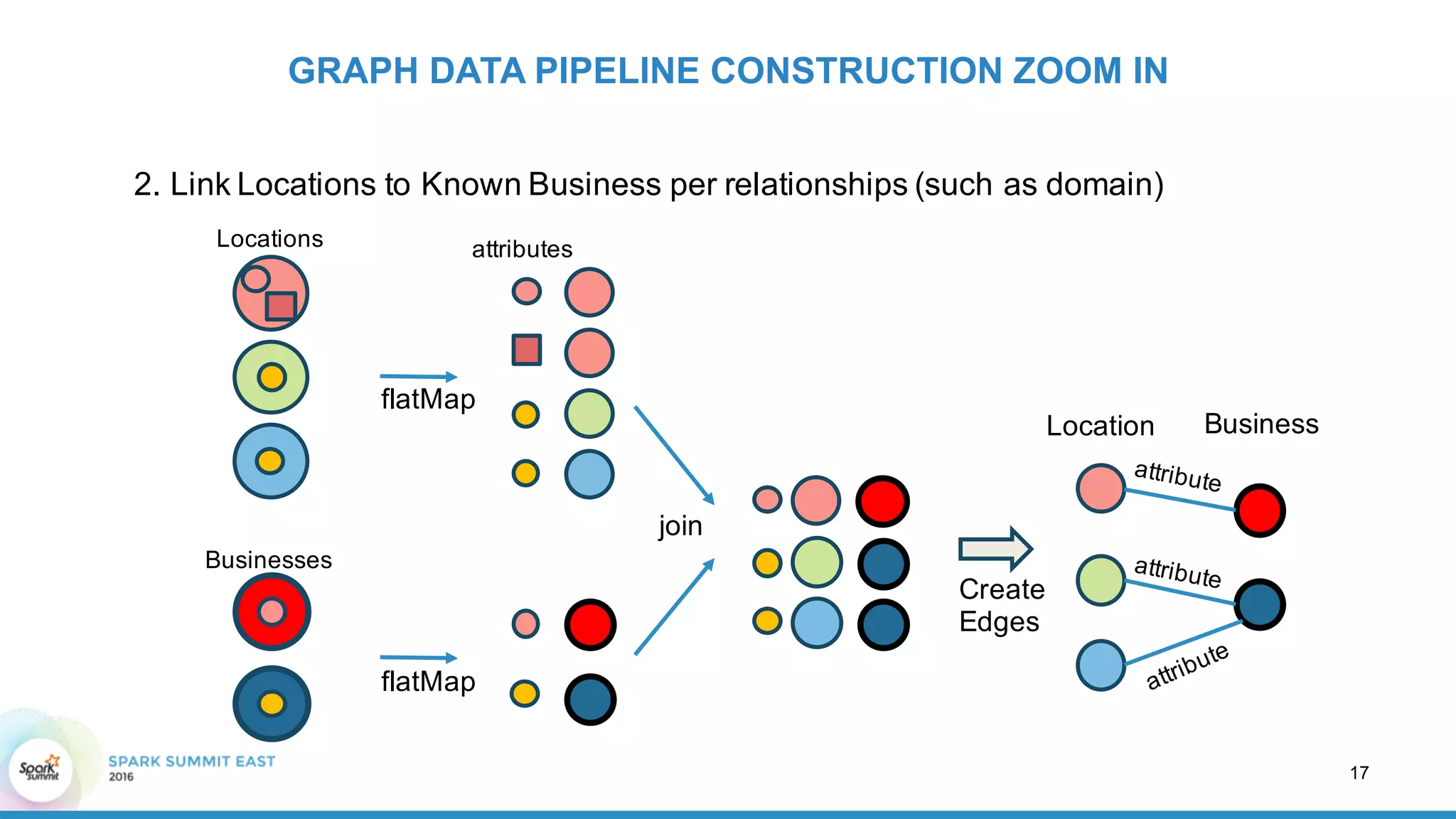
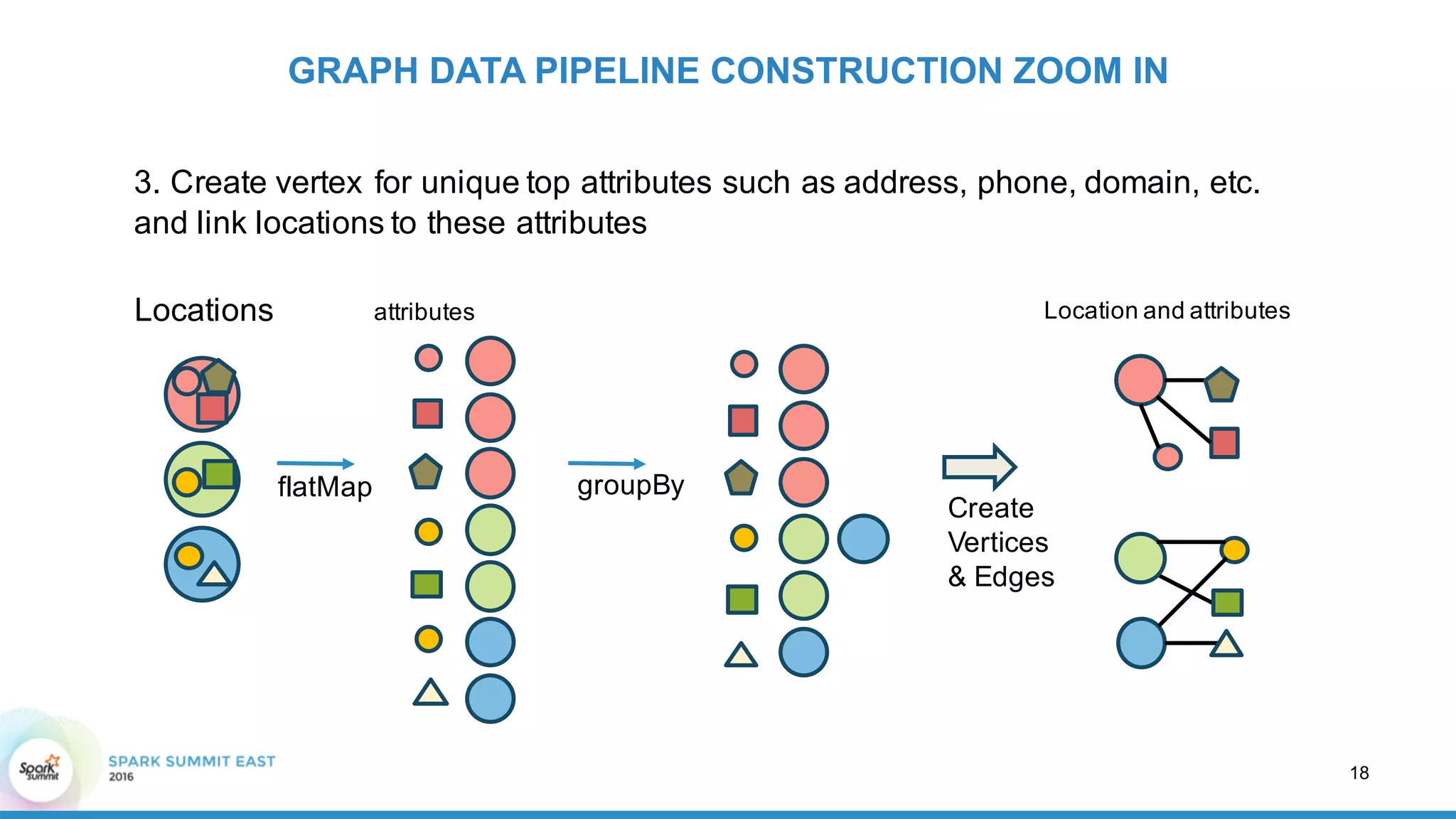
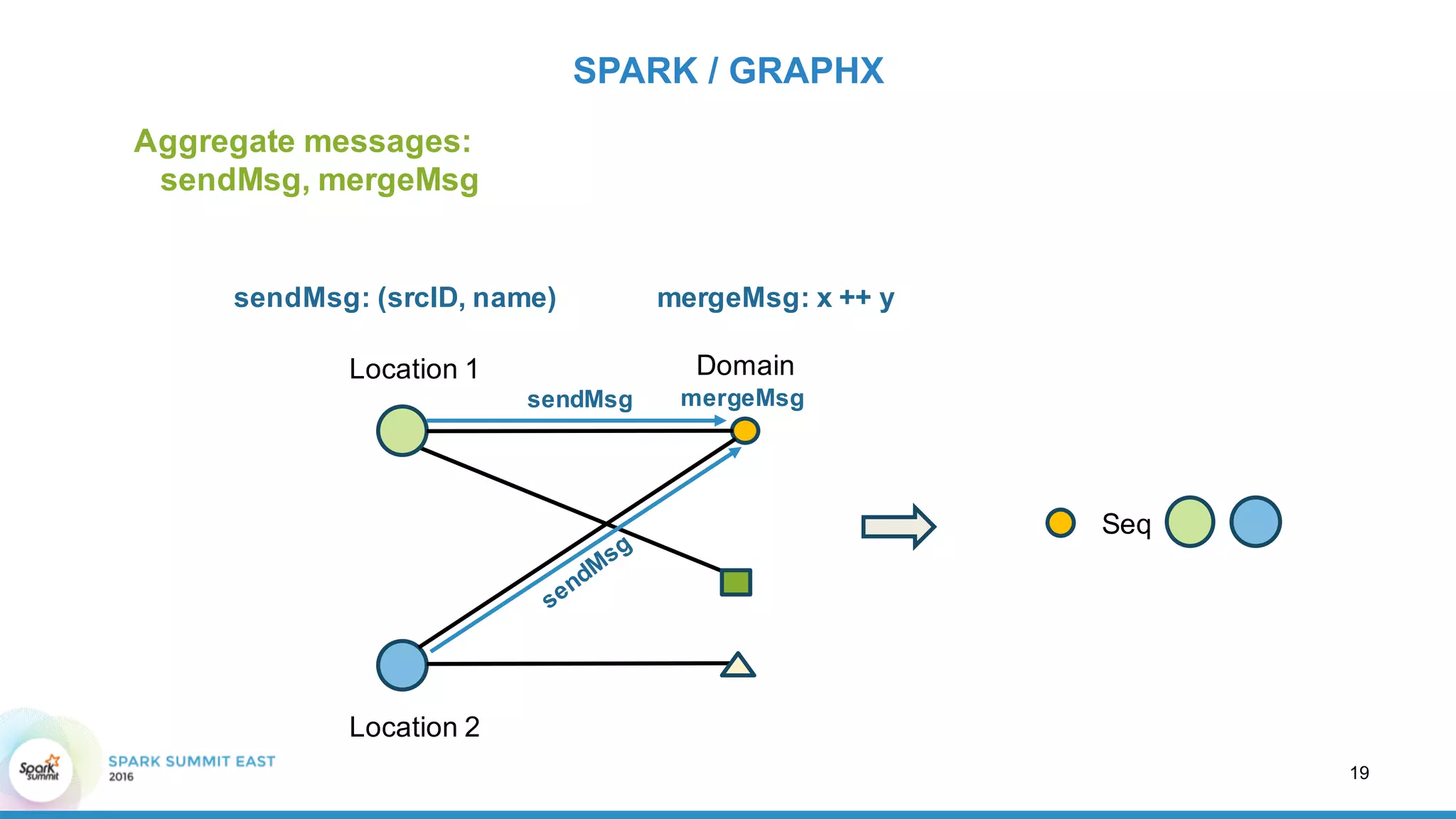
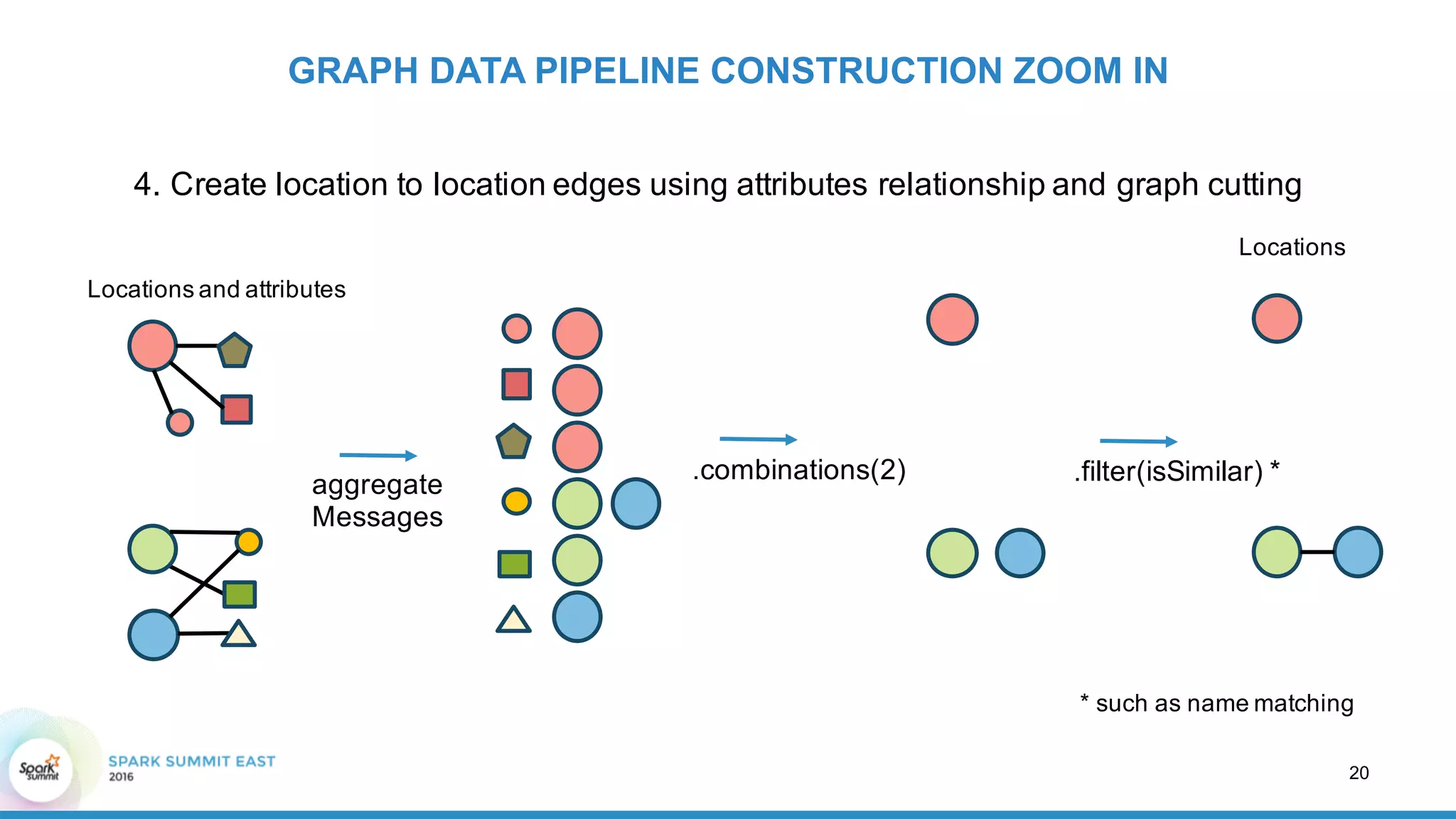
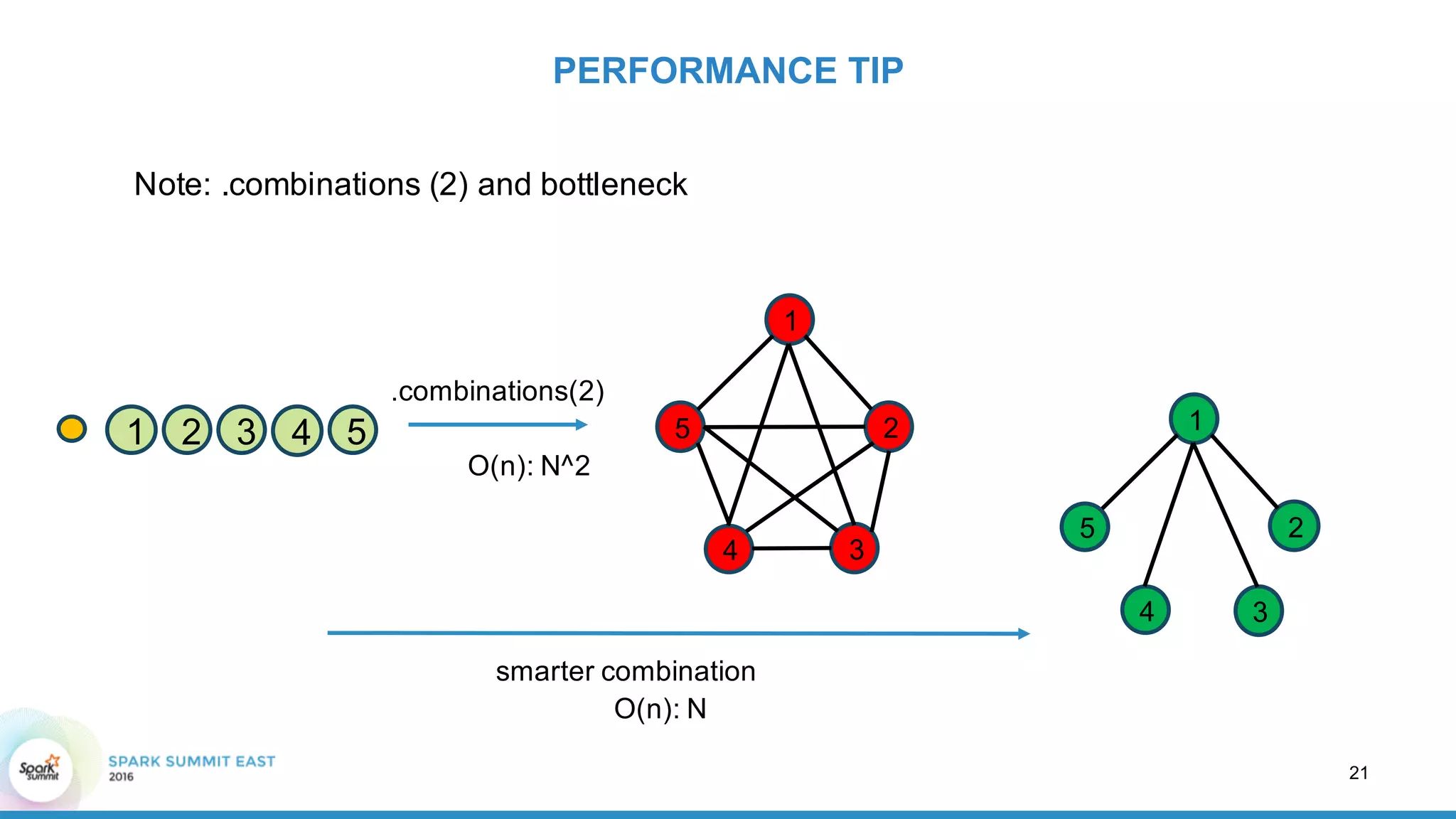
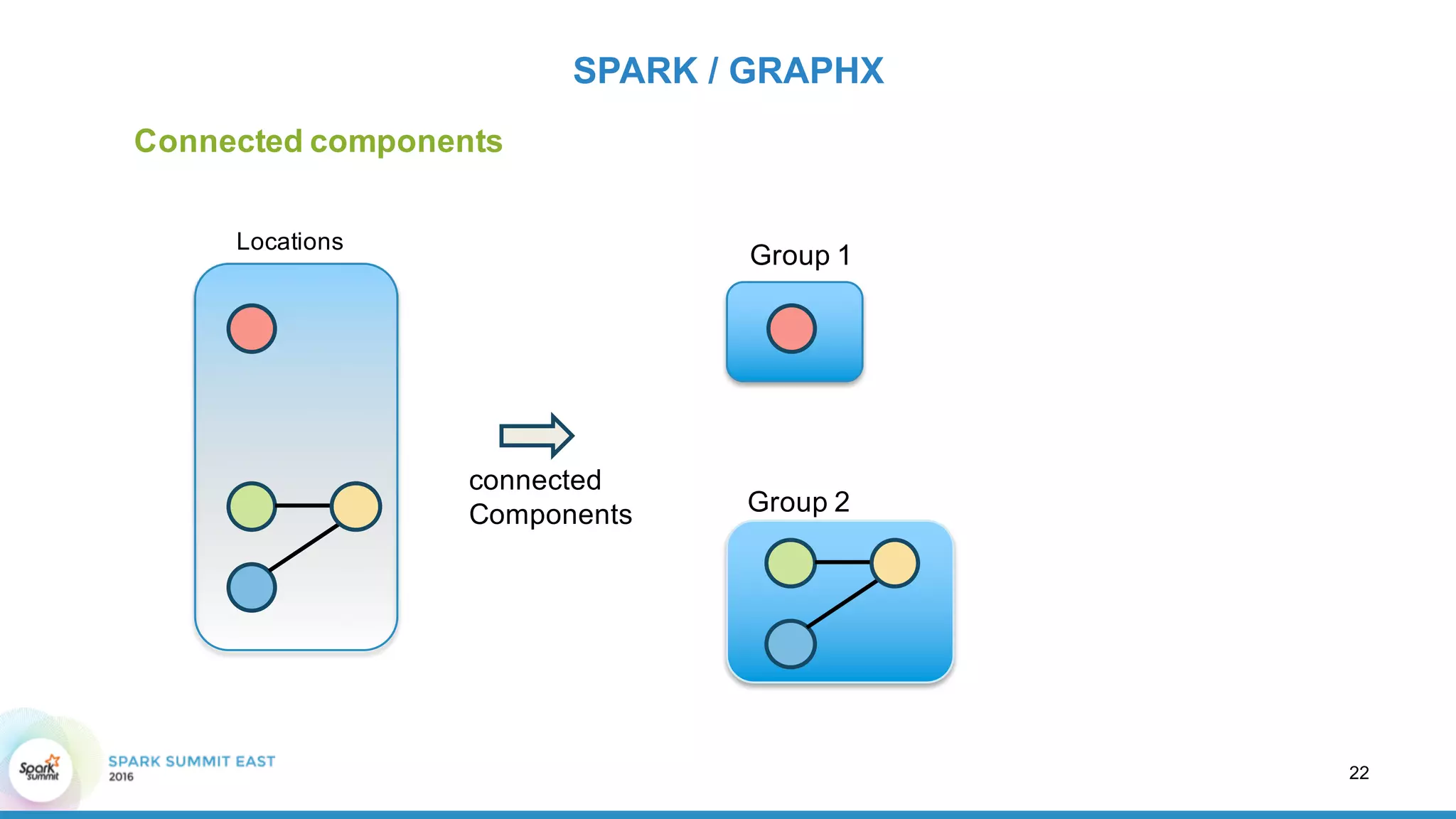
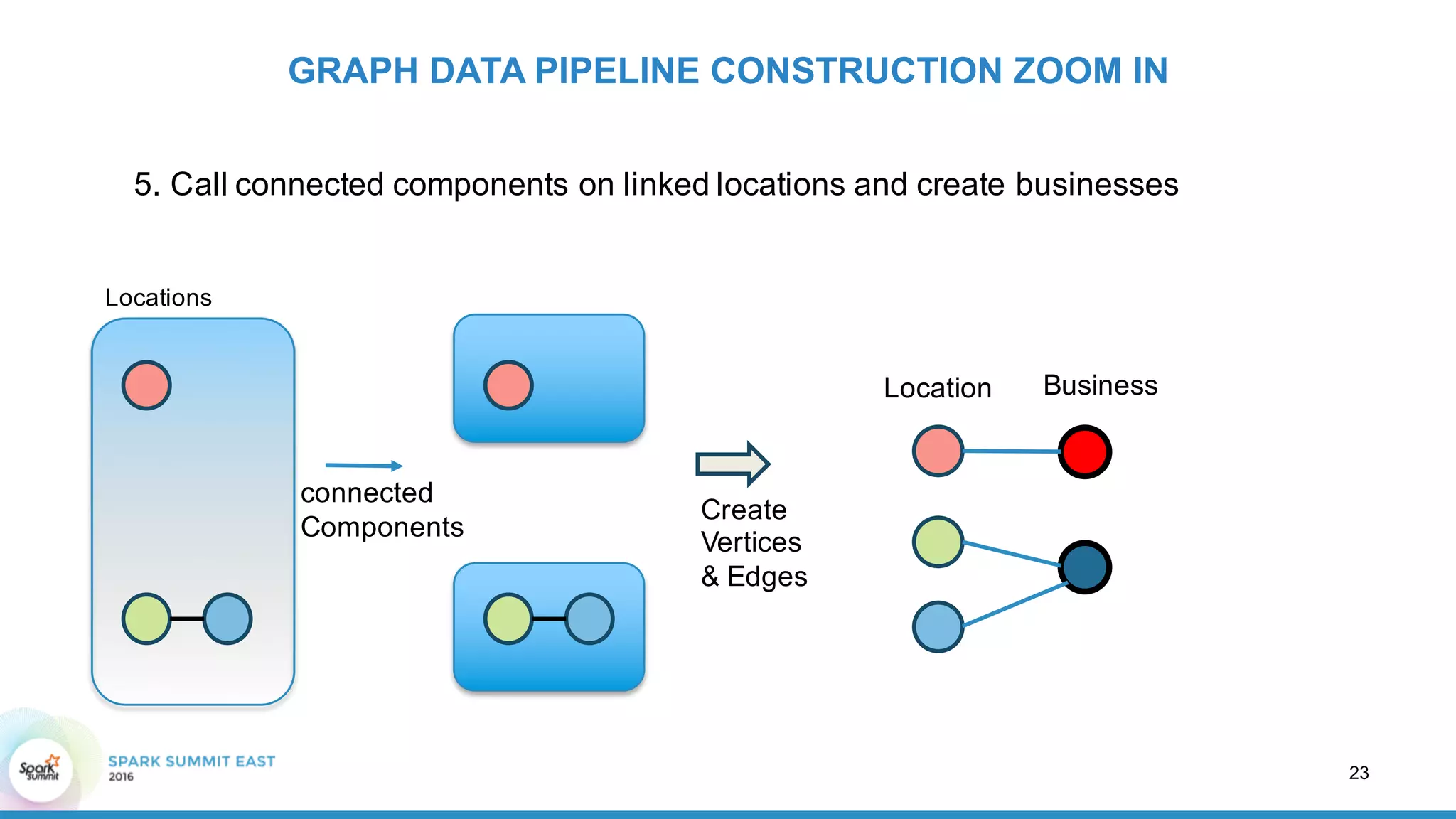
