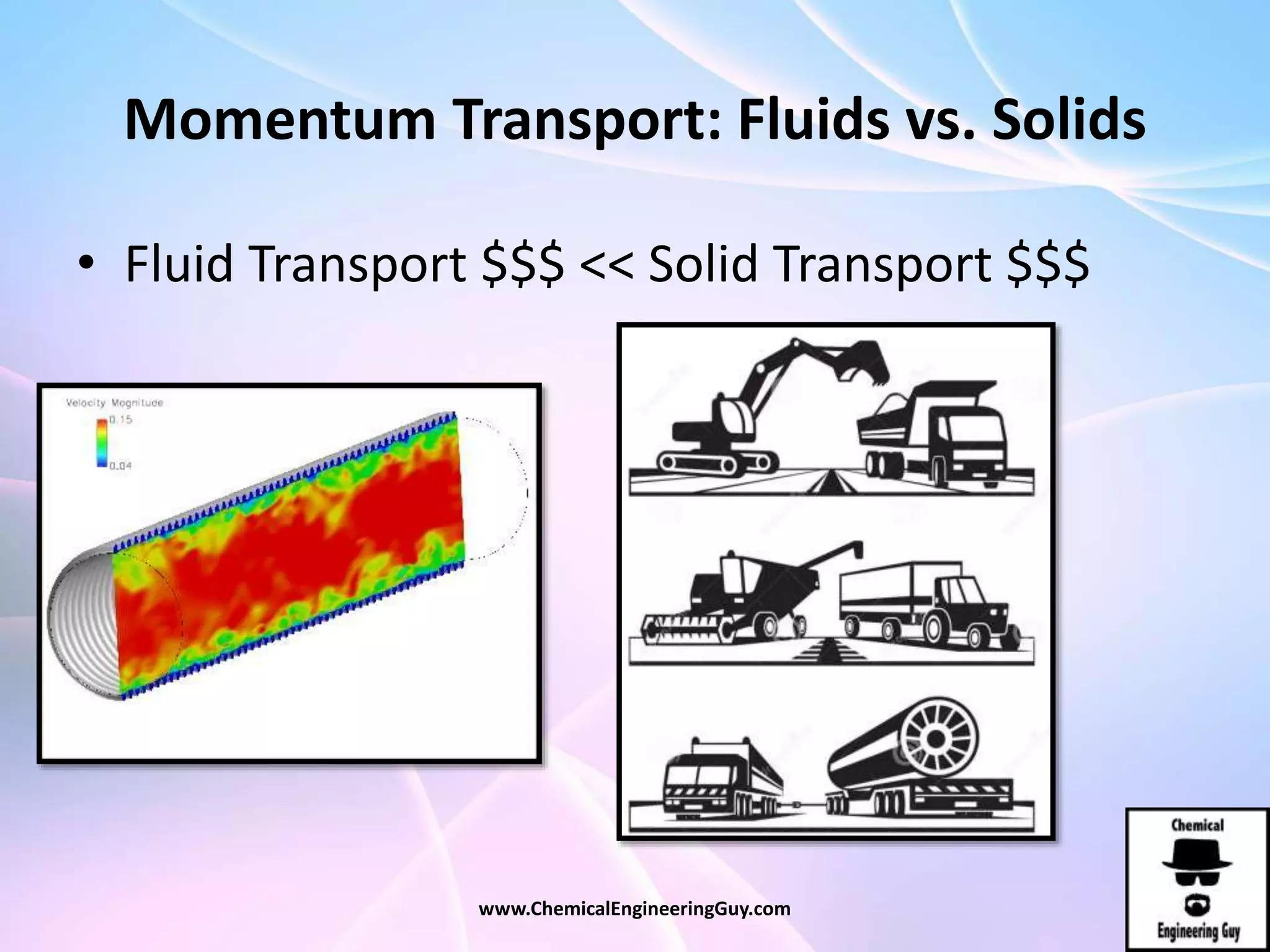
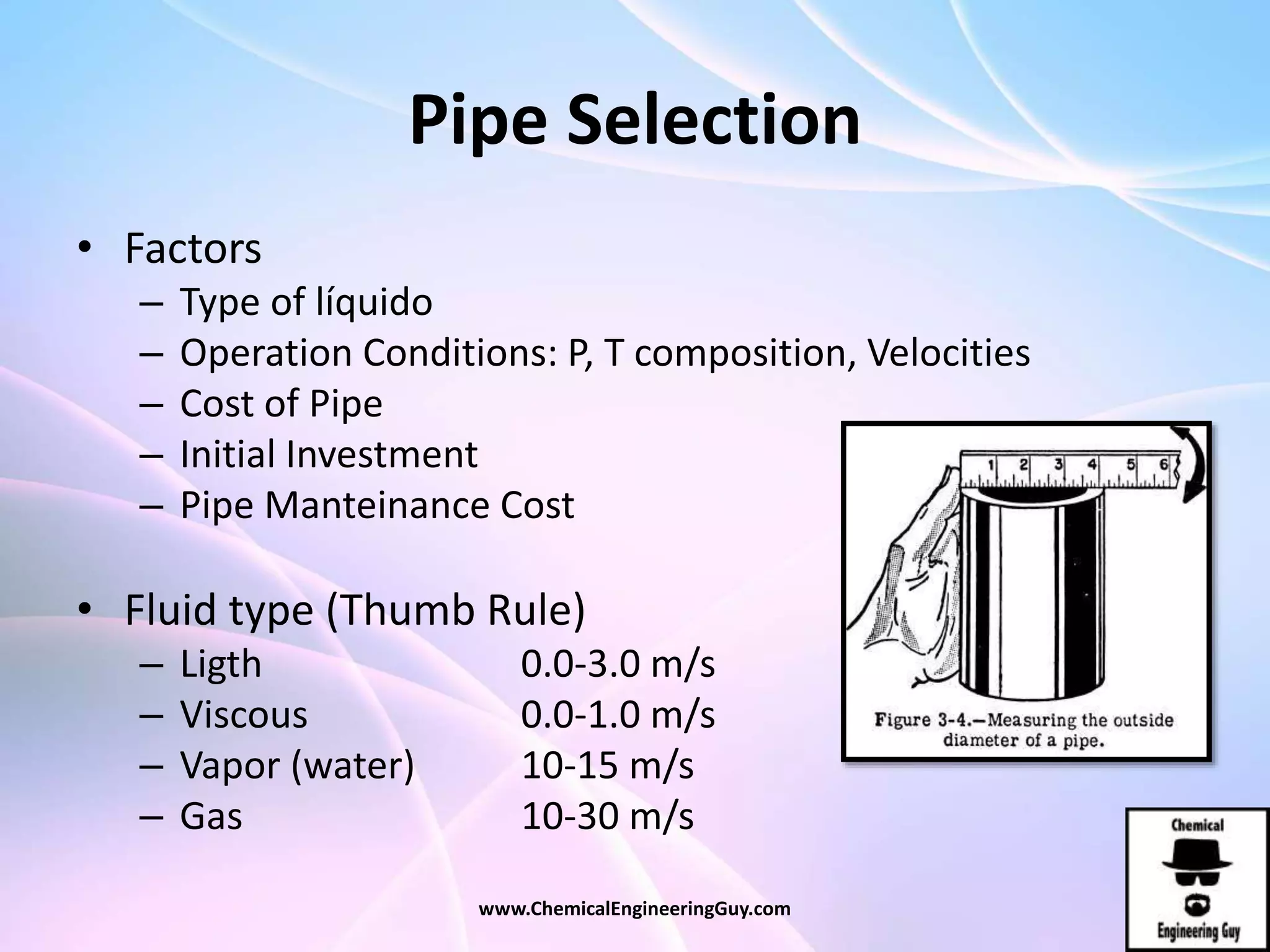
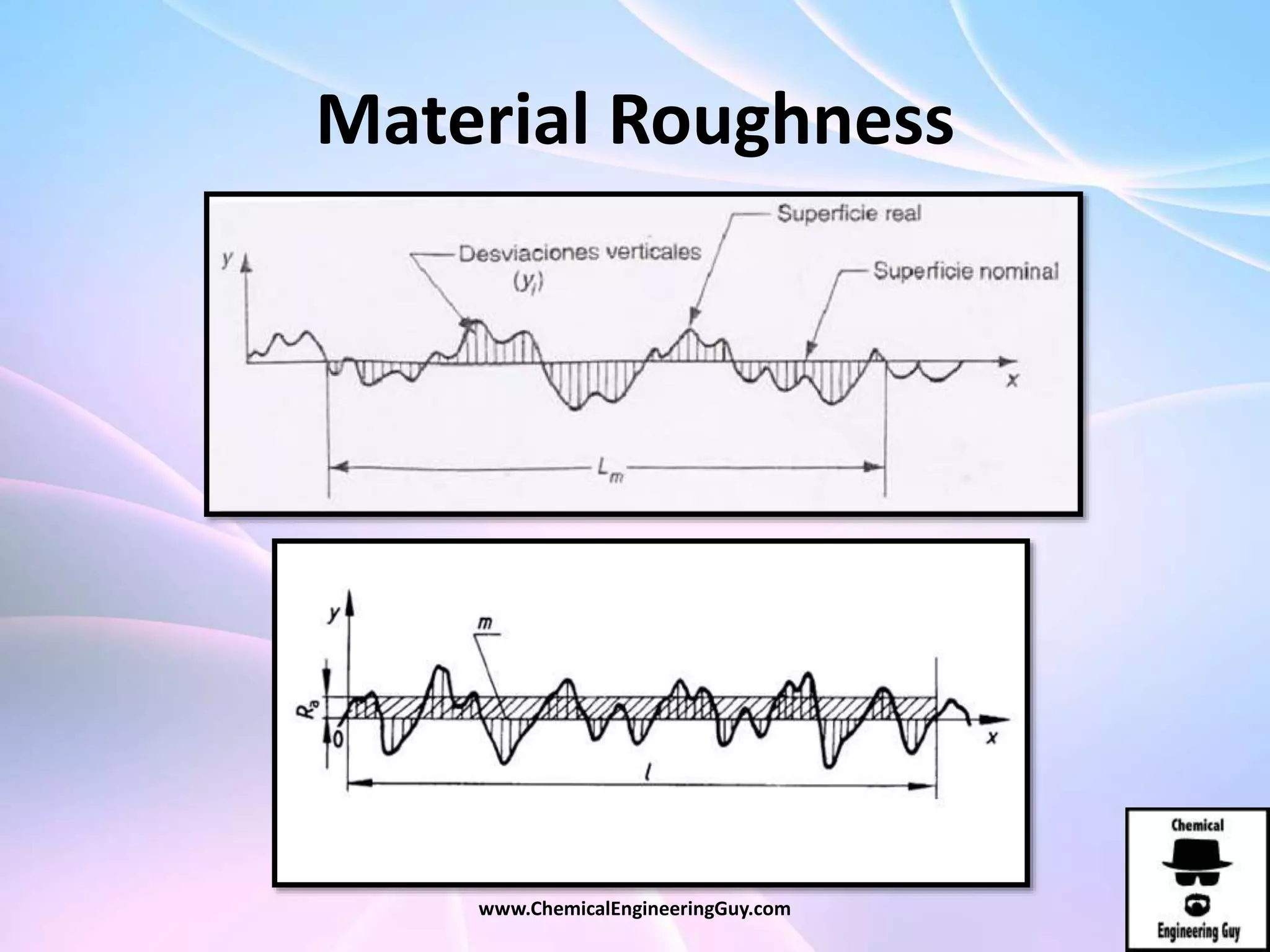
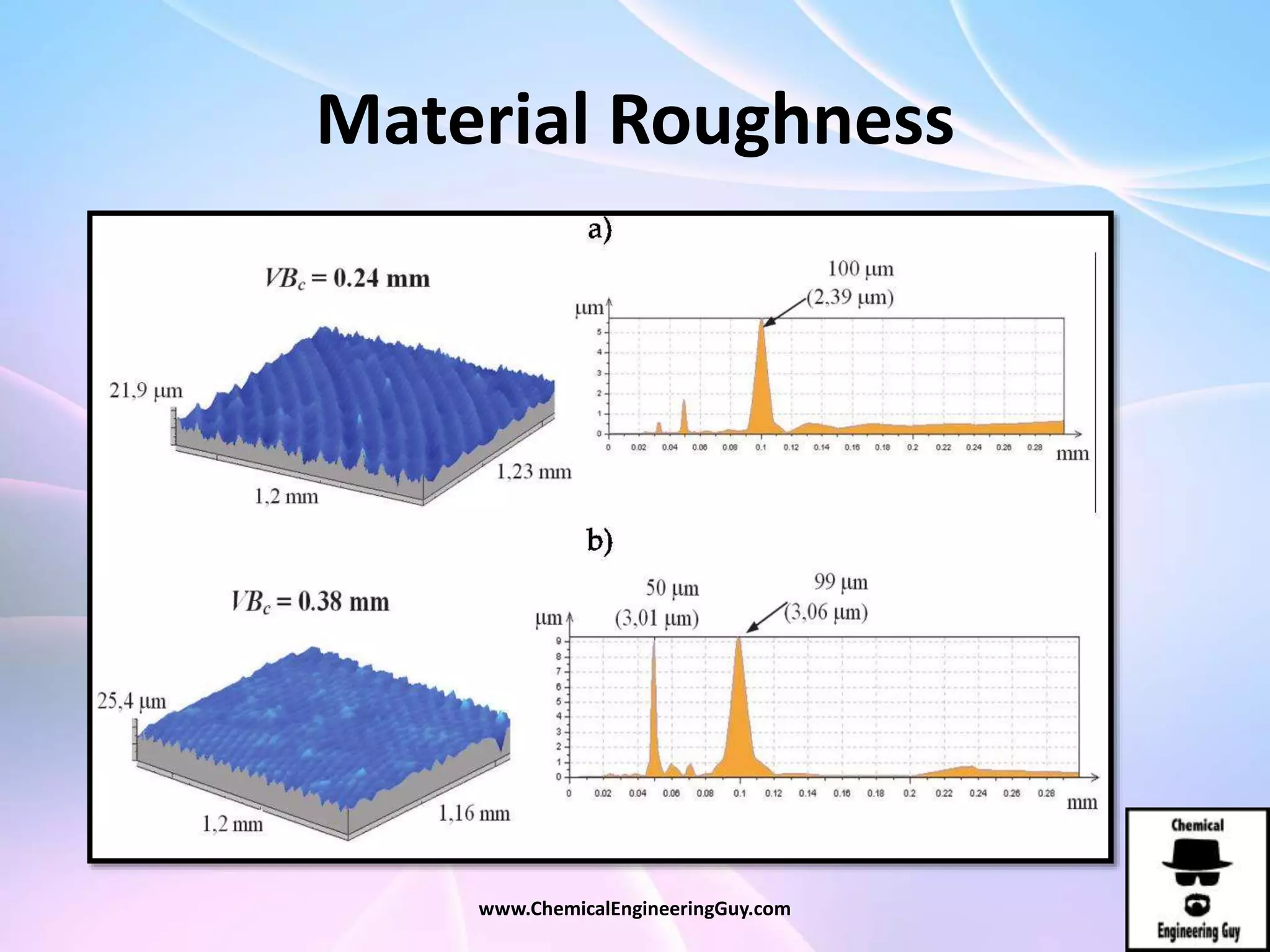
