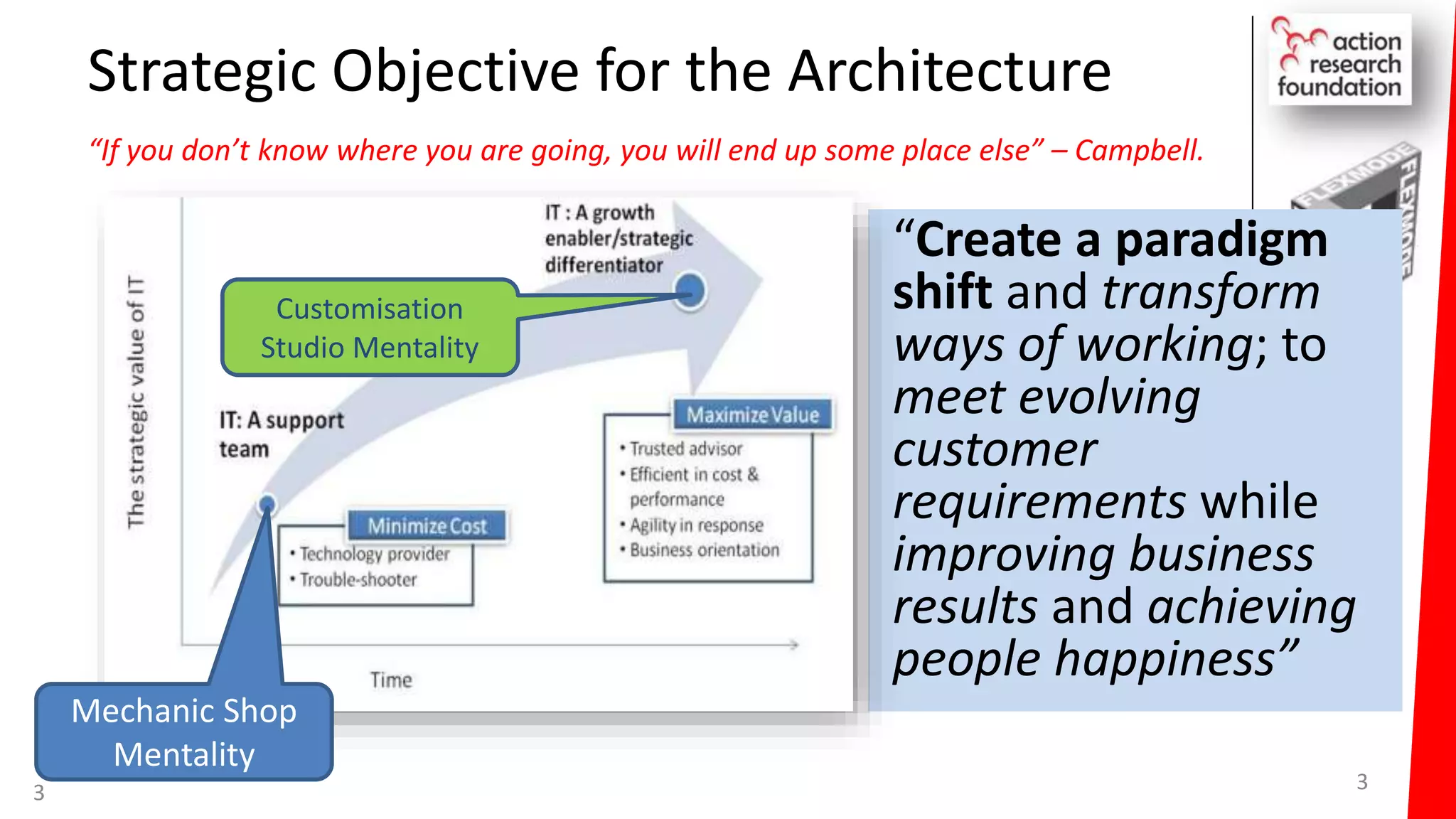
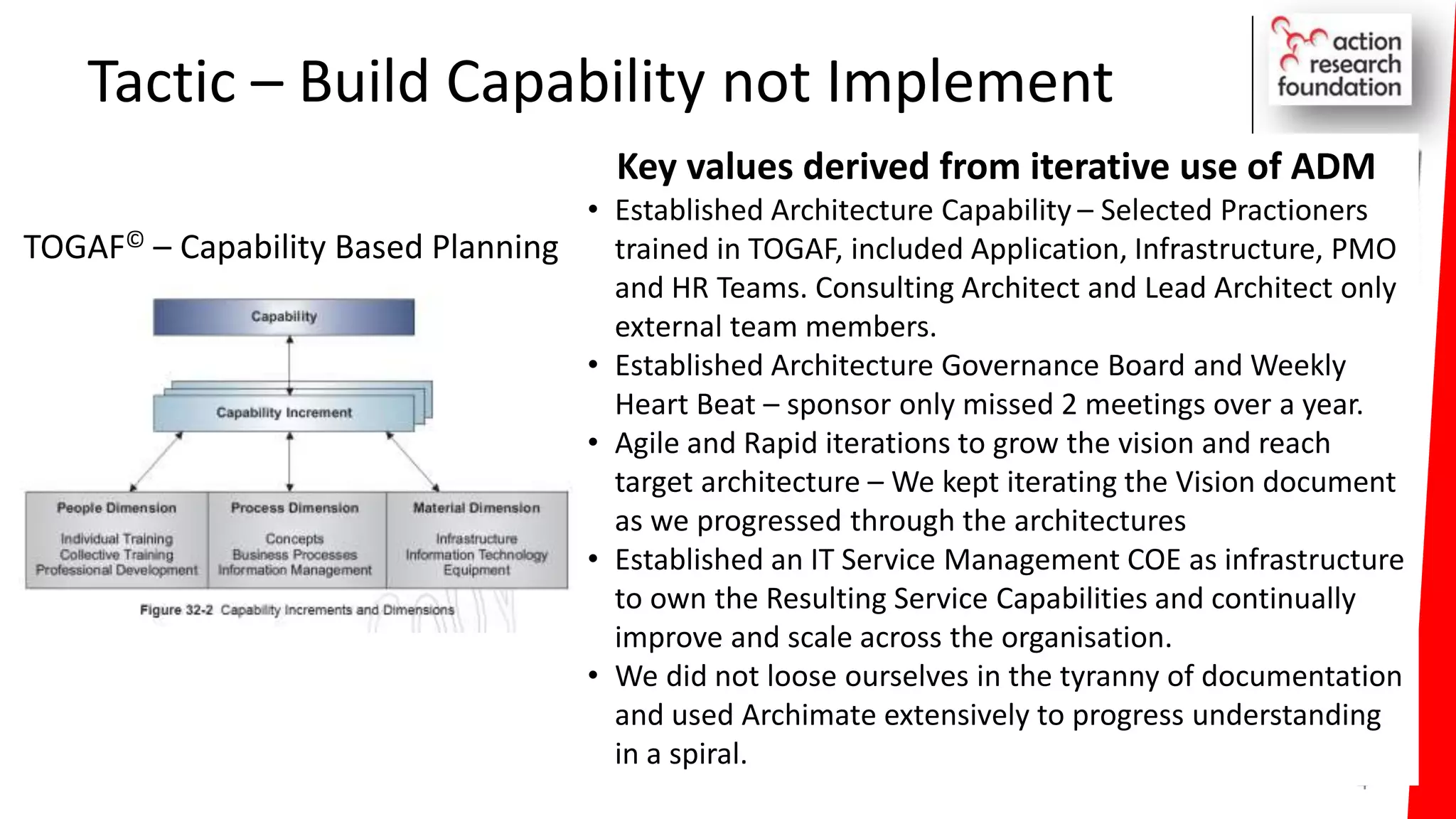
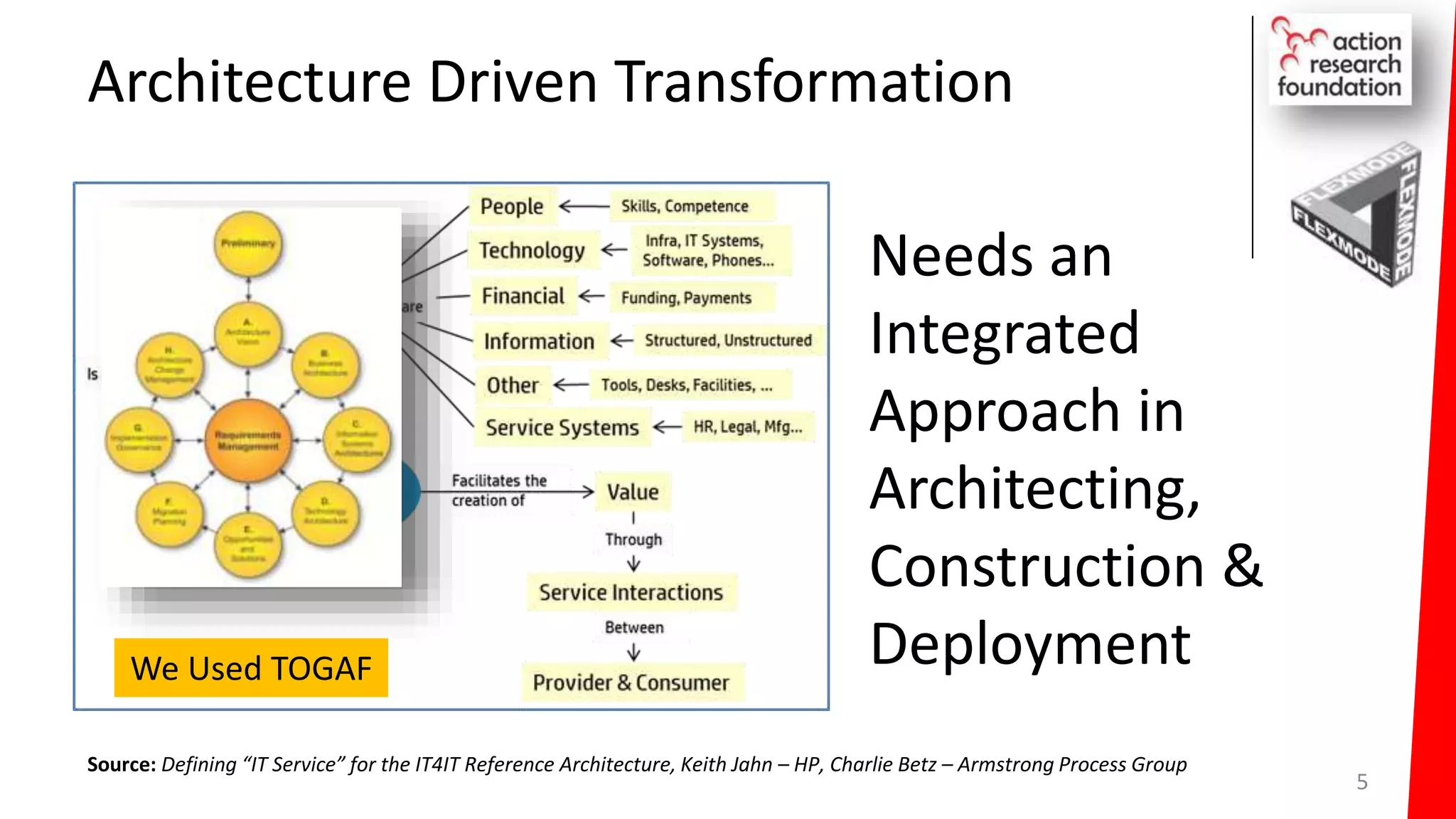
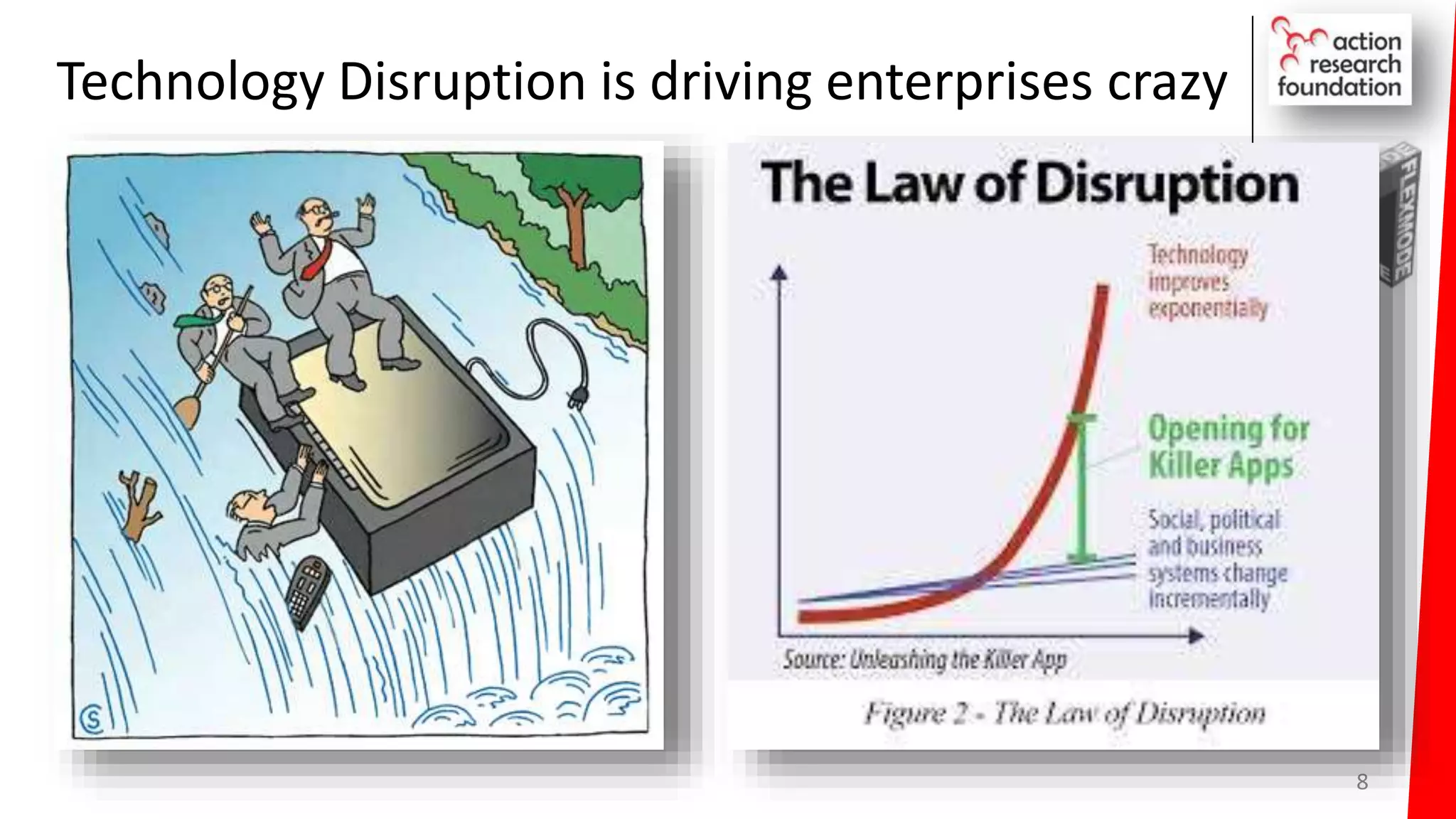
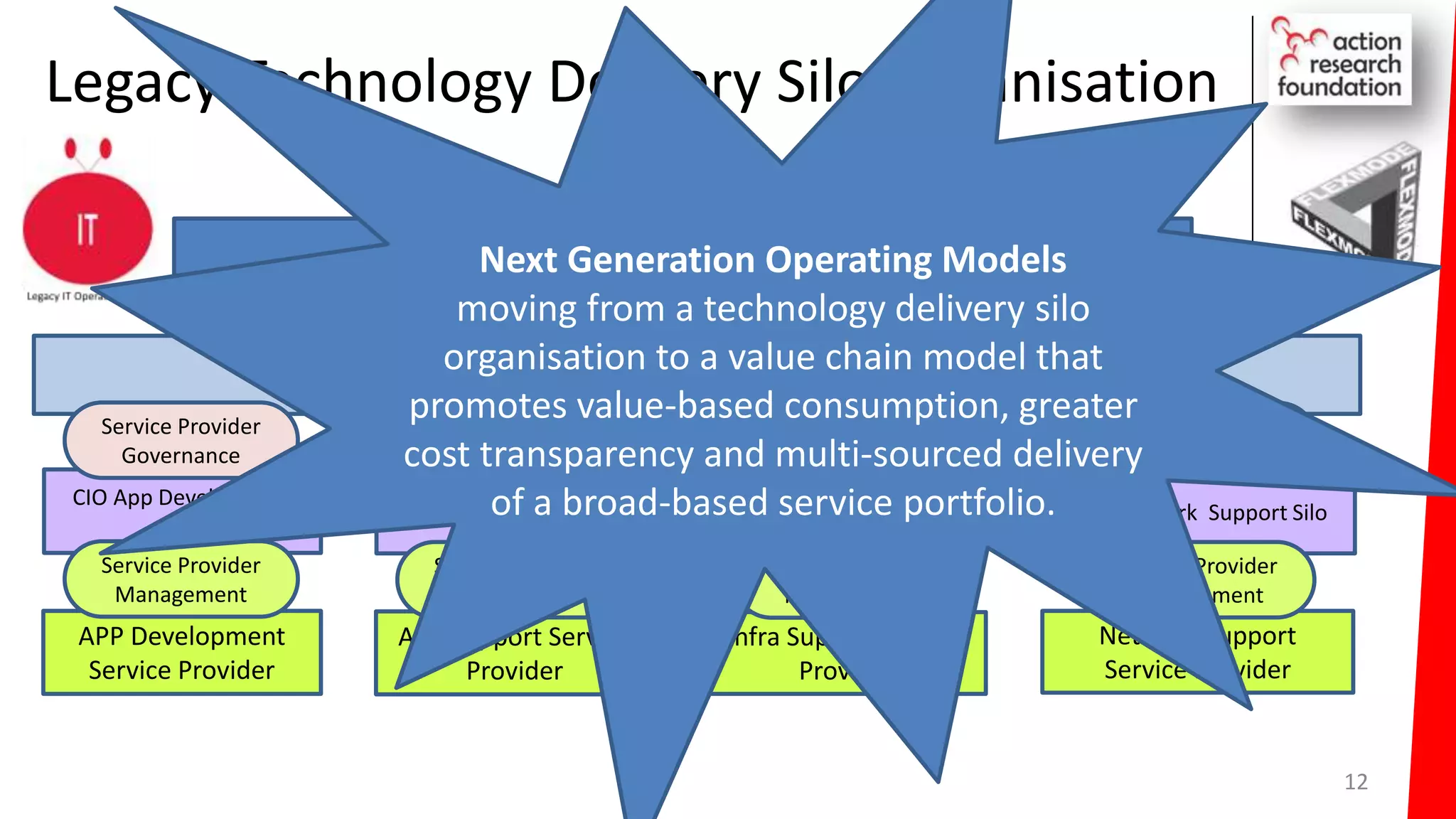
