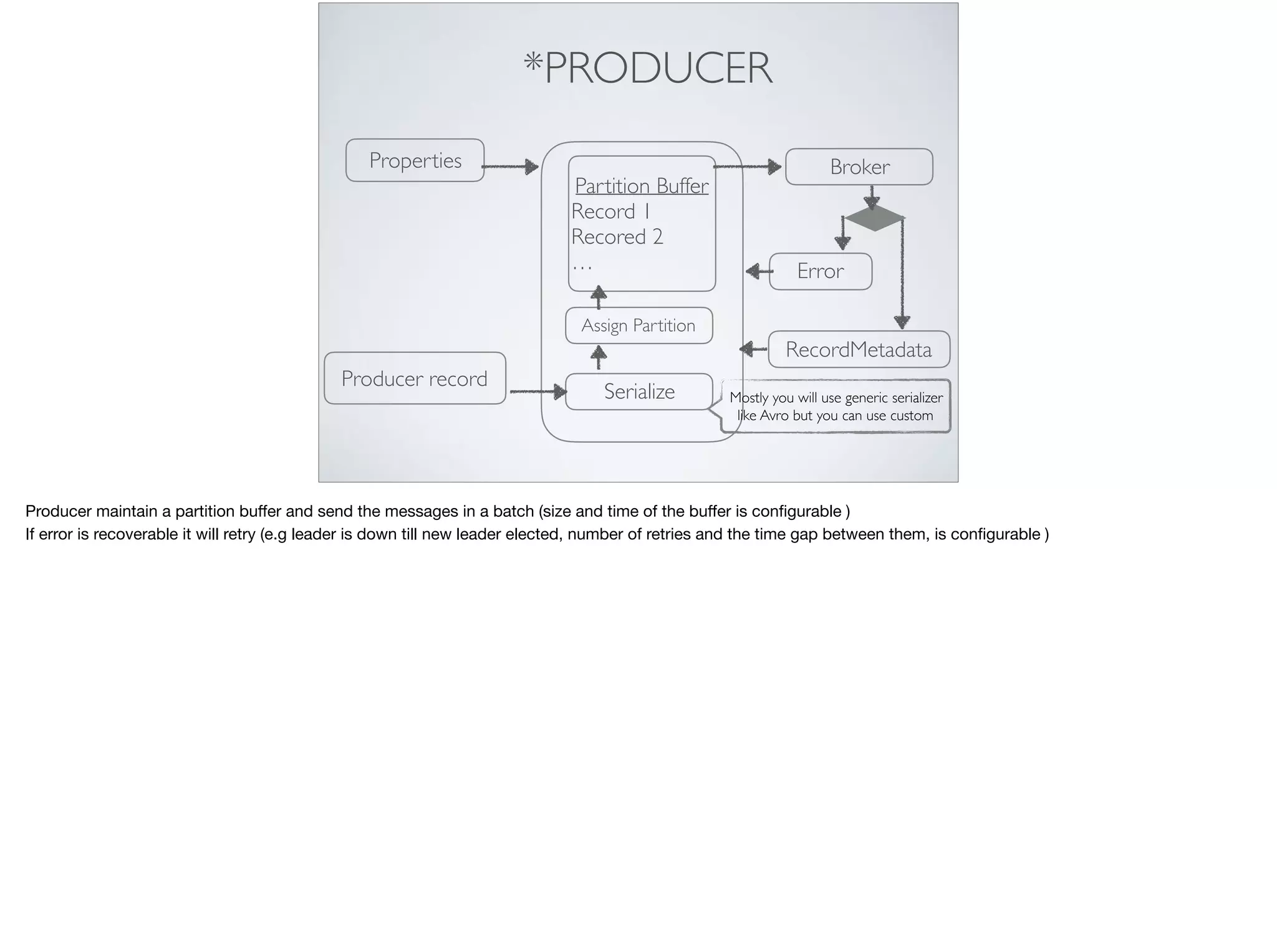
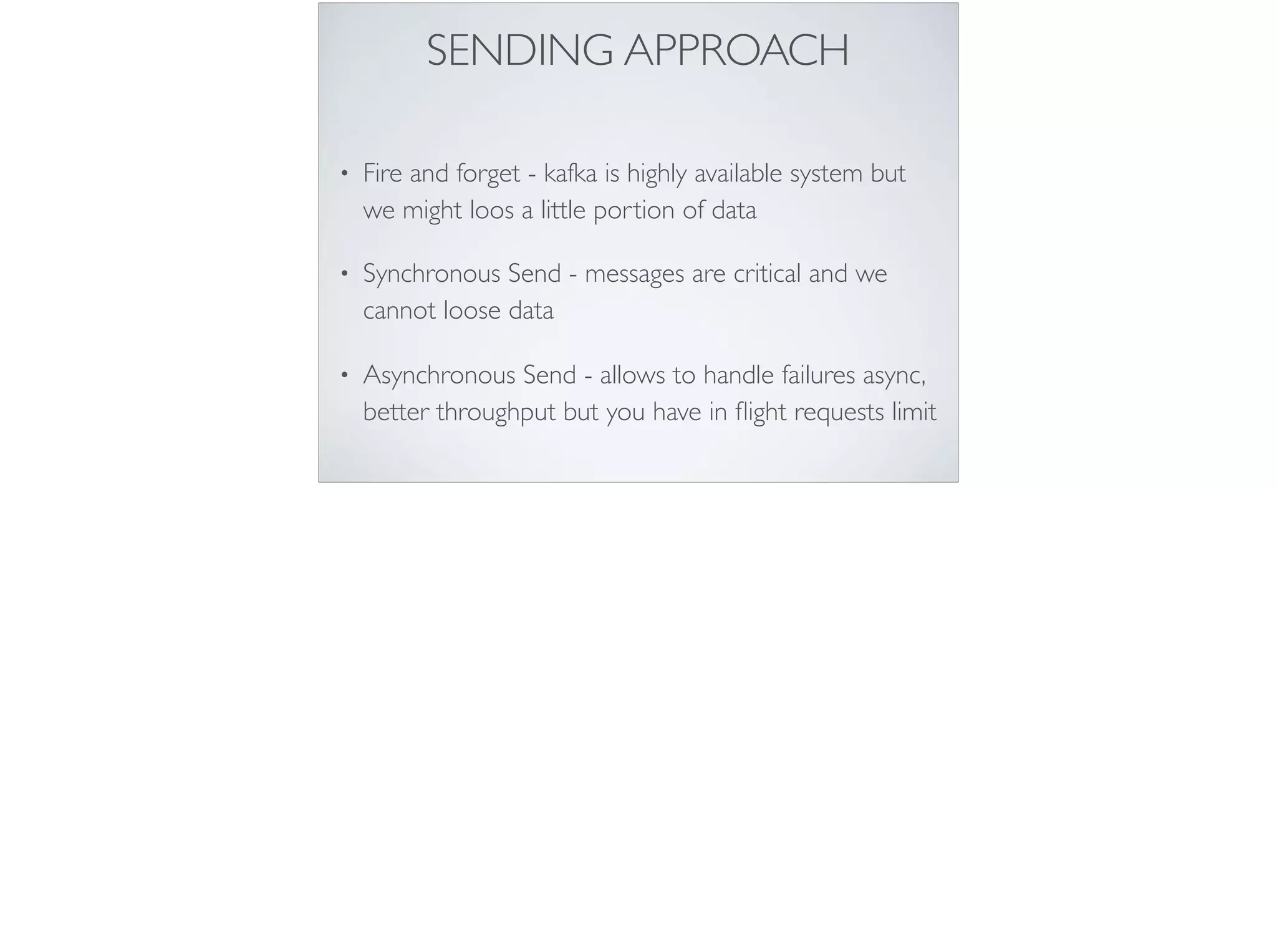
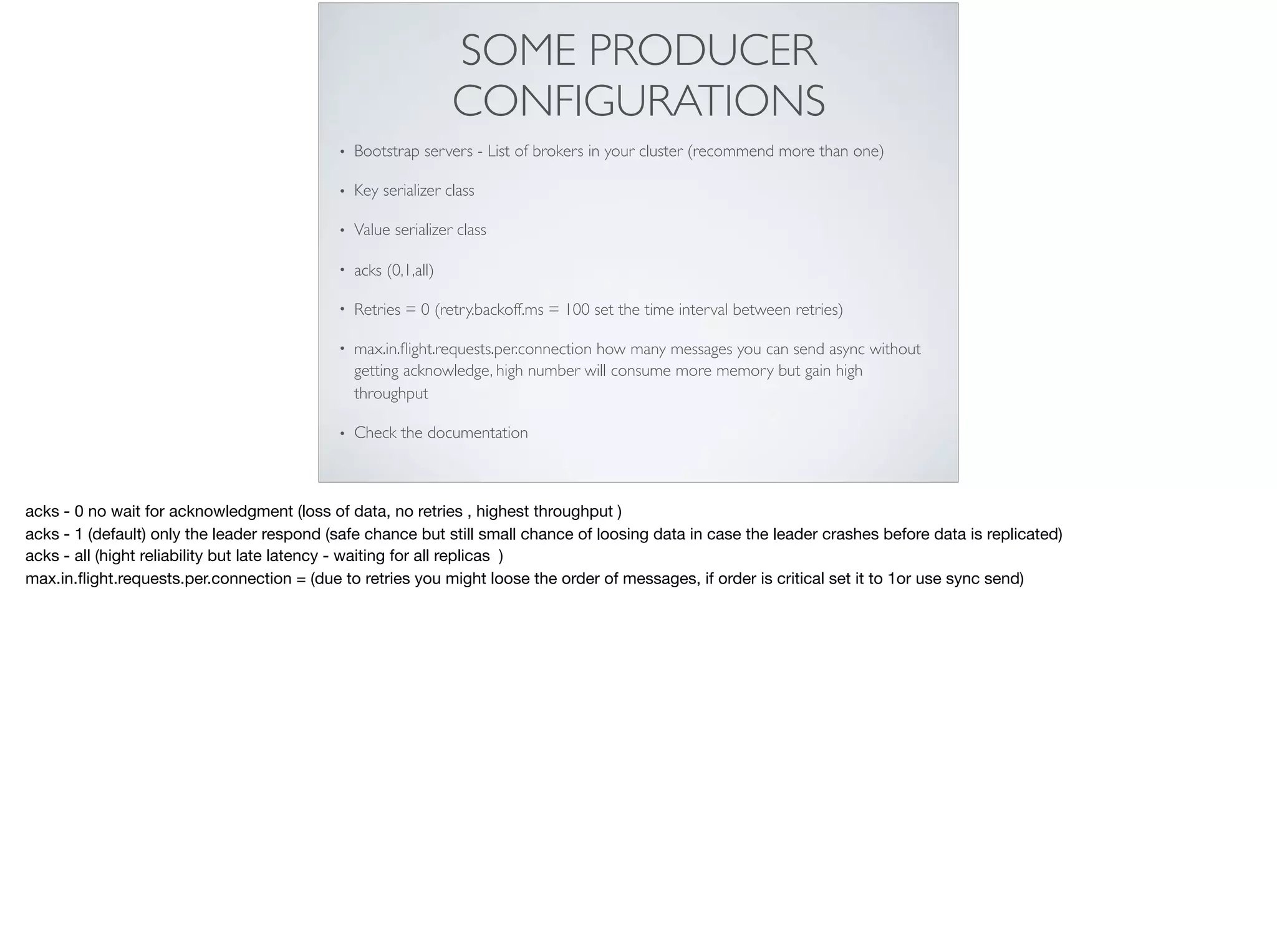
