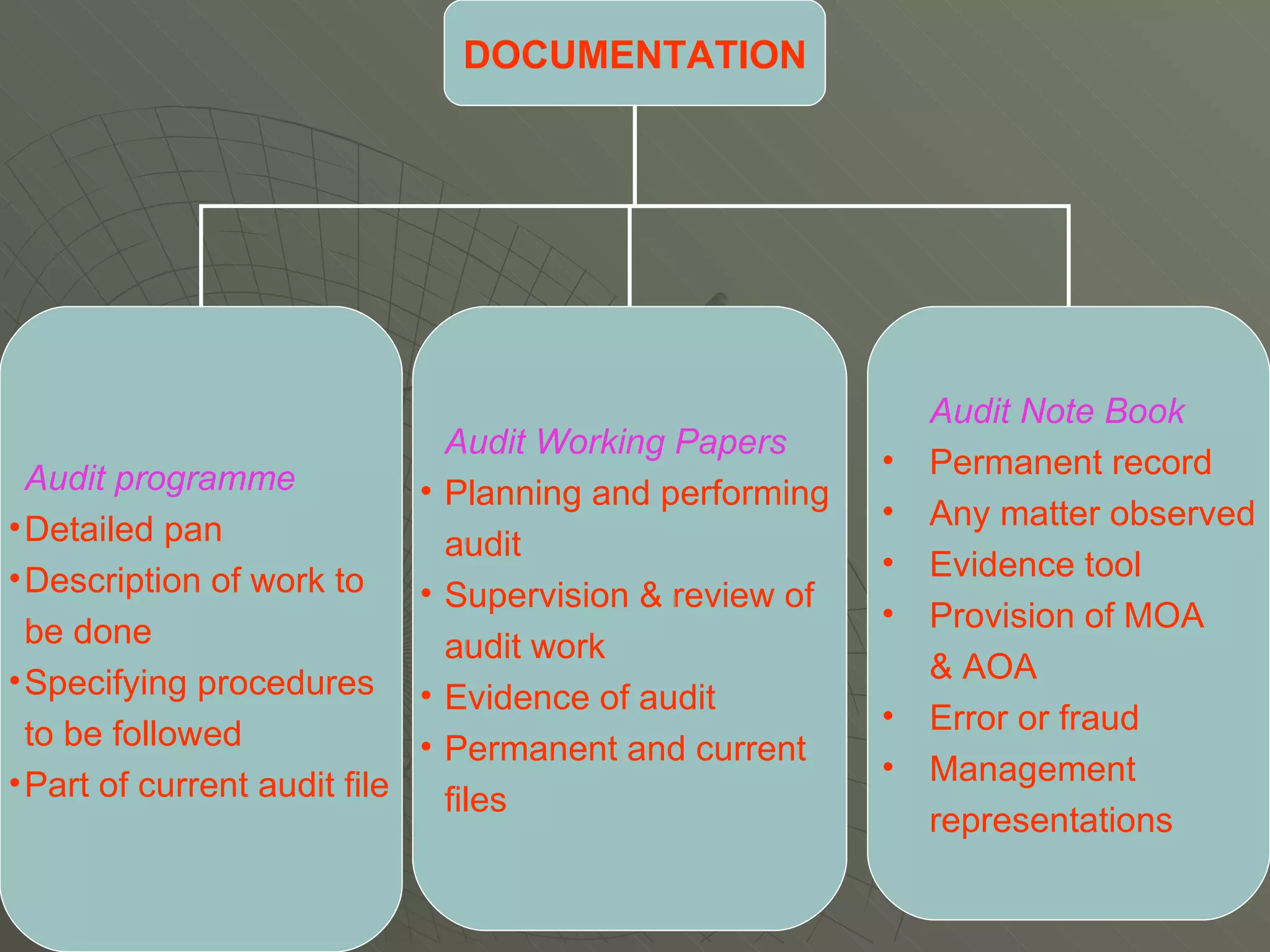
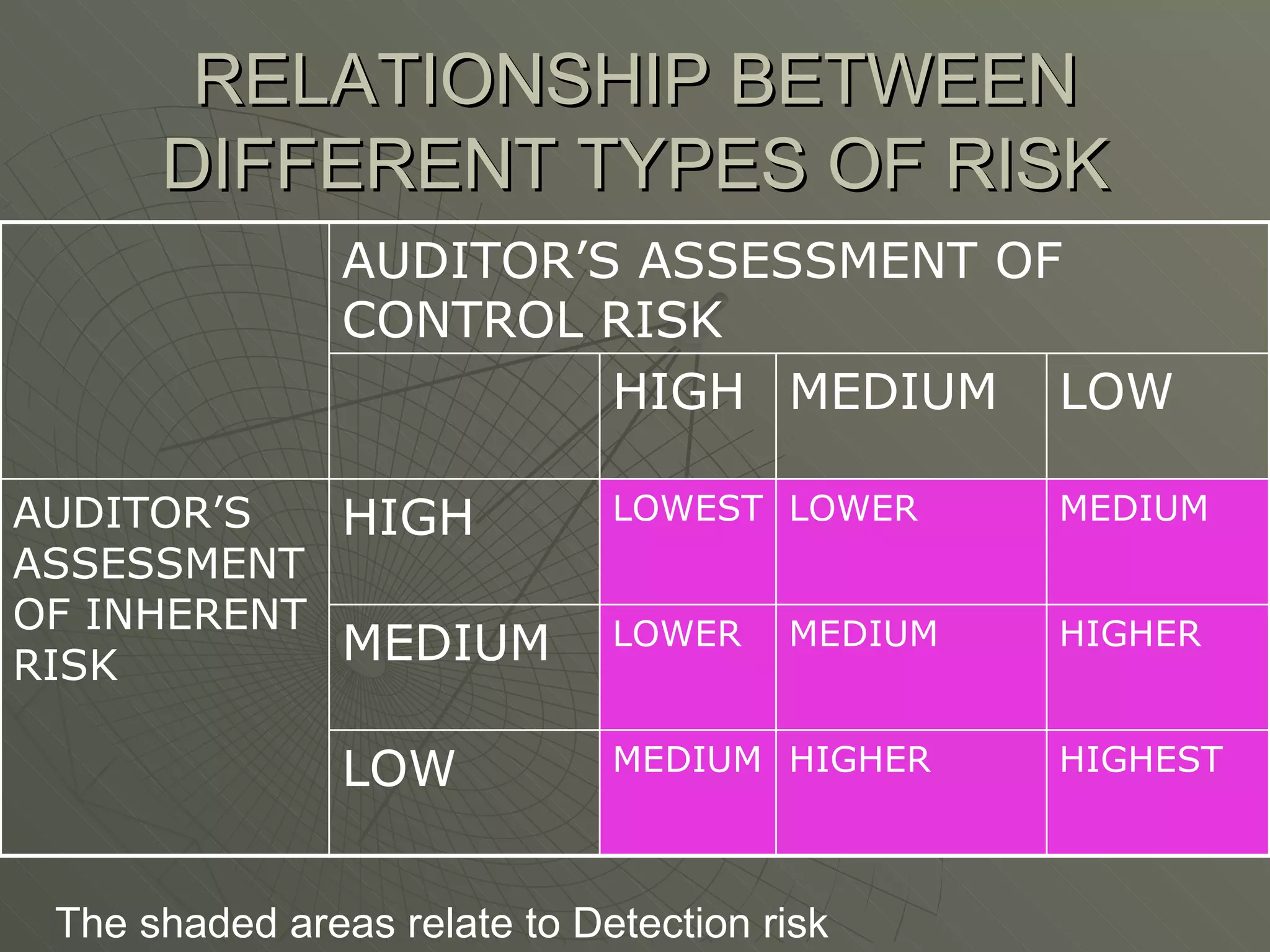
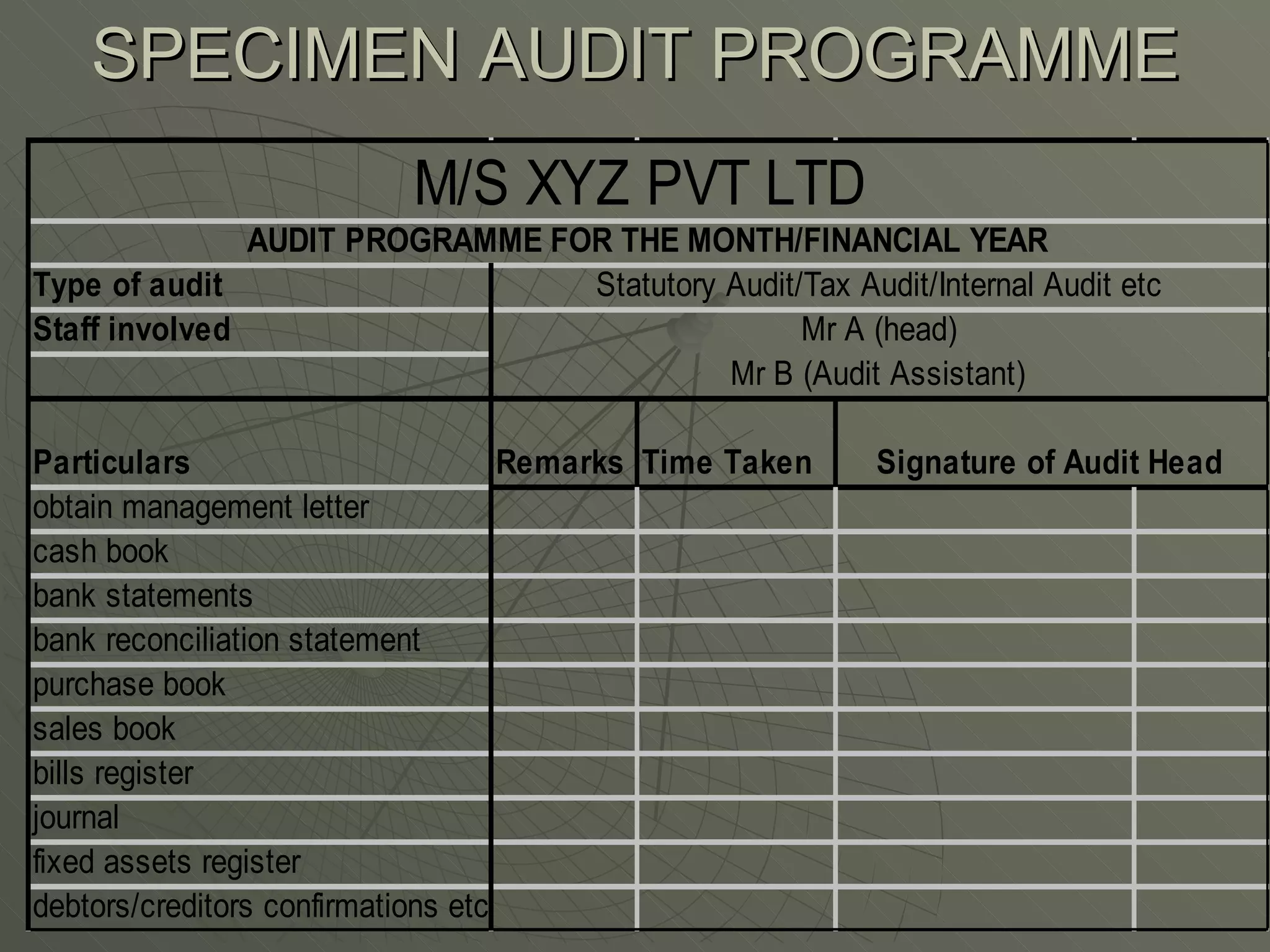
The document discusses the audit process in four phases - planning, execution, reporting, and compliance and substantive procedures. It covers the basic principles of auditing like integrity, objectivity, independence. It also discusses audit risk, documentation, auditor's report and qualifications in reports.