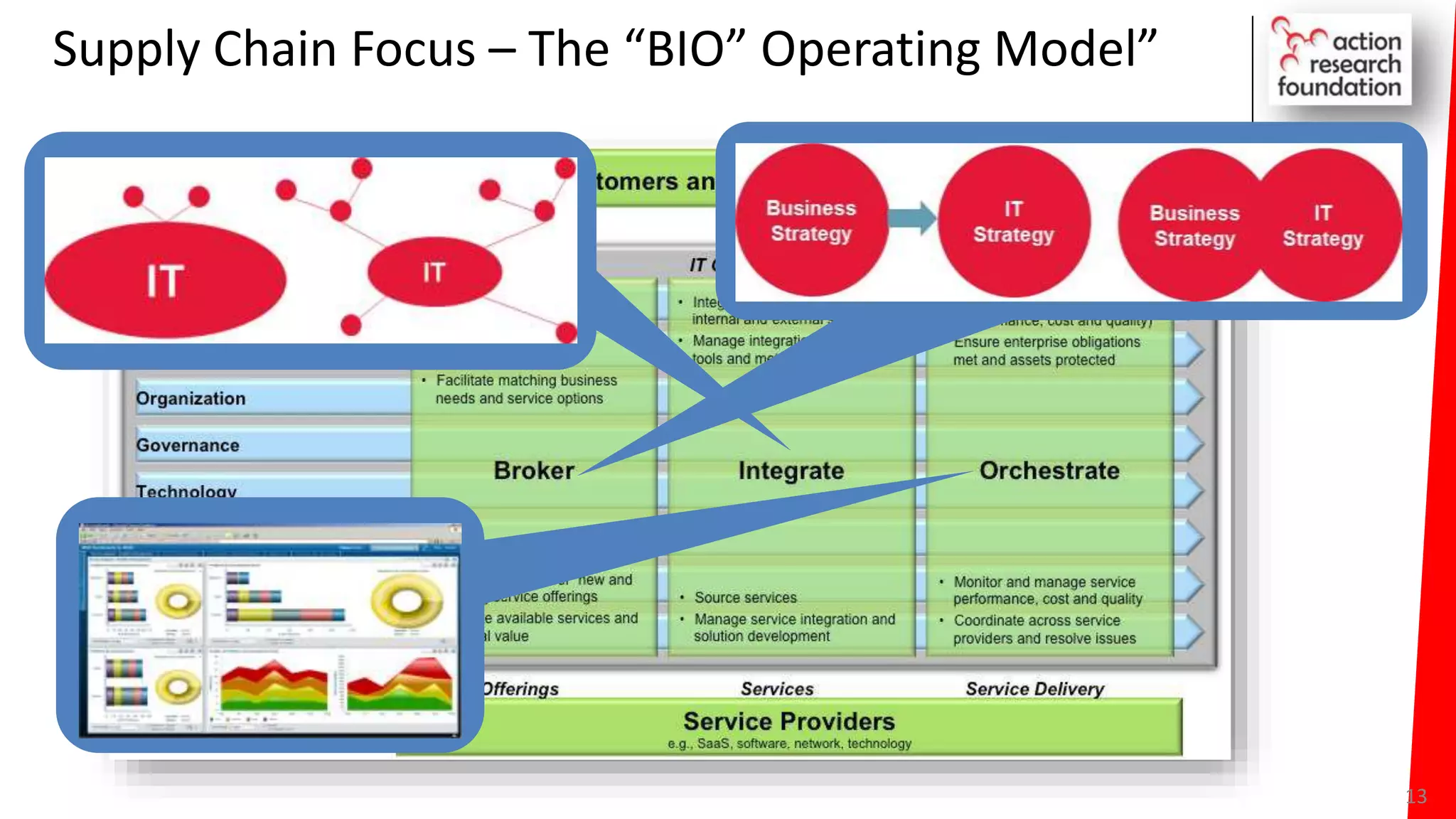
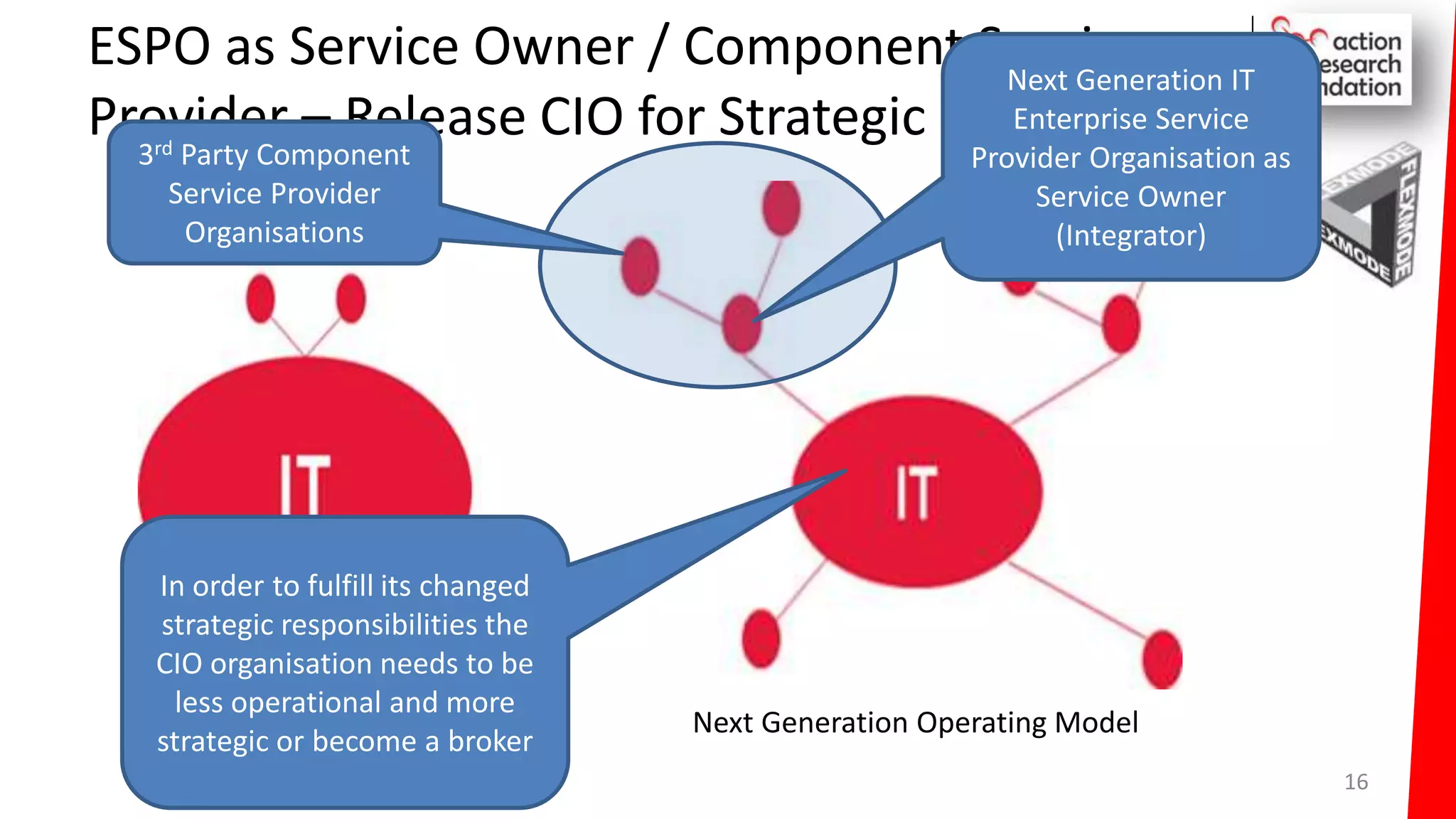
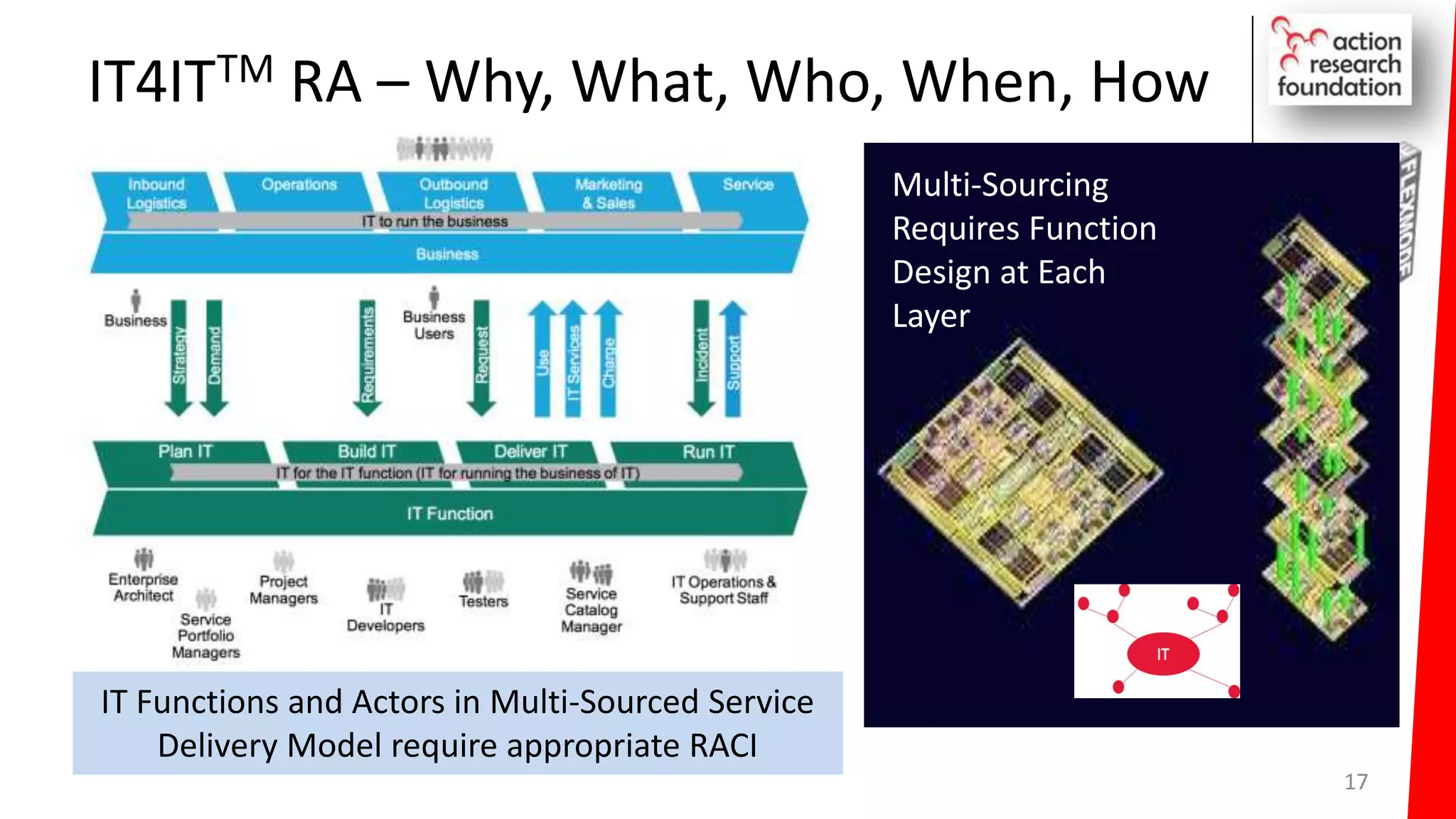
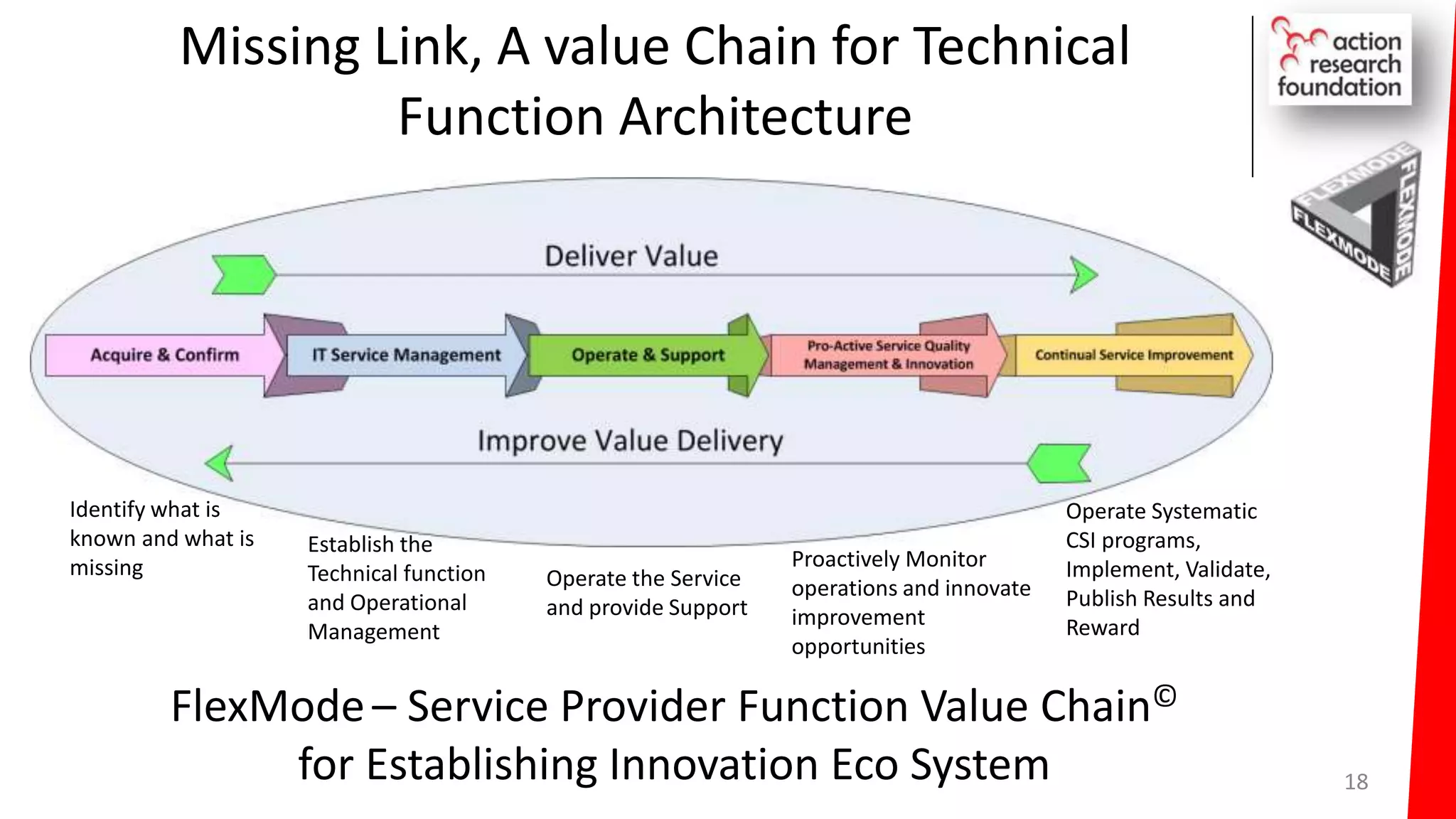
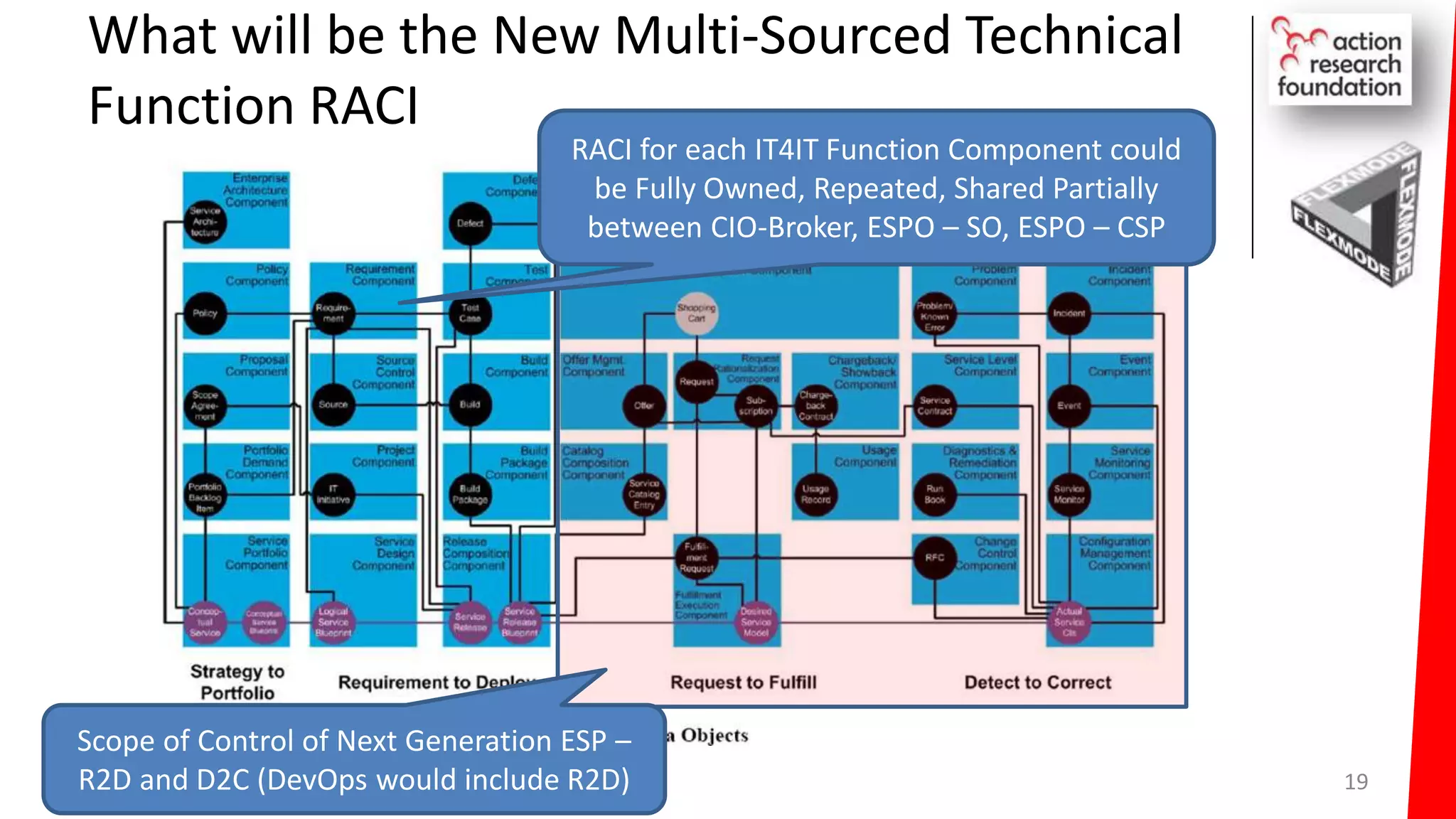