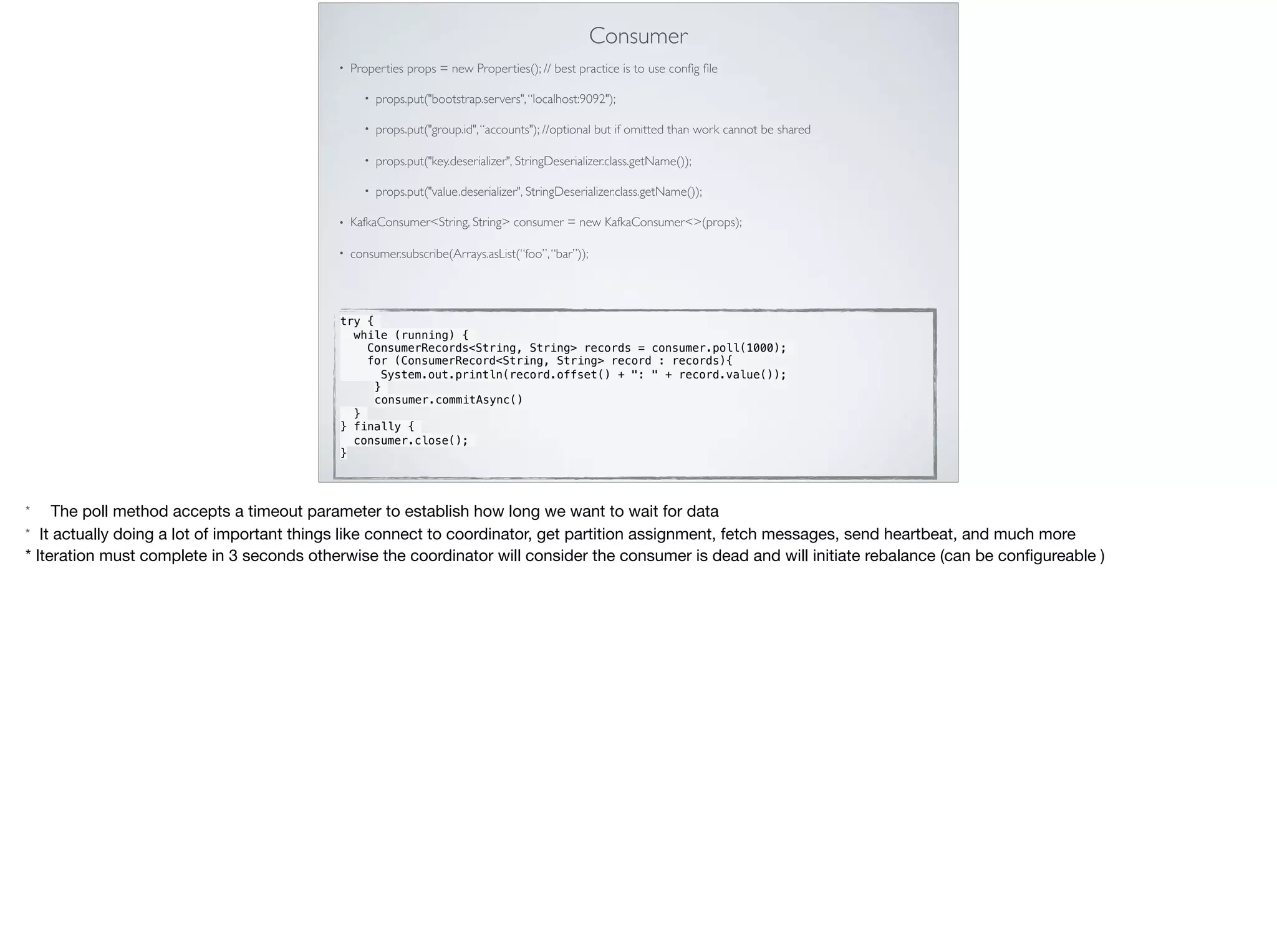
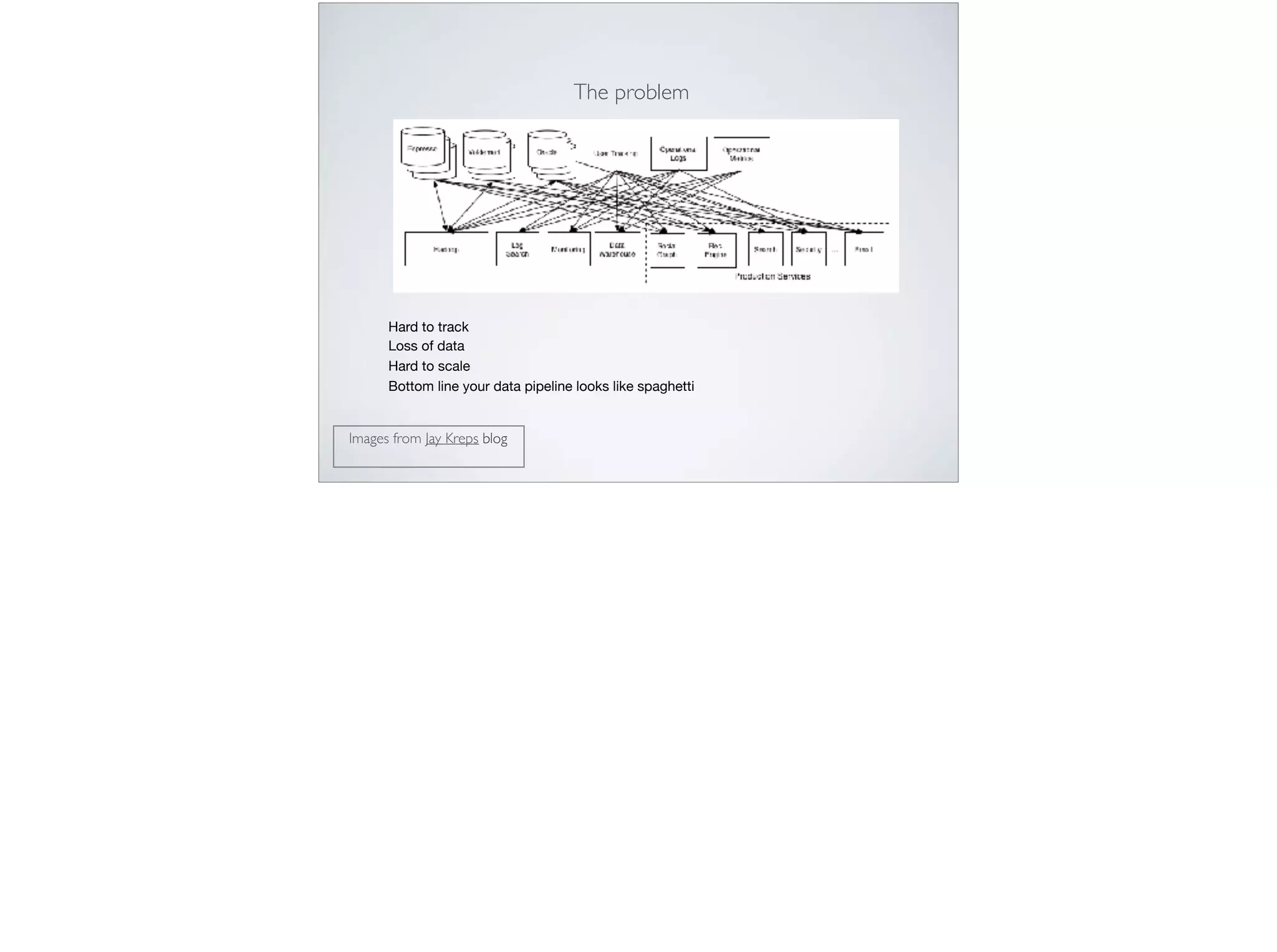
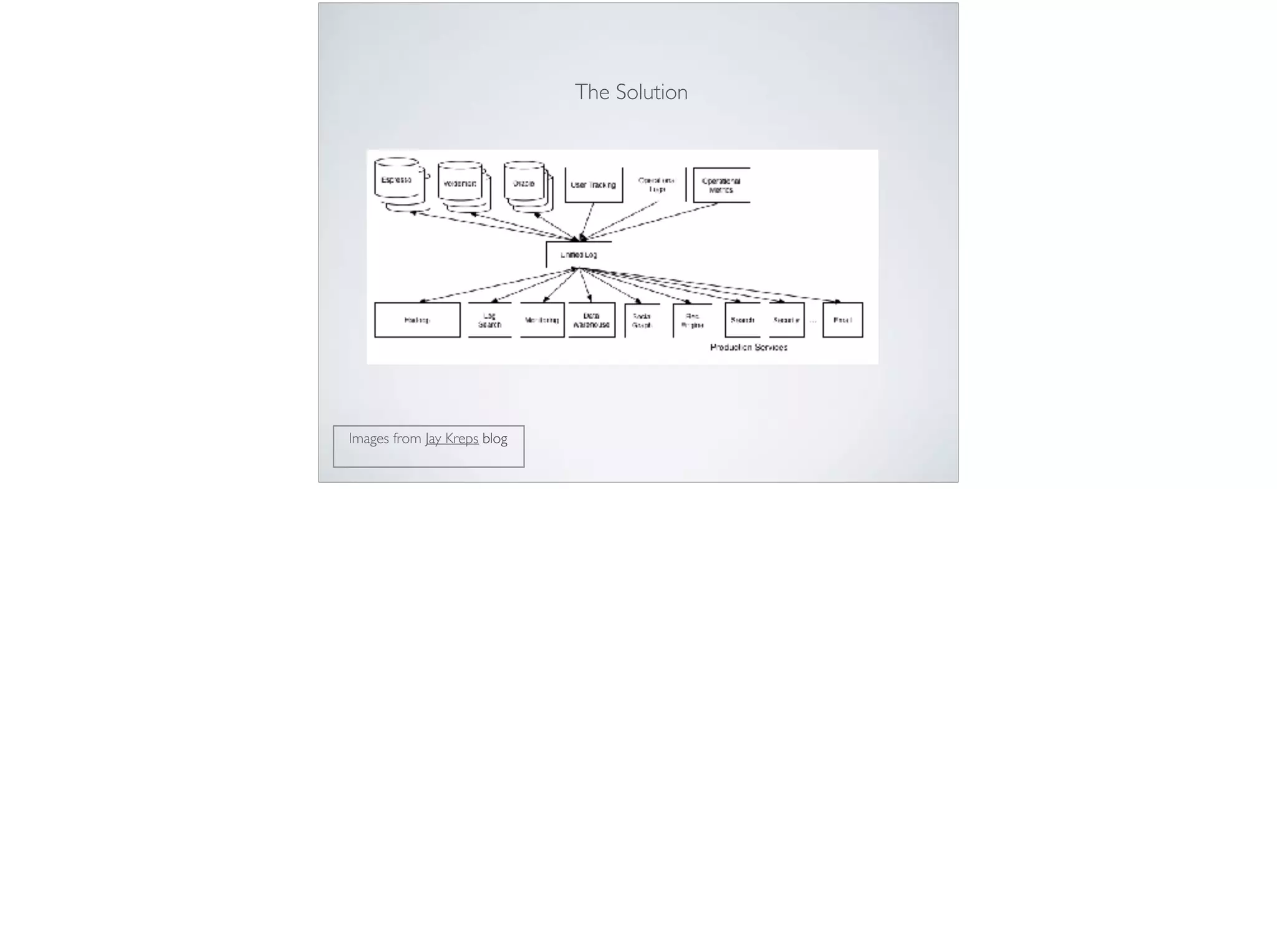
