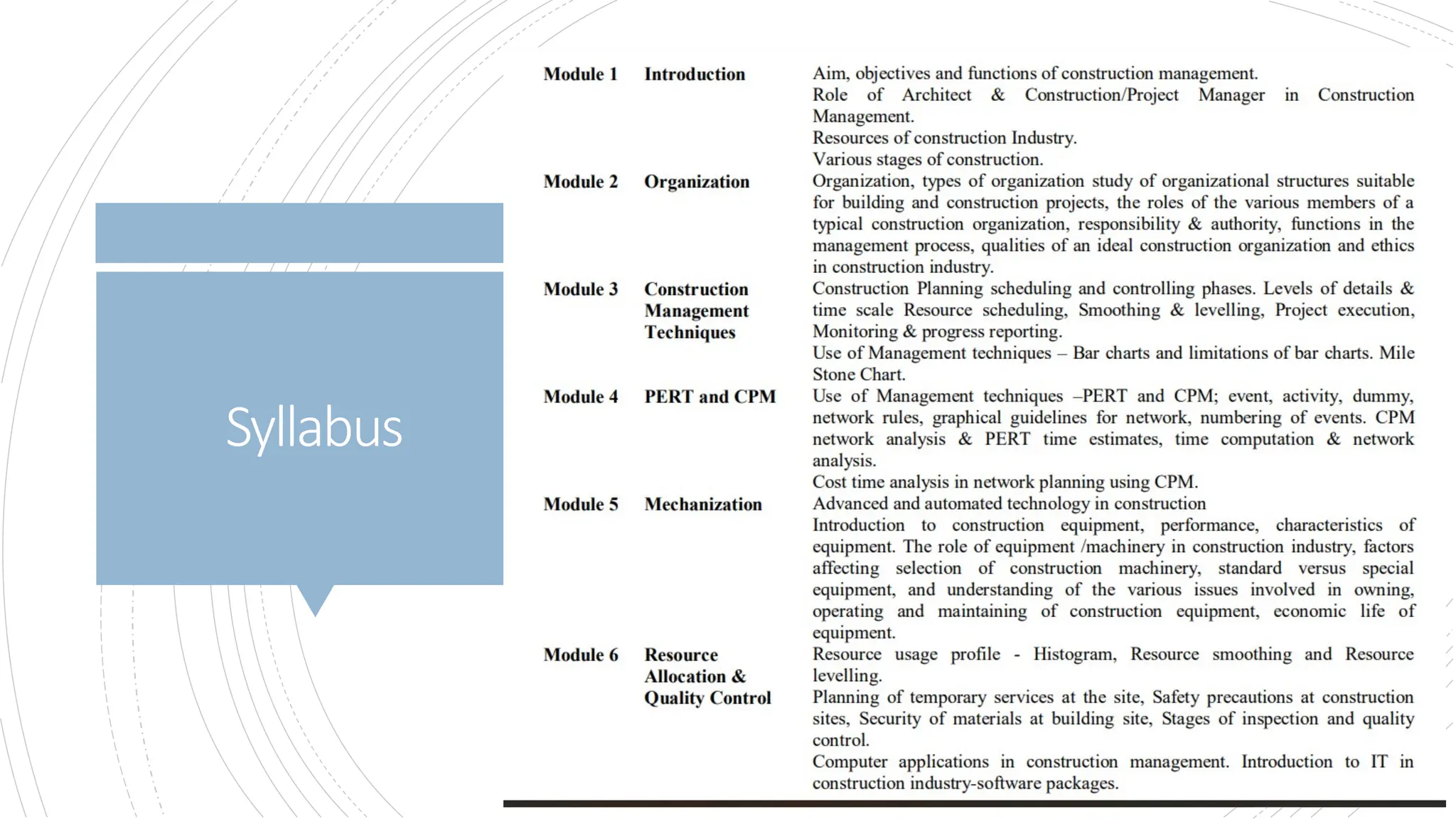
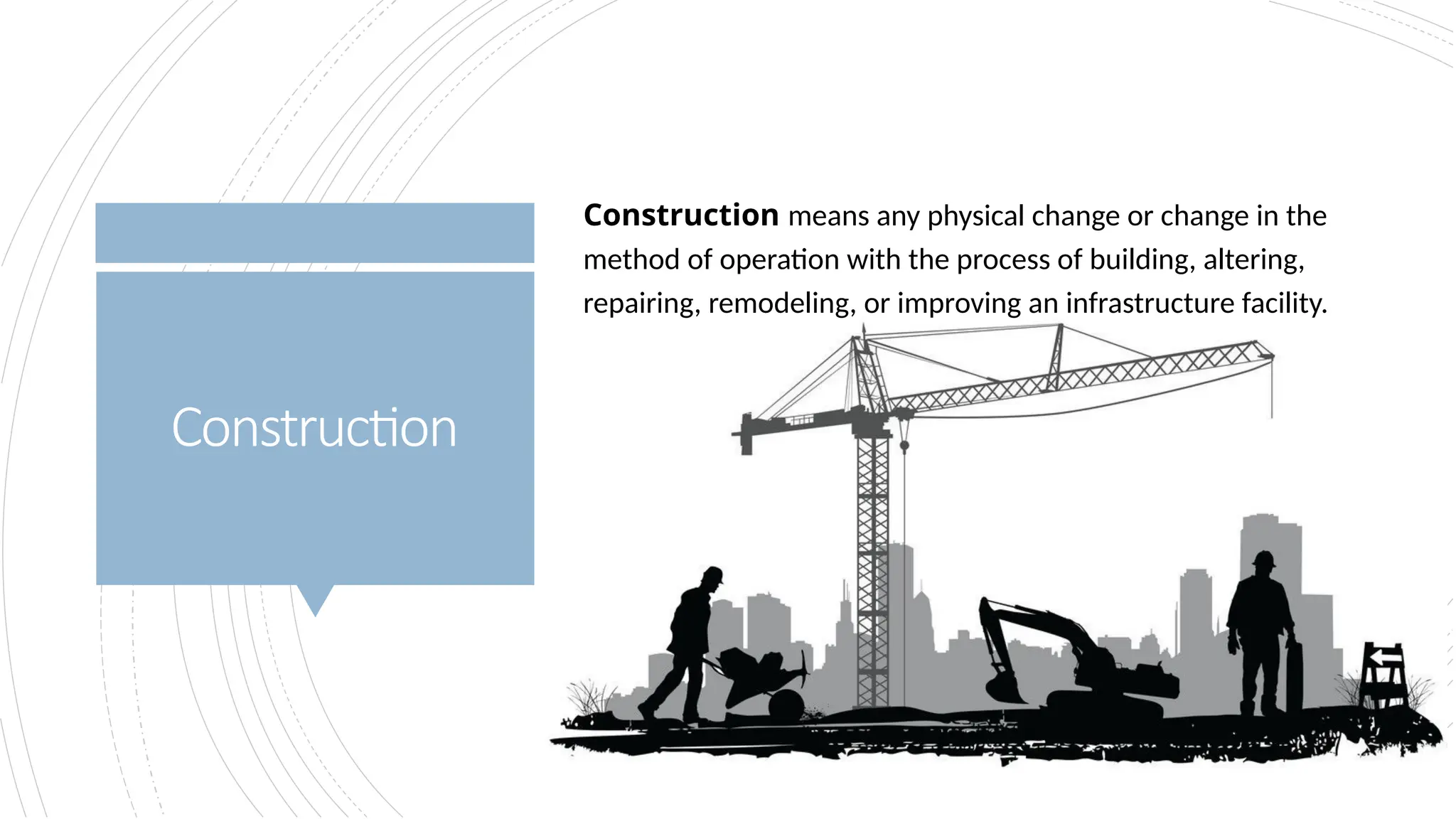
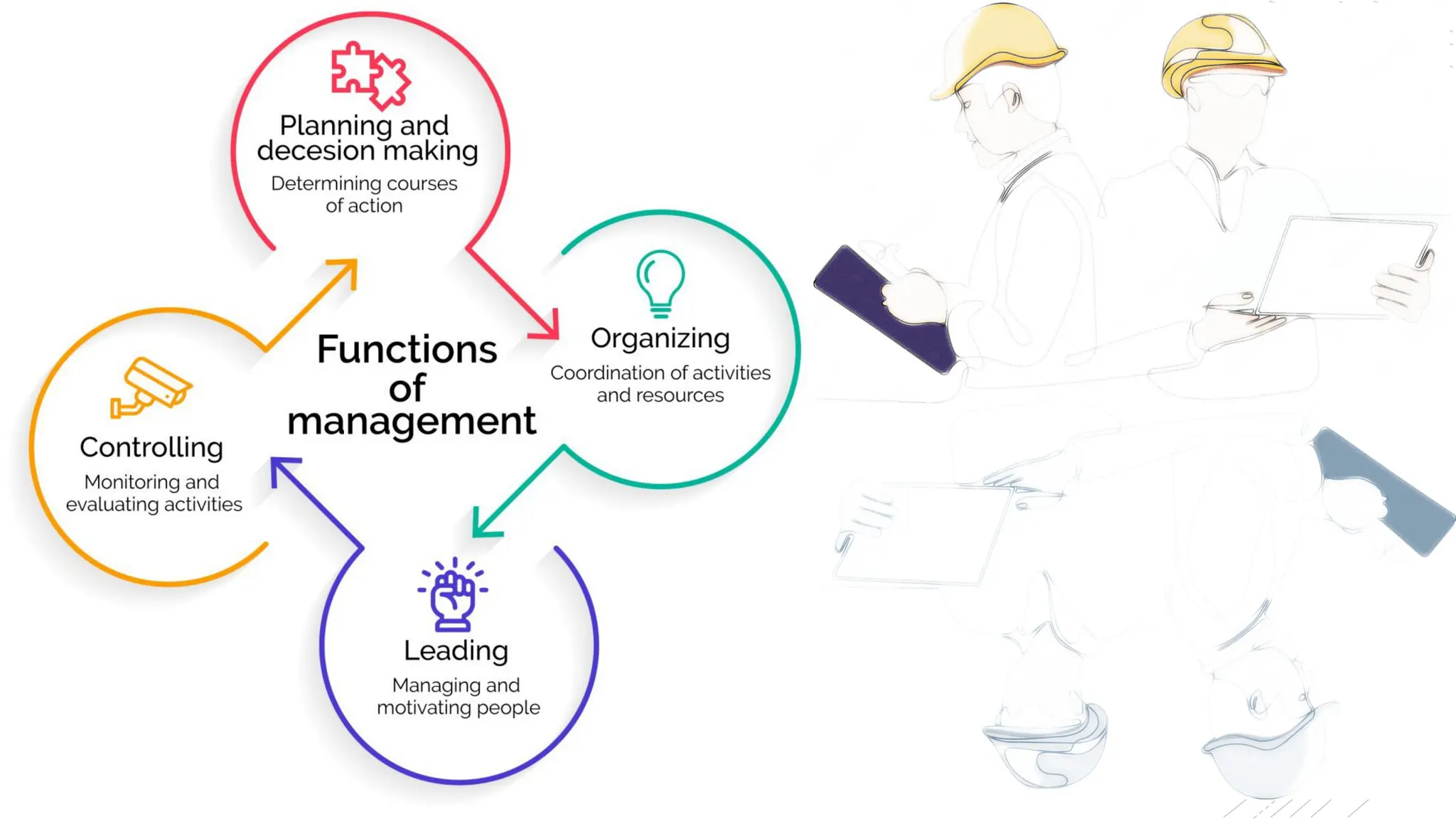
