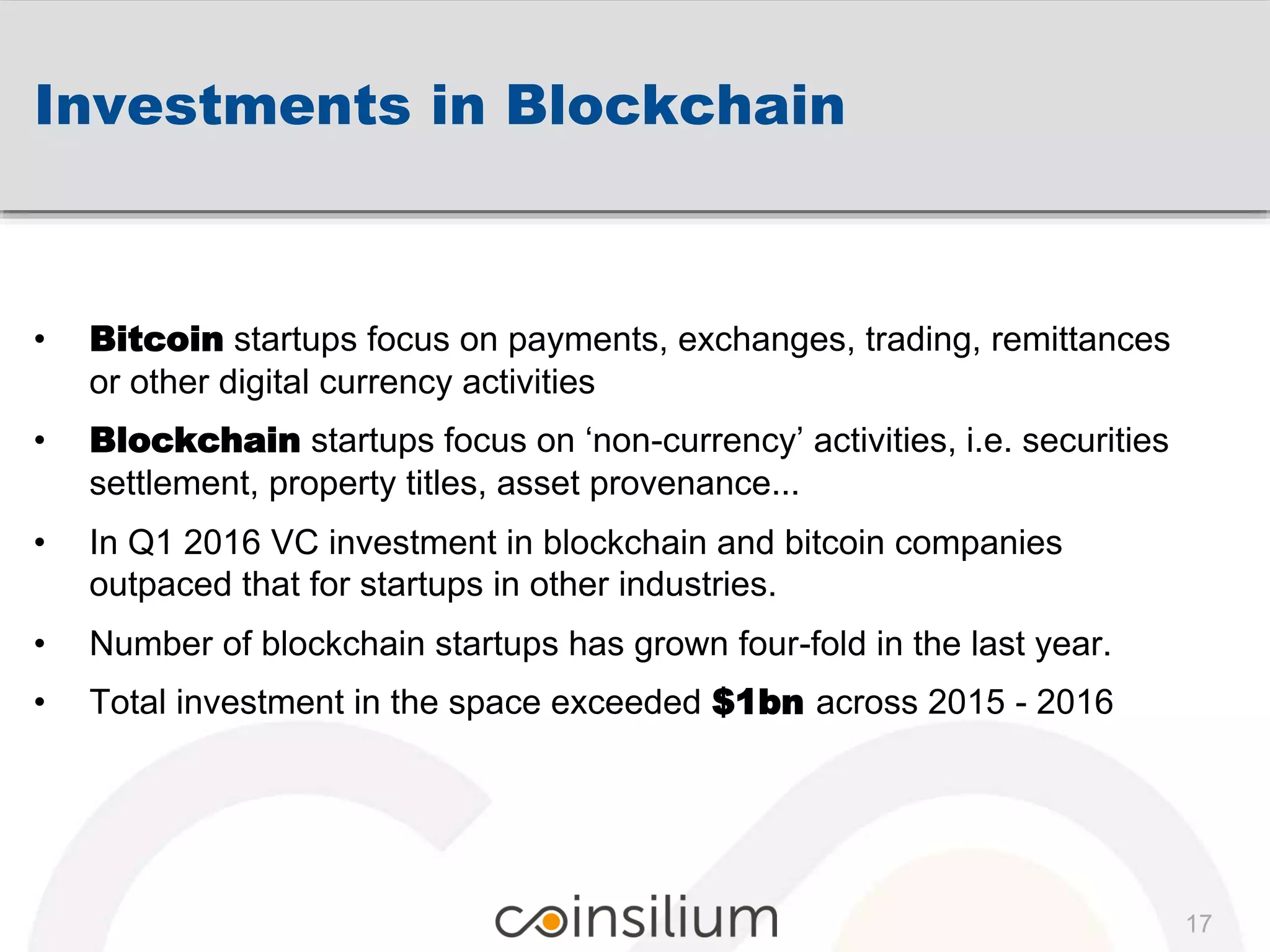
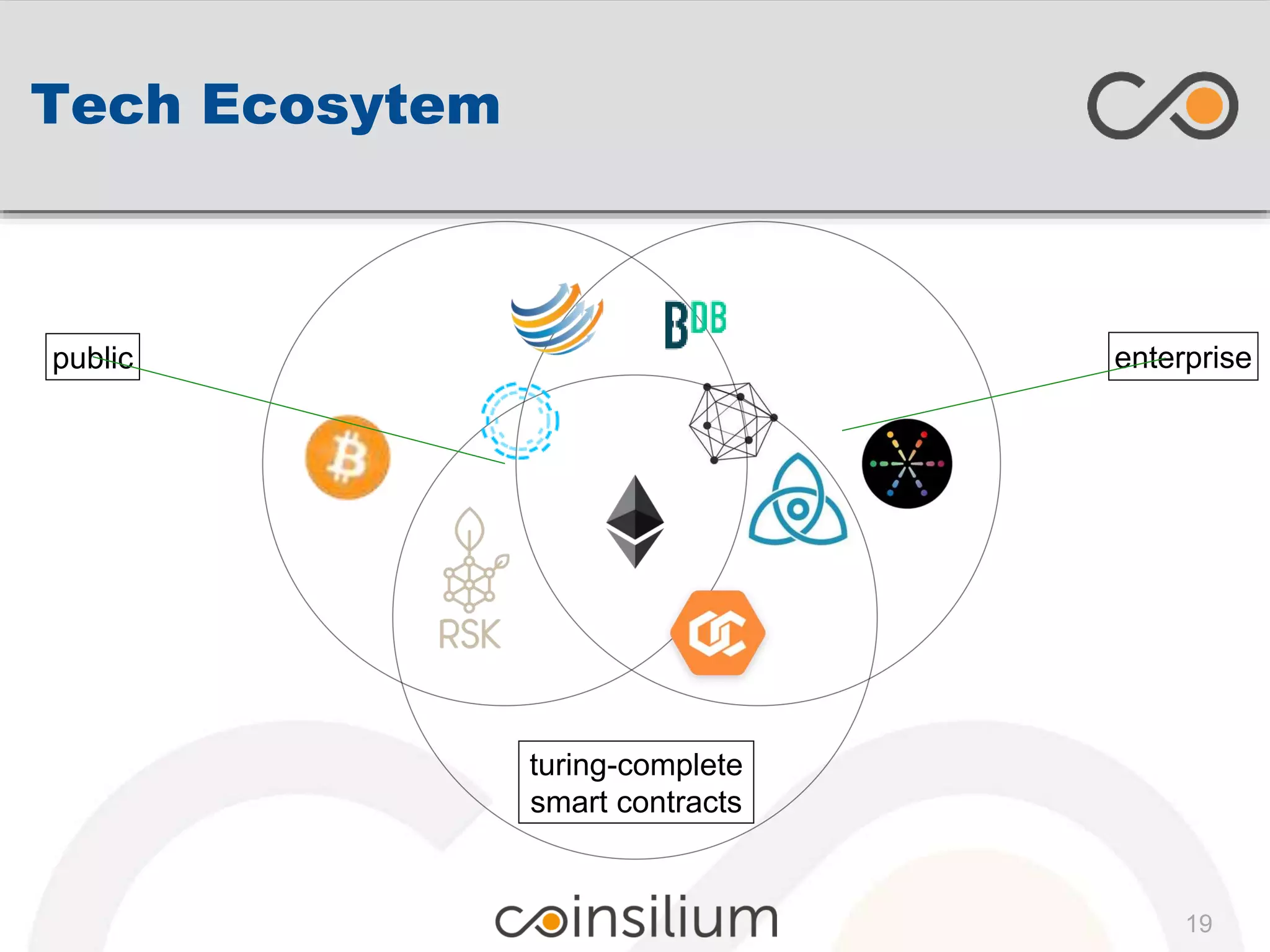
The document presents insights from Eddy Travia, CEO of Coinsilium, on blockchain technology and its potential to revolutionize transactional applications by ensuring trust and efficiency without centralized control. It discusses the origins of blockchain, its distinction between public and enterprise chains, and the increasing investments and interest in blockchain startups, especially regarding non-currency applications. Additionally, it highlights smart contracts, decentralized autonomous organizations, and the landscape of Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) while emphasizing the importance of collaborative industry initiatives like Hyperledger.










