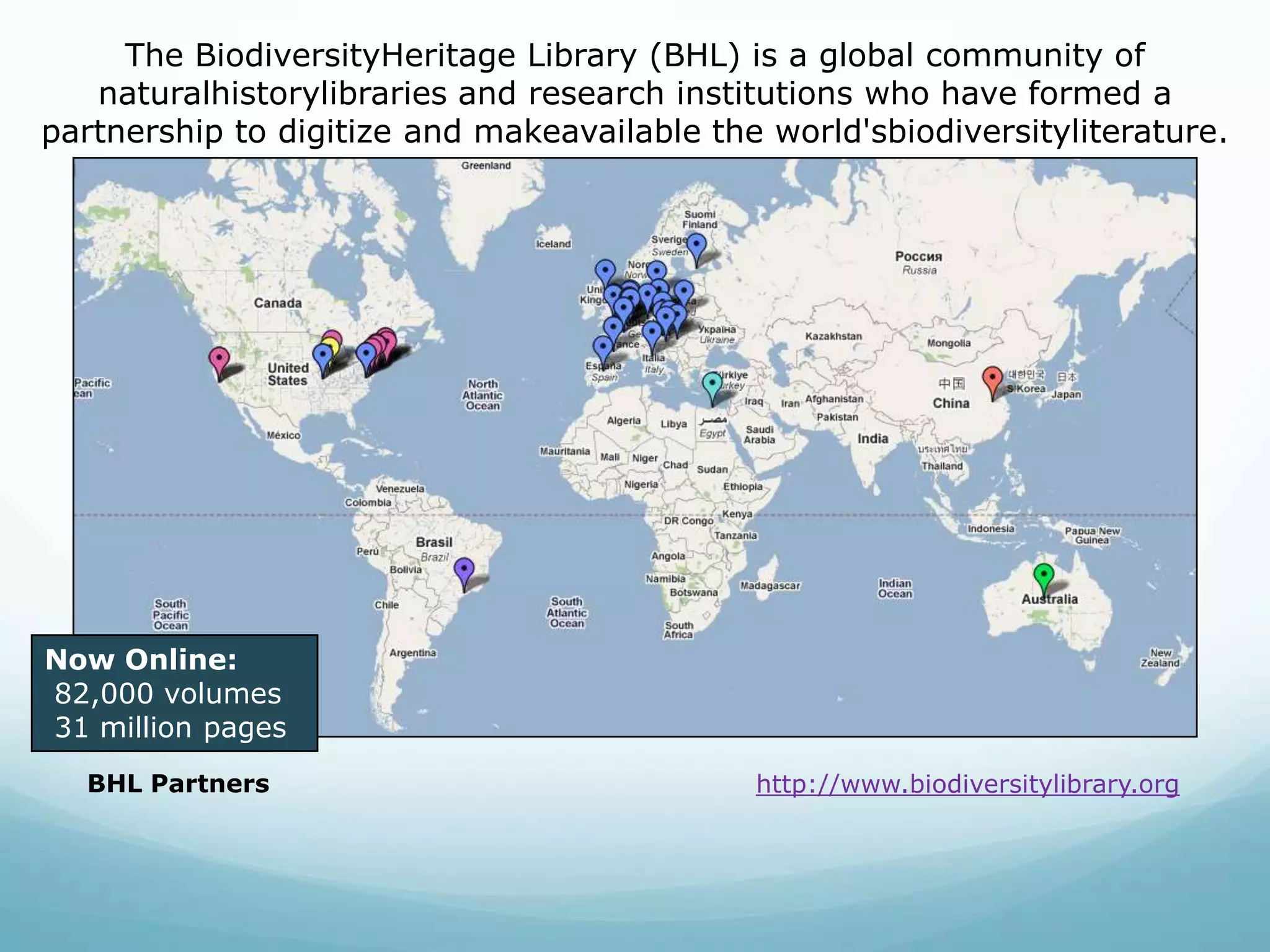
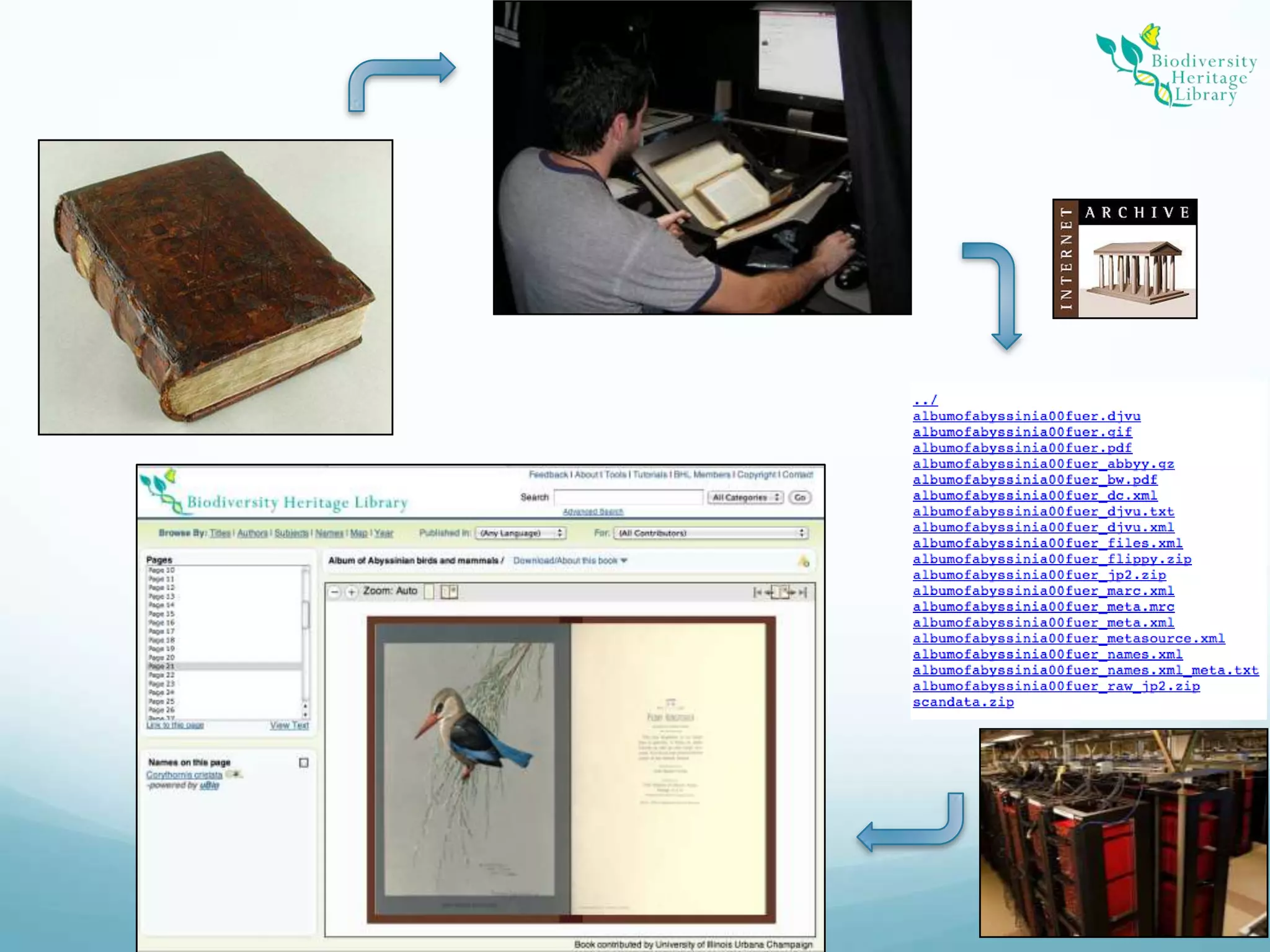
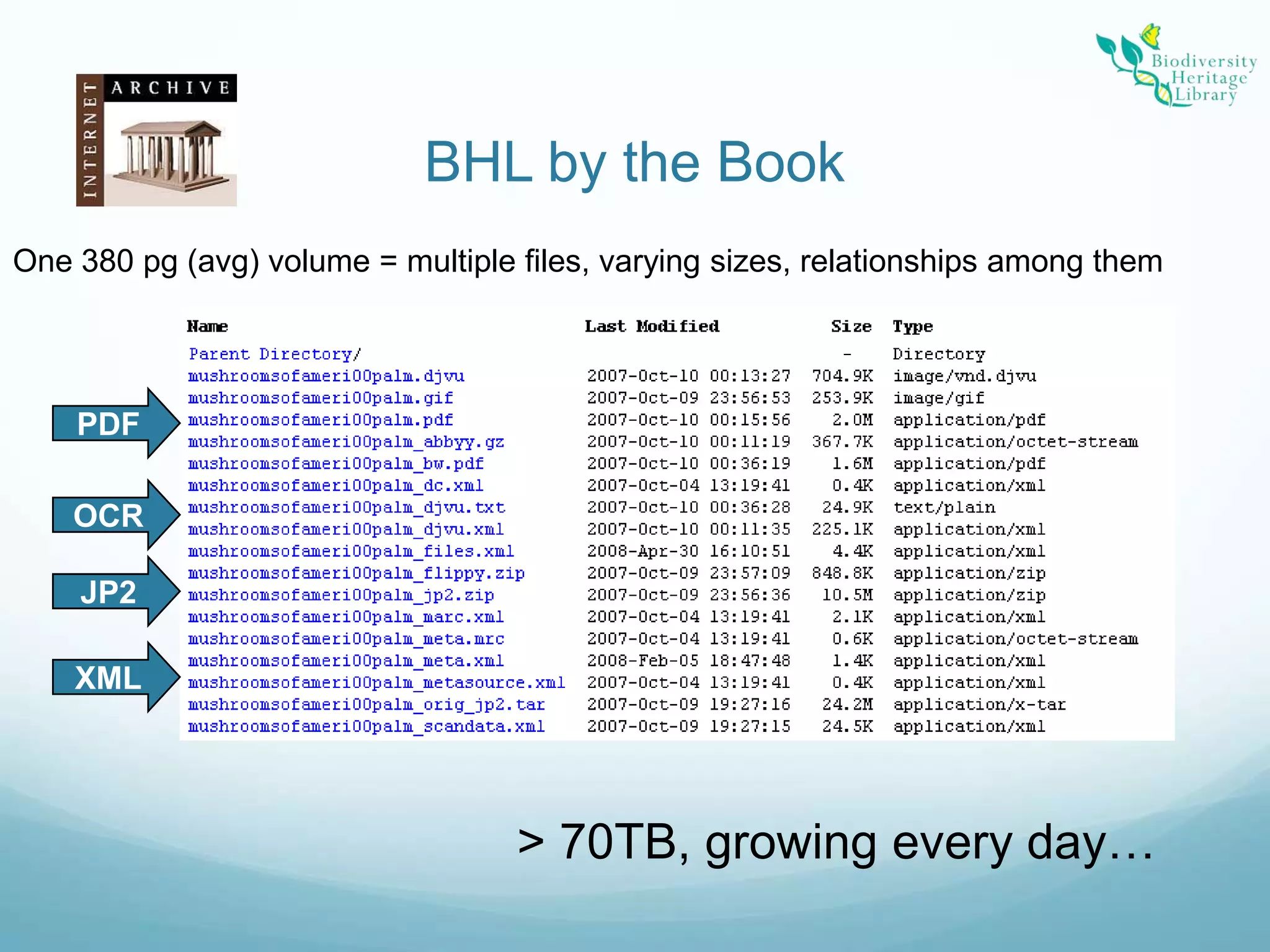
