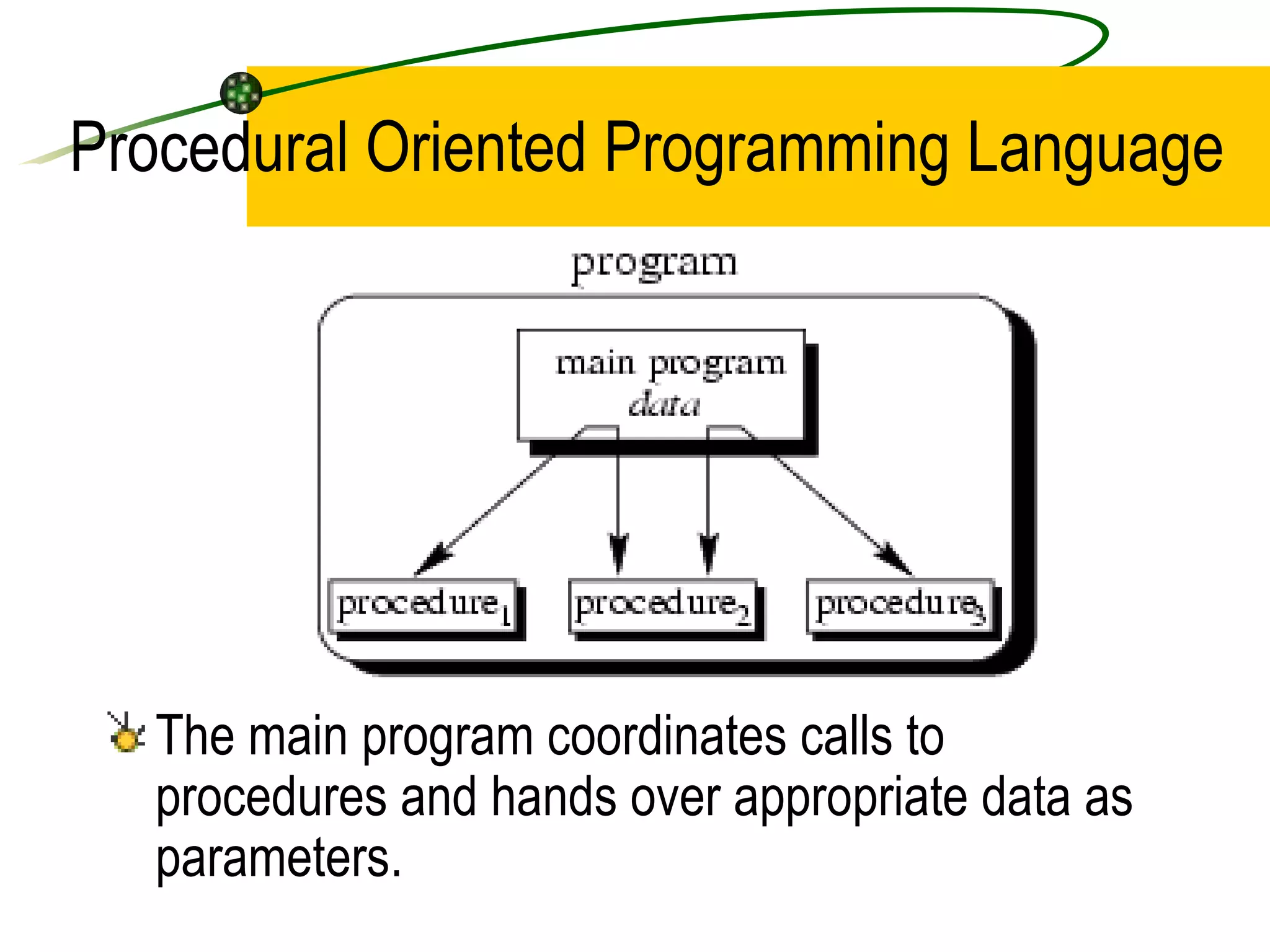
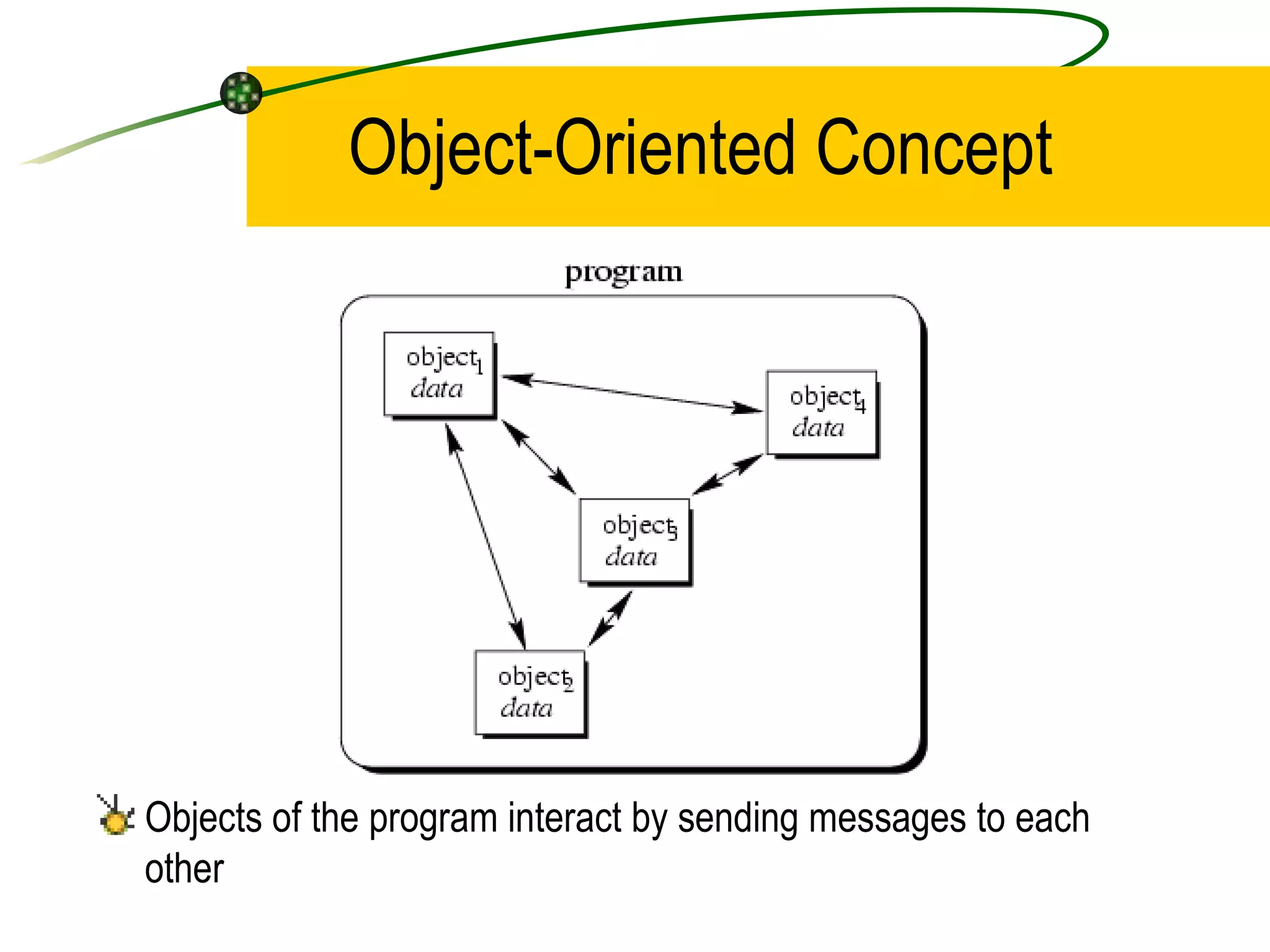
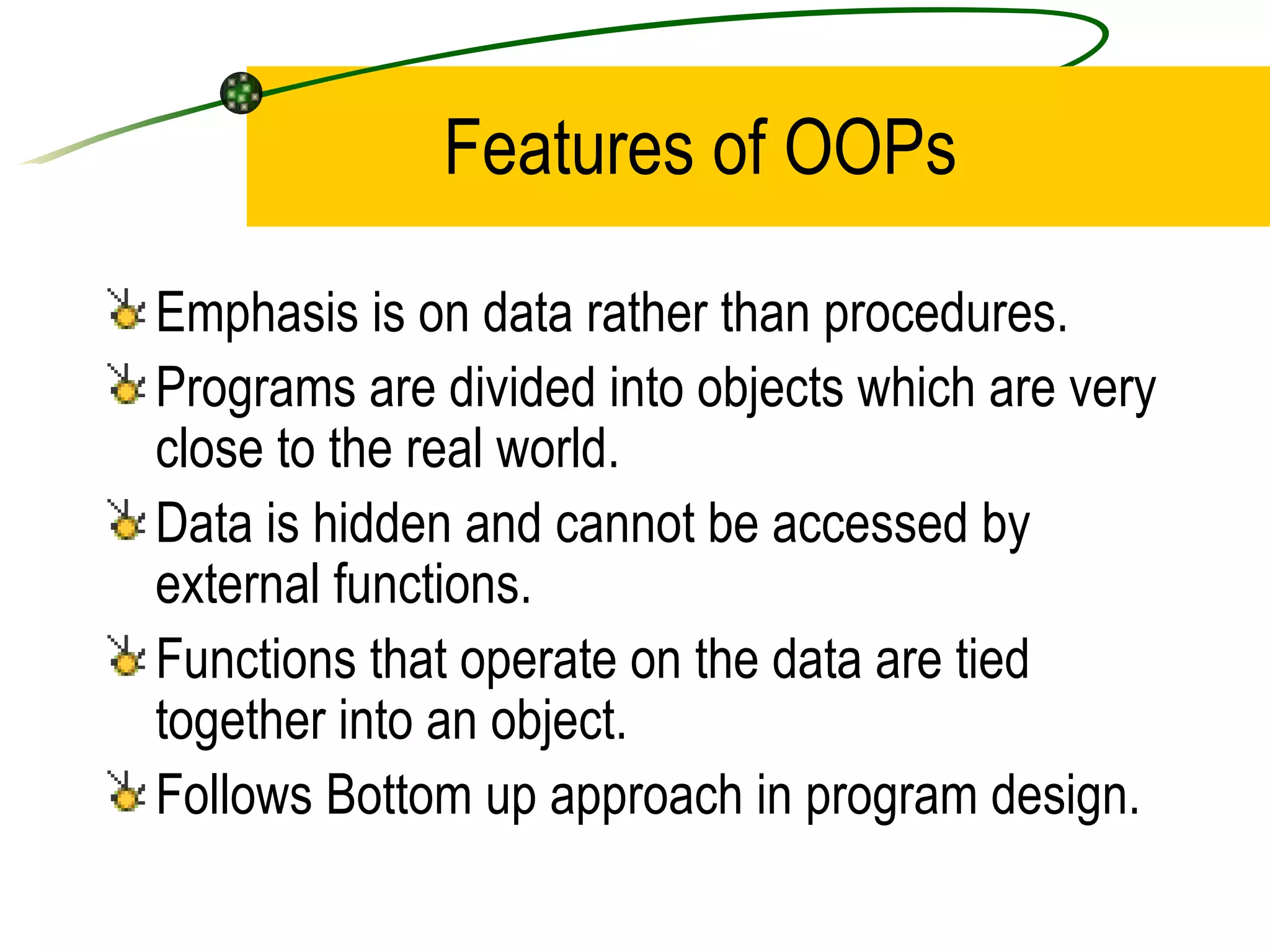
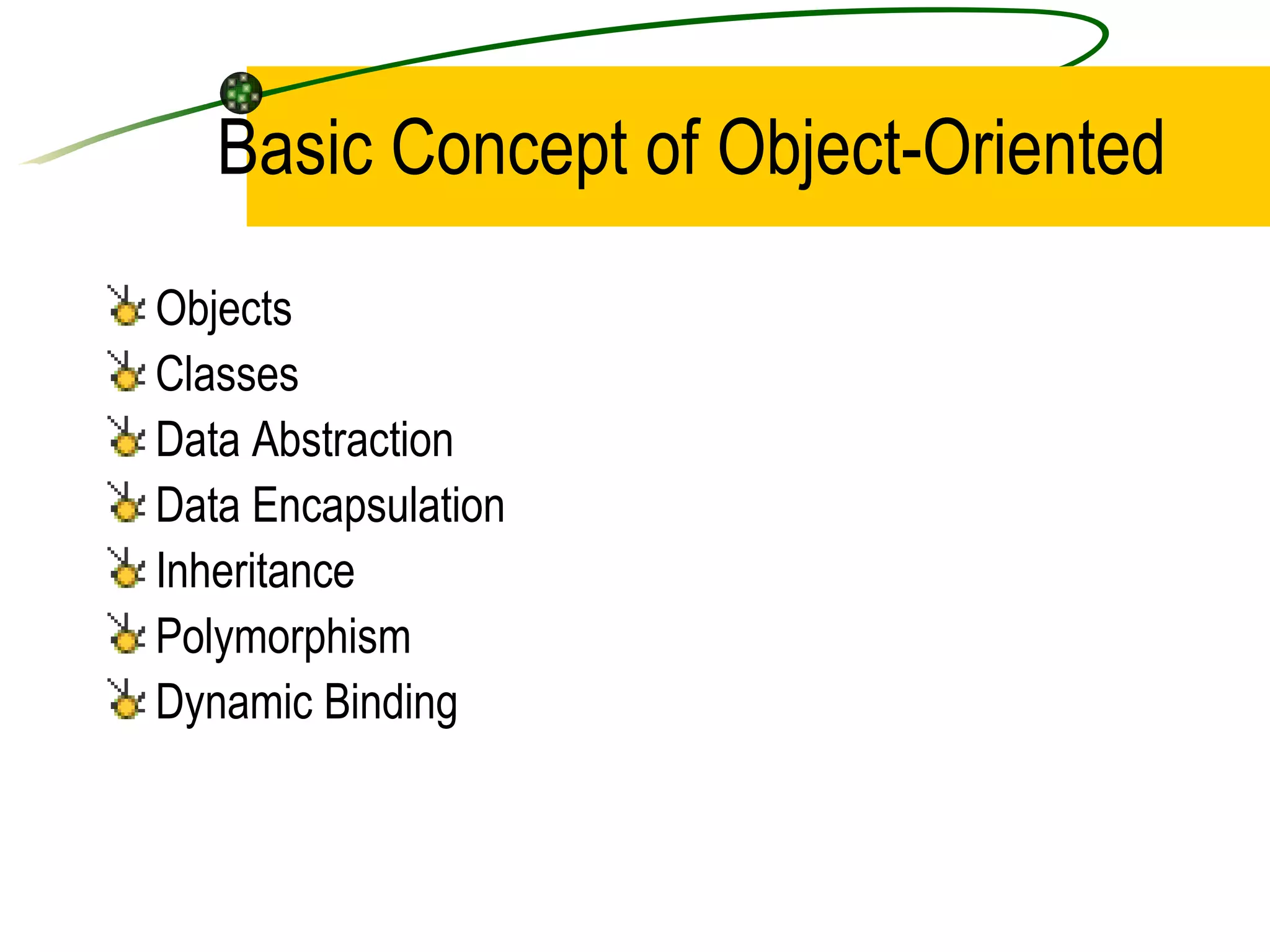