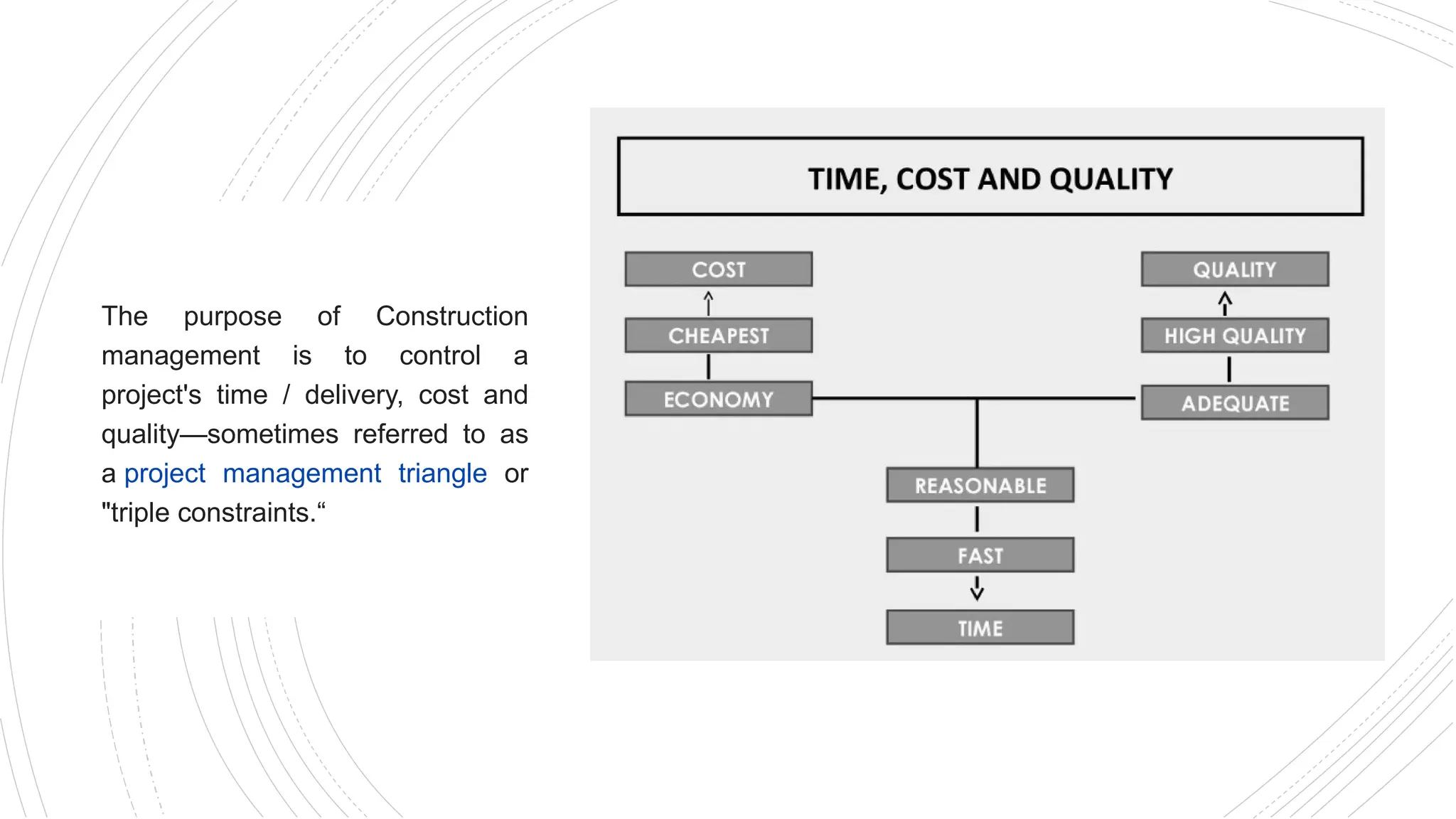
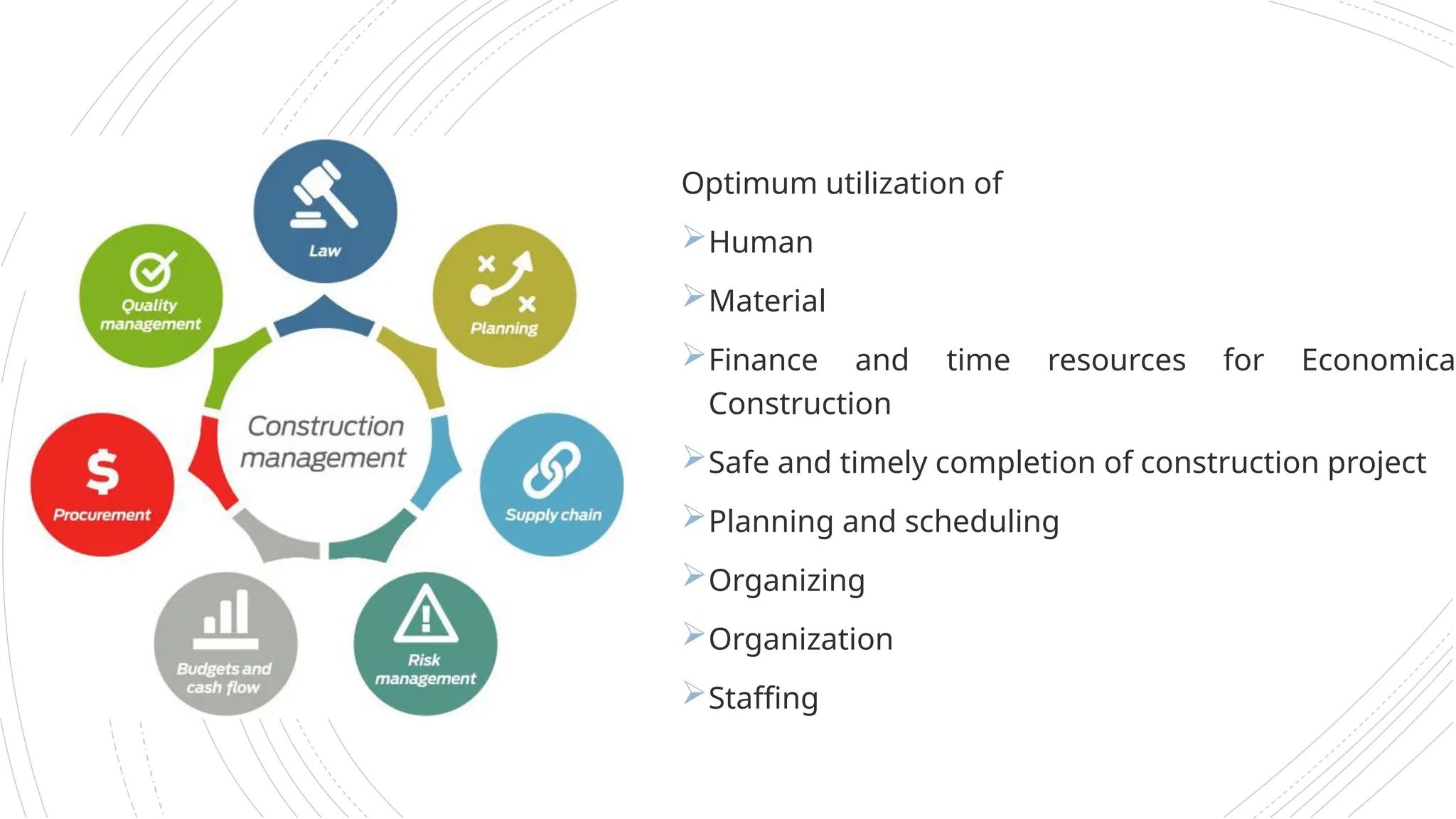
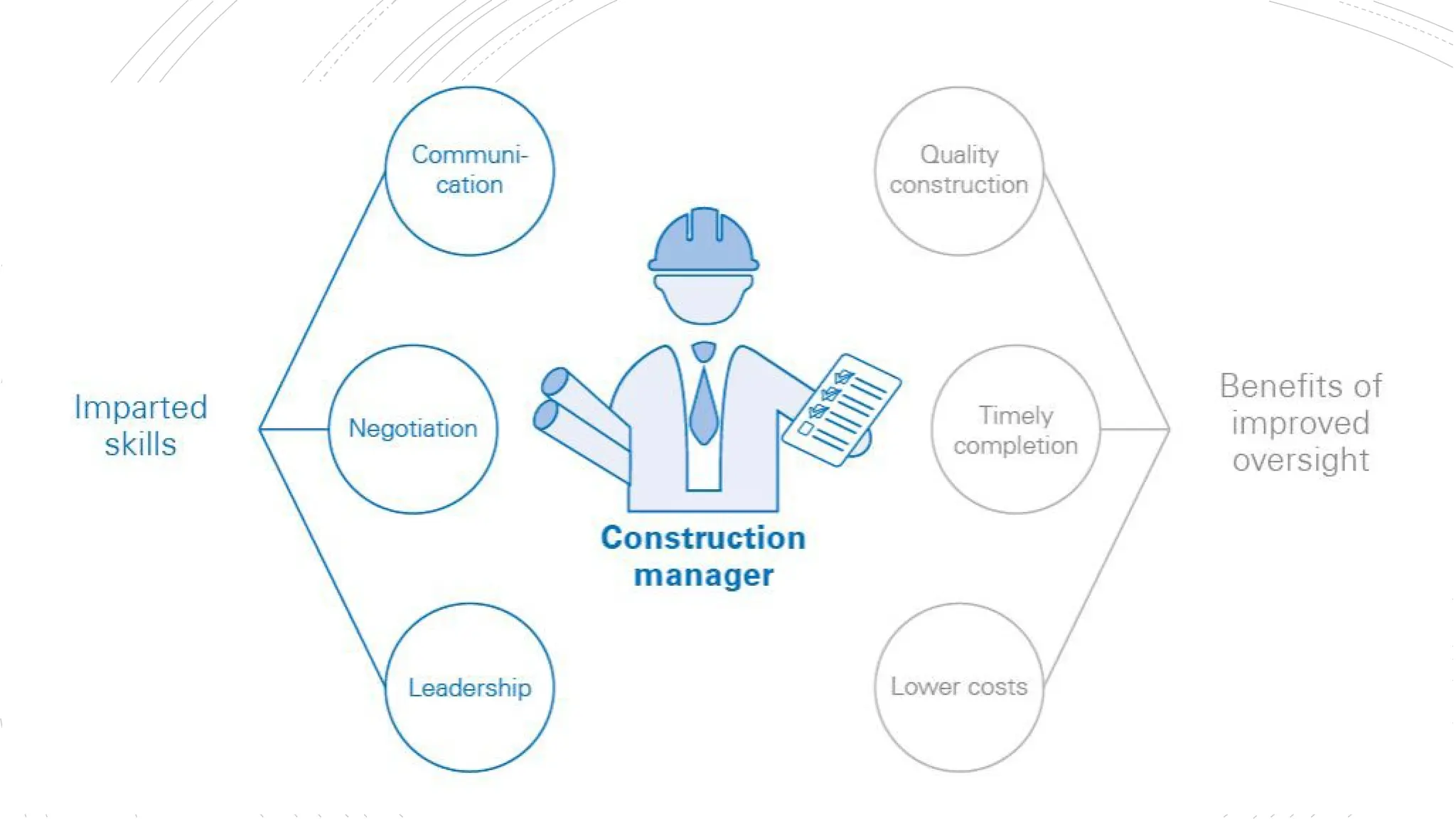