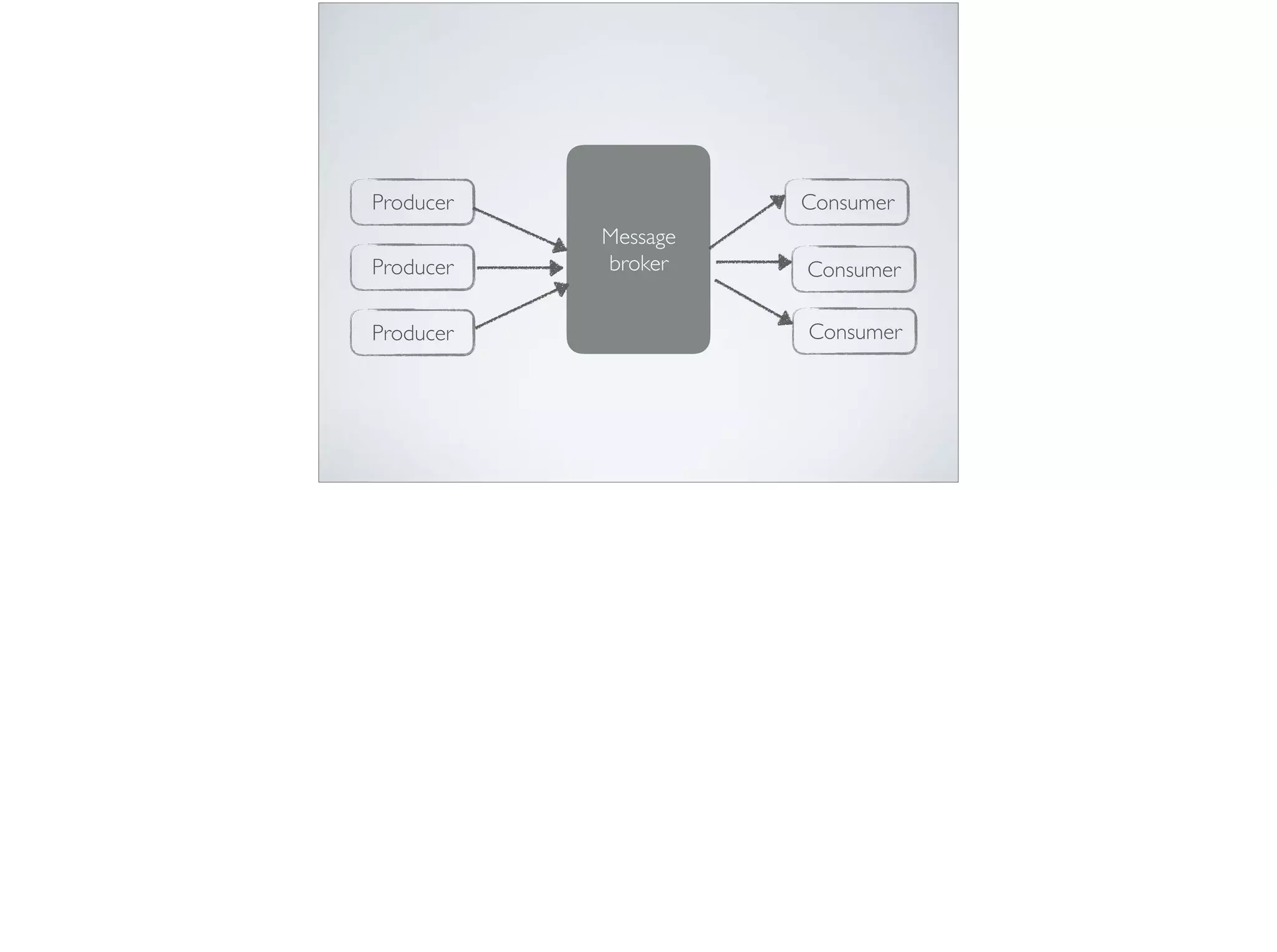
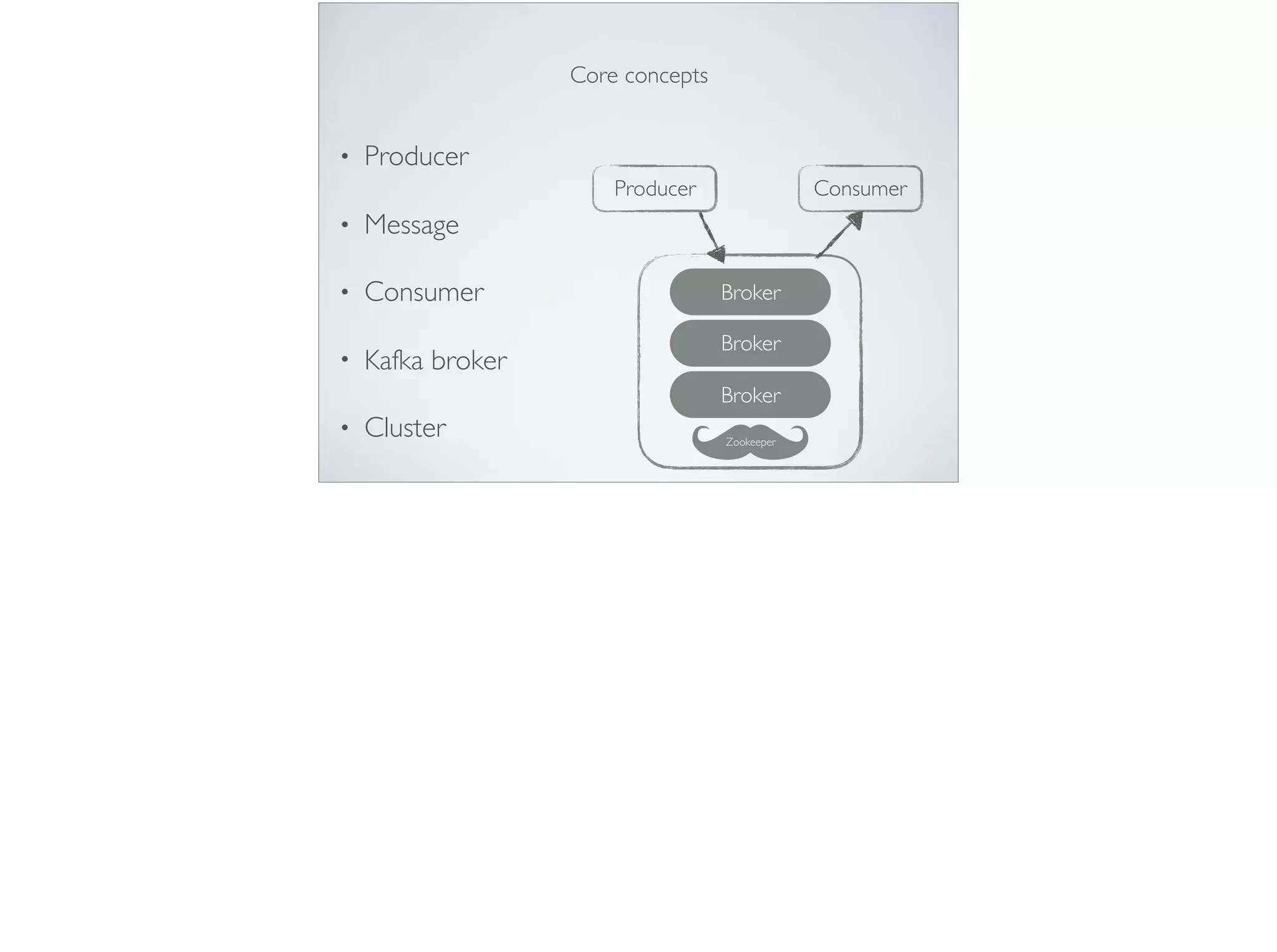
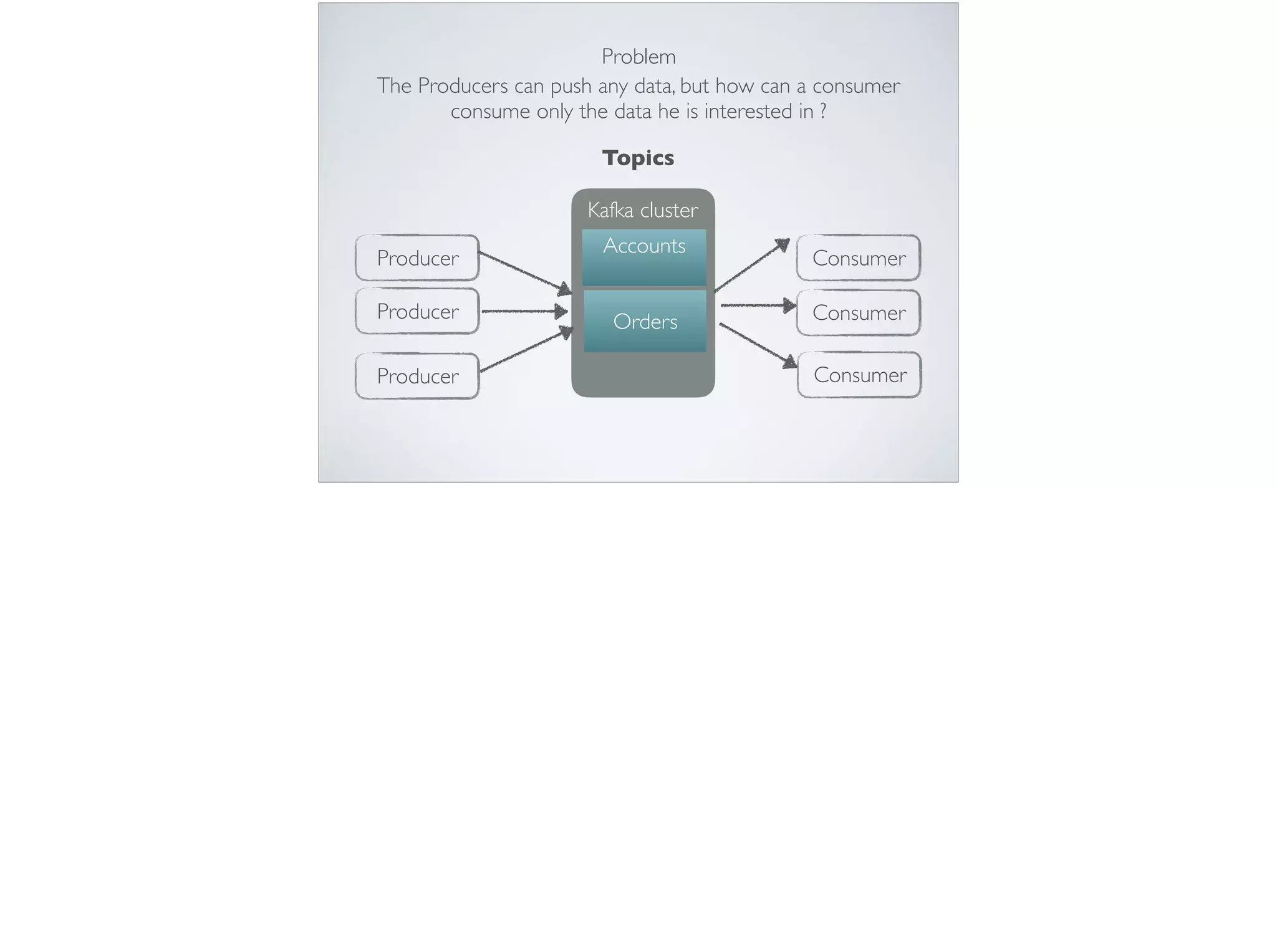
