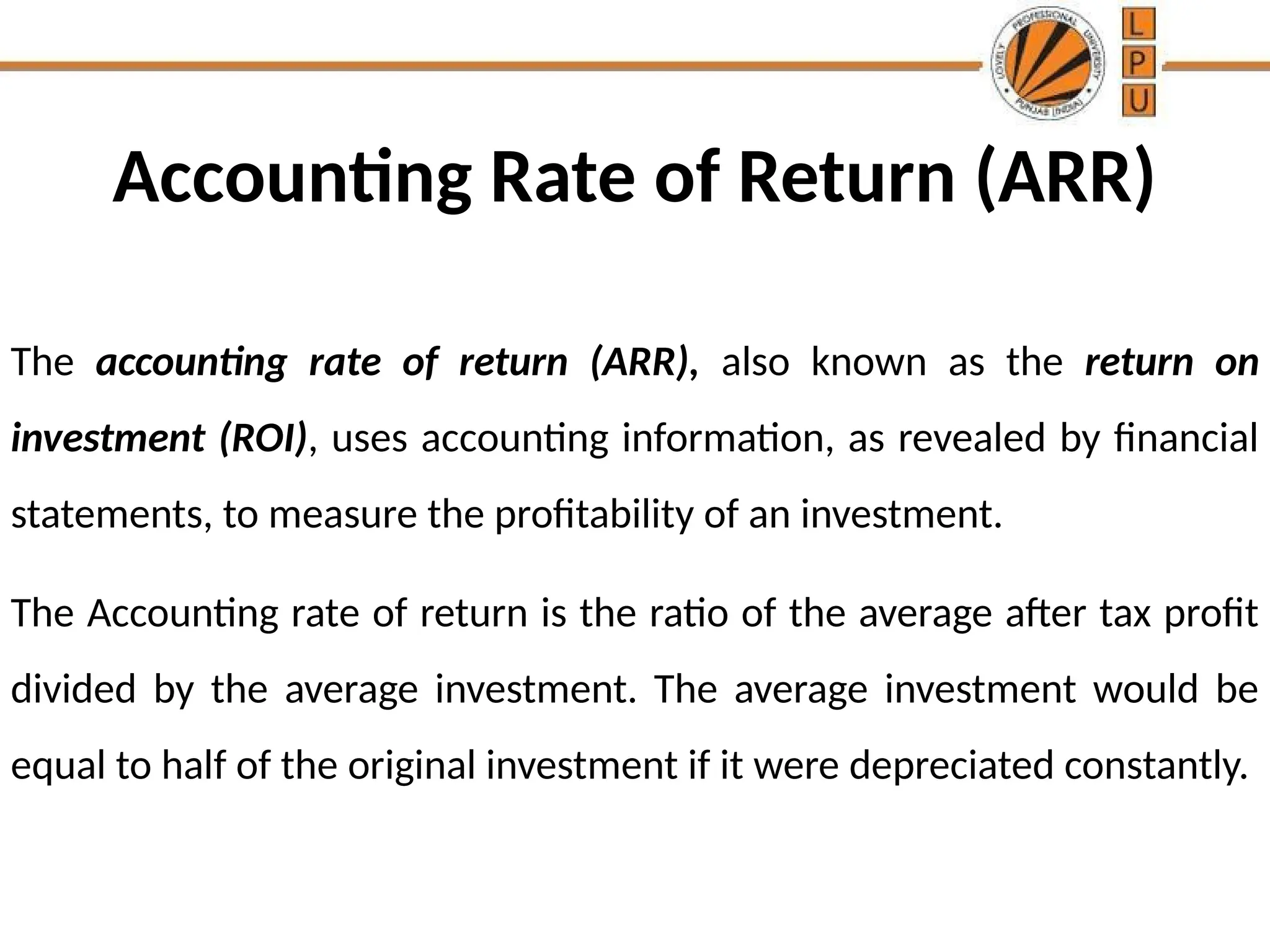
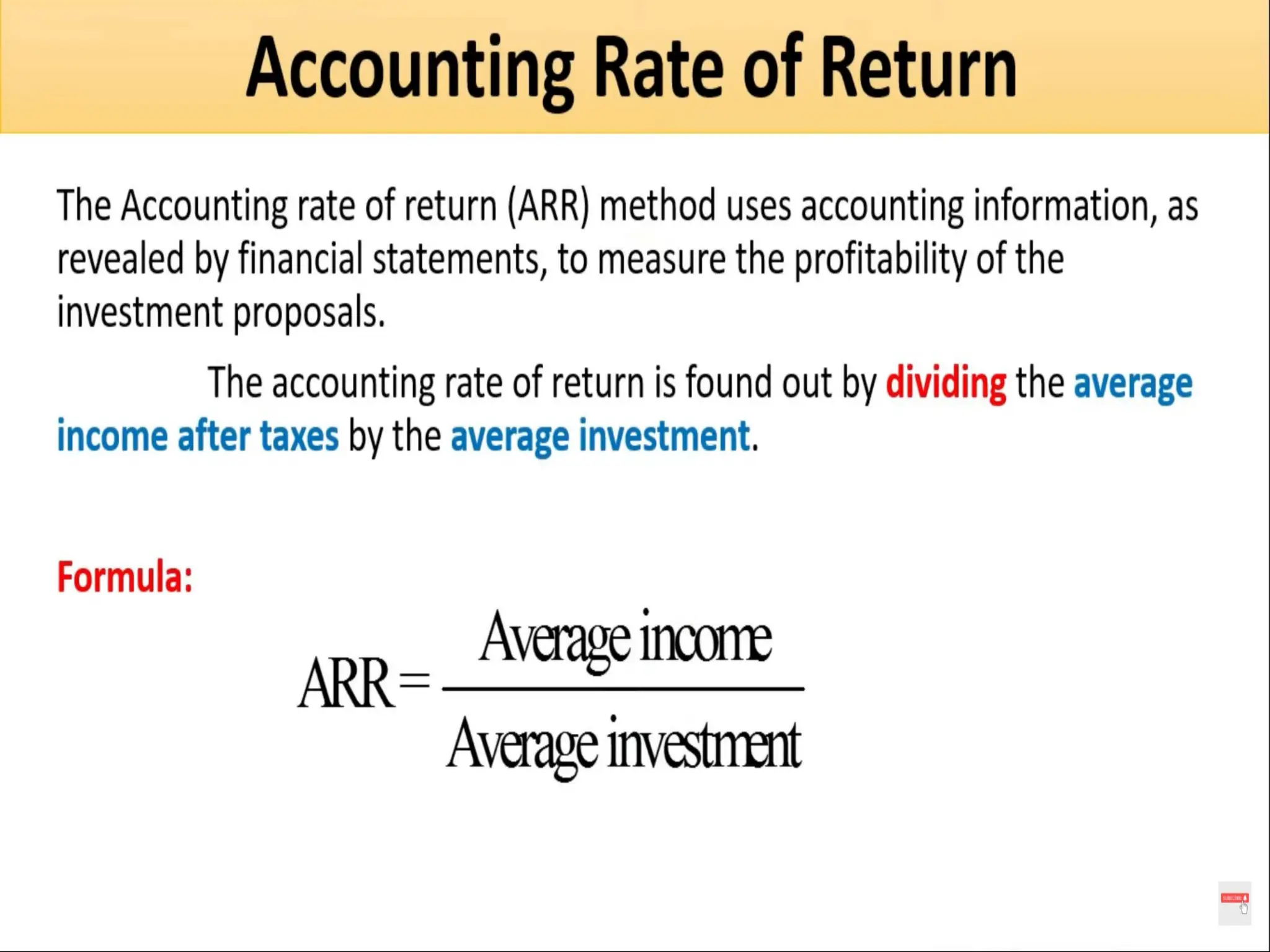
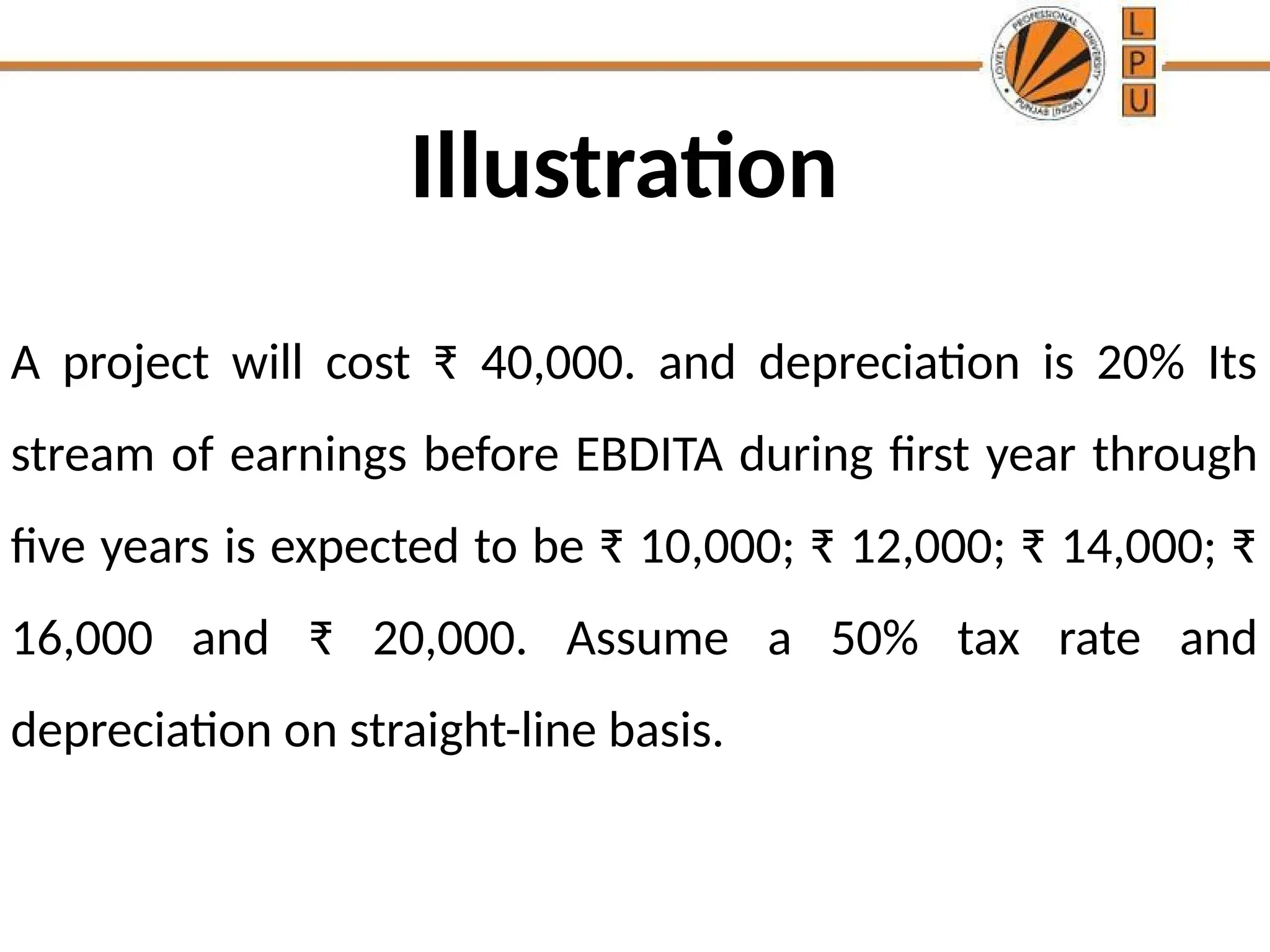