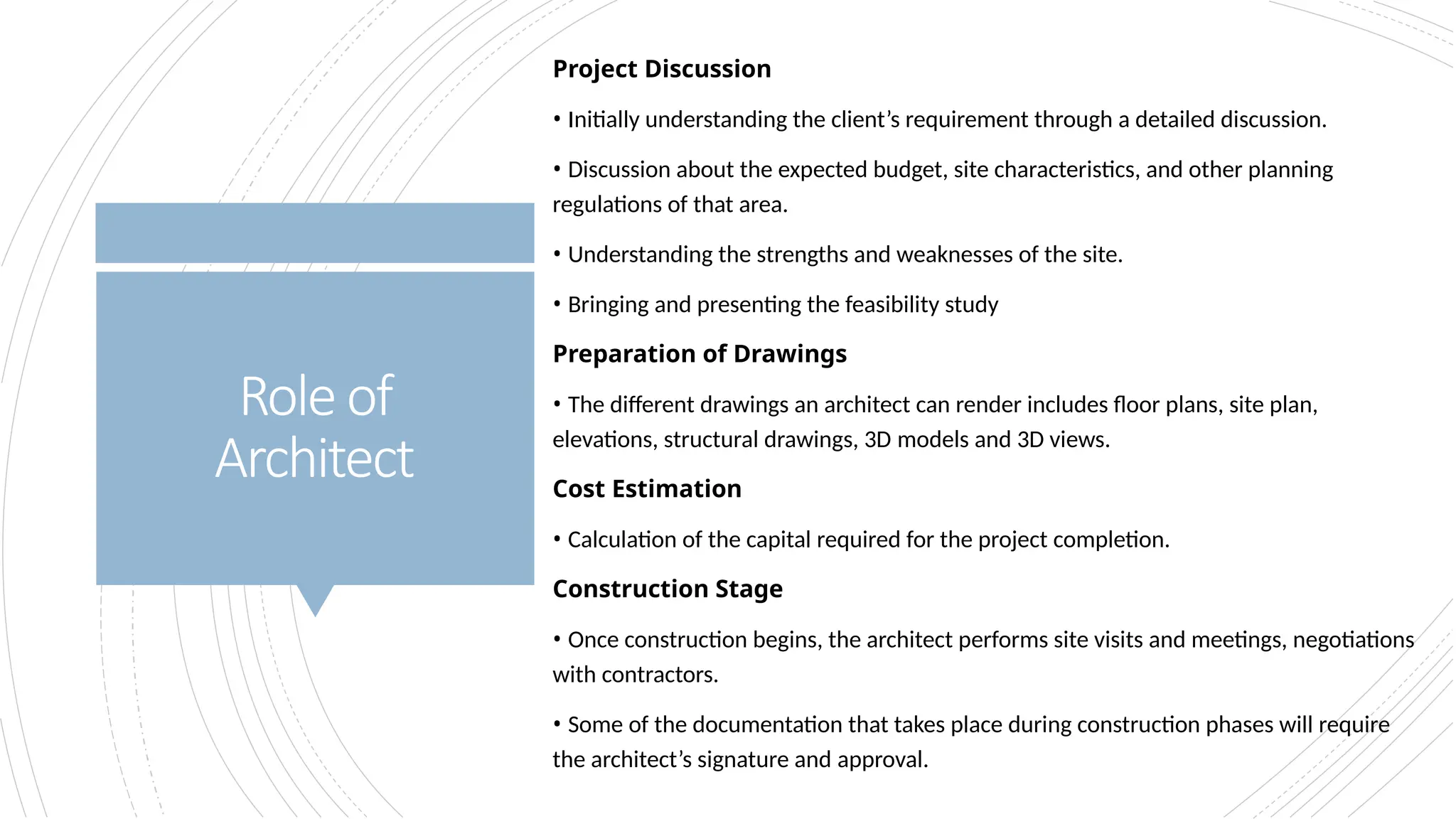
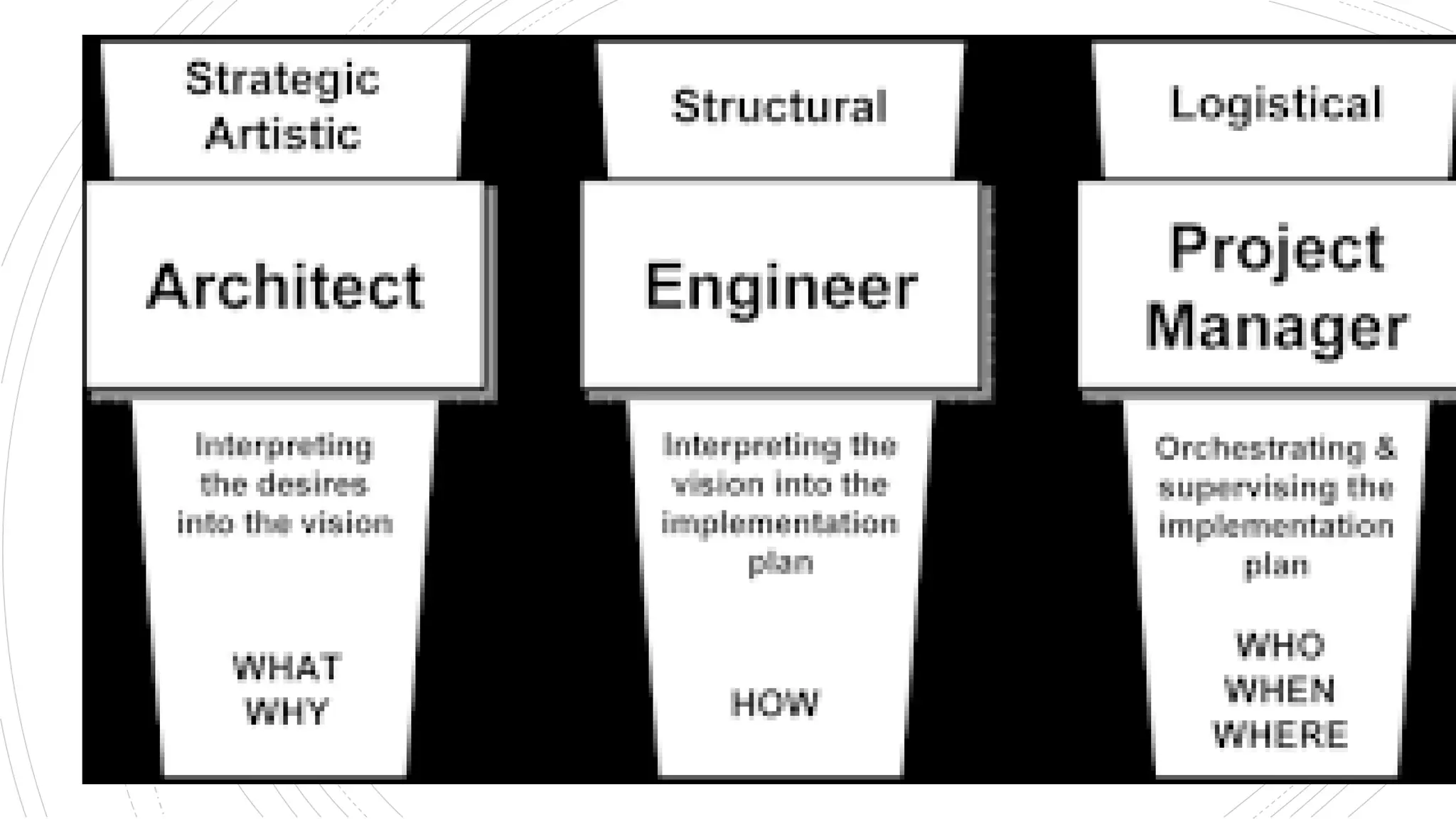
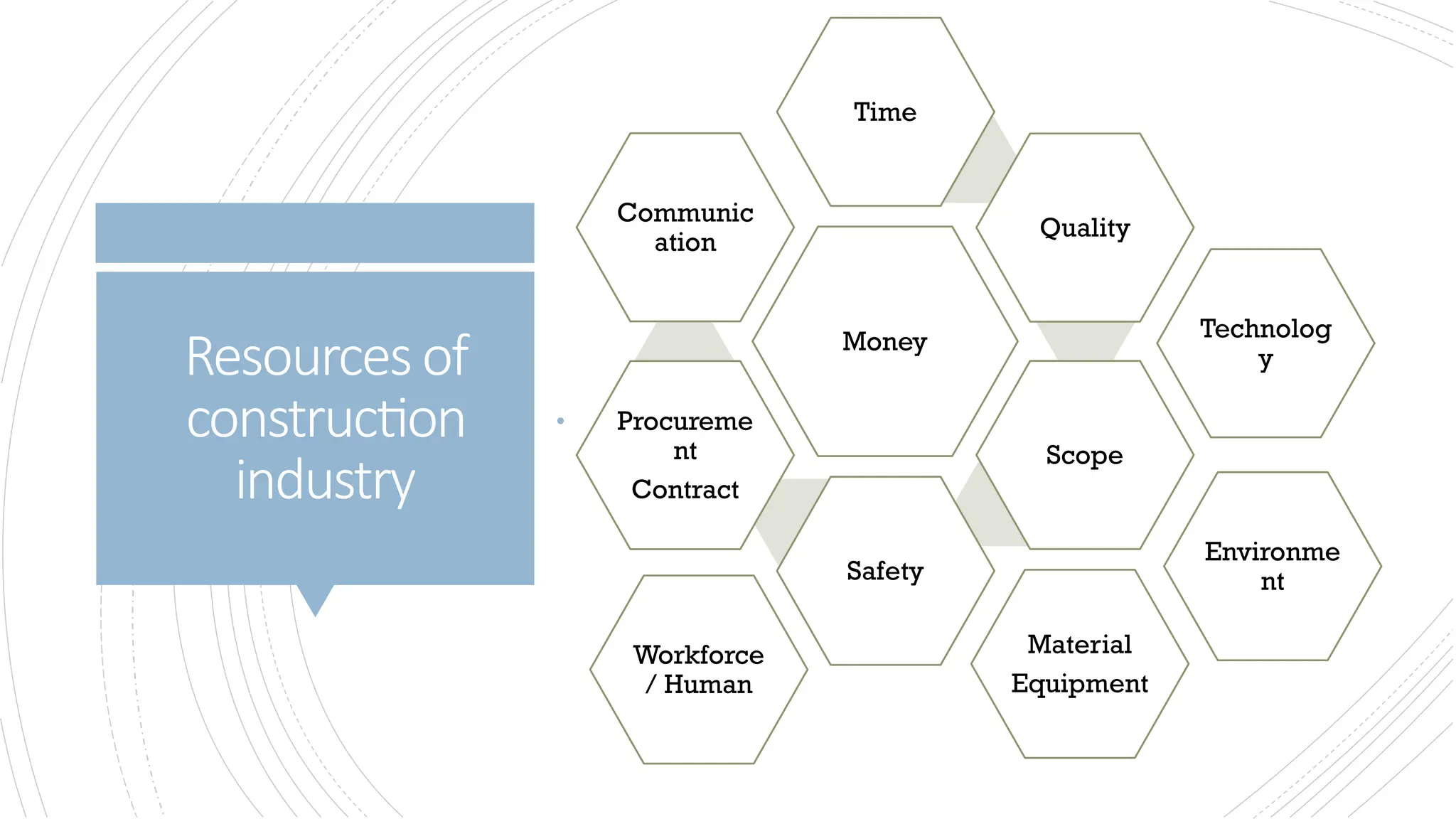
