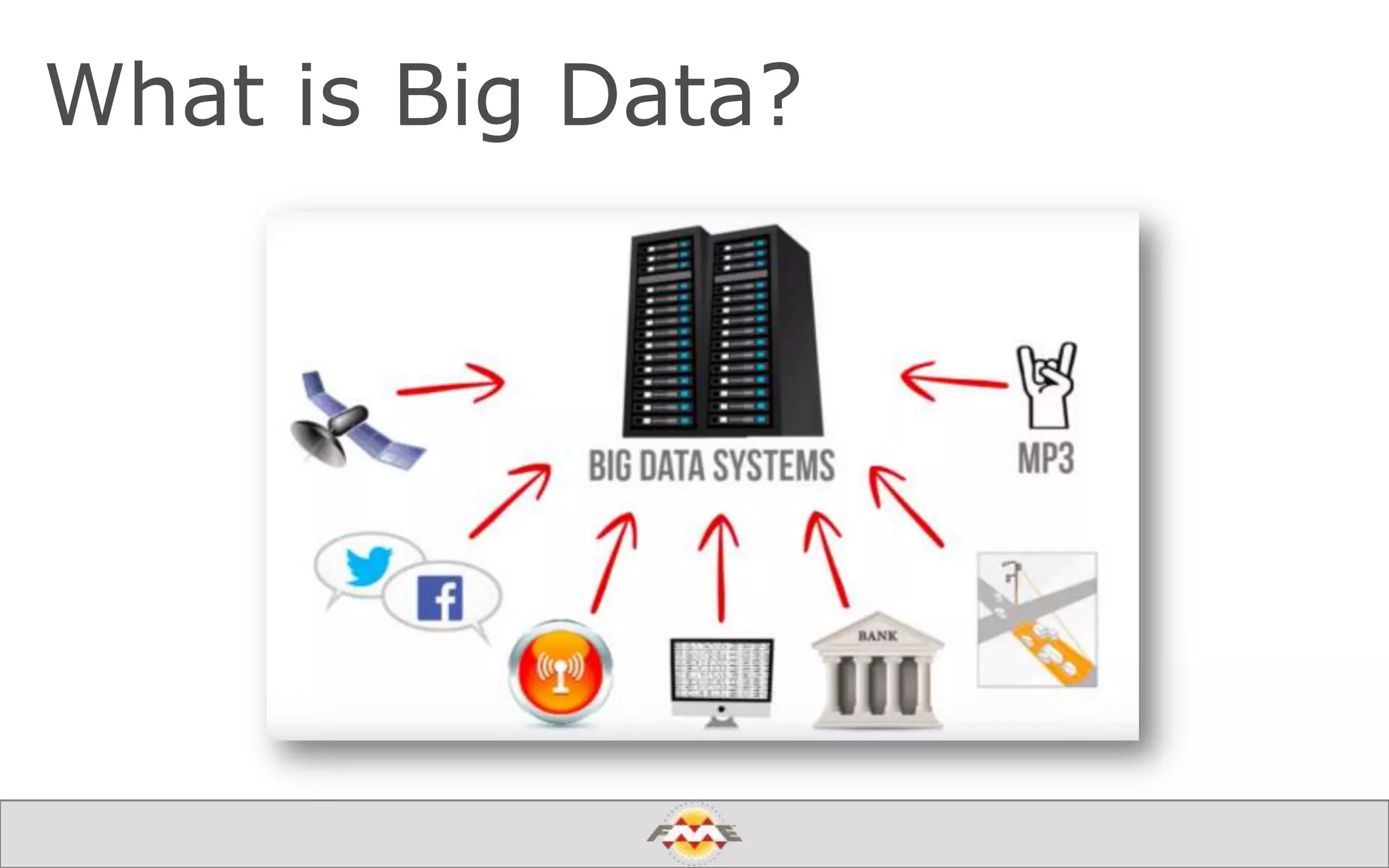
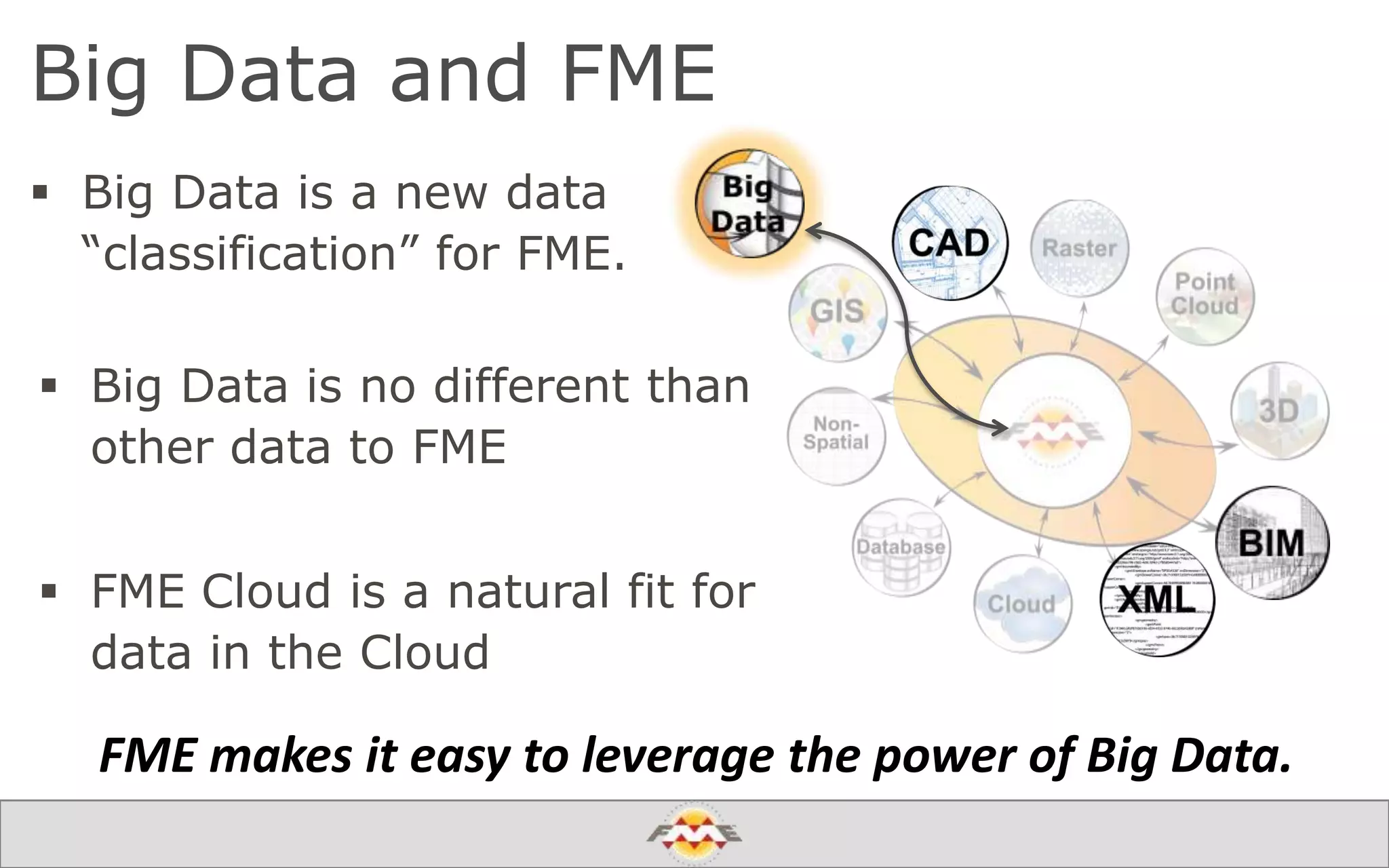
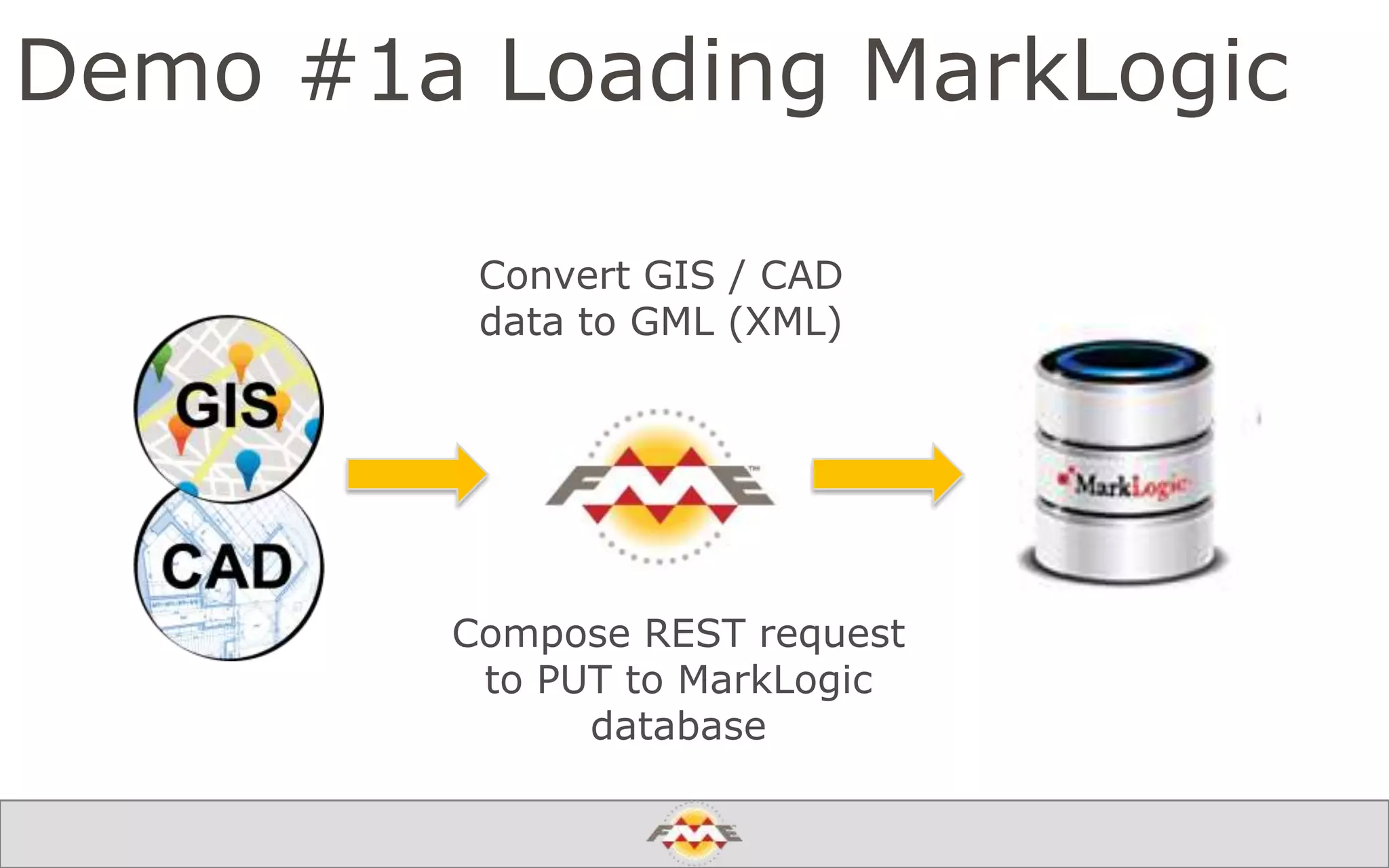