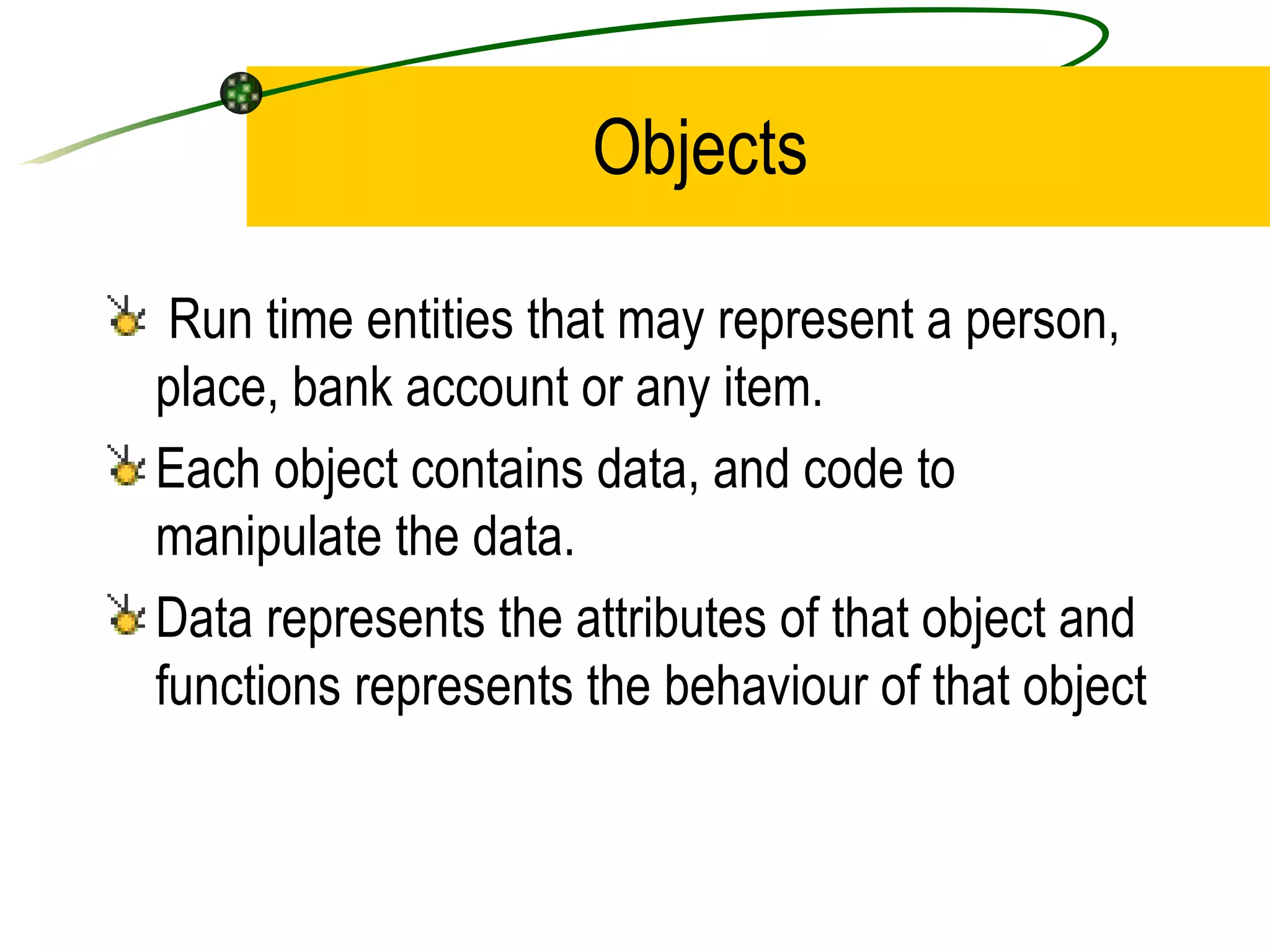
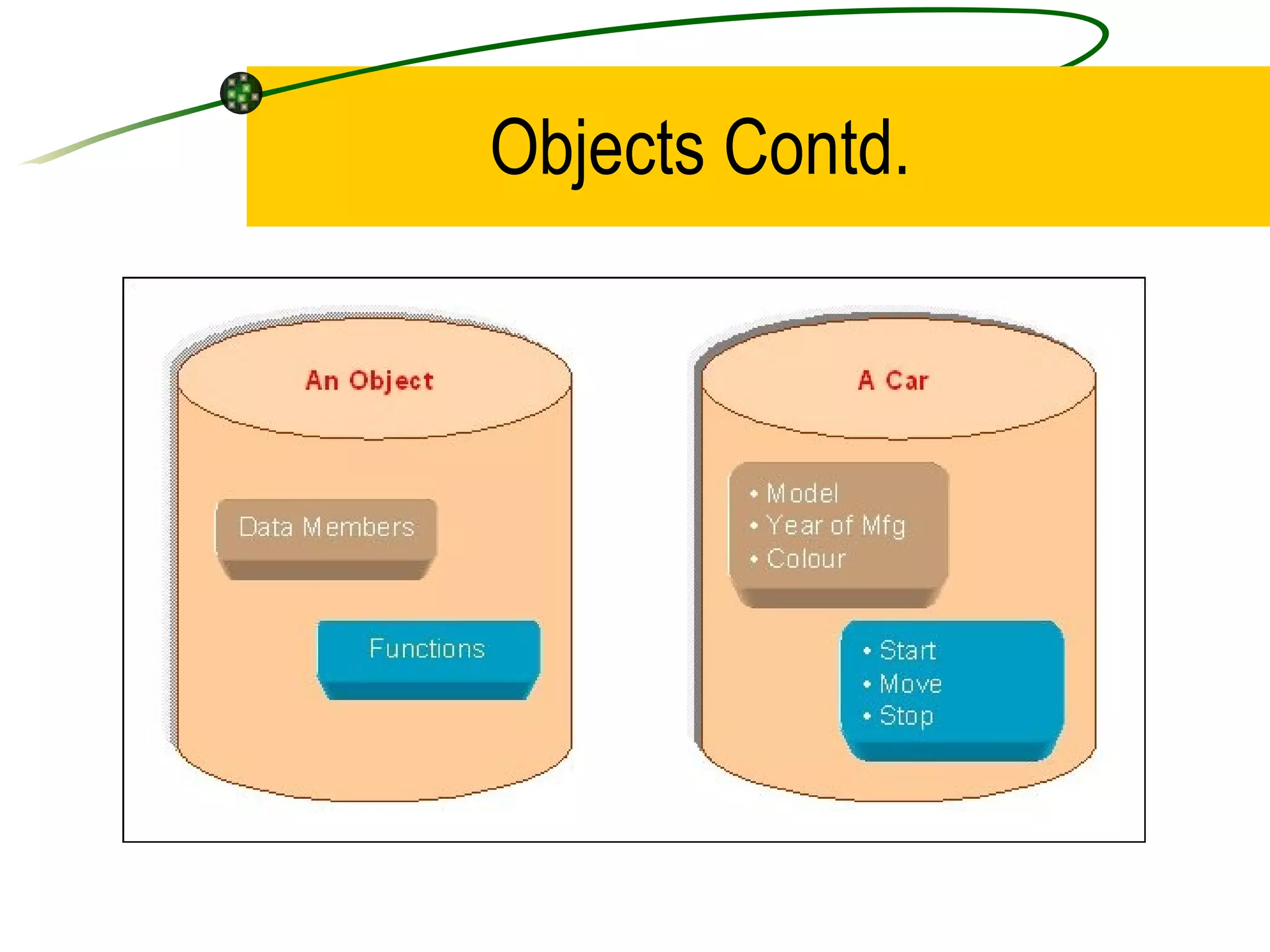
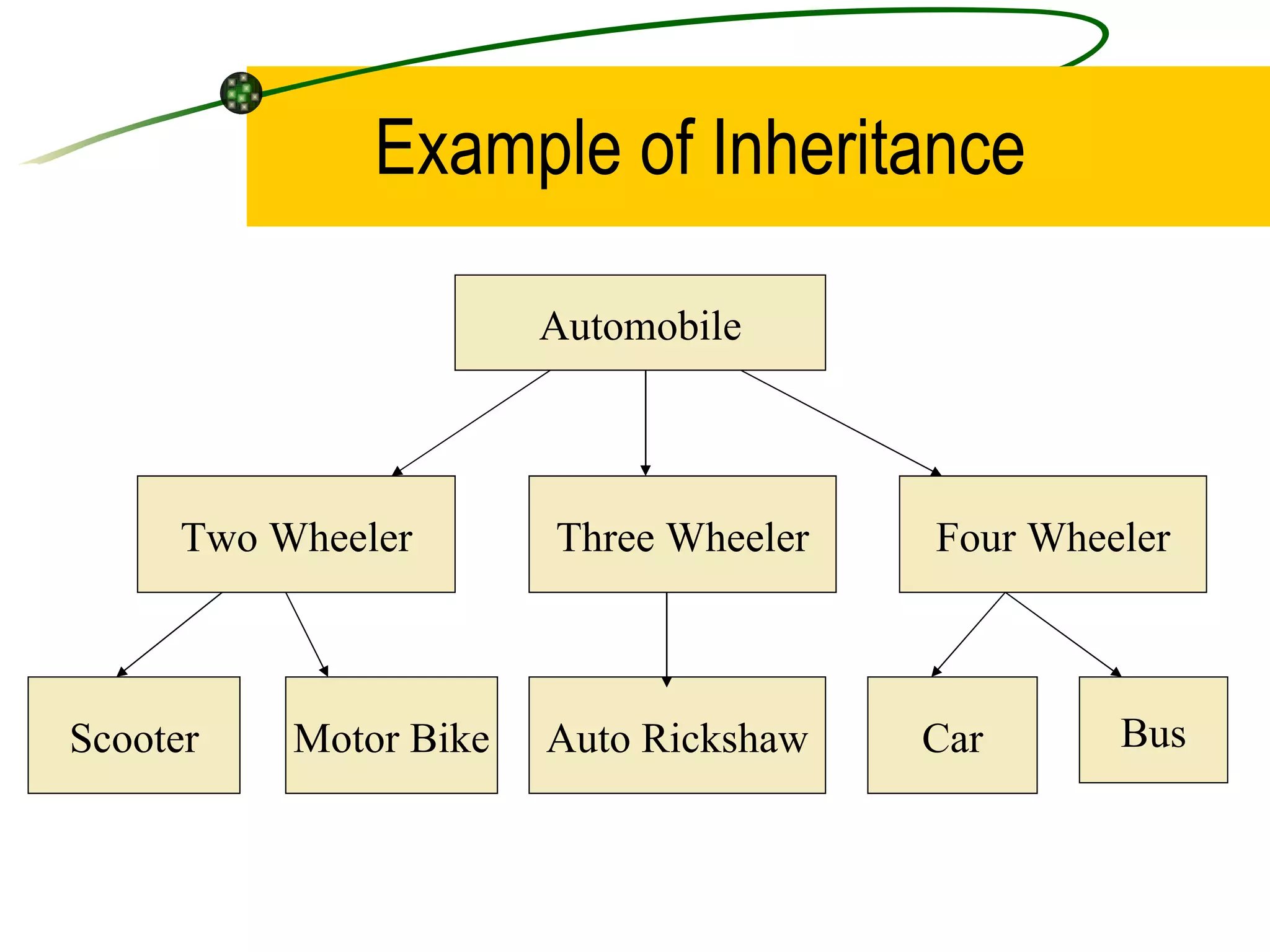