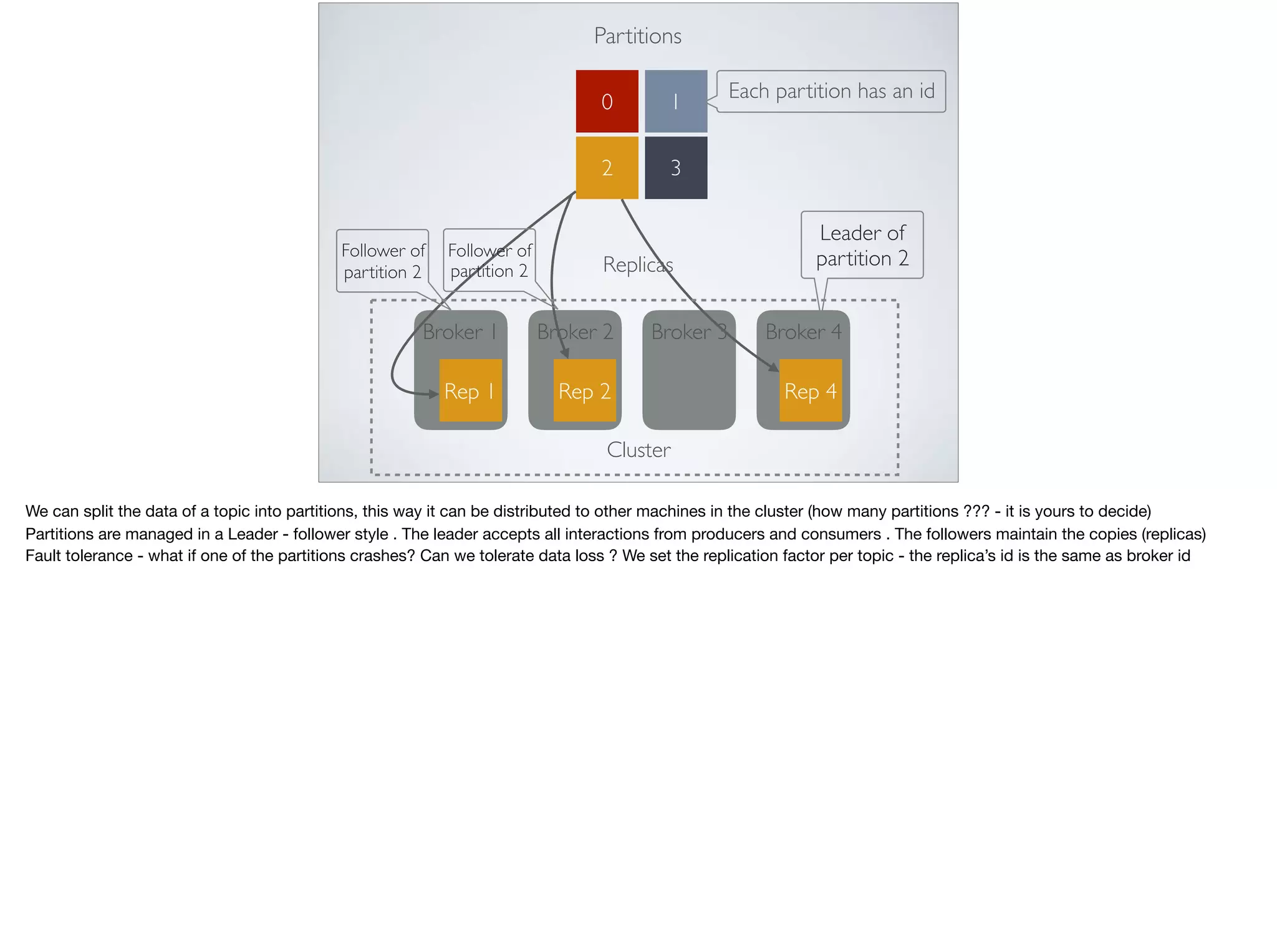
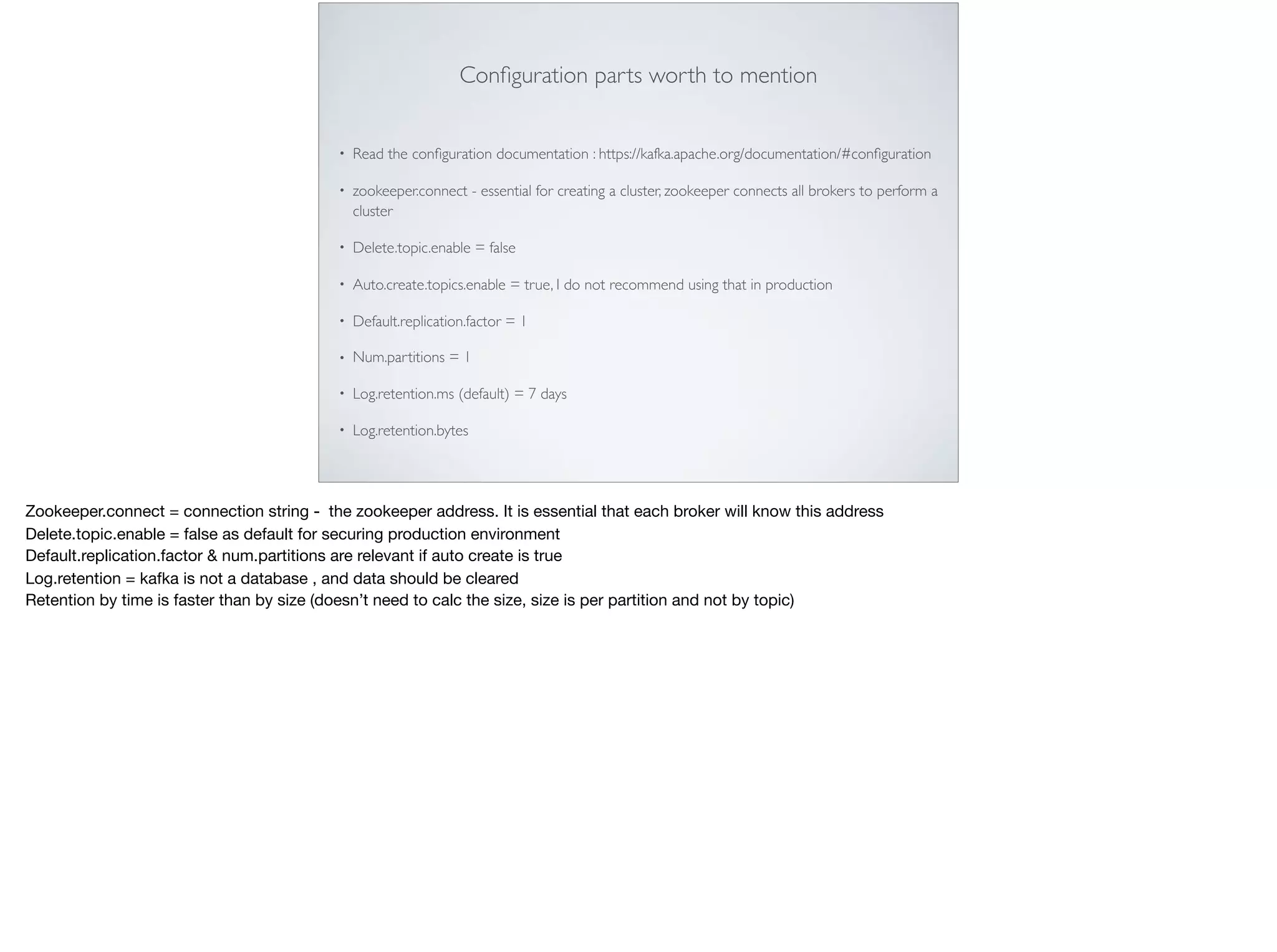
This document provides an introduction and overview of Apache Kafka. It discusses Kafka's core concepts including producers, consumers, topics, partitions and brokers. It also covers how to install and run Kafka, producer and consumer configuration settings, and how data is distributed in a Kafka cluster. Examples of creating topics, producing and consuming messages are also included.









