The document discusses various topics related to file handling and sorting algorithms in C programming. It begins with an introduction to file handling, describing how to open, write, and read from files. It then covers different modes for opening files and examples of writing data to multiple files. The document later discusses linear and binary search algorithms for arrays as well as bubble, selection, and insertion sorts. Code examples are provided for each algorithm discussed.




![#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i,j;
float x, y[1000];
i = 0;
for (x = 0; x<=10; x = x+0.1)
{
y[i] = x;
printf("%fn", y[i]);
i++;
}
getchar(); return 0;
}
/* We need to store y points in a file. So look at the following
program*/
Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22-190313191900/75/C-Language-Lecture-22-5-2048.jpg)
![// Graph of y versus x
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
float x, y[101];
FILE *fpx, *fpy;
fpx = fopen("x.txt","w");
fpy = fopen("y.txt","w");
i = 0;
for (x = 0; x<=10; x = x+0.1)
{
y[i] = x;
fprintf(fpx, "%fn", x);
fprintf(fpy, "%fn", y[i]);
i++;
}
printf("Data has been stored in the file");
getchar(); return 0; }
Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22-190313191900/75/C-Language-Lecture-22-6-2048.jpg)


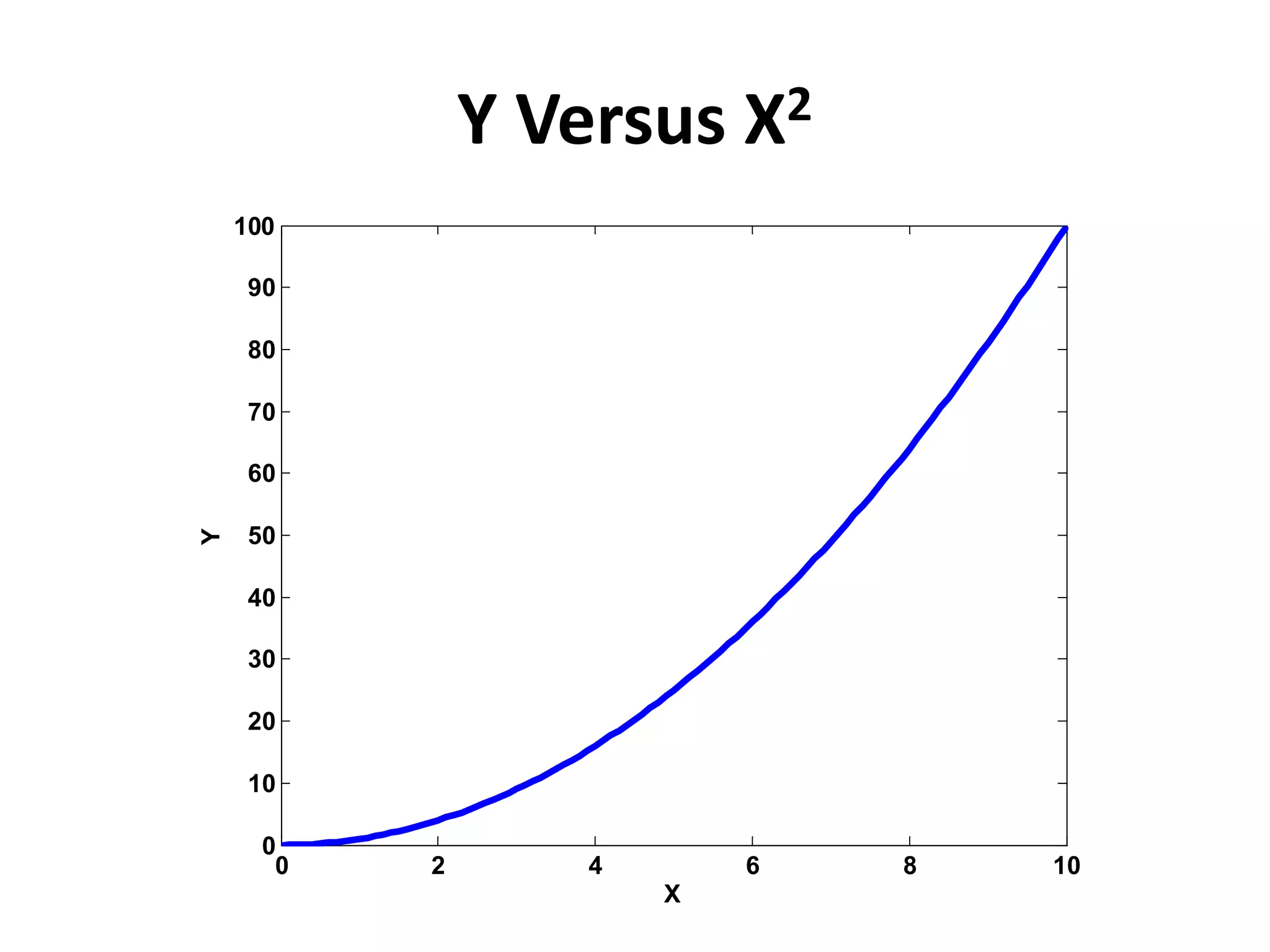
![// Graph of y versus x^2
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
int i;
double x, y[101];
FILE *fpx, *fpy;
fpx = fopen("xs.txt","w");
fpy = fopen("ys.txt","w");
i = 0;
for (x = 0; x<=10; x = x+0.1)
{
y[i] = pow(x,2);
fprintf(fpx, "%lfn", x);
fprintf(fpy, "%lfn", y[i]);
i++;
}
printf("Data has been stored in the file");
getchar(); return 0; }
Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22-190313191900/75/C-Language-Lecture-22-9-2048.jpg)

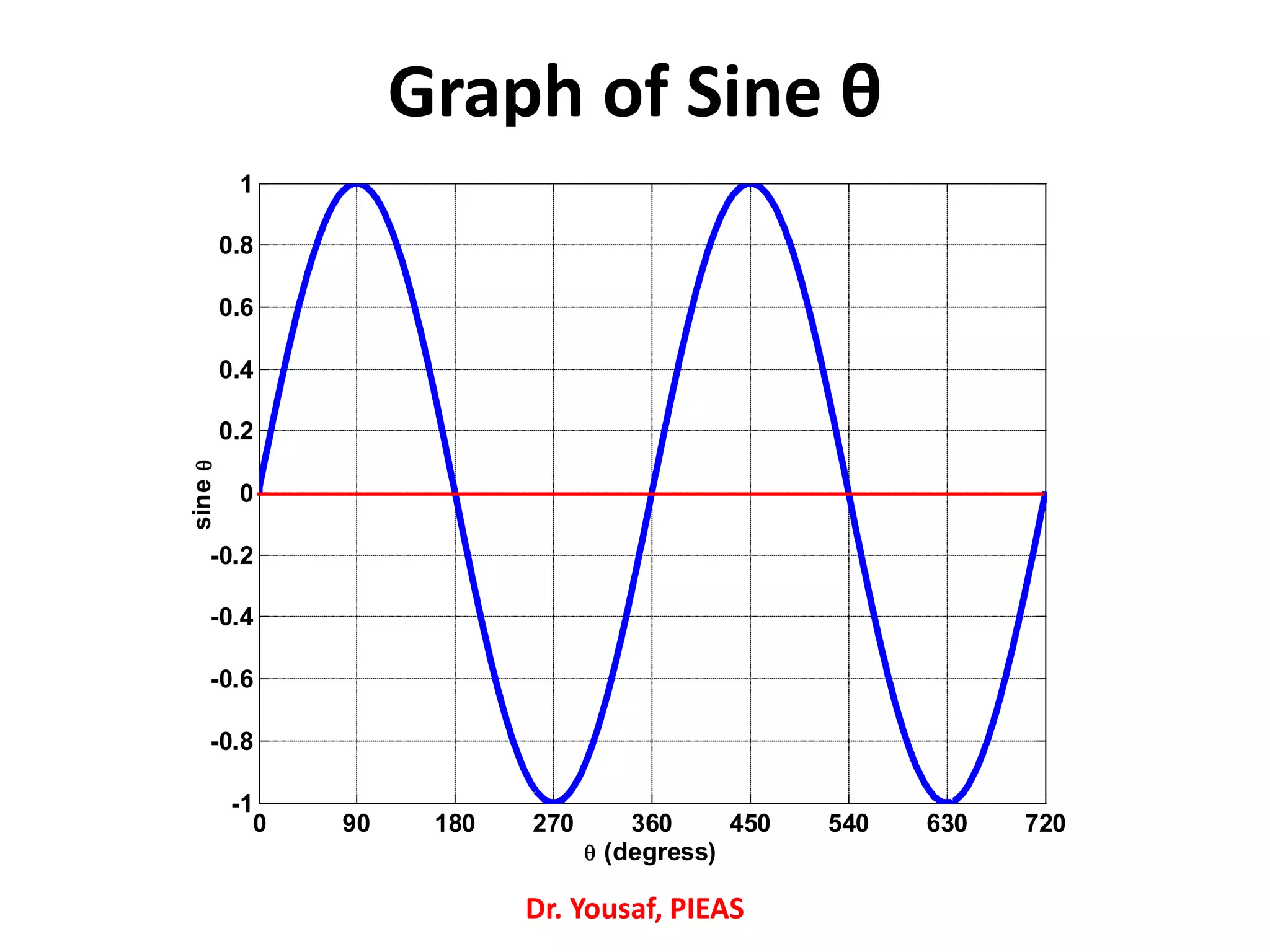
![/* Graph of sine(theta)
/* Graph of sine(theta)
Please read Page 378 for many
trigonometric functions*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
# define PI 22.0/7.0
int main()
{
double theta_deg, theta_rad, y[2000];
int i = 0;
FILE *fptheta, *fpsine;
fptheta = fopen("theta.txt","w");
fpsine = fopen("sine.txt","w");
for (theta_deg = 0;
theta_deg<=720; theta_deg++)
{
theta_rad =