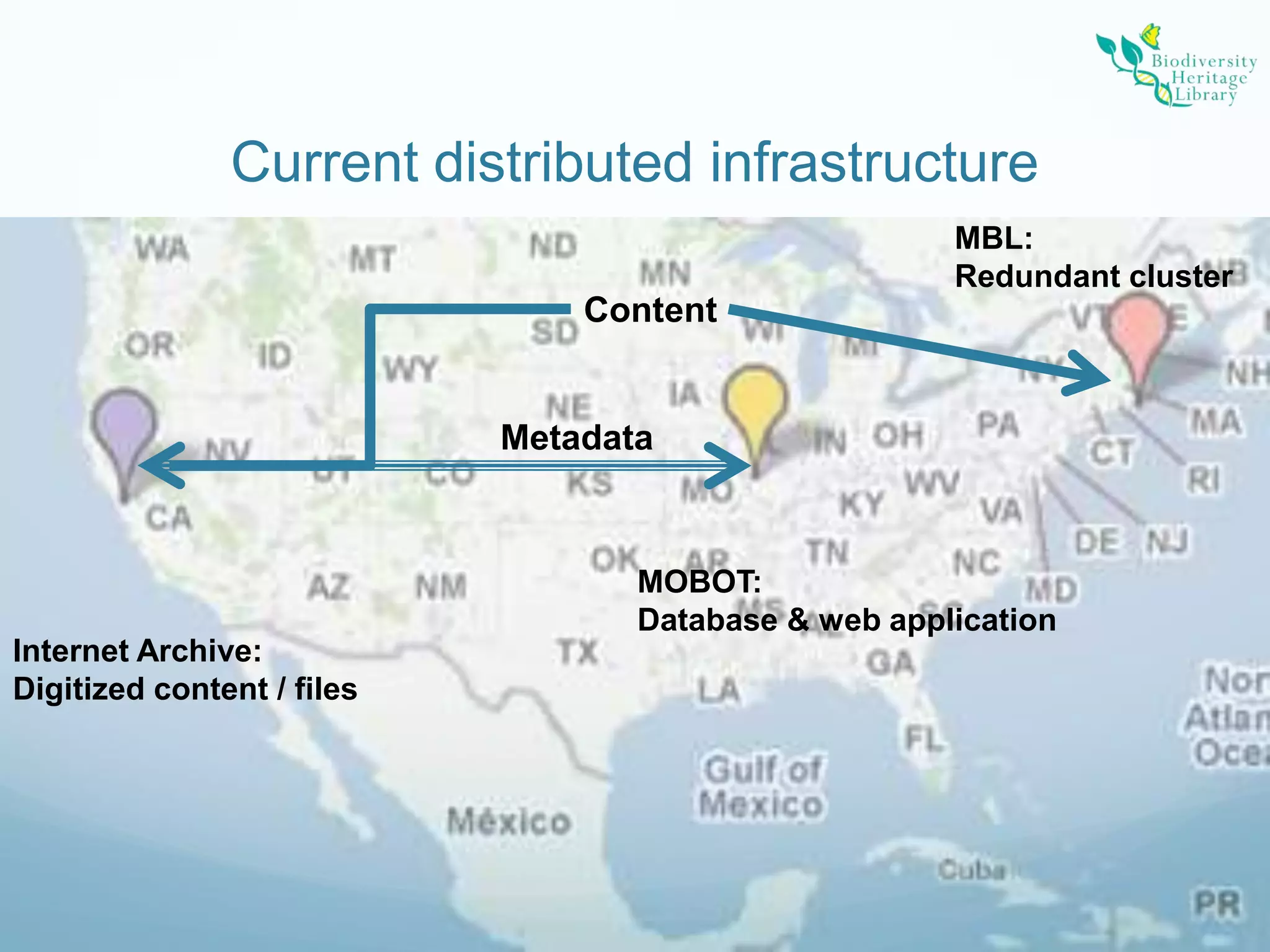
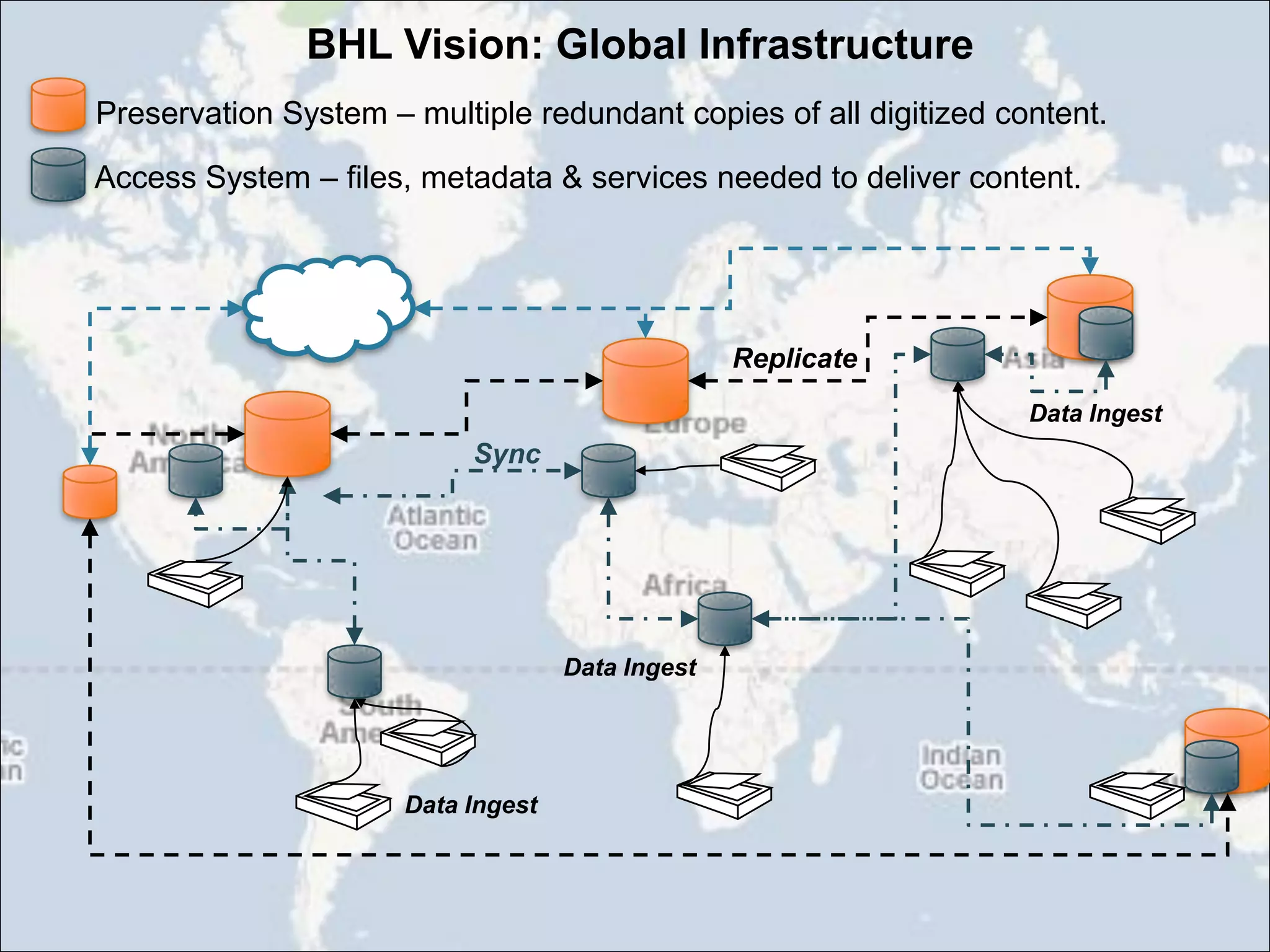
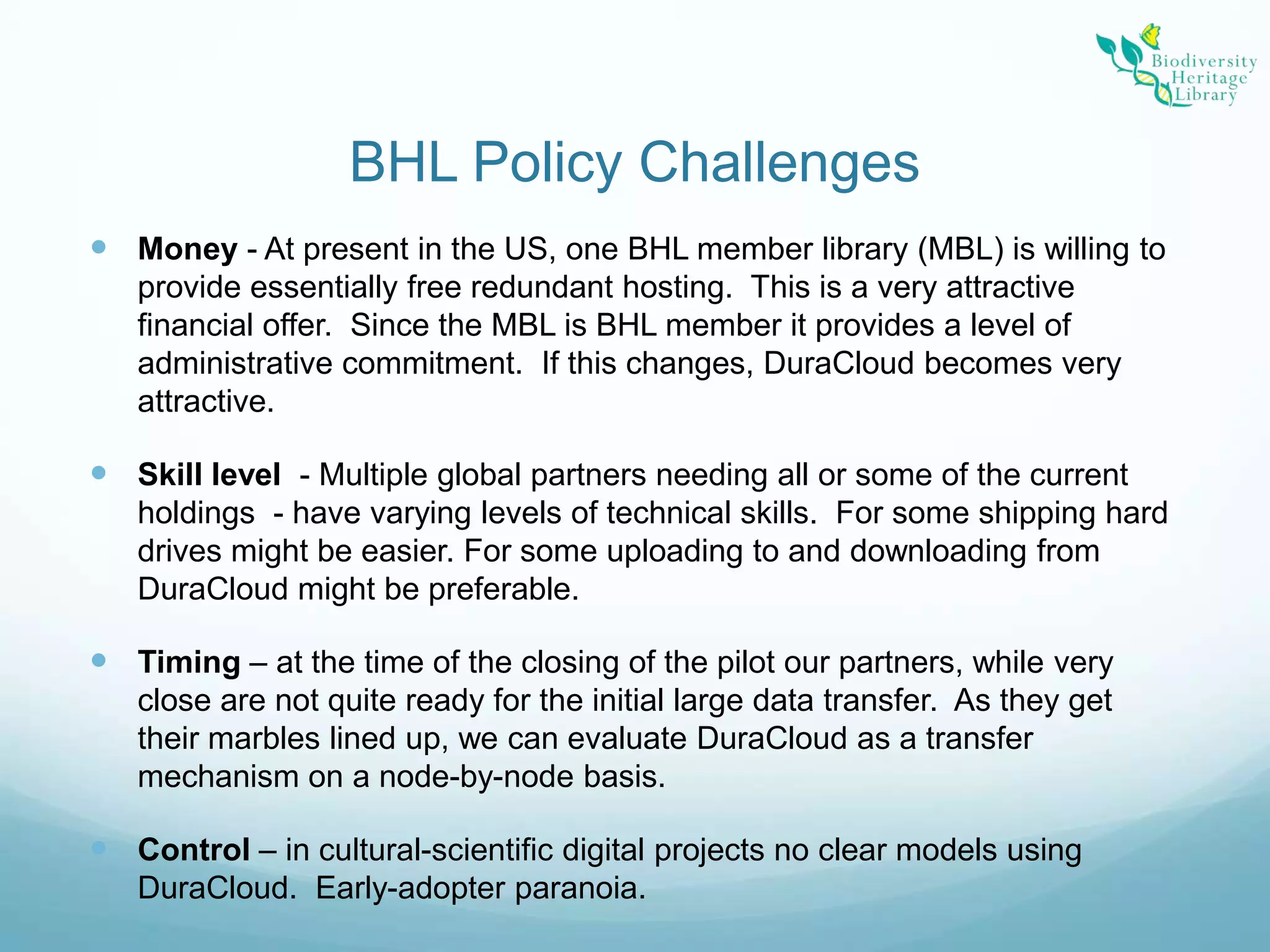
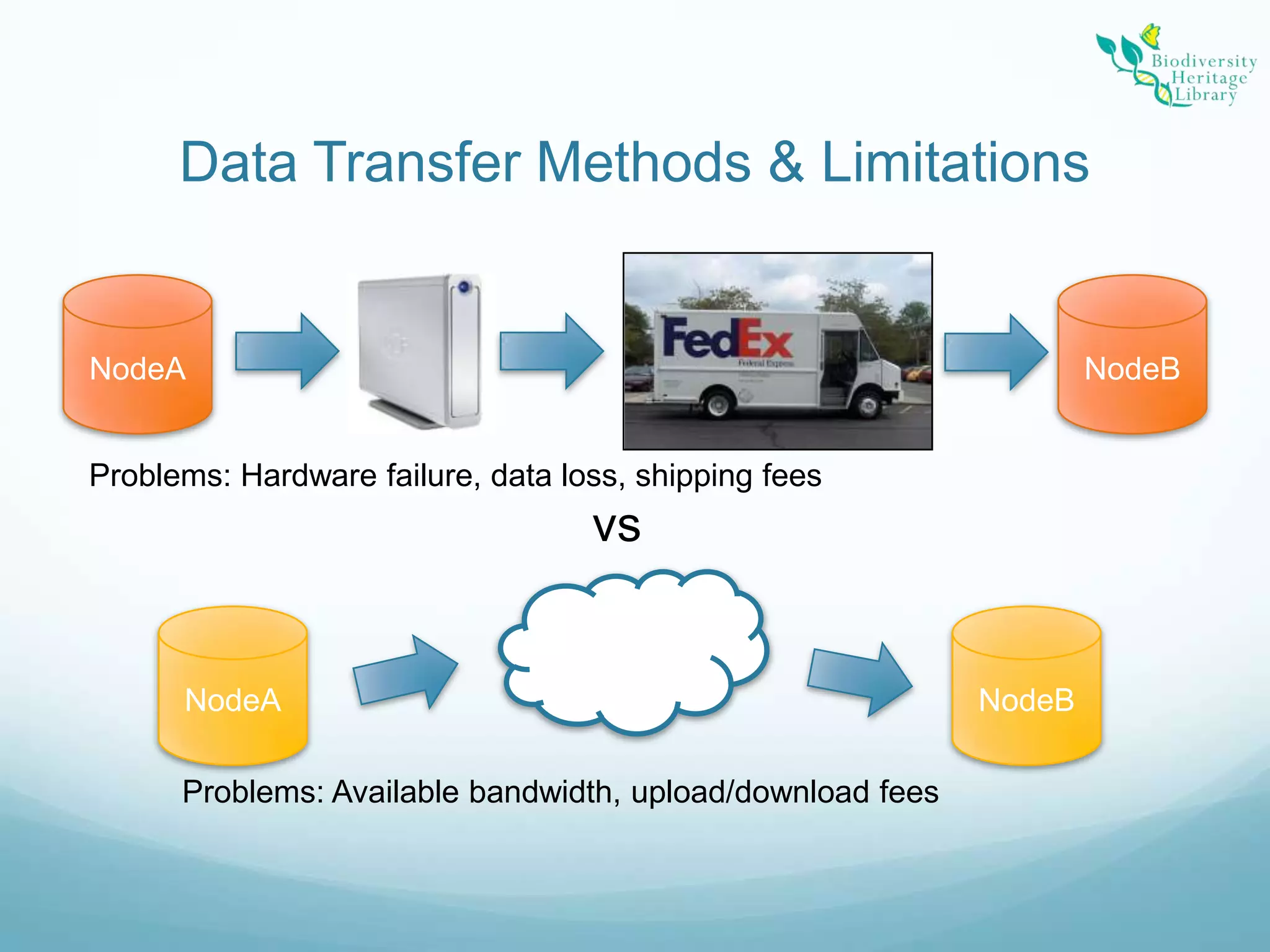
