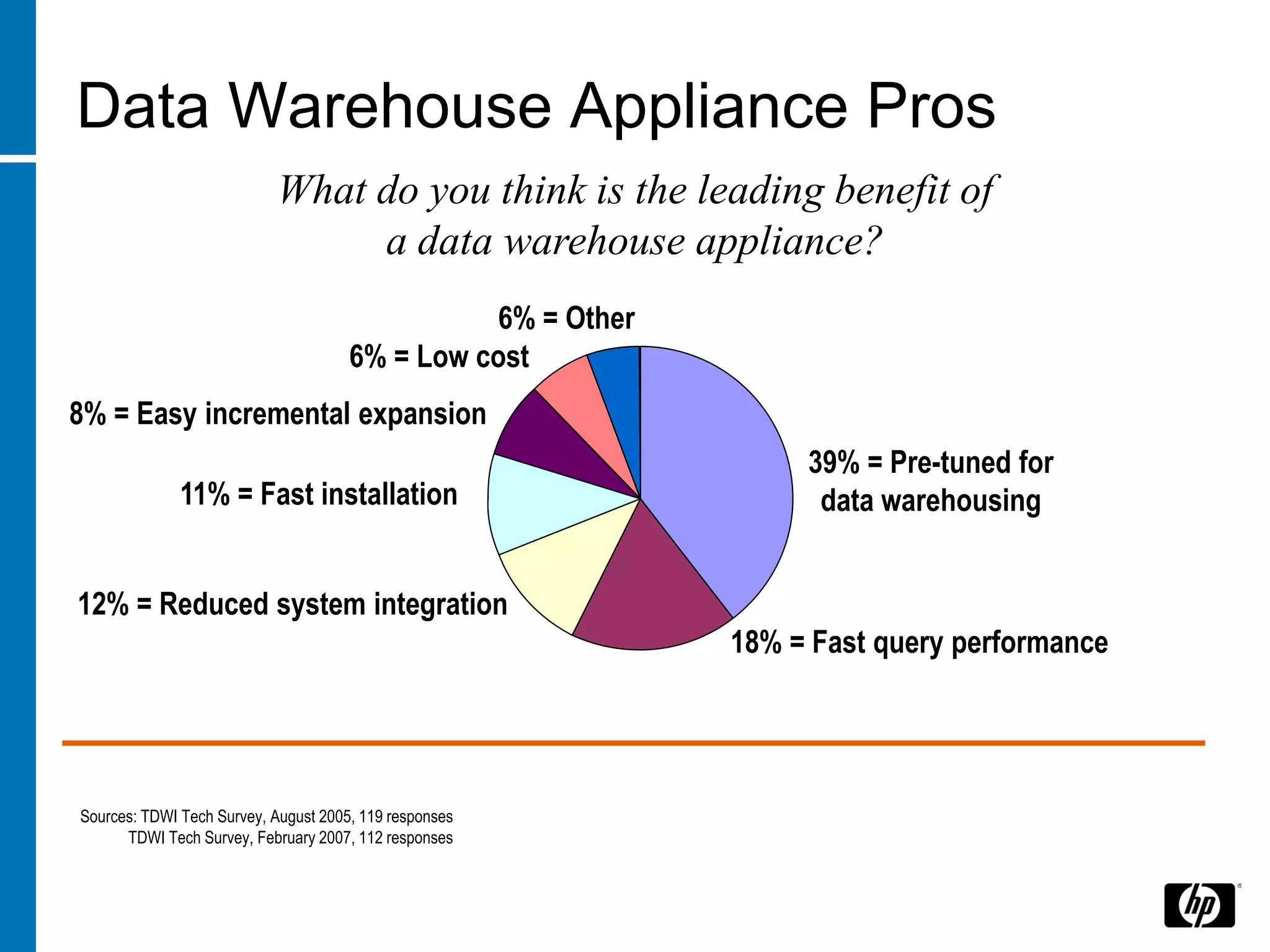
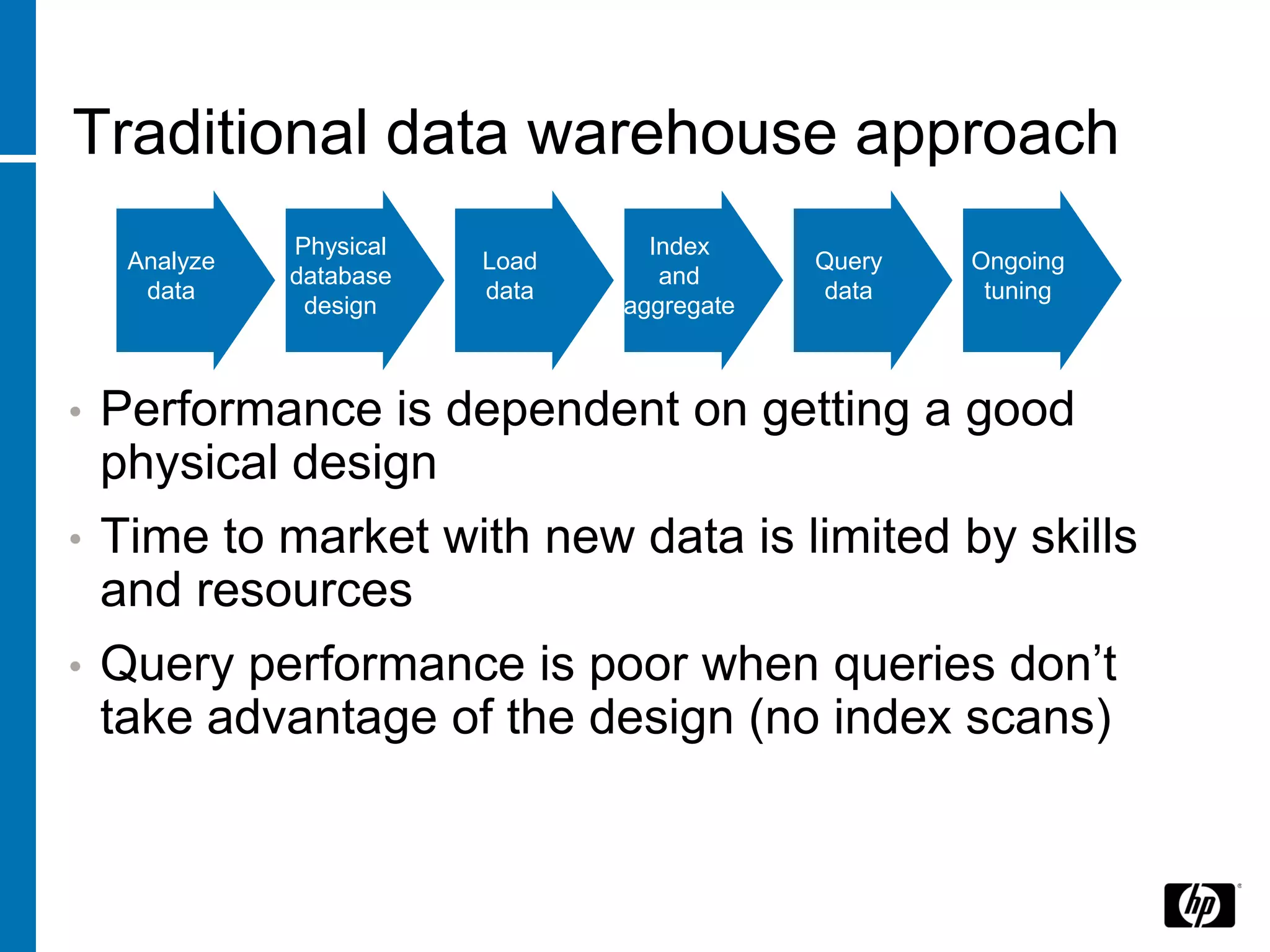
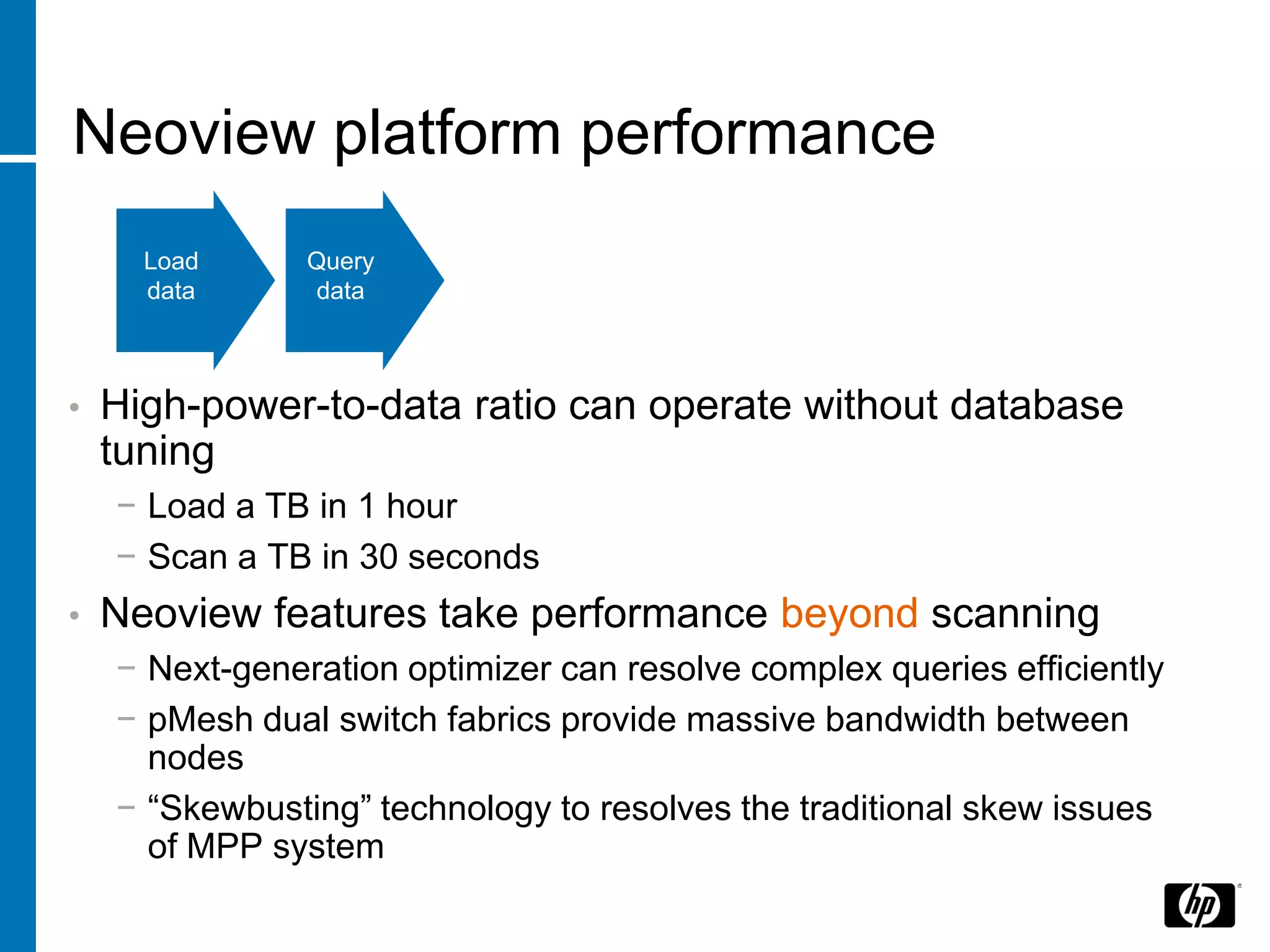
