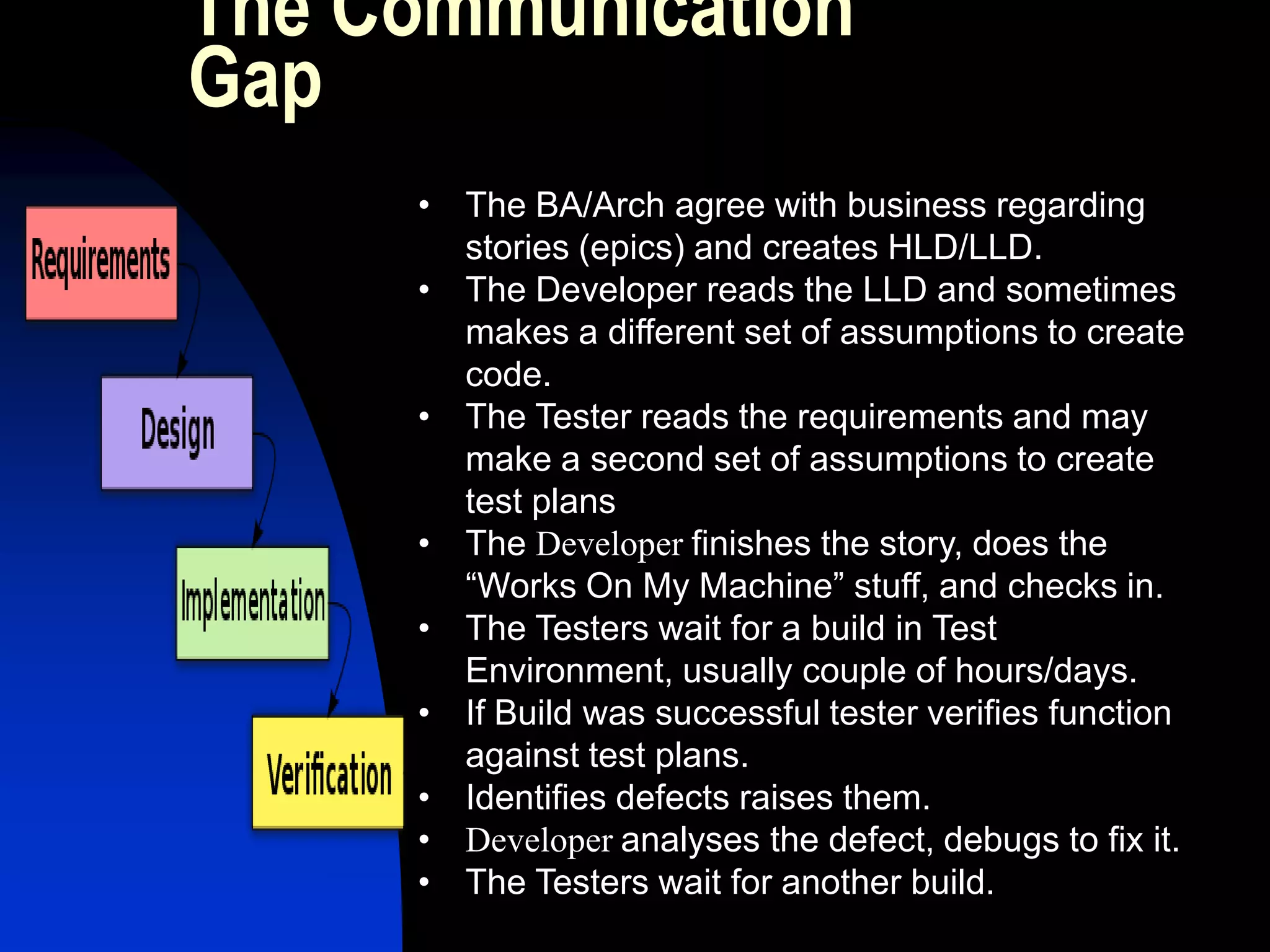
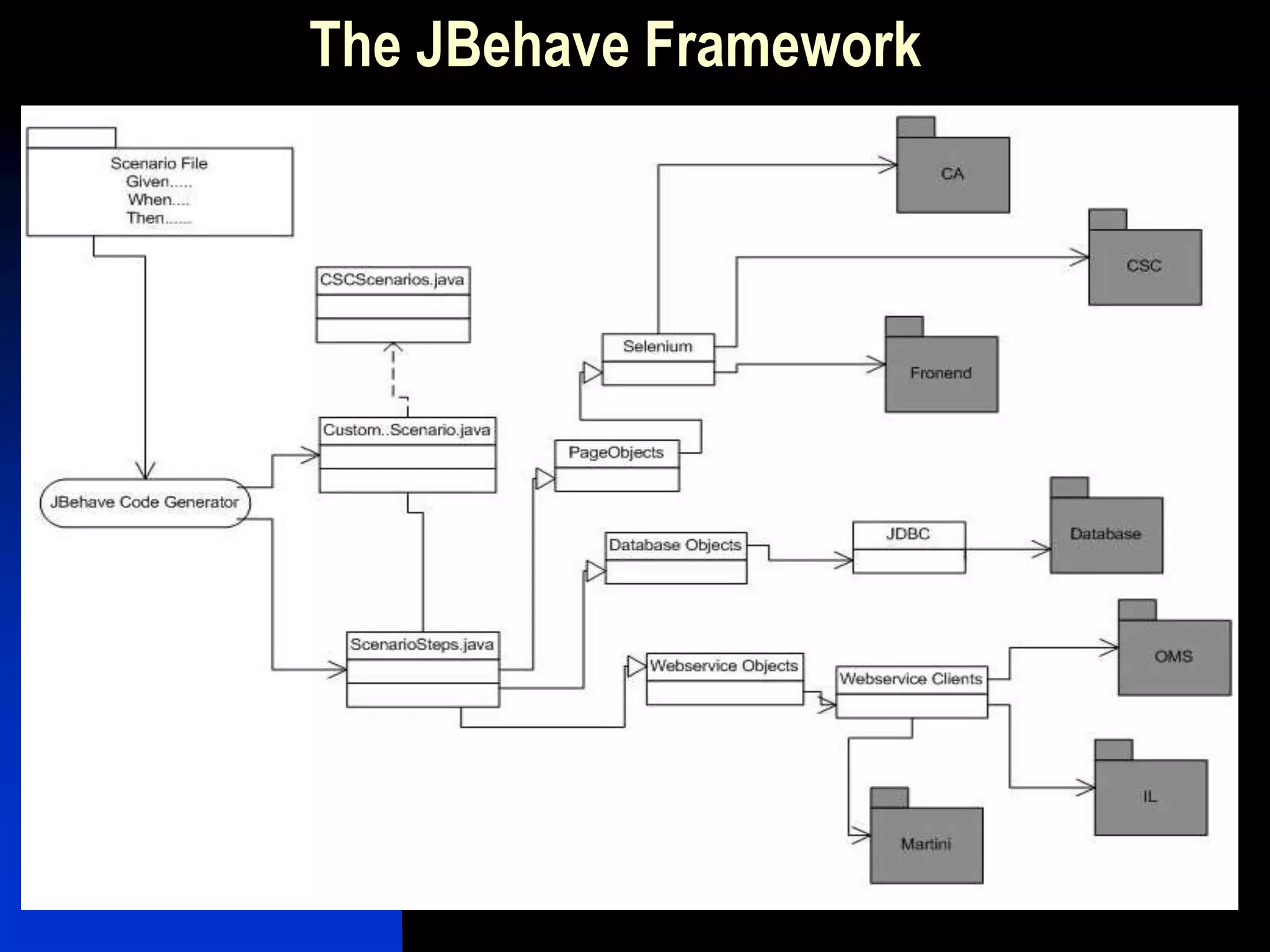
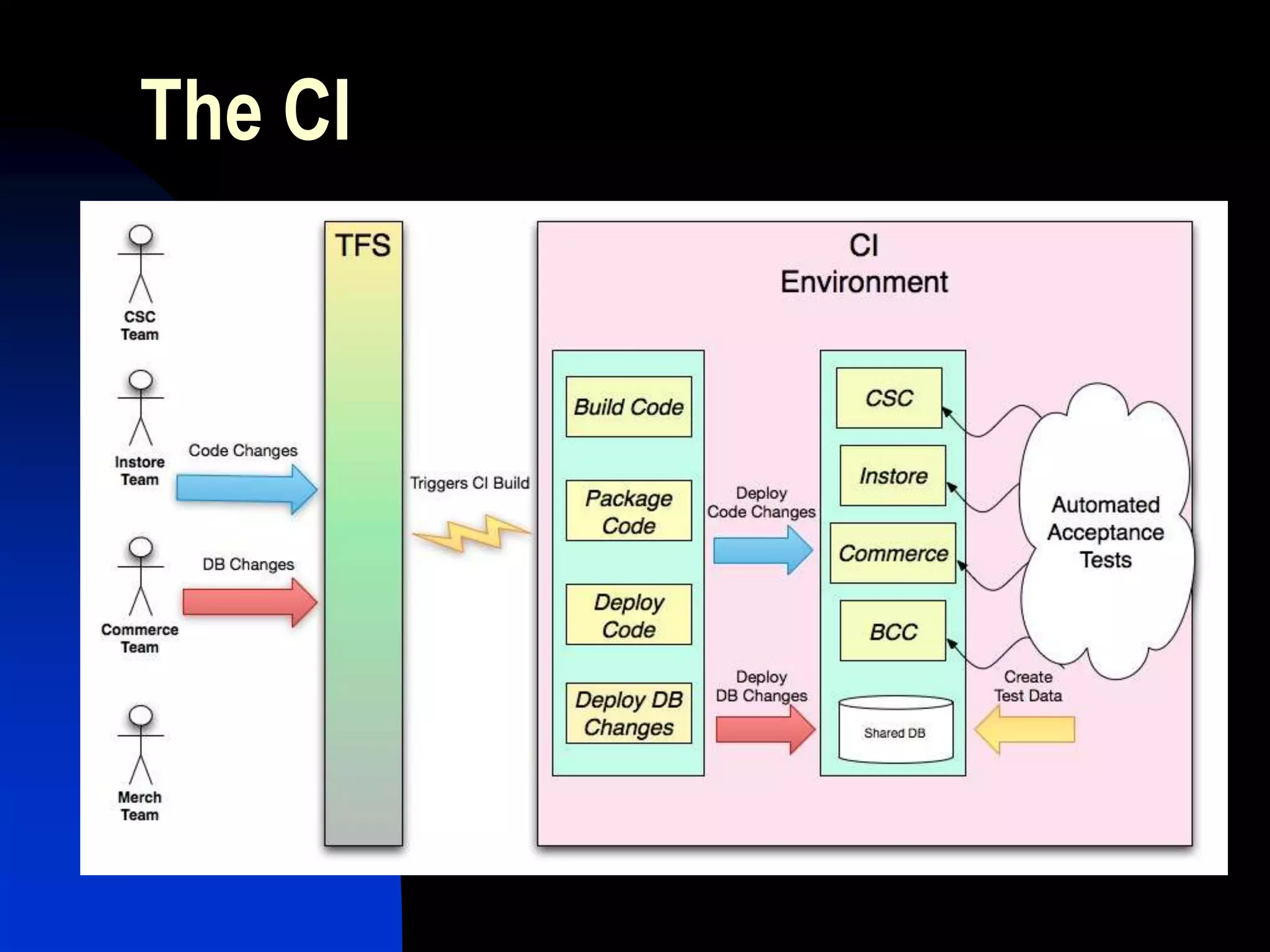
