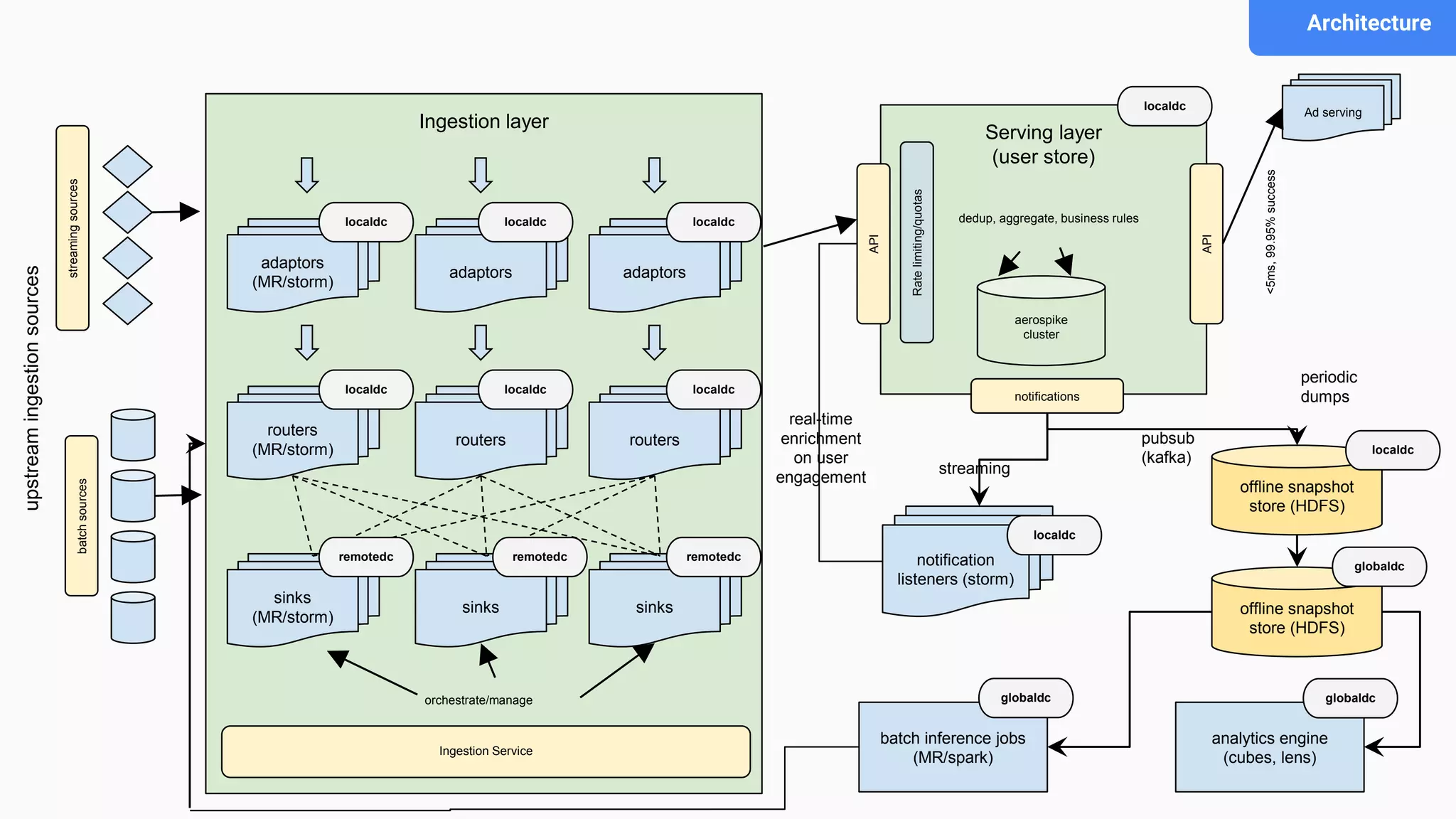
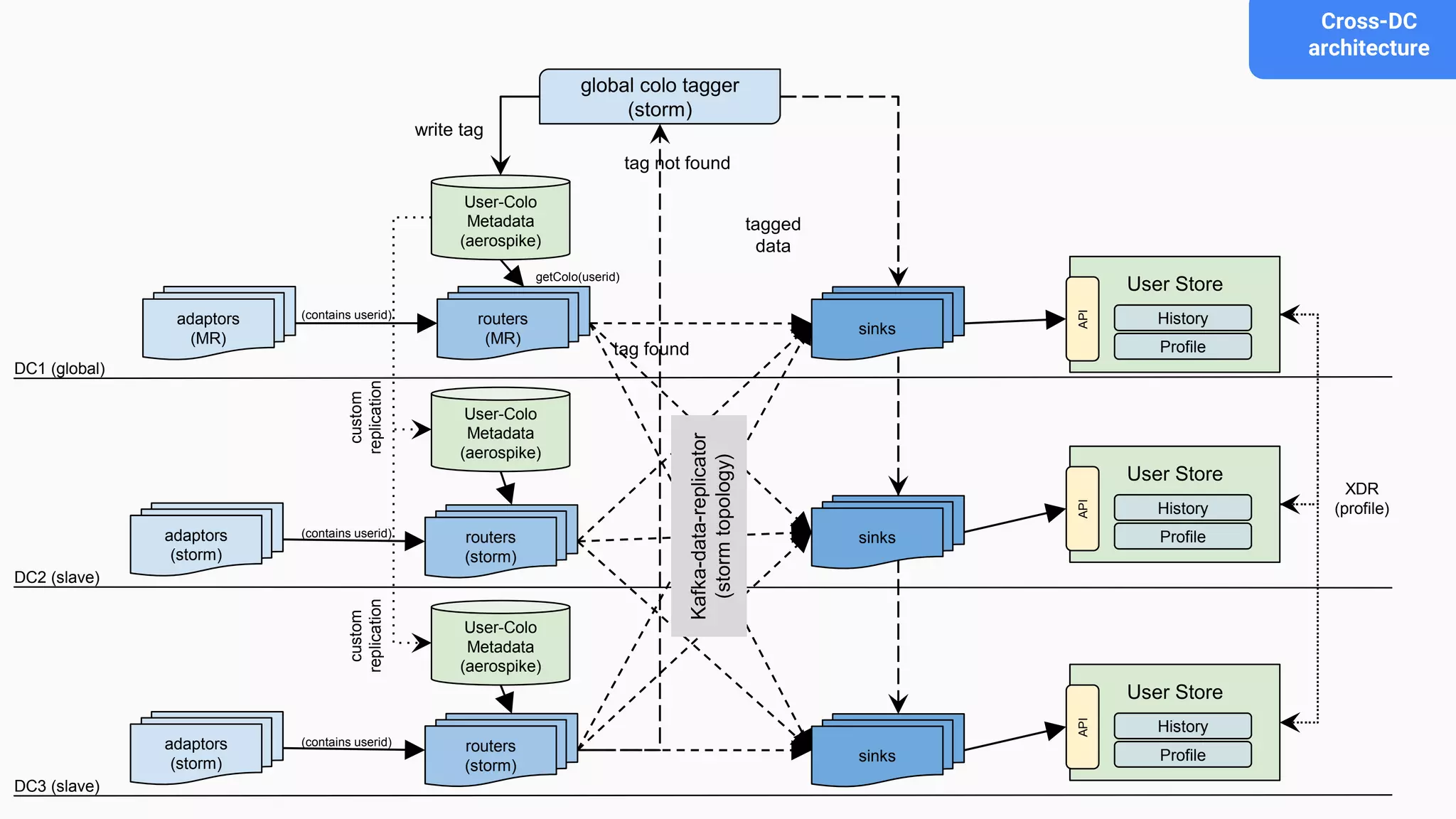
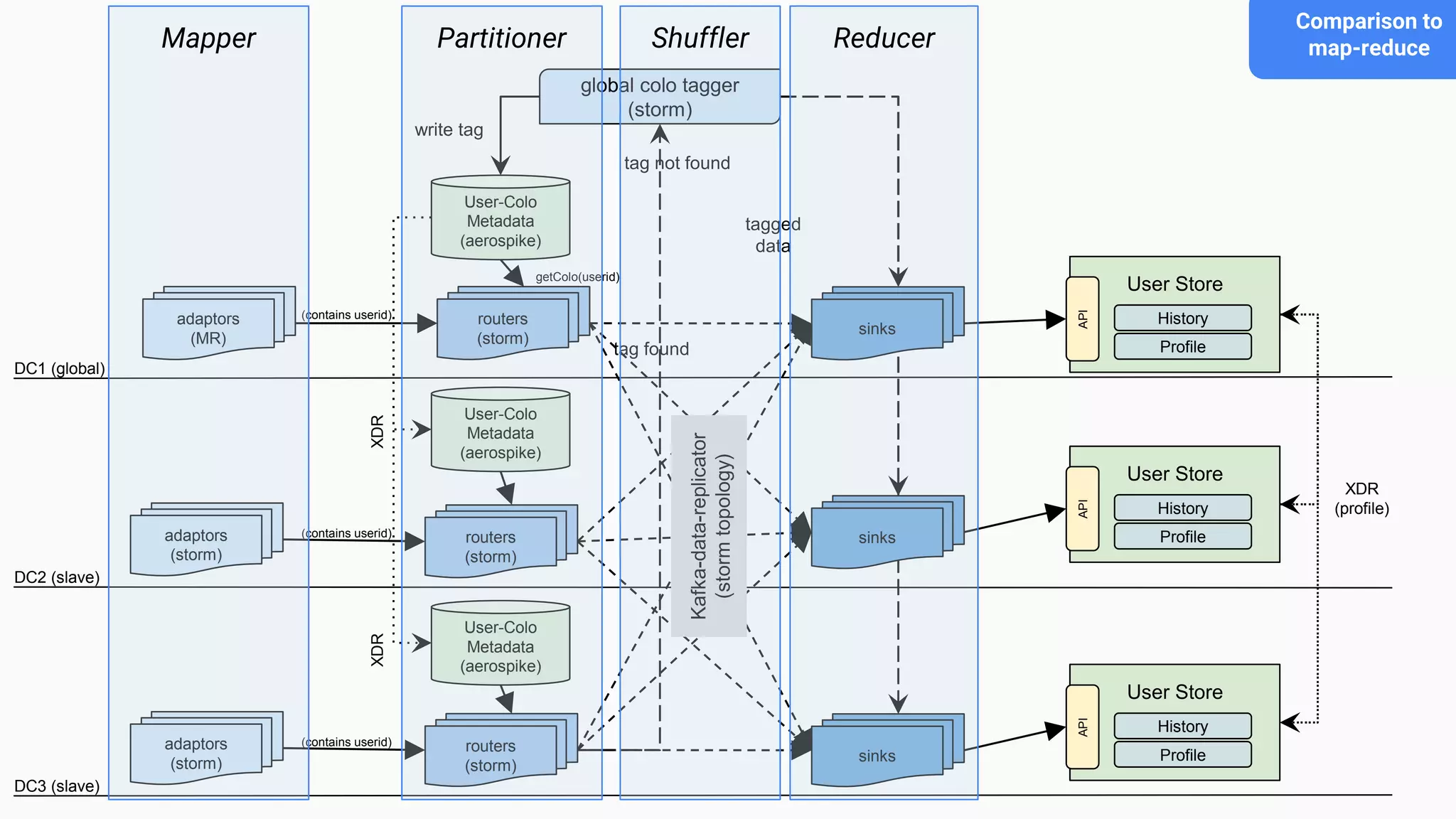
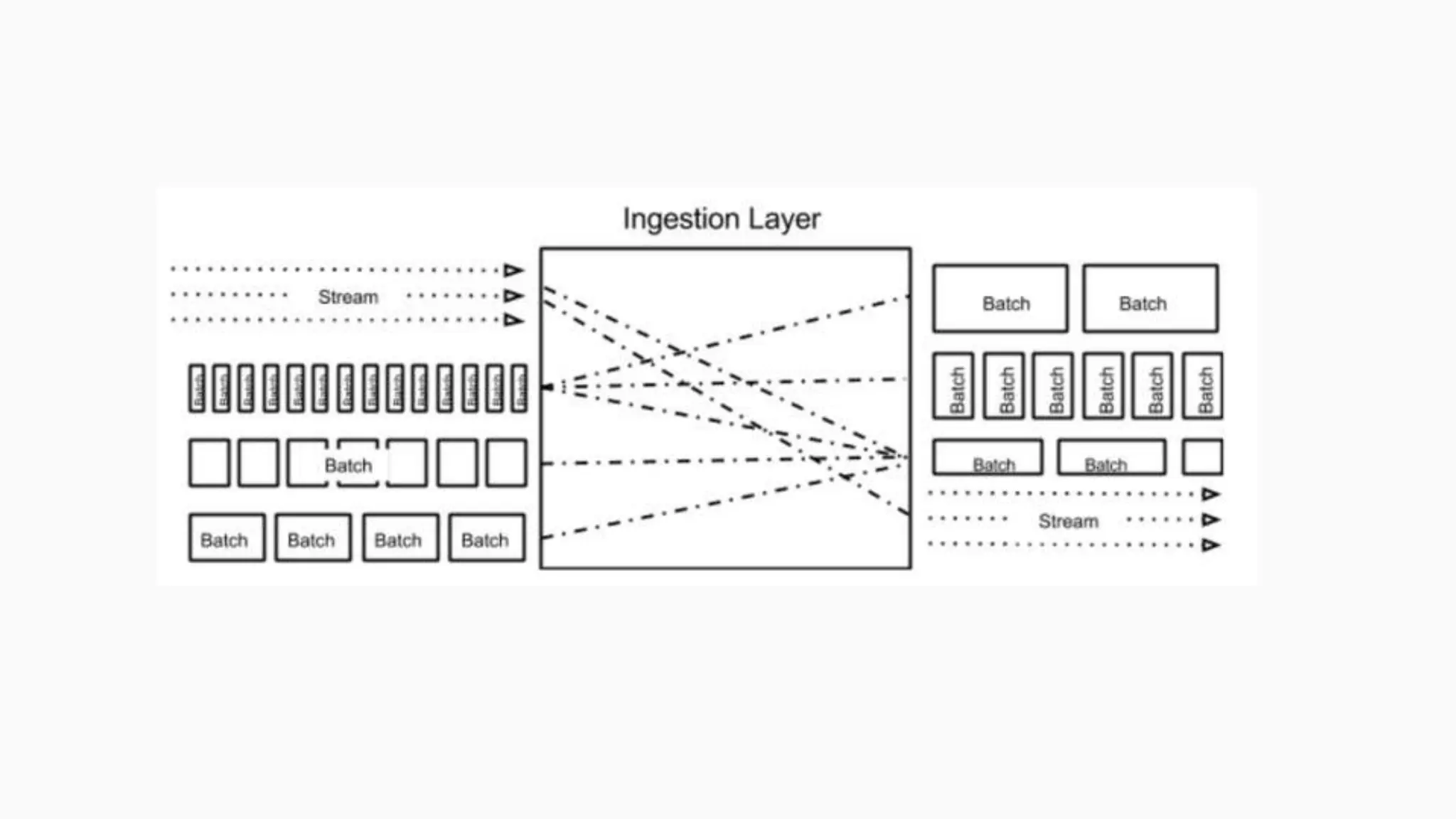
This document discusses an adaptive and self-healing framework for real-time data ingestion across geographically distributed data centers. It describes the problem domain of ingesting 15 billion events per day across multiple schemas and data types from various sources. The proposed architecture includes an ingestion layer using technologies like Storm, Kafka and HDFS to ingest, transform and replicate streaming and batch data. It also includes a serving layer using Aerospike to provide low-latency aggregated user views. Issues encountered with technologies like Storm and Kafka are discussed, as well as features still under development.