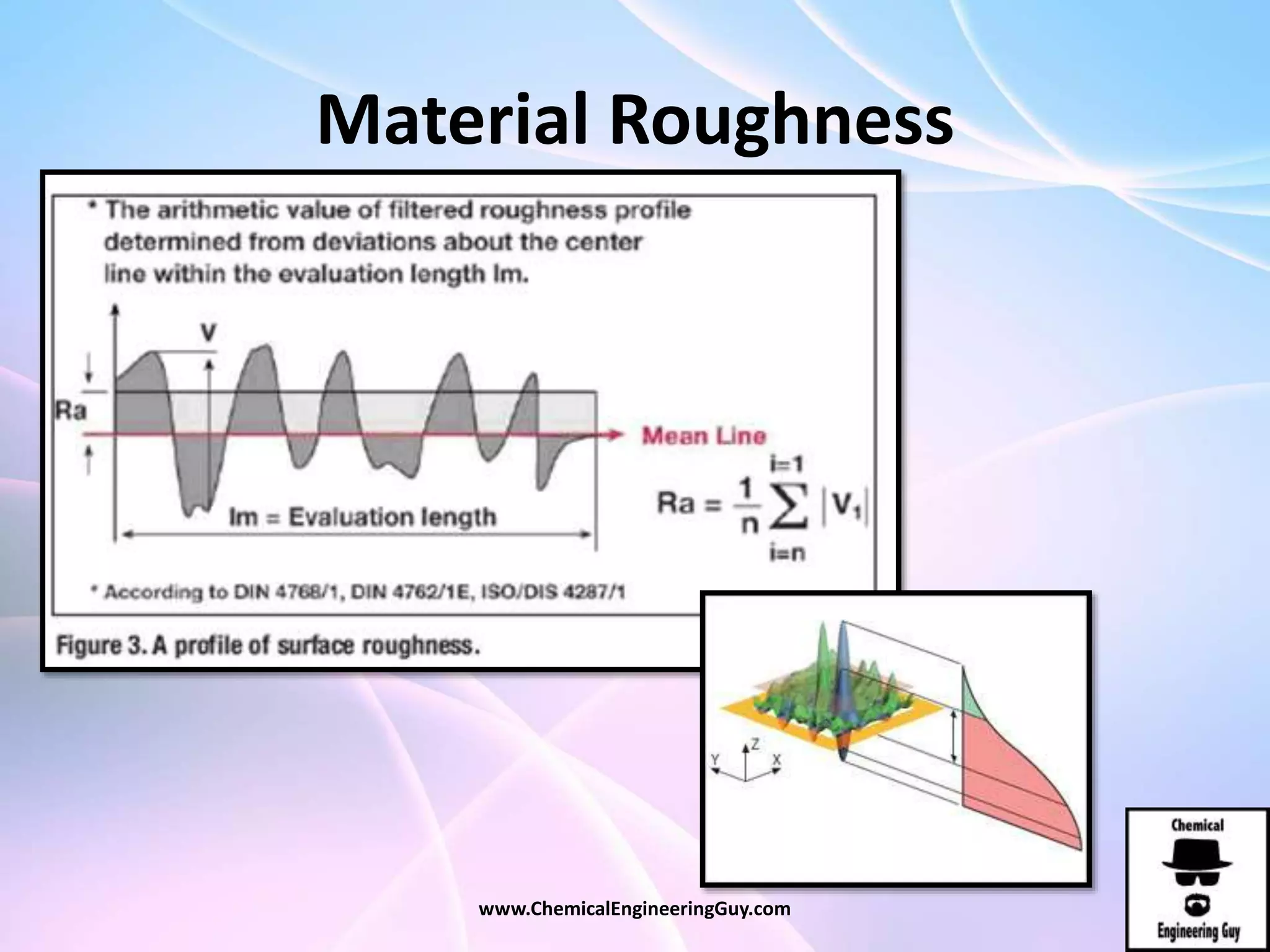
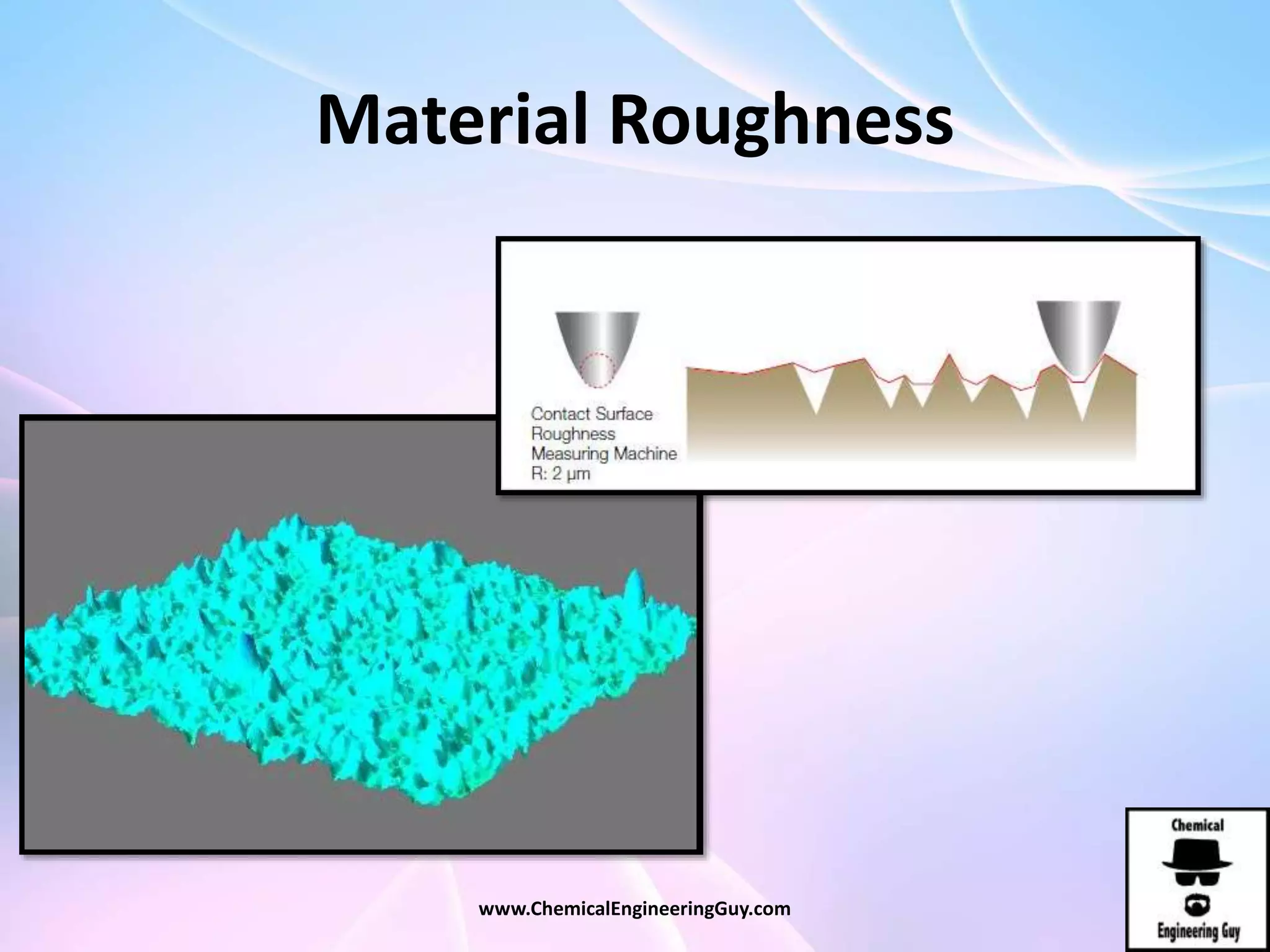
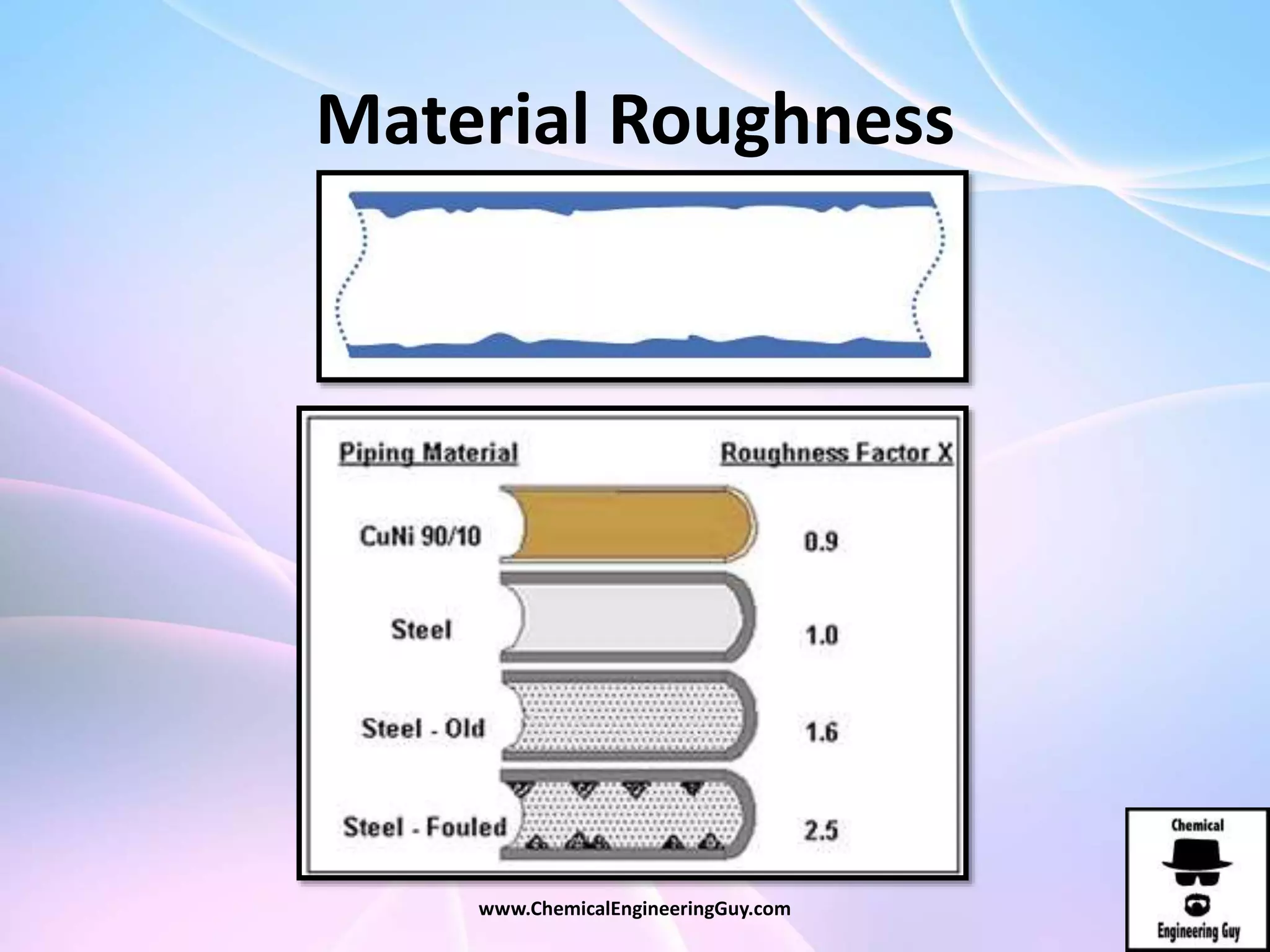
