Embed presentation
Downloaded 33 times









Cognitive appraisal and bodily symptoms occur first in the emotional experience sequence. This is followed by action tendencies for motor responses, facial and vocal expression, and subjective feelings. There are six main types of emotions: anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, and surprise. Surprise can fuel long-lasting associations and change behavior in an addictive way. Maslow's hierarchy of needs proposes that human motivation is based on unsatisfied needs, from basic physical needs to more complex psychological needs. As lower needs are satisfied, people advance to meet higher-level needs.
Describes the components of emotional experience: cognitive appraisal, bodily symptoms, action tendencies, expression, and feelings.
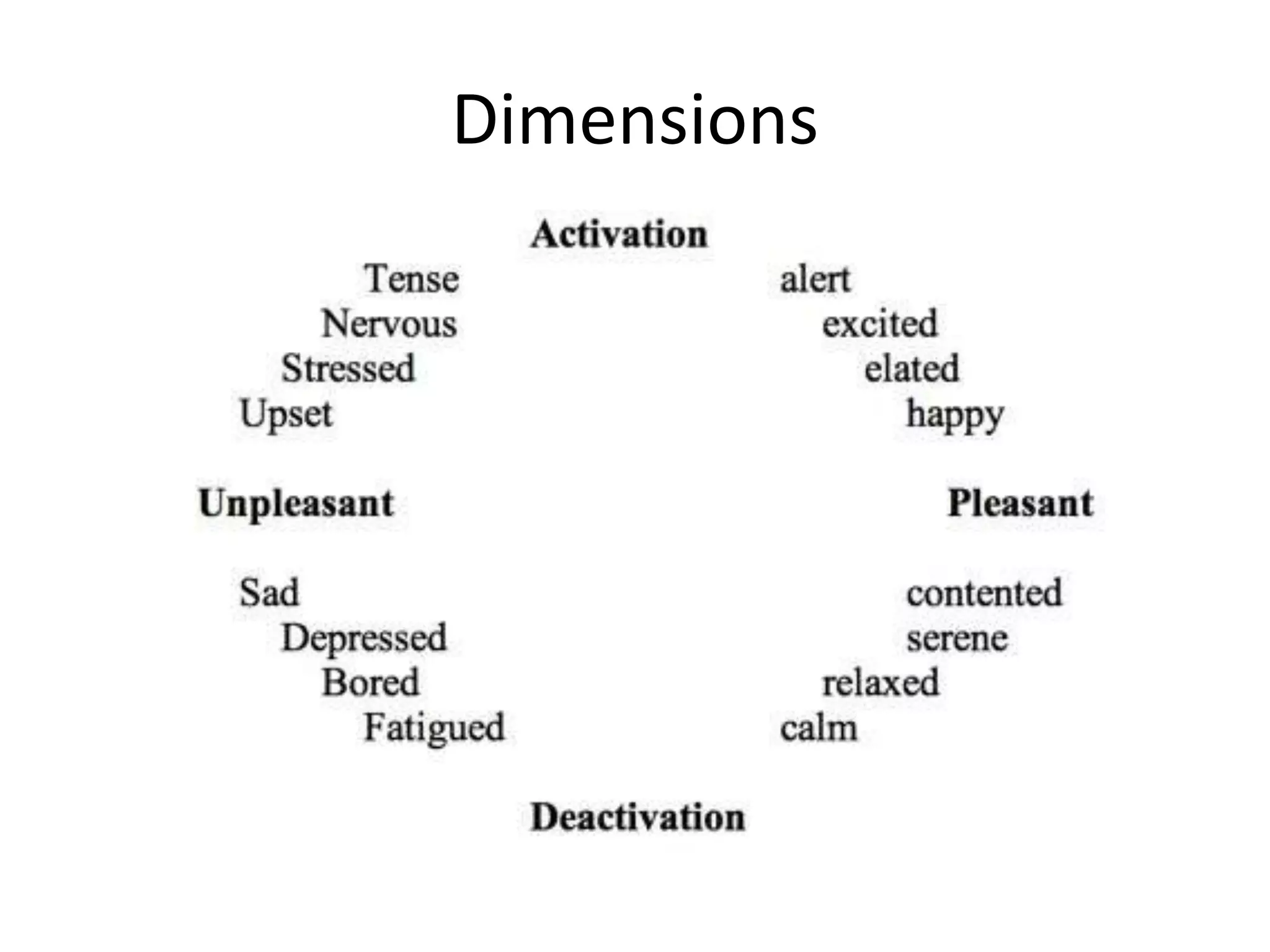
Presents the concept of dimensions relevant to emotions, indicating a classification or framework.
Lists six basic types of emotions: anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, and surprise.
Discusses the addictive nature of surprise, its behavioral influence, and its economical benefits.
Introduces motivation frameworks including Maslow's hierarchy and Herzberg's two-factor theory.
Explains how human needs influence behavior, structured in a hierarchy from basic to complex.
Presents Alderfer’s model which groups needs into three categories: existence, relatedness, growth.
Describes elements of attention including cognitive inhibition and the bottom-up and top-down processes.
Outlines Hofstede’s six dimensions of culture impacting behavior: power distance, individualism, and more.









