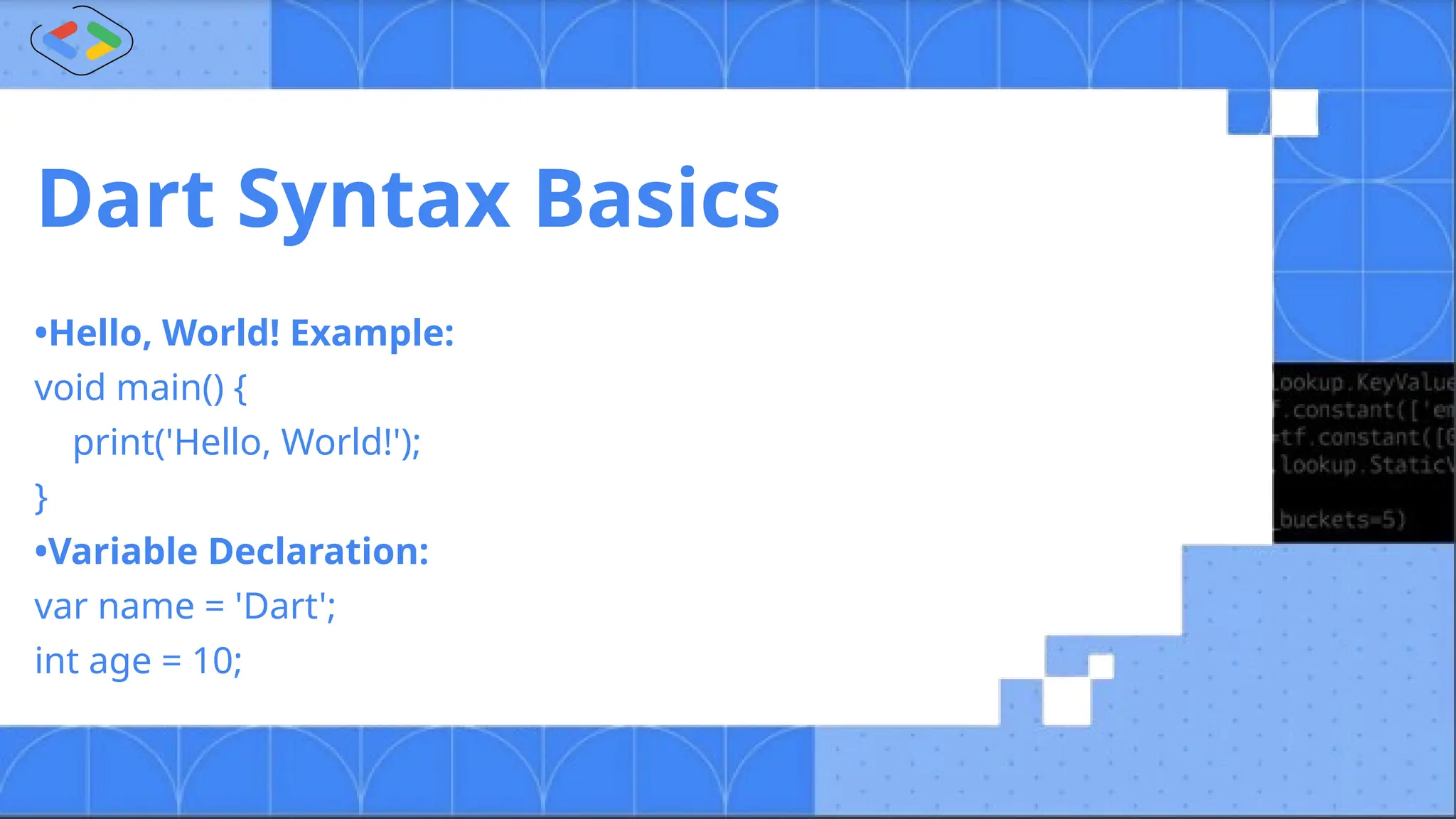
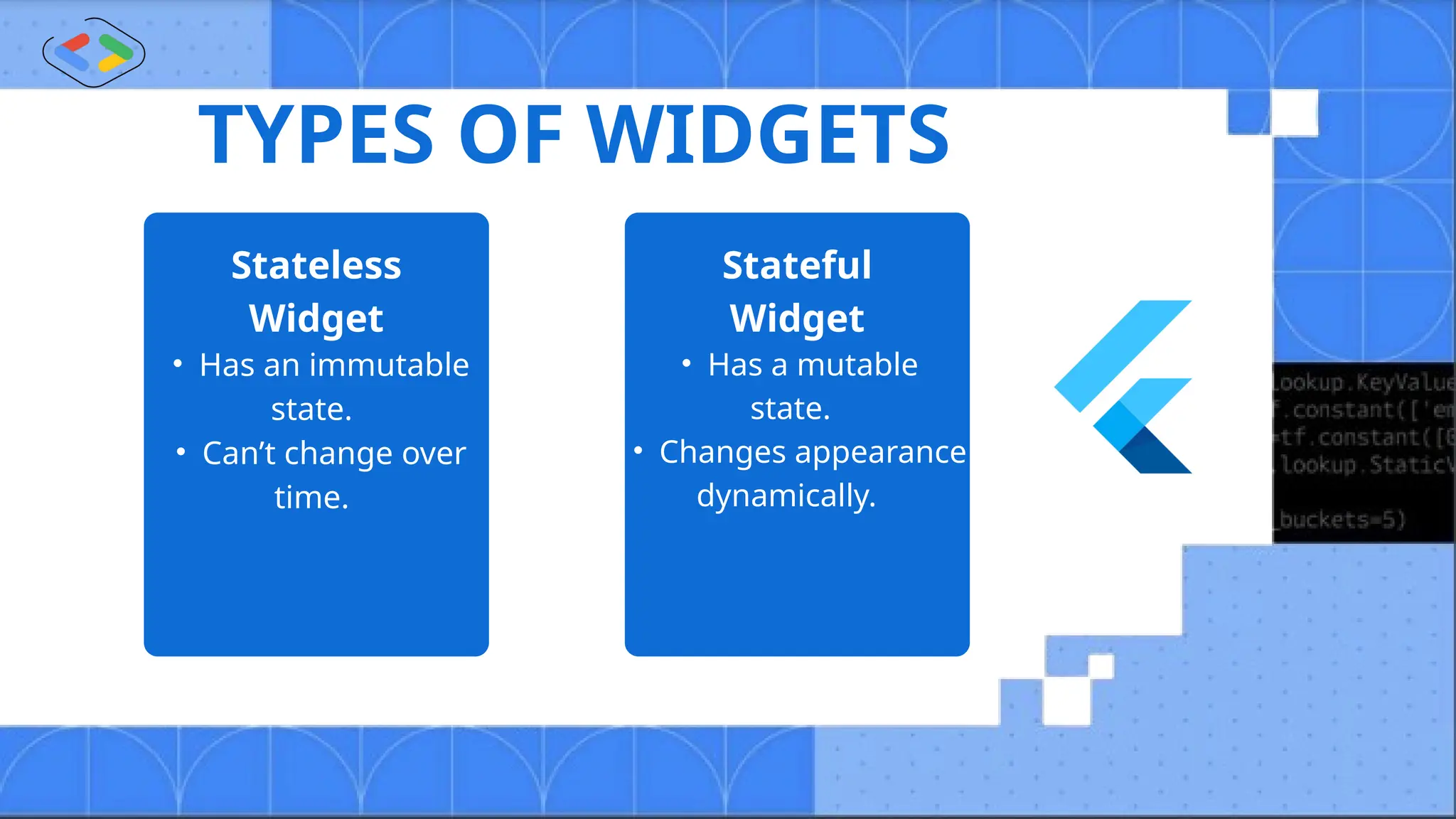
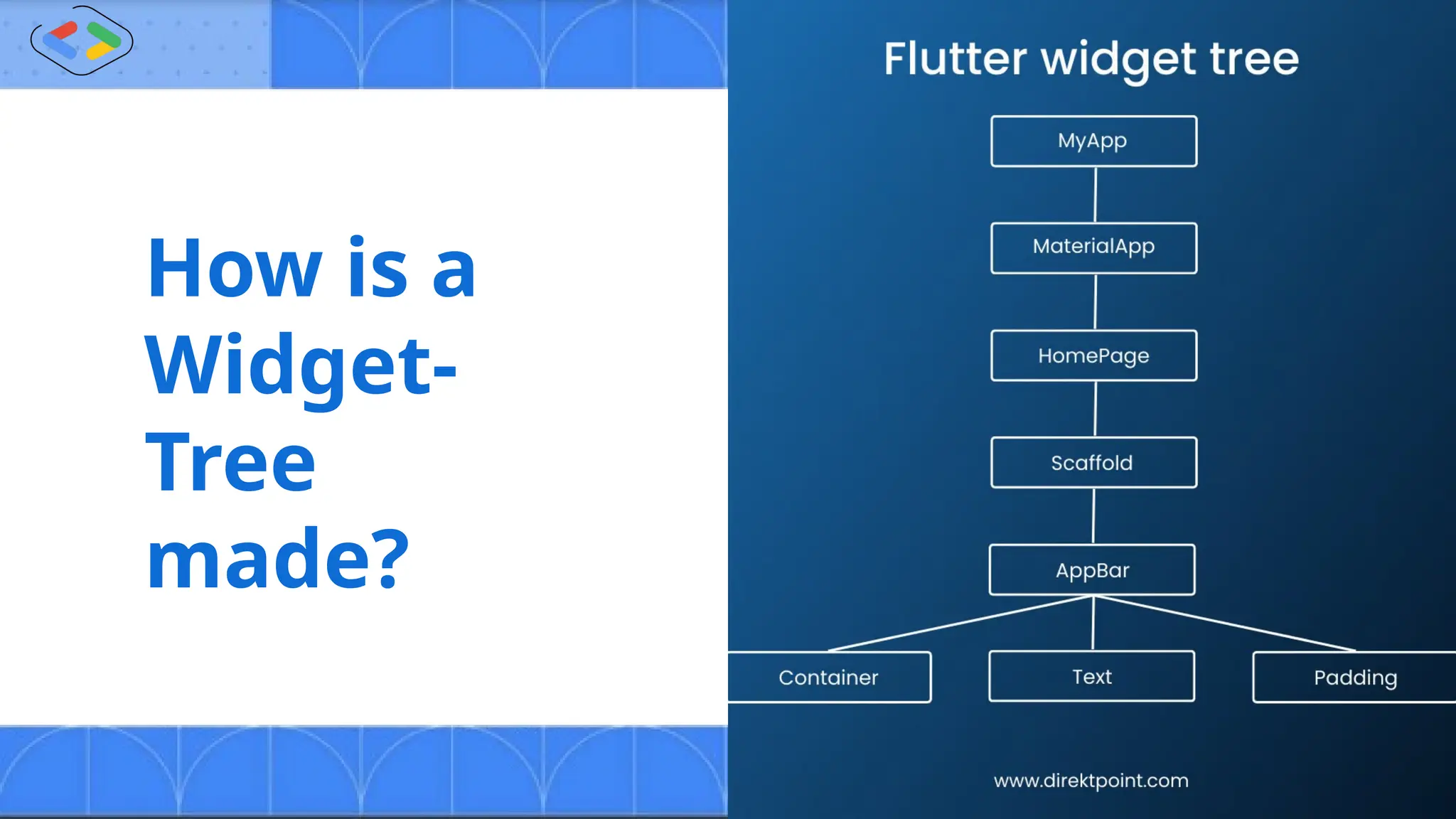