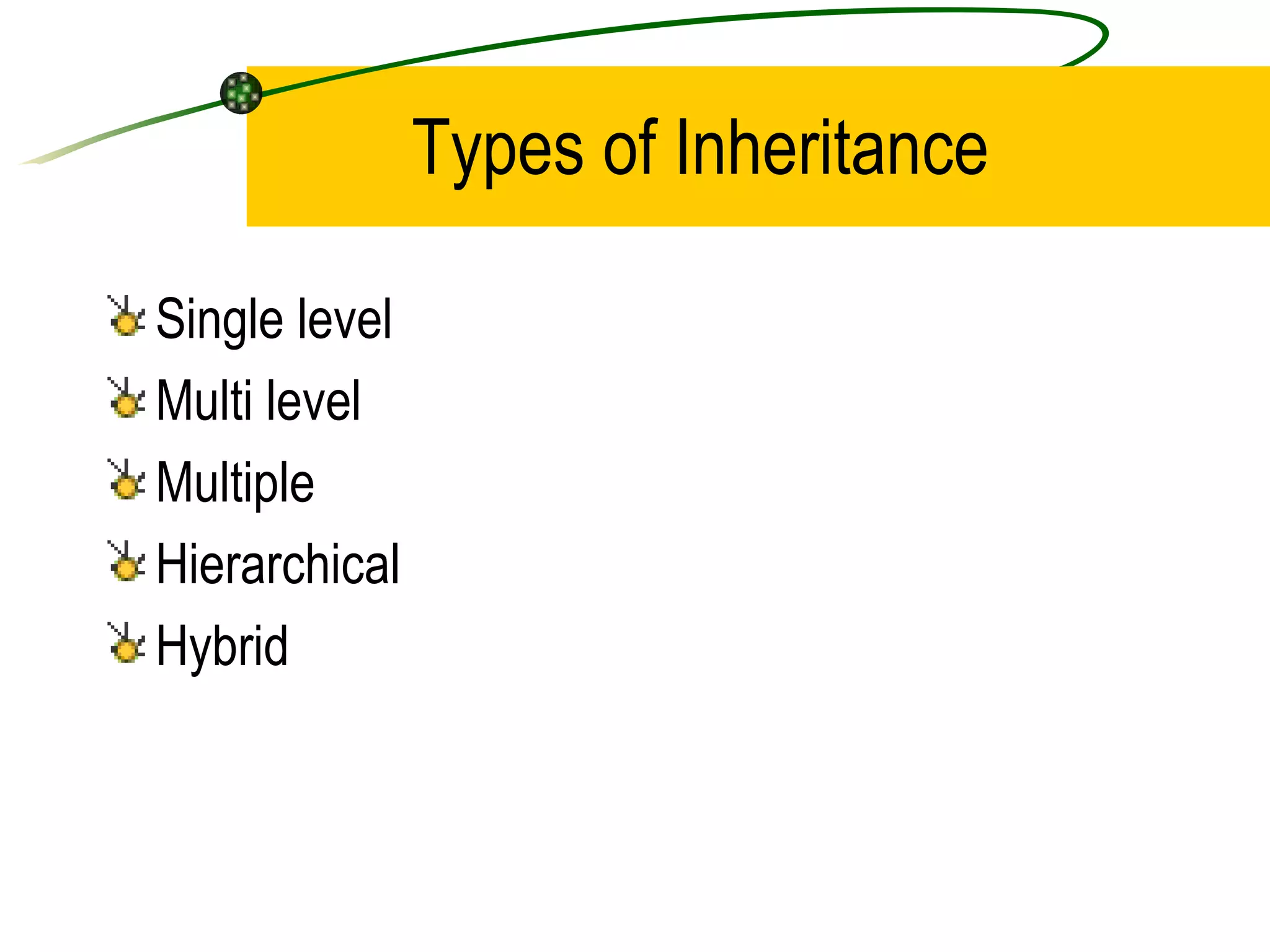
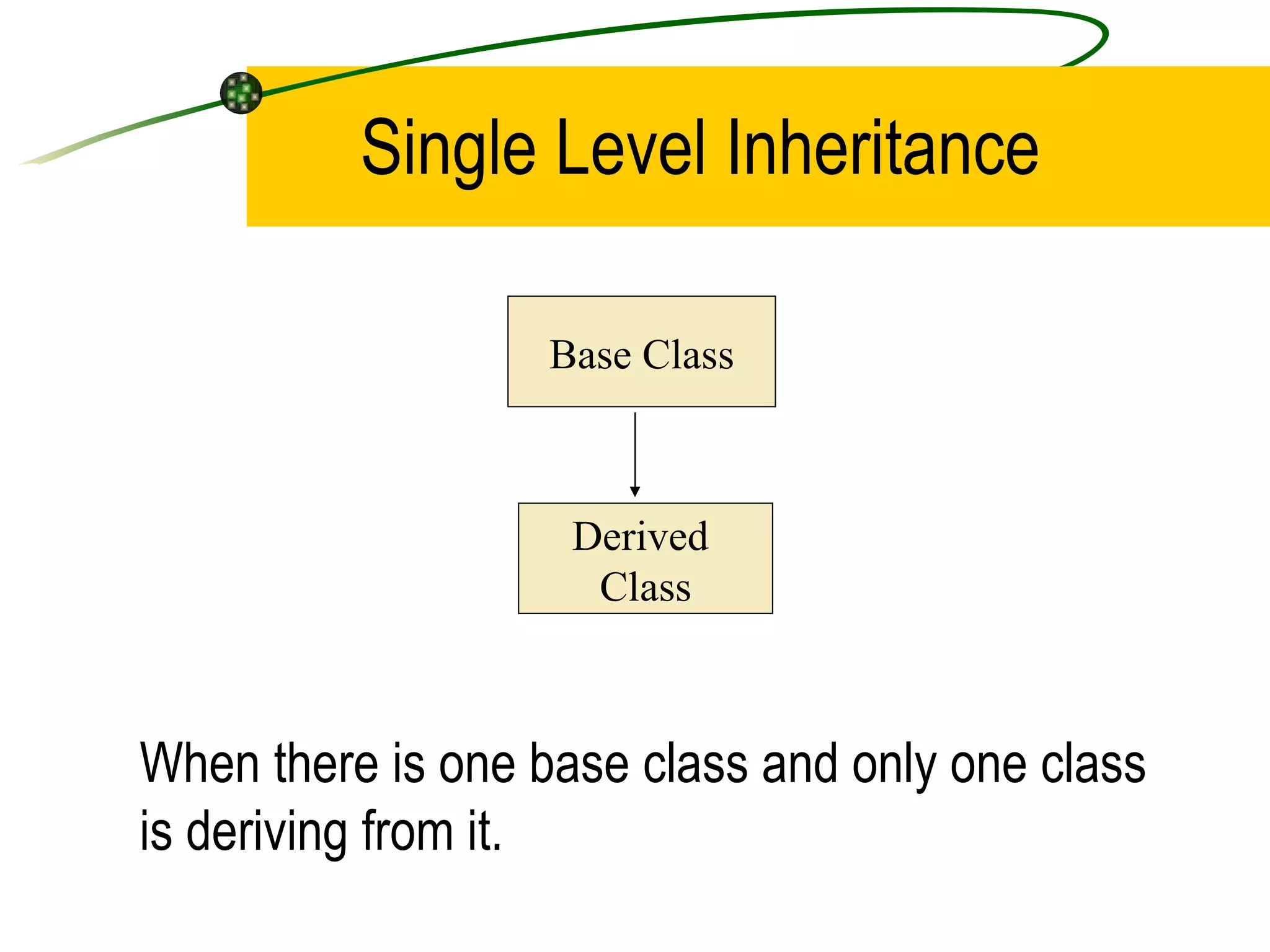
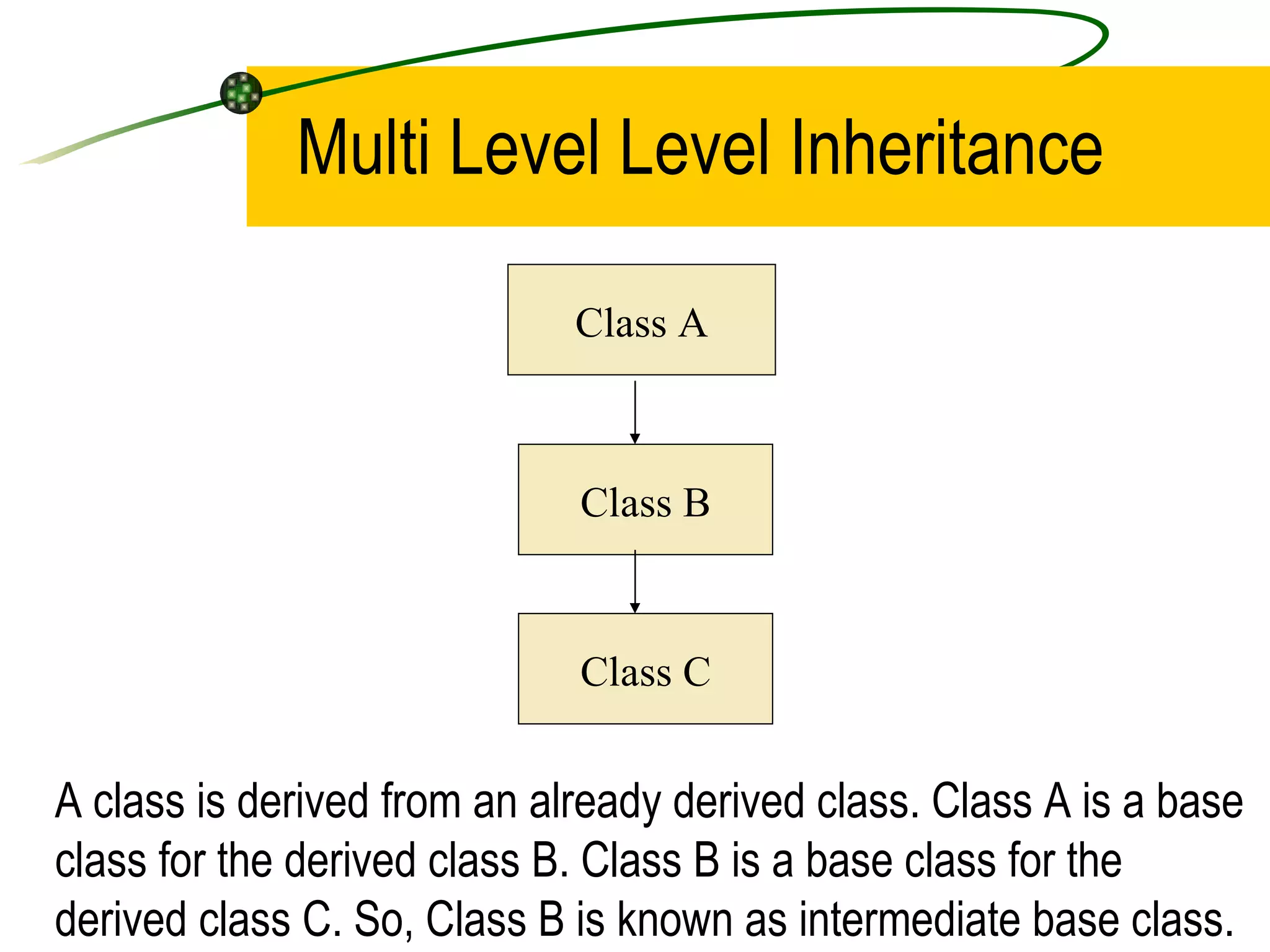
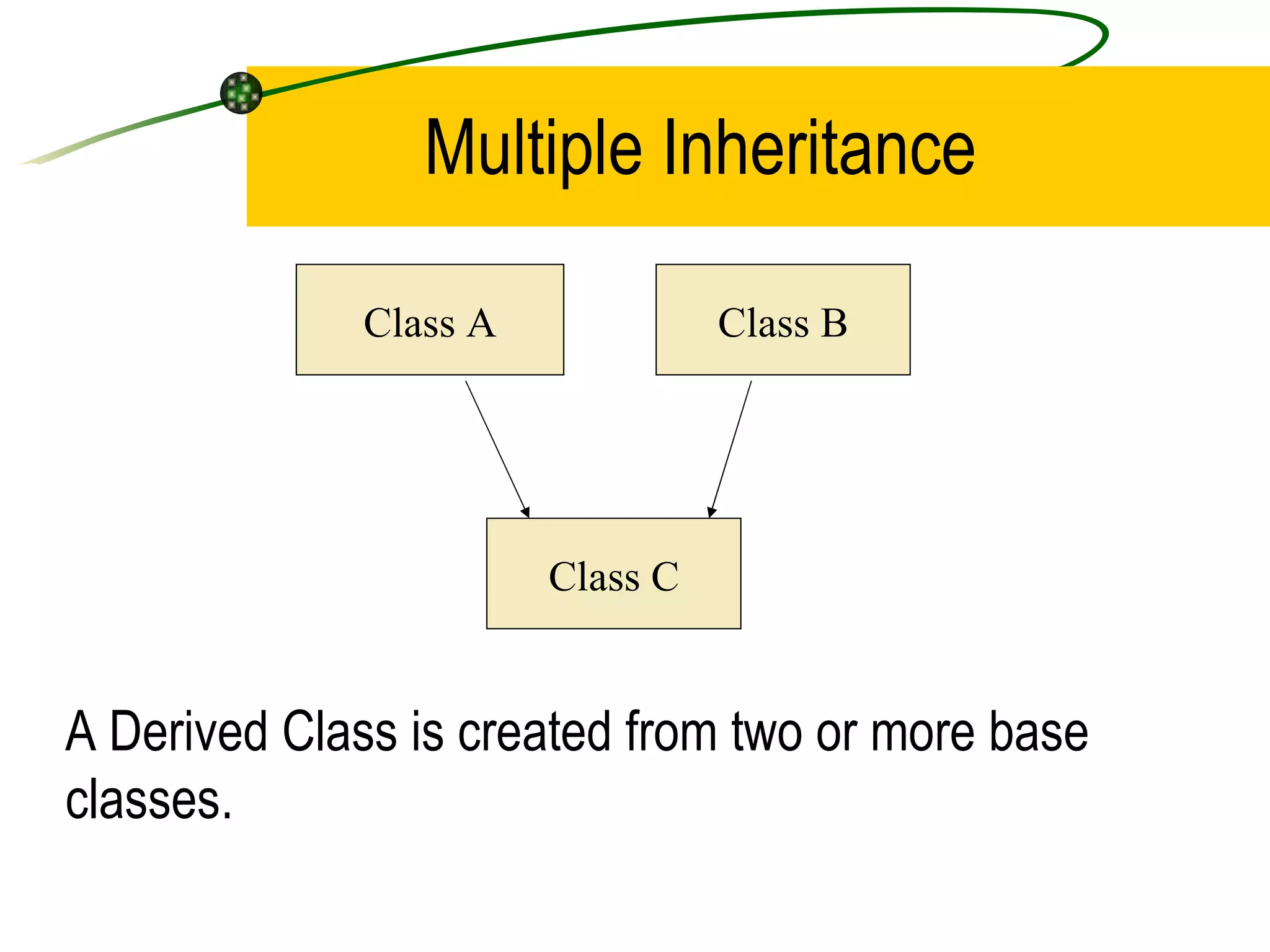