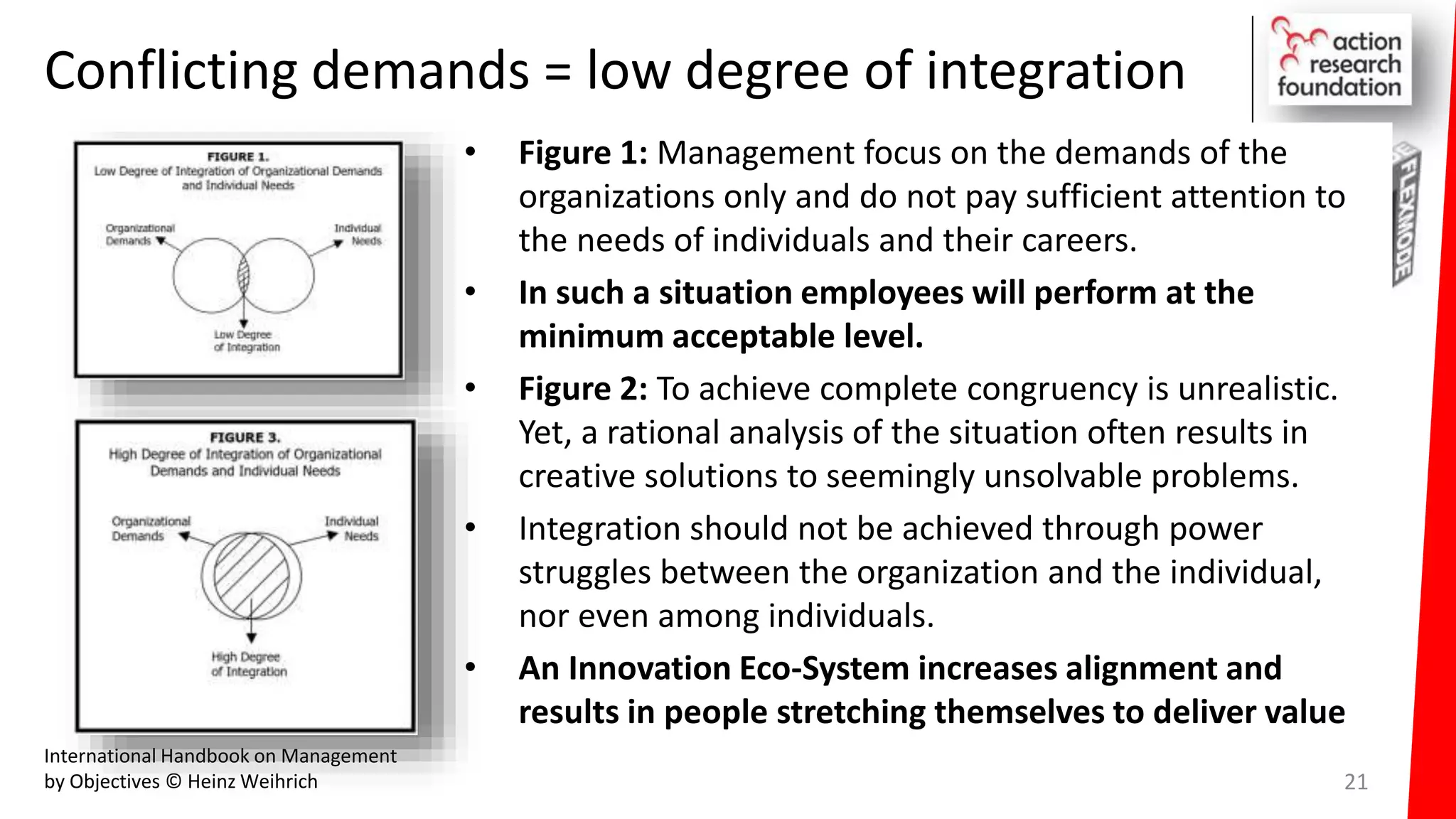
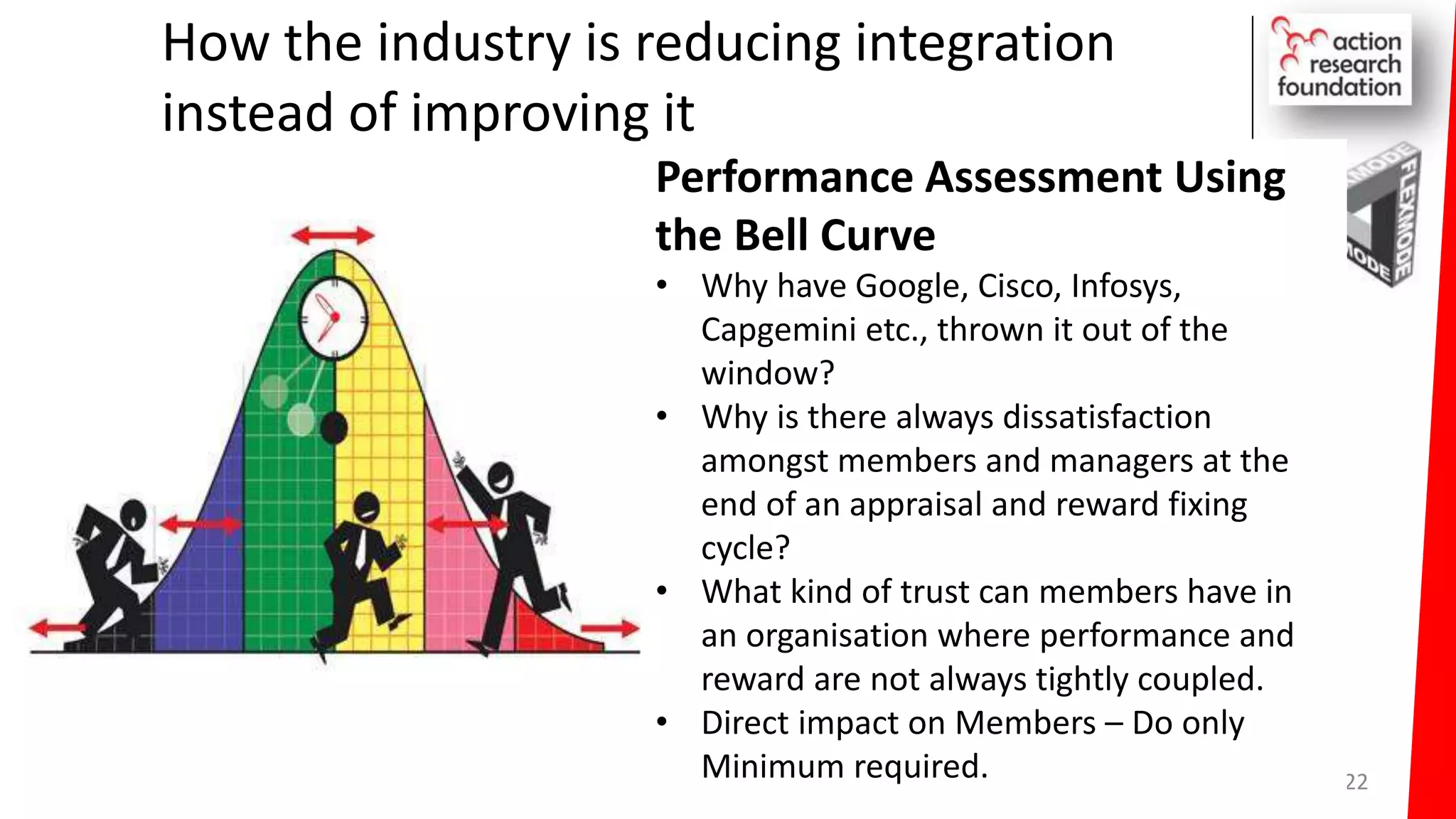
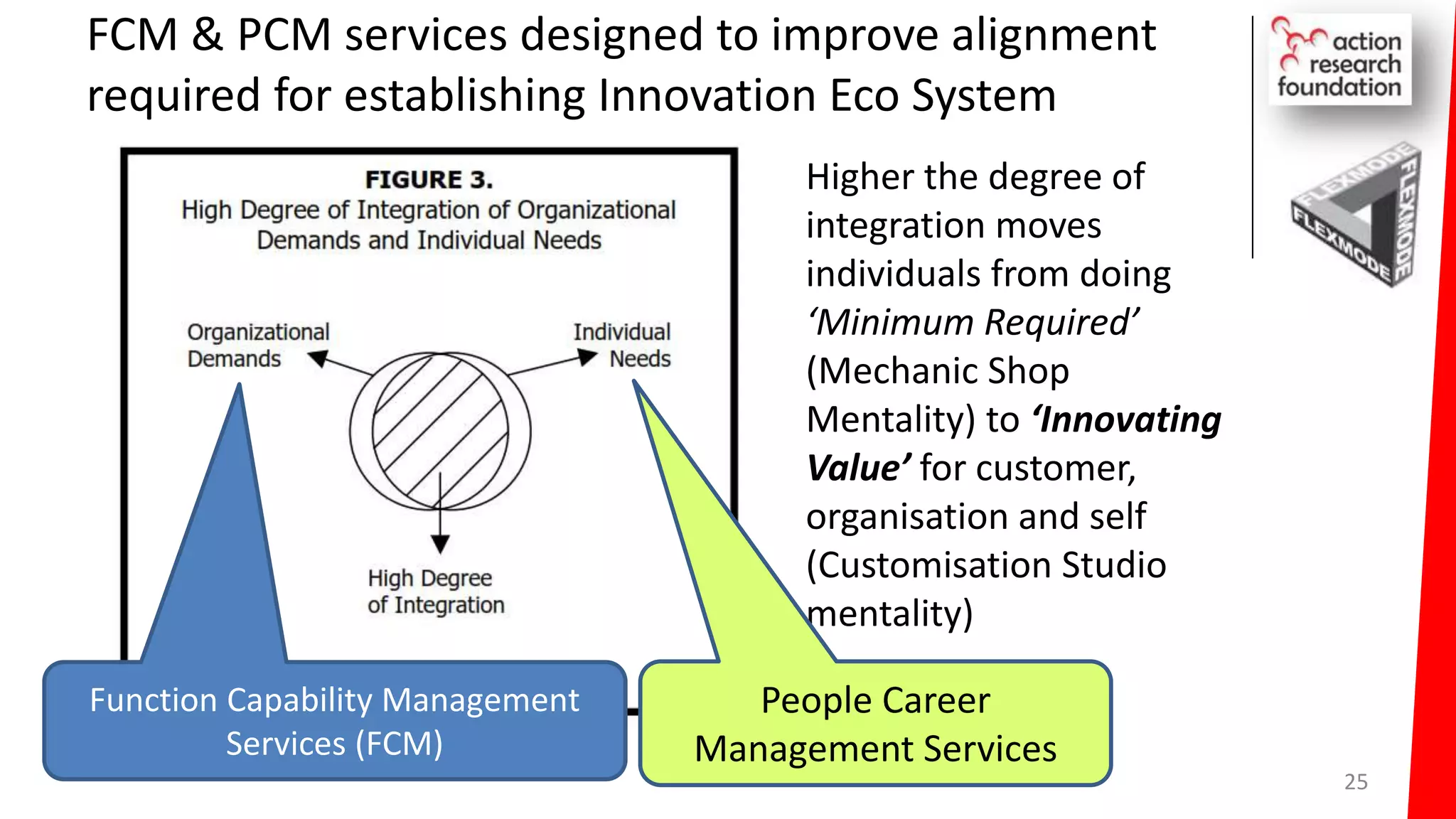
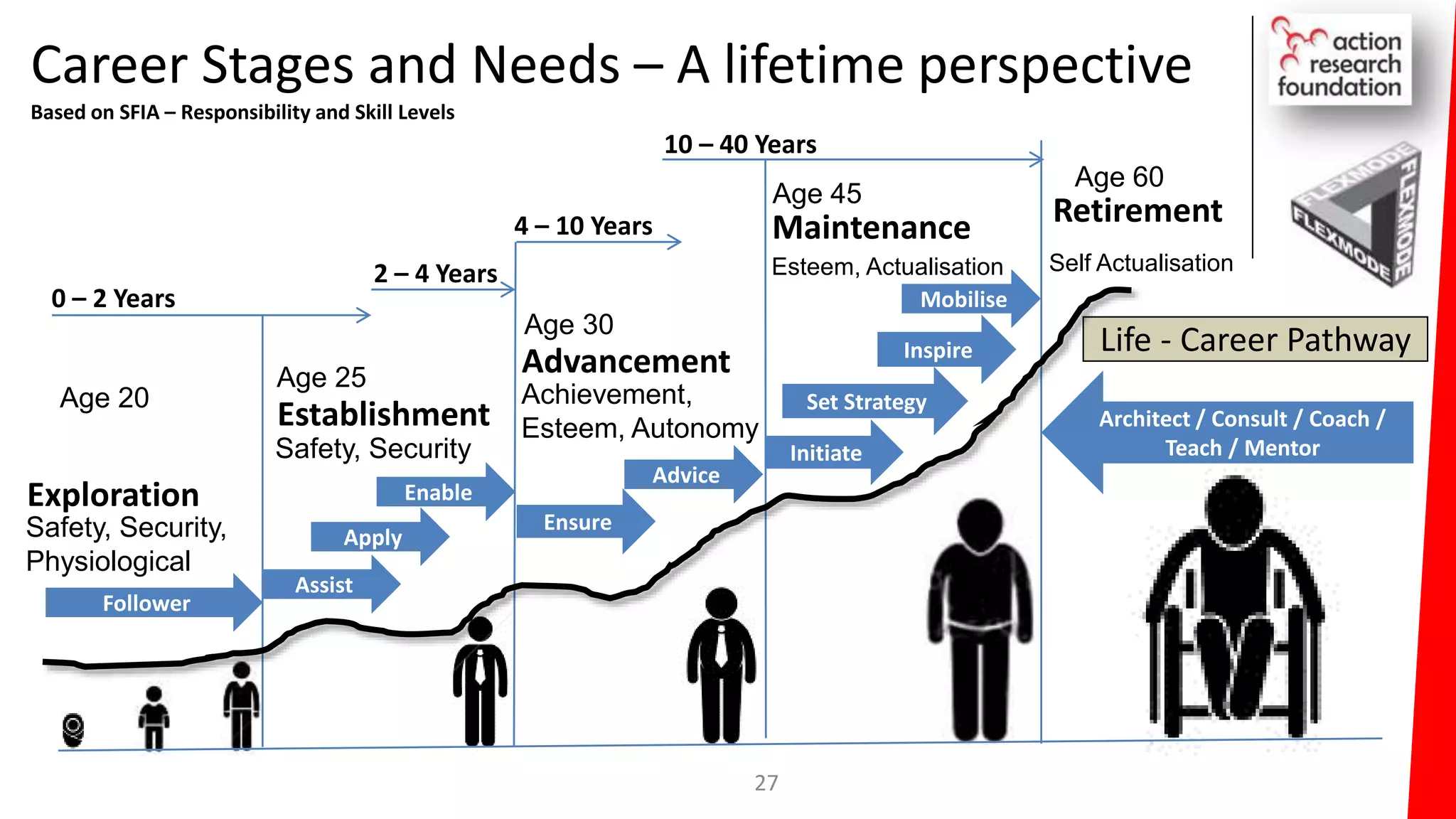
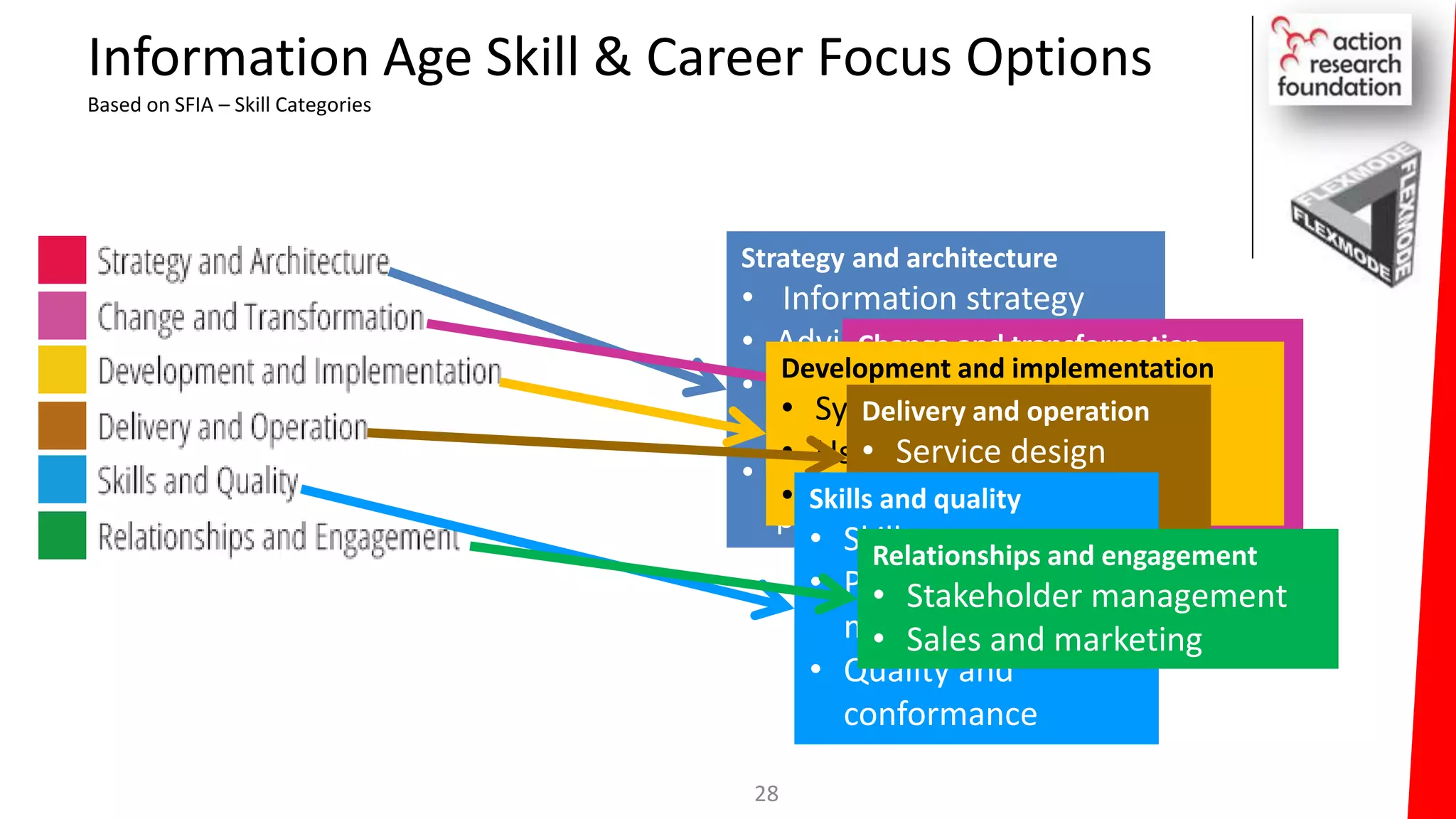
