This document describes Bloom filters, which provide an approximate and space-efficient way to check for set membership. A Bloom filter uses a bit array and k independent hash functions to represent a set S of m elements from a universe U. To check if an element x is in S, its k hash values are checked in the bit array - if any are 0, x is definitely not in S, but if all are 1, x is assumed to be in S, allowing for false positives. The probability of a false positive can be minimized by optimizing the number of hash functions k to be ln(2)*(n/m), where n is the size of the bit array. When optimized, a Bloom filter provides an efficient randomized



![Bloom filters
Consist of an arrays A[n] of n bits (space) , and k
independent random hash functions
h1,…,hk : U --> {0,1,..,n-1}
1. Initially set the array to 0
2. sS, A[hi(s)] = 1 for 1 i k
(an entry can be set to 1 multiple times, only the first
times has an effect )
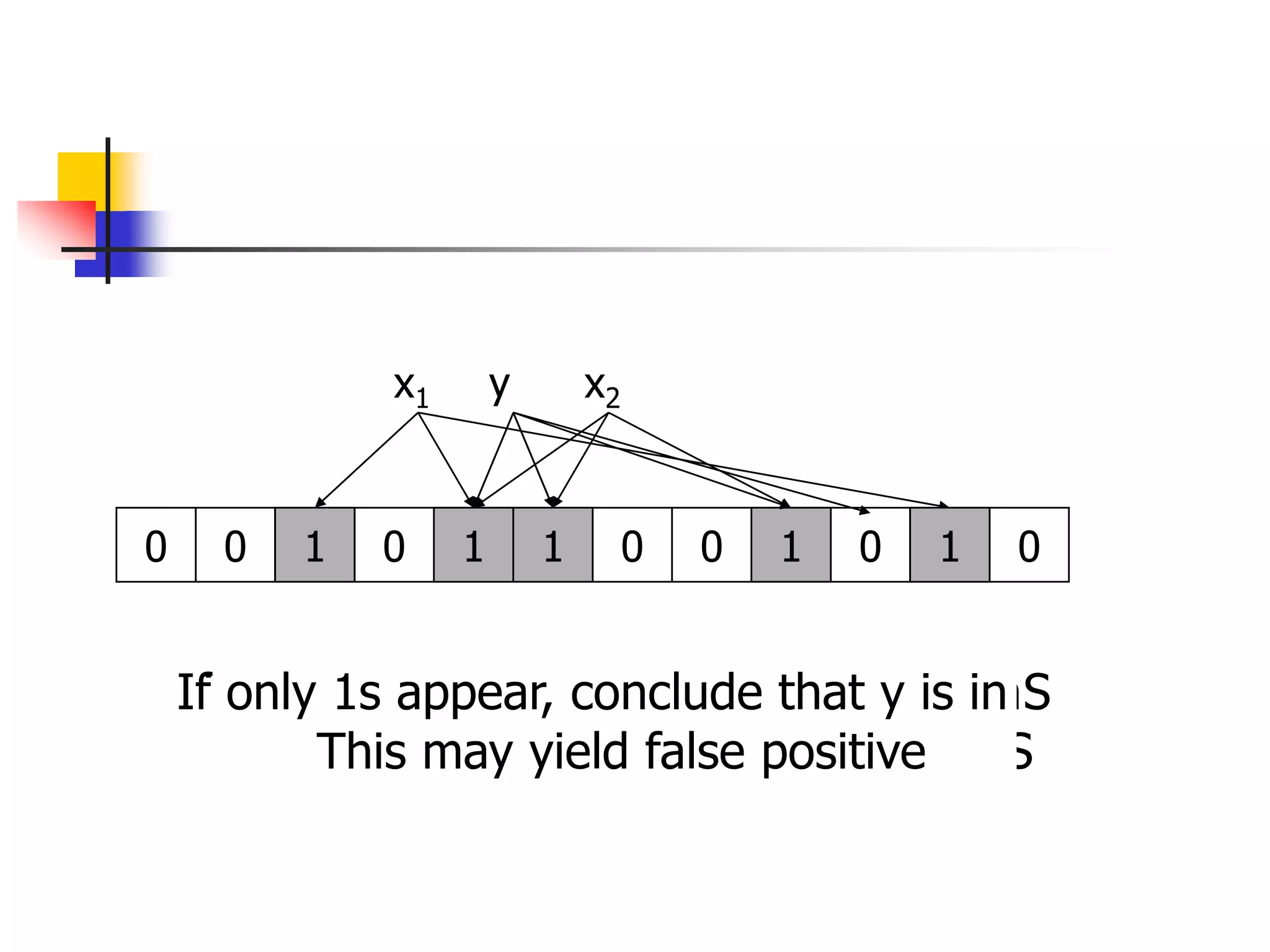
3. To check if xS , we check whether all location
A[hi(x)] for 1 i k are set to 1
If not, clearly xS.
If all A[hi(x)] are set to 1 ,we assume xS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bloomfilter-221226091738-b82799b7/75/bloomfilter-ppt-4-2048.jpg)