![DAO
“ A DAO (decentralized autonomous organization) is
[…] an entity that lives on the internet and exists
autonomously, but also heavily relies on hiring
individuals to perform certain tasks that the automaton
itself cannot do. “
source: Vitalik Buterin - May 2014
“DAOs, DACs, DAs and More: An Incomplete Terminology Guide”
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2wfkfqp8tamocqzqamwh-signature-b9b1ece0b876197369ac861badb6dd57aa69266b0a2b4f07c64f60bbdc024a90-poli-161211133512/75/Blockchain-a-Game-Changing-Technology-12-2048.jpg)


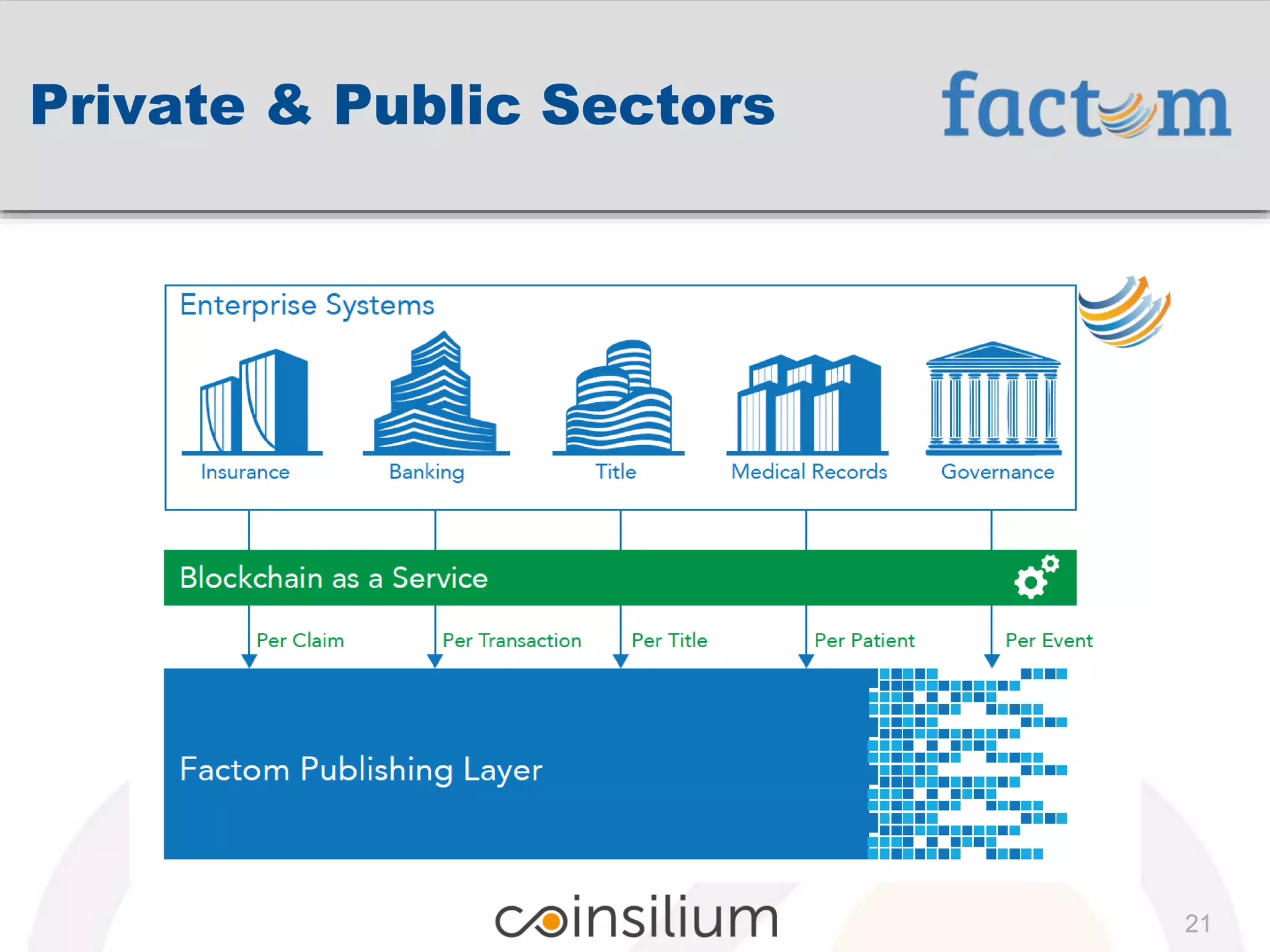
![“ Businesses and governments can use Factom
to simplify records management, record
business processes, and address security and
compliance issues. ”
“ [Factom enables developers to] create
applications that store data in the blockchain
without the speed, cost, or size limitations of
writing data directly to the Bitcoin blockchain. “
source: factom.org
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2wfkfqp8tamocqzqamwh-signature-b9b1ece0b876197369ac861badb6dd57aa69266b0a2b4f07c64f60bbdc024a90-poli-161211133512/75/Blockchain-a-Game-Changing-Technology-20-2048.jpg)