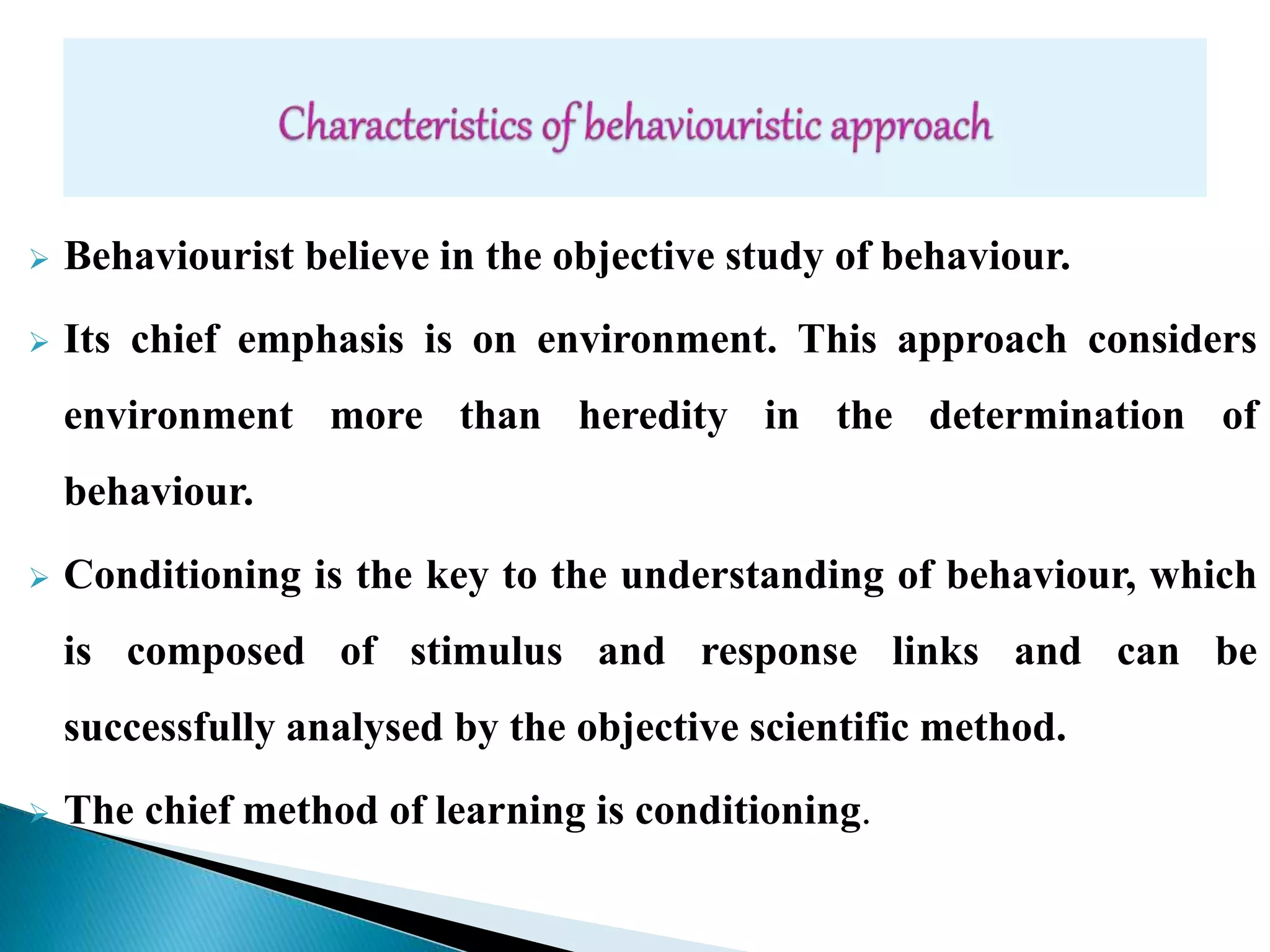
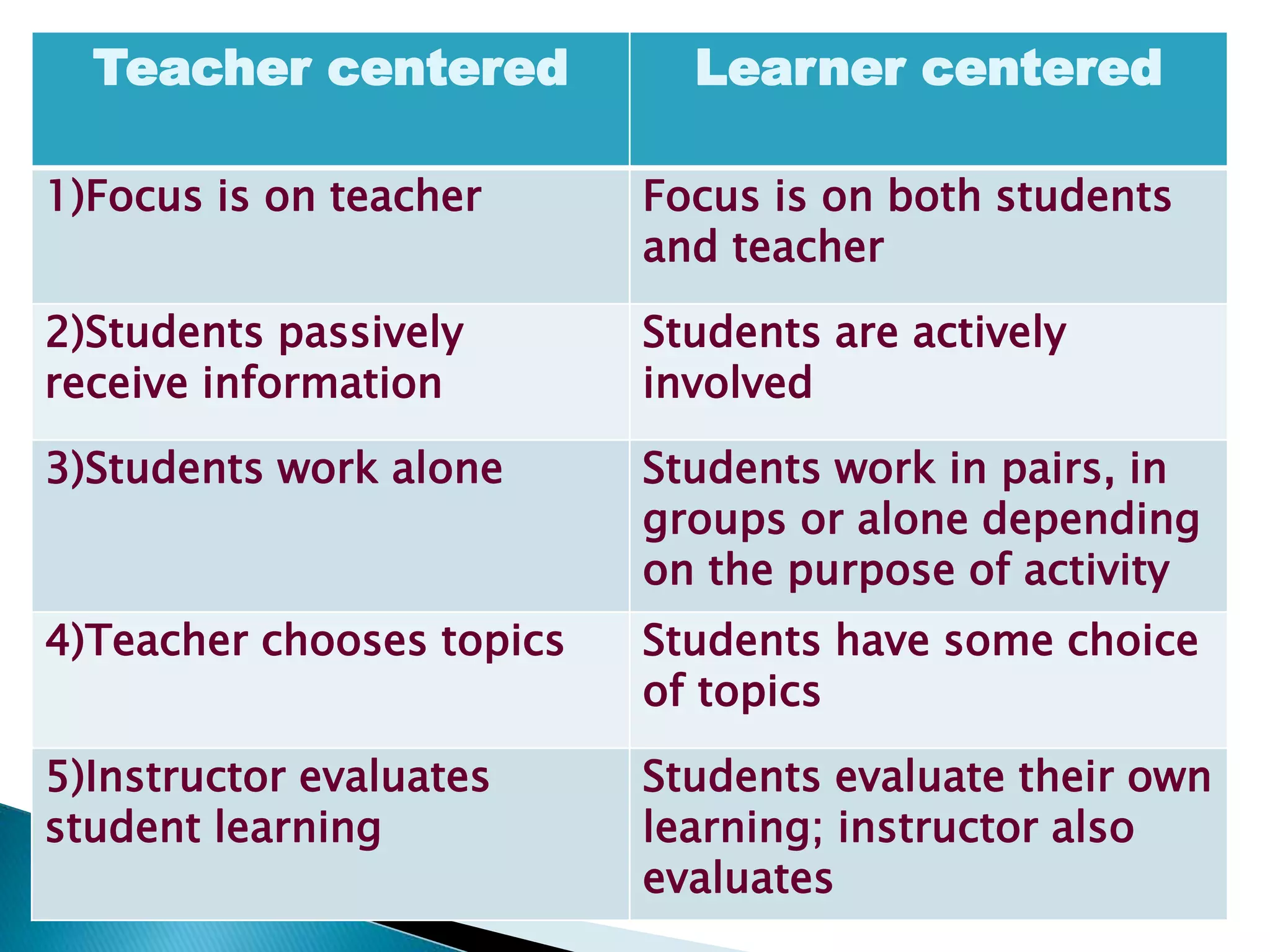
This document discusses different approaches to teaching and learning, including behaviorism, constructivism, teacher-centered approaches, and learner-centered approaches. Behaviorism views learning as stimulus-response connections and emphasizes conditioning, while constructivism sees learning as knowledge construction through experience and interaction with the environment. Teacher-centered approaches focus on the teacher as instructor and controller of content, whereas learner-centered approaches place the learner at the center and see the teacher's role as facilitating learning. The document provides advantages of learner-centered approaches over teacher-centered ones.