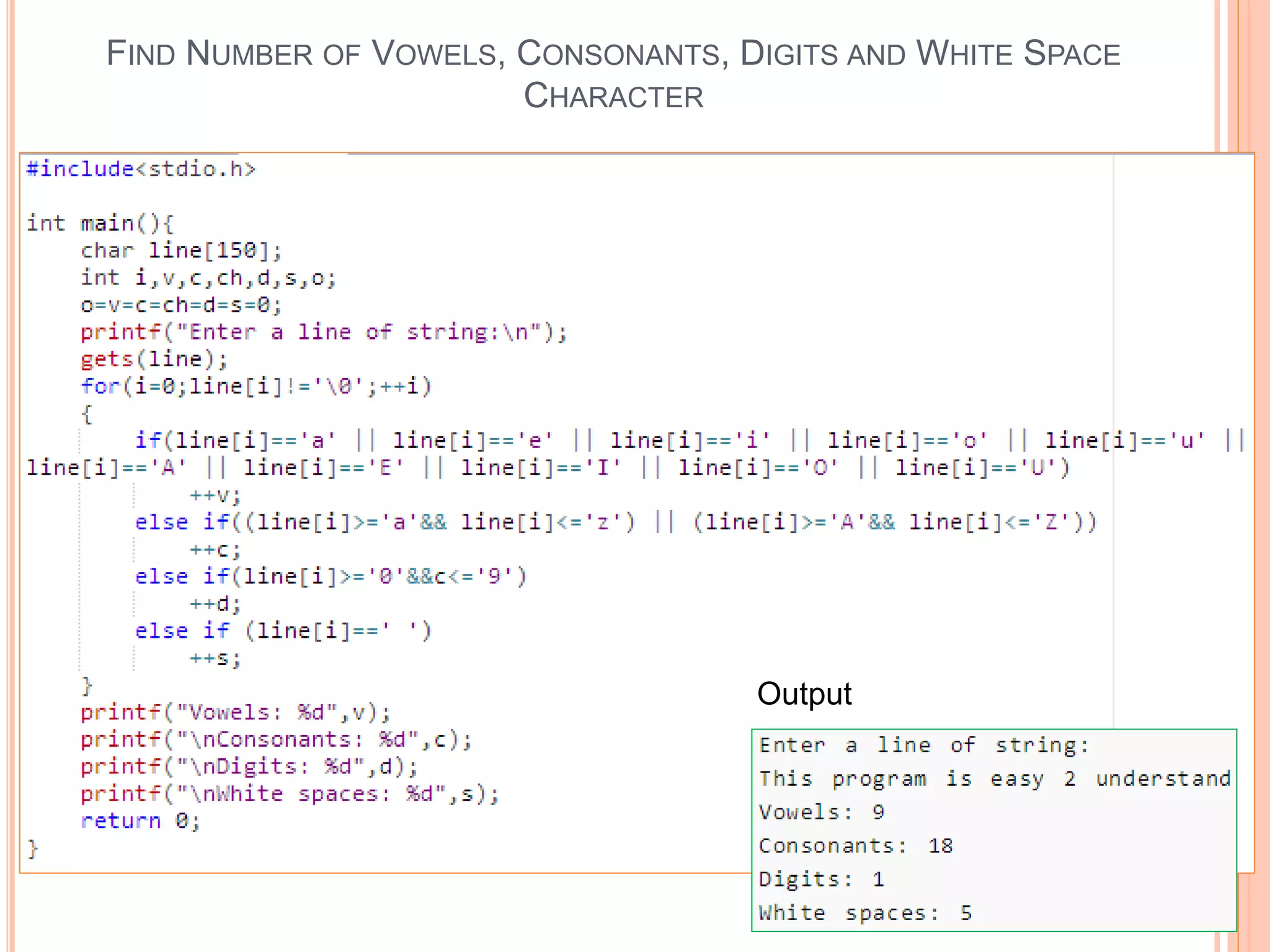
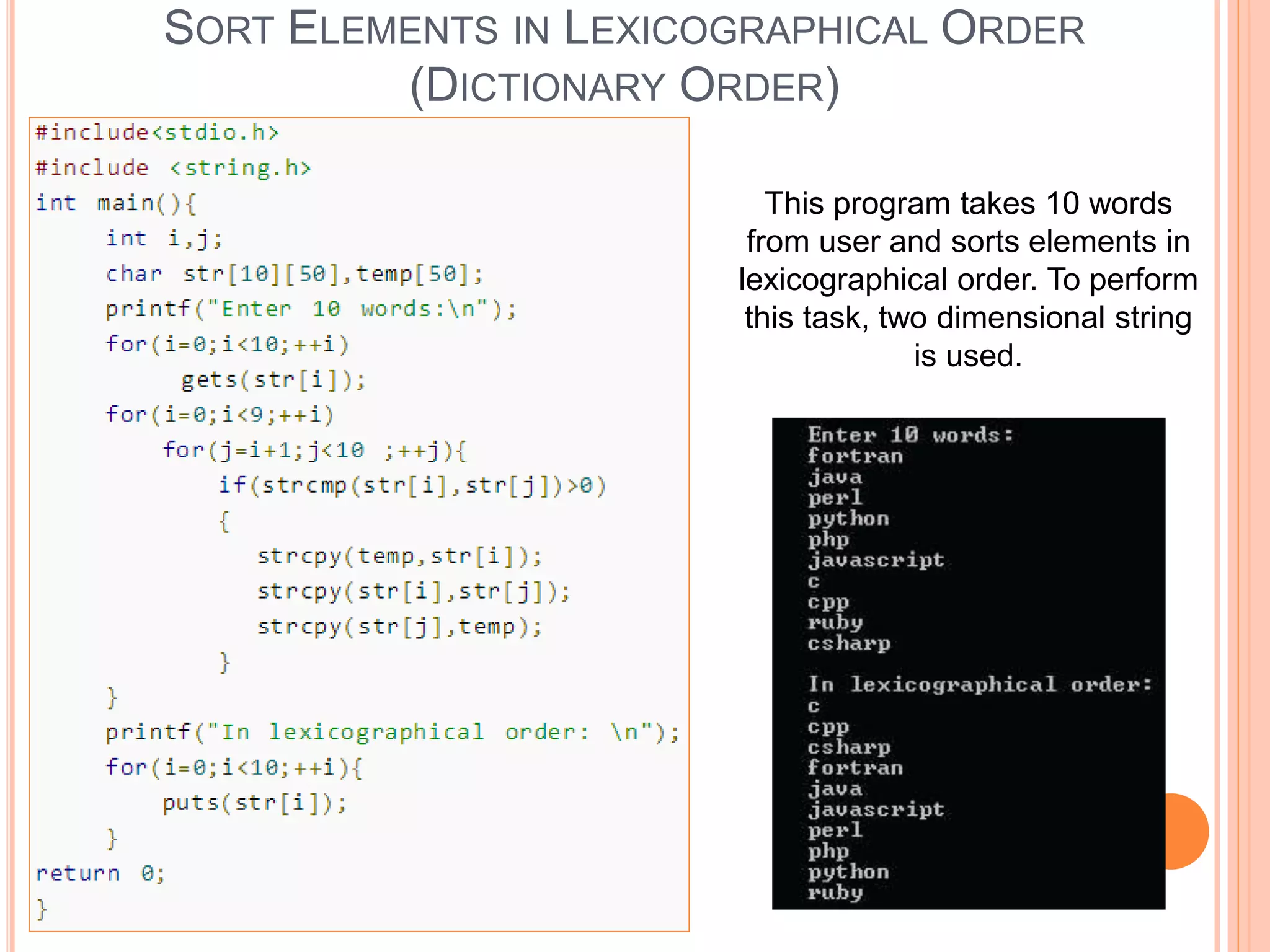
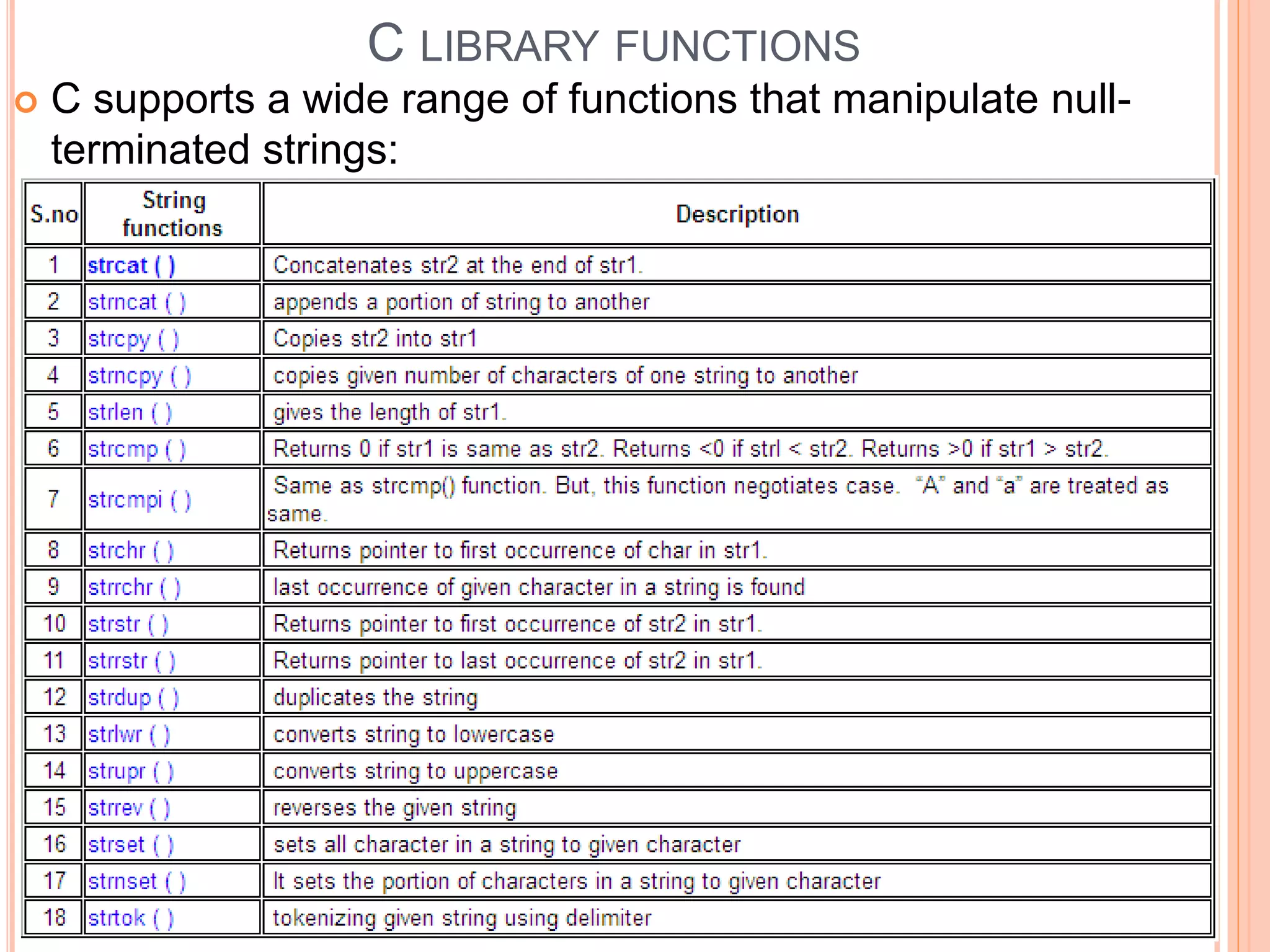
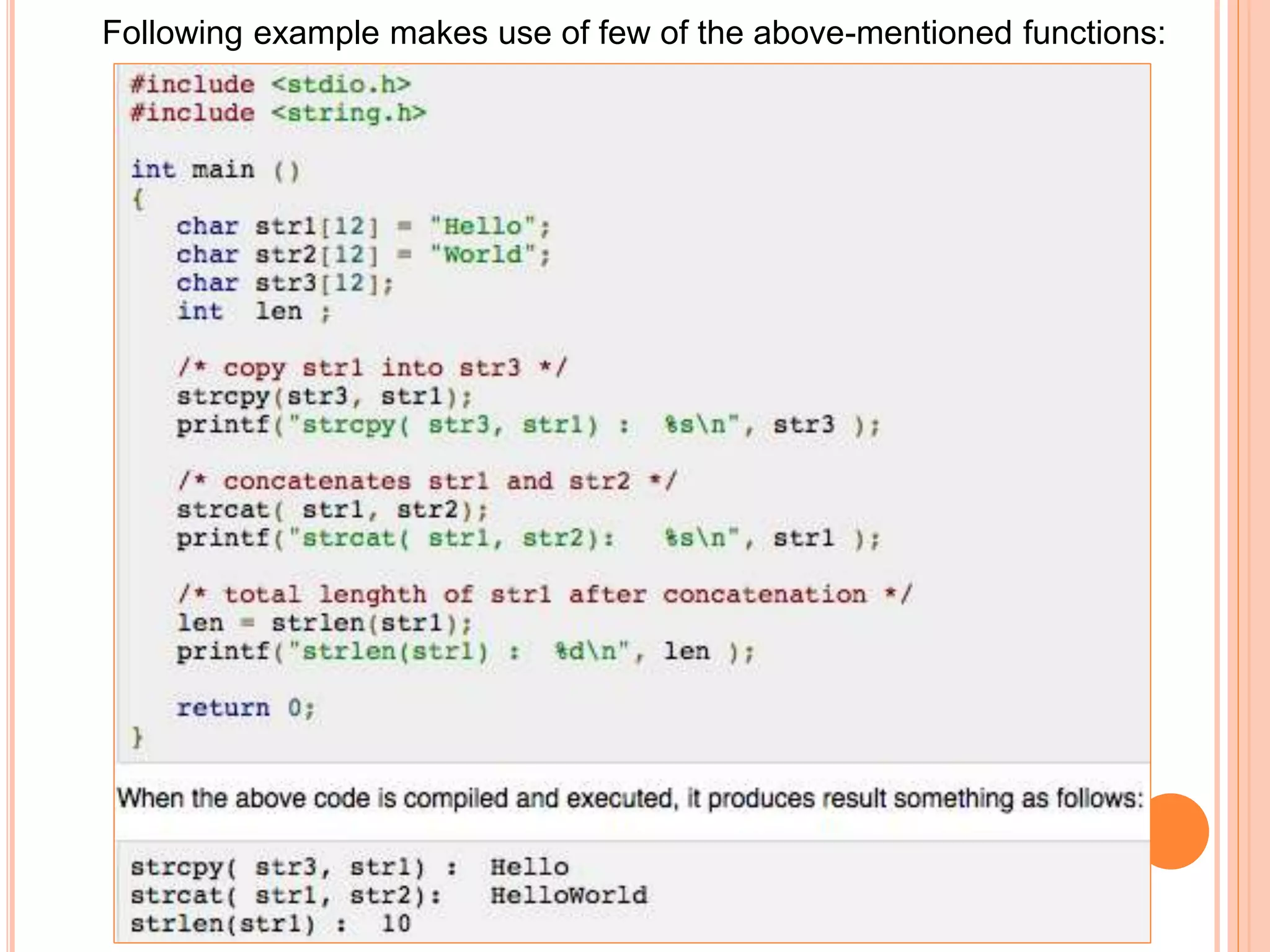
