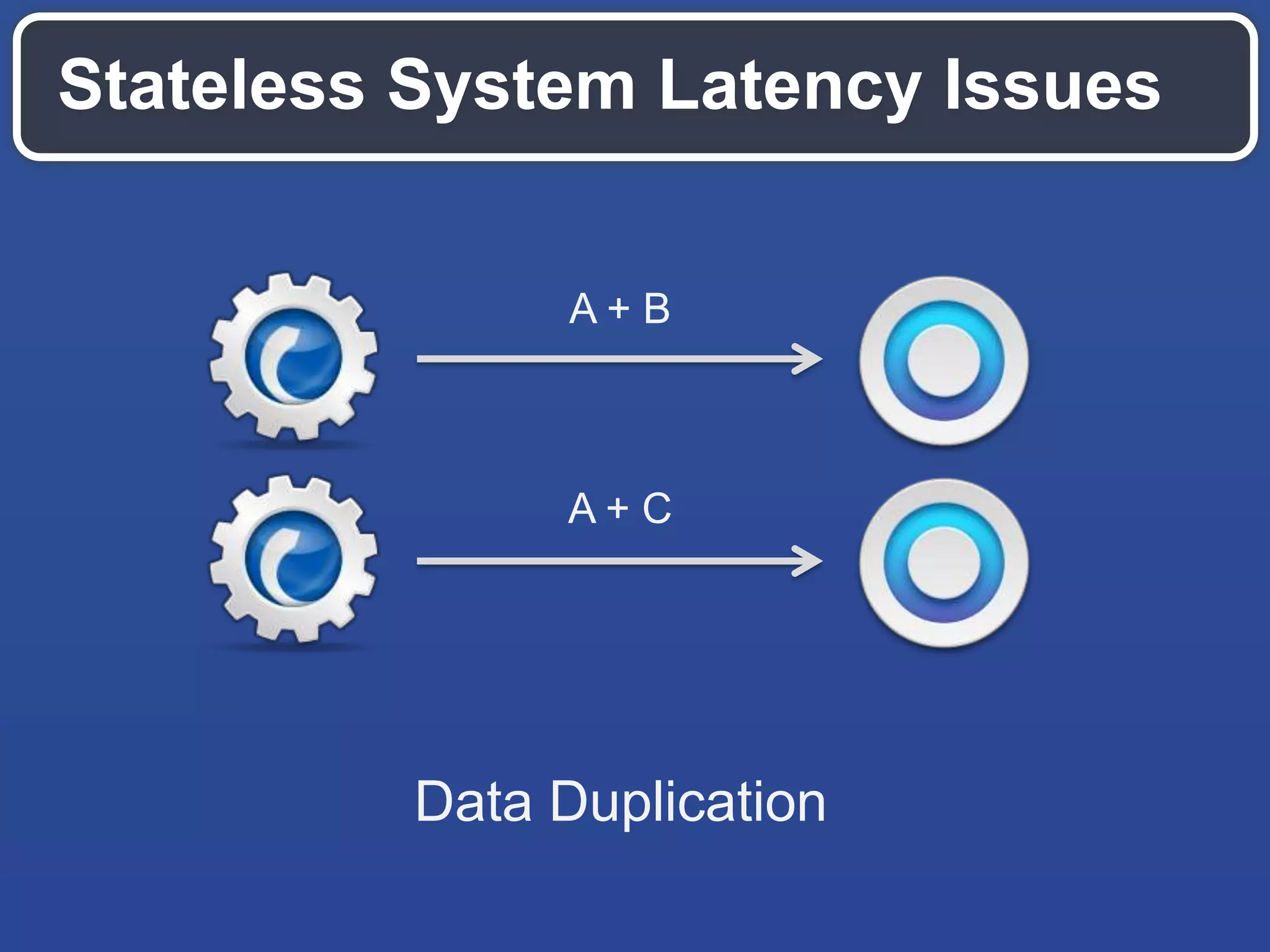
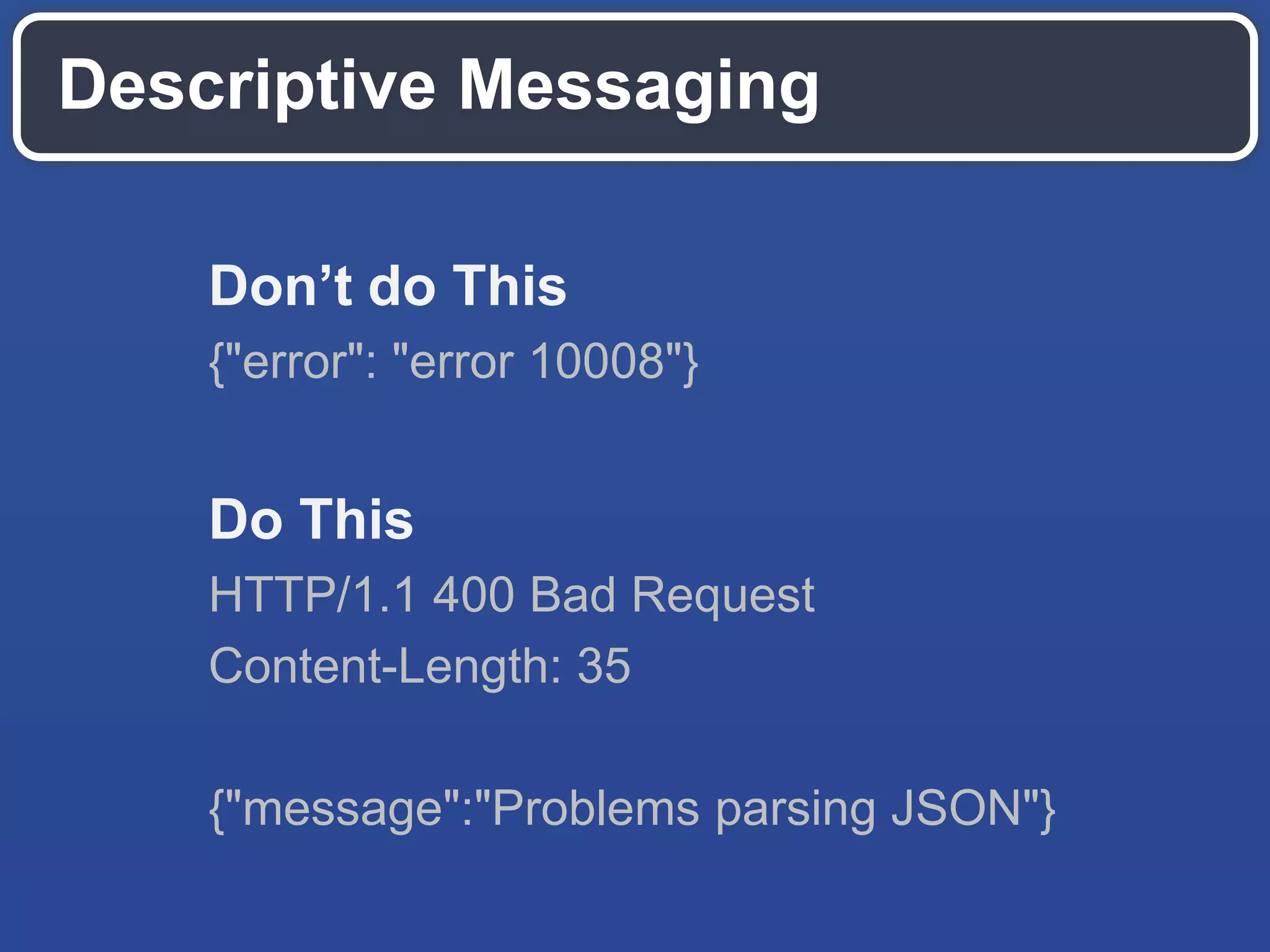
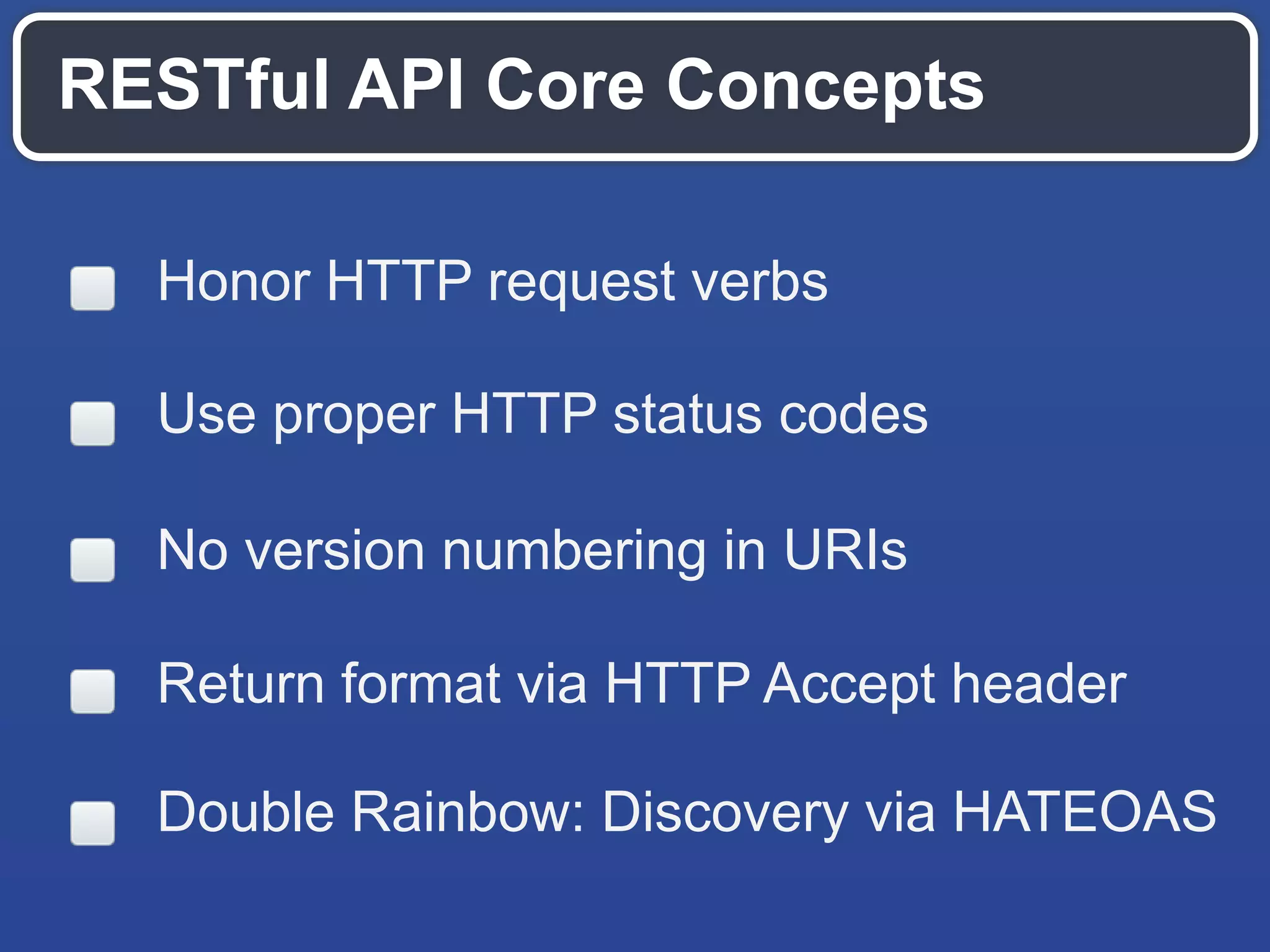