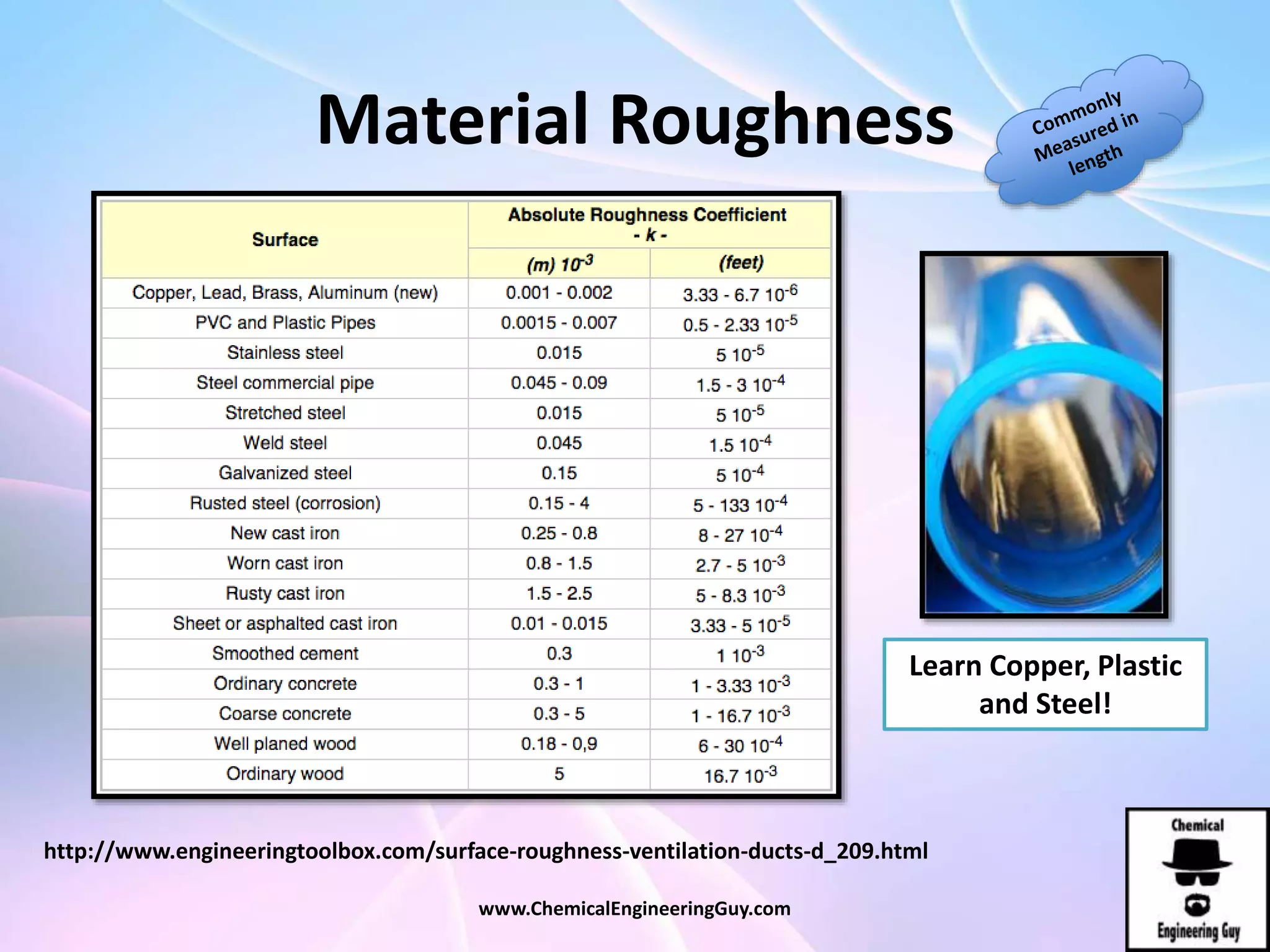
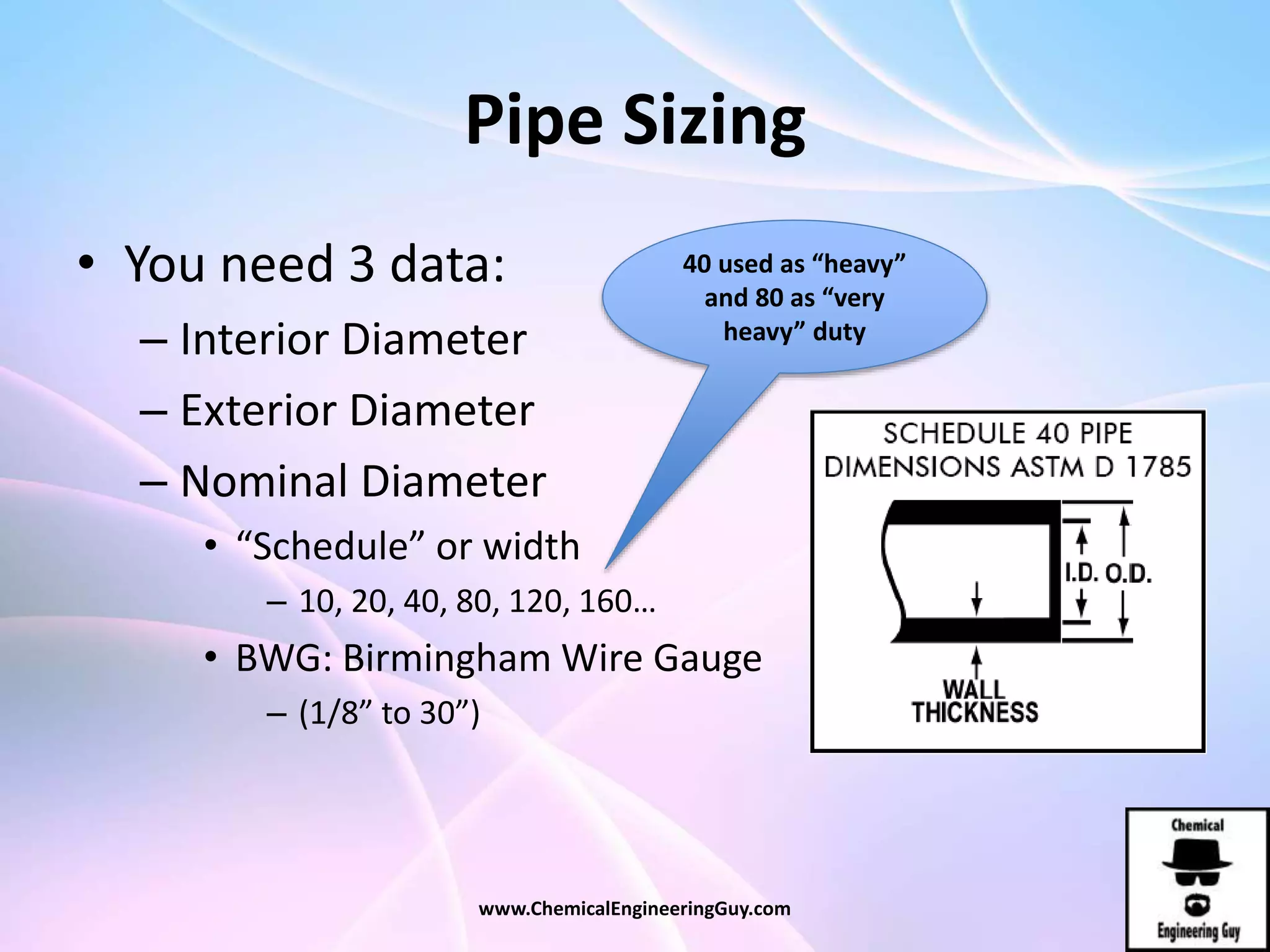
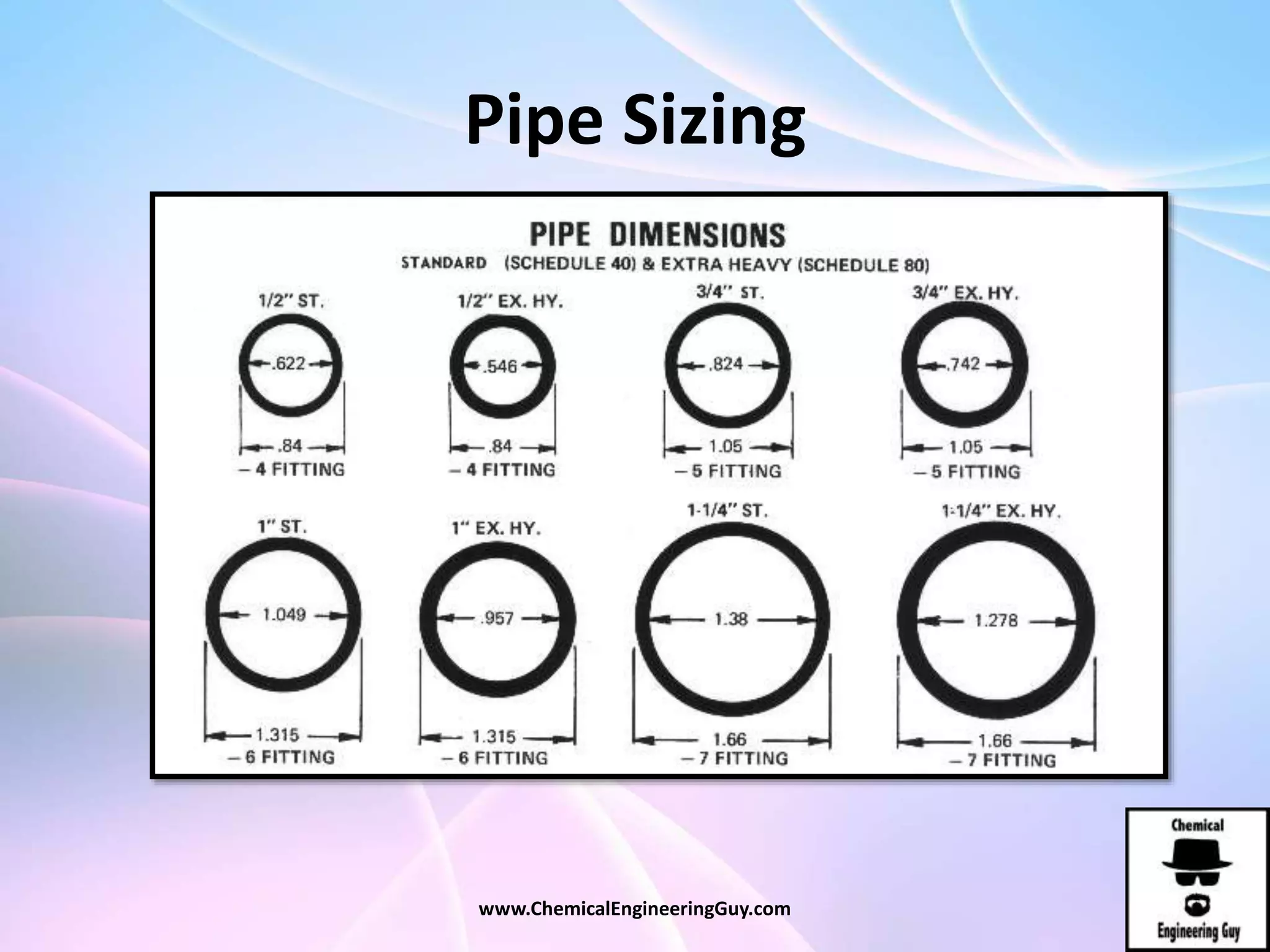
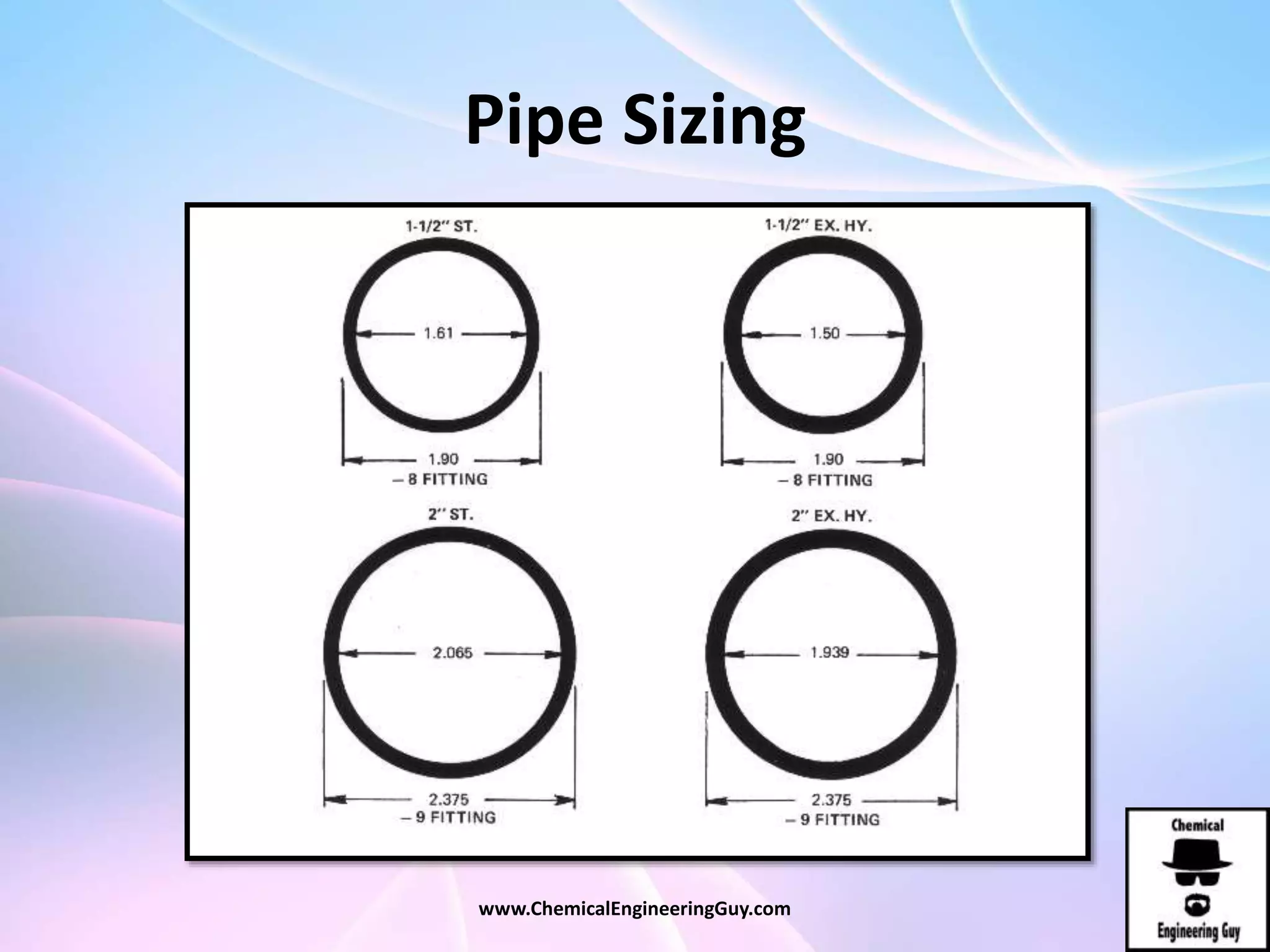
