- An array is a collection of consecutive memory locations that all have the same name and type. An array allows storing multiple values of the same type using a single name.
- Arrays in C++ must be declared before use, specifying the type, name, and number of elements. Elements are accessed using an index.
- The main advantages of arrays are that they allow storing and processing large numbers of values efficiently using a single name. Arrays also make sorting and searching values easier.


![DECLARATION OF AN
ARRAY:
Like a regular variable, an array must be declared
before it is used. A typical declaration for an array
in Visual C++ is:
type name [elements];
type is a valid type (like int, float...)
name is a valid identifier
elements field (which is always enclosed in
square brackets []), specifies how many of these
elements the array has to contain.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayinc-170104161722/75/Array-in-c-3-2048.jpg)
![EXPLANATION:
INT NUM[6]
size of the
array
Base name of
type array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayinc-170104161722/75/Array-in-c-4-2048.jpg)

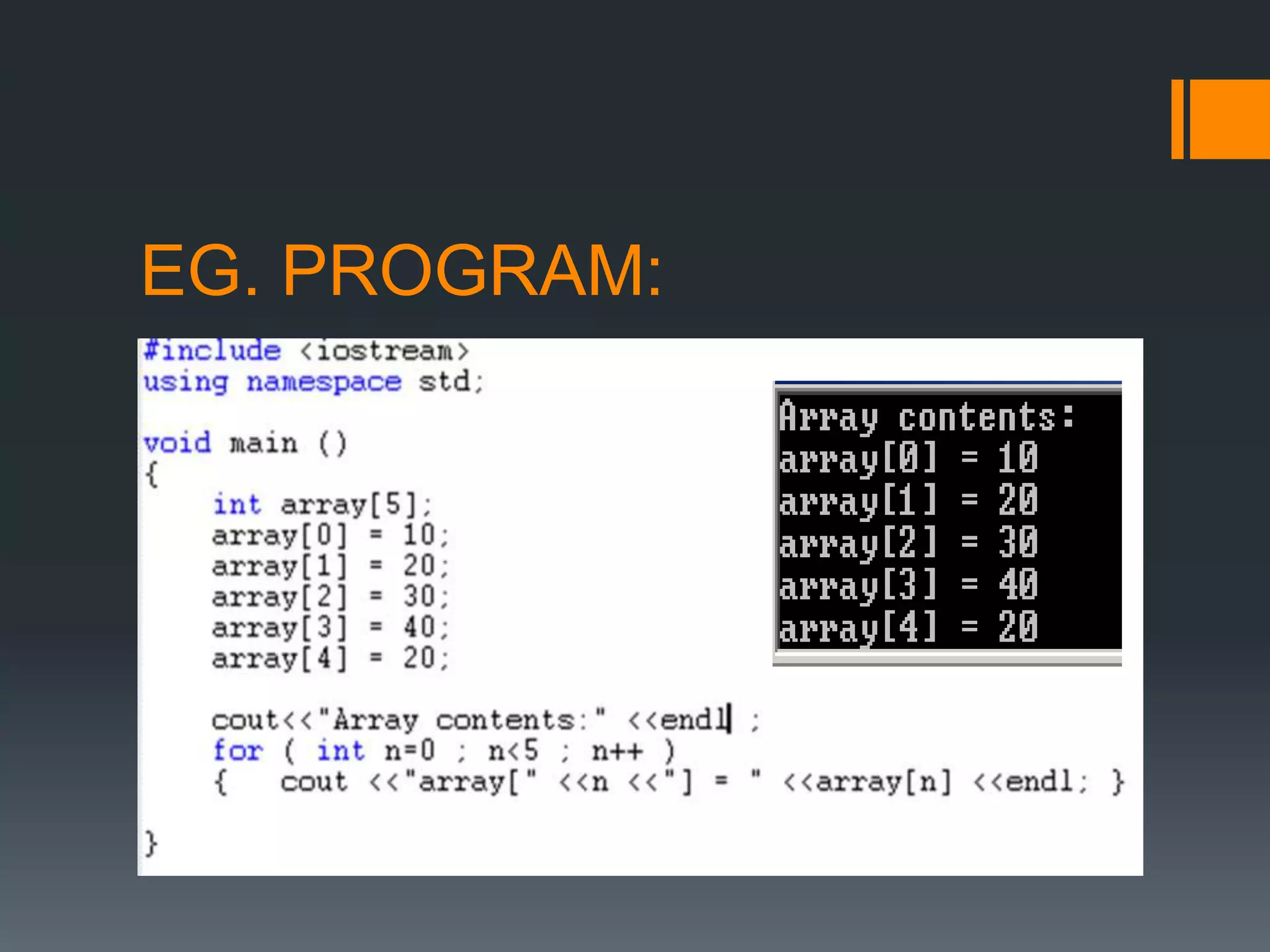

![ONE DIMENSIONAL ARRAY:
A one dimensional array is one in which one
subscript /indices specification is needed to
specify a particular element of array
Declaration :
Data_type array_name [size of array ];
Eg:
Int num[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayinc-170104161722/75/Array-in-c-8-2048.jpg)
![MEMORY REPRESENTATION:
num[0] num[1] num[2] num[3] num[4] num[5] num[6] num[7] num[8] num[9]
2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 2012 2014 2016 2018
starting Address of location
Totalmemoryinbytesthatanarray is occupied:
Size of array=size of array*size of(base type)
Hear,
10*2=20
39 56 23 98 6 56 9 2 54 67](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayinc-170104161722/75/Array-in-c-10-2048.jpg)
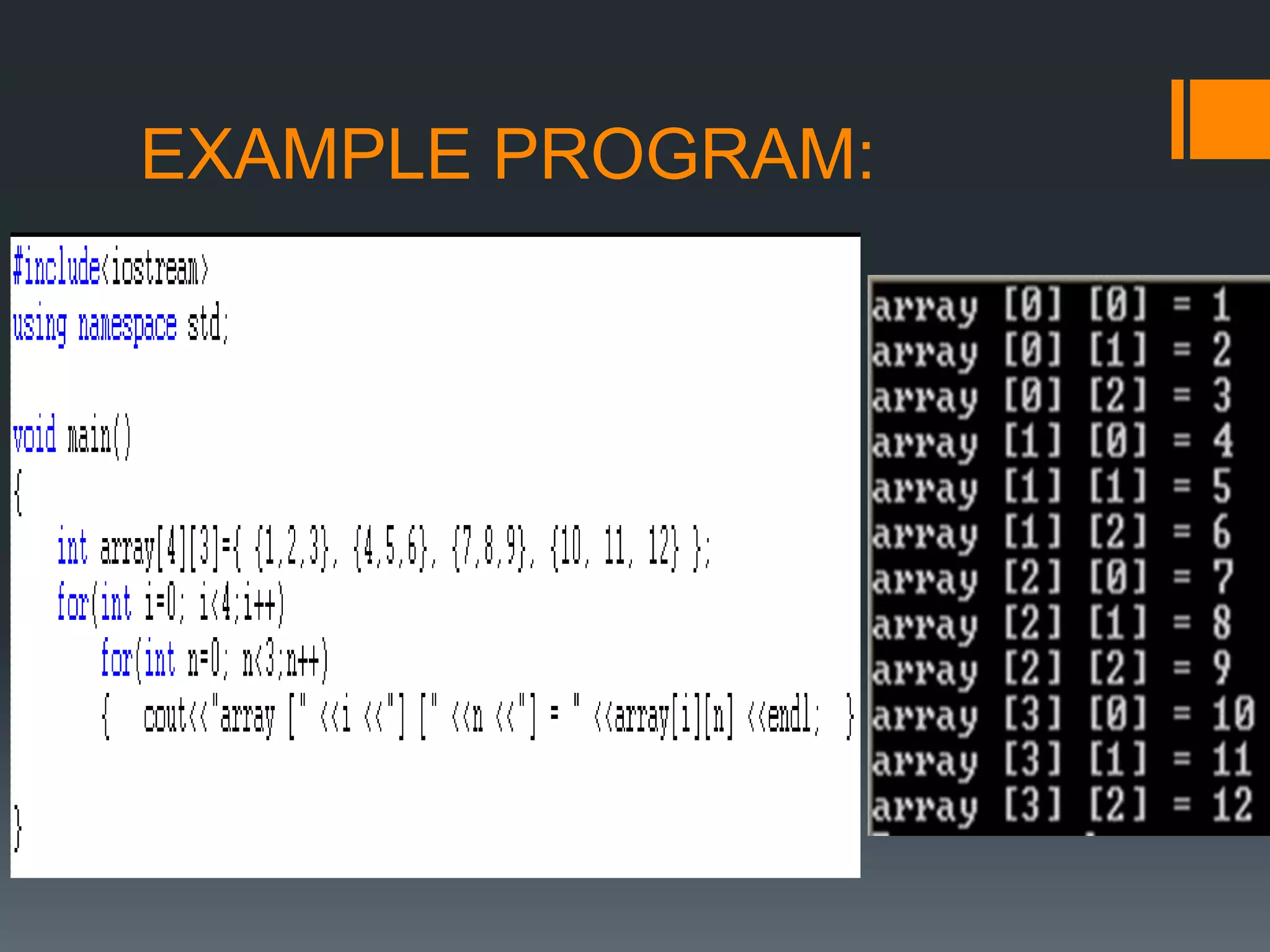
![TWO DIMENSIONAL ARRAY:
A 2-d array is an array in which each element is
itself an array
i.e int num[4][3]
0 1 2
0
1
2
3
No of
rows
No
of
colu
mns
No of element in
2-D array =M*N
Num [2][1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayinc-170104161722/75/Array-in-c-11-2048.jpg)