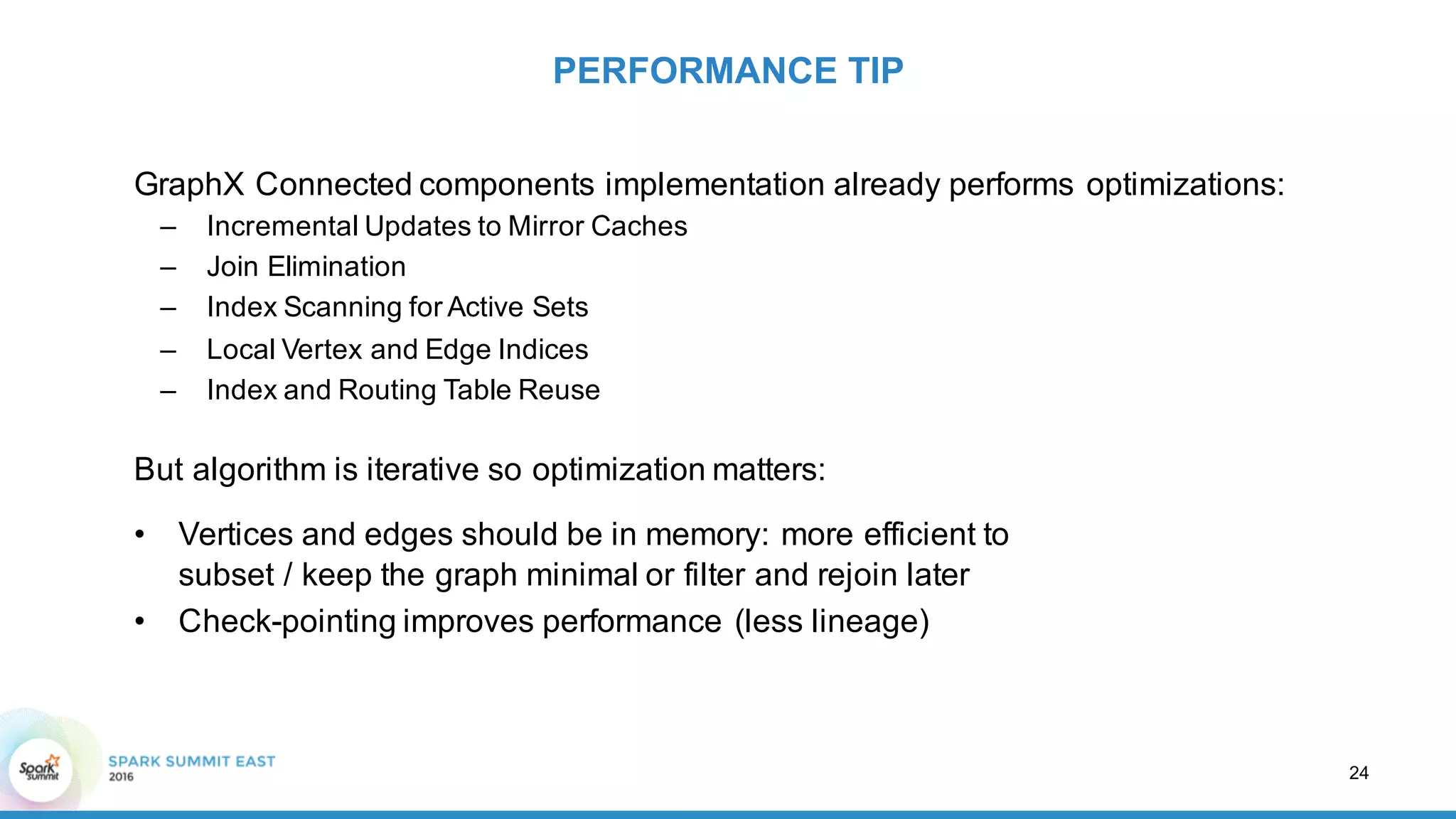
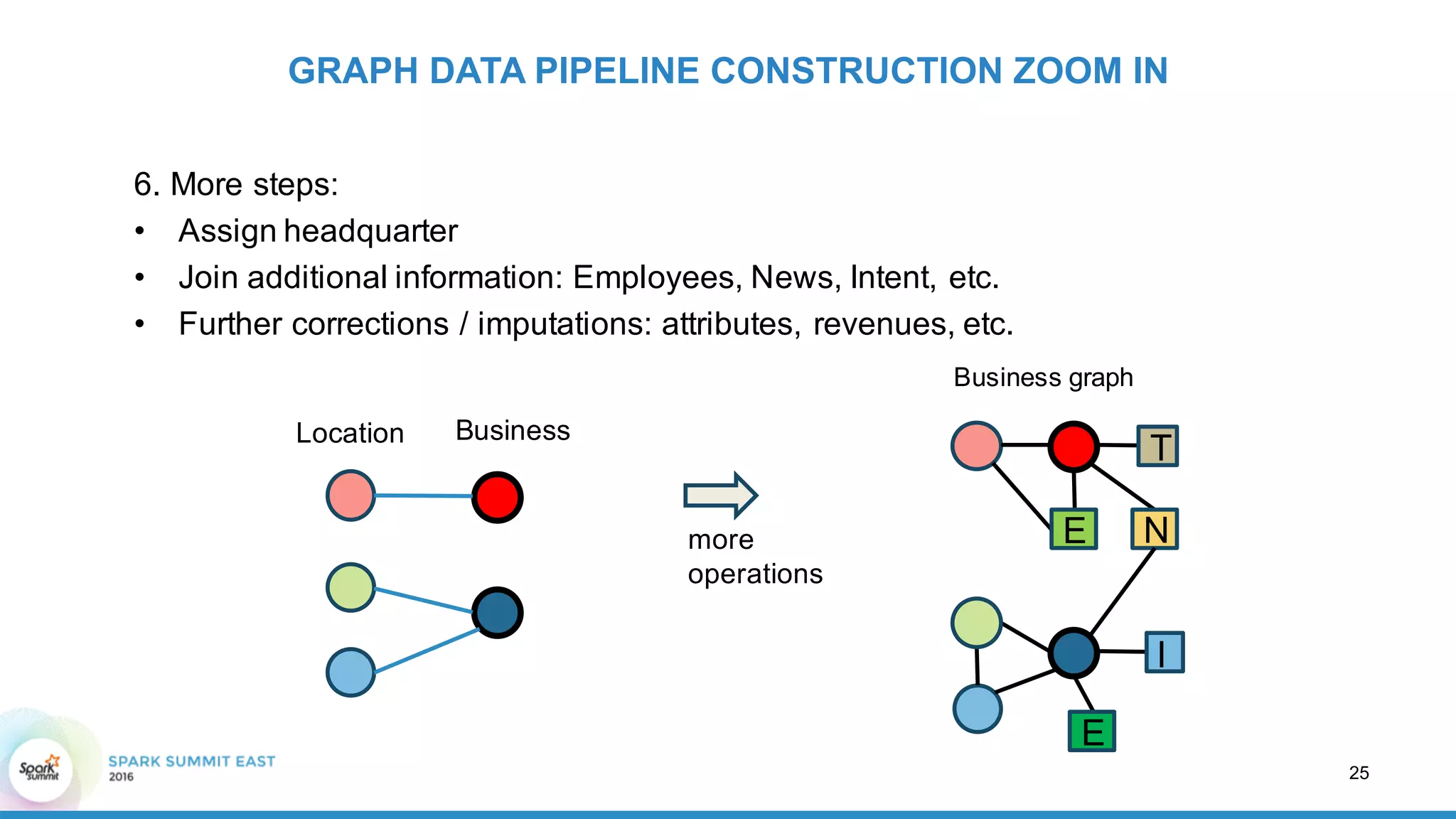
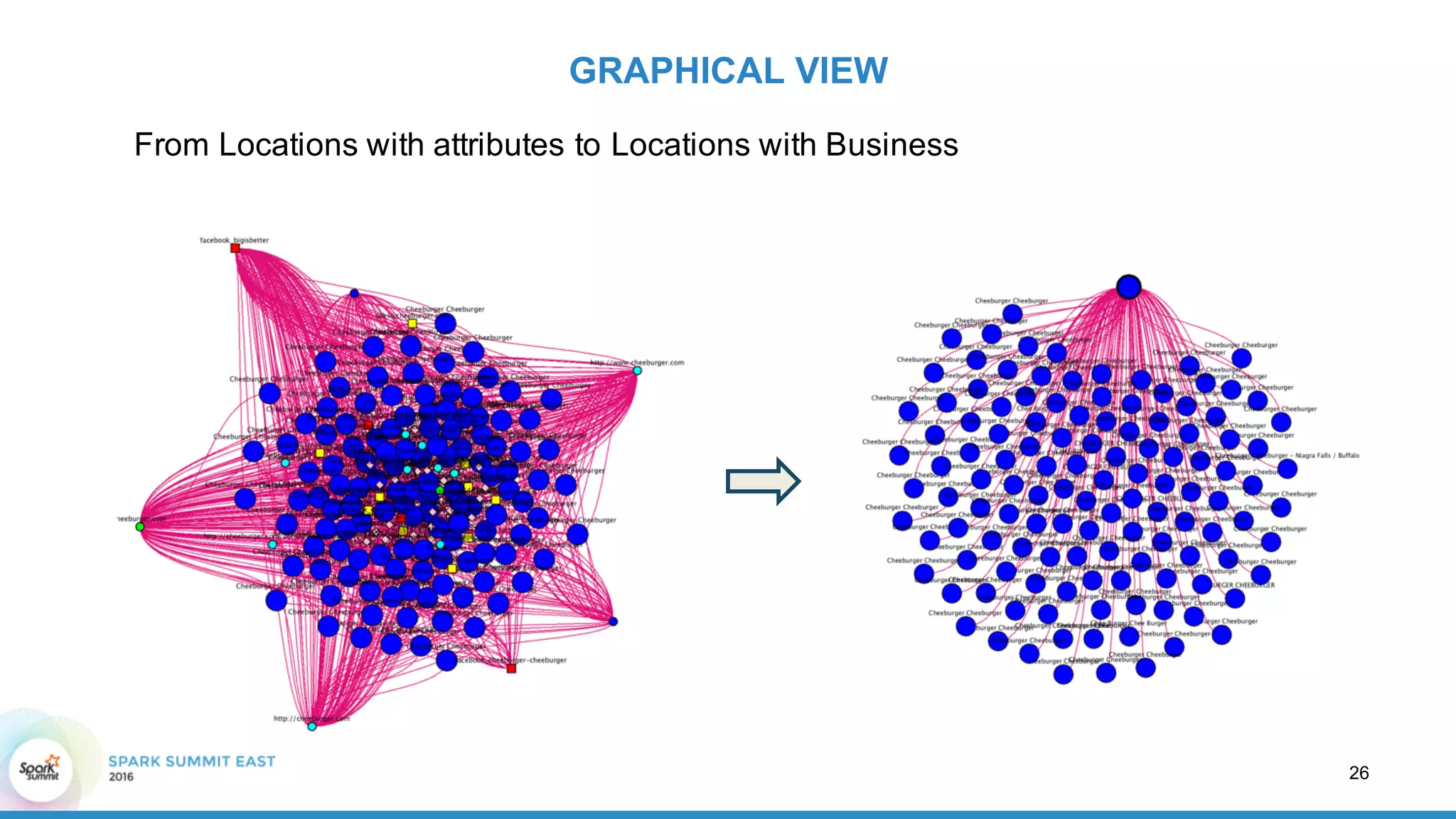
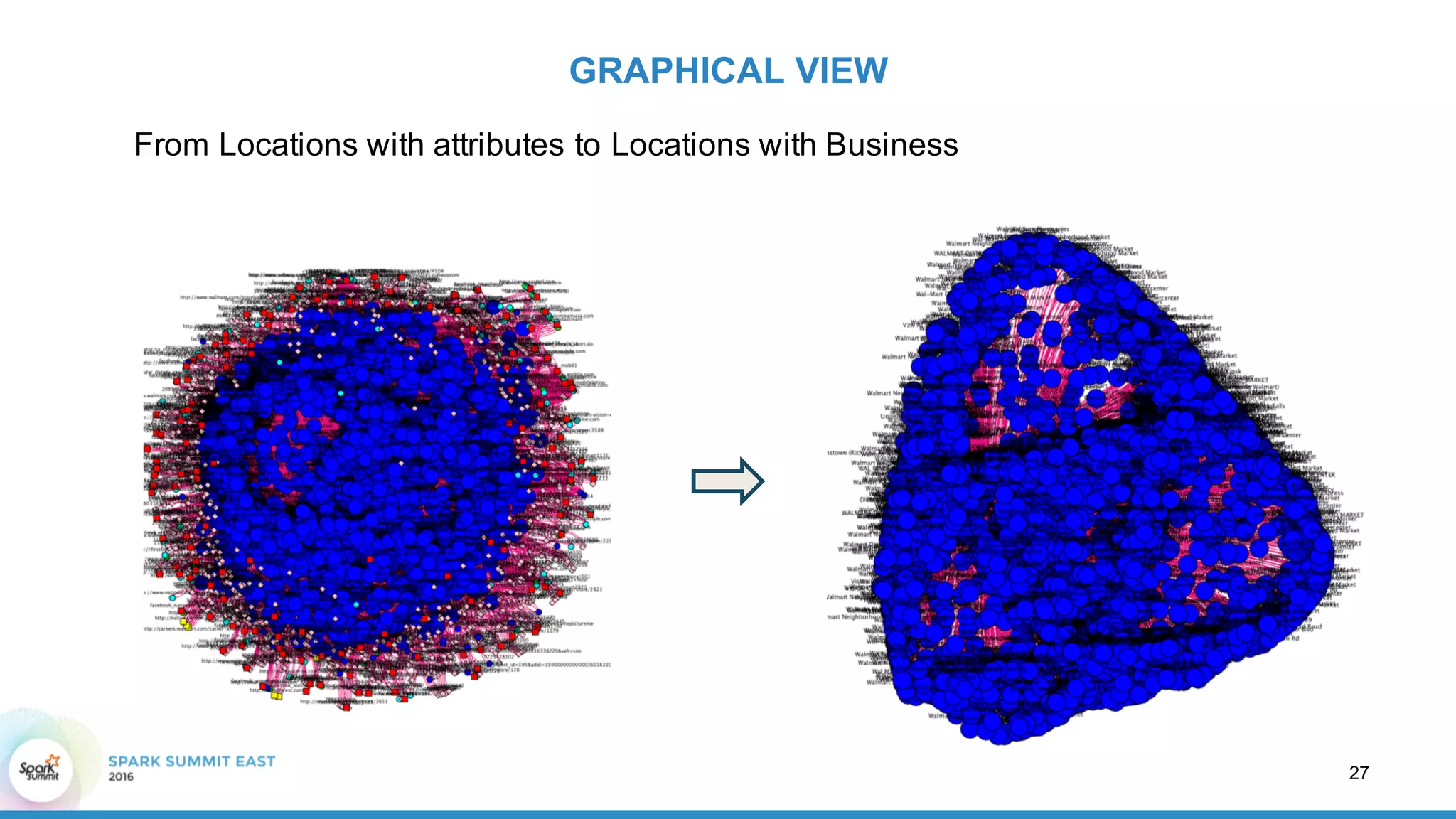
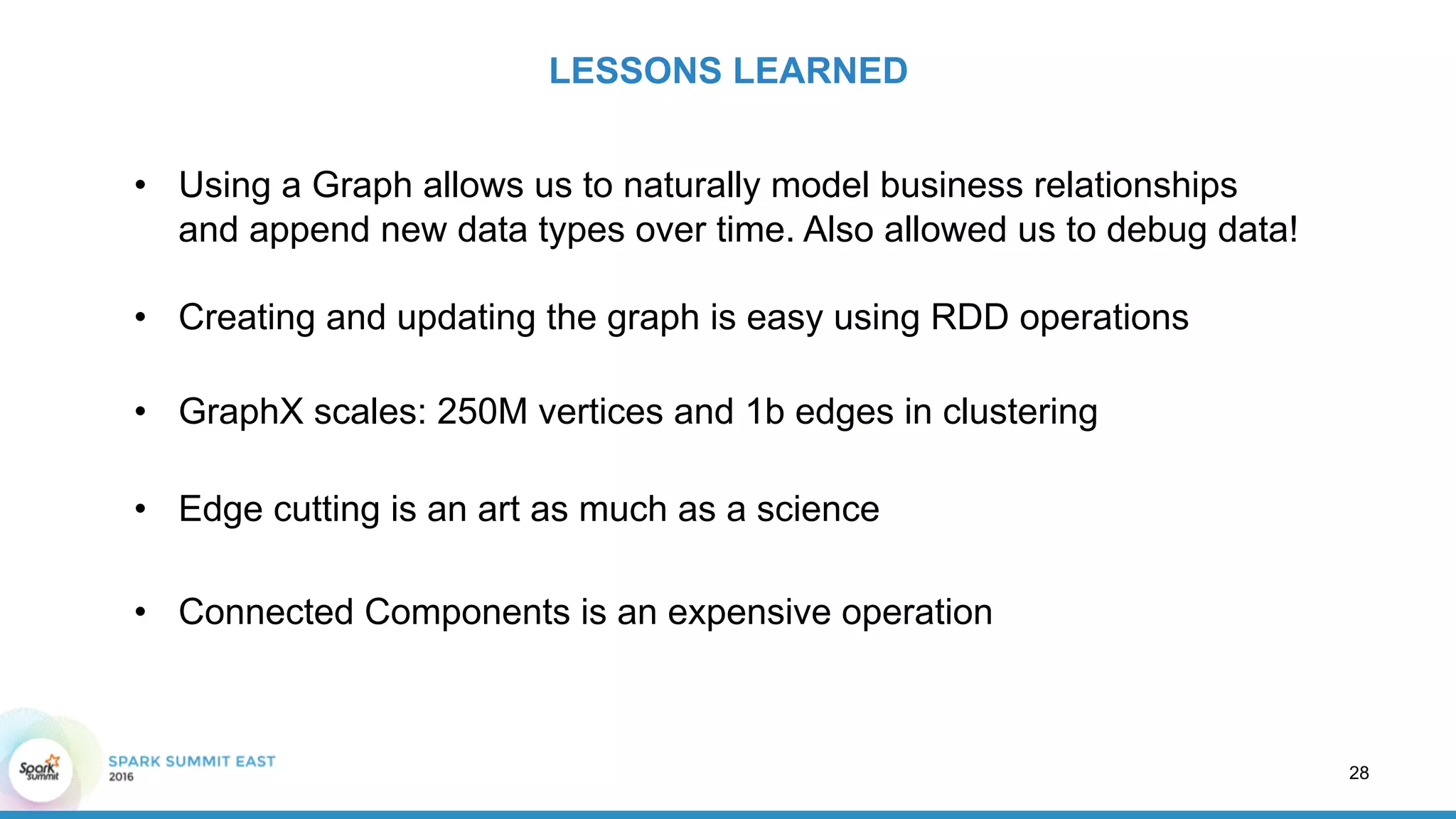
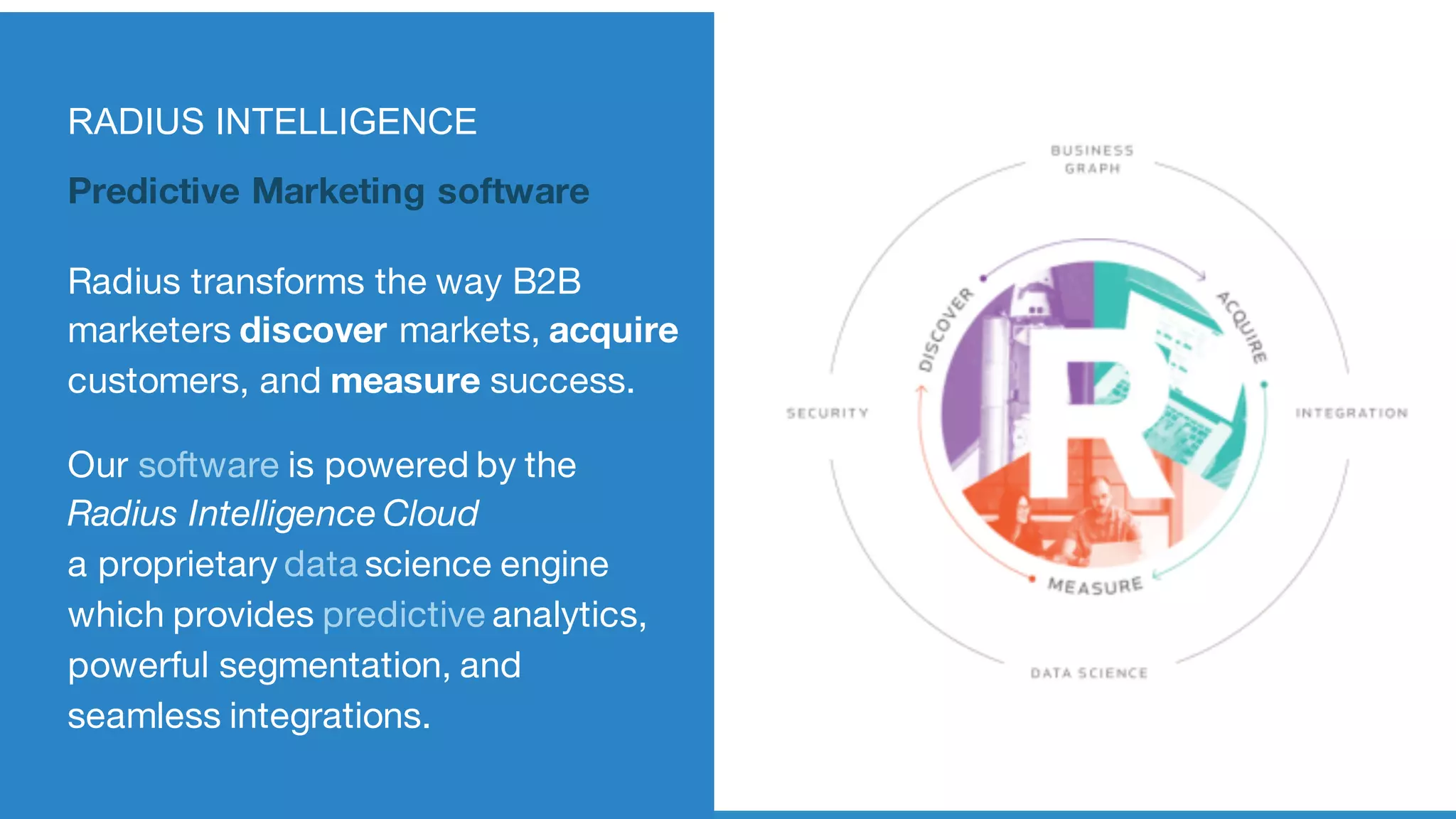
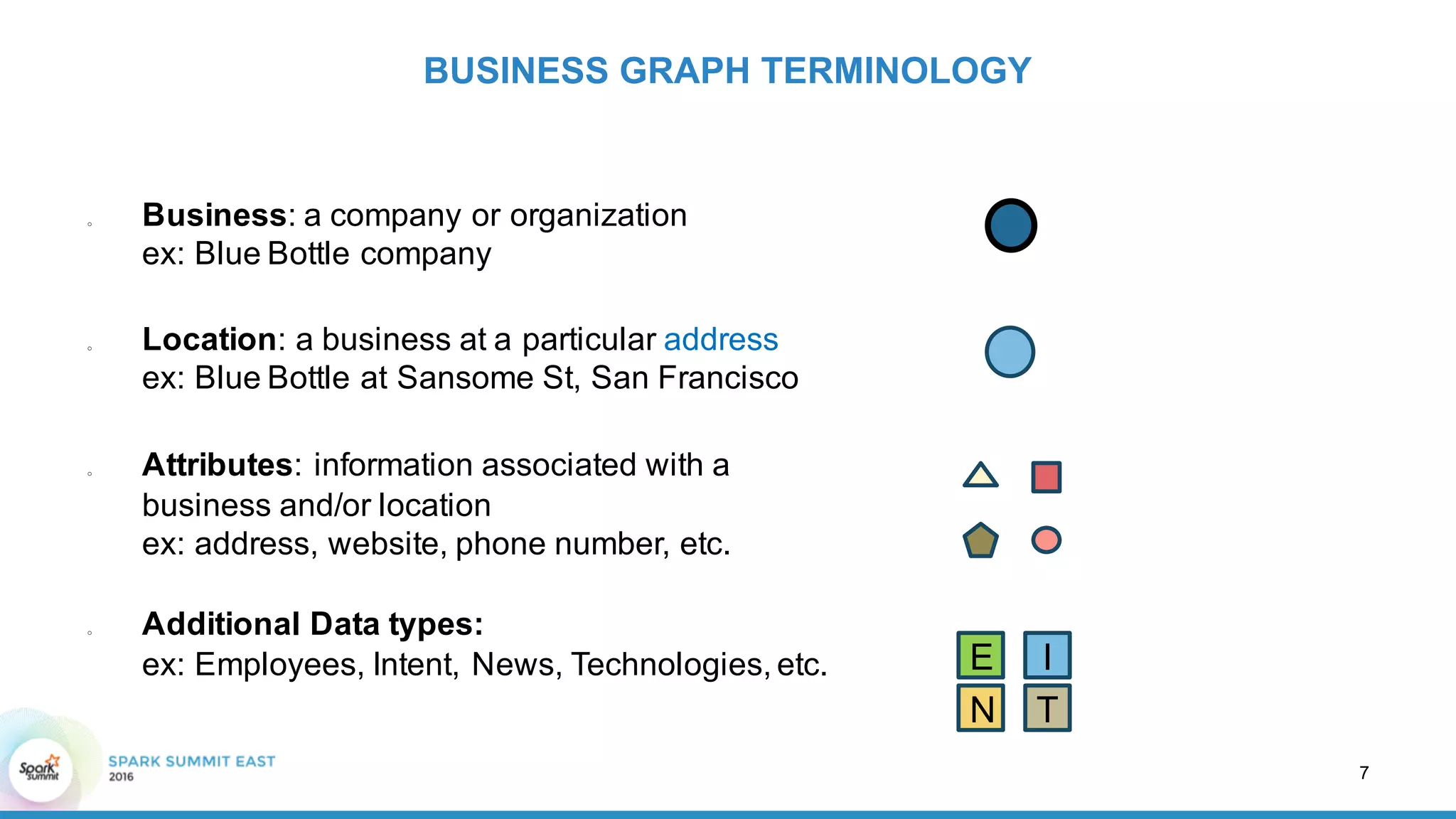