((PI)/180.0)*theta_deg;
y[i] = sin(theta_rad);
fprintf(fptheta, "%lfn",
theta_deg);
fprintf(fpsine, "%lfn", y[i]);
i++;
}
printf("Data has been stored in
the file");
getchar(); return 0; }
Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22-190313191900/75/C-Language-Lecture-22-12-2048.jpg)


![//Linear Search
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int array[100], search, c, n;
printf("Enter the number of elements in
arrayn");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter %d integer(s)n", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
printf("Enter the number to searchn");
scanf("%d", &search);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
{
if (array[c] == search)
{
printf("%d is present at location
%d.n", search, c+1);
break;
}
}
if (c == n)
printf("%d is not present in
array.n", search);
getchar();
return 0;
}
Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22-190313191900/75/C-Language-Lecture-22-16-2048.jpg)
![/*Binary Search (only for arrays which
are already sorted). */
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int c, first, last, middle, n, search,
array[100];
printf("Enter number of elementsn");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter %d integers in asending
ordern", n);
for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ )
scanf("%d",&array[c]);
printf("Enter value to findn");
scanf("%d",&search);
first = 0;
last = n - 1;
middle = (first+last)/2;
while( first <= last )
{
if ( array[middle] == search )
{
printf("%d found at location
%d.n", search, middle+1);
break;
}
else if ( array[middle] < search )
first = middle + 1;
else
last = middle - 1;
middle = (first + last)/2;
}
if ( first > last )
printf("Not found! %d is not present
in the list.n", search);
return 0;
}
Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22-190313191900/75/C-Language-Lecture-22-17-2048.jpg)
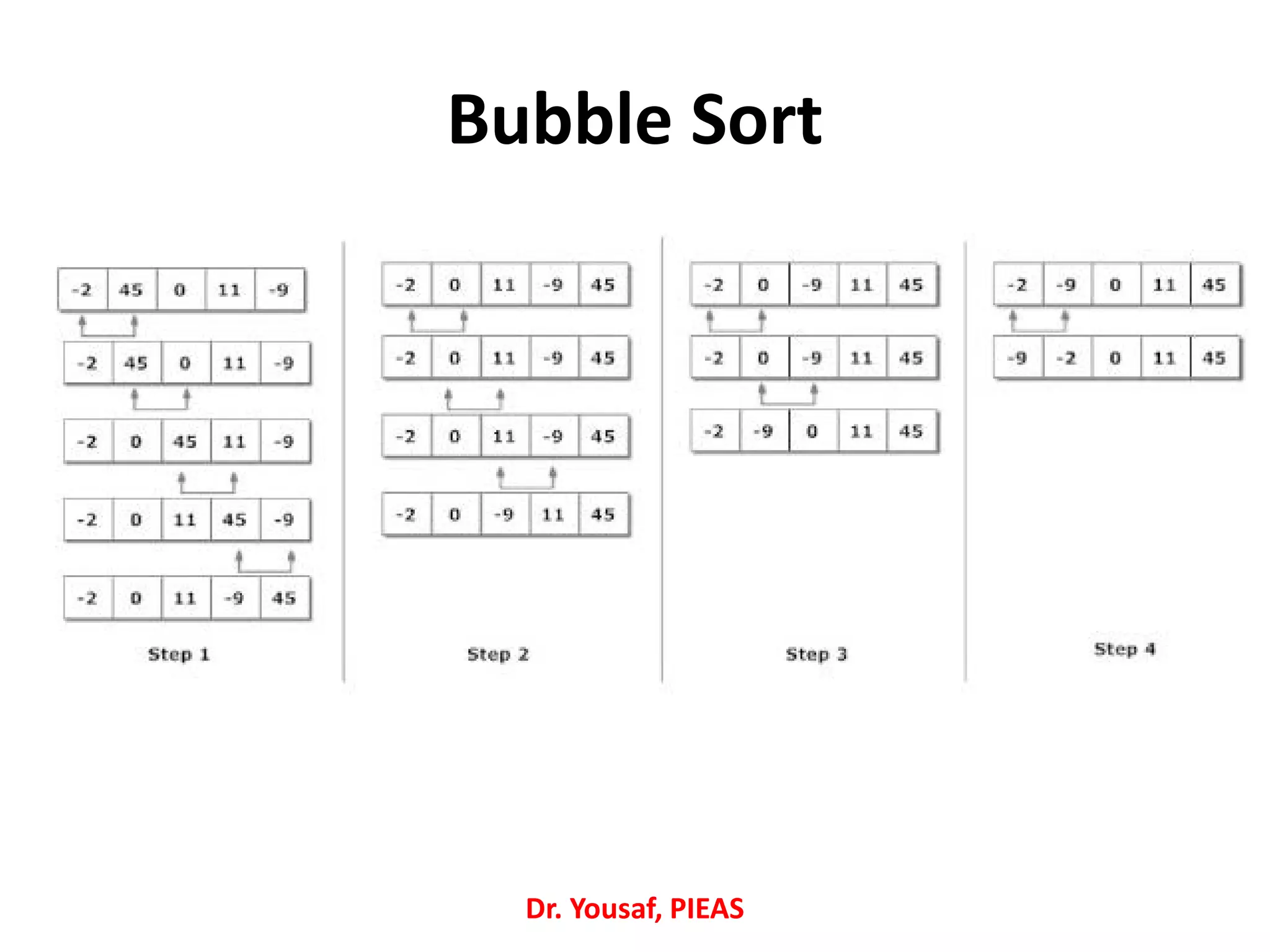
![//Bubble Sort
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n,temp,i,j,a[20];
printf("Enter total numbers of elements:
");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter %d elements: ",n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
//Bubble sorting algorithm
for(i=n-2; i>=0; i--)
{
for(j=0;j<=i;j++)
{