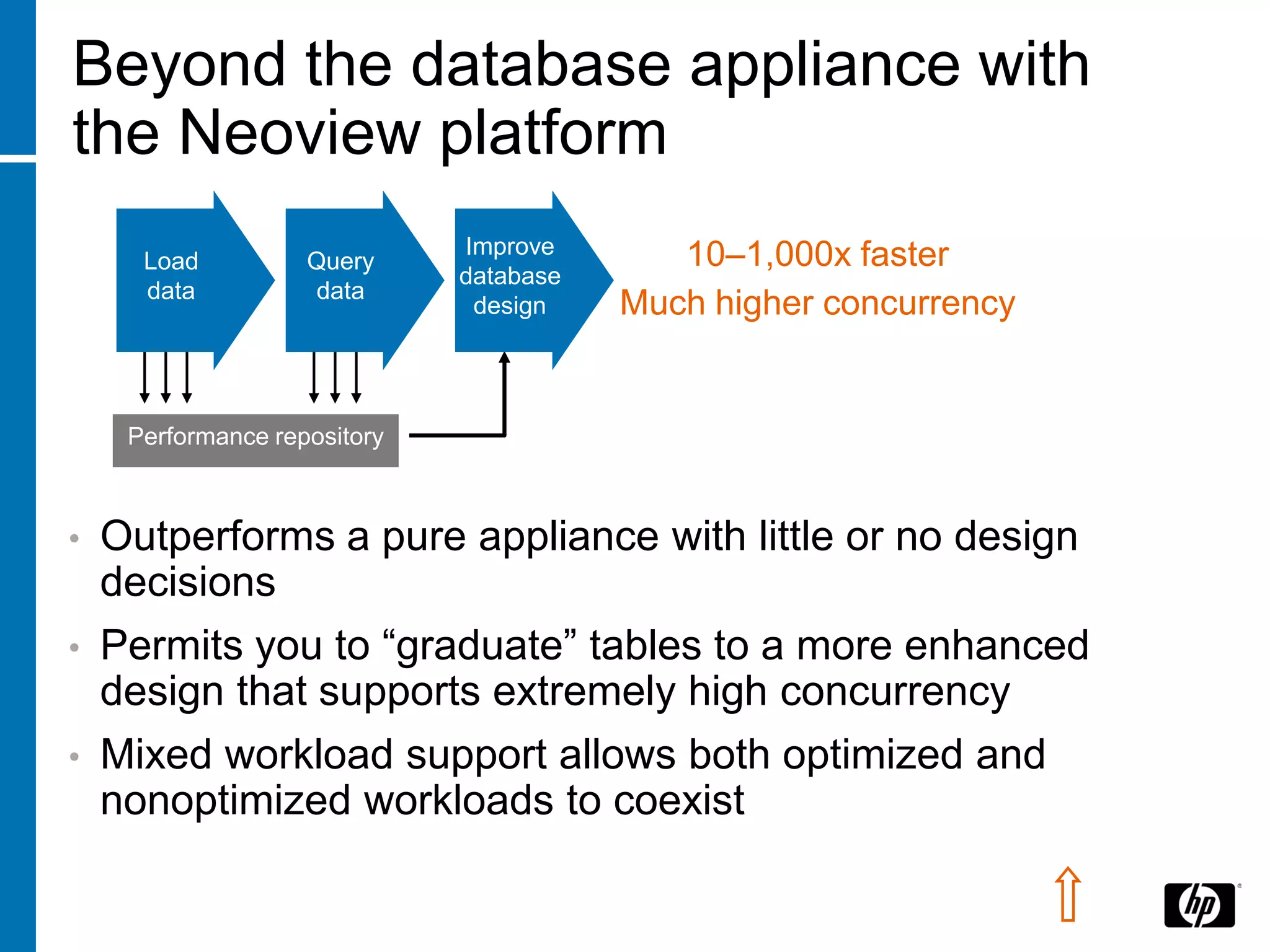
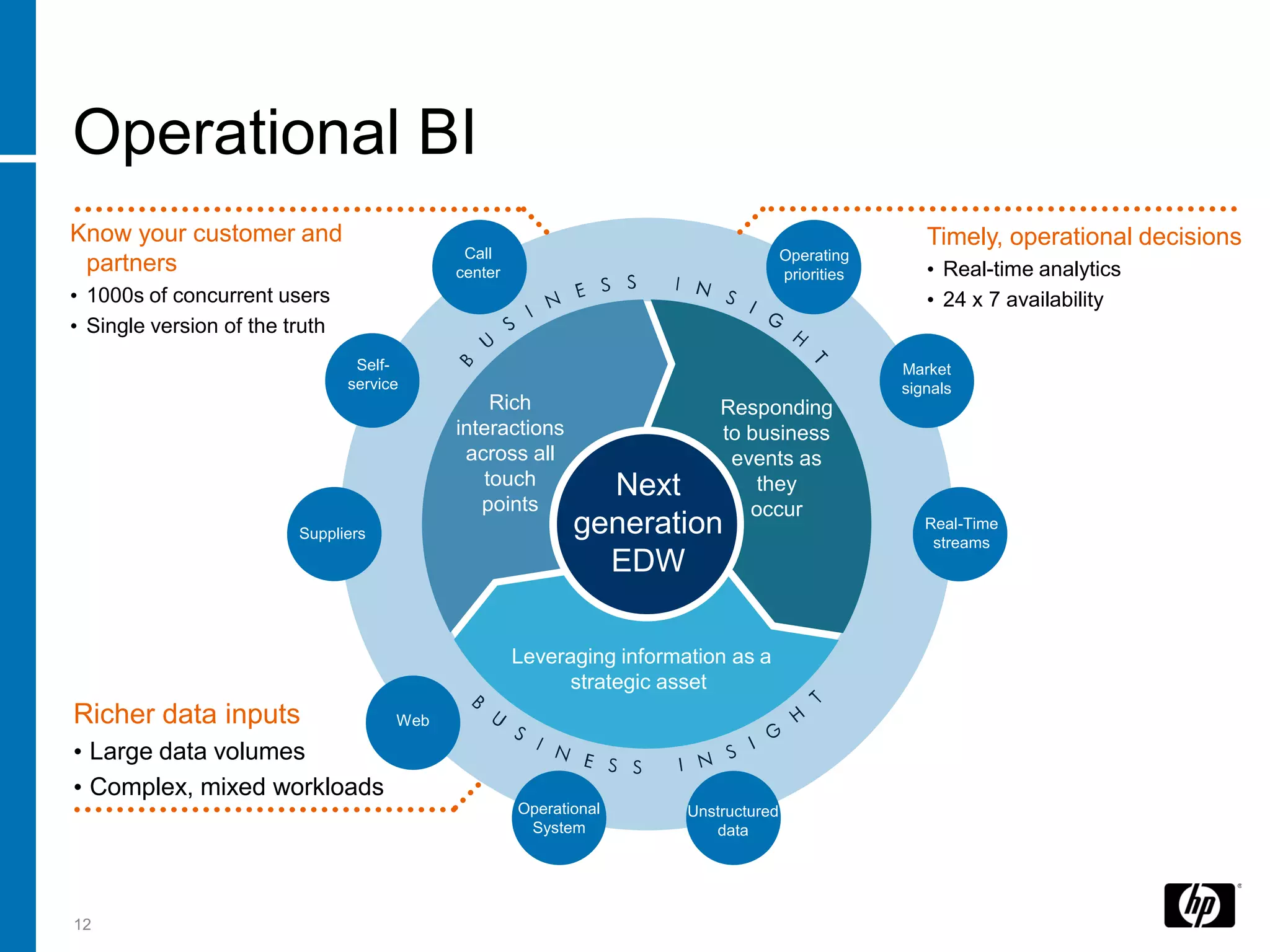
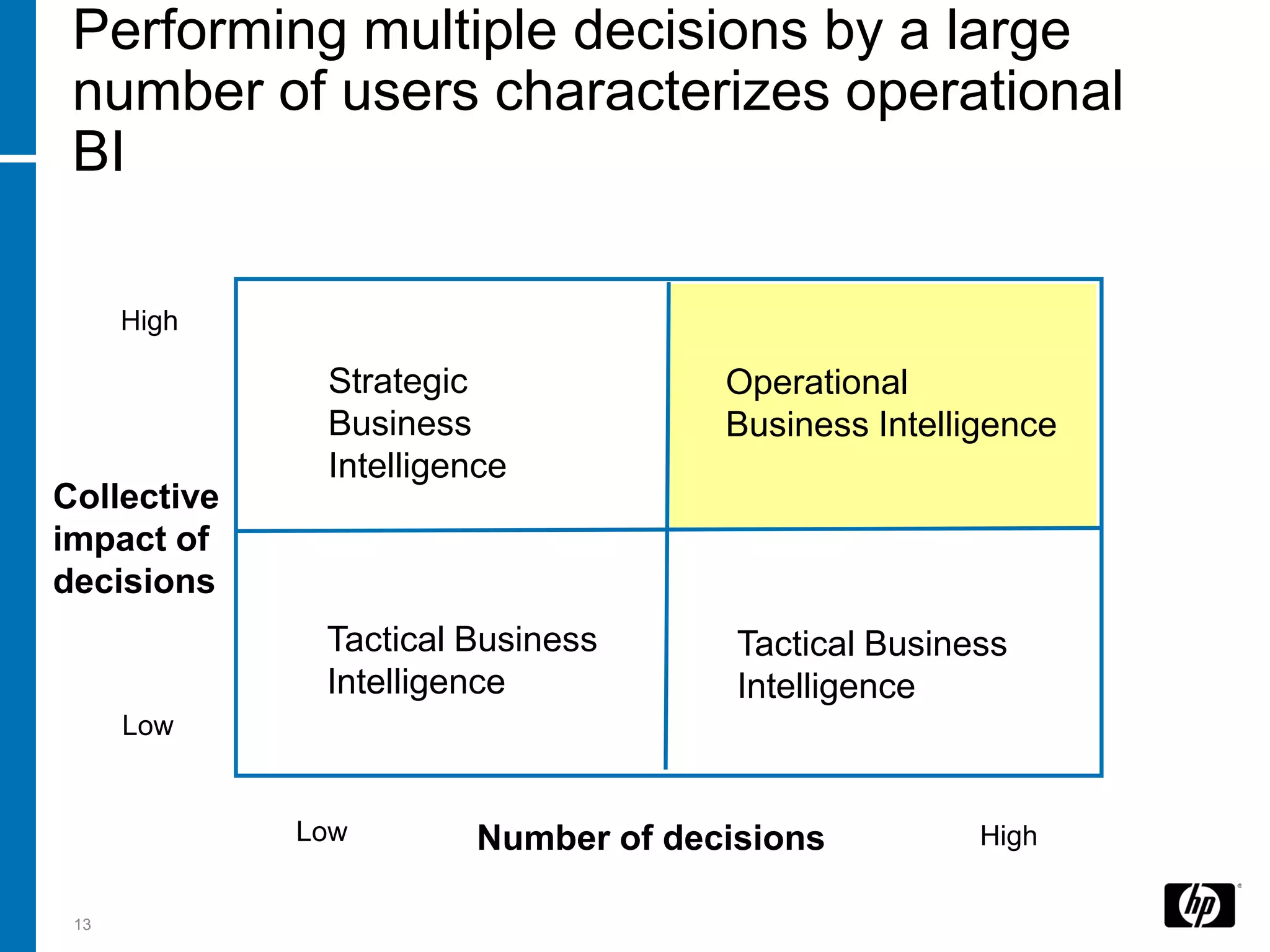
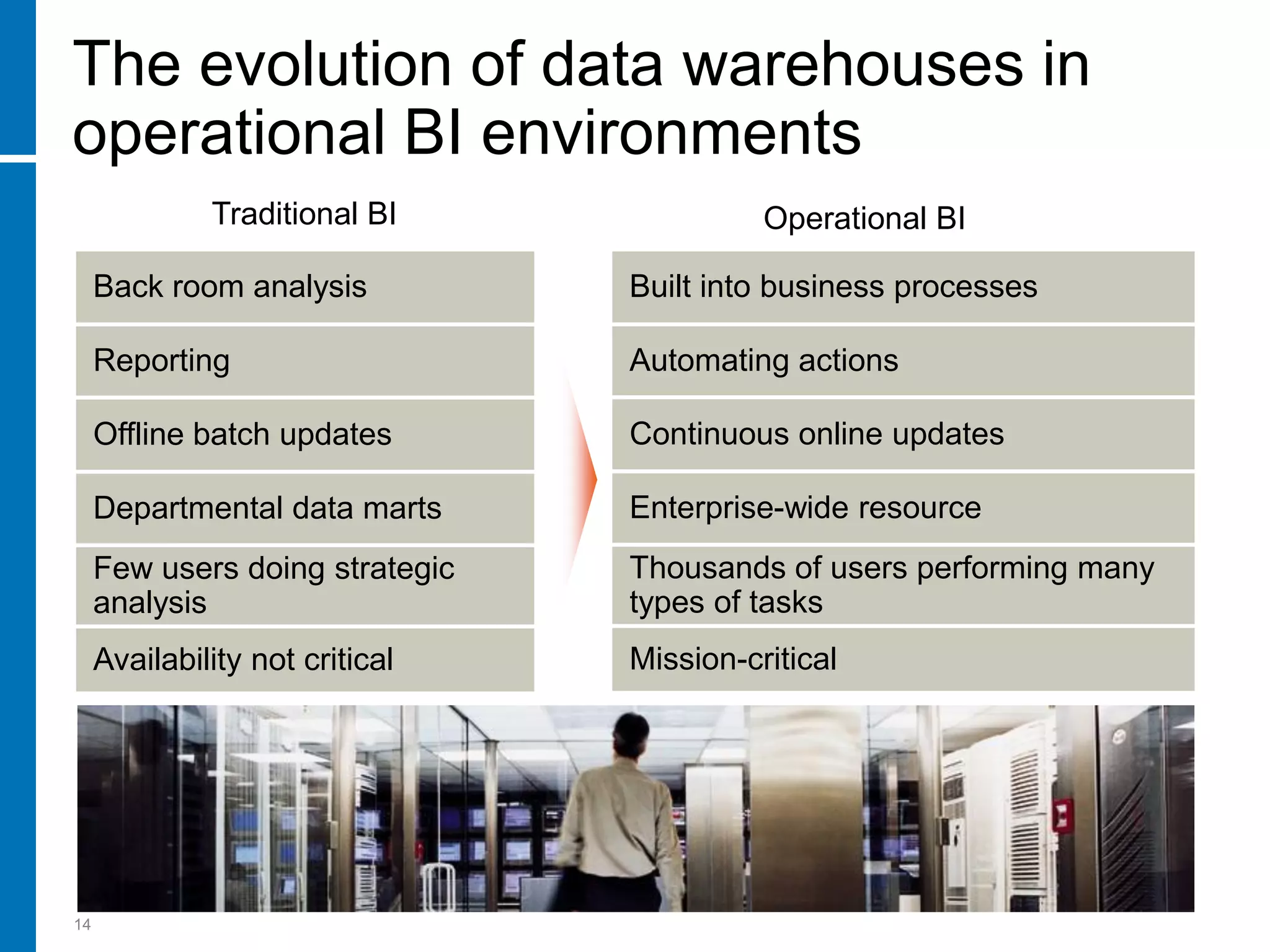
