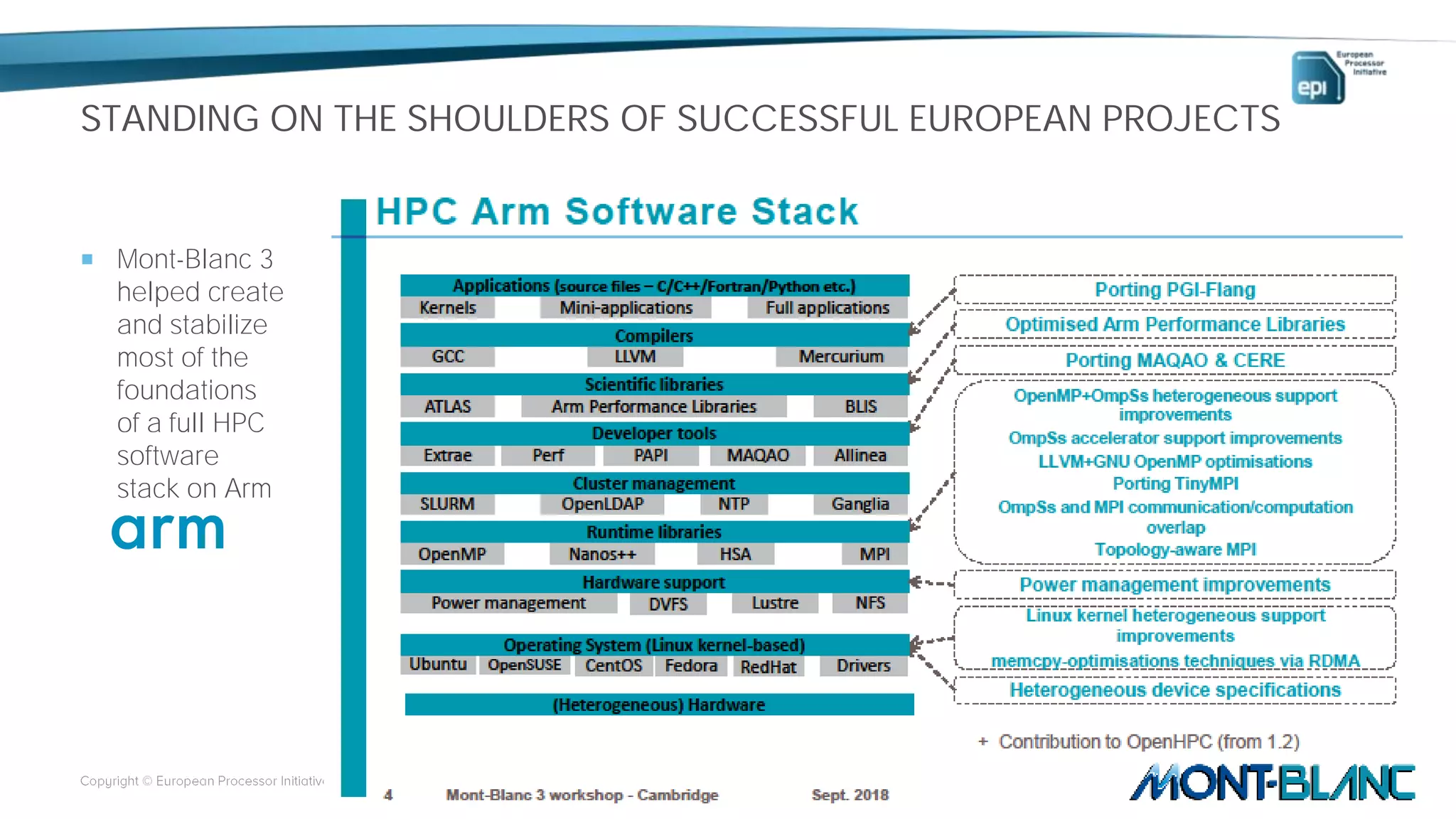
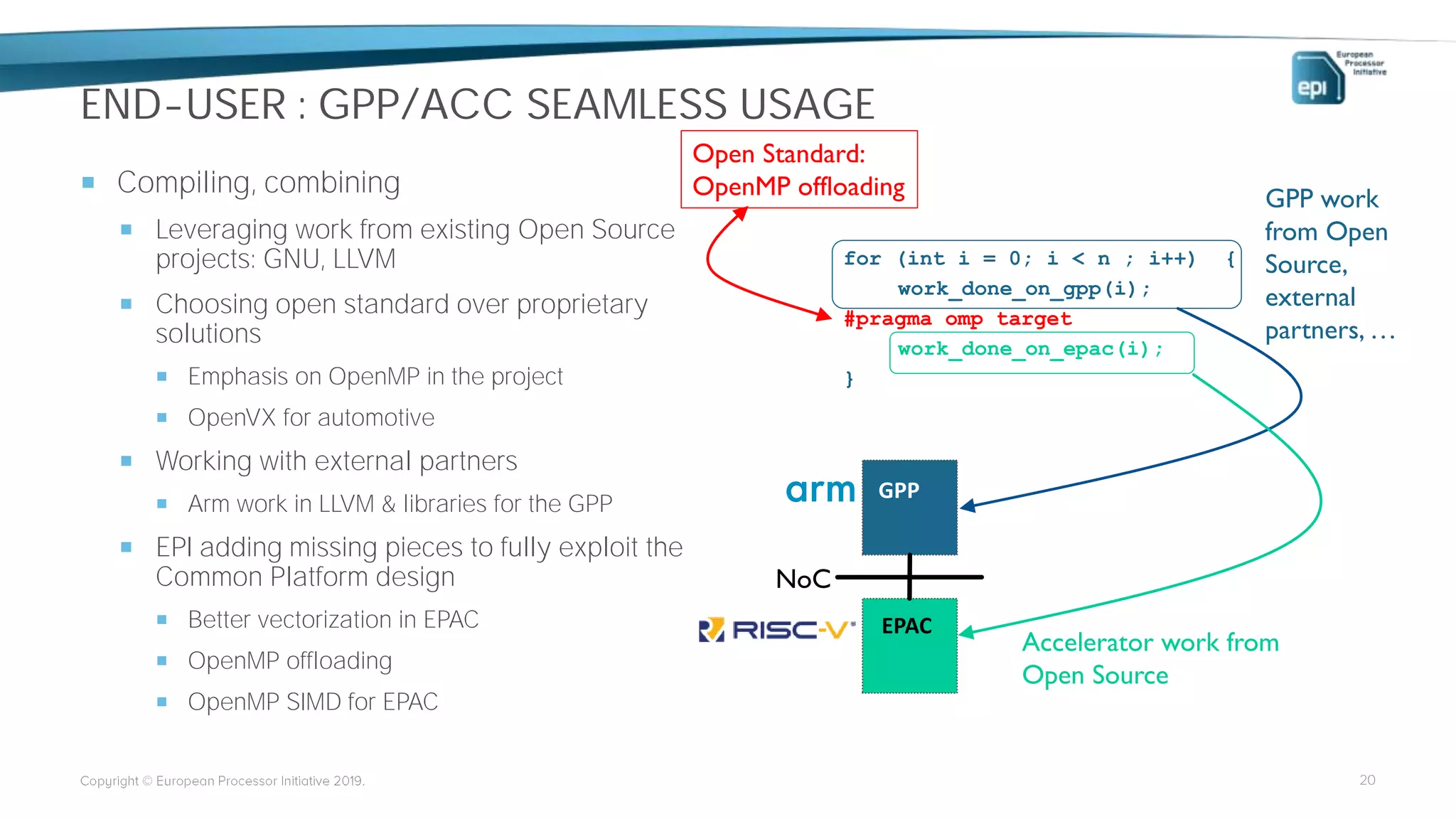
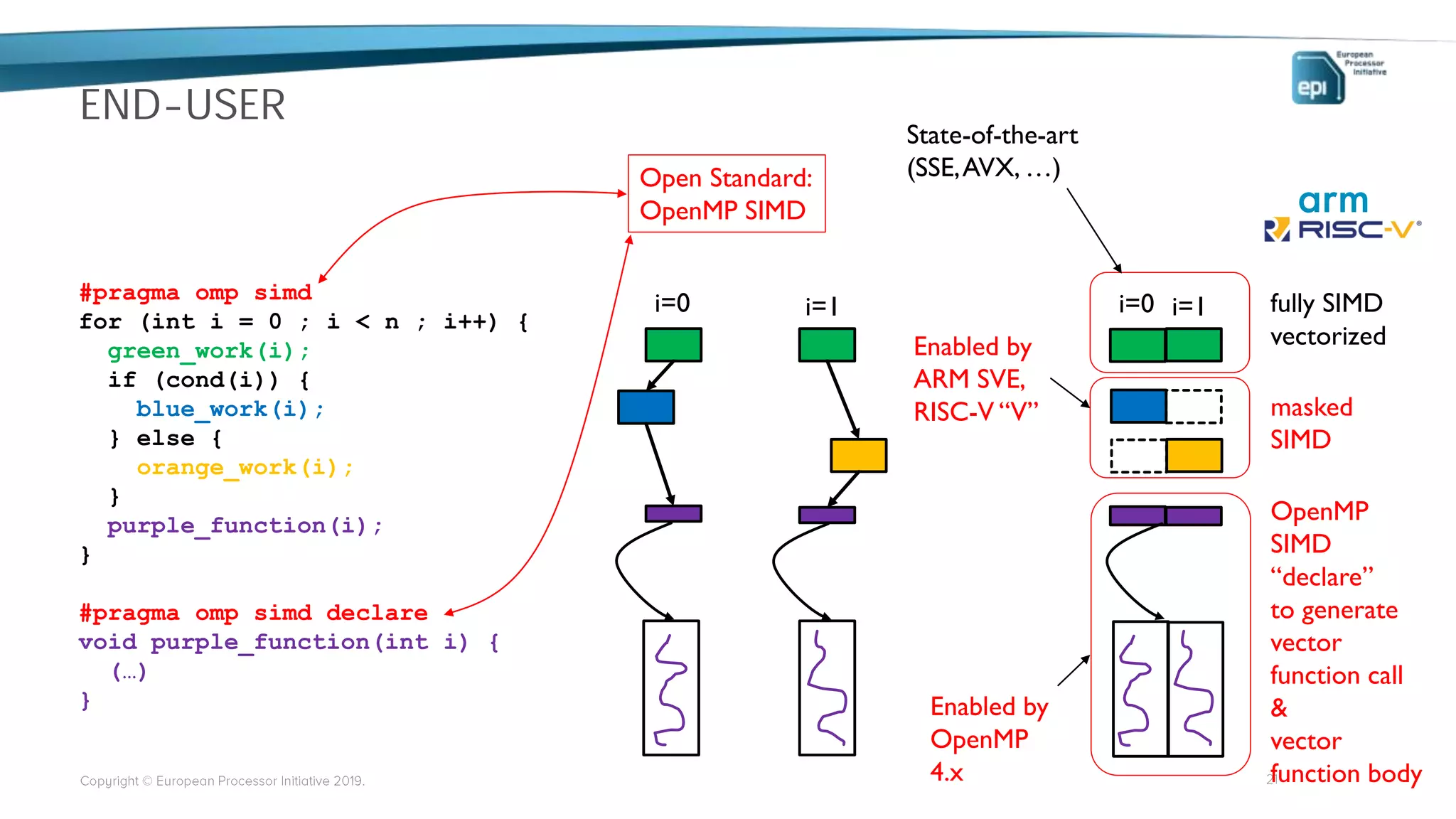
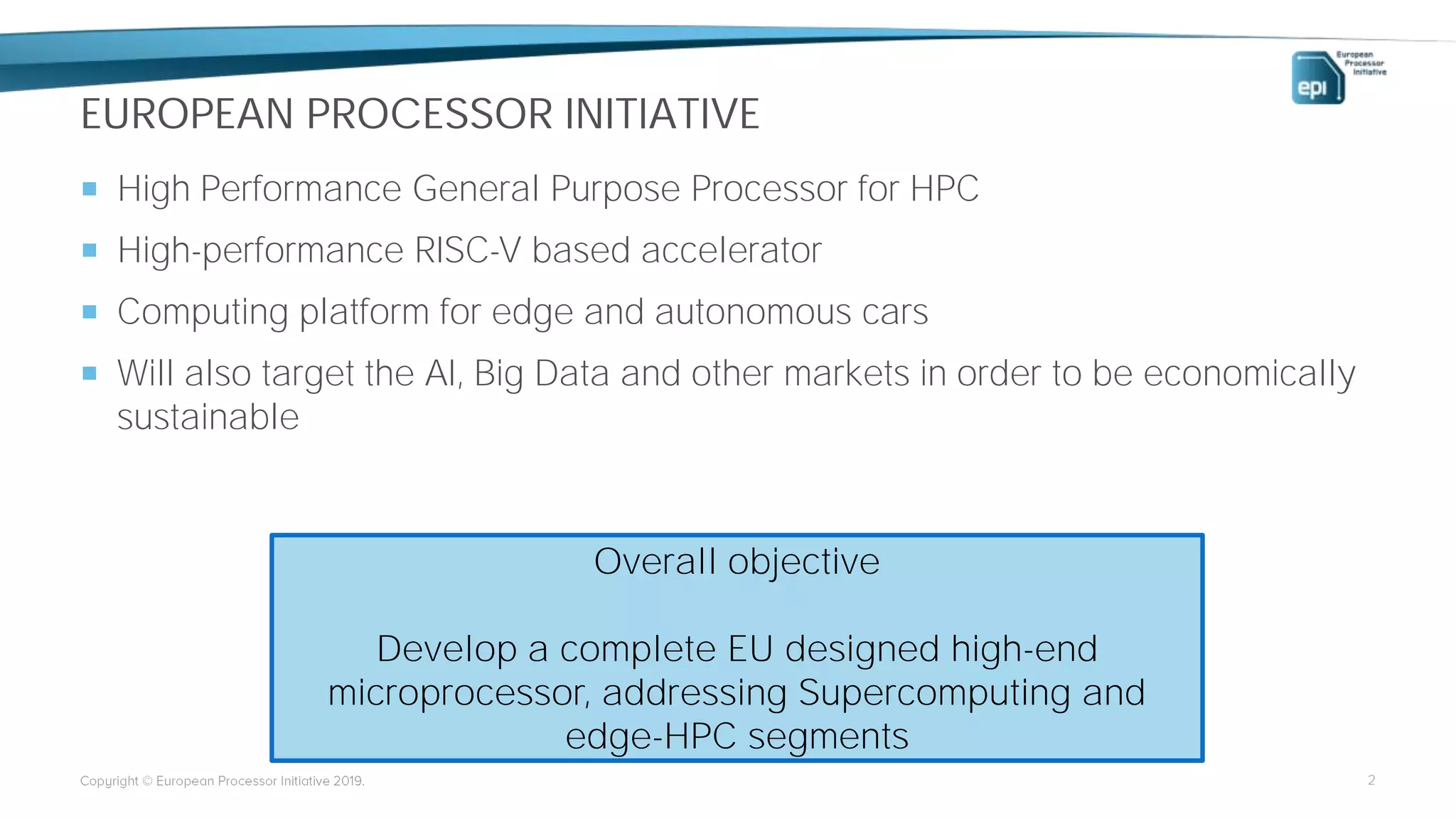