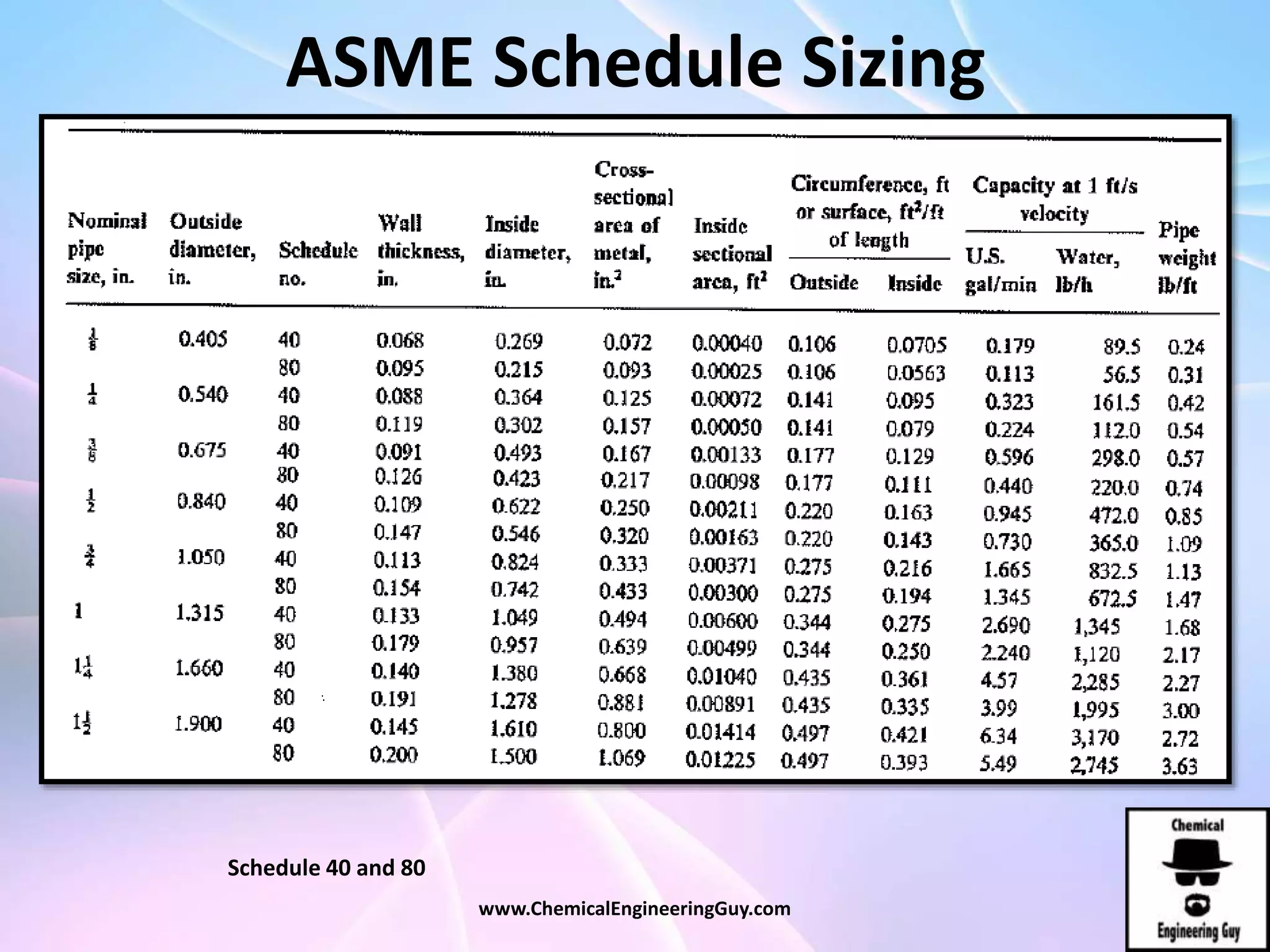
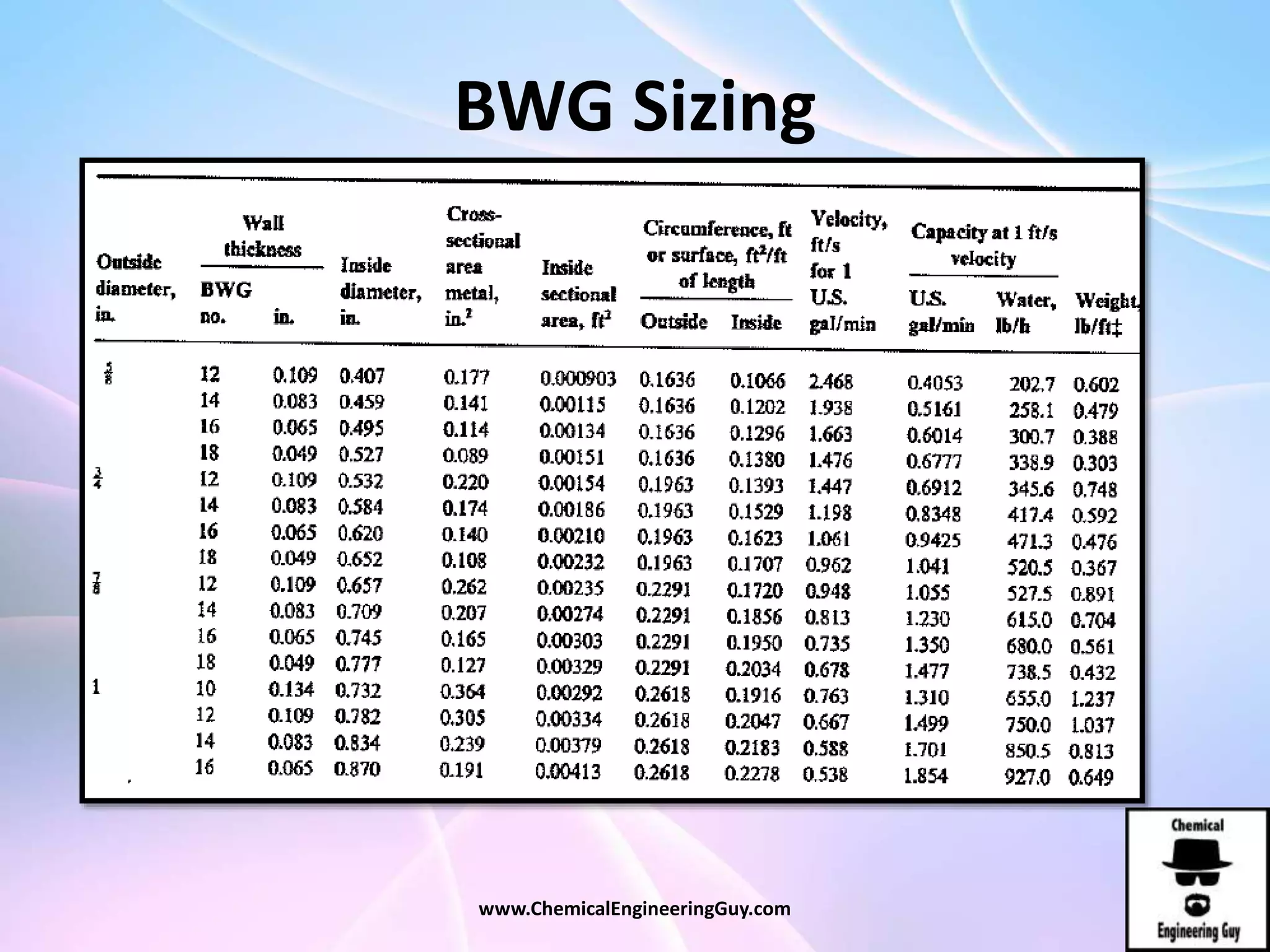
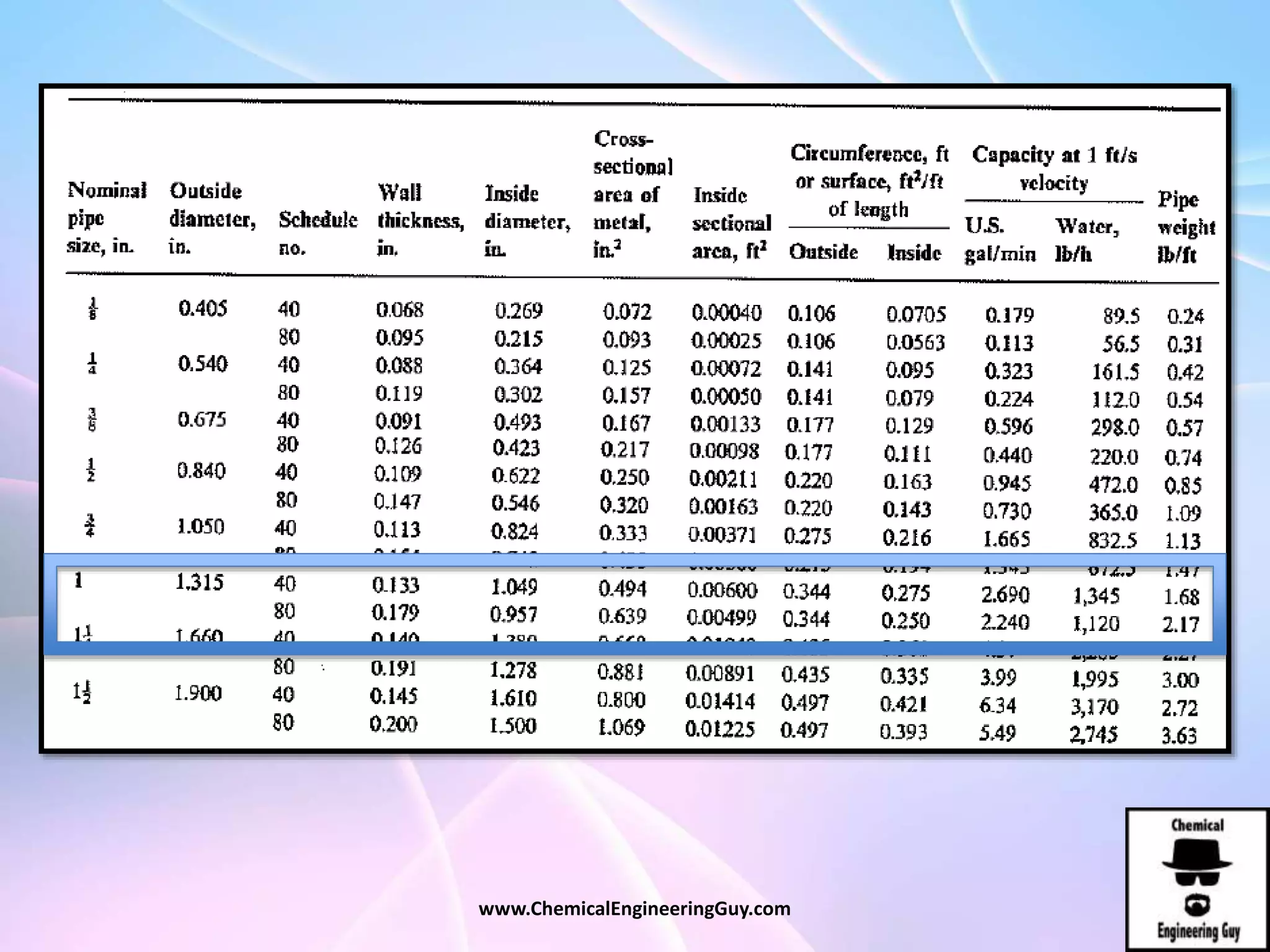
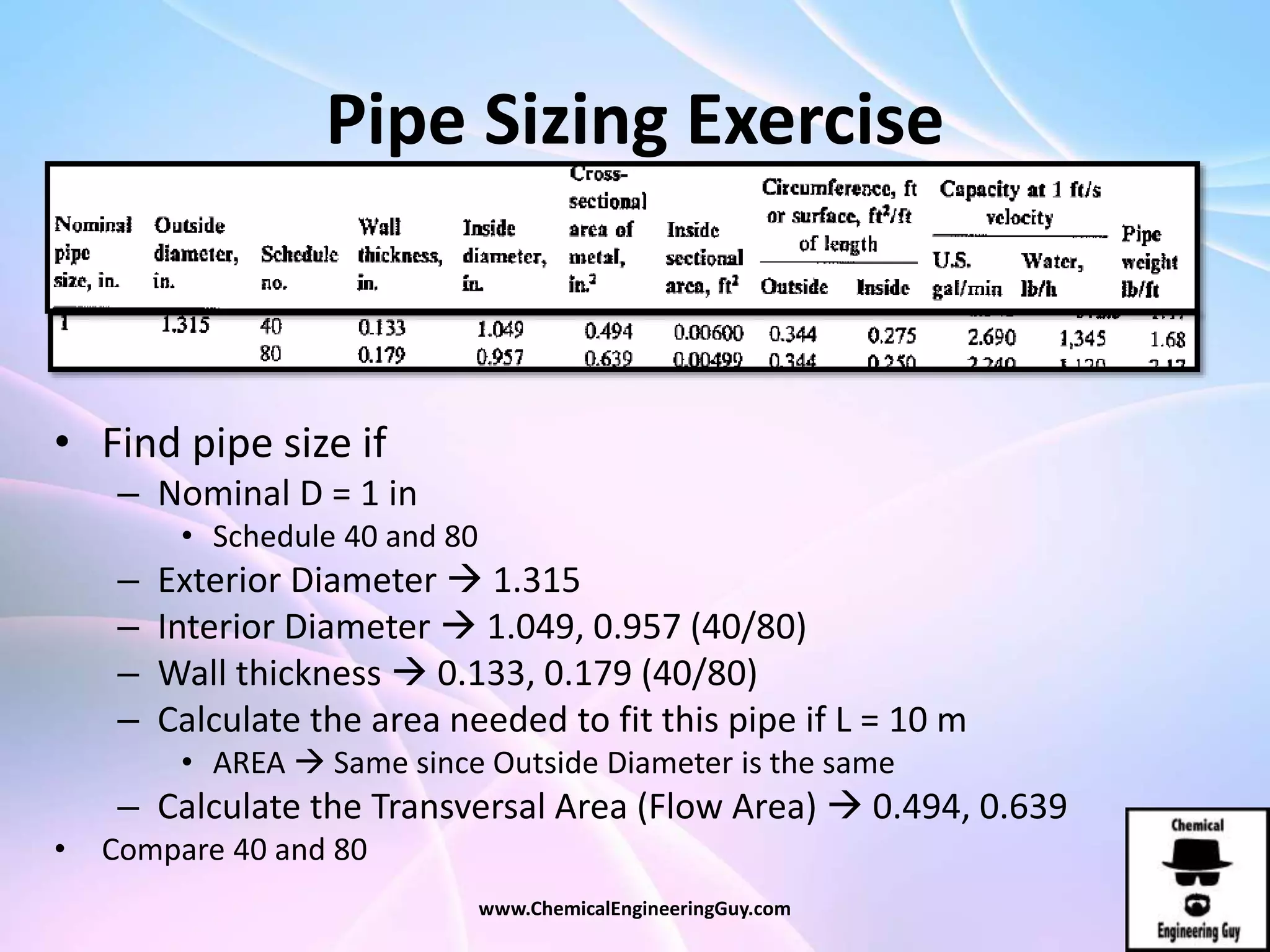