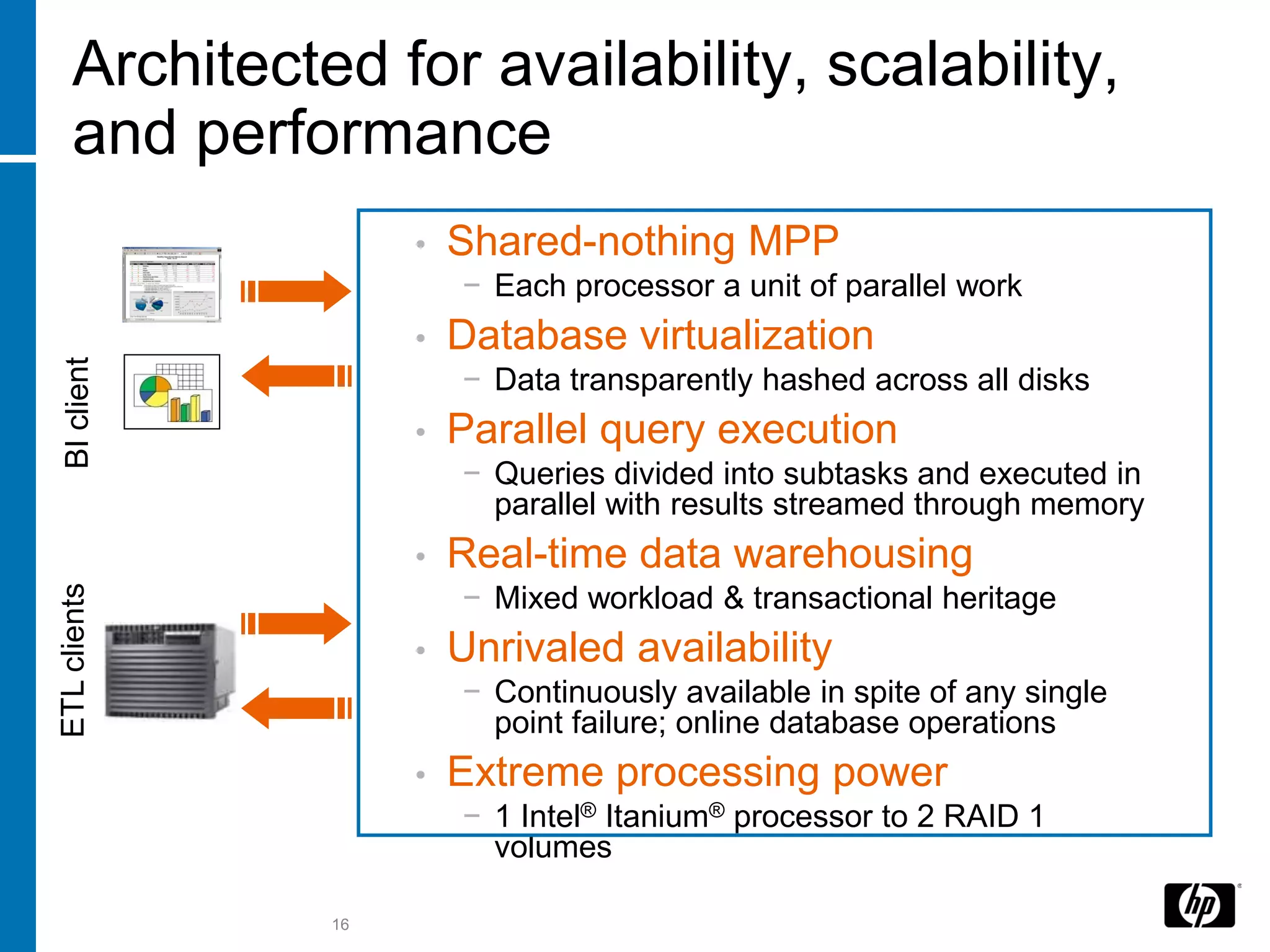
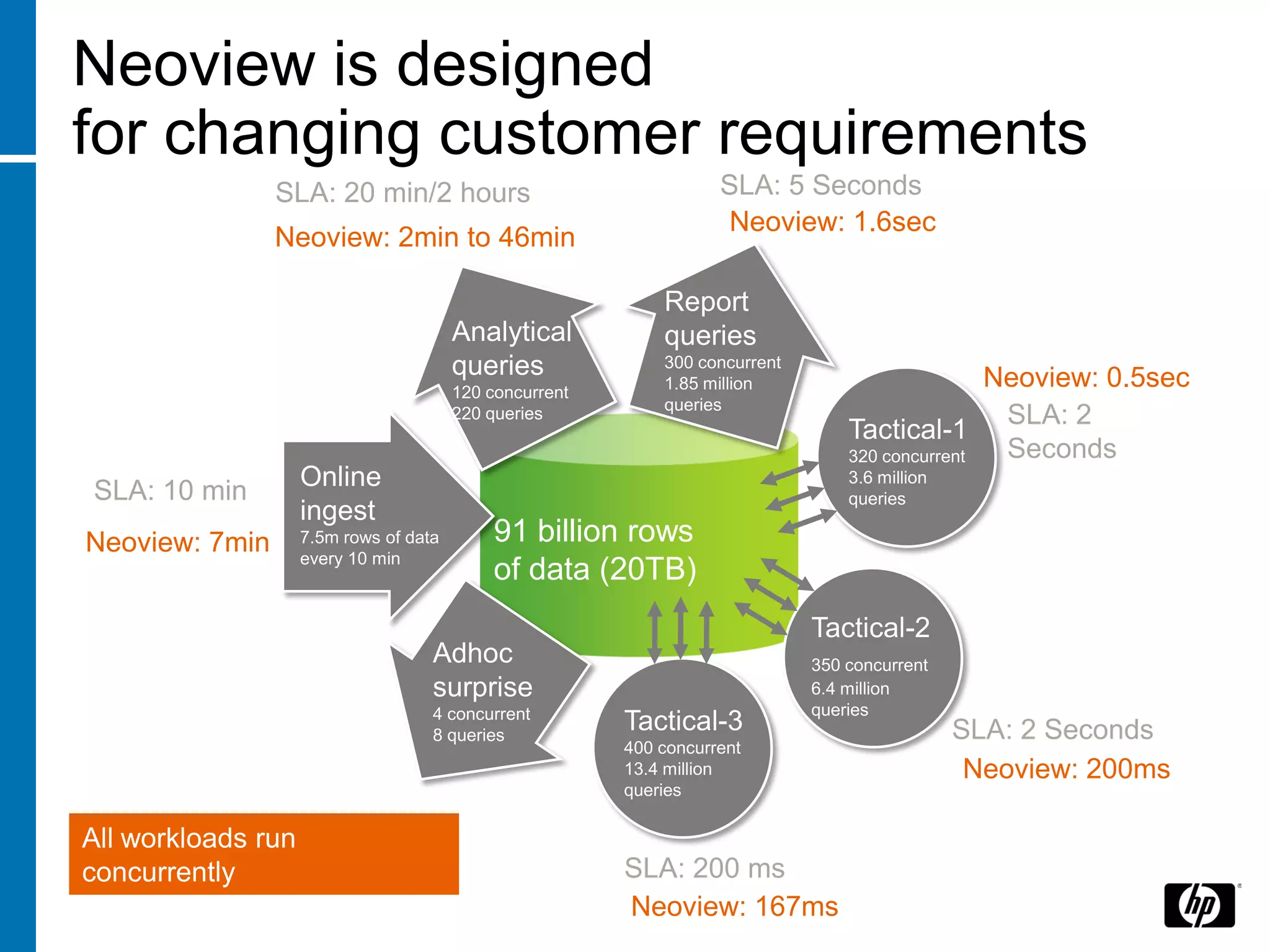
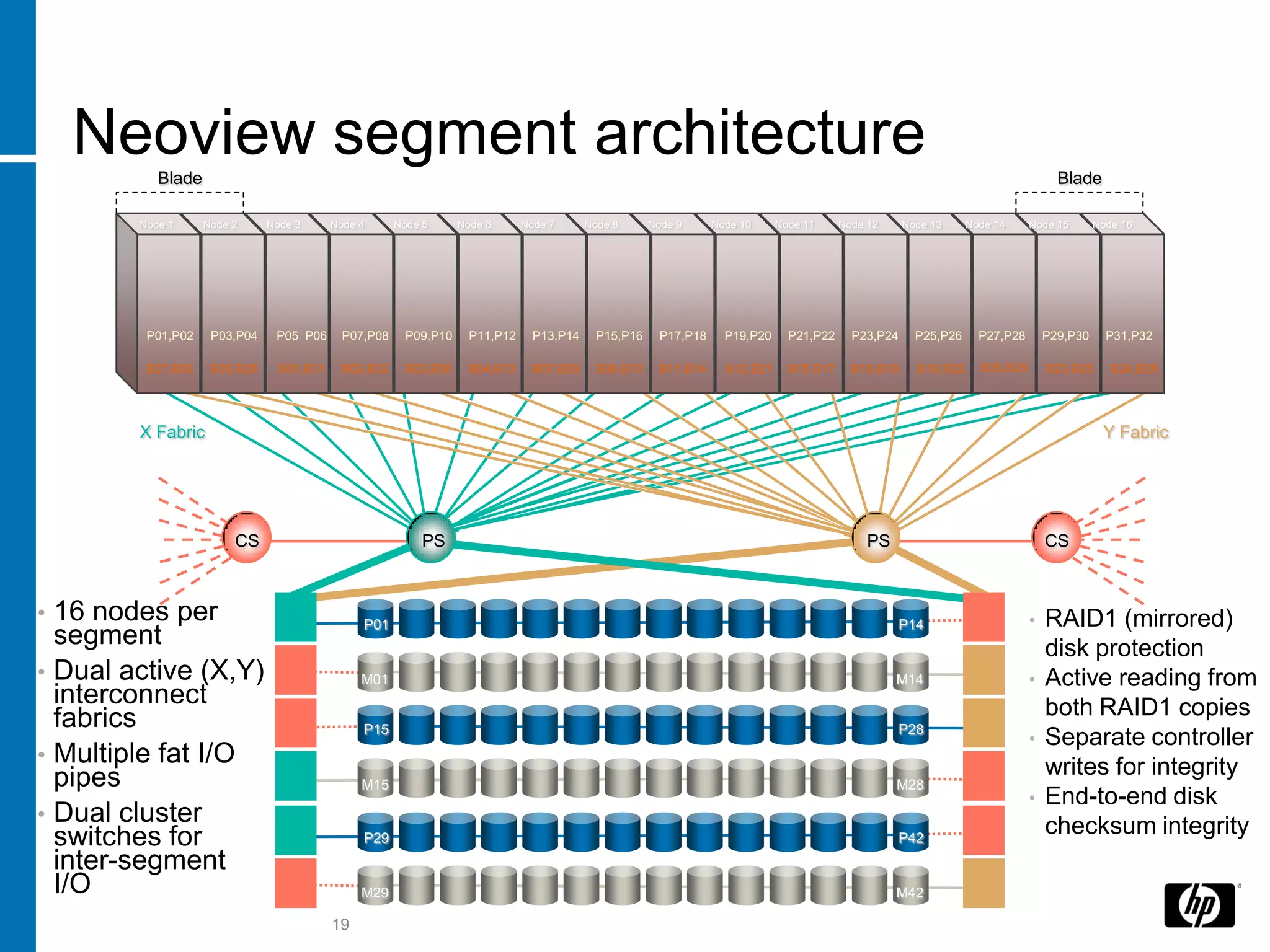