if(a[j]>a[j+1])
{
temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
printf("After sorting: ");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf(" %d",a[i]);
getchar(); return 0;
}
Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22-190313191900/75/C-Language-Lecture-22-19-2048.jpg)
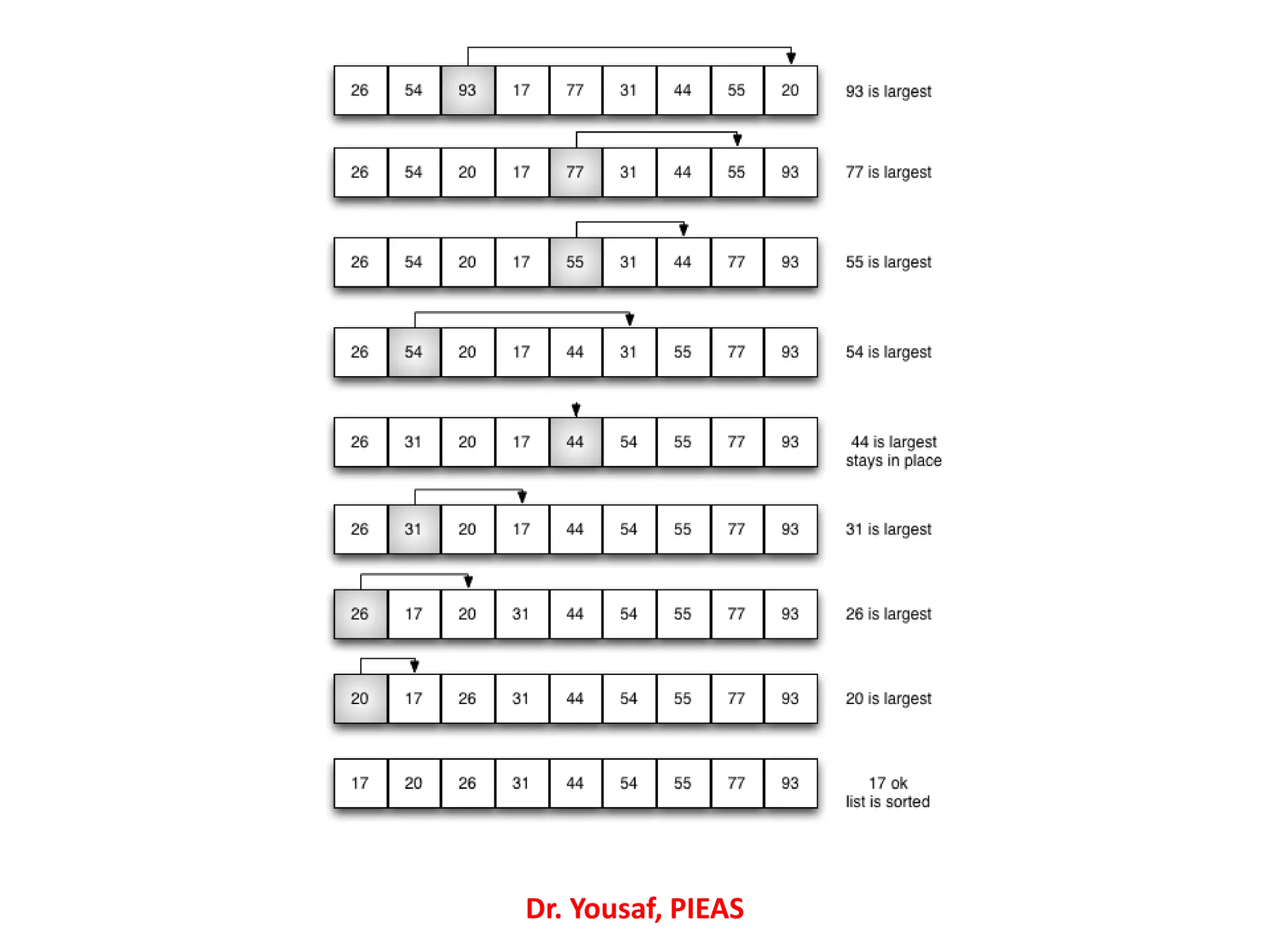
![//Selection Sort
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{ int array[100], n, c, d, position, swap;
printf("Enter number of elementsn");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d integersn", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
for (c = 0; c < (n - 1); c++)
{ position = c;
for (d = c + 1; d < n; d++)
{ if (array[position] > array[d])
position = d;
}
if (position != c)
{ swap = array[c];
array[c] = array[position];
array[position] = swap; }
}
//Selection Sort
printf("Sorted list in ascending
order:n");
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
printf("%dn", array[c]);
getchar();
getchar();
return 0;
}
Dr. Yousaf, PIEAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22-190313191900/75/C-Language-Lecture-22-21-2048.jpg)