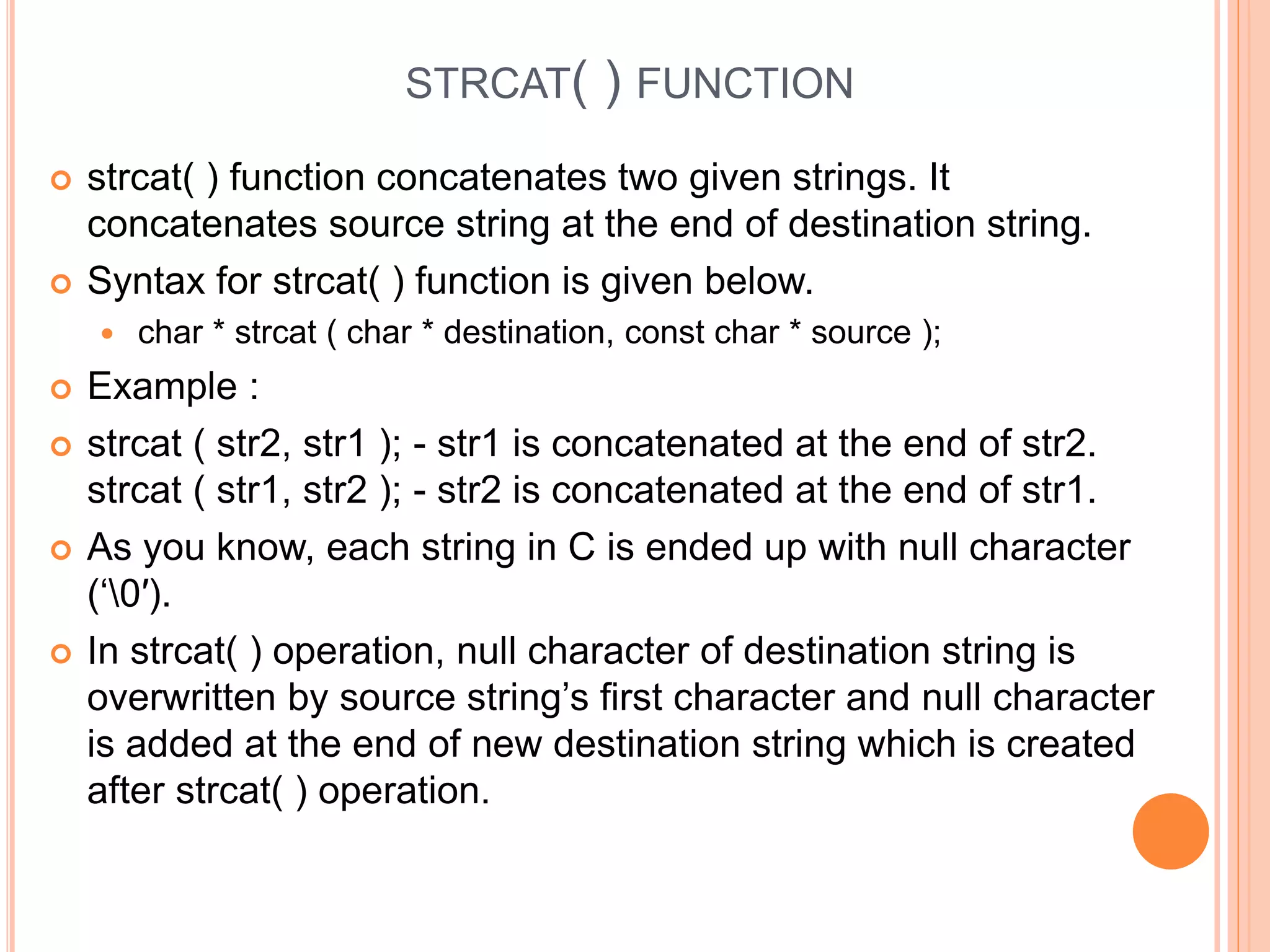
The document discusses the implementation and manipulation of strings in the C programming language, highlighting that strings are null-terminated character arrays. It covers string declaration methods, common string operations such as finding character frequency, concatenating, and copying strings, as well as the usage of various string functions from the C library like strcat(). Additionally, it includes practical examples and explains how to manually perform string operations without using standard library functions.