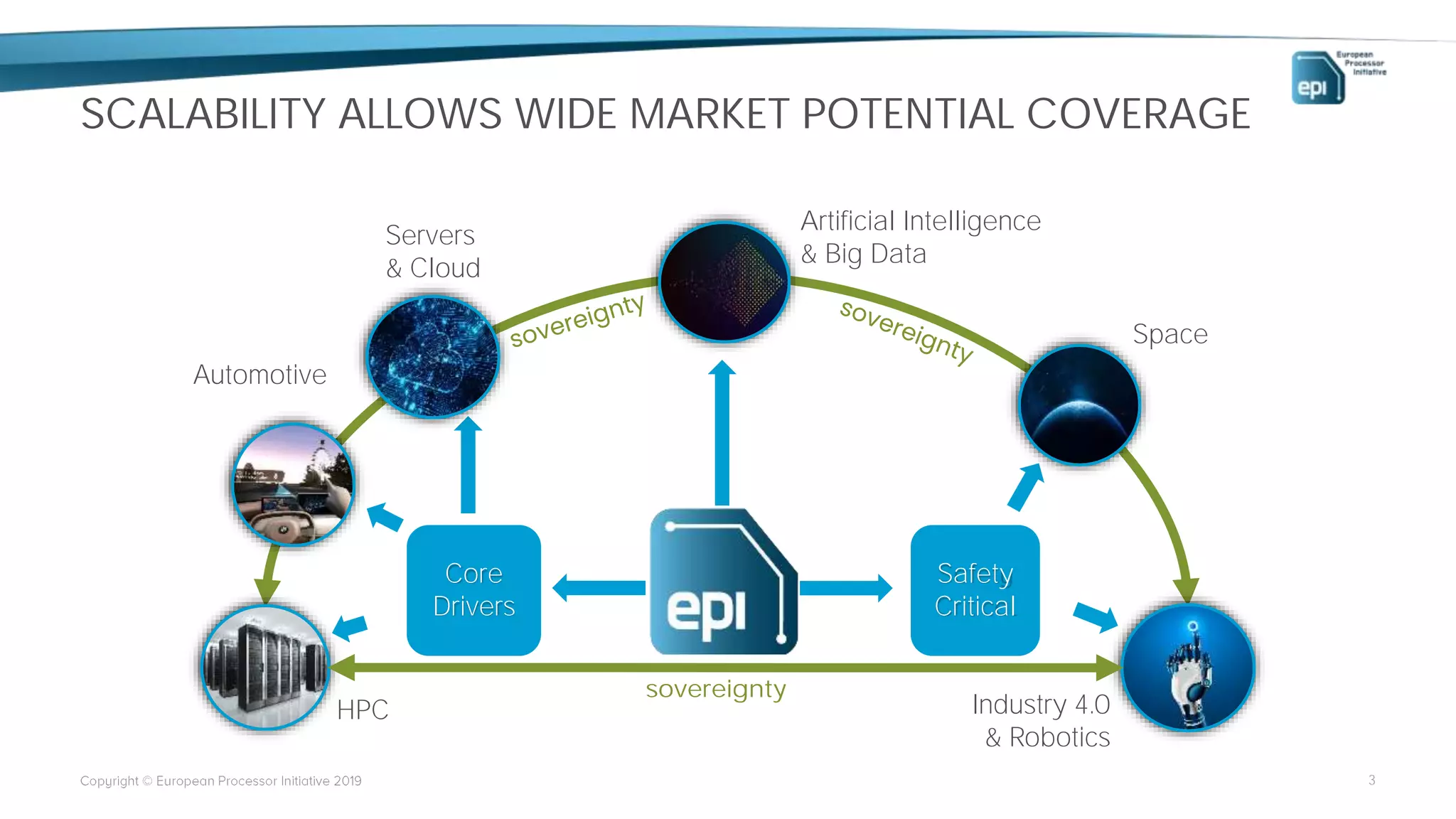
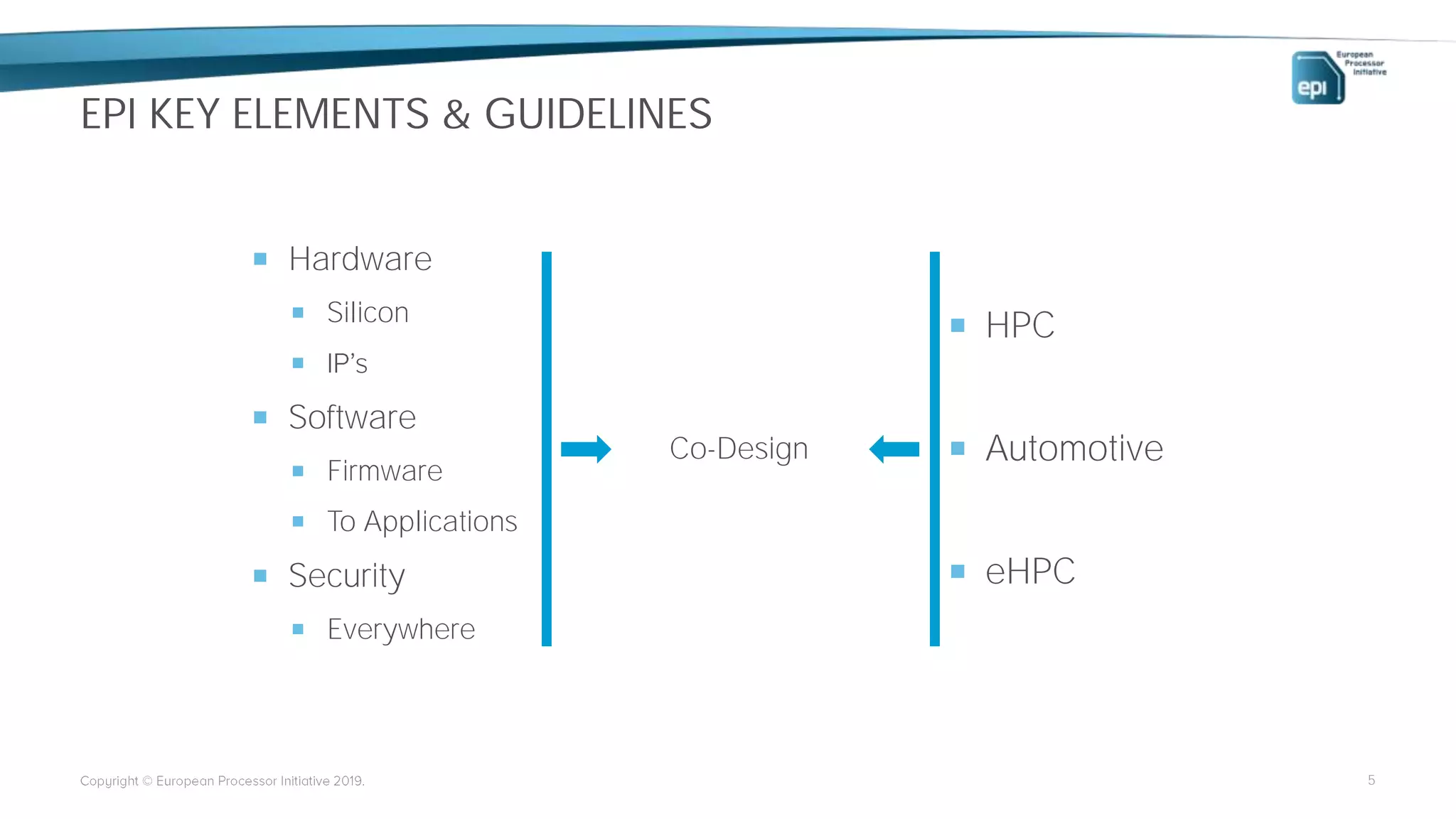
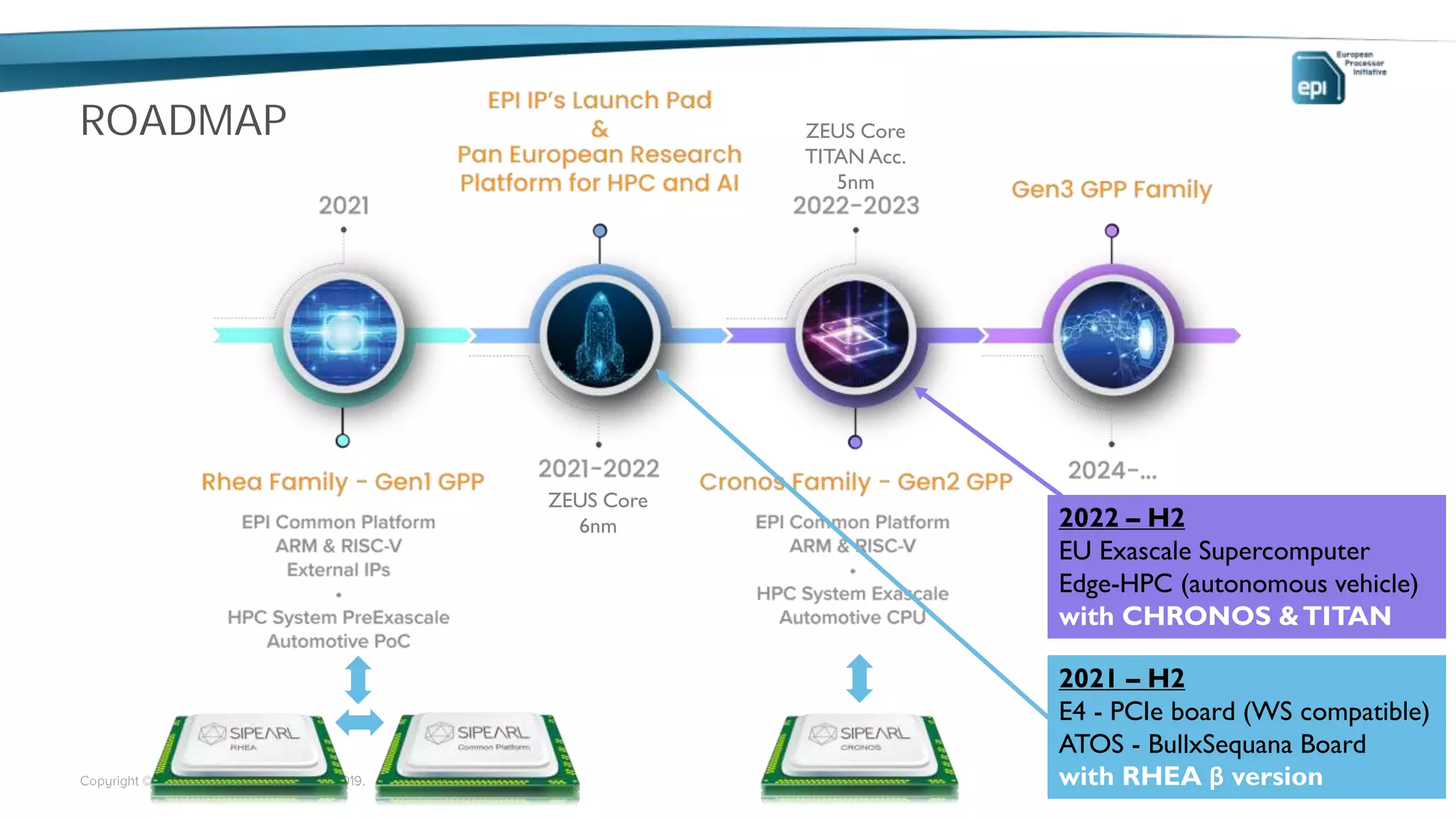
The European Processor Initiative aims to develop a high-end microprocessor for supercomputing and edge-HPC through a collaborative framework agreement under the Horizon 2020 program. This initiative seeks to enhance Europe's technological sovereignty while targeting diverse markets, including AI, big data, and automotive industries. Key elements include co-design of hardware and software, a comprehensive roadmap for technology development, and an emphasis on open standards to ensure a robust ecosystem.




![ARM WW HPC
-06-26 15
CPU & server
manufacturer,
upcoming
“Fugaku”
system
CPU
manufacturer,
2 server
manufacturers,
“Astra” system at
Sandia,
upcoming system
at Stony Brook
CPU & server
manufacturer
[geopolitical
issues regarding
the license]
Upcoming CPU
manufacturer,
Server manufacturer,
system at CEA, UK,
MontBlanc, EPI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/epiupdatehpcuserforum2019-09-010-190925194452/75/An-Update-on-the-European-Processor-Initiative-14-2048.jpg)