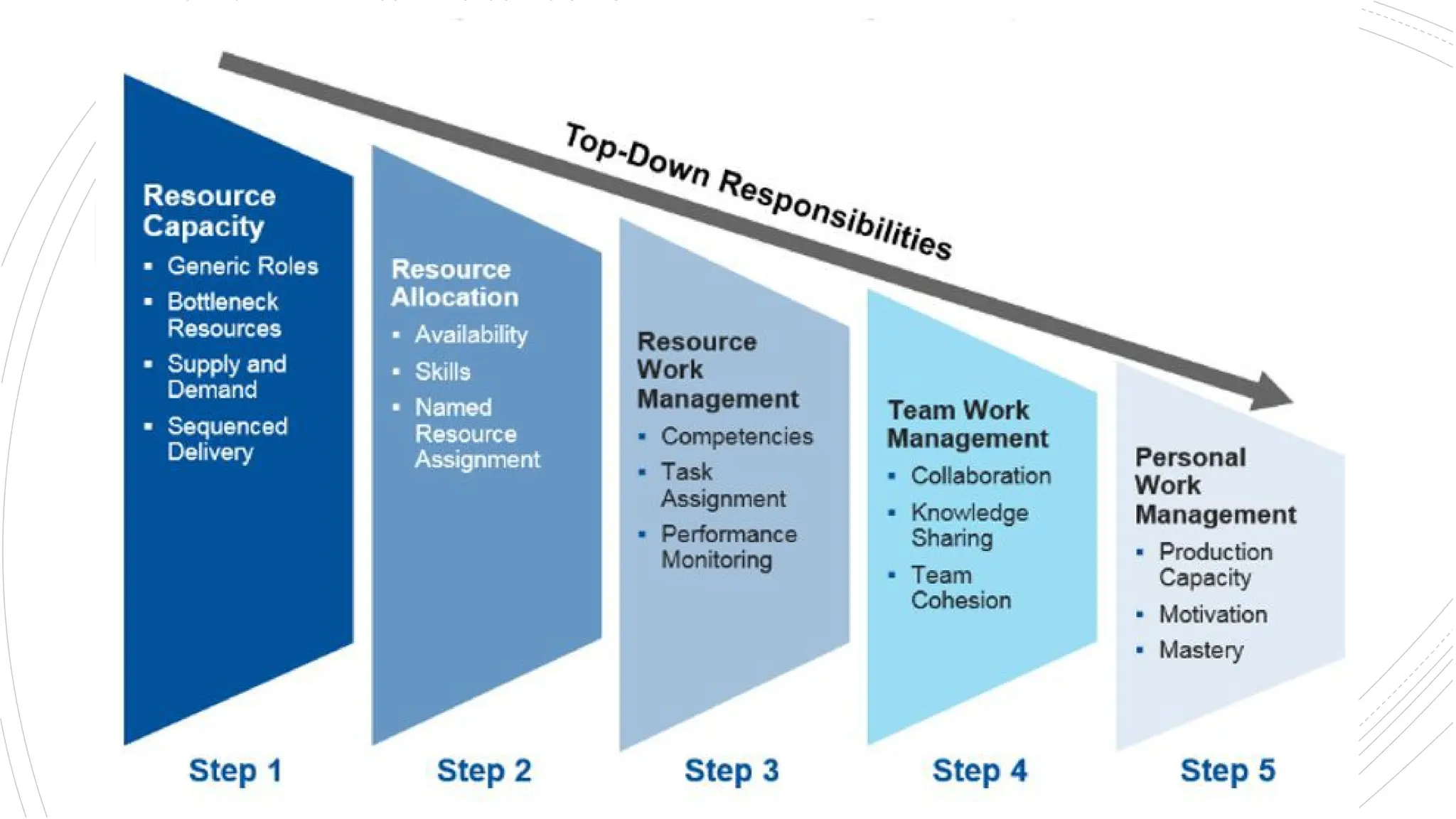
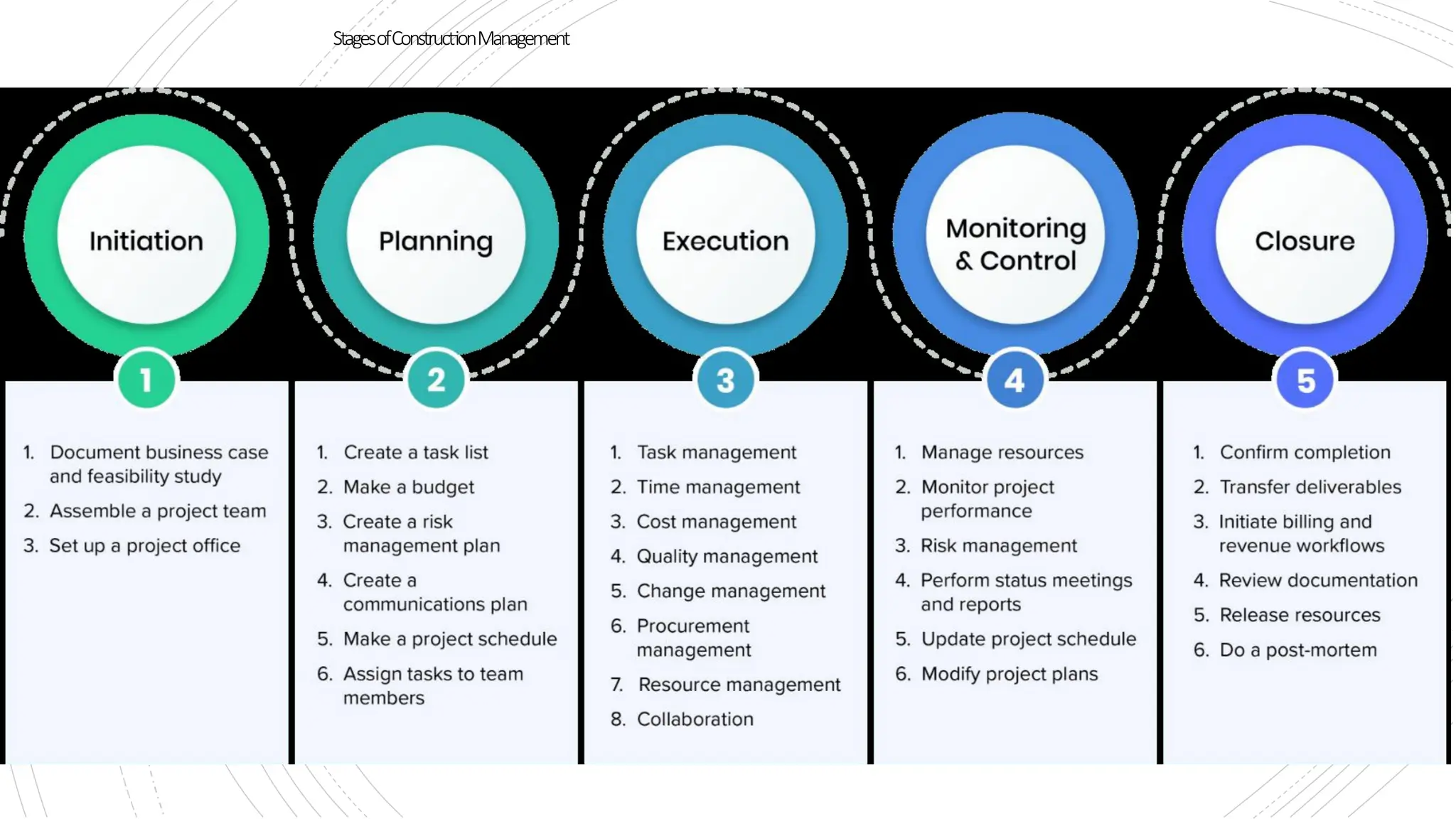
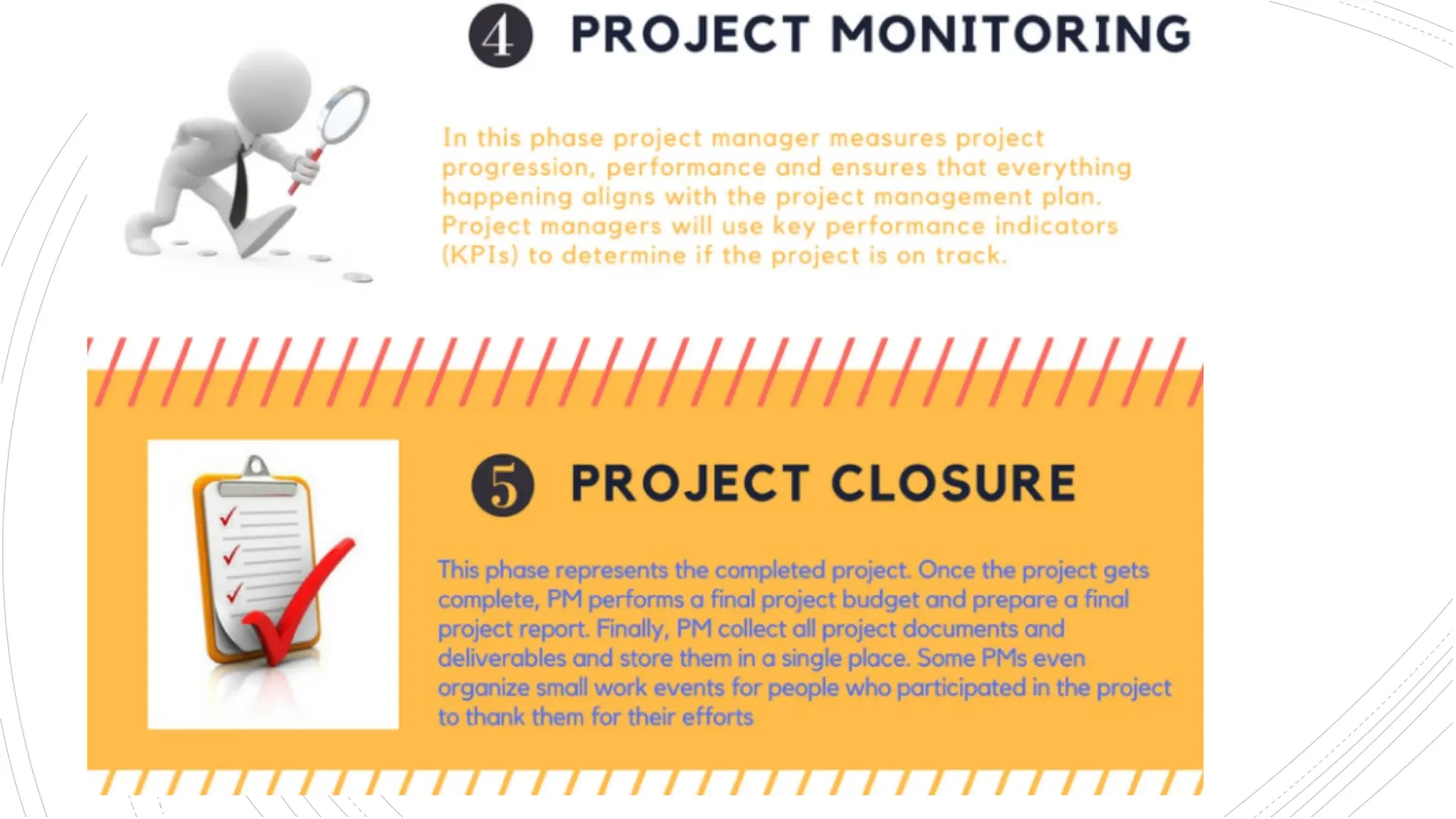