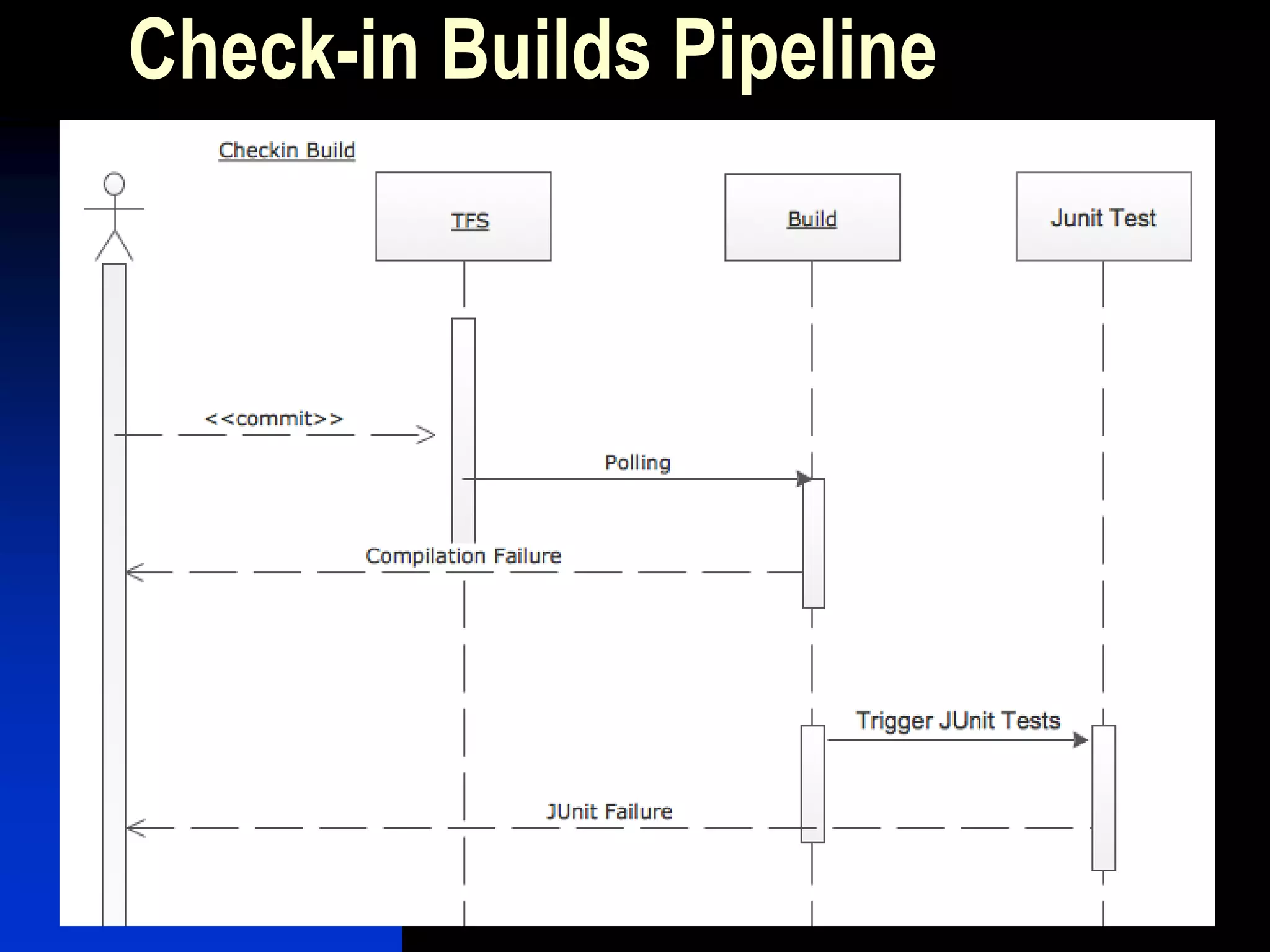
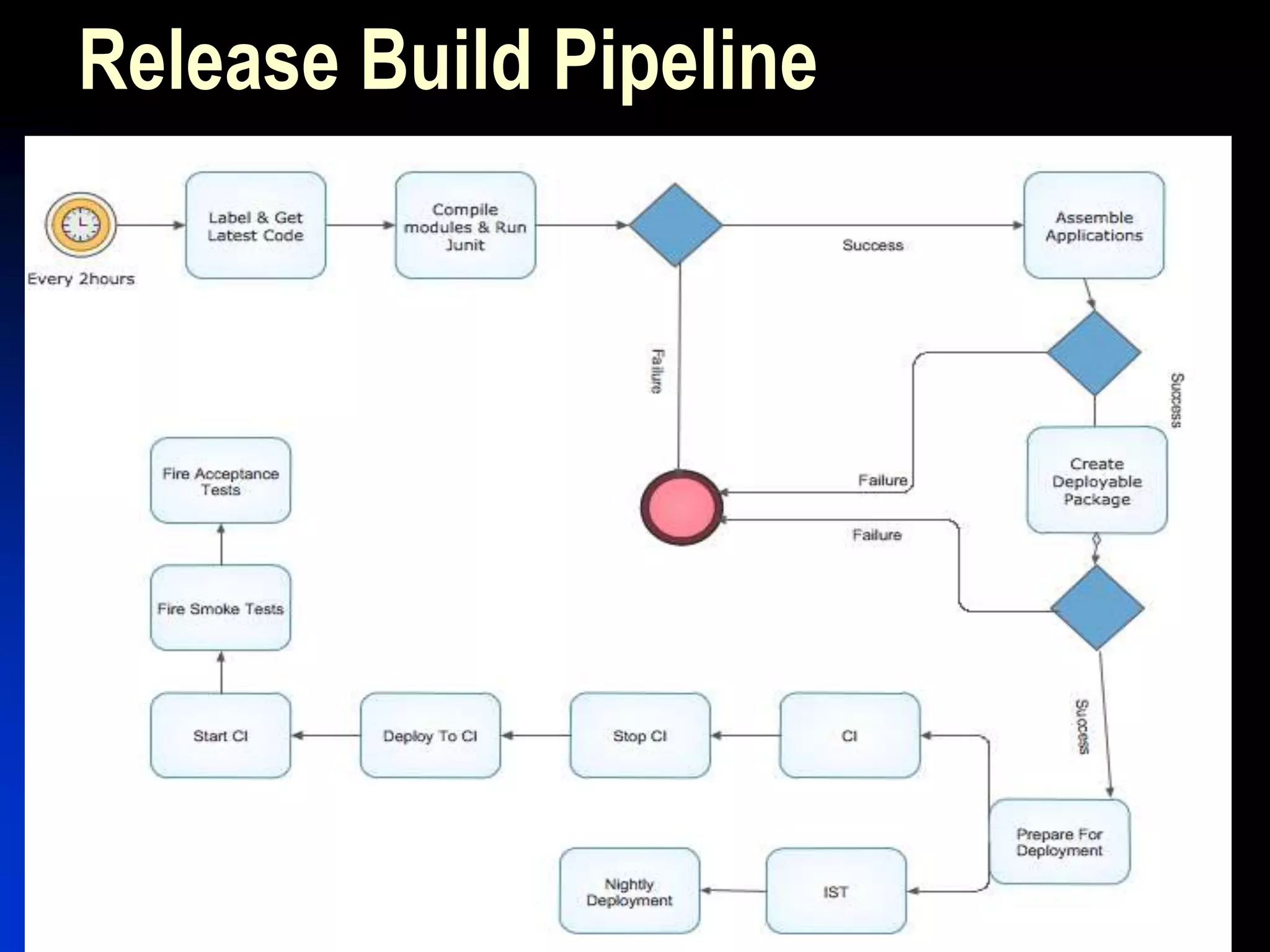