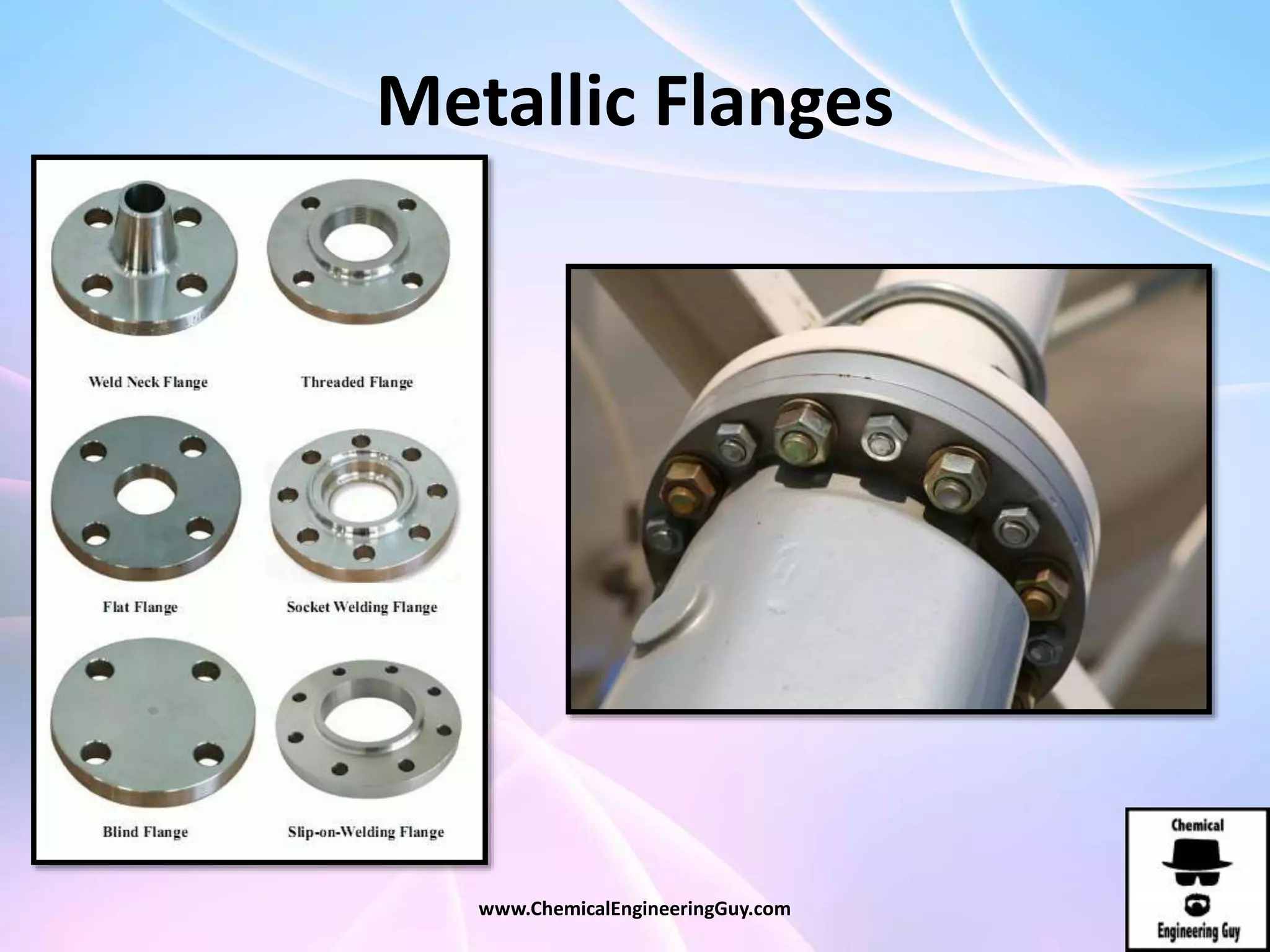
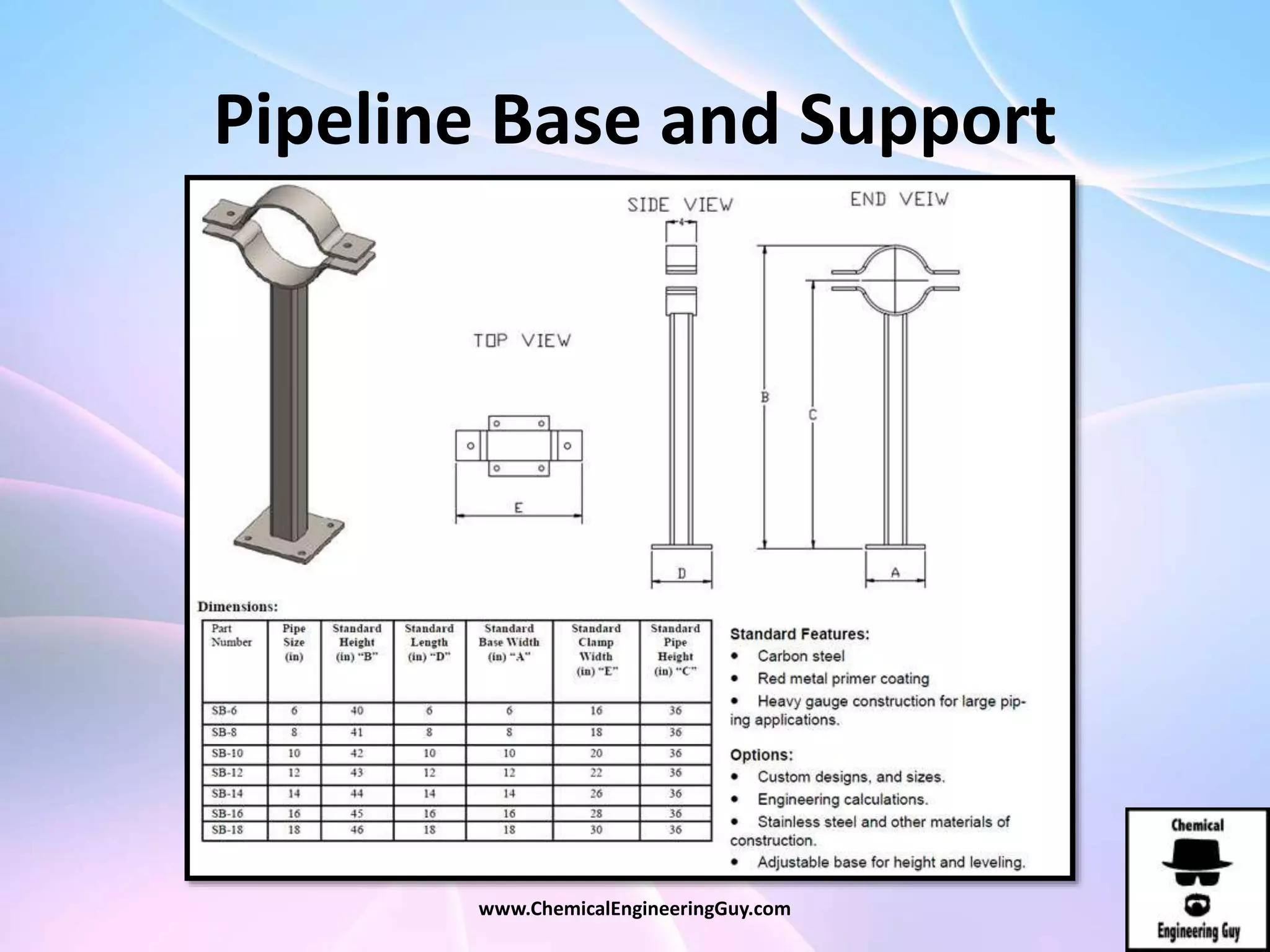
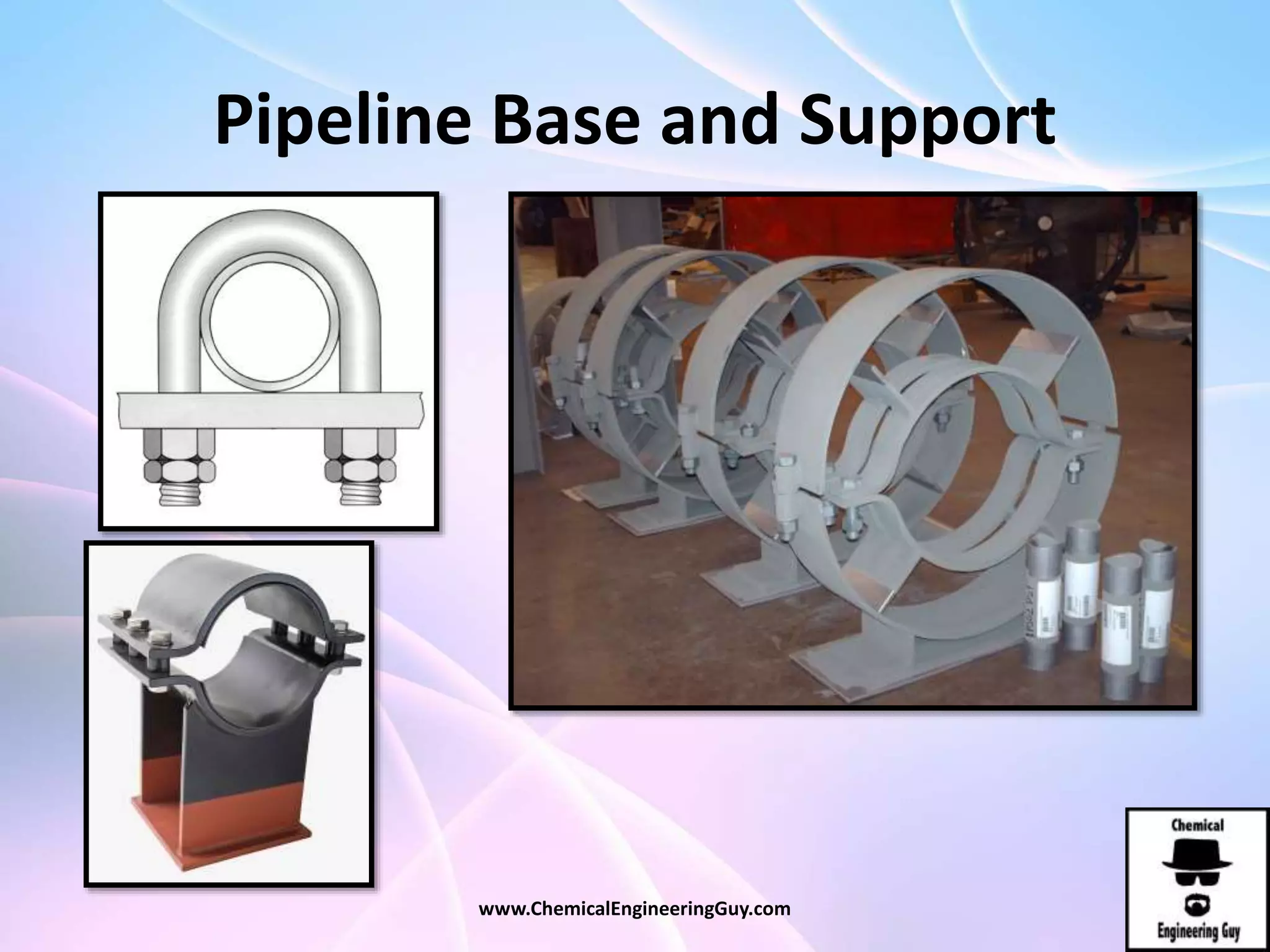
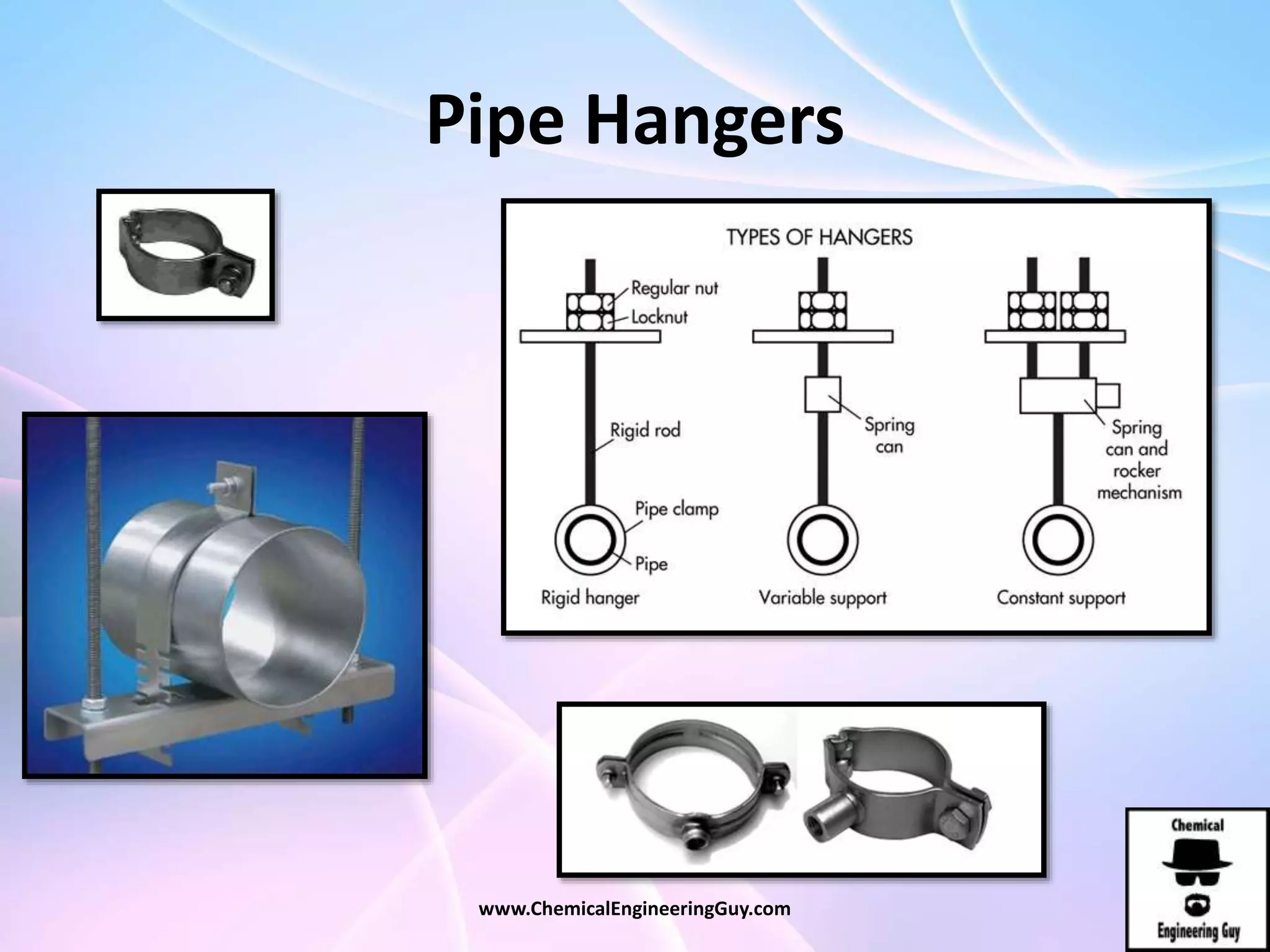