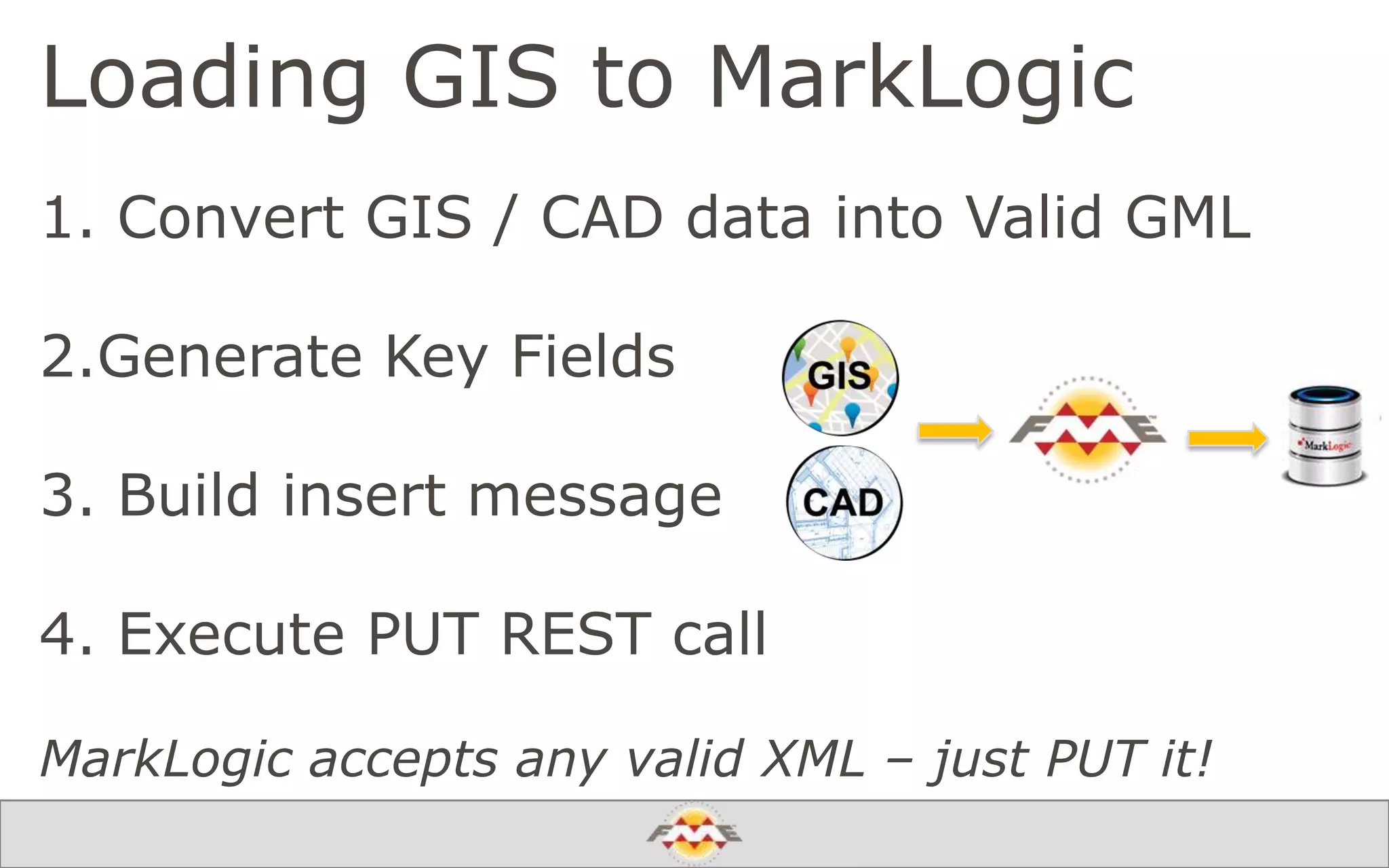
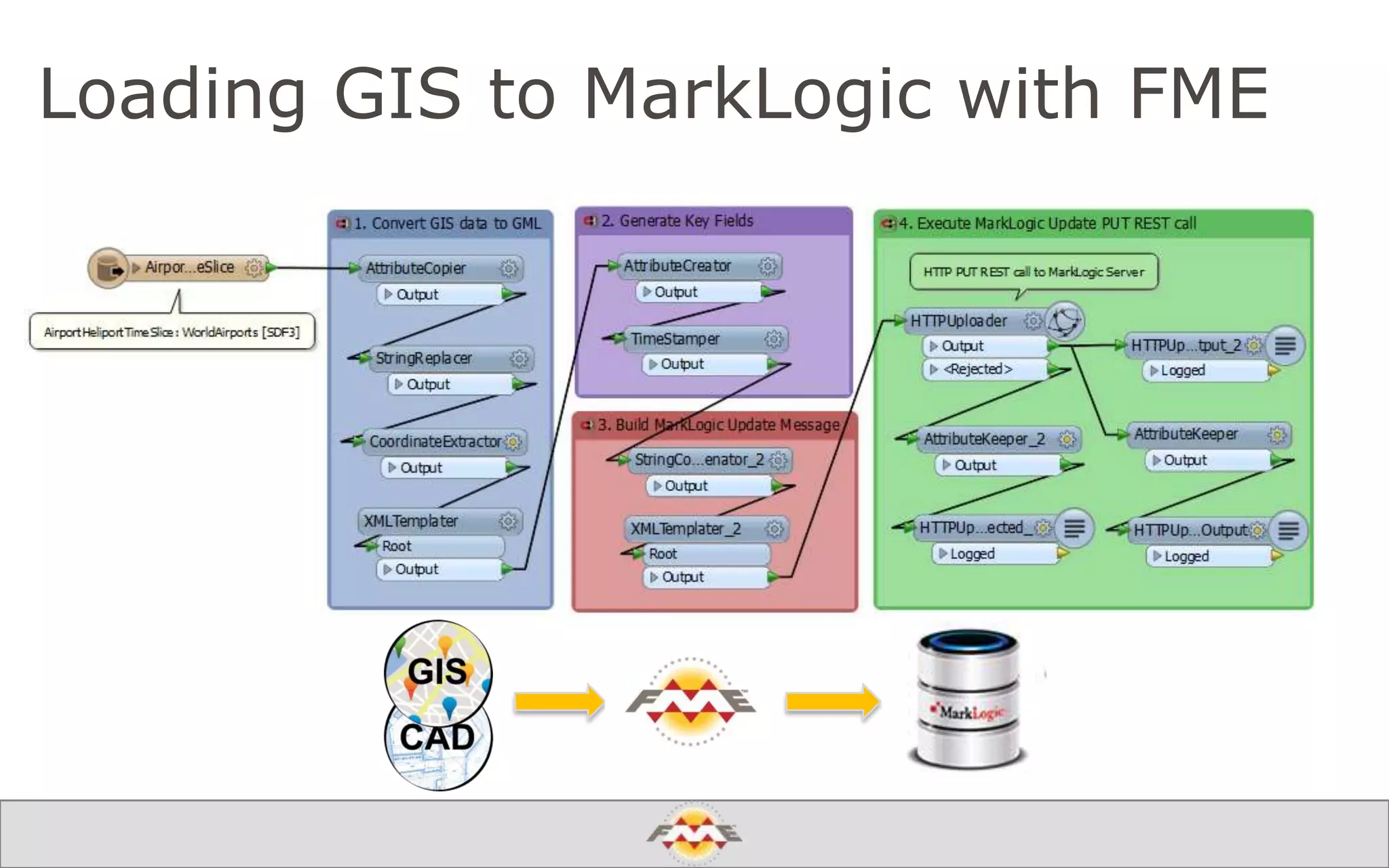
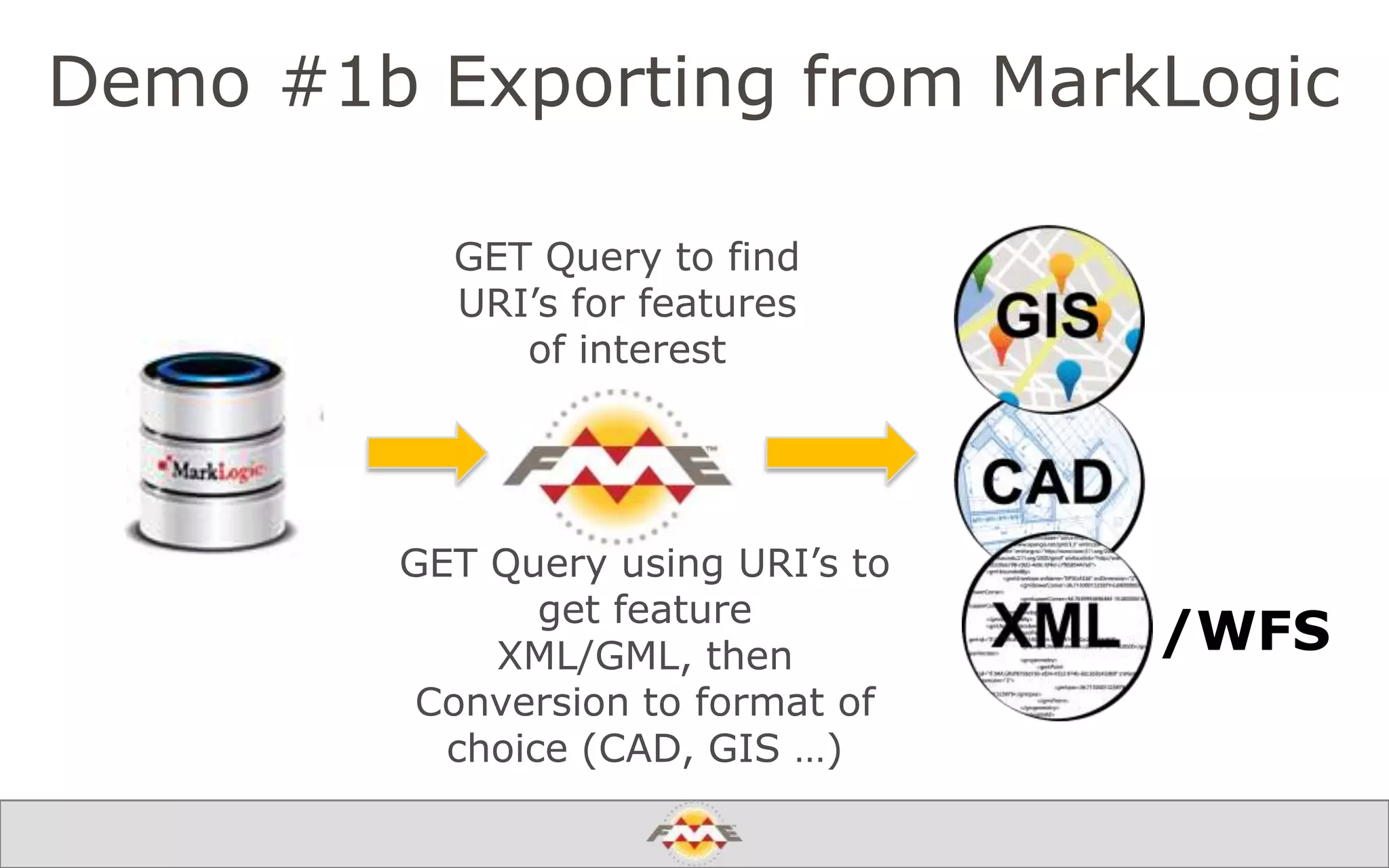
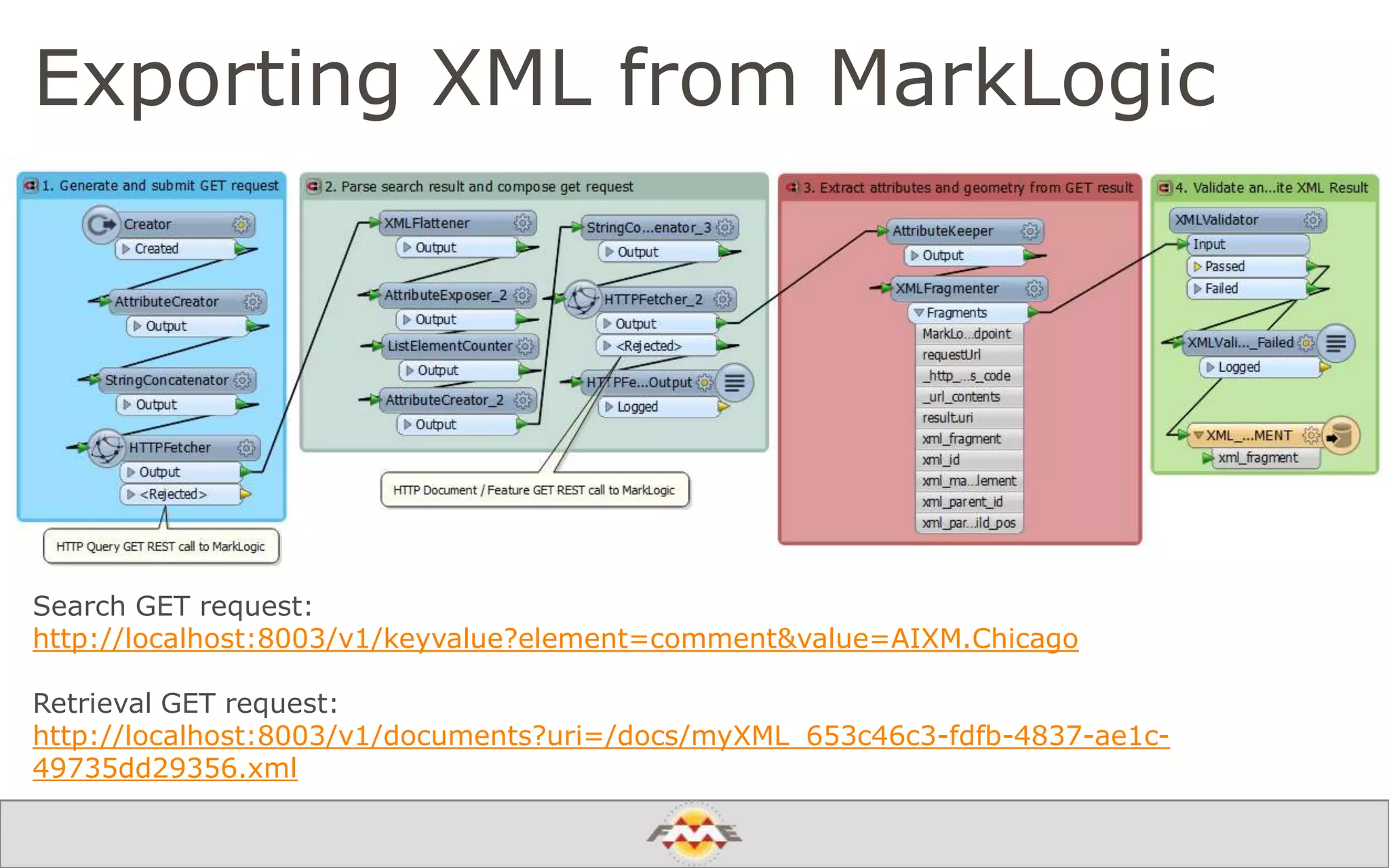