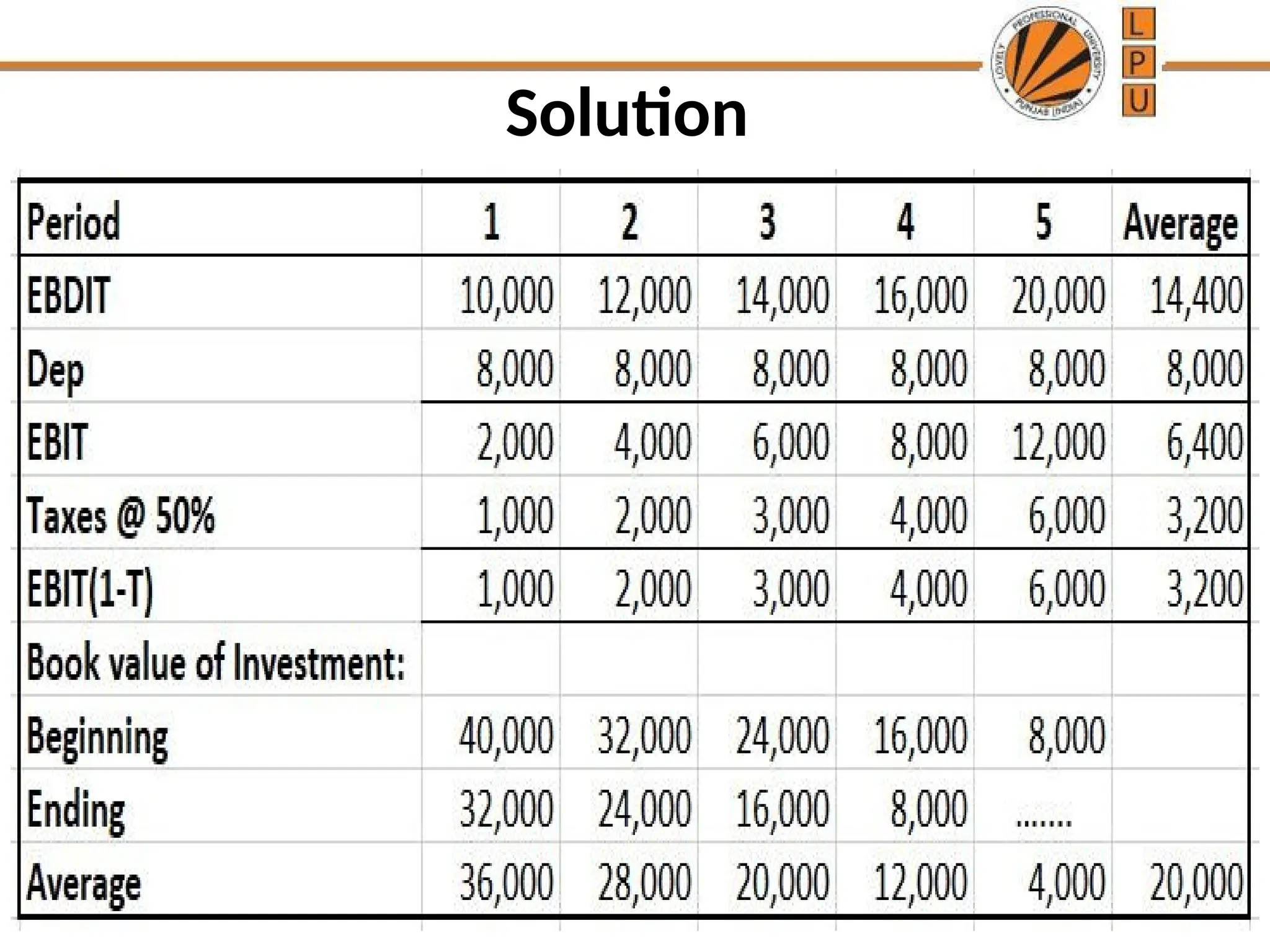
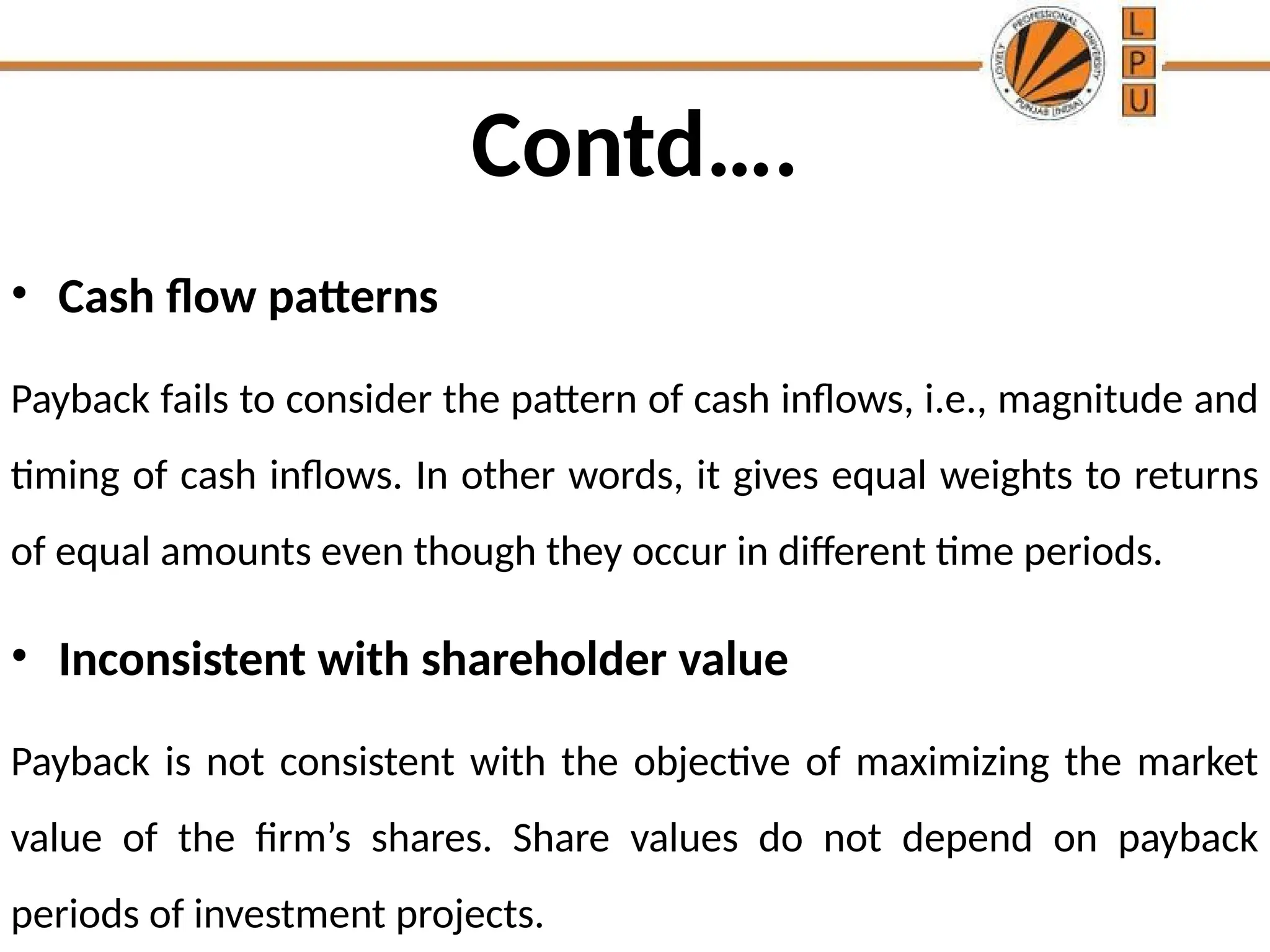
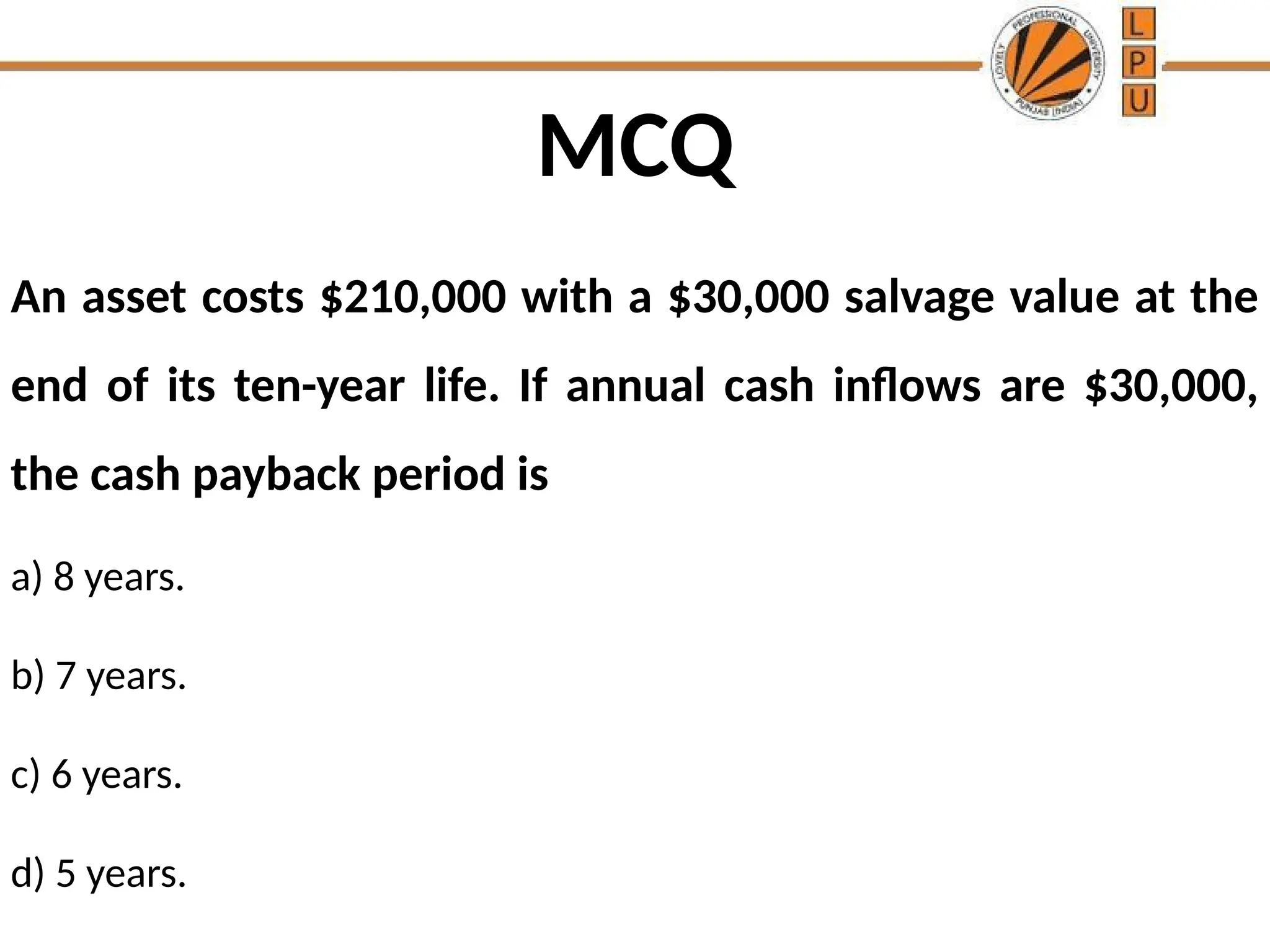
The document discusses the concept of capital budgeting, emphasizing its role in long-term investment decisions and the importance of cash flow over accounting profit. It outlines various capital budgeting techniques, including discounted and non-discounted cash flow criteria, while elaborating on the payback period method, its advantages, and criticisms. The document also highlights the significance of careful evaluation in capital budgeting due to the substantial funds involved and the potential long-term impact on a firm's growth and risk.