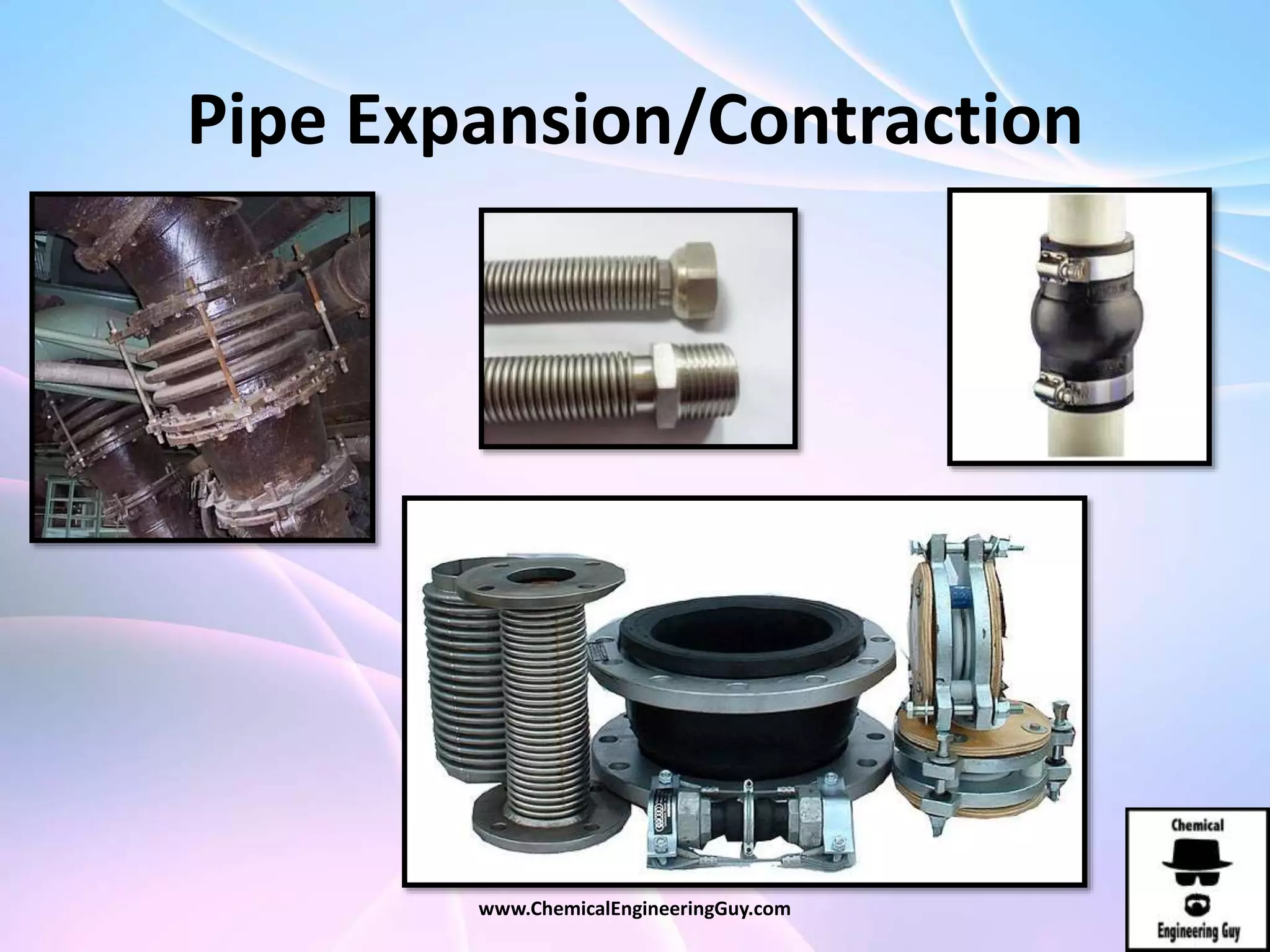
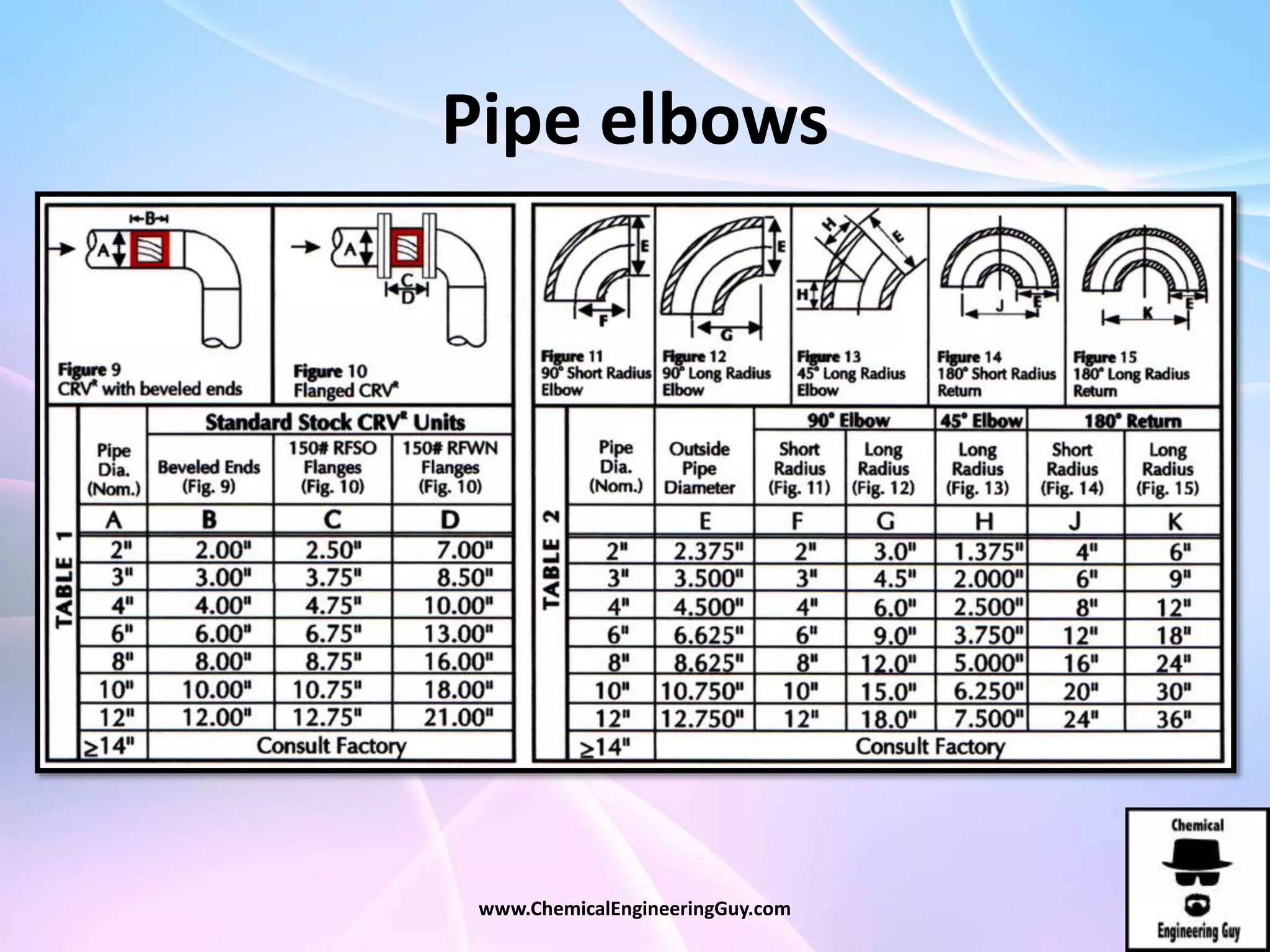
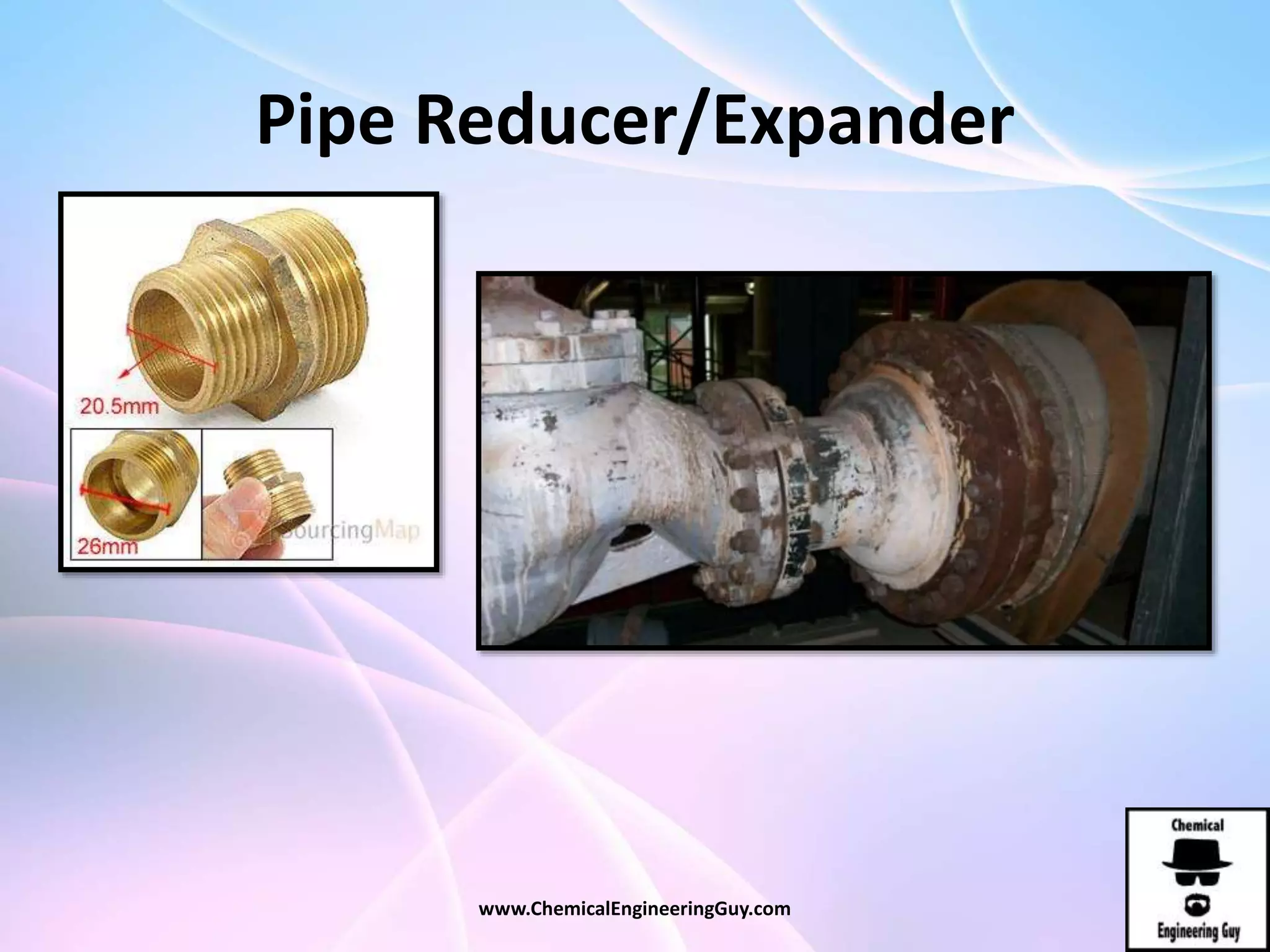