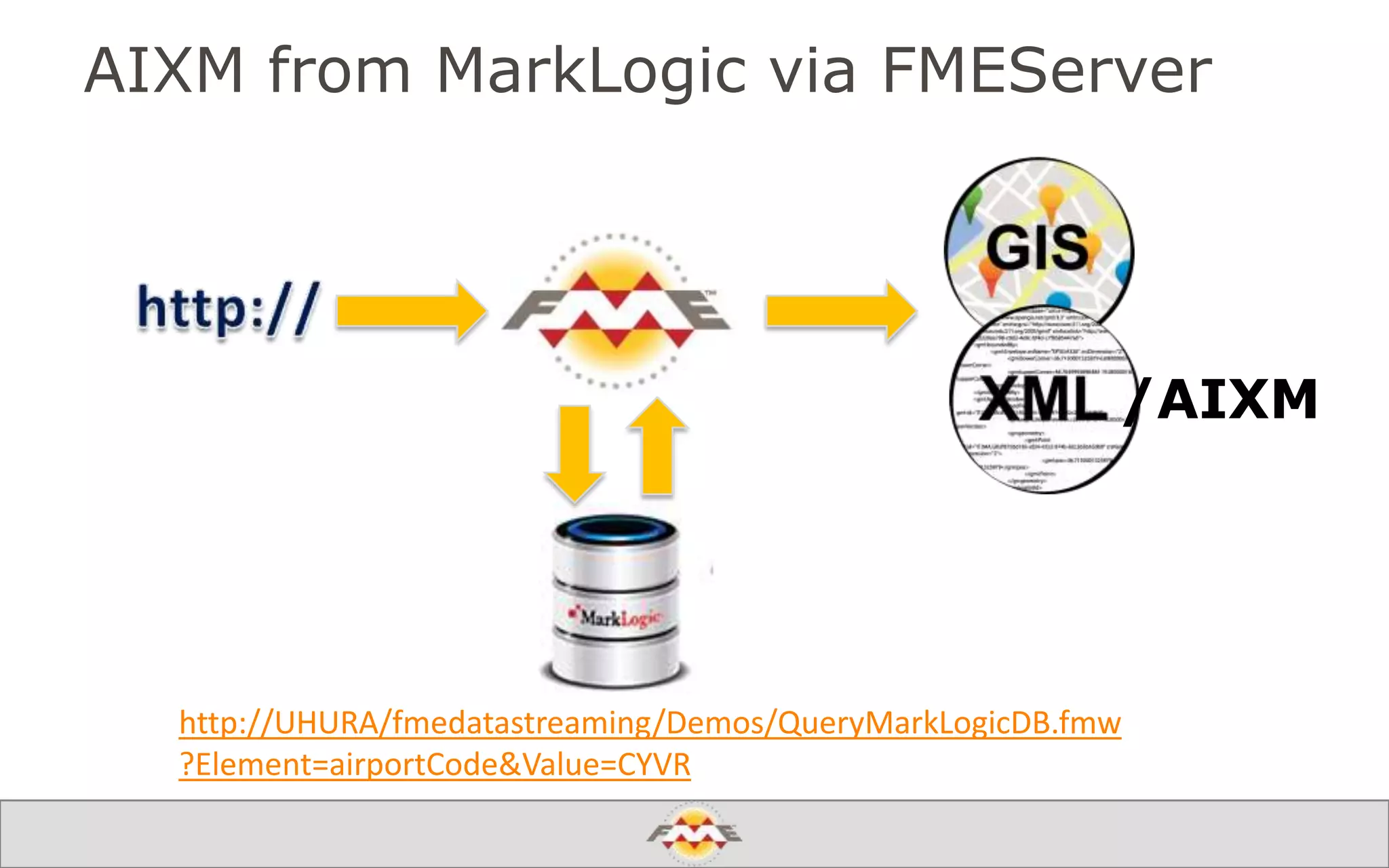
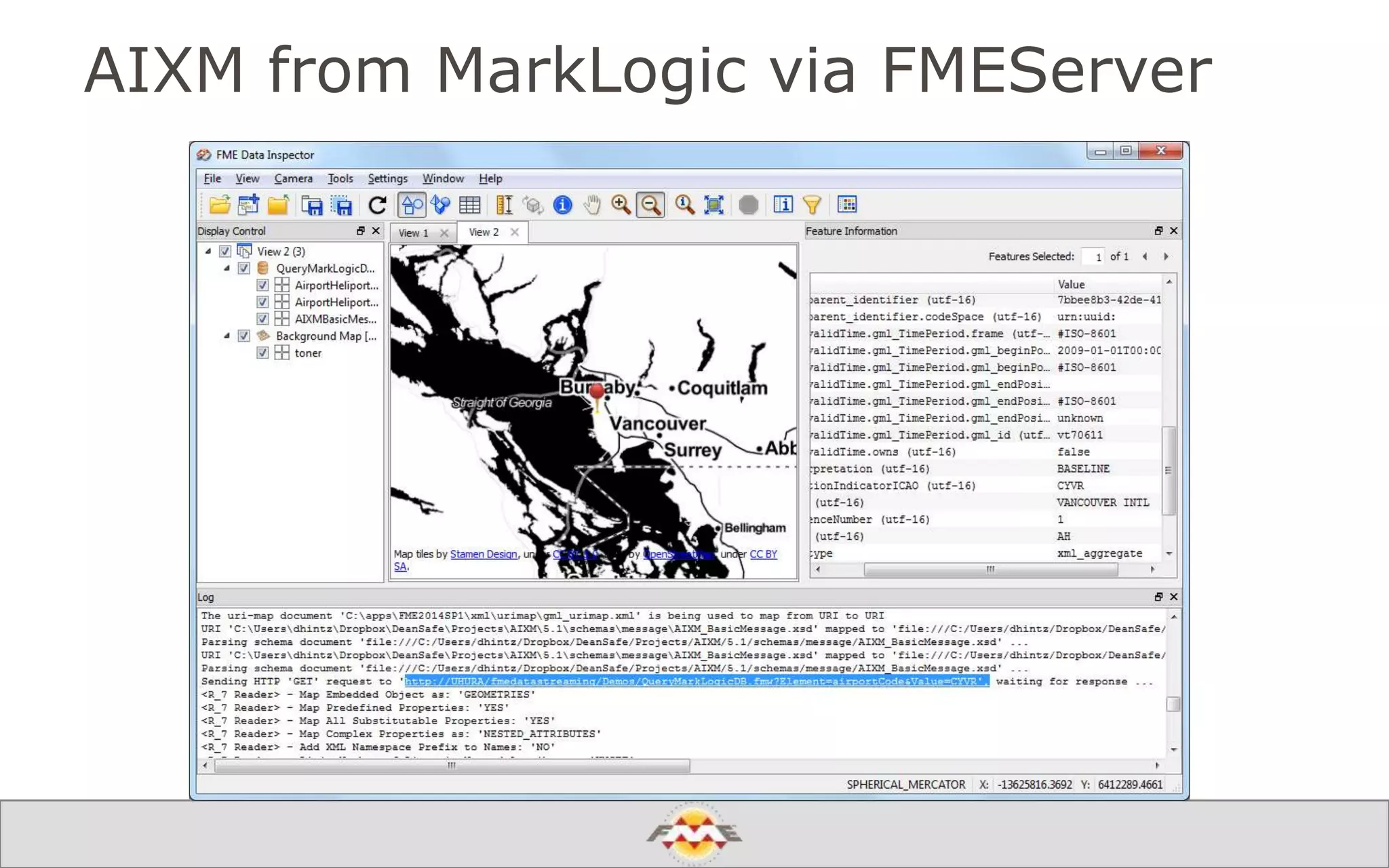
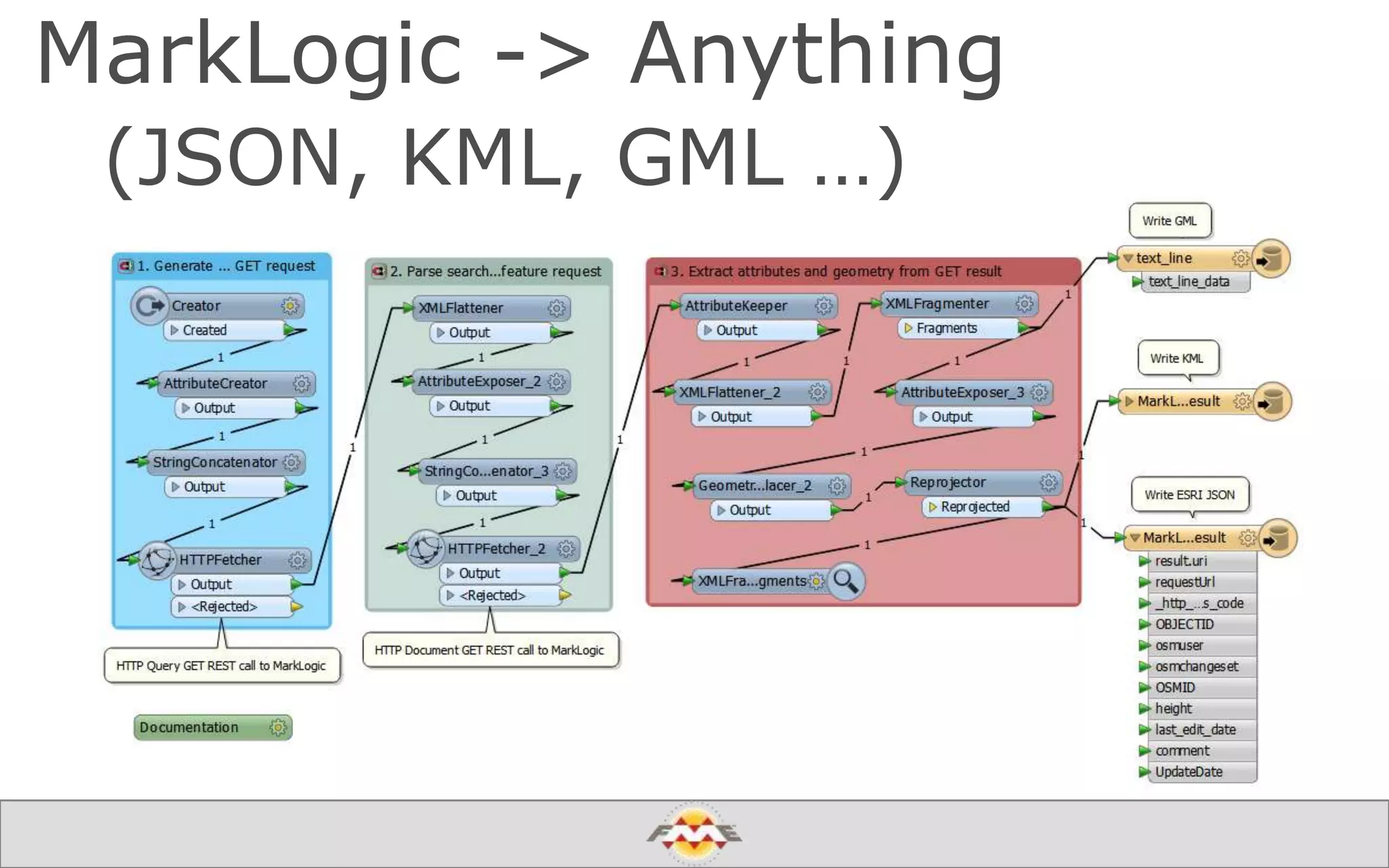