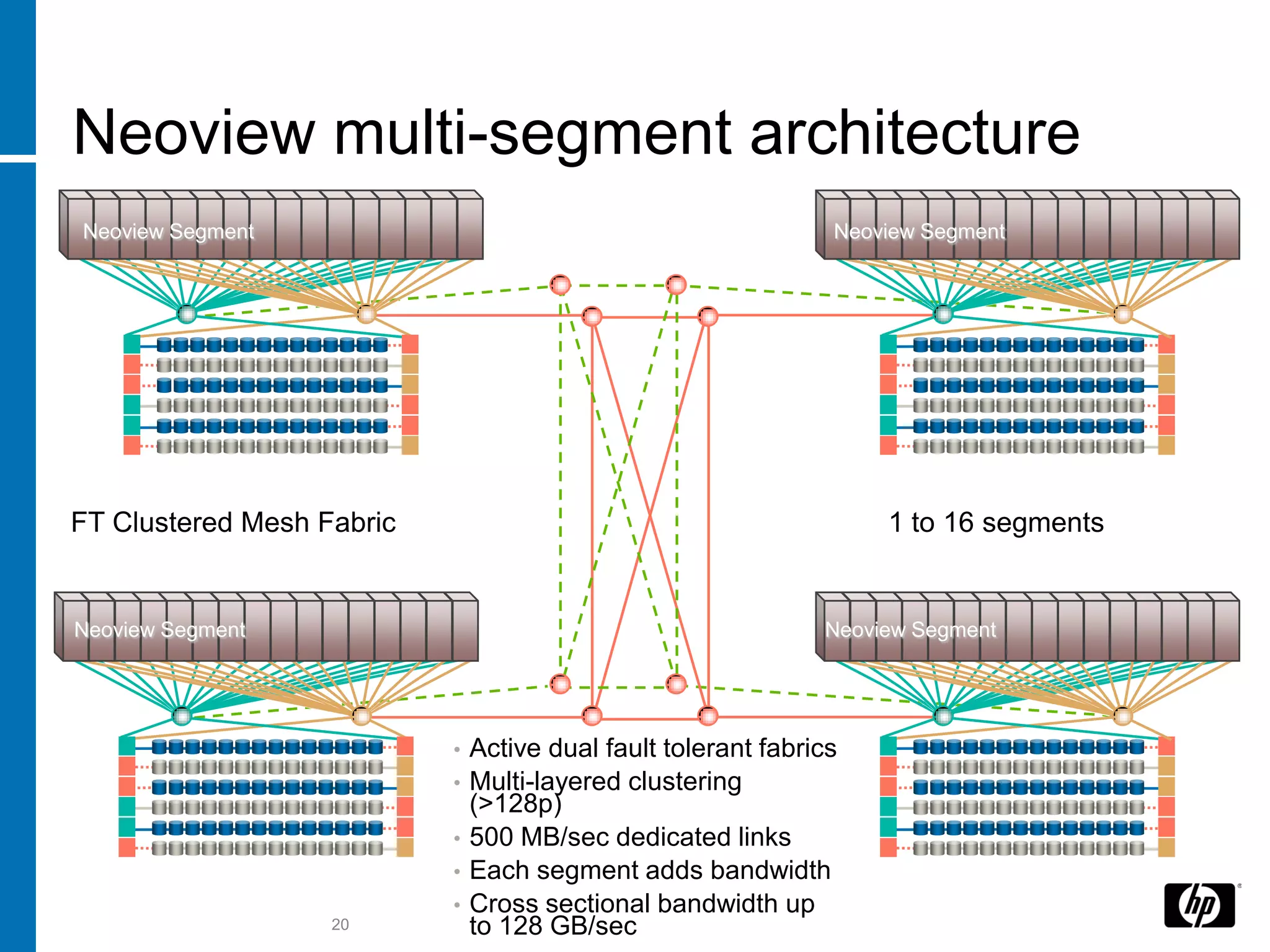
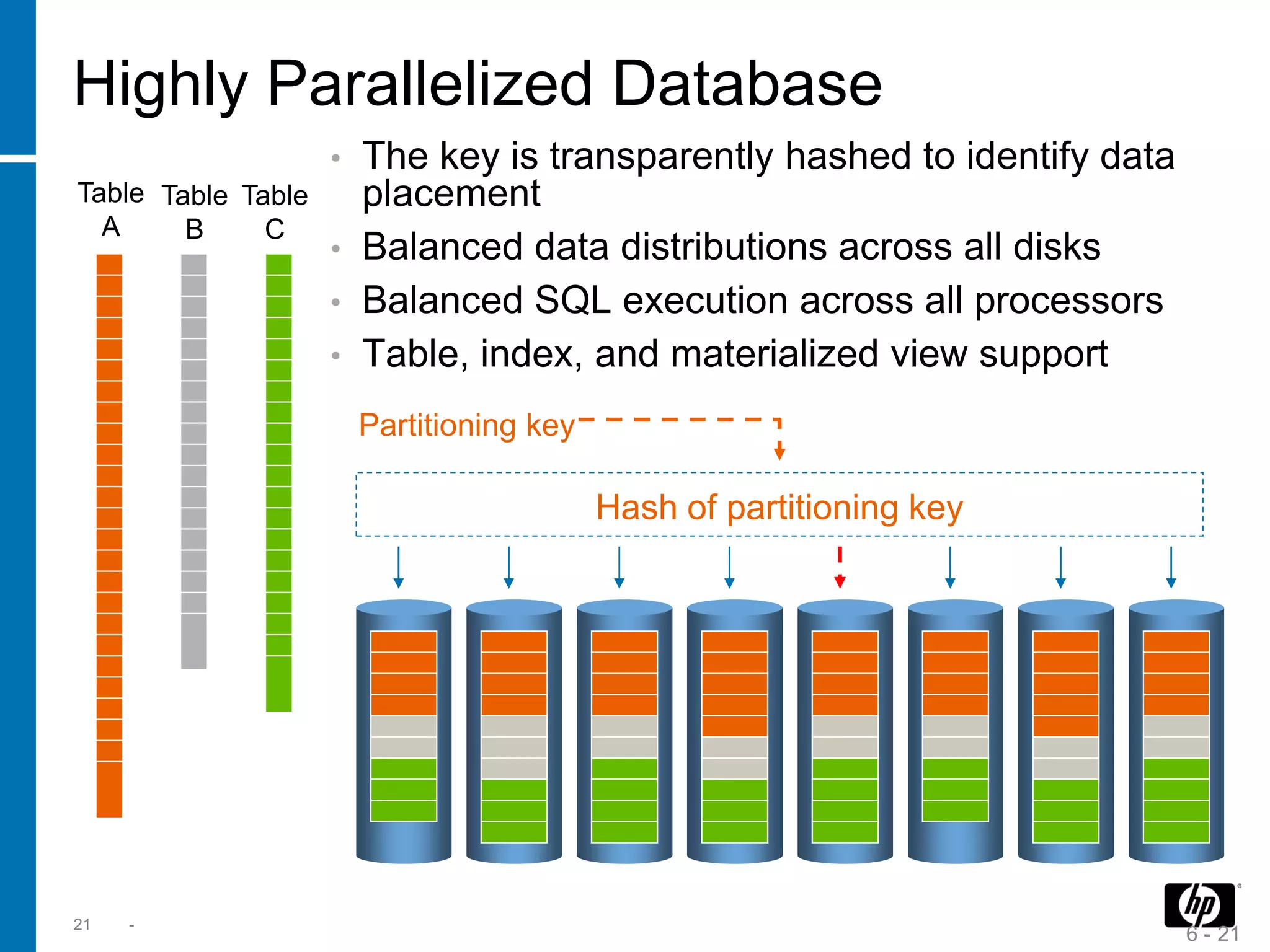
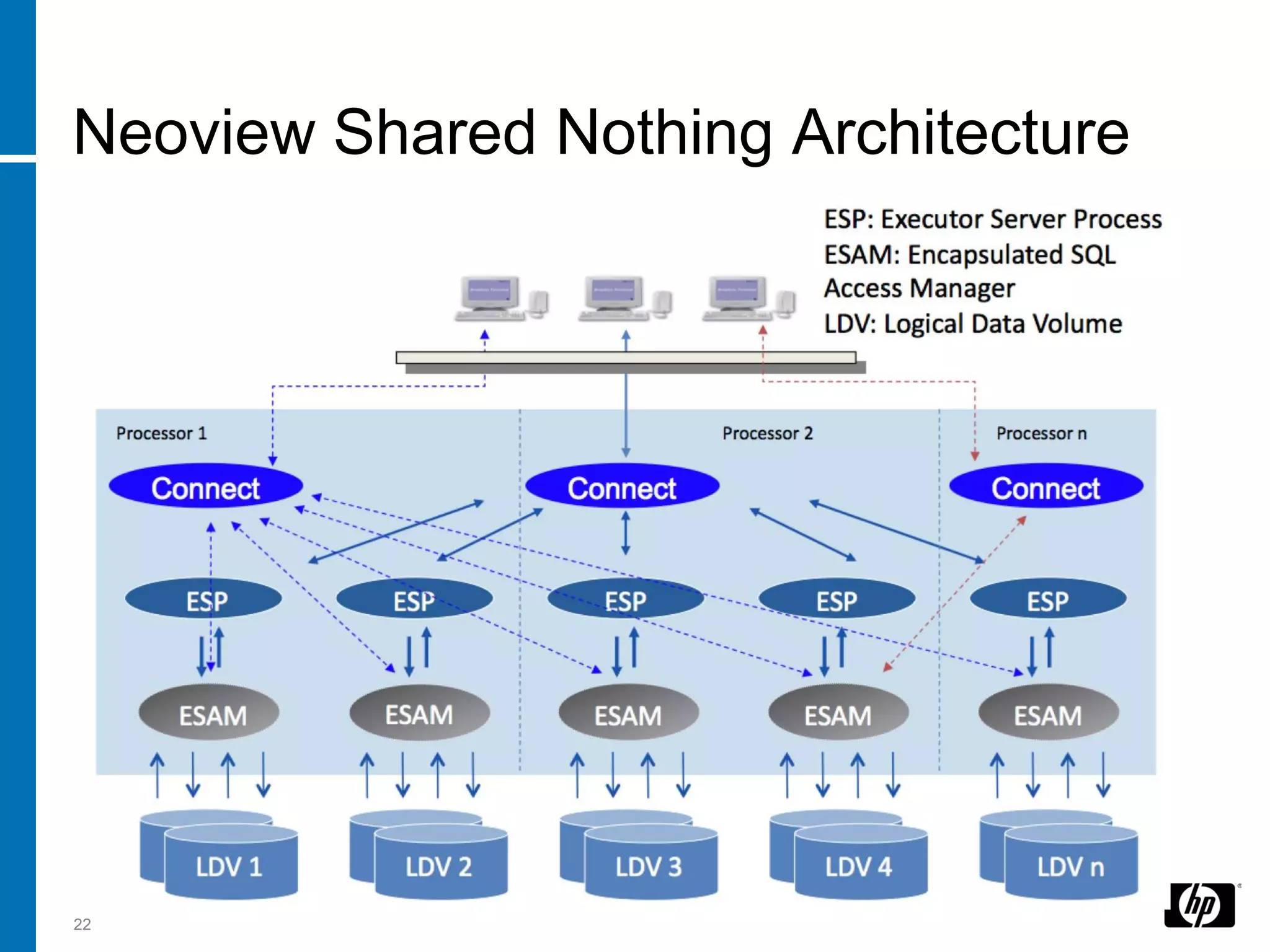