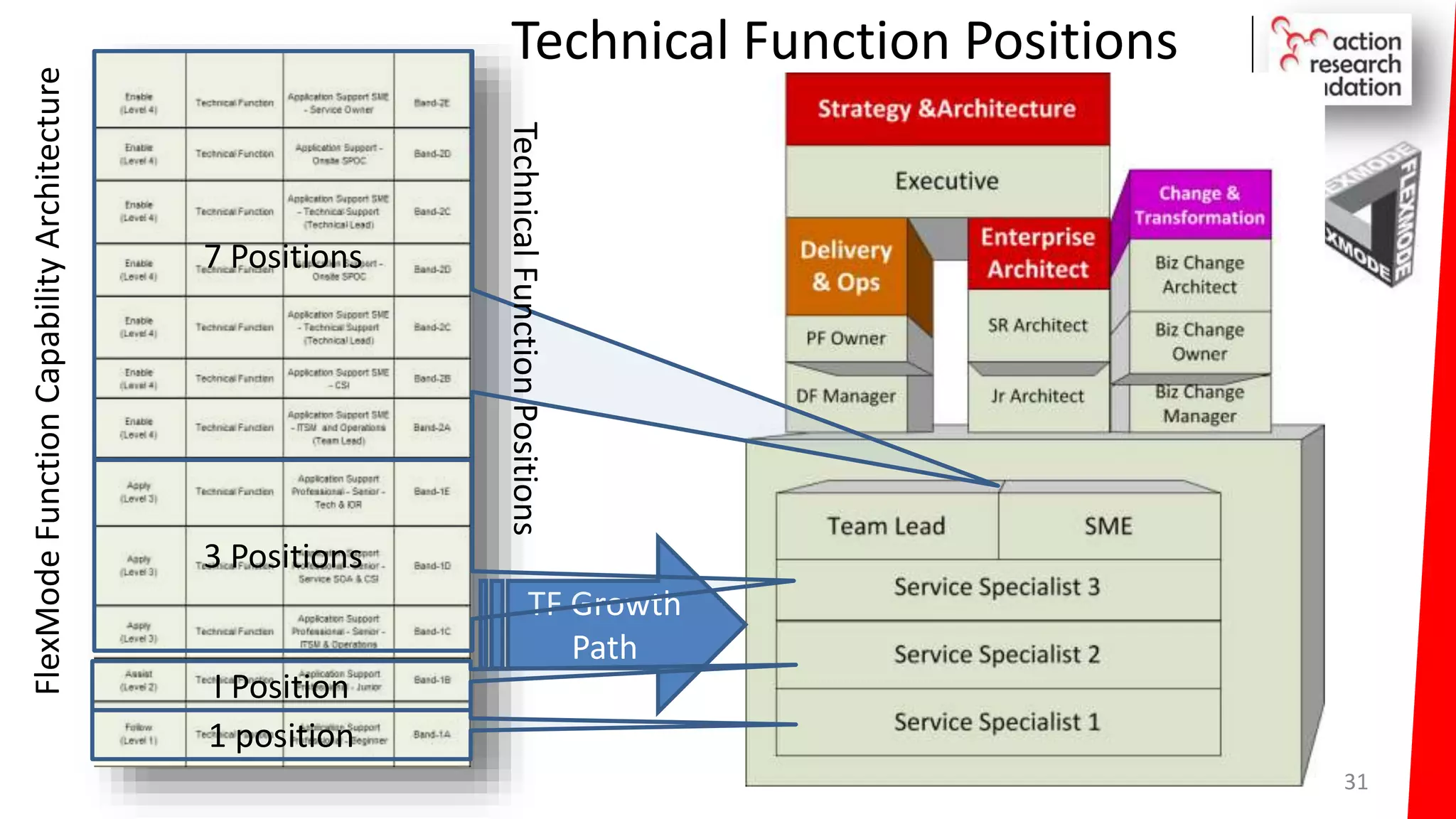
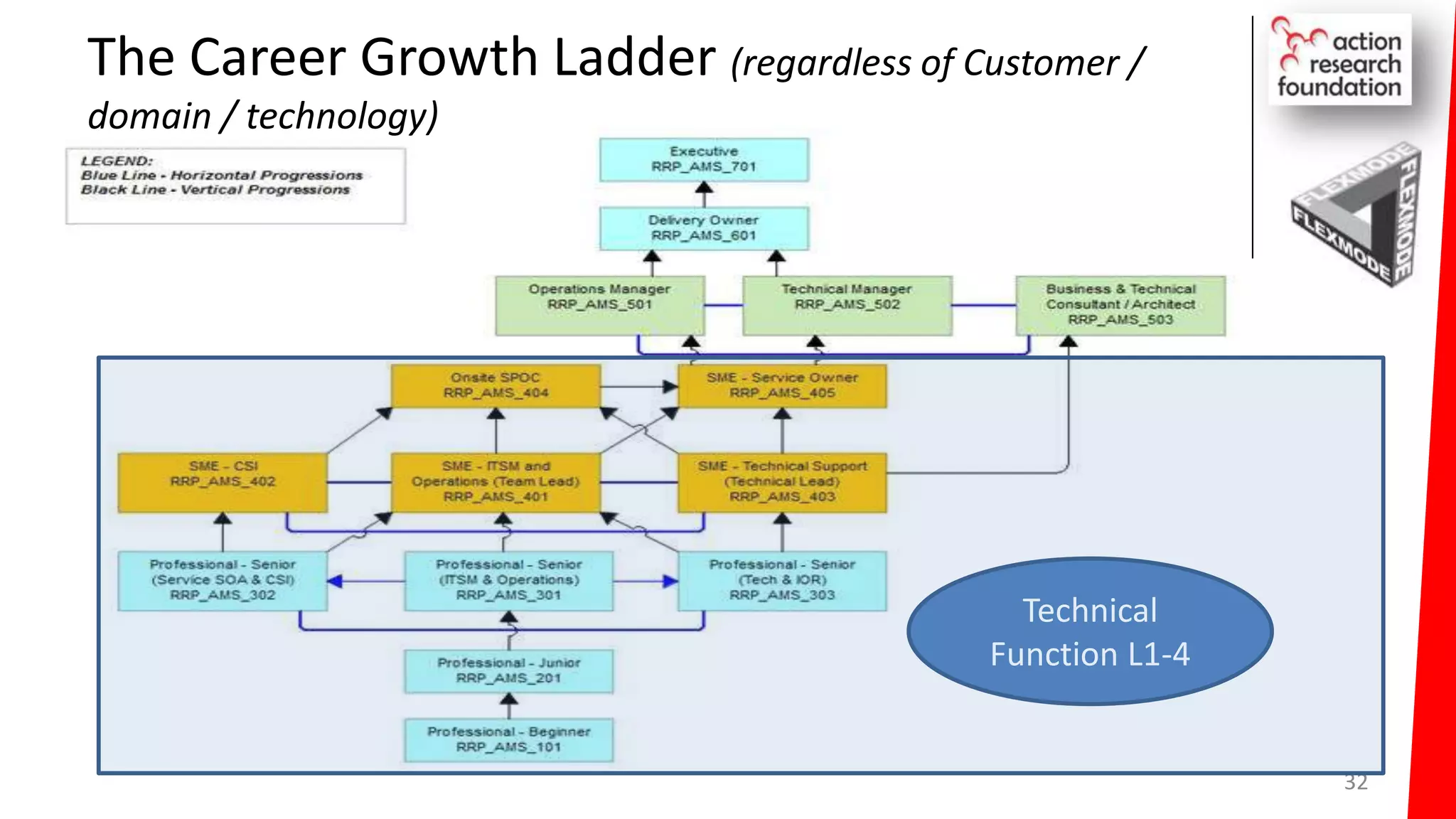
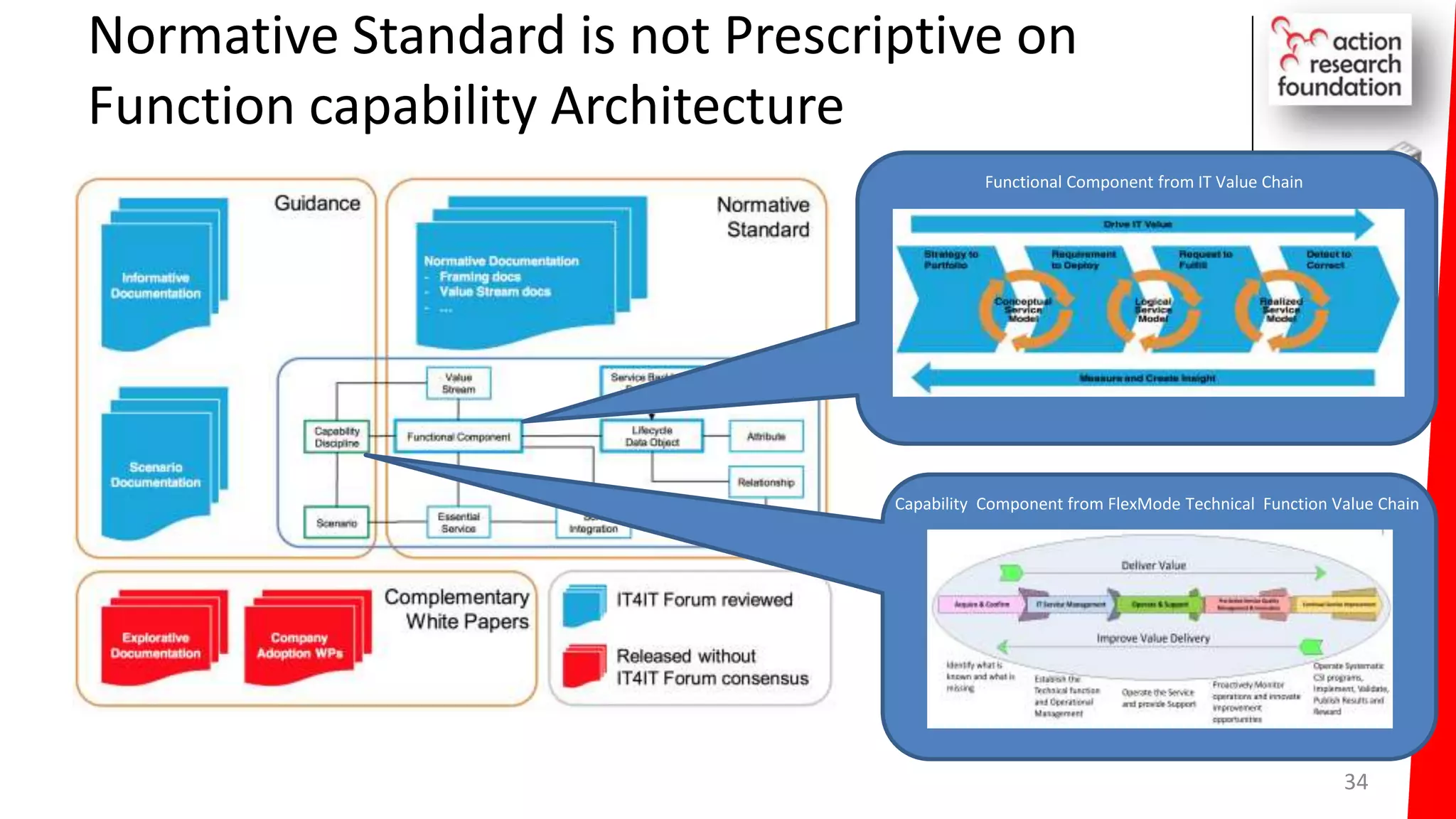
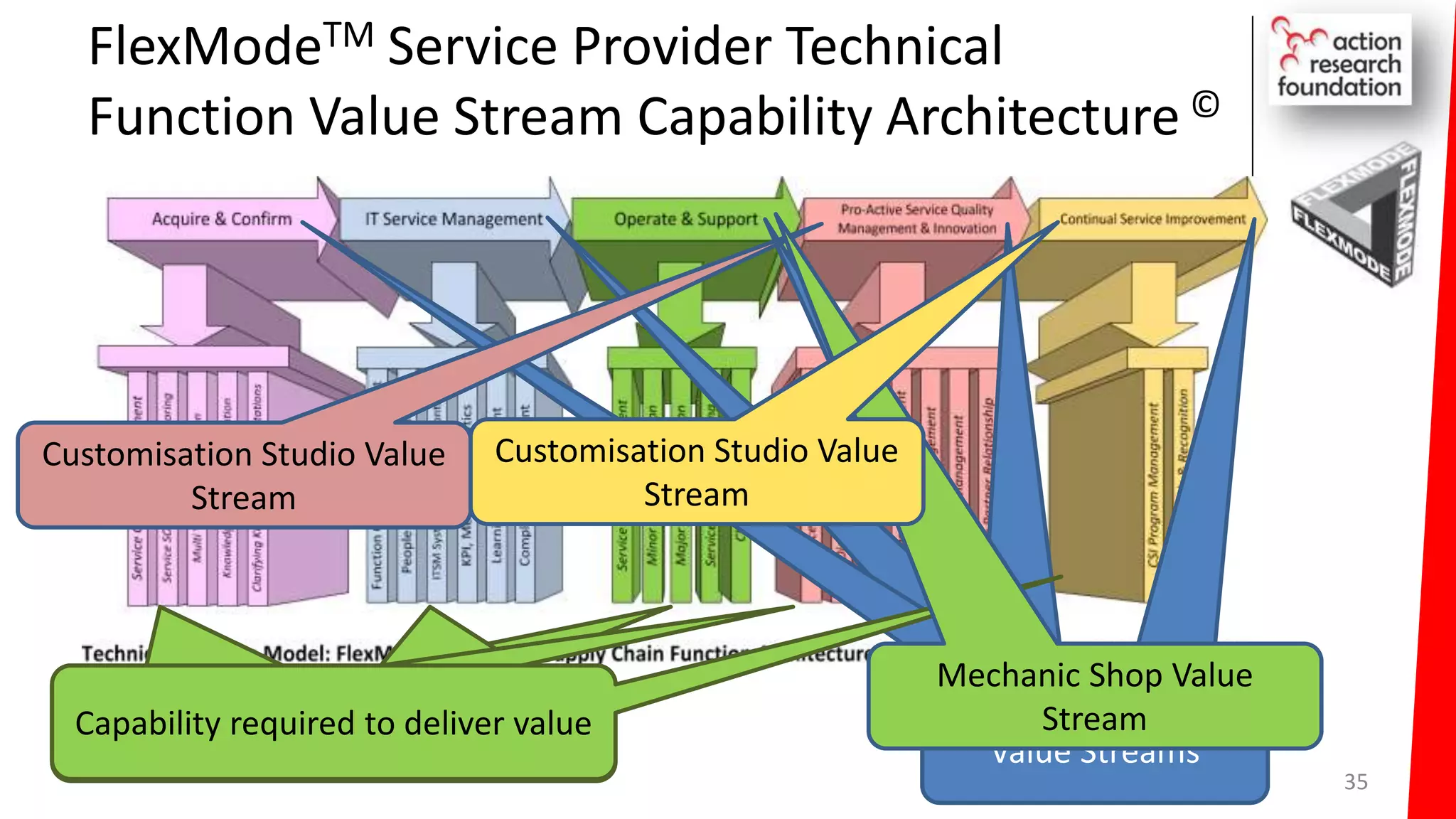