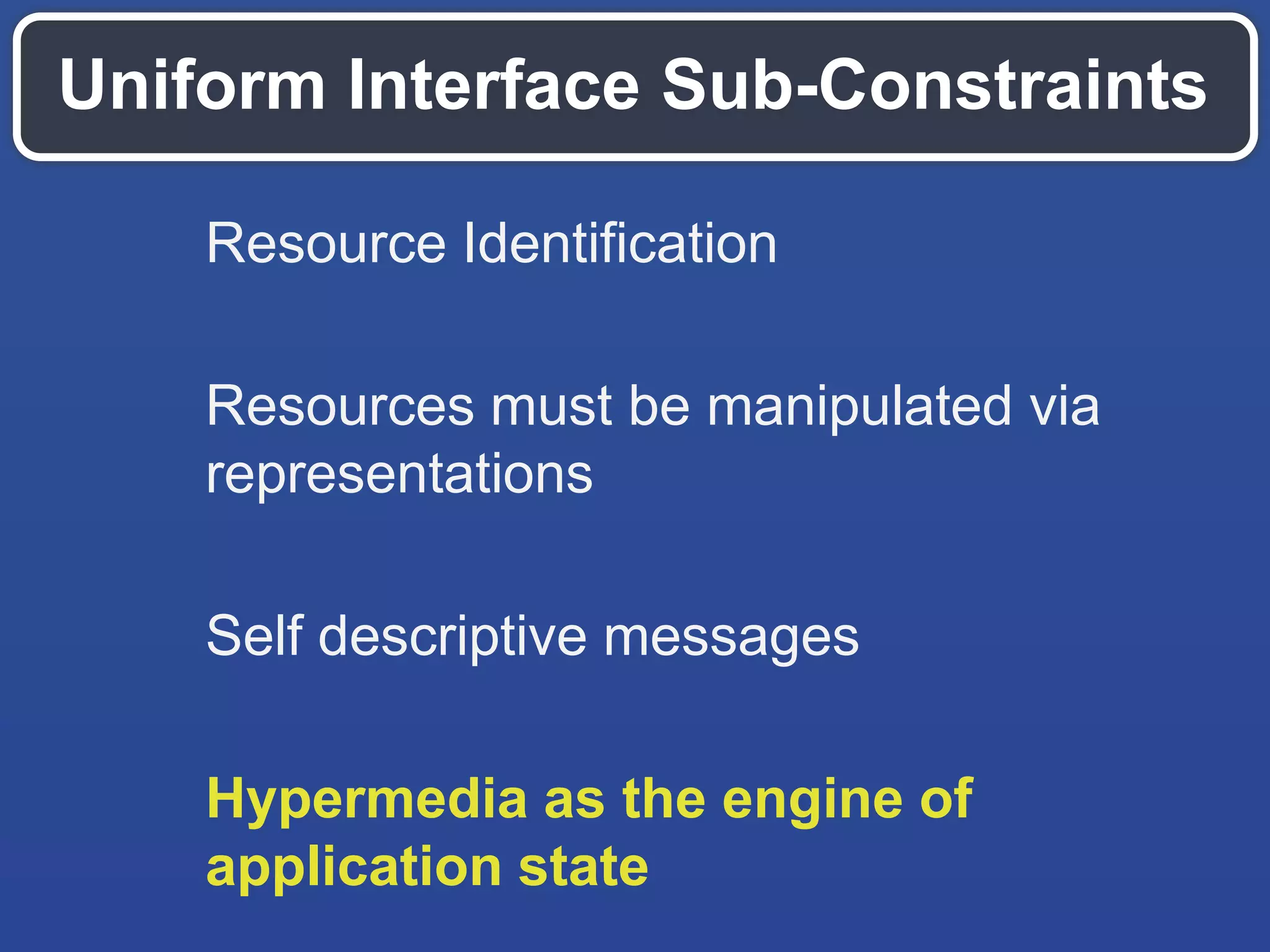
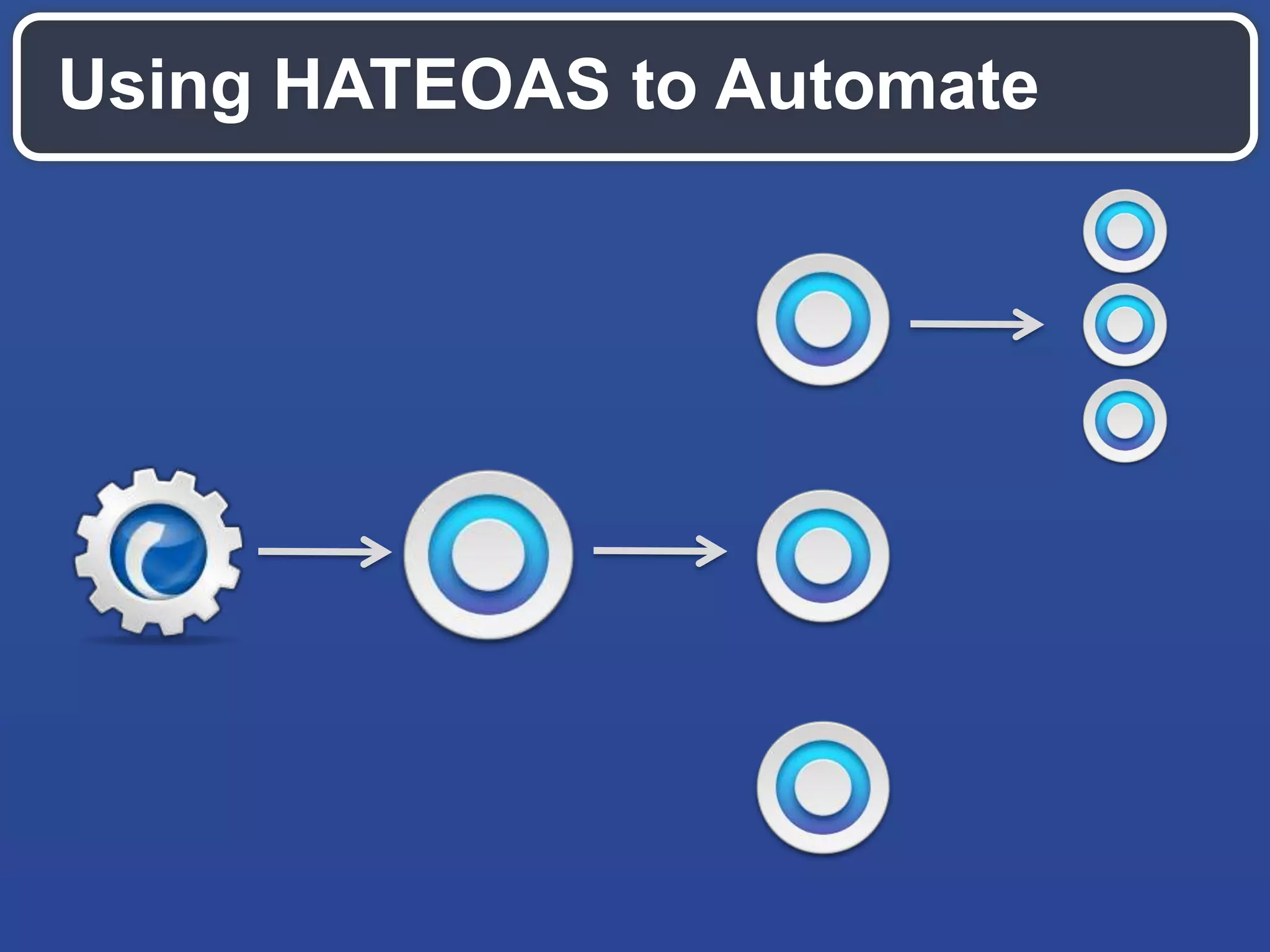
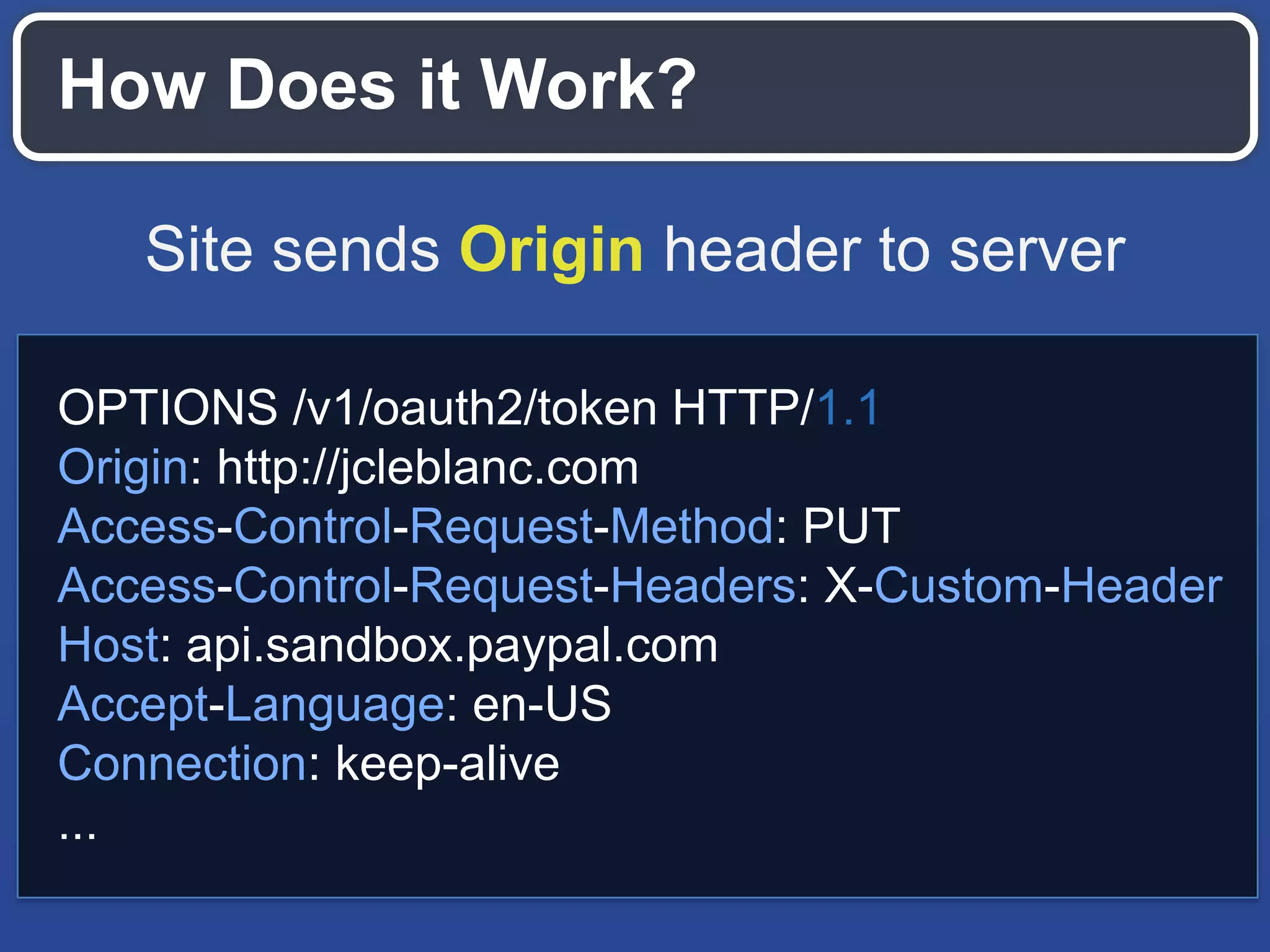