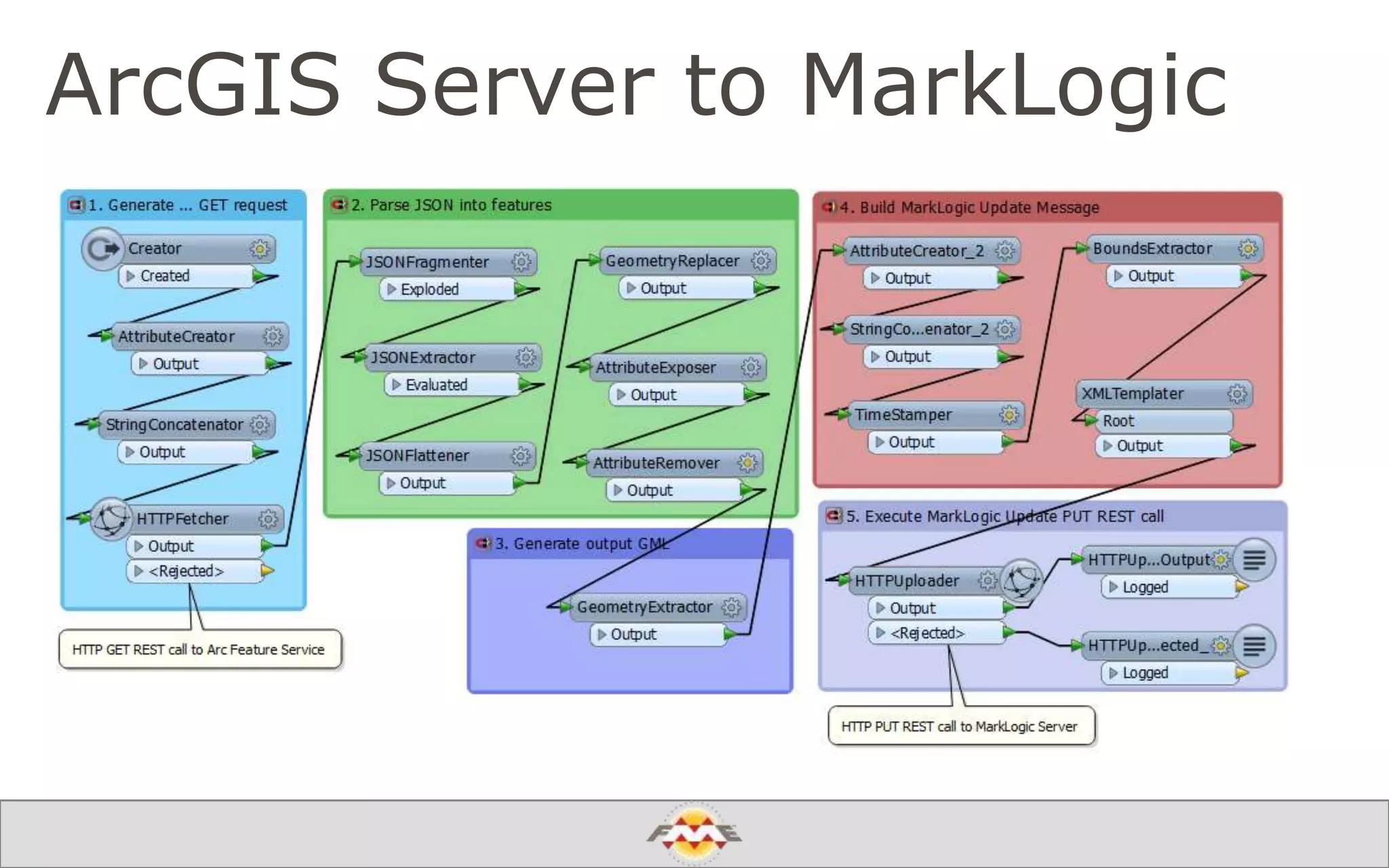
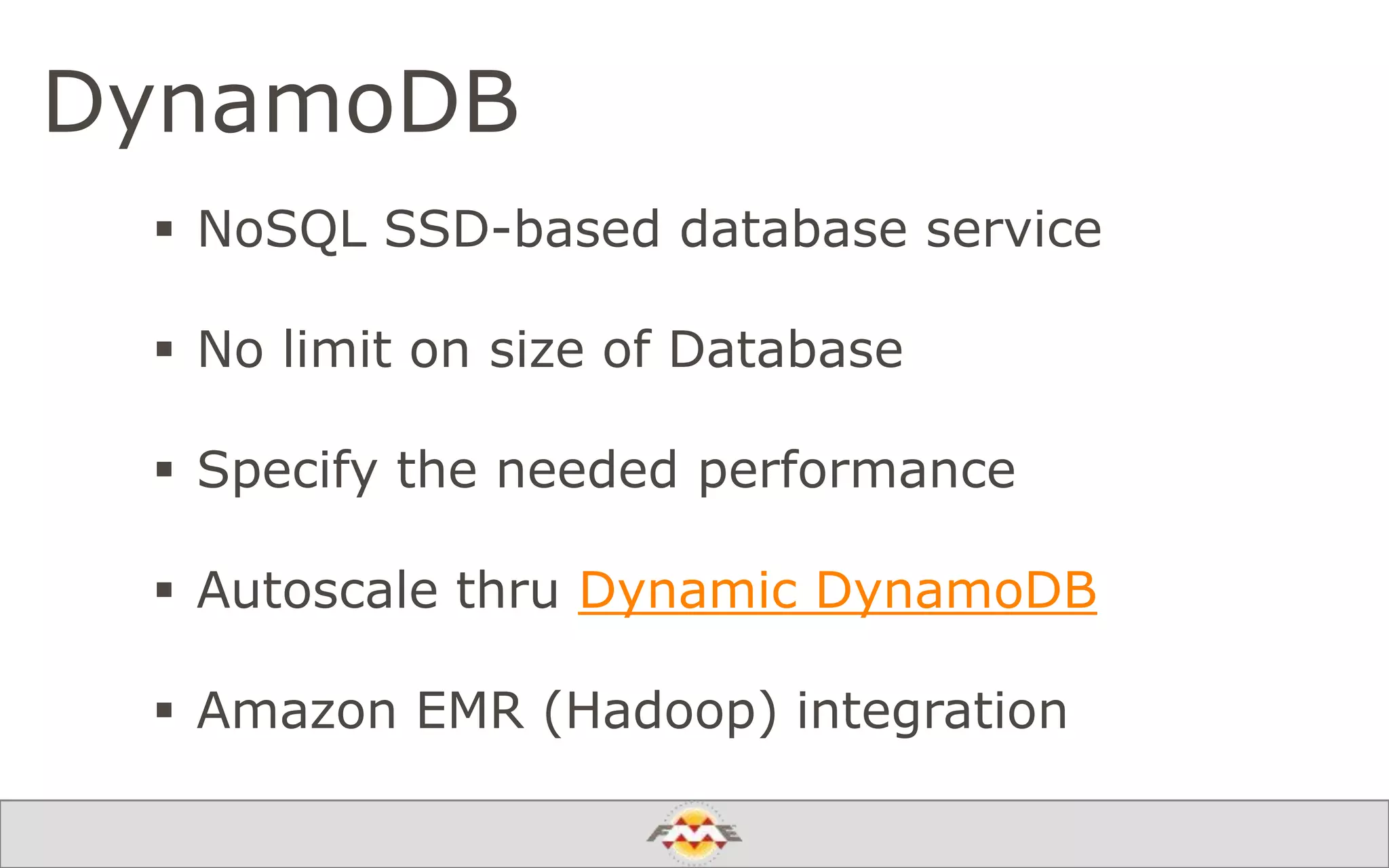
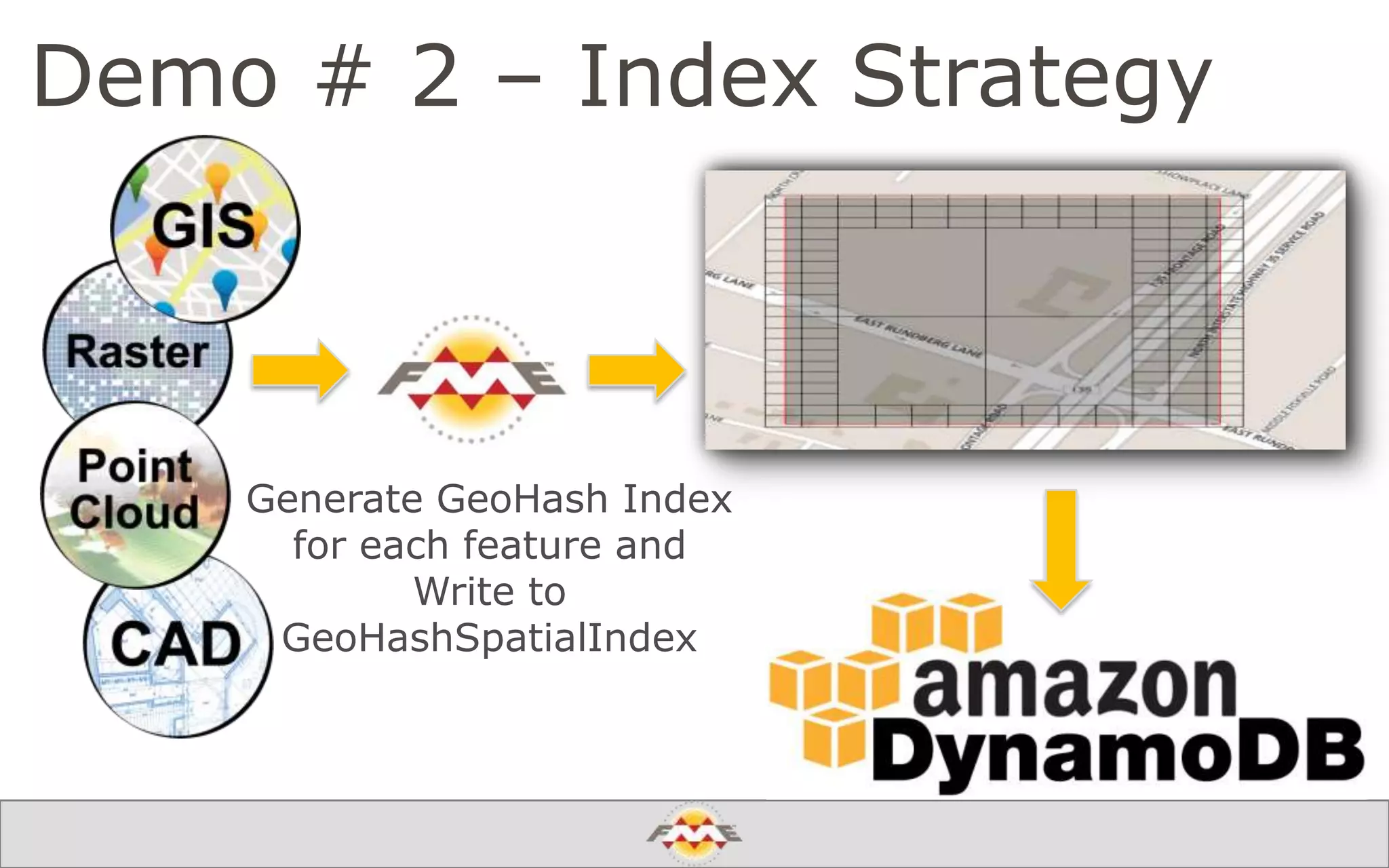
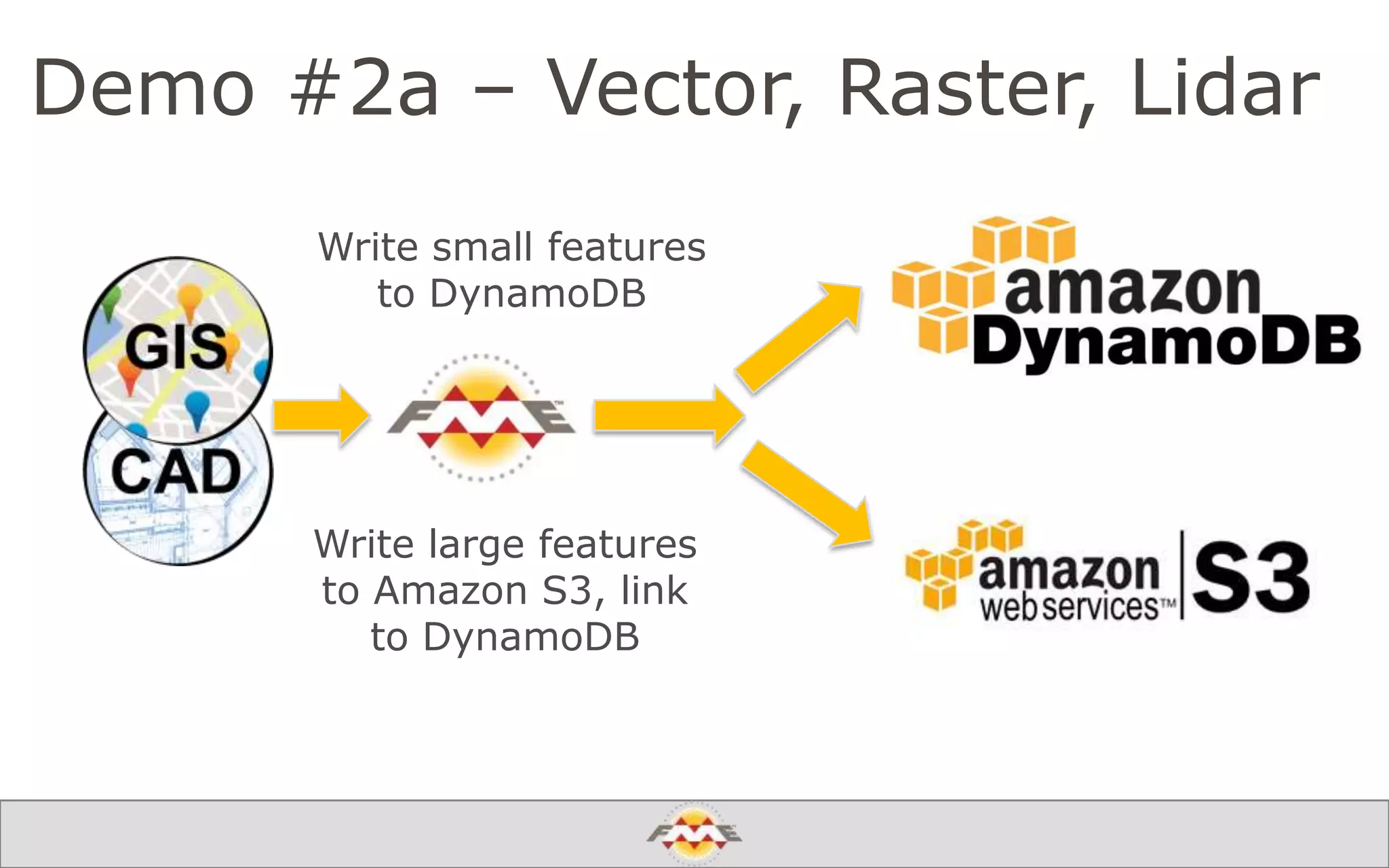