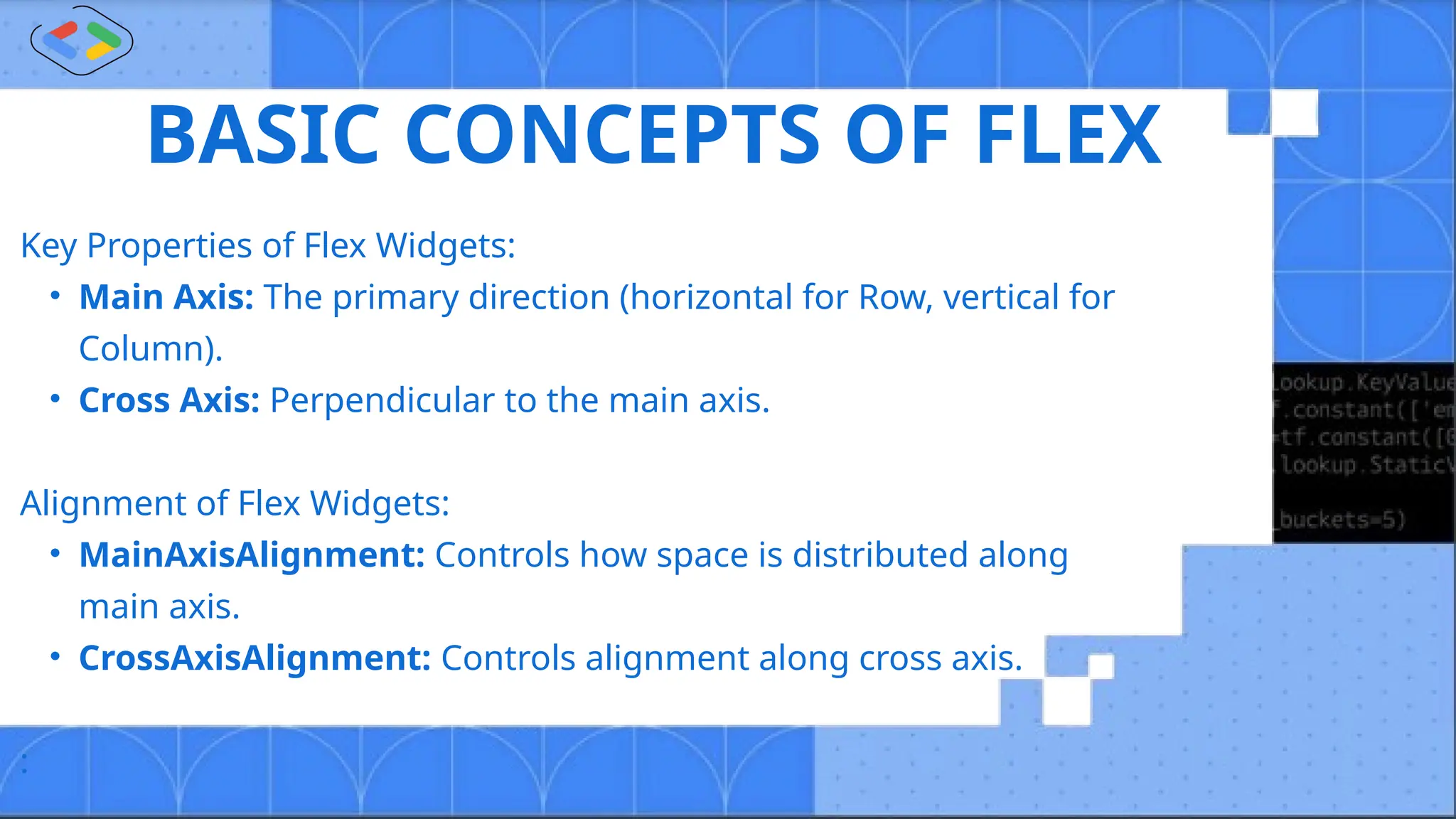
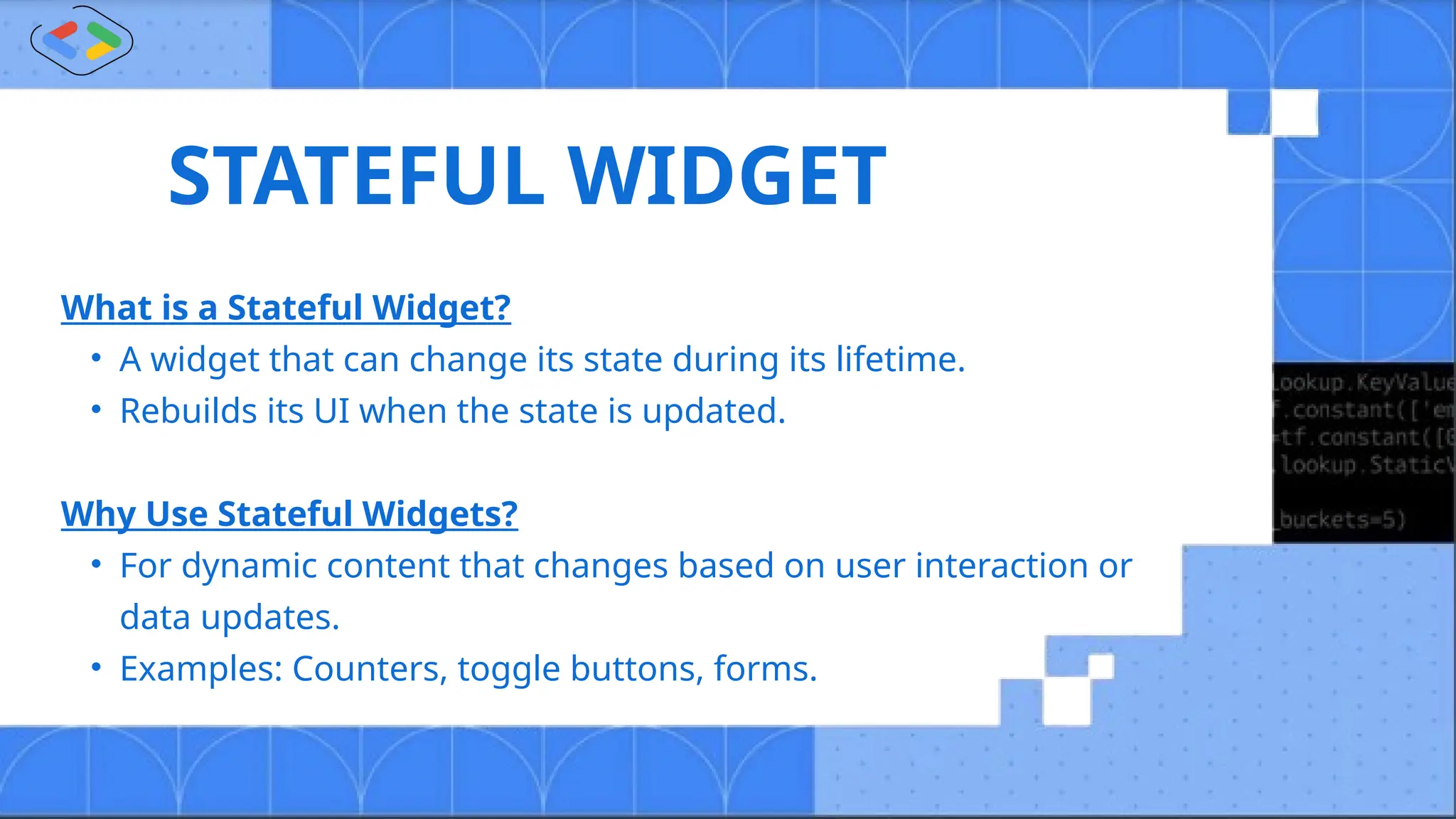
The document discusses Android development using Flutter, highlighting its advantages as a customizable, open-source toolkit that supports various platforms from a single codebase. It introduces Dart, the programming language associated with Flutter, and explains fundamental concepts such as widgets, navigators, and the structure of Flutter applications. Key takeaways emphasize Flutter's efficiency and flexibility in building responsive apps with features like widgets and state management.