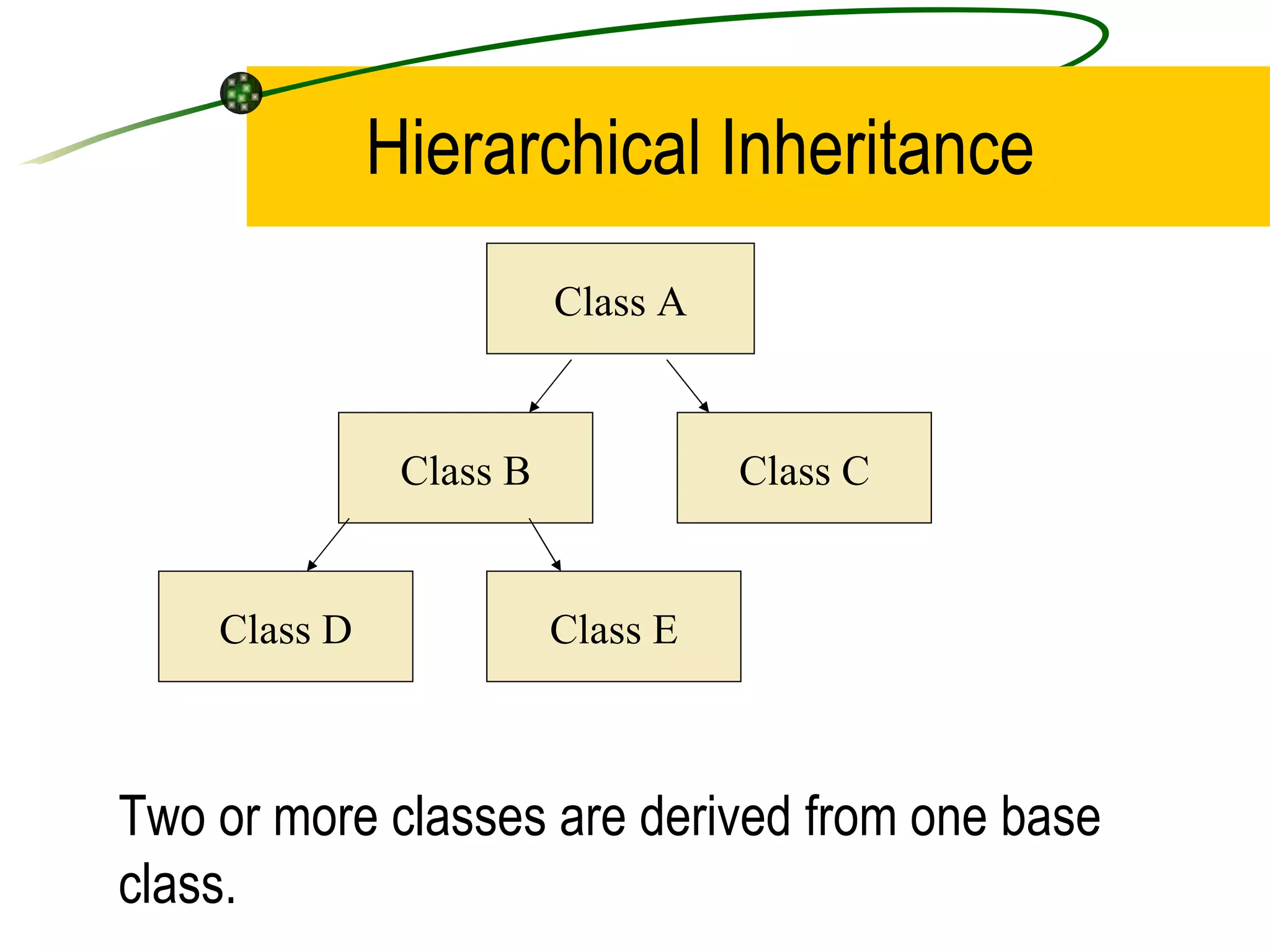
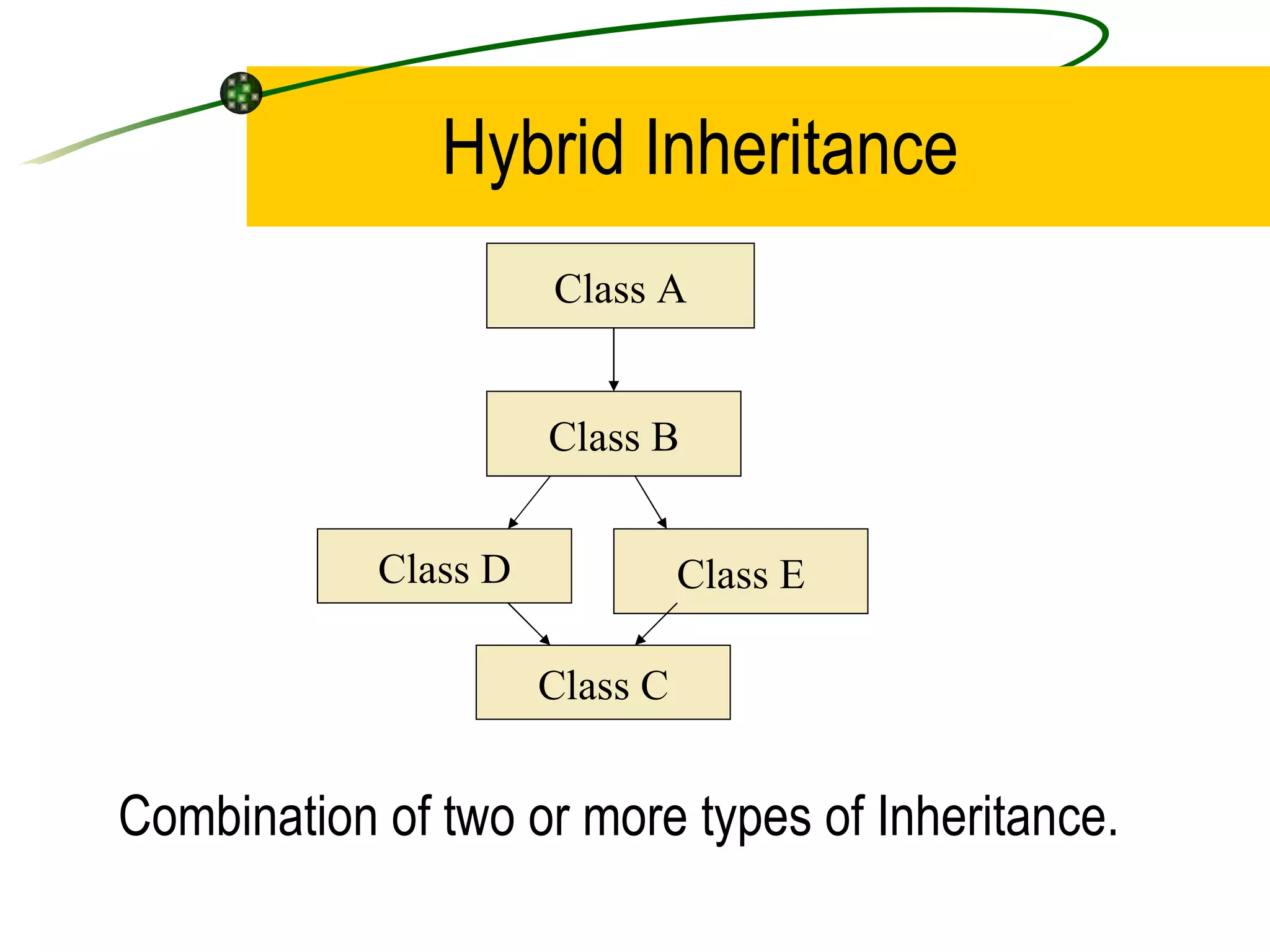
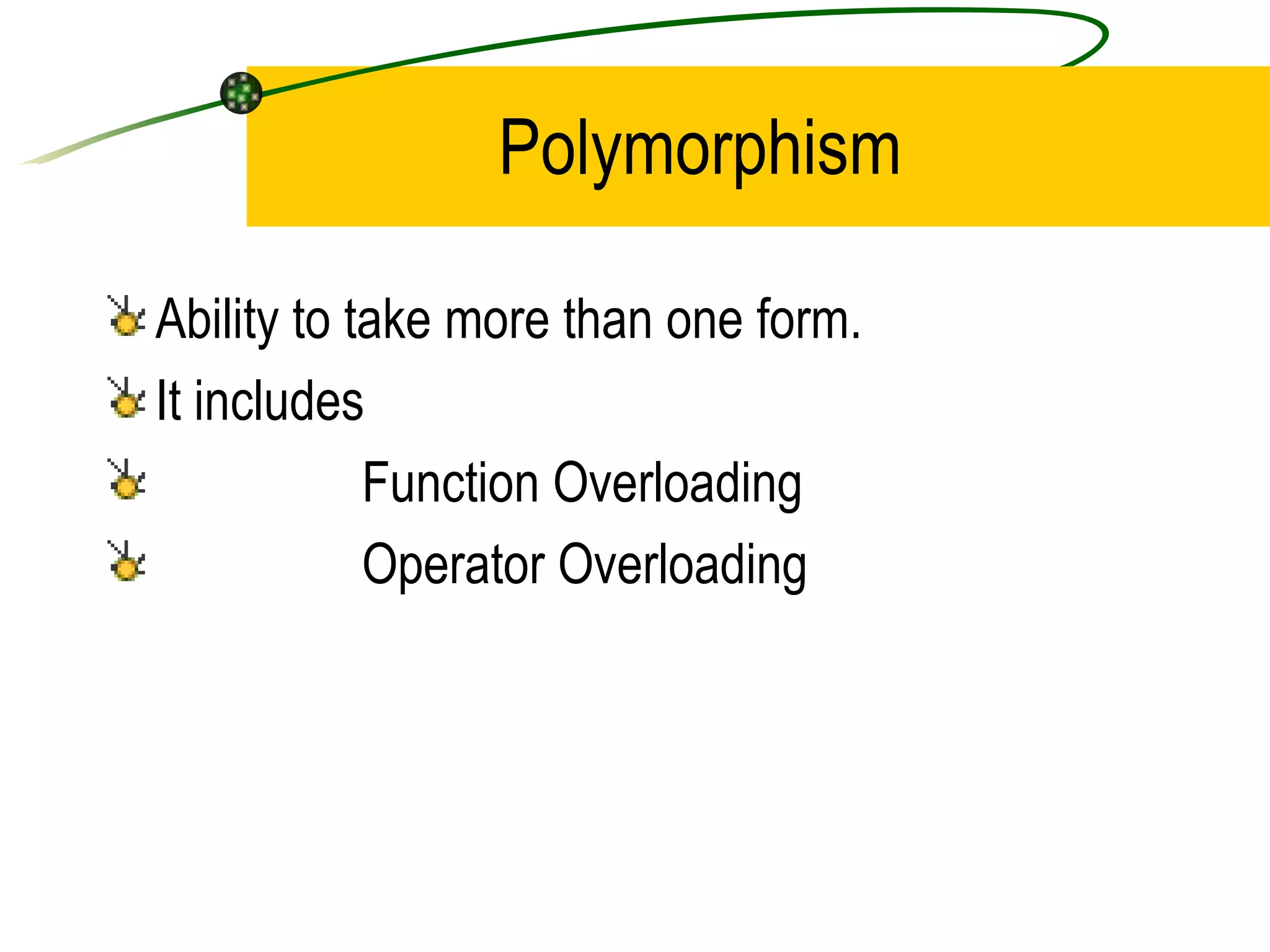
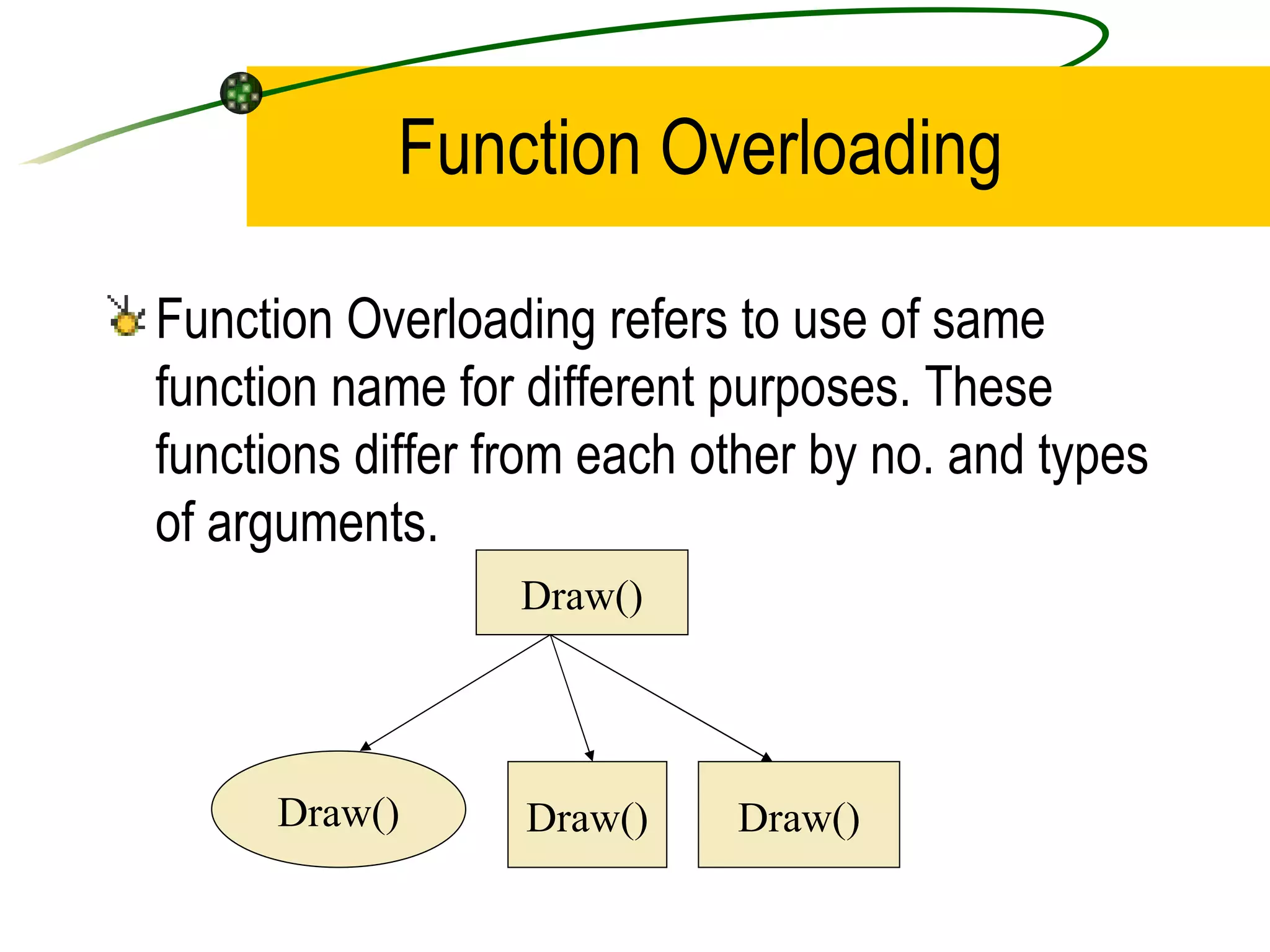
