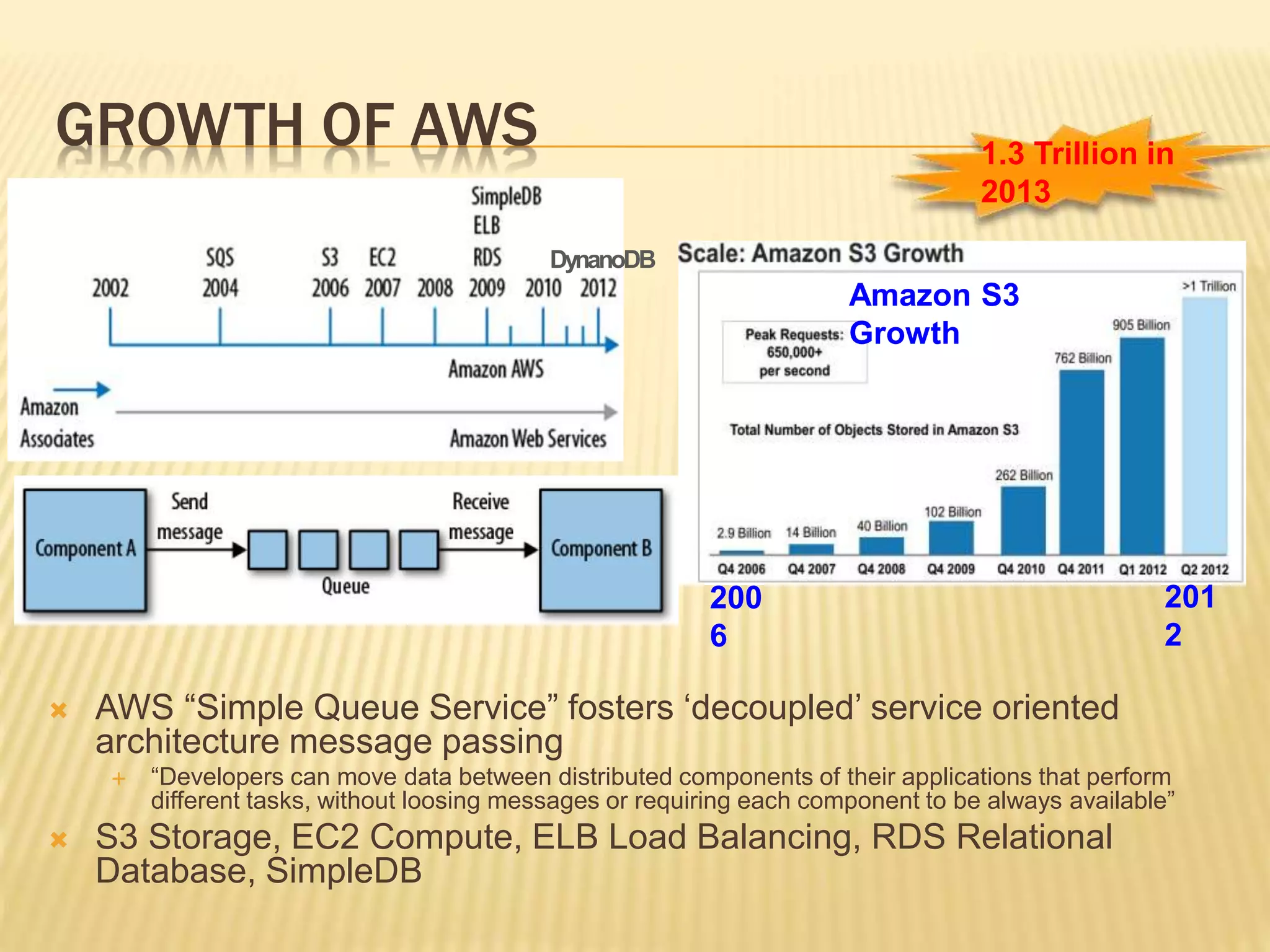
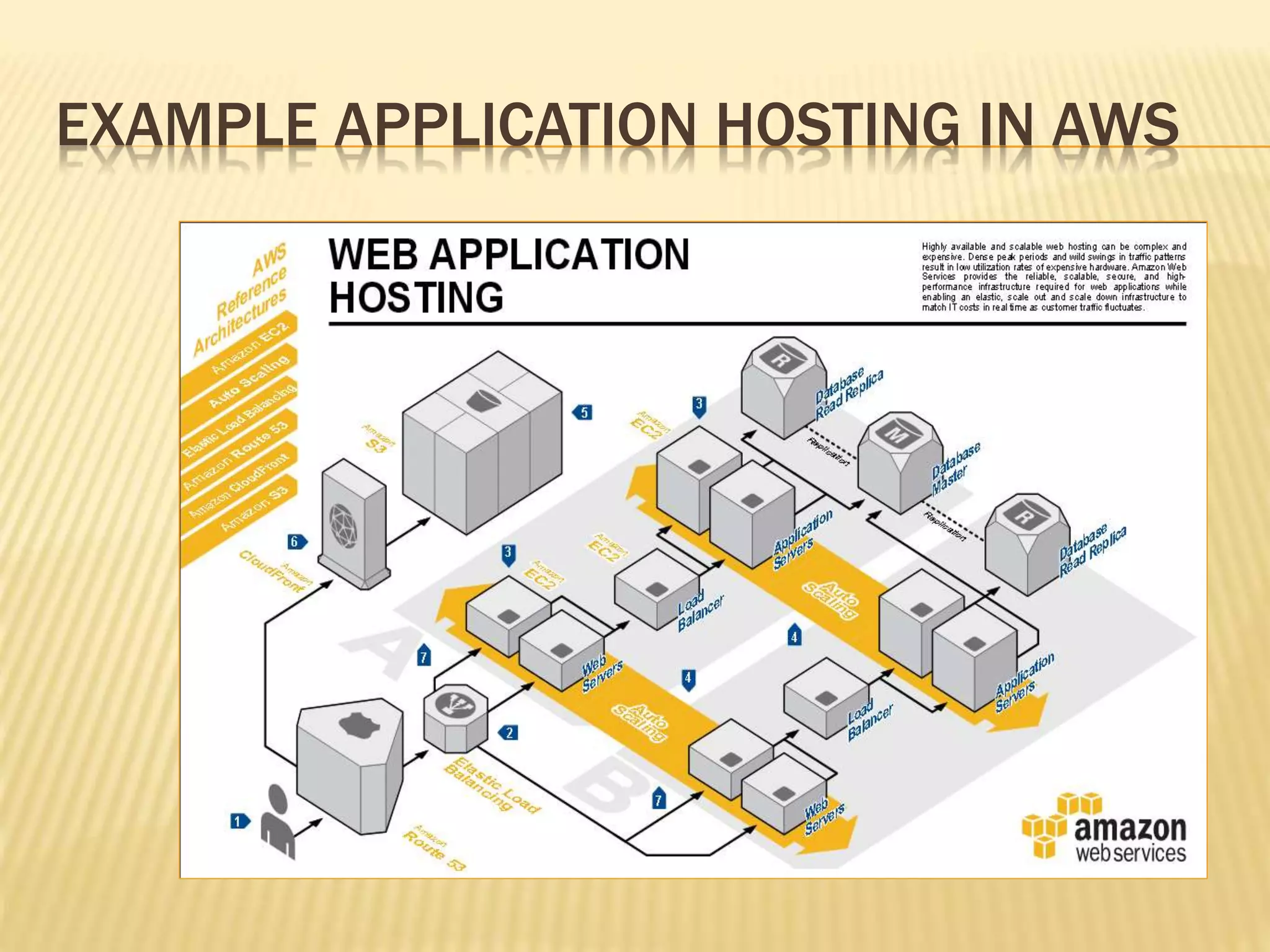
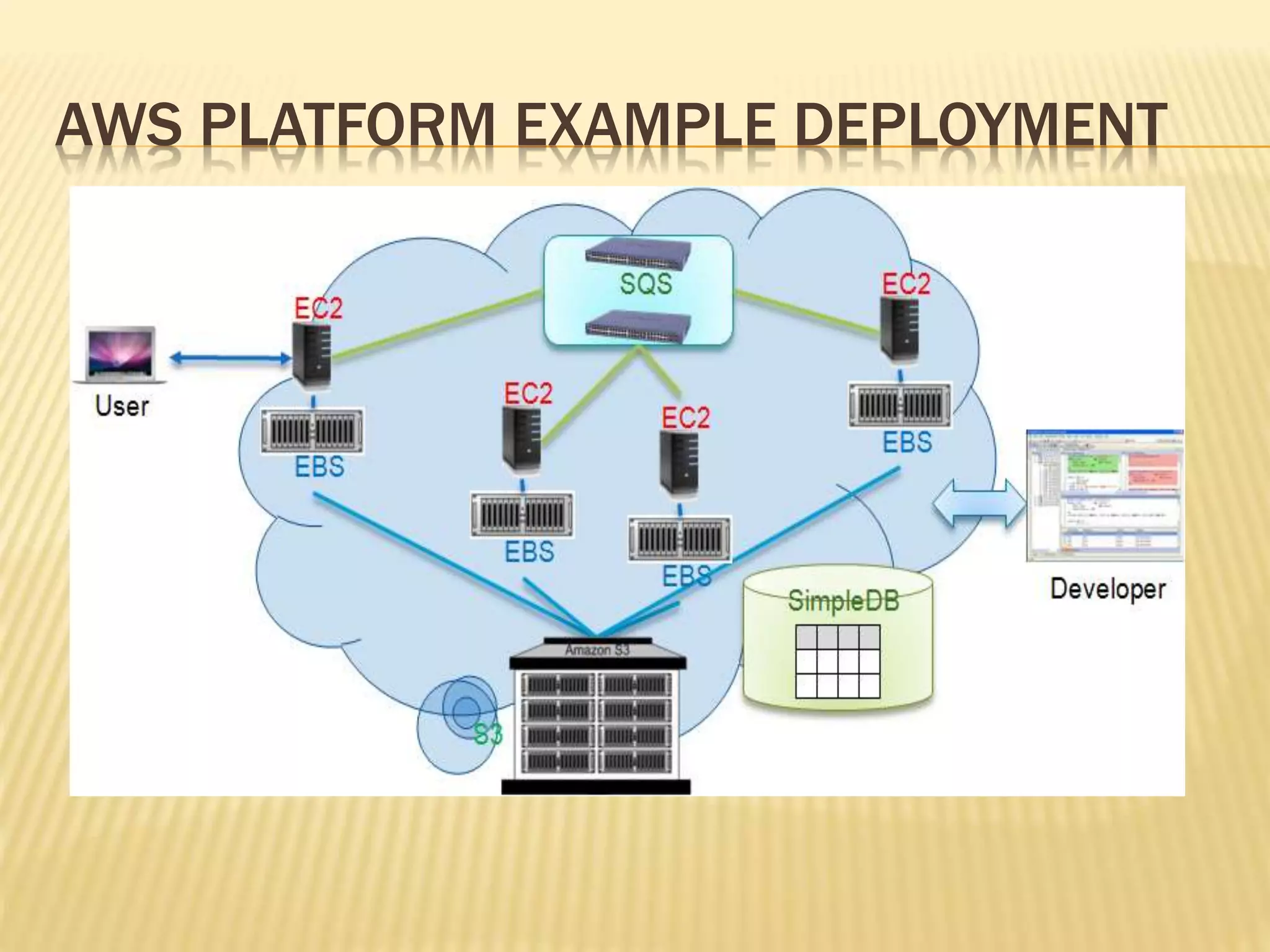
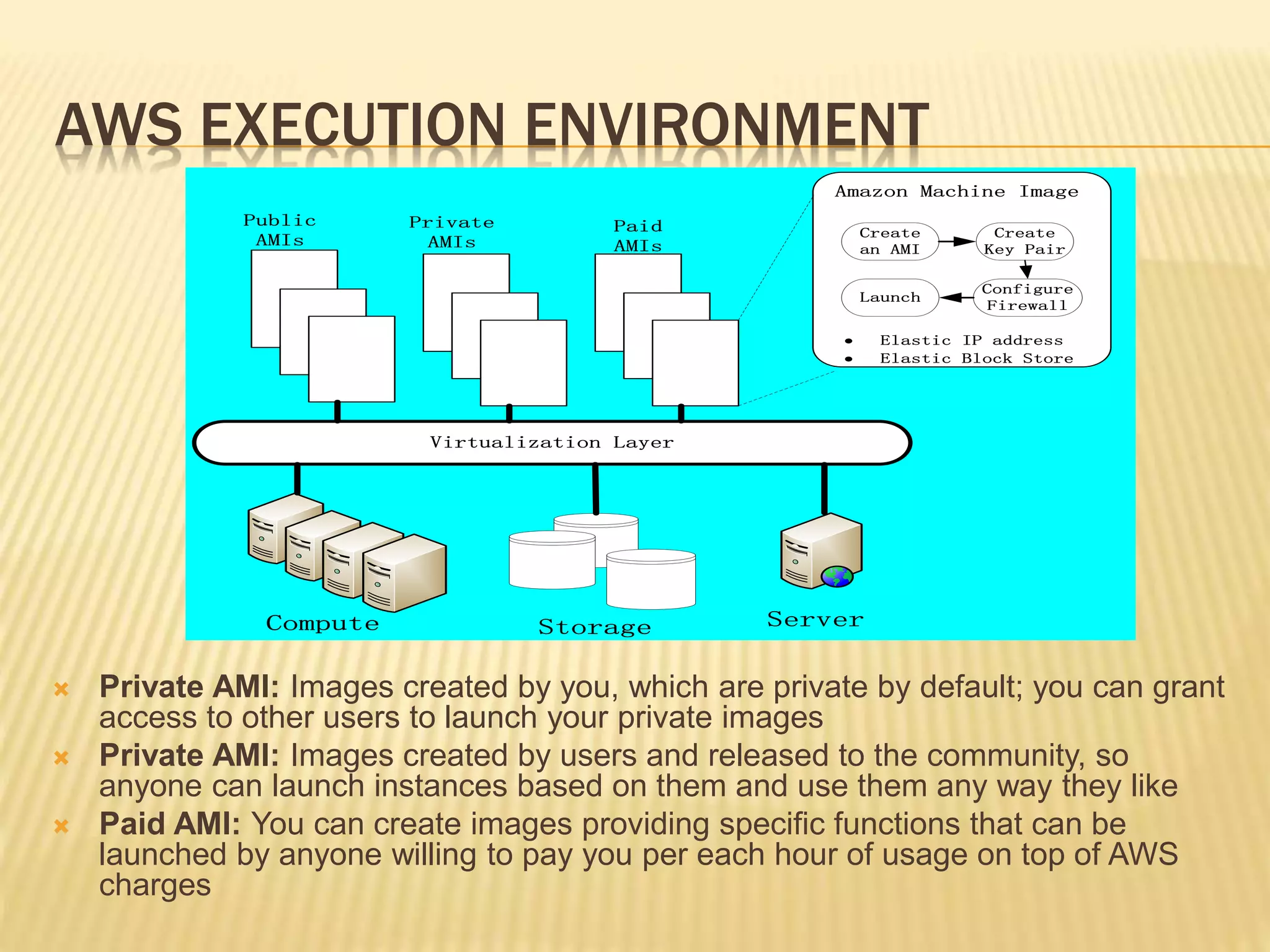
This document provides an overview of Amazon Web Services (AWS) including key services like Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), and Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS). It describes how AWS services can be used to build scalable applications and discusses common concepts like virtual servers, storage options, and security configurations. Examples are given around hosting applications in AWS and using services like S3, EC2, and CloudFront for storage, compute, and content delivery needs.