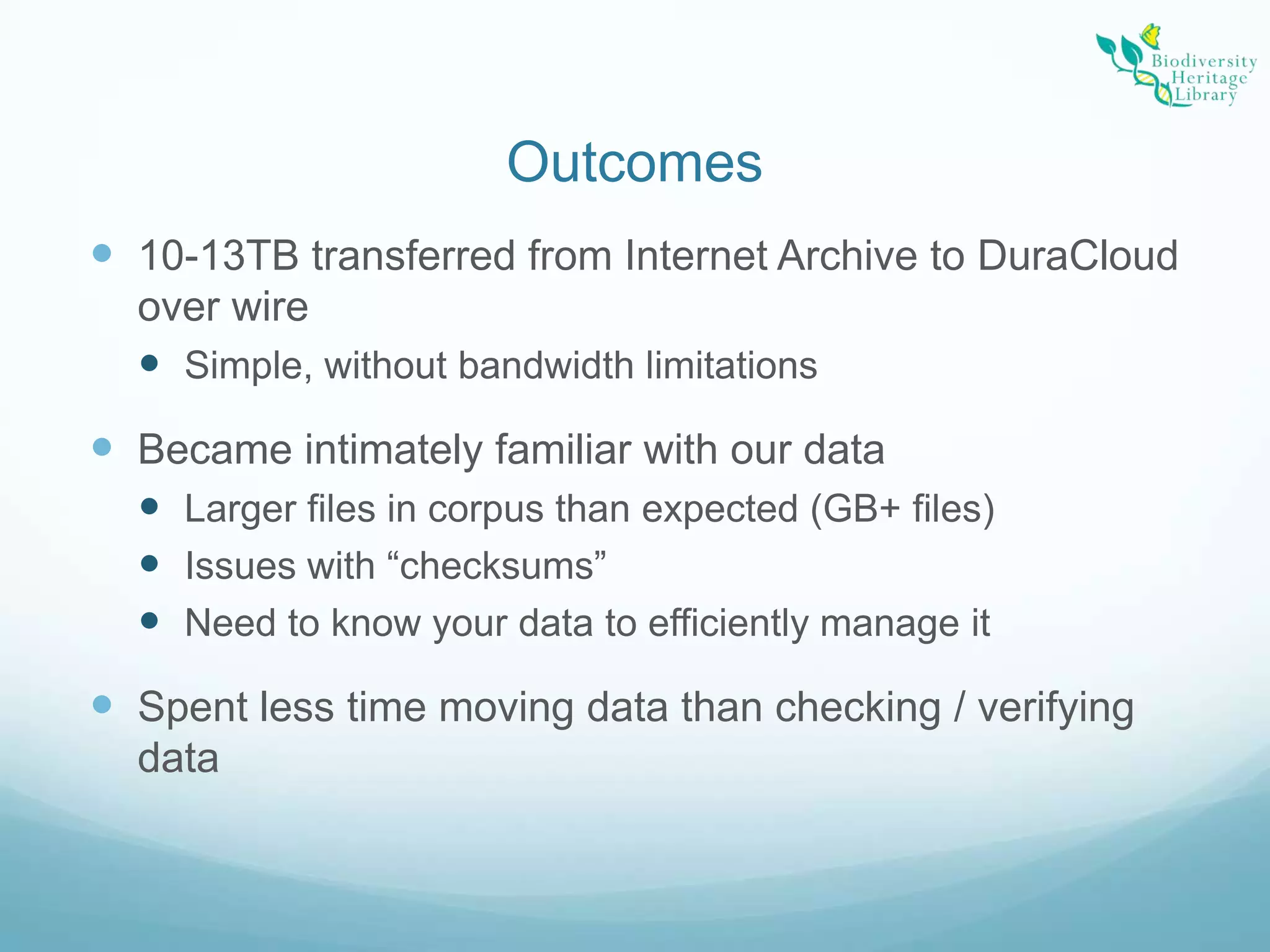
The Biodiversity Heritage Library (BHL) conducted a pilot project using the DuraCloud cloud storage service to evaluate its applicability for the BHL's large-scale digitization activities. The project involved transferring over 10 terabytes of content from the Internet Archive to DuraCloud. While cloud storage could provide benefits like scalability and redundancy, the BHL faces challenges around funding, technical skills of partners, and cultural preferences for control over digital materials. The pilot demonstrated that cloud is viable for storage and transfer but not a perfect solution, as large file sizes in the BHL corpus pose problems. Future uses of cloud infrastructure will depend on the needs and abilities of BHL partners.