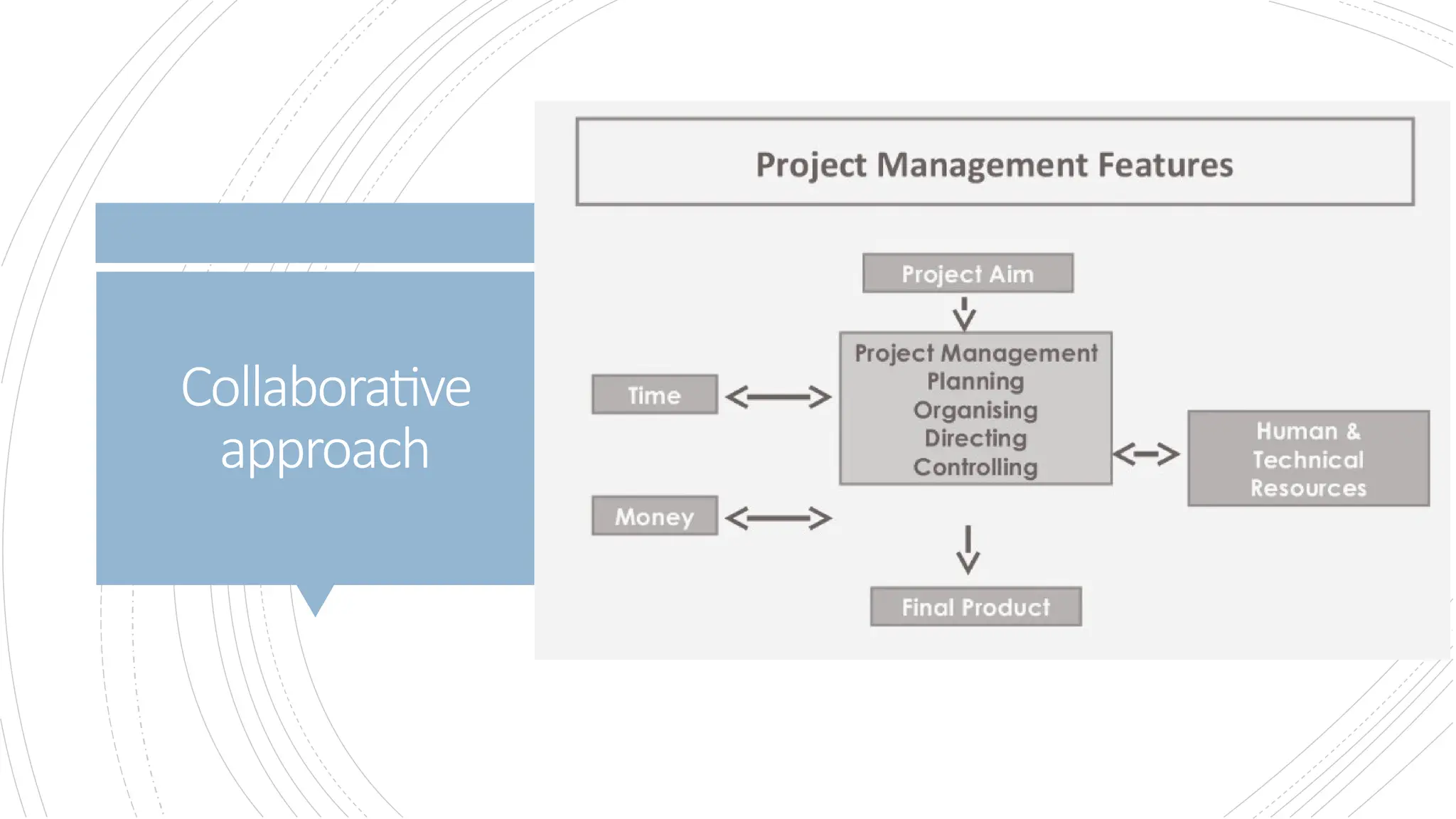
The document provides an overview of construction management covering its aims, objectives, and the roles of architects and project managers. It emphasizes the importance of effective planning, organizing, and resource management to ensure construction projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. Key aspects include managing costs, safety, quality, and communication throughout the project lifecycle.