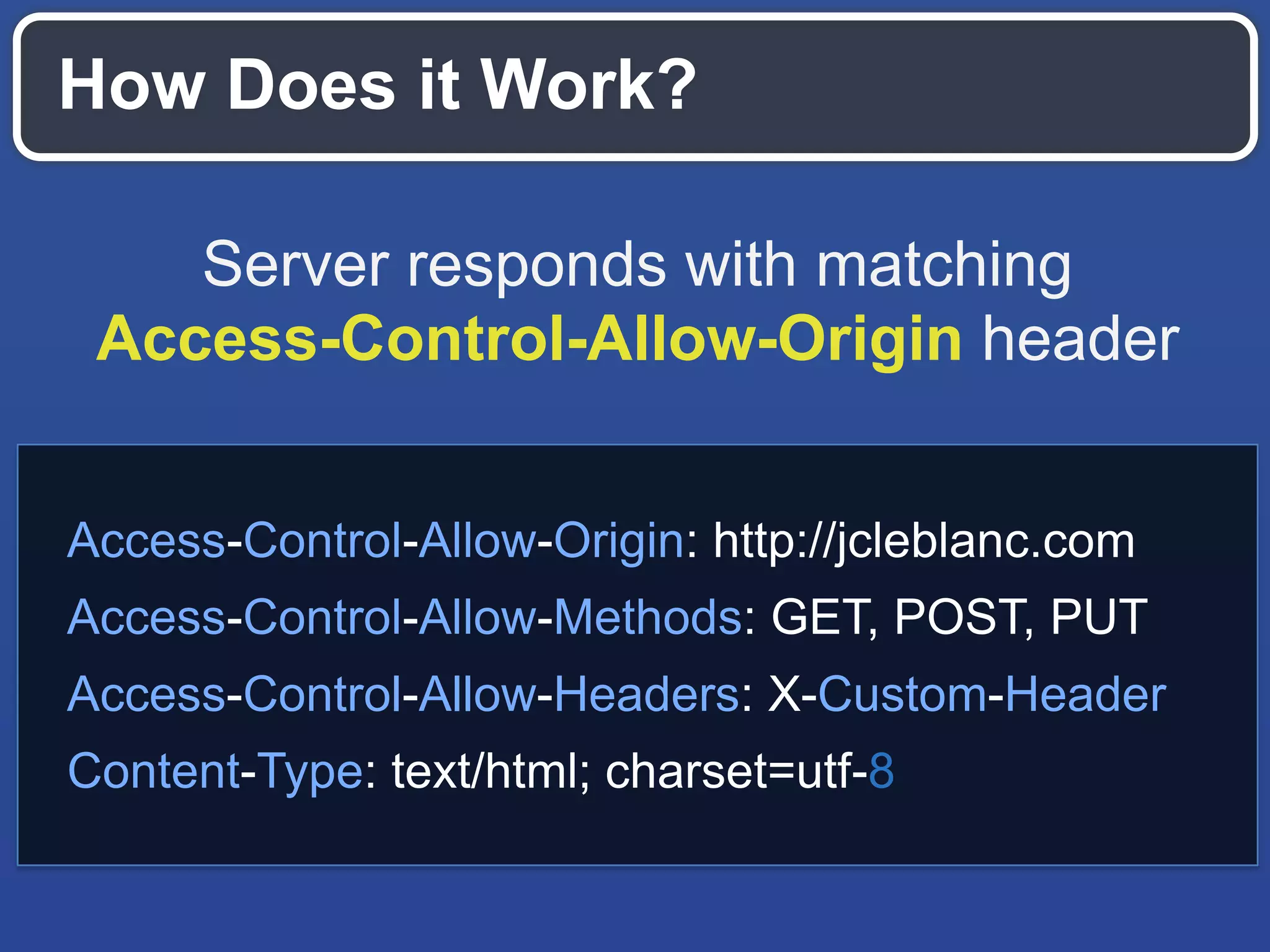
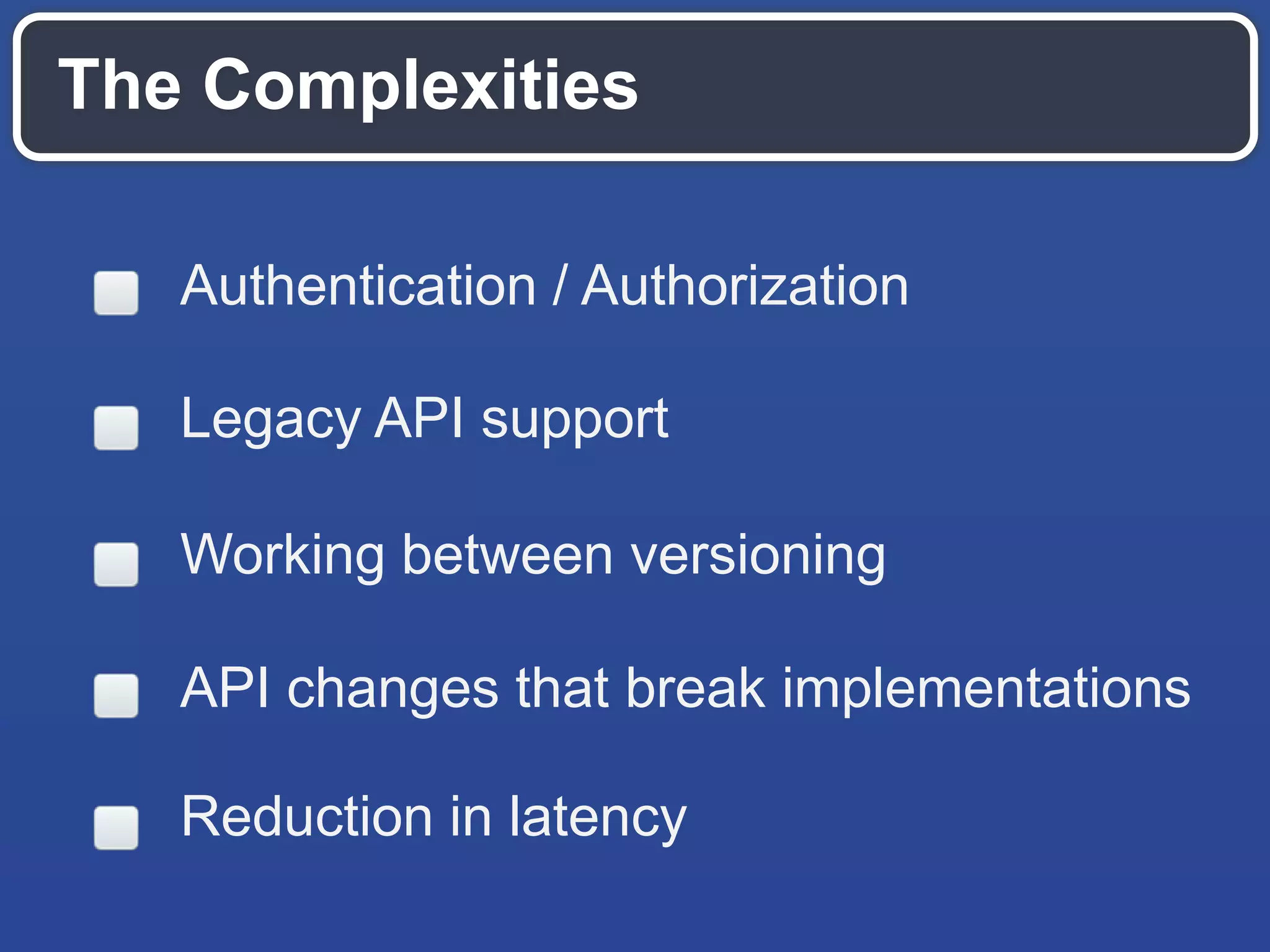
The document outlines key API design principles aimed at enhancing developer efficiency, including strategies for reducing latency, properly utilizing HTTP methods, and securing data resources. It emphasizes important practices such as using correct status codes, leveraging hypermedia as the engine of application state (HATEOAS), and adopting modern security models like OAuth. The document also highlights the importance of offloading complexity to providers and making thoughtful tradeoffs in API architecture to meet developers' needs.
















