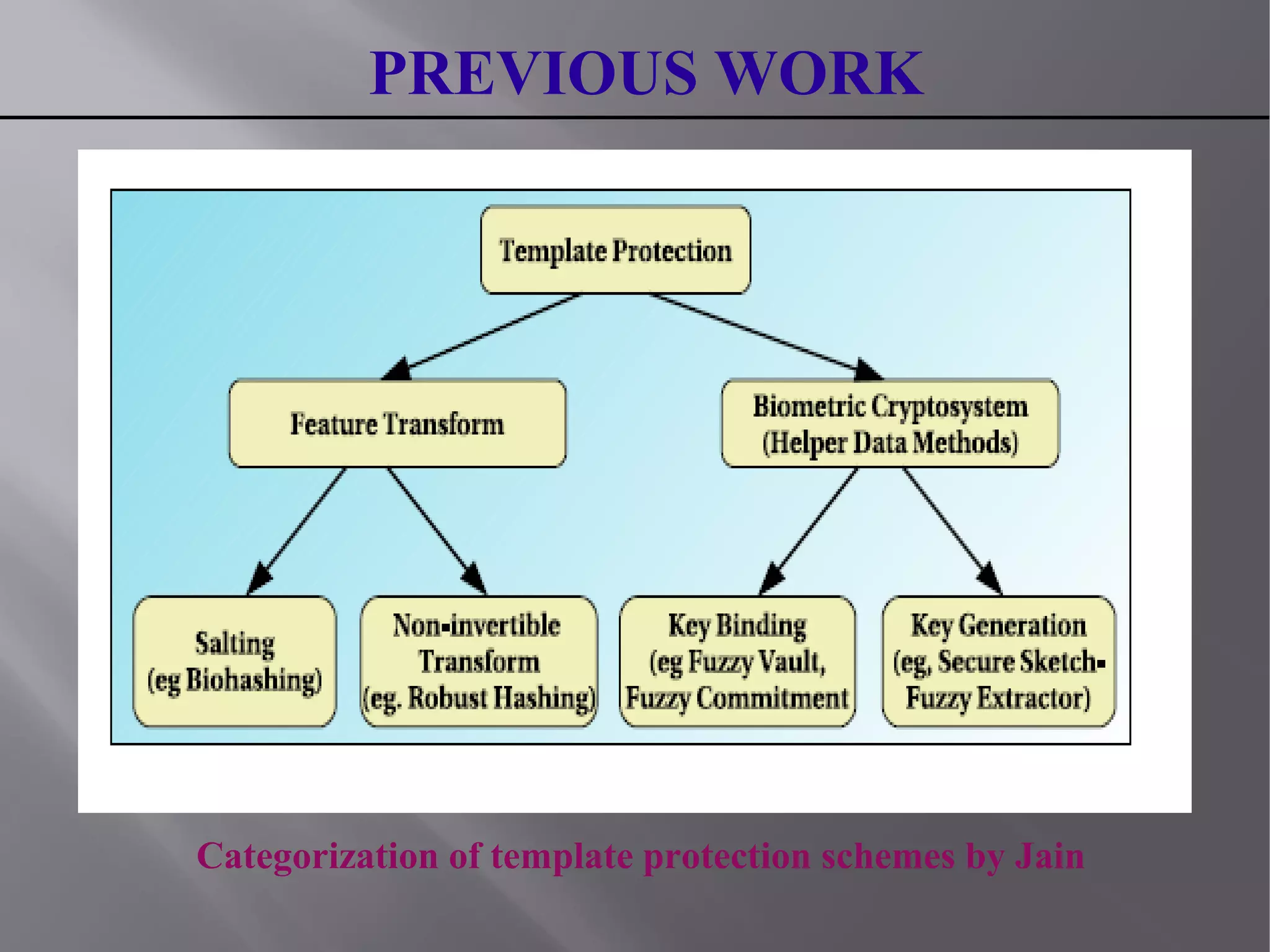
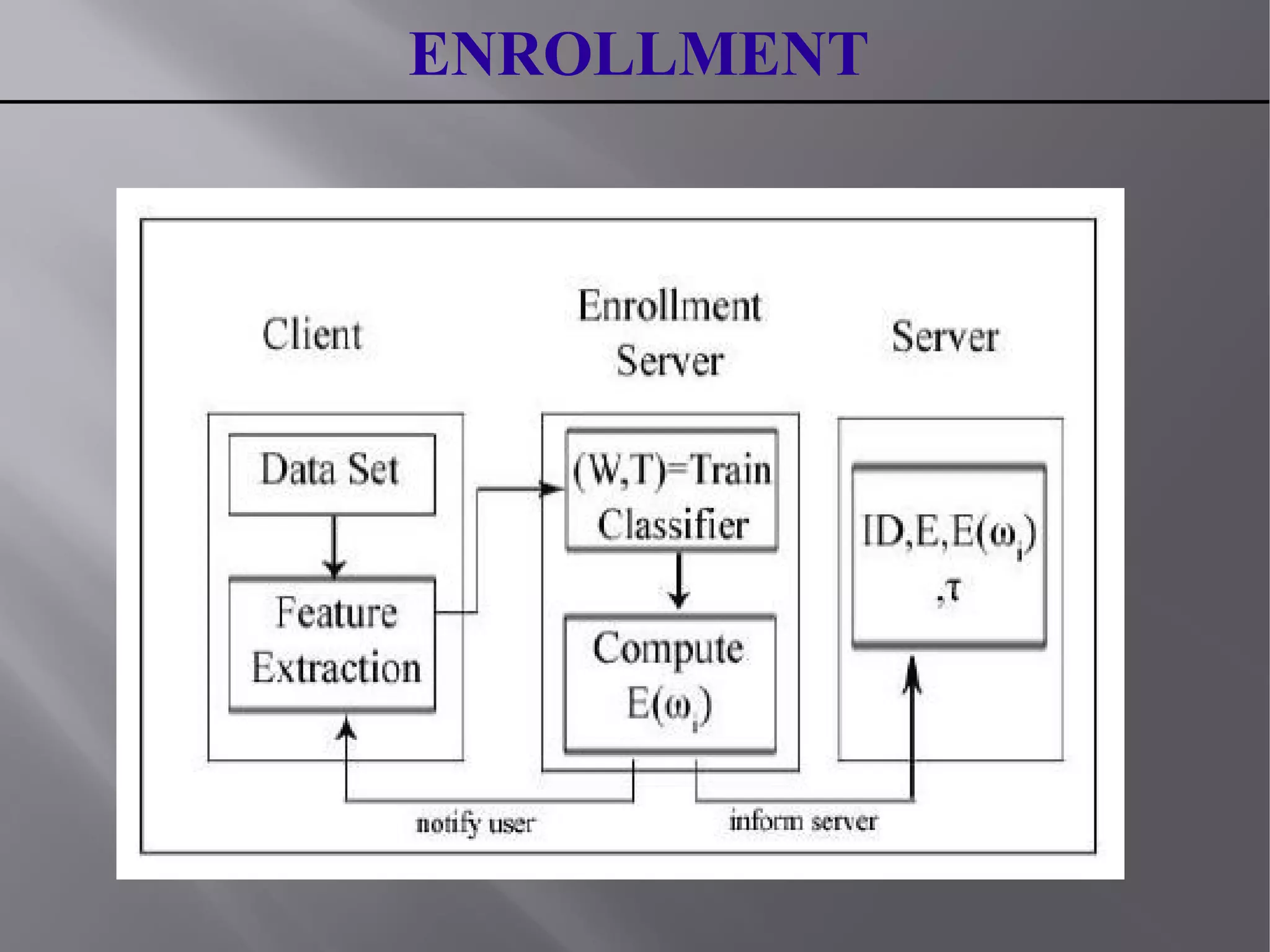
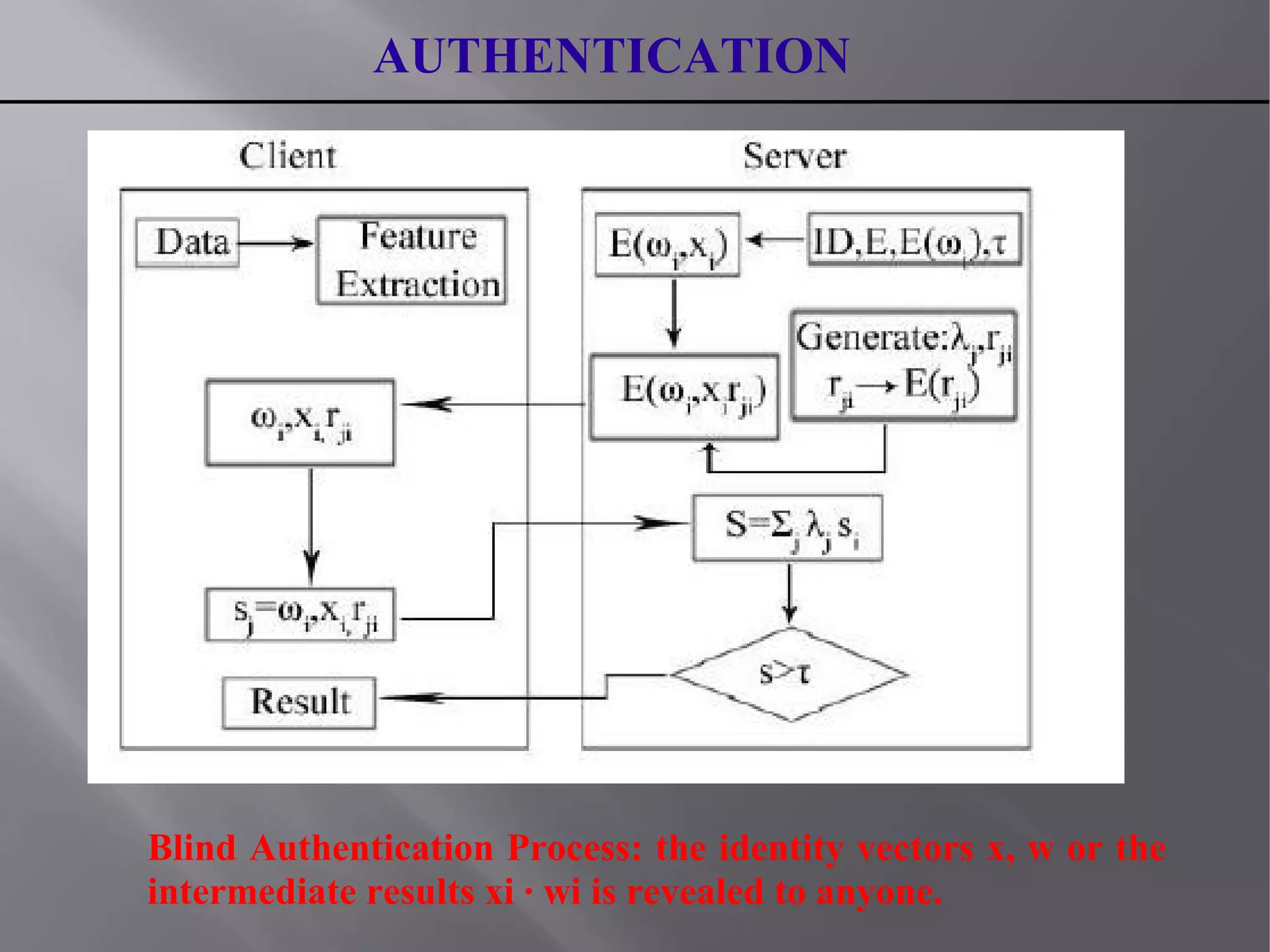
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on blind authentication, a secure crypto-biometric authentication protocol. The presentation discusses biometrics and biometric authentication systems, then defines blind authentication as a protocol that only reveals a user's identity and no other information to authenticating servers. It describes the enrollment and authentication processes, which use cryptography techniques like encryption to protect biometric templates and allow for template revocation. The presentation highlights advantages like fast, secure authentication without compromising accuracy or privacy by revealing personal information like biometric templates. It concludes that blind authentication provides real-time verification with minimal user-server interaction and leaves room for further work on secure enrollment protocols.