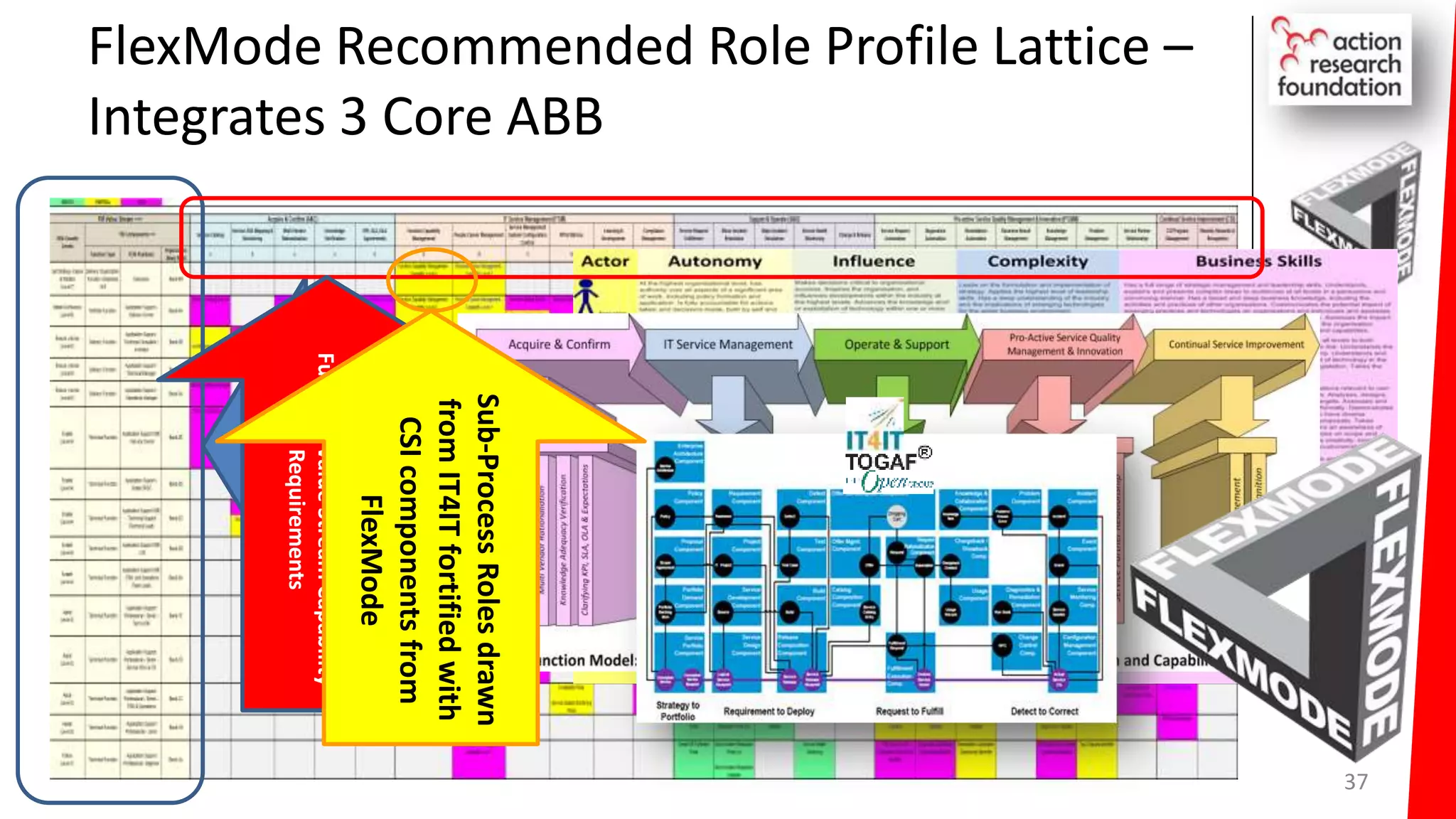
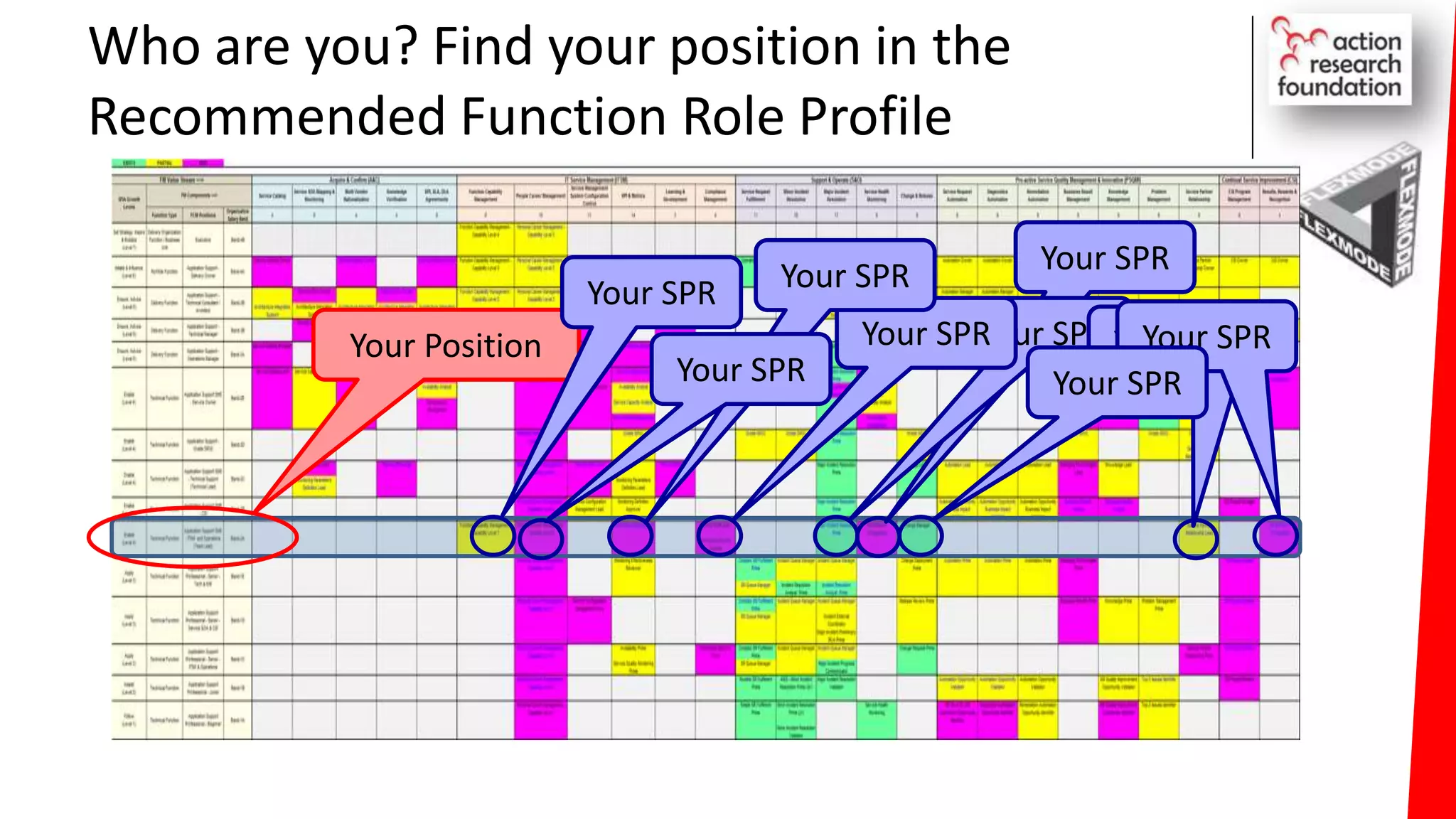
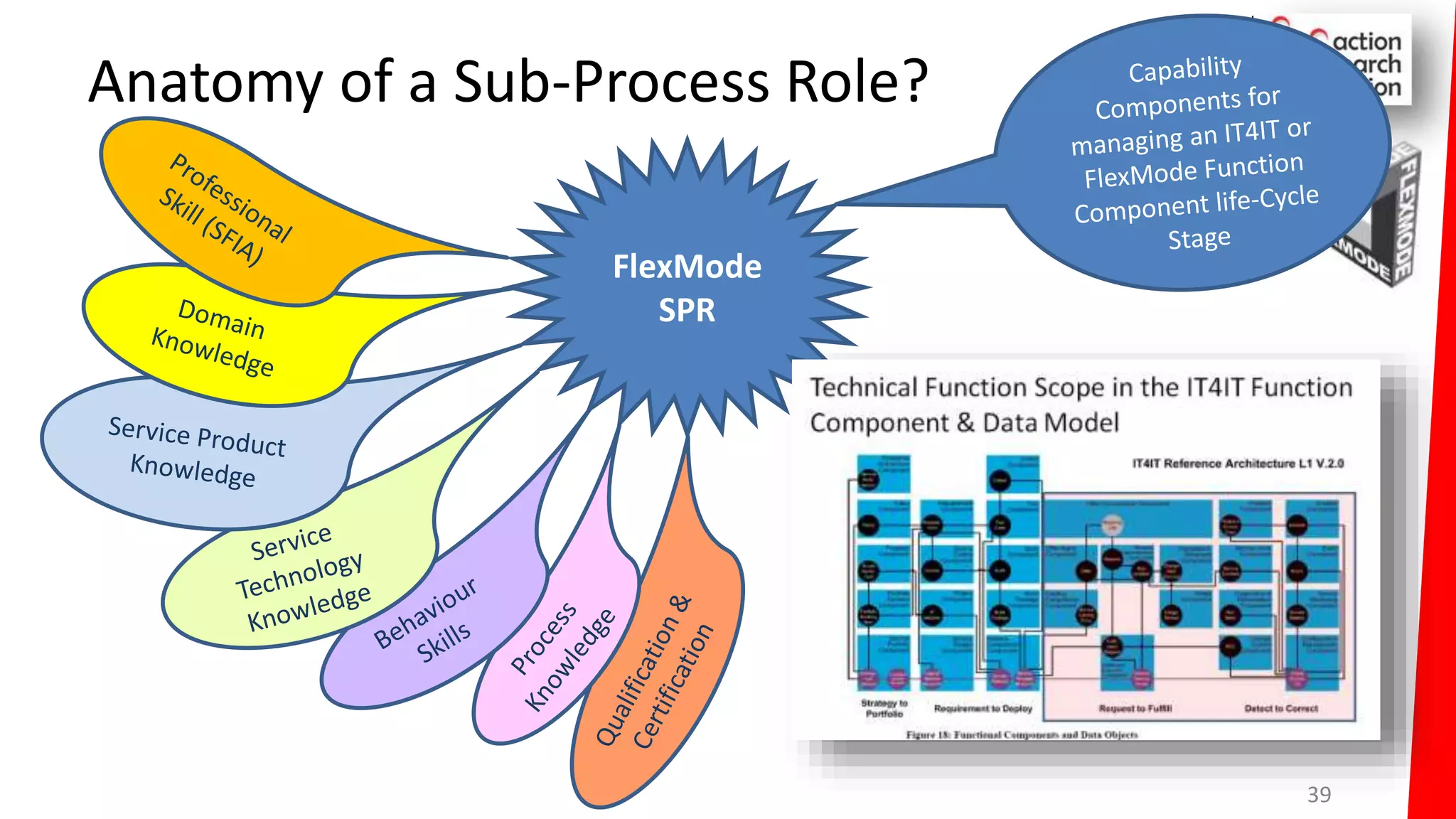
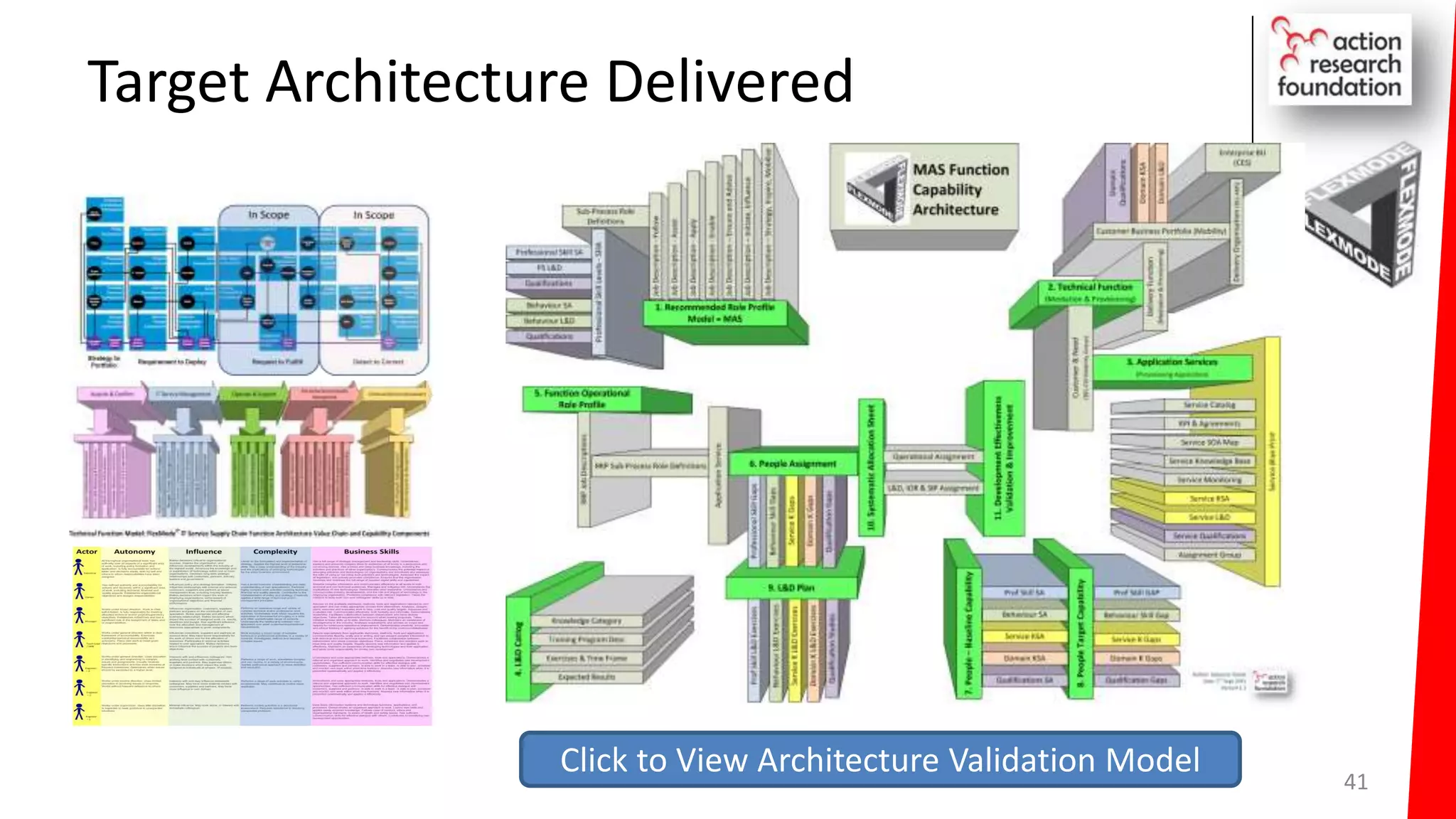
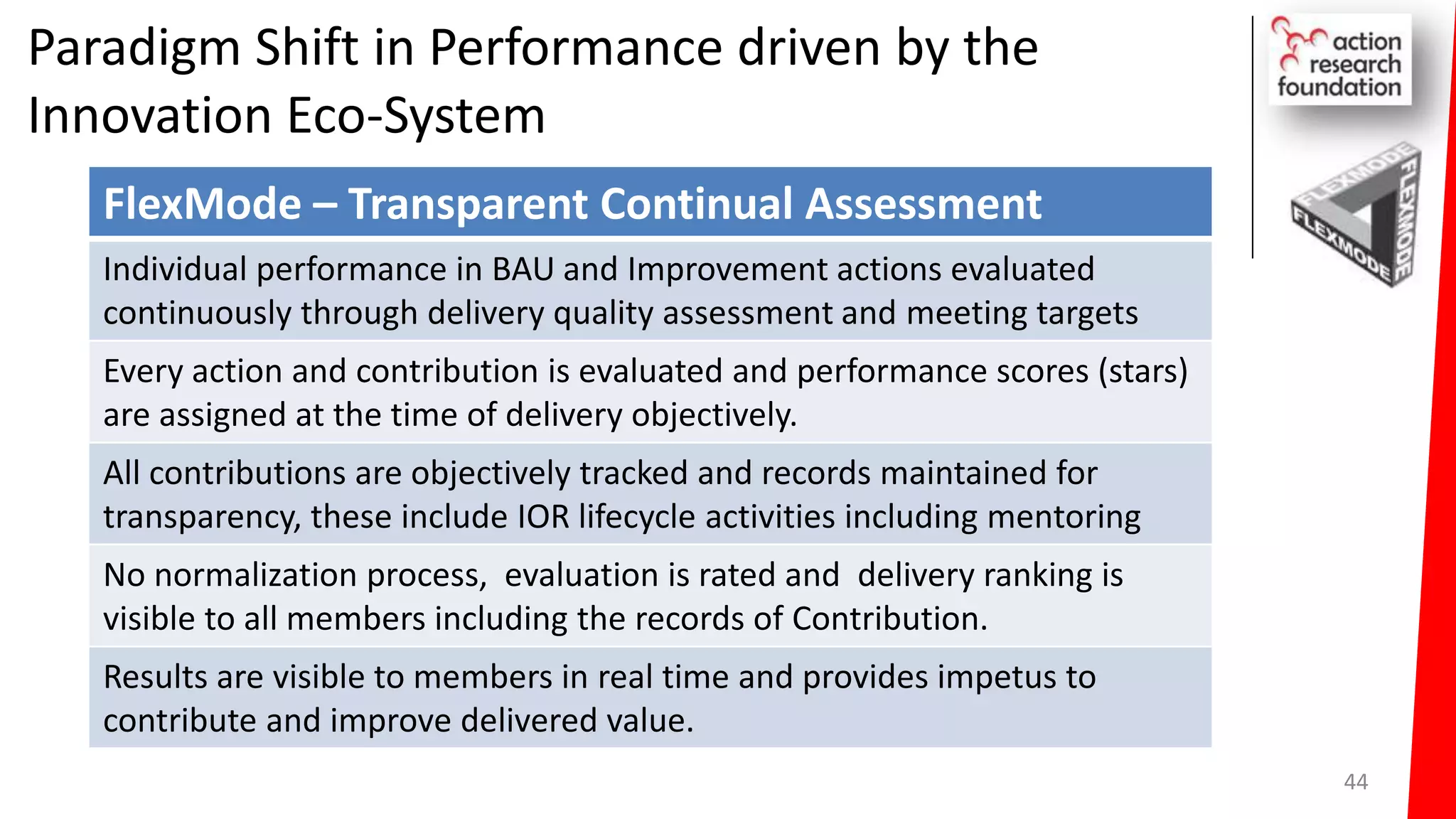
The document summarizes an architecture initiative undertaken by Action Research Foundation to transform an organization's IT operating model. The initiative involved applying TOGAF and IT4IT frameworks to architect the next generation service provider organization. Key aspects included establishing an architecture capability, governance processes, and iteratively developing visions and architectures. The delivered solution established function and people management services to improve alignment and establish an innovation ecosystem needed for the target operating model of a customization studio.