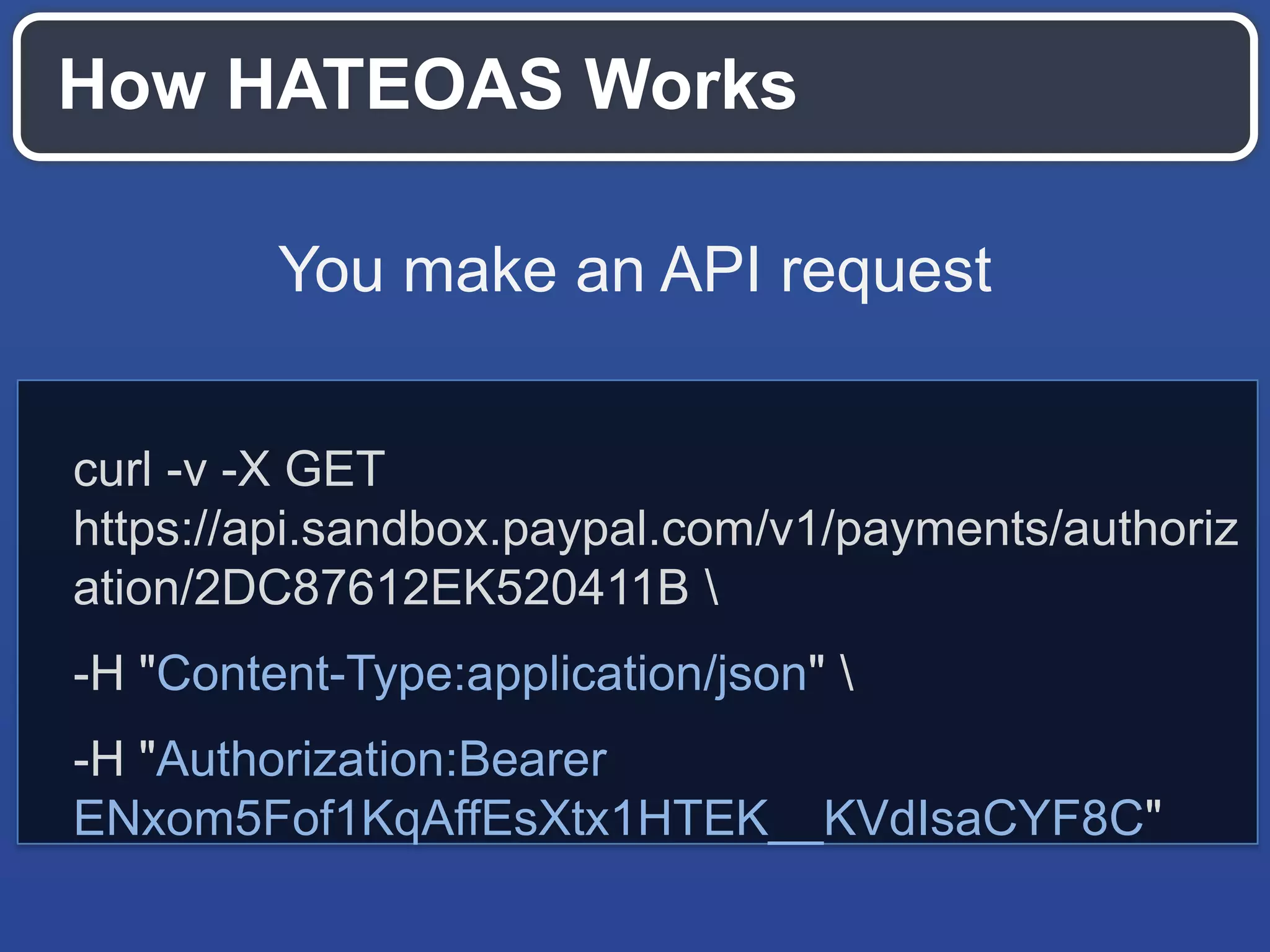
!["links": [
{
"href":"https://api.sandbox.paypal.com/v1/payments/
authorization/6H149011U8307001M",
"rel":"self",
"method":"GET"
},{
"href":"https://api.sandbox.paypal.com/v1/payments/
authorization/6H149011U8307001M/capture",
"rel":"capture",
"method":"POST"
},{
"href":"https://api.sandbox.paypal.com/v1/payments/
authorization/6H149011U8307001M/void",
"rel":"void",
"method":"POST"
}
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2013octsvcodecampapidesignaccelerateddevelopment-131004130412-phpapp02/75/API-design-principles-for-accelerated-development-26-2048.jpg)






![Representations on Update / Create
{ "id": "PAY-17S8410768582940NKEE66EQ",
"create_time": "2013-01-31T04:12:02Z",
"update_time": "2013-01-31T04:12:04Z",
"state": "approved",
"intent": "sale",
"payer": {...},
"transactions": [{...}],
"links": [{...}] }
Send enough detail to not have to make another
request to the API](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2013octsvcodecampapidesignaccelerateddevelopment-131004130412-phpapp02/75/API-design-principles-for-accelerated-development-39-2048.jpg)

