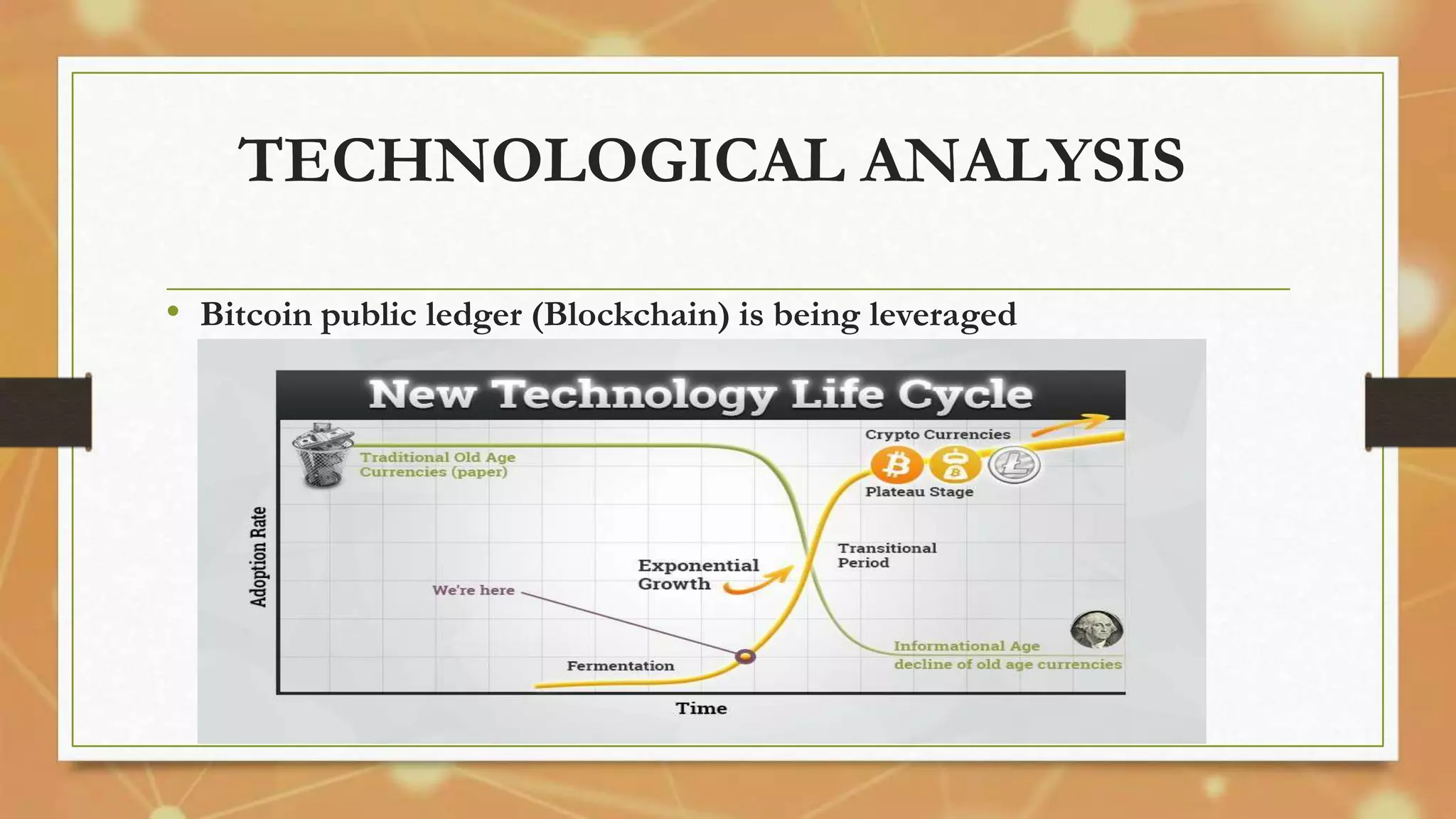
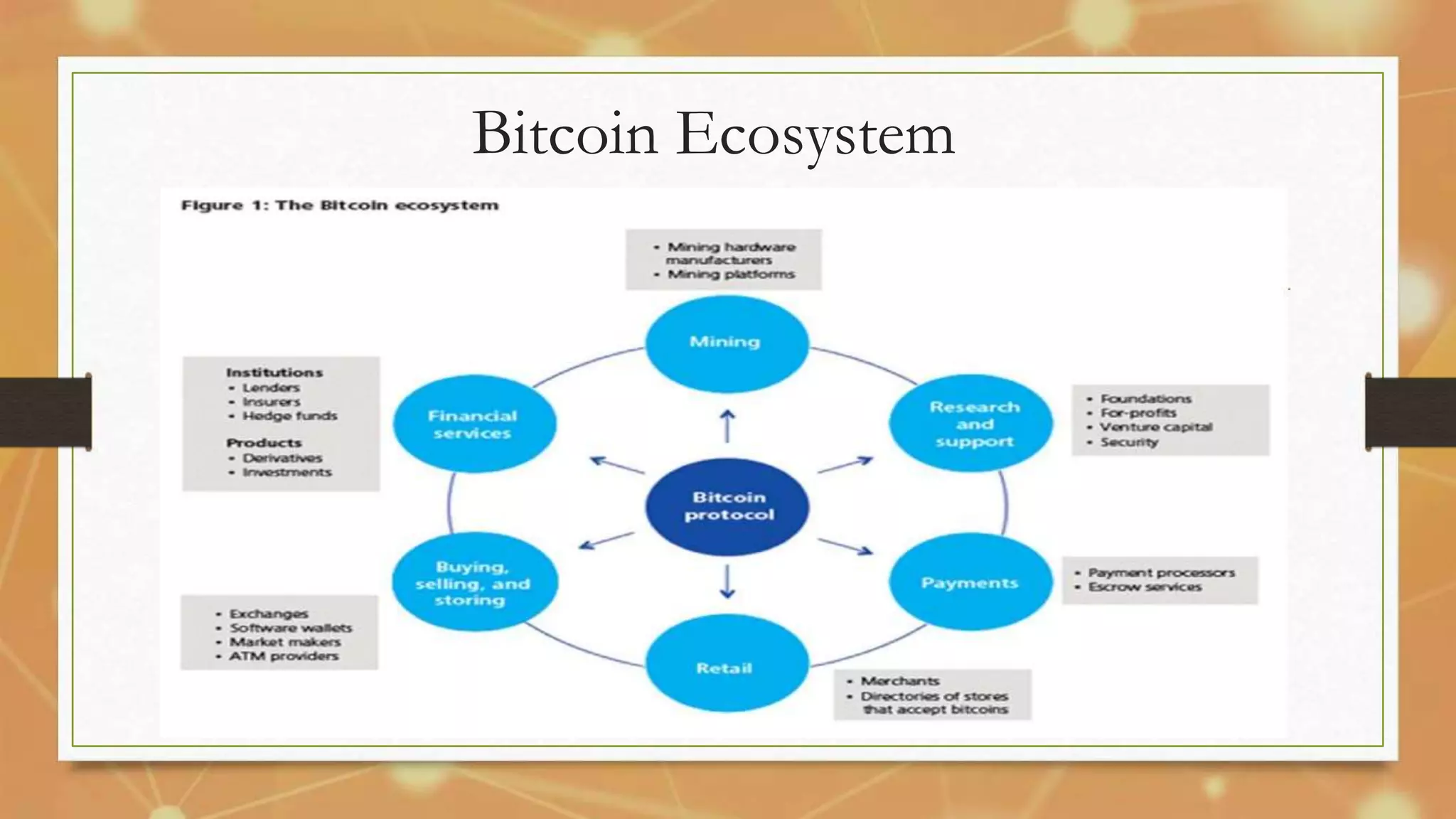
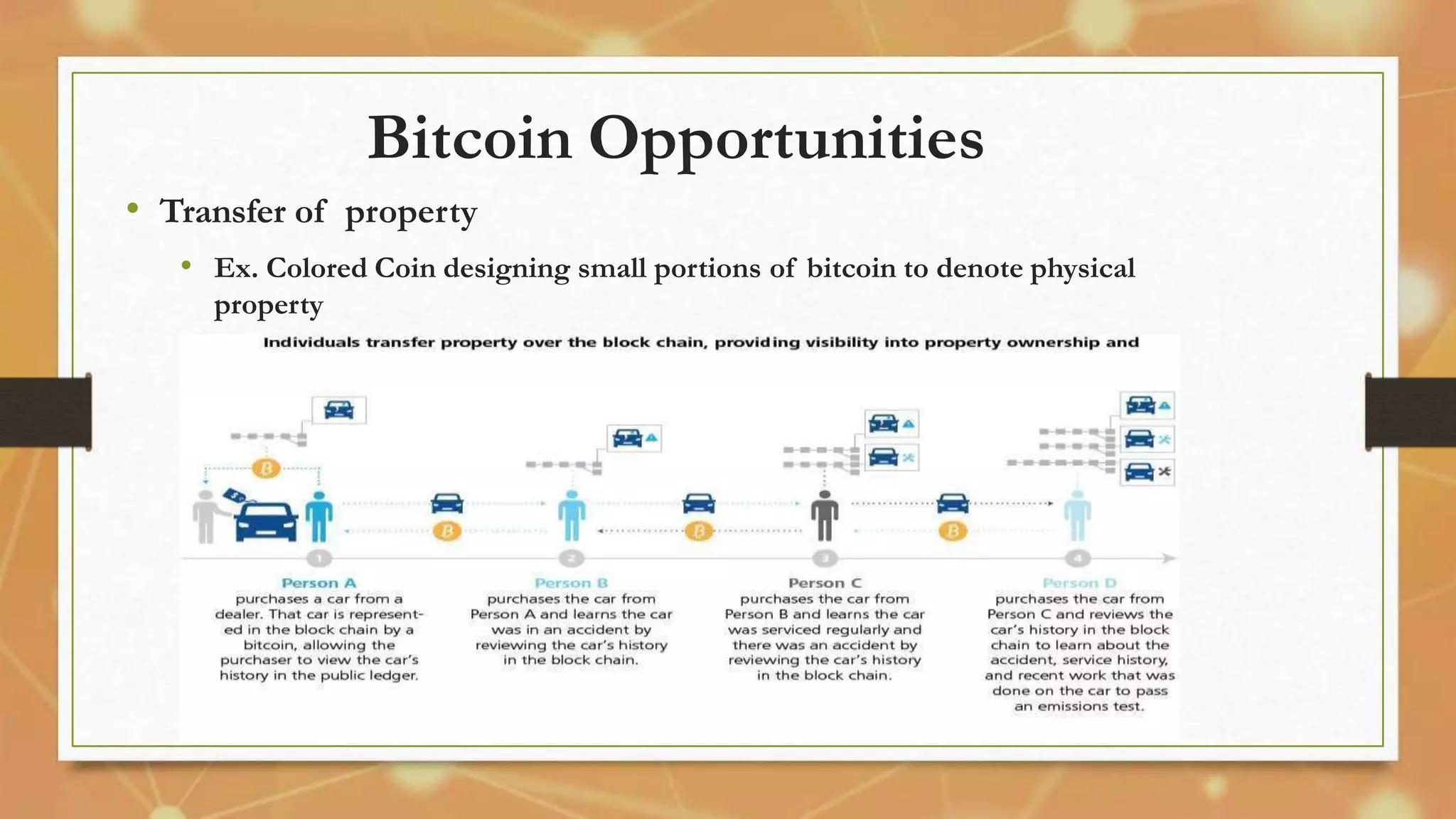
Bitcoin, introduced in 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto, is a decentralized and secure digital currency that uses blockchain technology for transactions. It has gained traction as a mainstream financial alternative with various applications, advantages, and challenges, while a competitive mining process generates new coins. Despite facing obstacles such as lack of acceptance and awareness, Bitcoin's evolving ecosystem suggests a potential for growth in the digital economy.