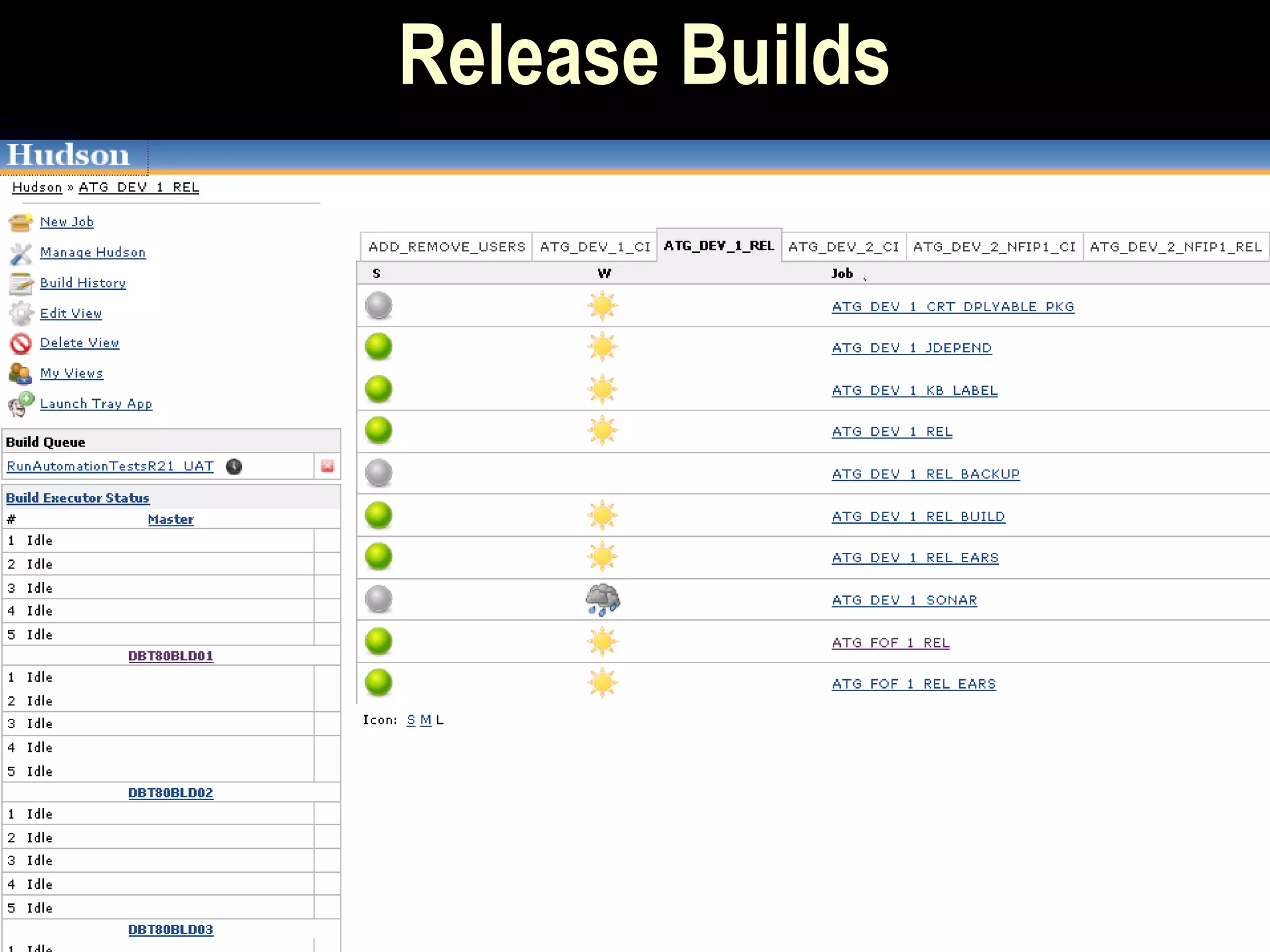
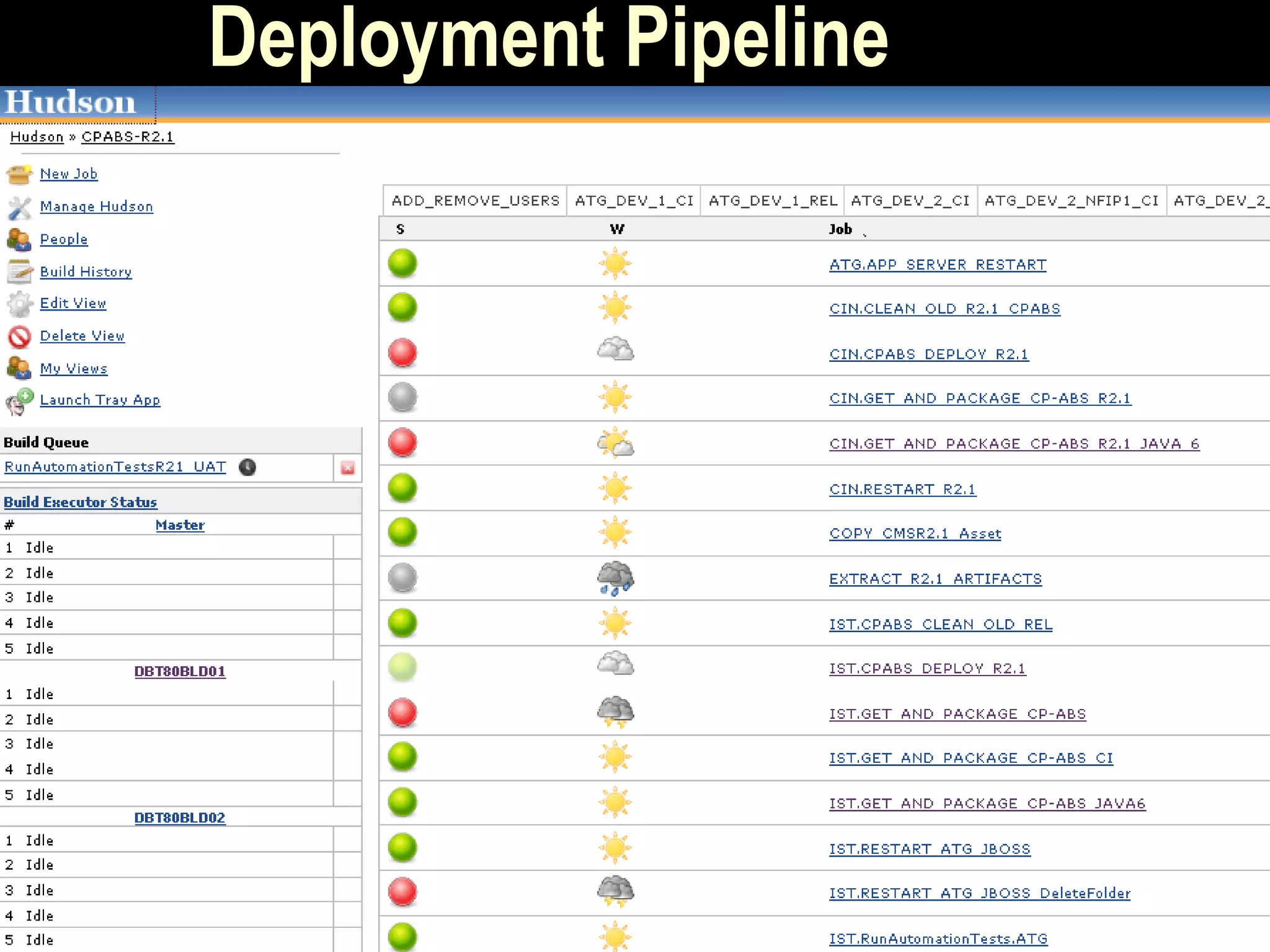
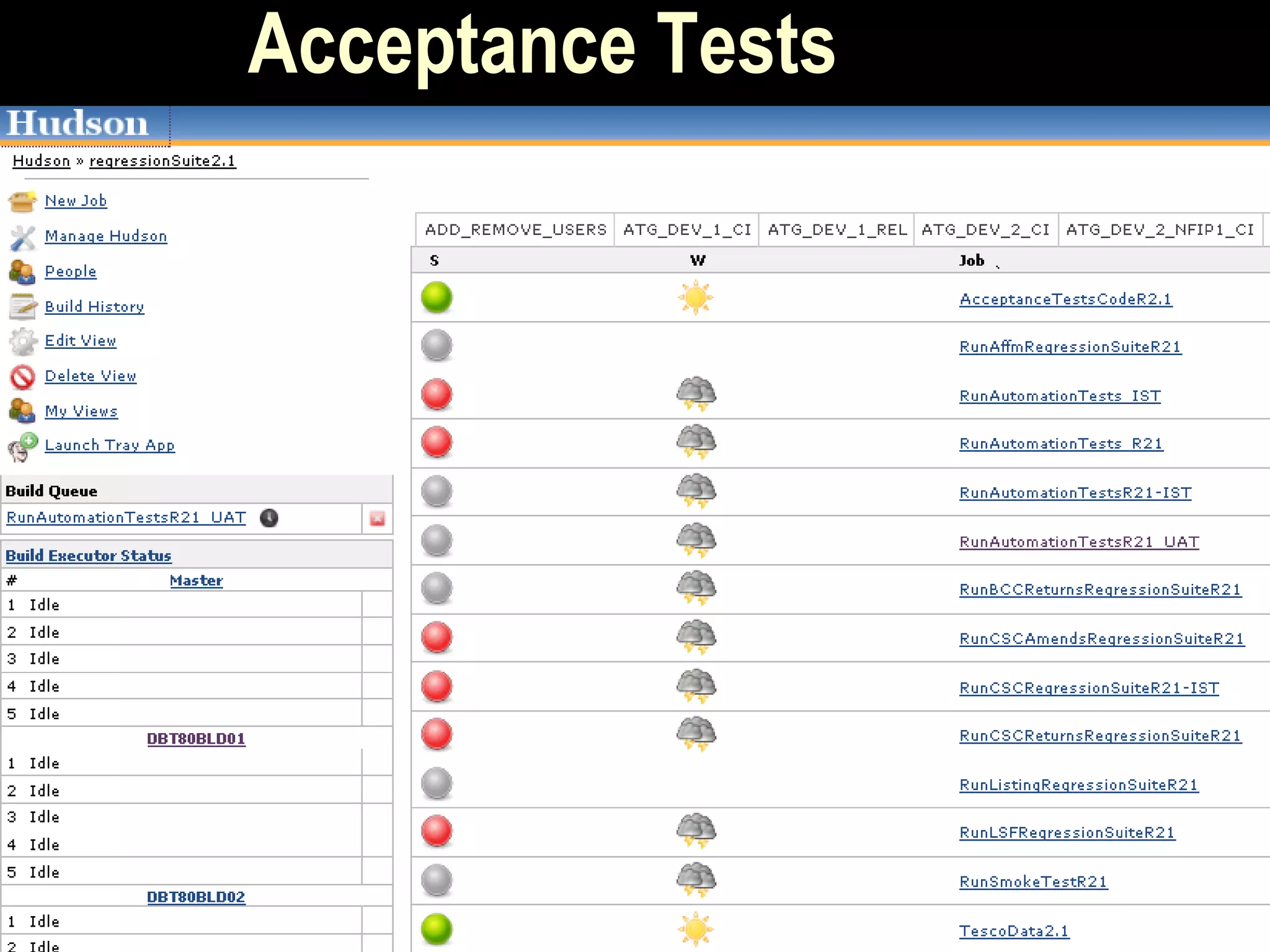
The document presents a case study on bridging communication gaps and achieving continuous delivery in a UK retailer. It discusses the issues arising from miscommunication among stakeholders during the development and testing phases and outlines a solution focused on collaboration, a shared vocabulary, and the use of automated testing tools like JBehave and Mockito. The results achieved include quicker feedback, clearer requirements communication, and alignment between business and engineering teams.