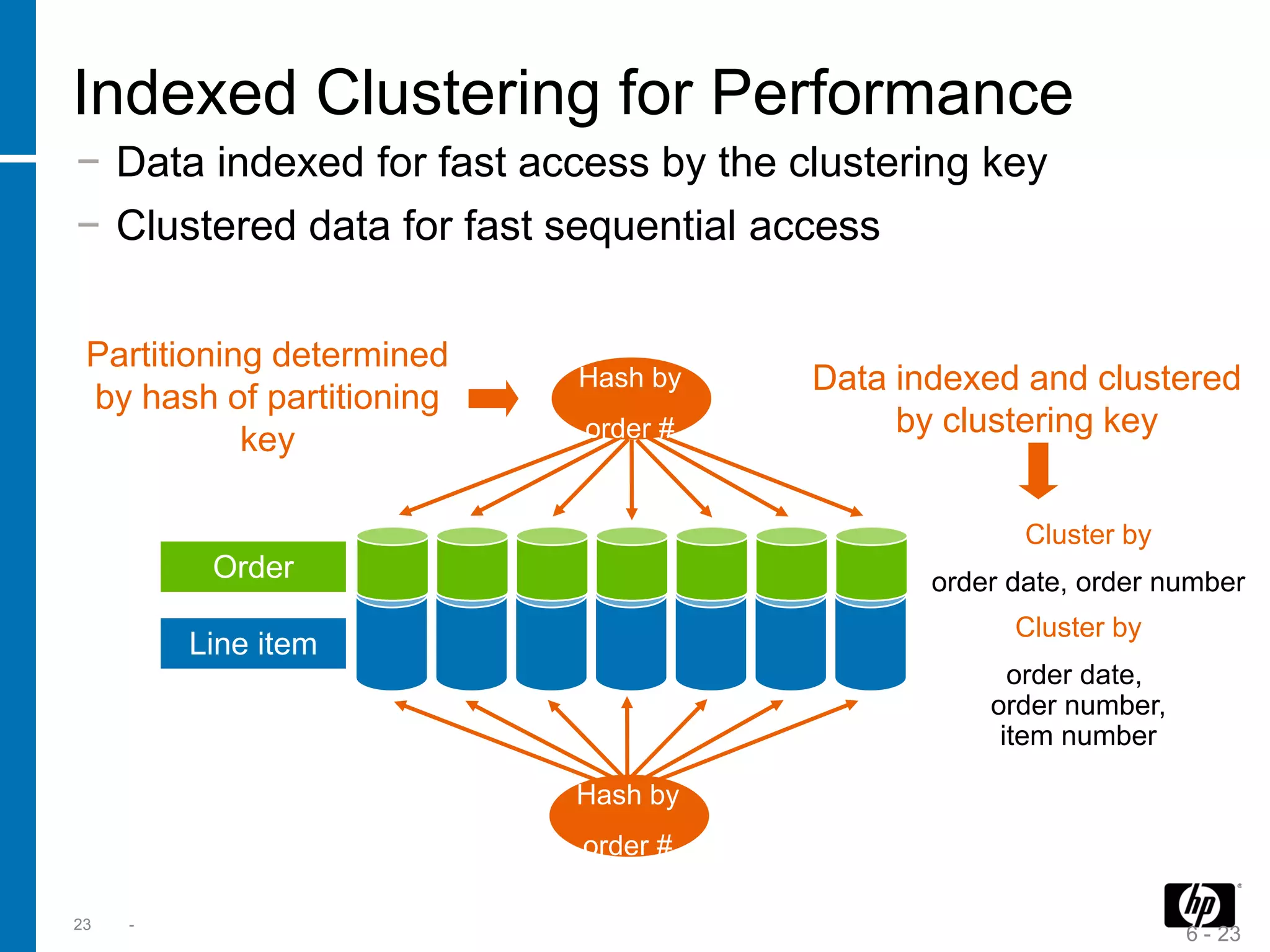
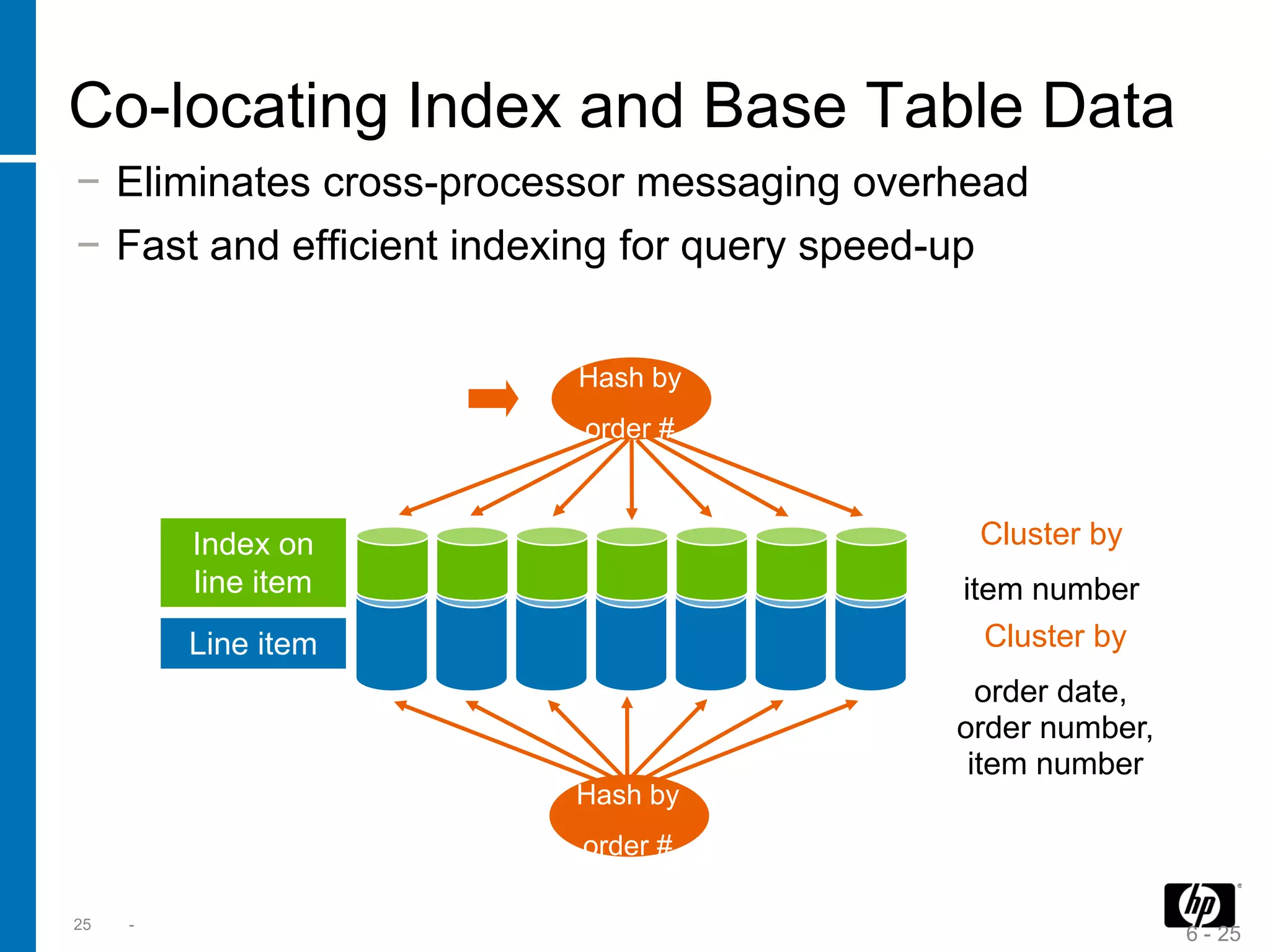
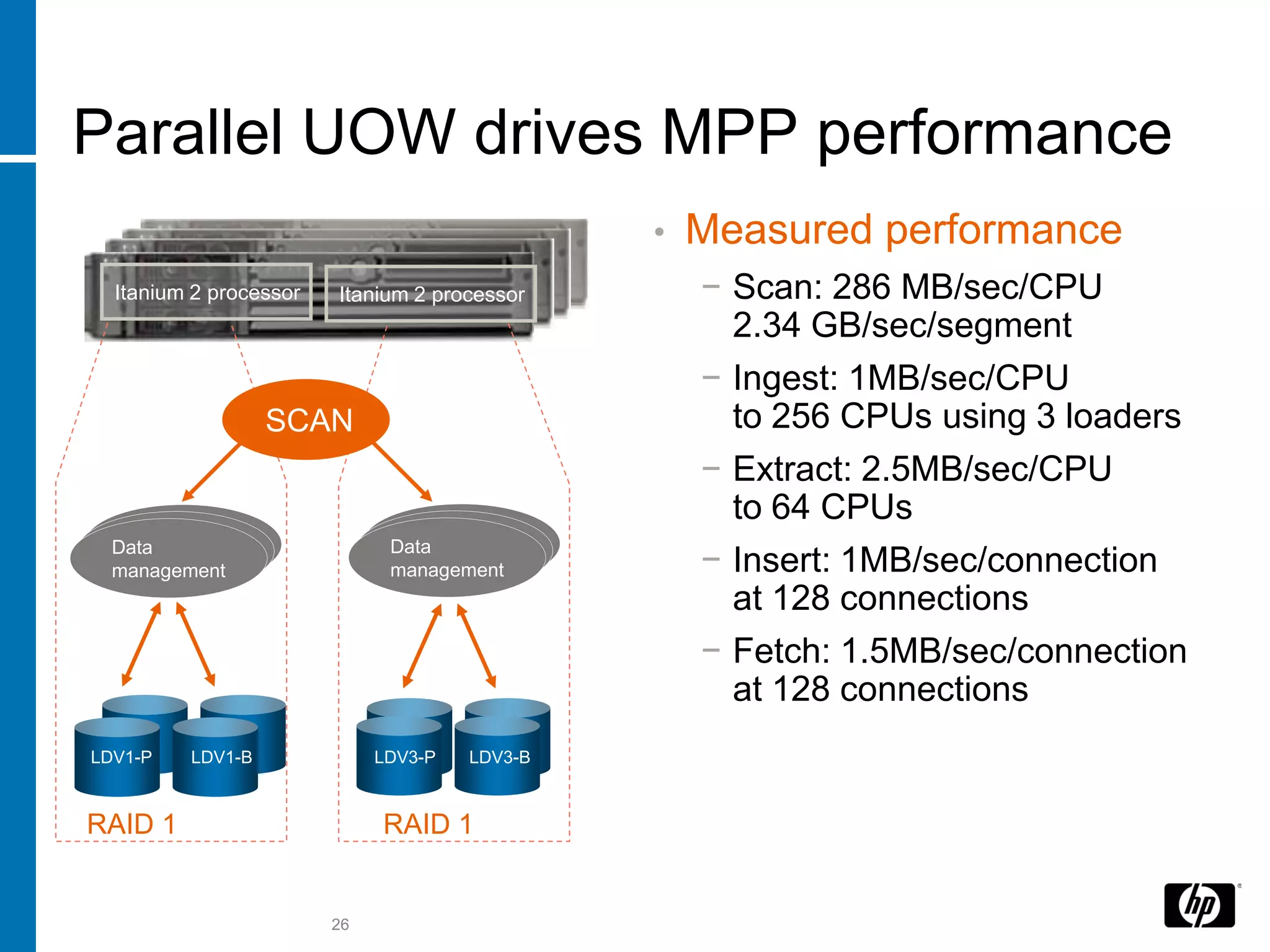
The document summarizes a presentation about data warehouse appliances and the principles of designing a data warehouse on an "EDWH appliance" platform. It discusses how appliances provide optimized, pre-tuned systems for BI workloads. It also presents the architecture of a massively parallel processing (MPP) data warehouse for operational data warehousing, including features like shared-nothing architecture and parallel query execution.