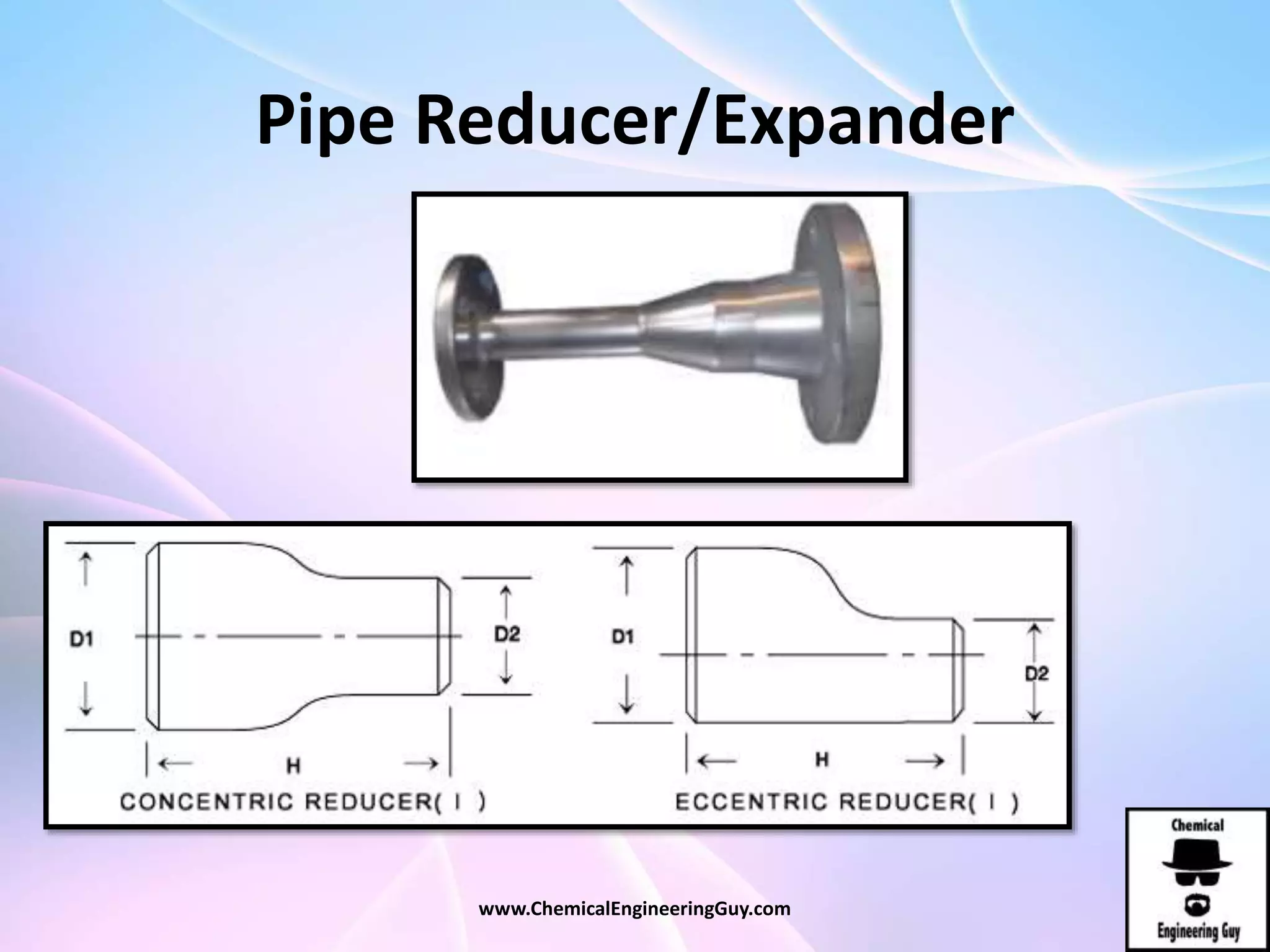
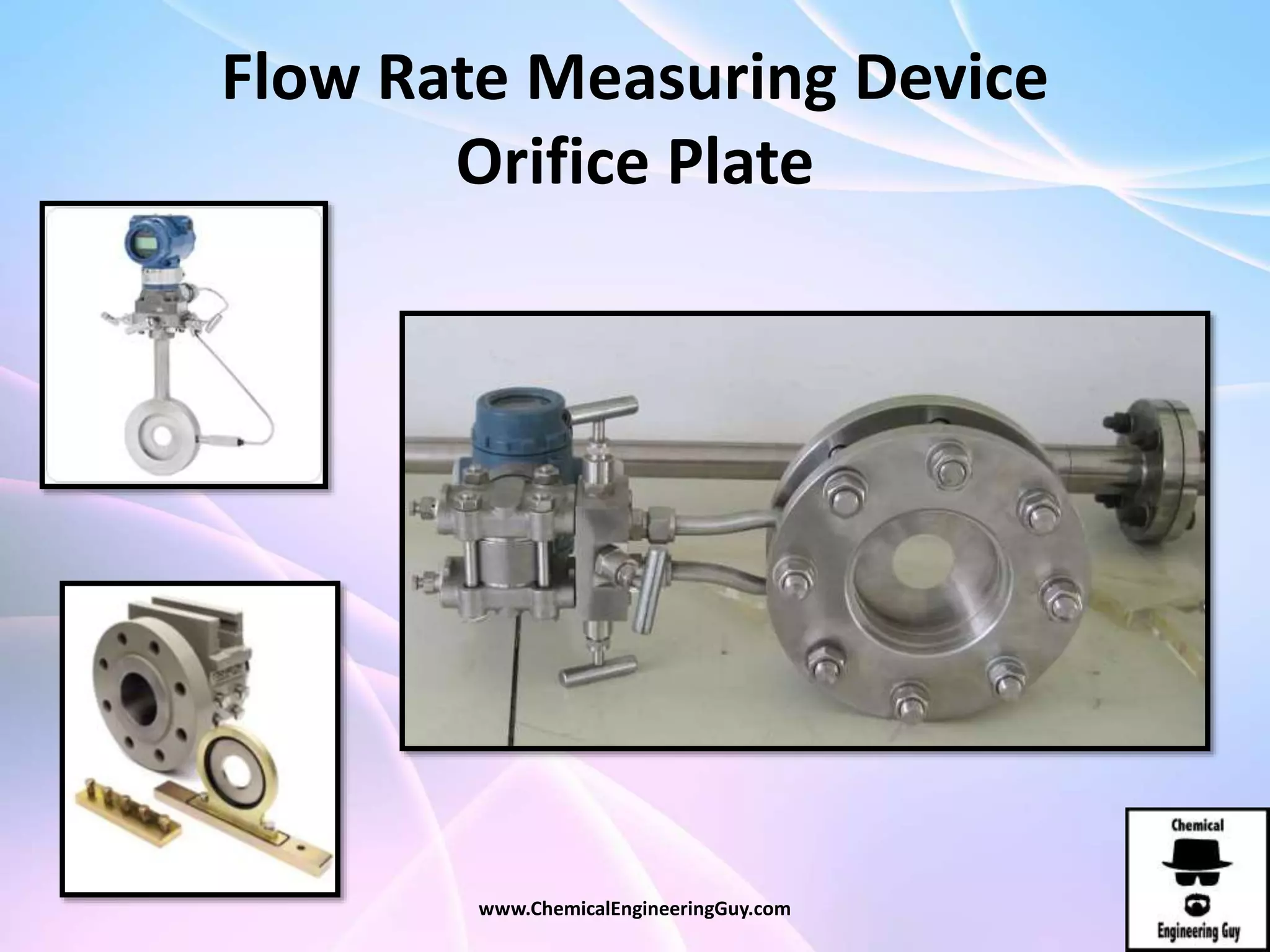
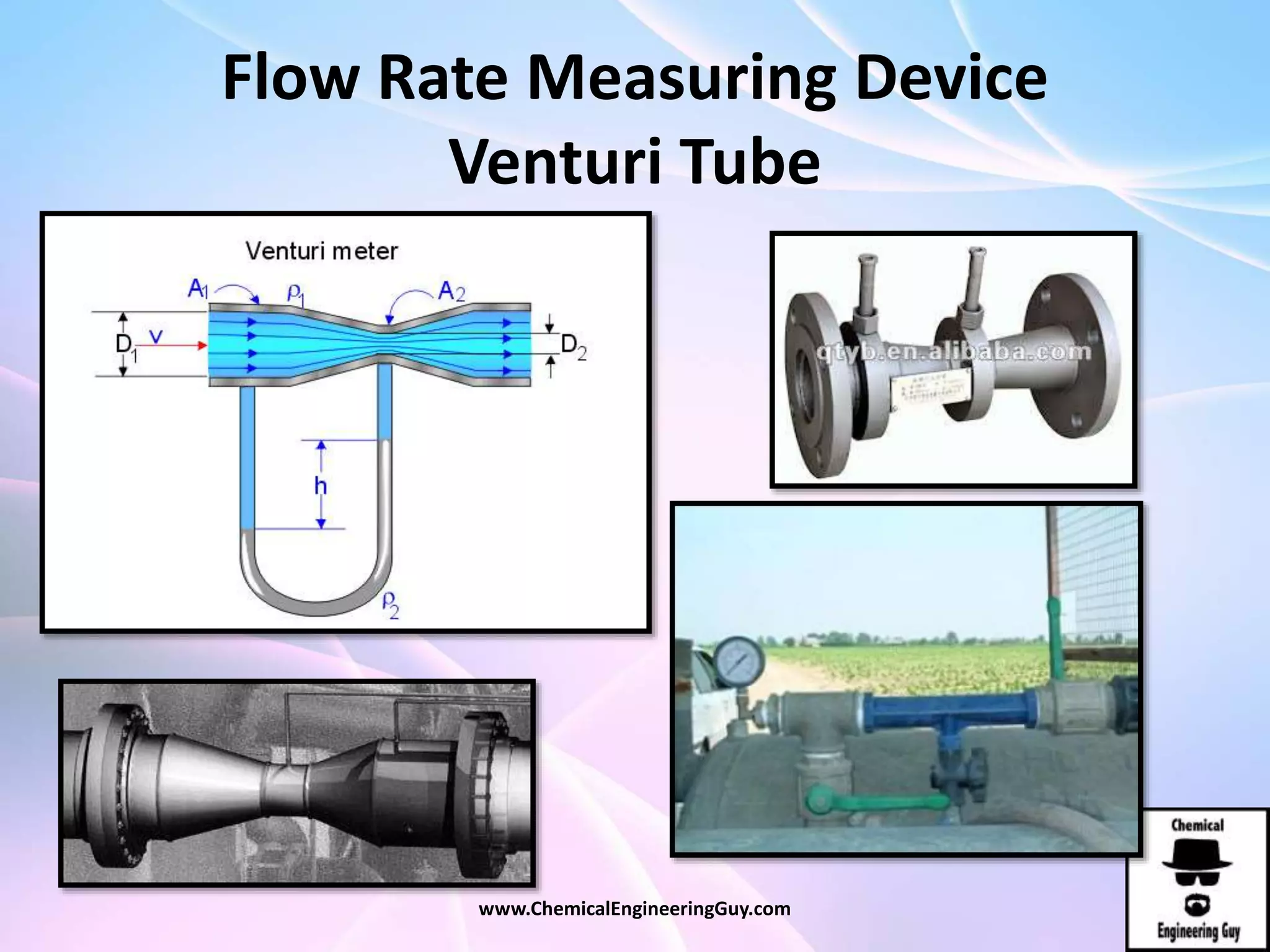
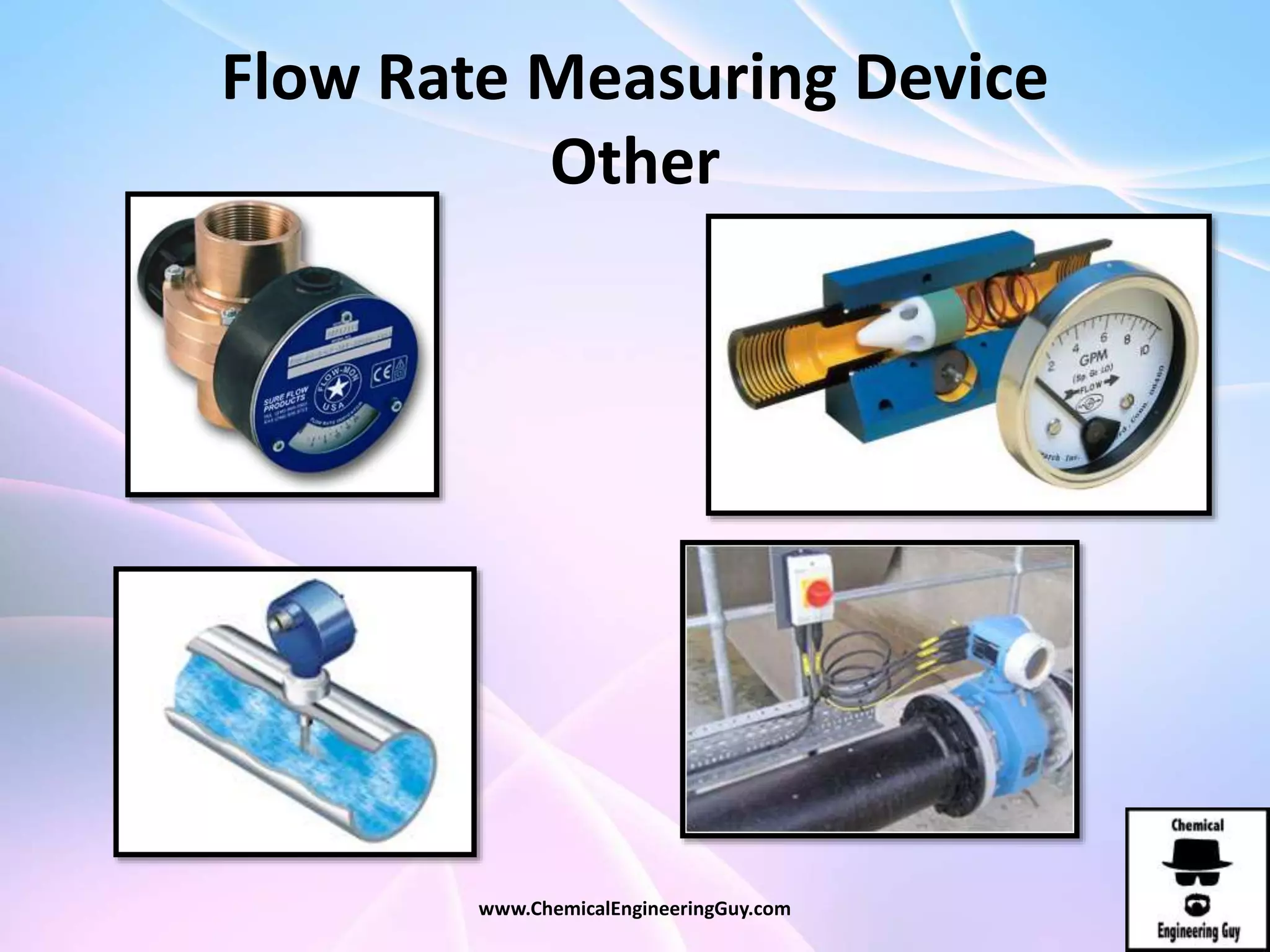