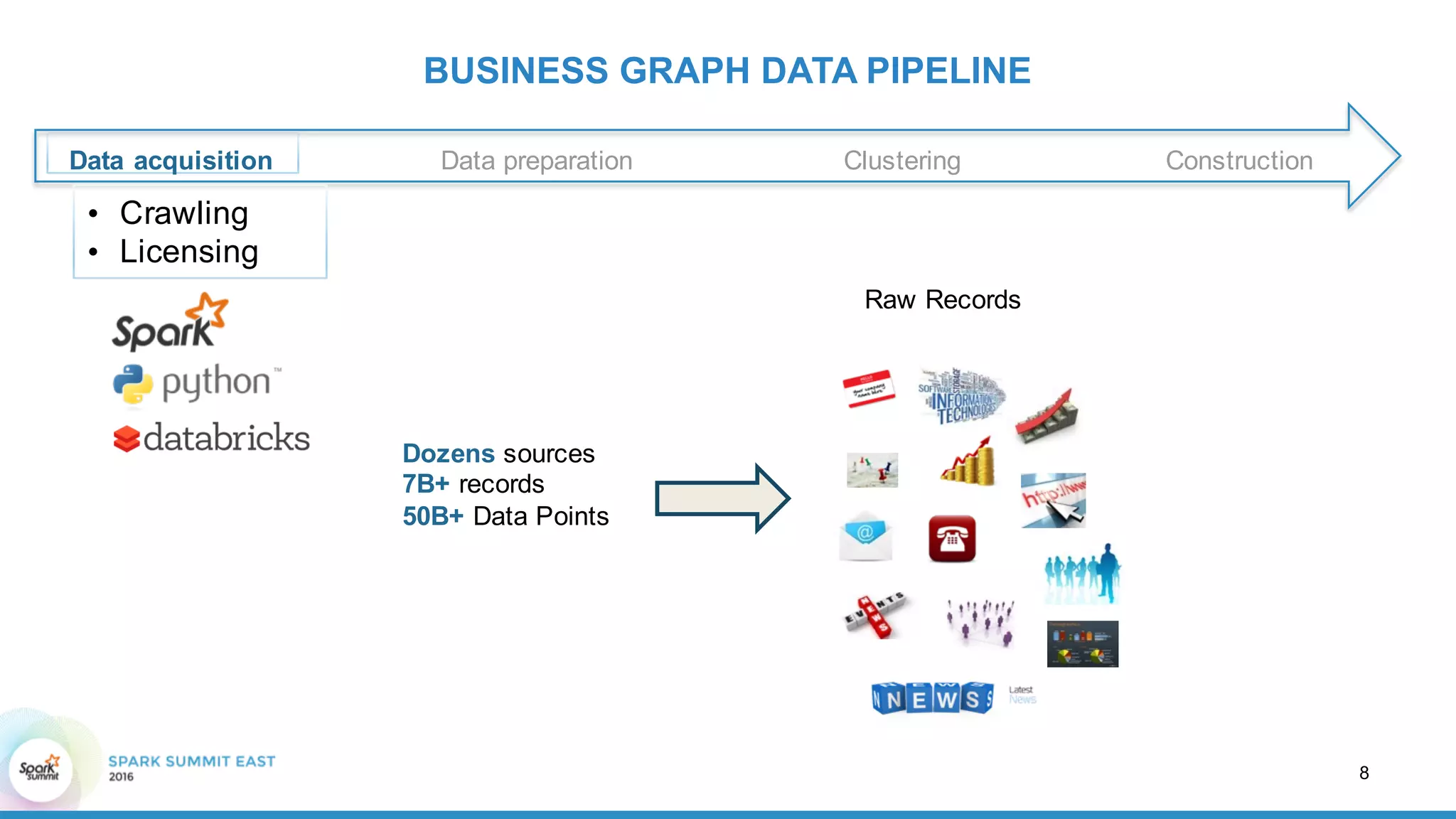
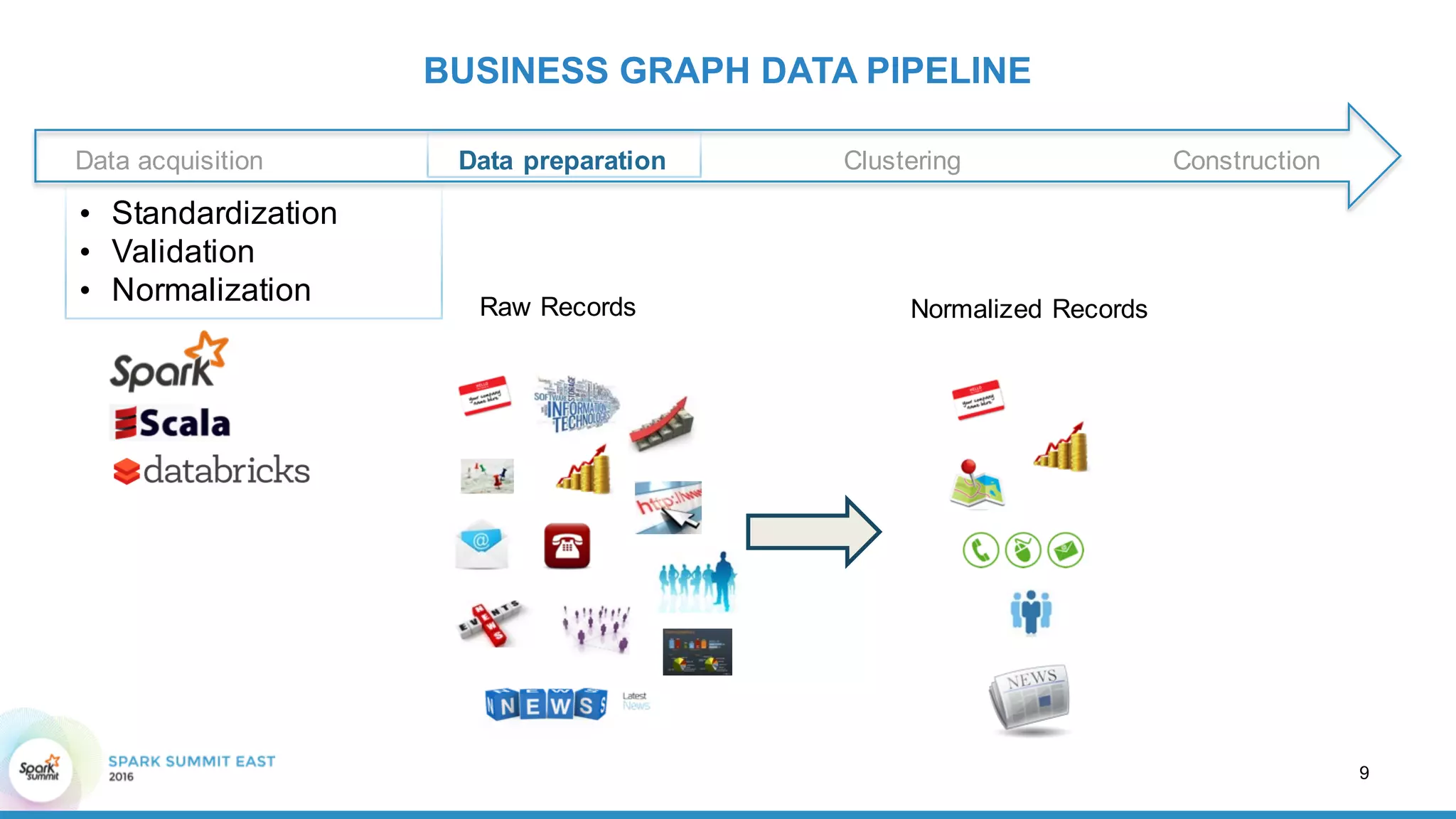
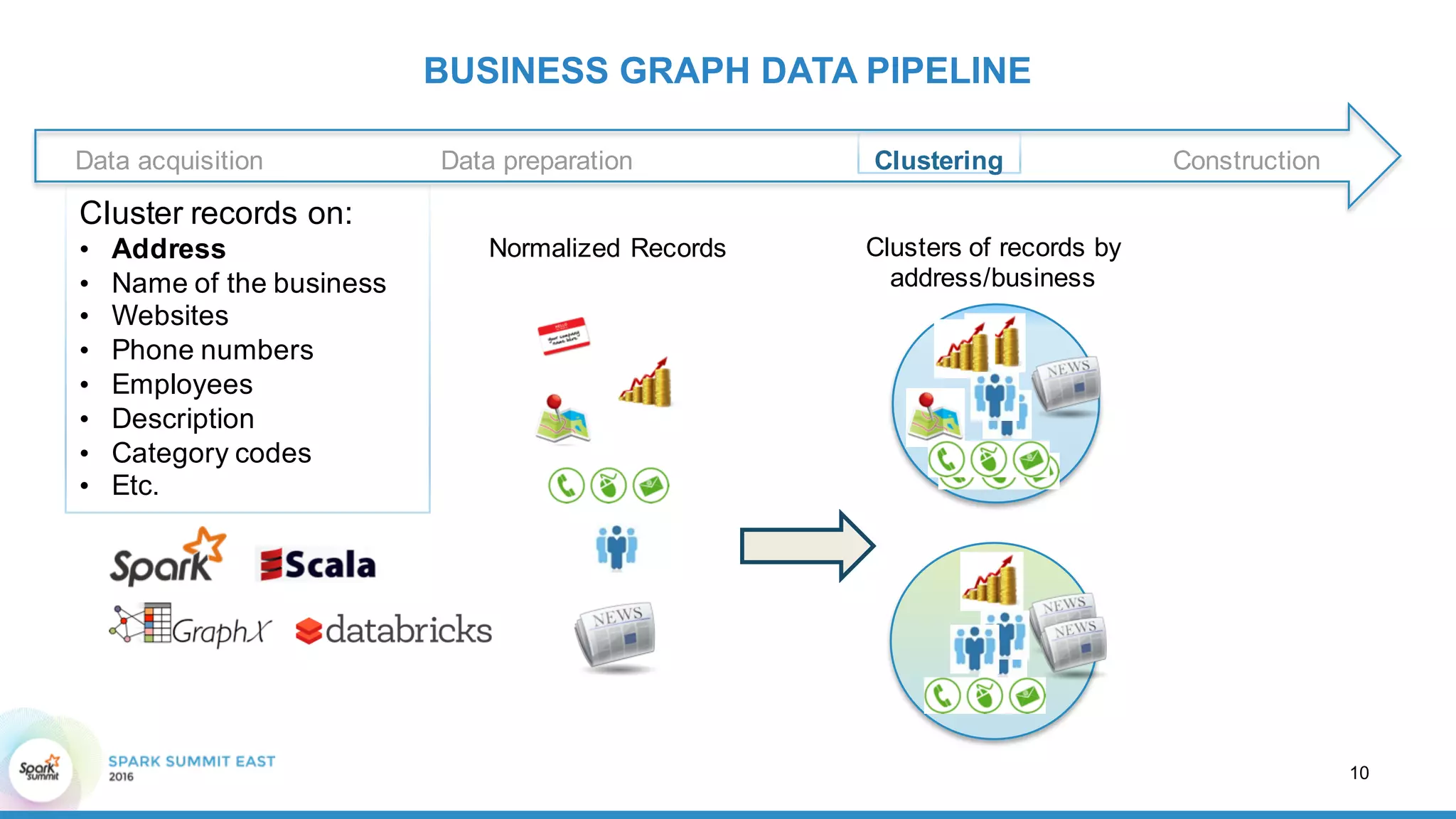
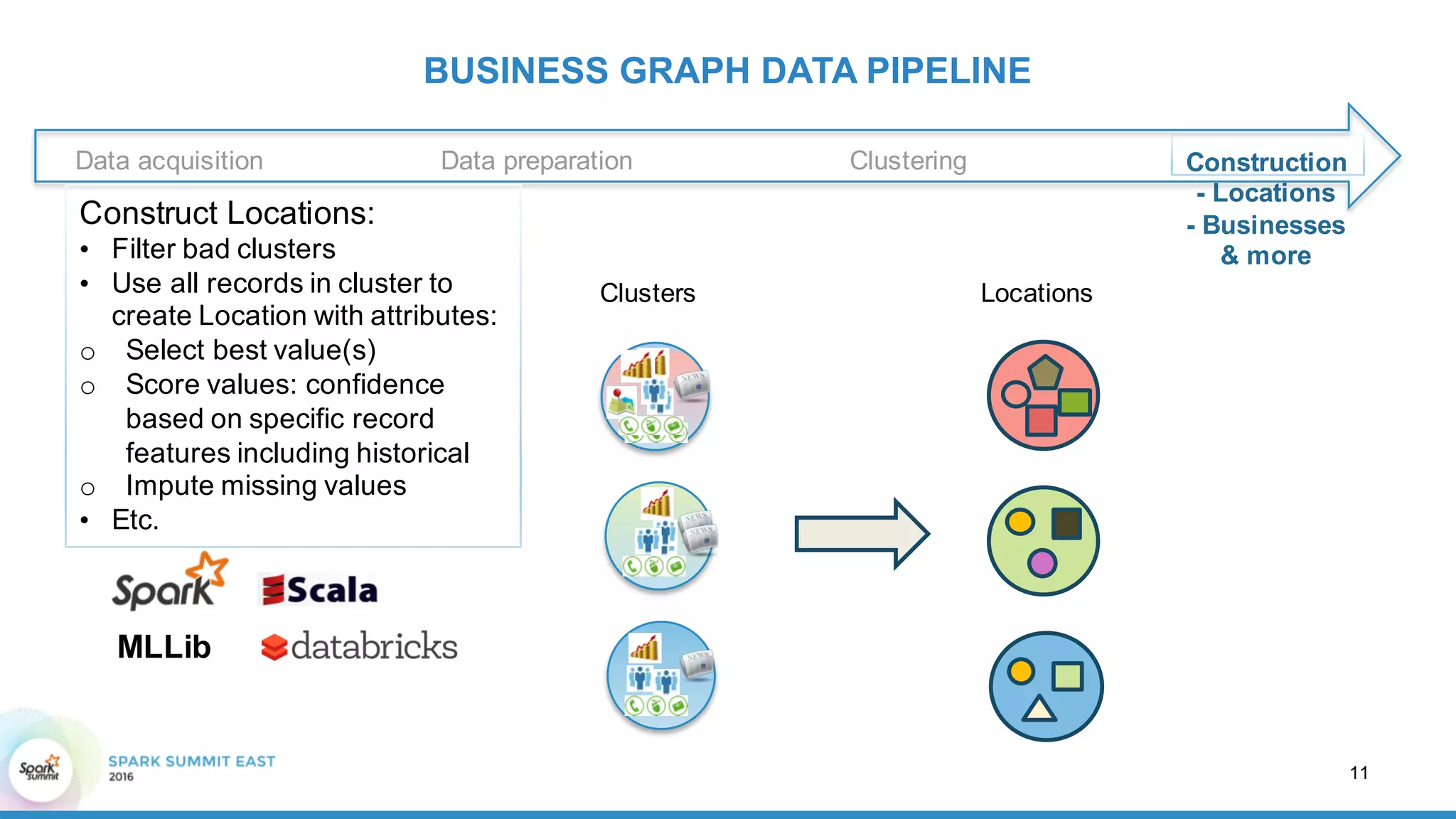
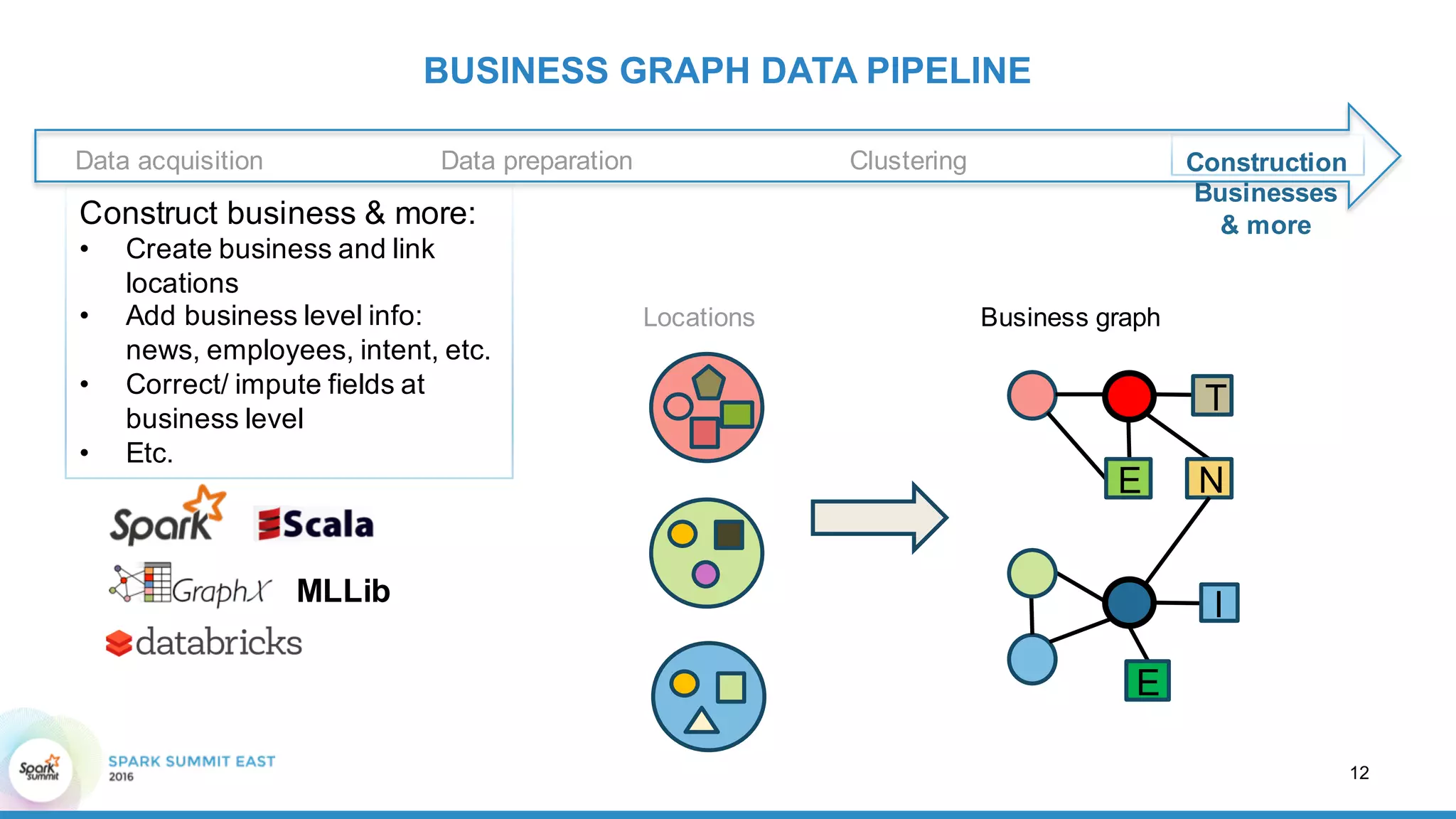
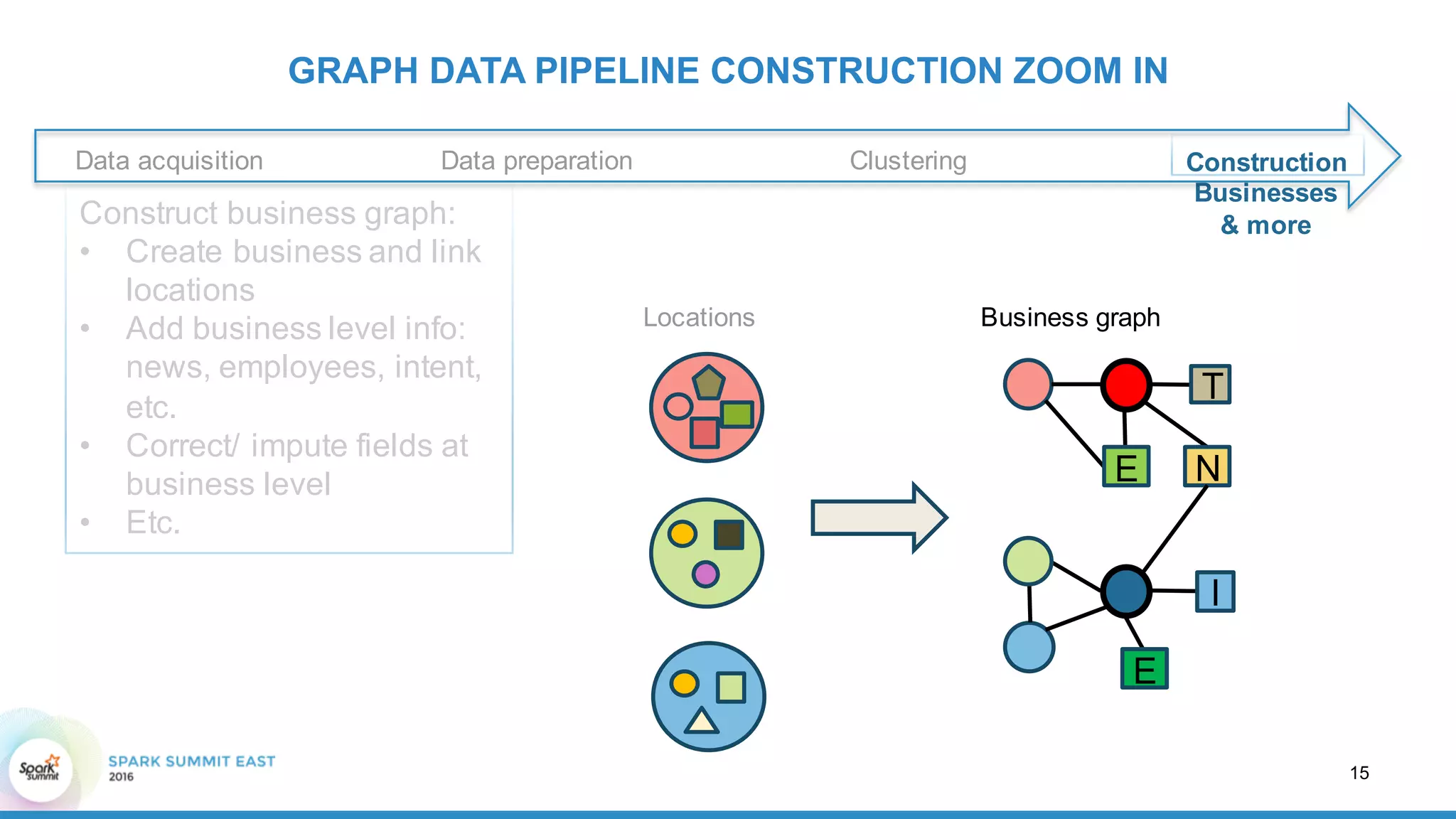
This document discusses building a graph of U.S. businesses using Spark