![MEMORY REPRESENTATION:
Total bytes= no of rows*no of columns*size of(base type)
Memory reprsentation in 2-D array:
char A [2][3]
A[0][0] A[0][1] A[0][2] A[1][0] A[1][1] A[1][2]
5001 5002 5003 5004 5005 5006](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayinc-170104161722/75/Array-in-c-13-2048.jpg)
![MULTI DIMENSIONAL ARRAY:
An array with dimensions more than two
.The maximum limit of array is compiler
dependent
Declaration:
Data_type name [a][b][c][d][e][f]…….[n];
Array of 3 or more dimensional are not often
use because of huge memory requirement
and complexity involved](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayinc-170104161722/75/Array-in-c-14-2048.jpg)

![ARRAY INITIALIZATION:
C++ provides the facility of array initialization at the time of
declaration .General form of array initialization is as:
Type array_name[size 1]…..[size N] ={vale list};
Eg:
Int days_month[12]={31,25,29,03,31,19,20,31,18,20,31,29};
Char string[6]={‘a’,’r’,’g’,’y’,’d’,’0’};
2-D array are also initialized in same way as linear array
Int cube[4][2]={ 1,3,
4,6,
9,37,
5,78
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayinc-170104161722/75/Array-in-c-16-2048.jpg)
![UNSIZED ARRAY INITIALIZATION:
C++ allowed you to skip the size of array in an array
initialization statement C++ automatically create an array
big enough to hold all the initializers present
Char S1[] =“ first string ”;
you skip the size, you must give list of initializers so that
C++ can calculate the size of array
Int val []={3,5,6,2,8,9,6,4};
Int cube [] [2] ={ 1,3,
67,7,
6,87,
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayinc-170104161722/75/Array-in-c-17-2048.jpg)
![STRING AS ARRAY:
C++ does not have a String data type ,it
impairments string as 1-D character Arrray
.A string as a character array is terminate
by a null character ‘0’
Char str 1 [11];
Char square [][]={ ‘first string’,
‘second string’,
‘third string’
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayinc-170104161722/75/Array-in-c-18-2048.jpg)