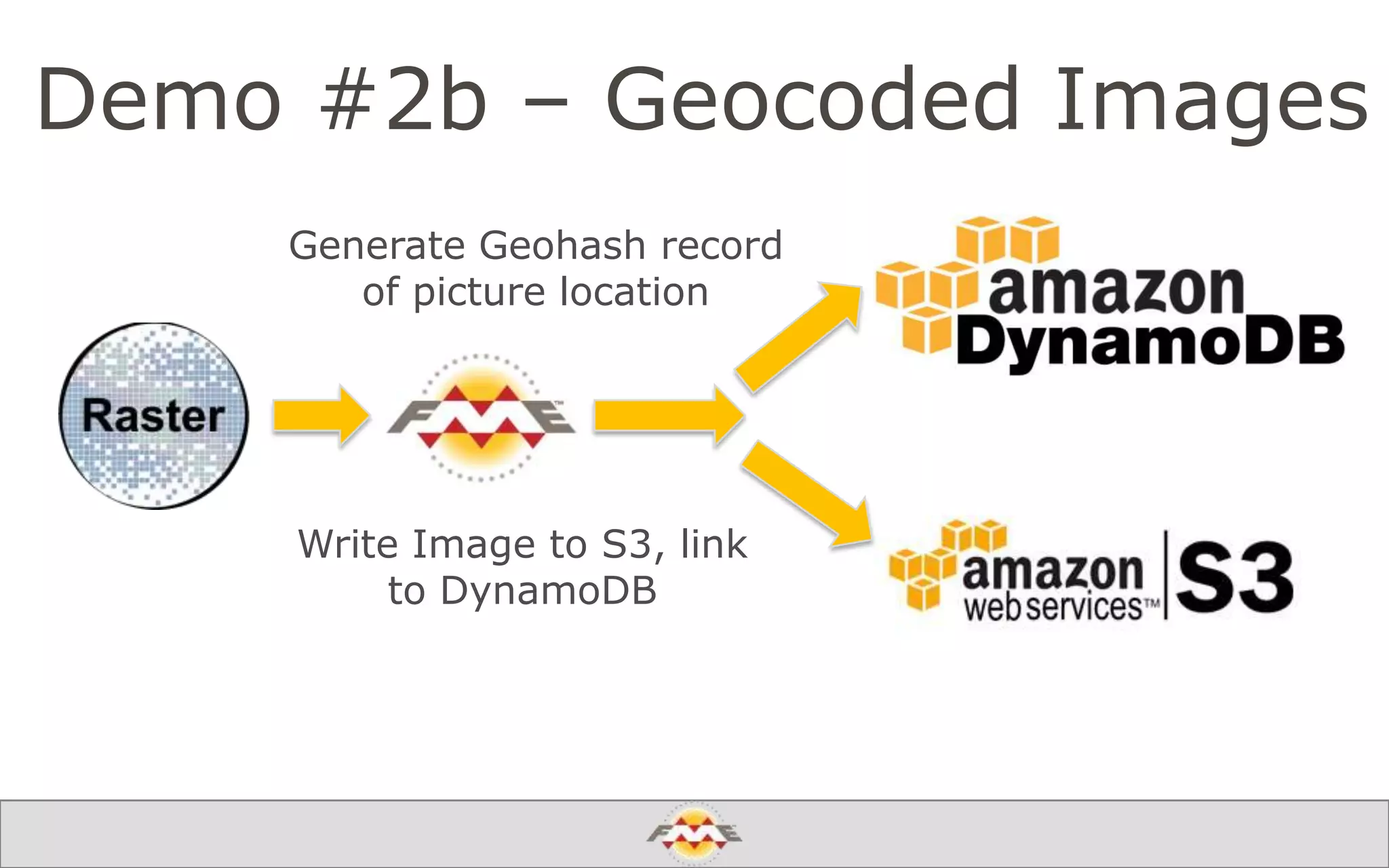
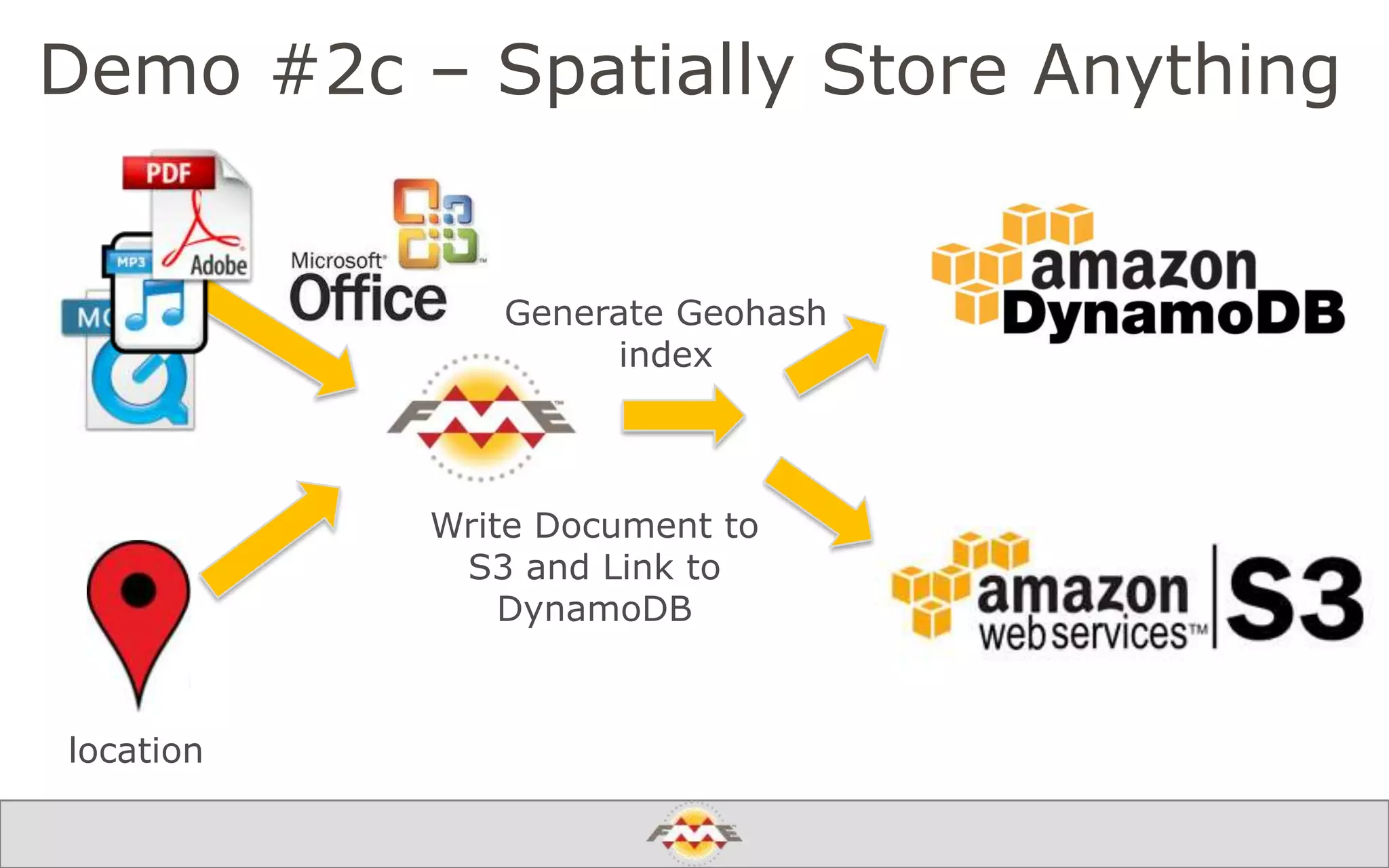
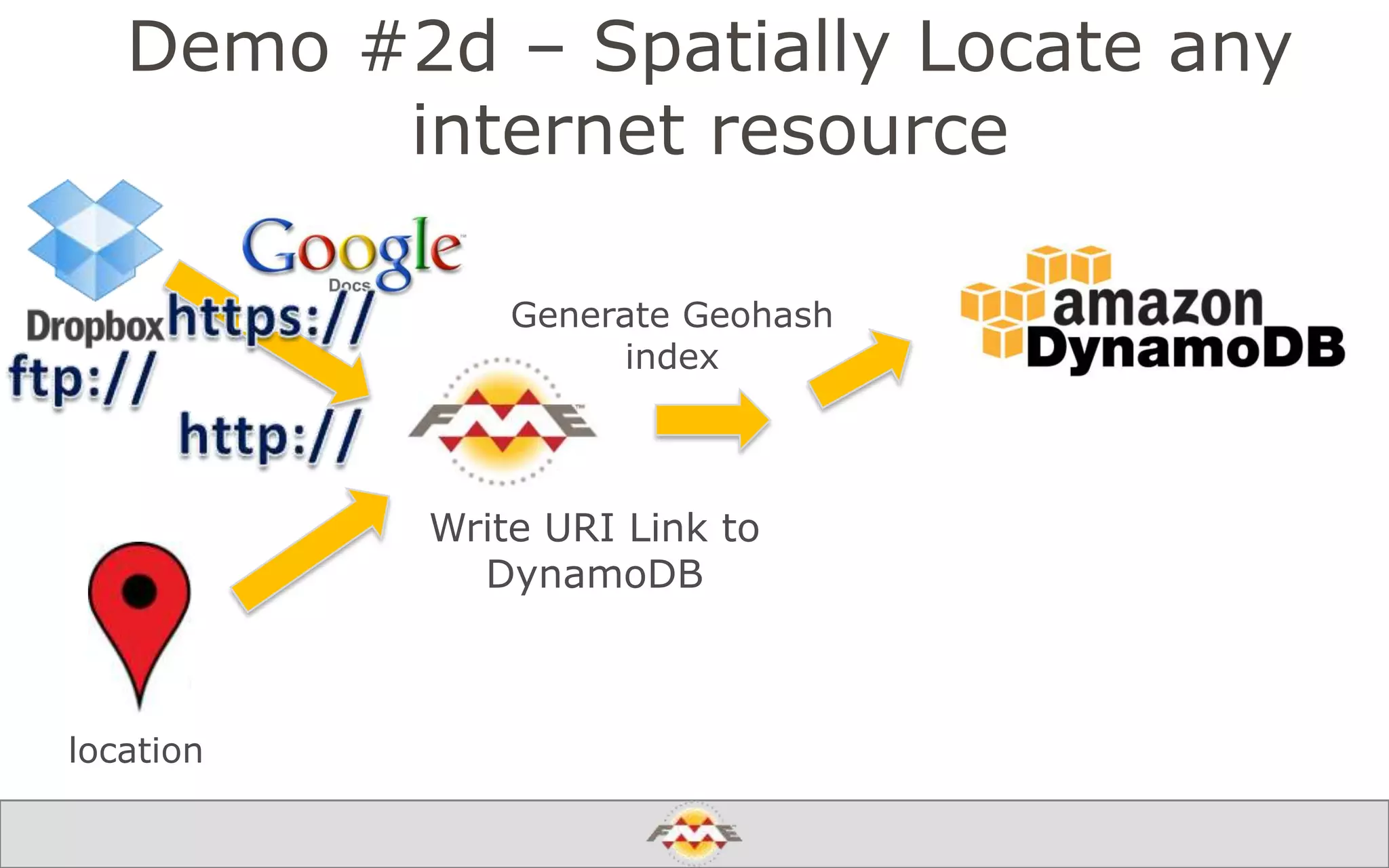