technologies. It describes how Radius Intelligence builds a comprehensive business graph from multiple data sources by acquiring and preparing raw data, clustering records, and constructing the graph by linking business and location vertices and attributes through techniques like connected components analysis. Key lessons learned include that GraphX scales well, graph construction and updates are easy using RDD operations, and connected components analysis is an expensive graph operation.





![GraphX models a “property graph” which is an multi directed, attributed graph.
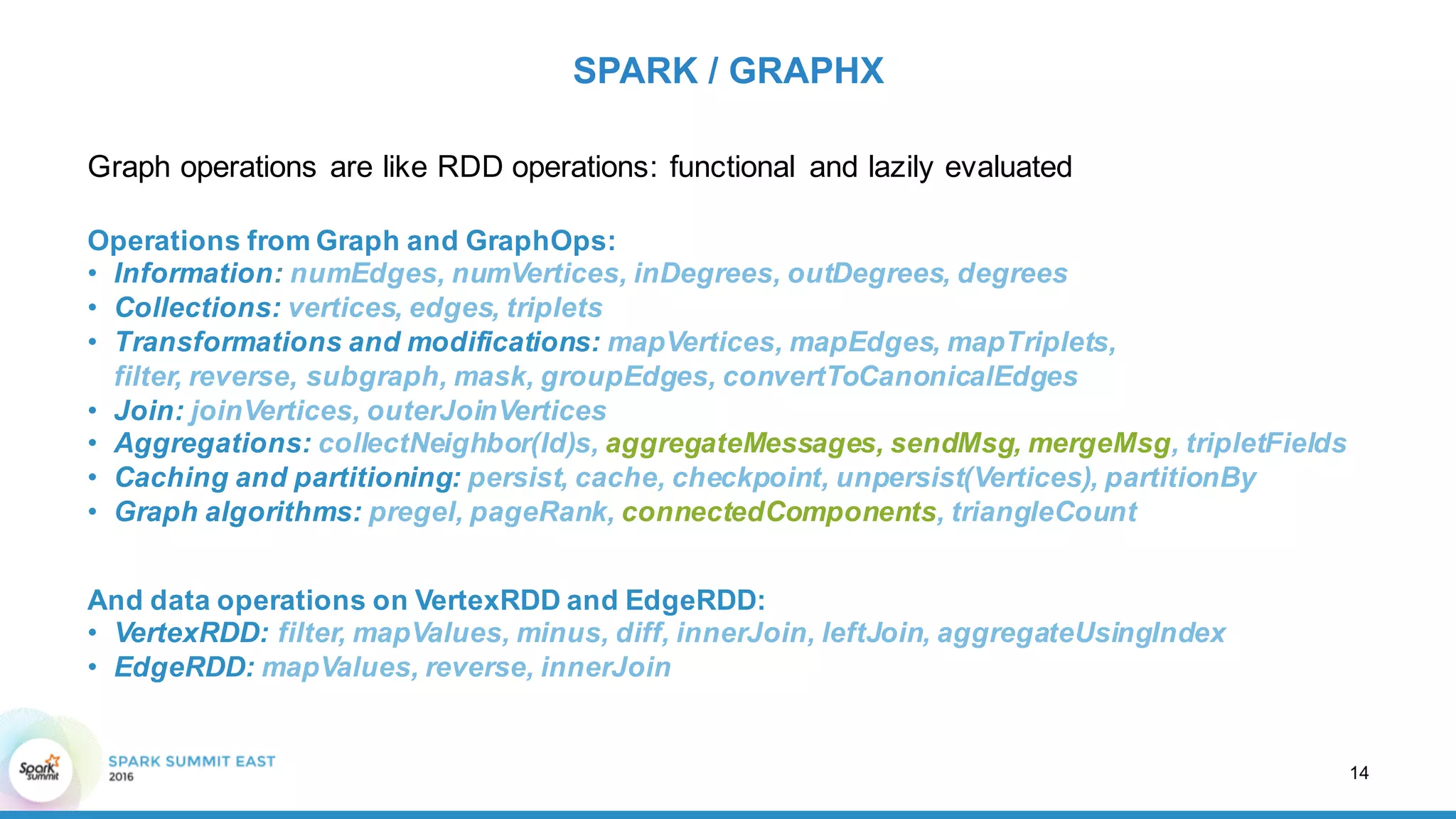
SPARK / GRAPHX
13
(1, Location) (2, Domain)
(1, 2, source1)
(3, Phone)
(1, 2, source2)
class Graph[VD, ED] {
val vertices: VertexRDD[VD]
val edges: EdgeRDD[ED]
val triplets: RDD[EdgeTriplet[VD, ED]]
}
VertexRDD[VD] extends RDD[(VertexID, VD)]
EdgeRDD[ED] extends RDD[Edge[ED]]
VD - Vertex data attribute type
ED - Edge data attribute type](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6gbalexisroos-160224014843/75/Building-a-Graph-of-all-US-Businesses-Using-Spark-Technologies-by-Alexis-Roos-13-2048.jpg)
![1. Create vertex for each location and each known business
GRAPH DATA PIPELINE CONSTRUCTION ZOOM IN
16
VertexRDD[Location]
Clusters
map
VertexRDD[Business]
Curated list
map](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6gbalexisroos-160224014843/75/Building-a-Graph-of-all-US-Businesses-Using-Spark-Technologies-by-Alexis-Roos-16-2048.jpg)