![REPLICAS IN ACTION
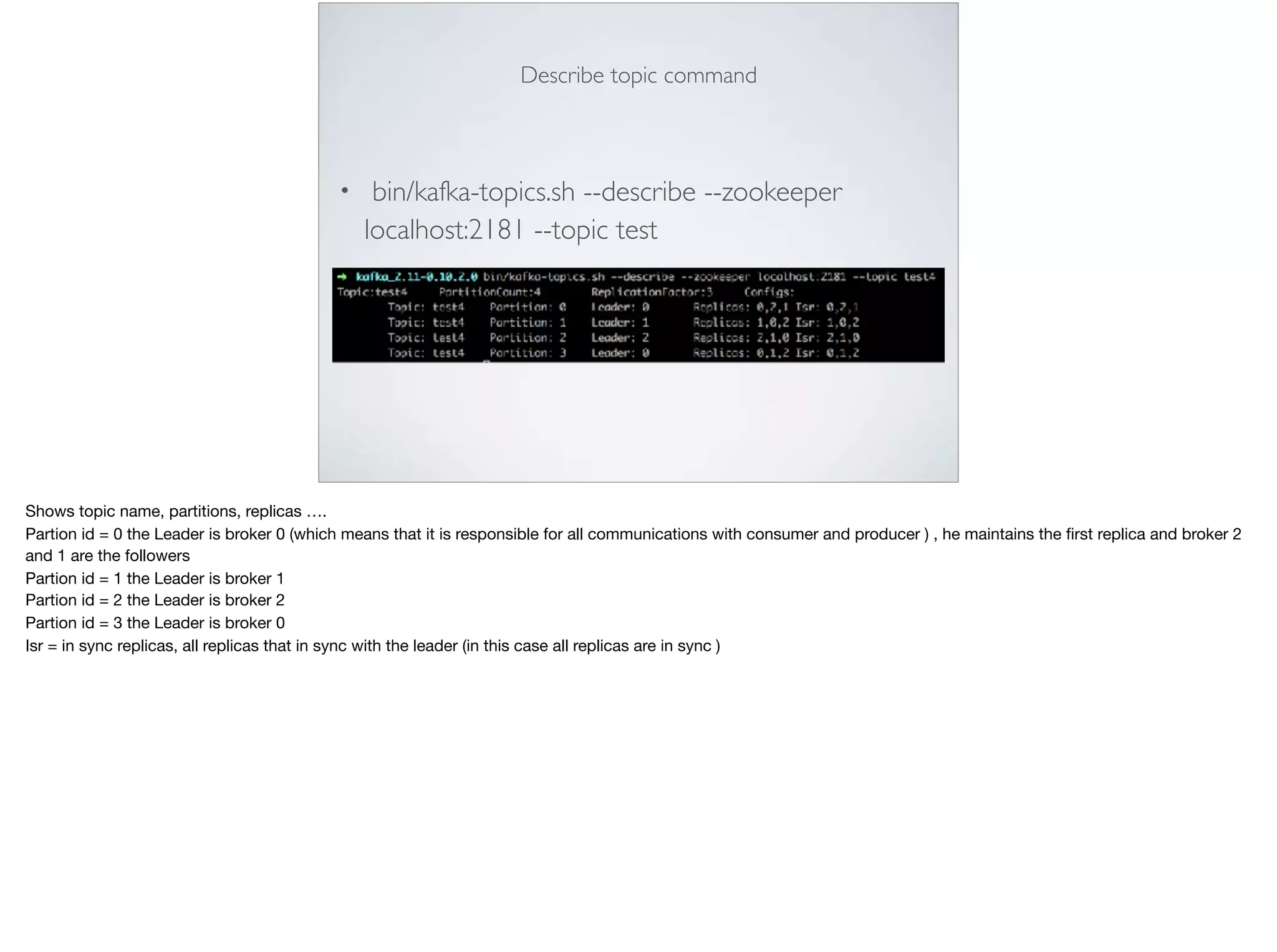
• bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 3 --
partitions 4 --topic test4 (in case we have two brokers we will get an error)
Try to create a topic with multiple replicas
Add more brokers - cp the server.properties file (* 3) to server[n].properties
Change broker_id (the default is 0)
Change broker port (just if in the same machine)
Change broker log](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kafkazerotoherocopy-171015063304-171016205802/75/Apache-Kafka-From-zero-to-hero-16-2048.jpg)




![Producer
• Properties props = new Properties() //map that must include
bootstrap.servers(list of brokers), key serializer, value serializer
• Producer< String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer(props)
• ProducerRecord<String, String> = ProducerRecord<>(topicName,
[partition num], [timestamp], [key], value)
• producer.send(record) //.get or producer.send(record, callback)
• producer.close() // after sending all we need to free resources
• * max.in.flight.requests.per.connection = 5 (for async calls - how
many requests are sent without response)
* Producer<key type, value type>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kafkazerotoherocopy-171015063304-171016205802/75/Apache-Kafka-From-zero-to-hero-23-2048.jpg)