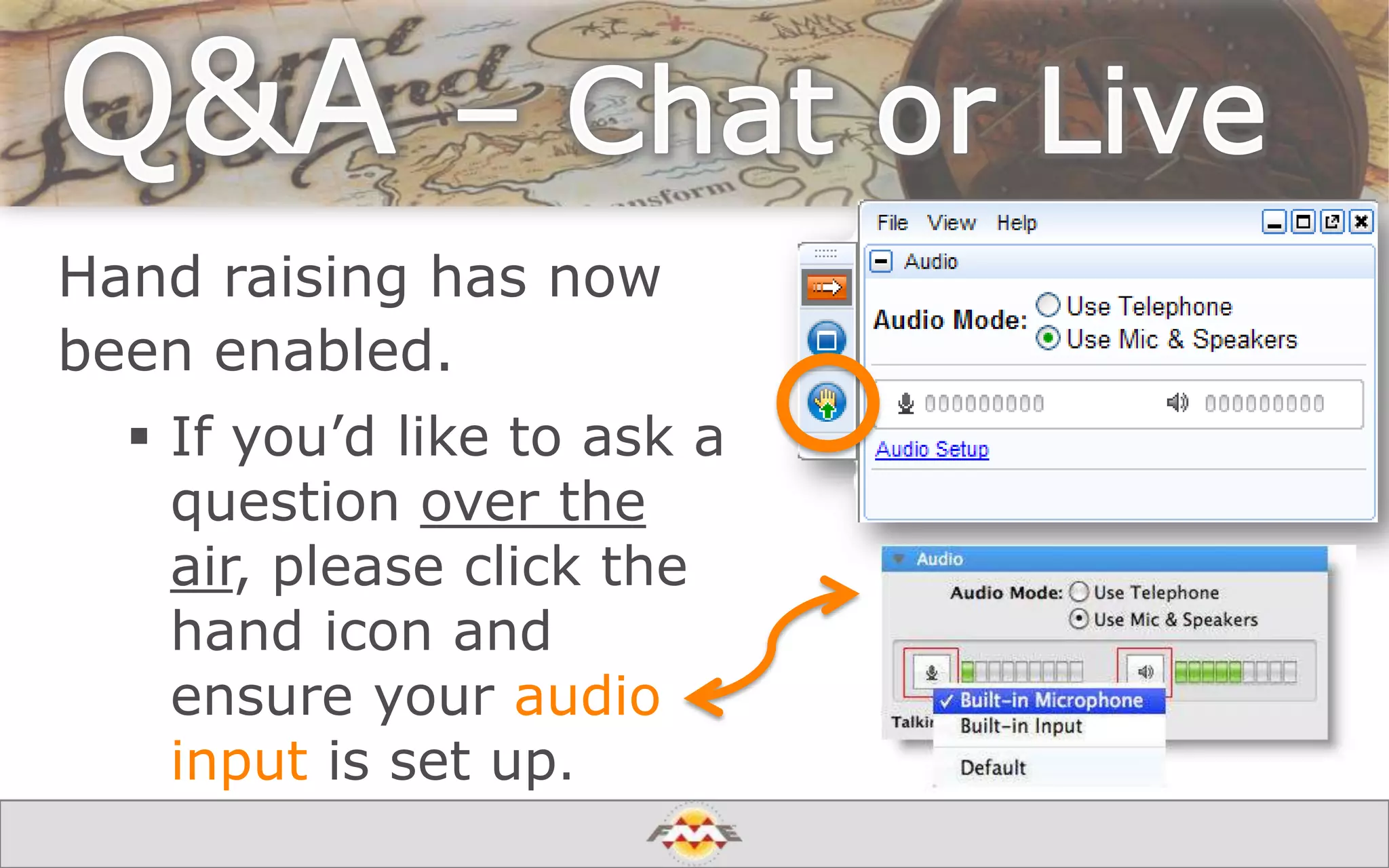
The document provides an overview of a webinar about leveraging FME technology for big data management within cloud infrastructure. It discusses big data challenges, technologies like Amazon DynamoDB and MarkLogic, and includes demonstrations on loading and exporting data. The session emphasizes the benefits of cloud solutions for big data and highlights upcoming webinars and events.