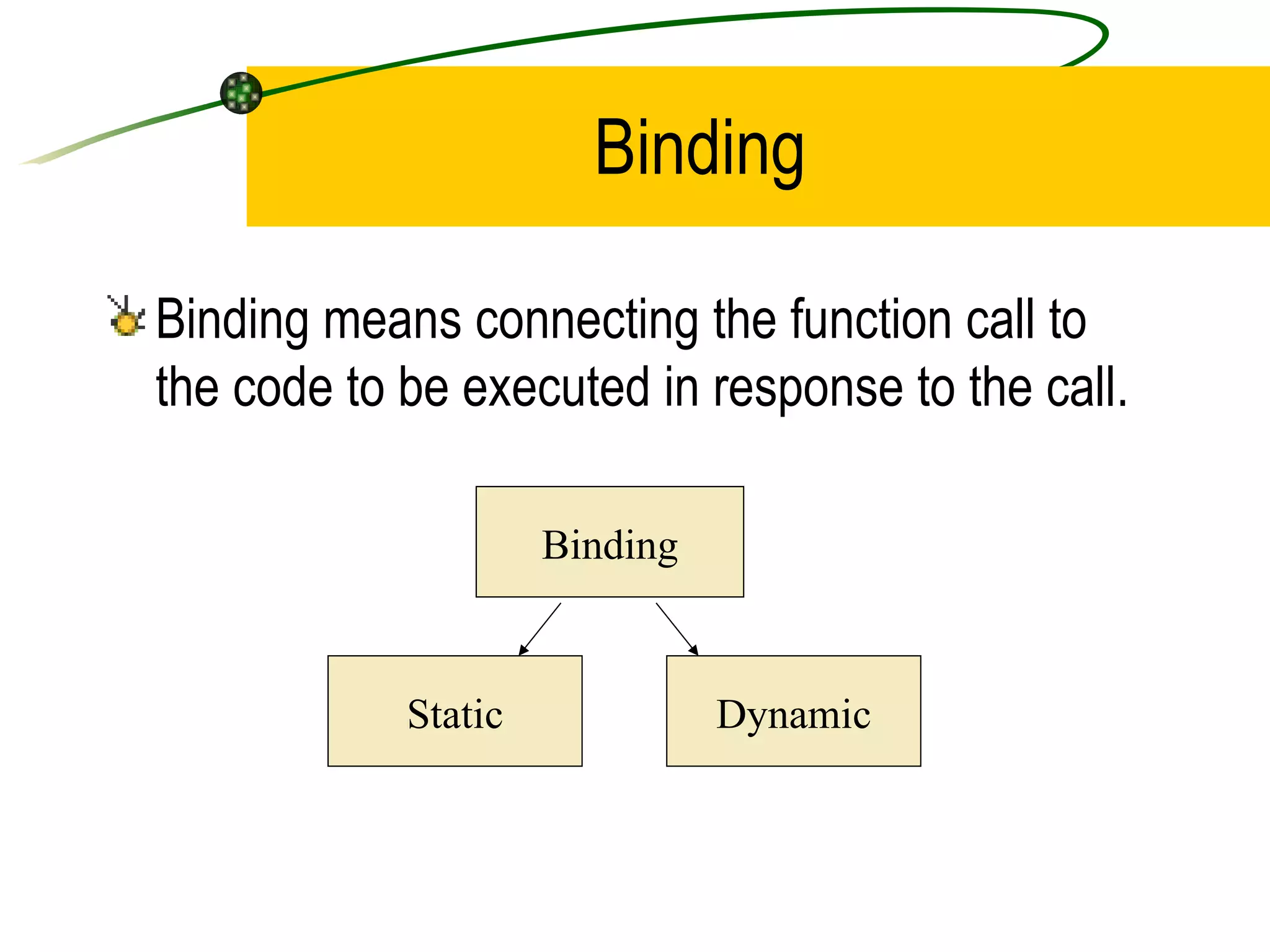
The document discusses the key concepts of object-oriented programming (OOP) in C++ including objects, classes, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and binding. It explains that OOP focuses on data and objects that interact by sending messages, whereas procedural programming focuses on functions and global data. Some key OOP concepts are classes as user-defined types that group similar objects, encapsulation which wraps data and functions into a single unit, and inheritance which allows deriving new classes from existing classes.