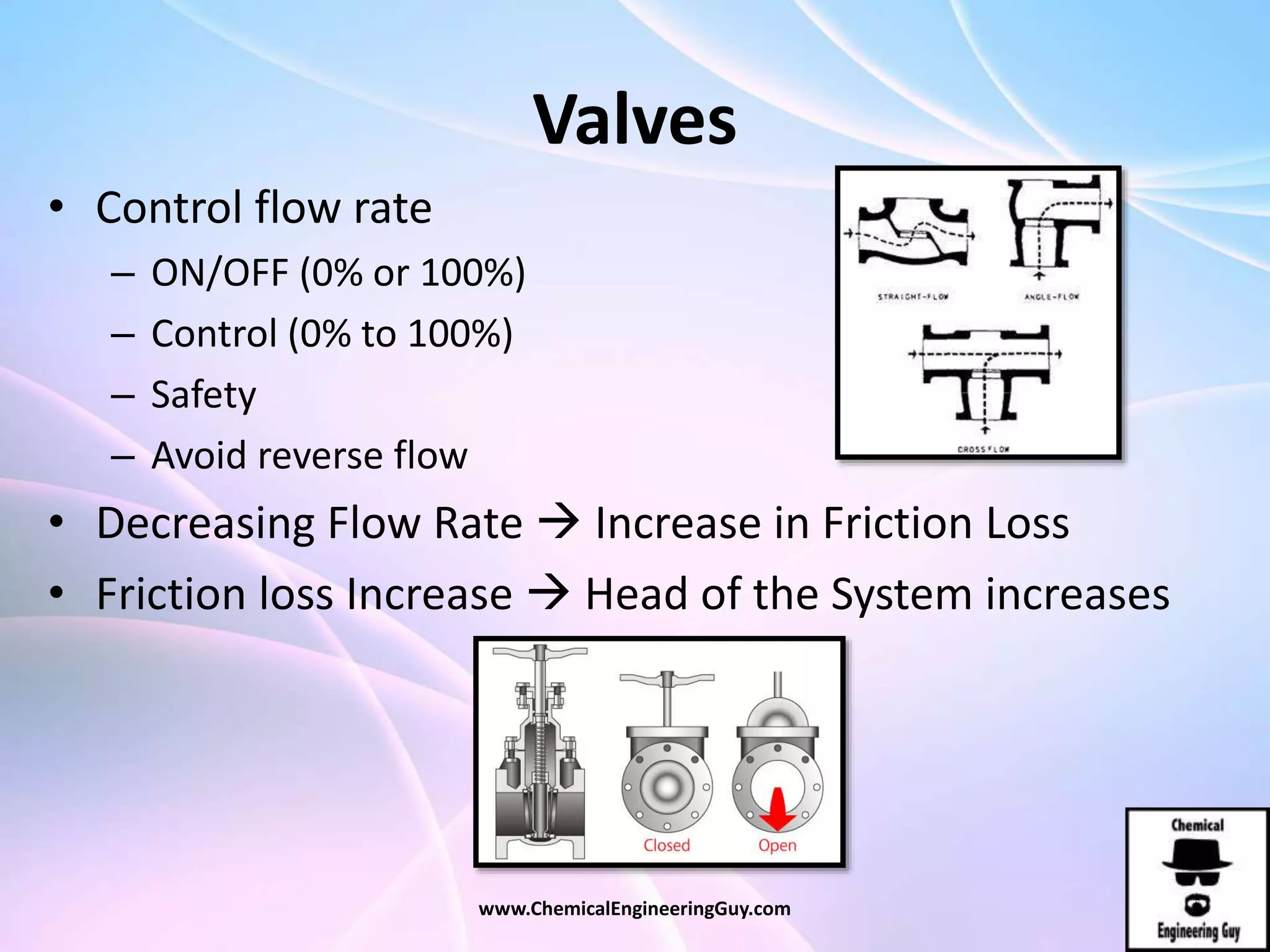
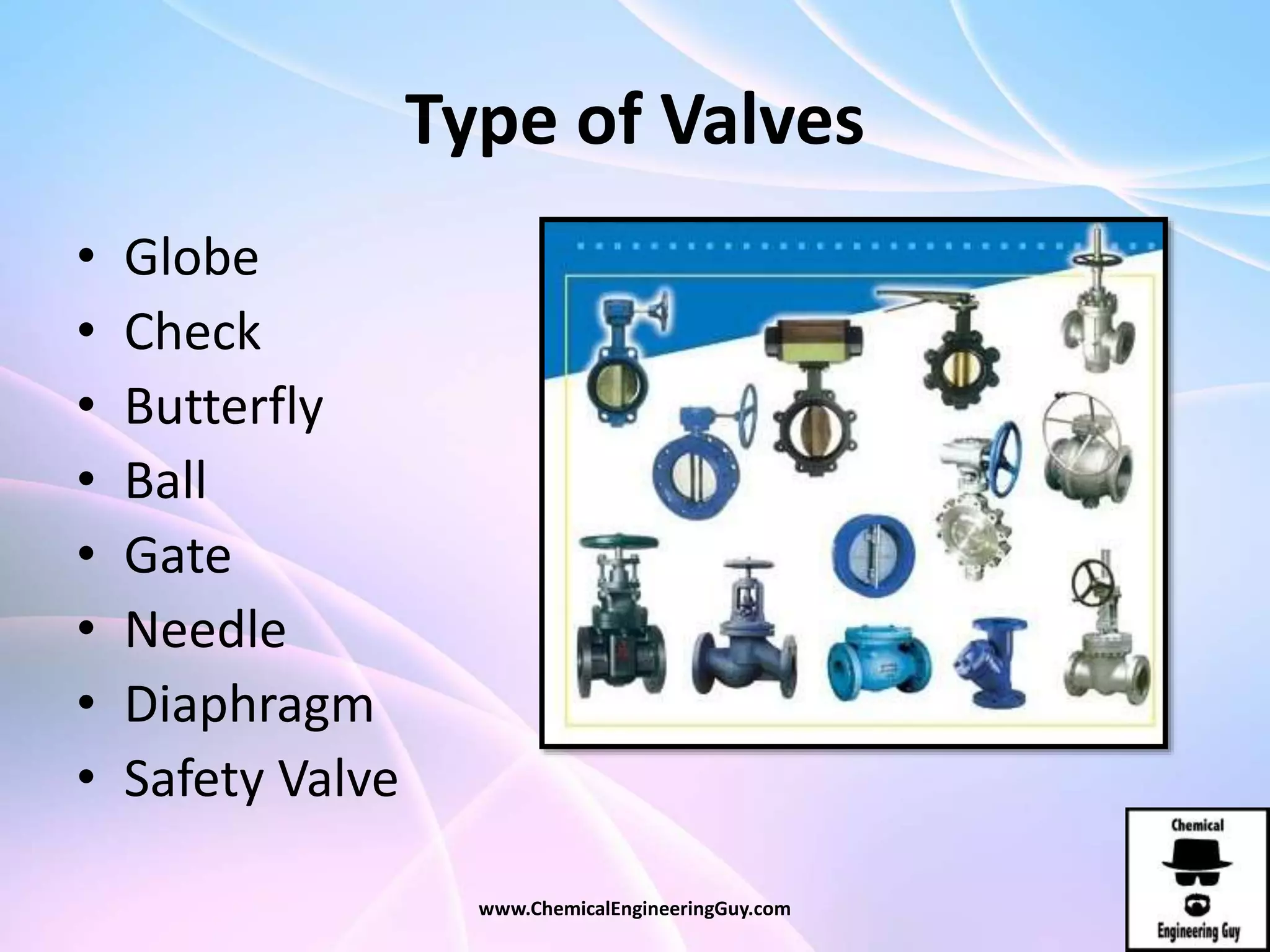
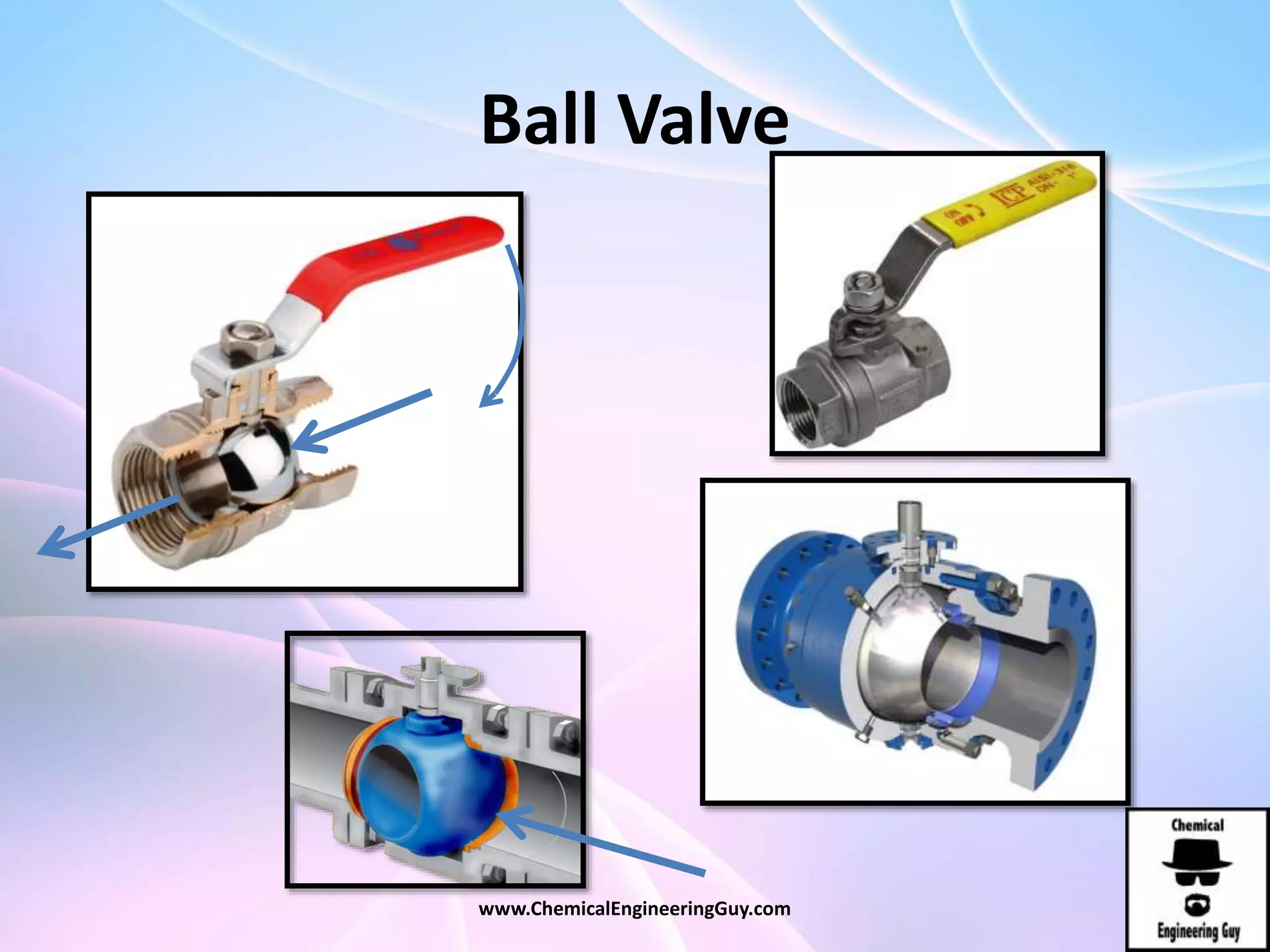
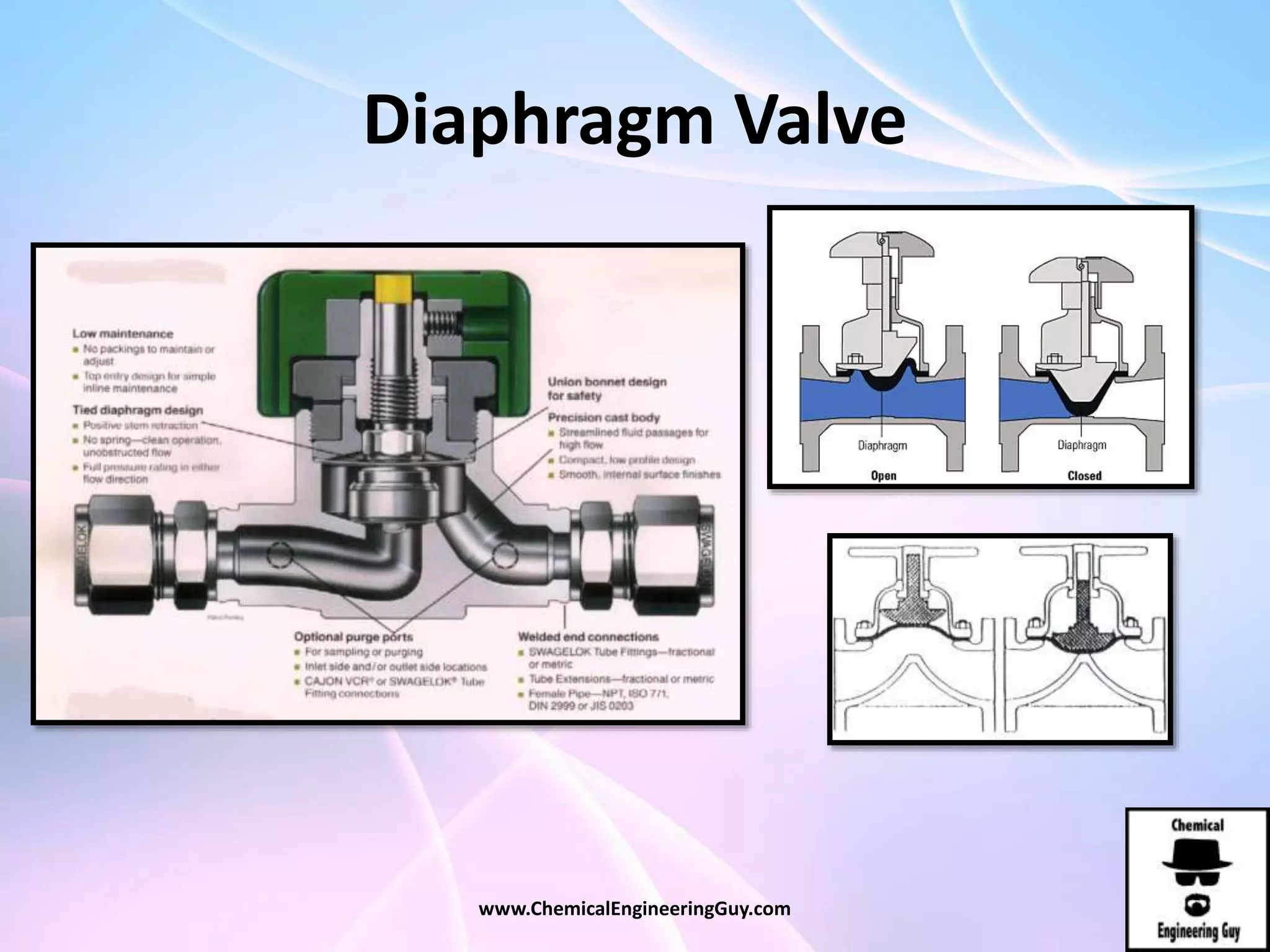
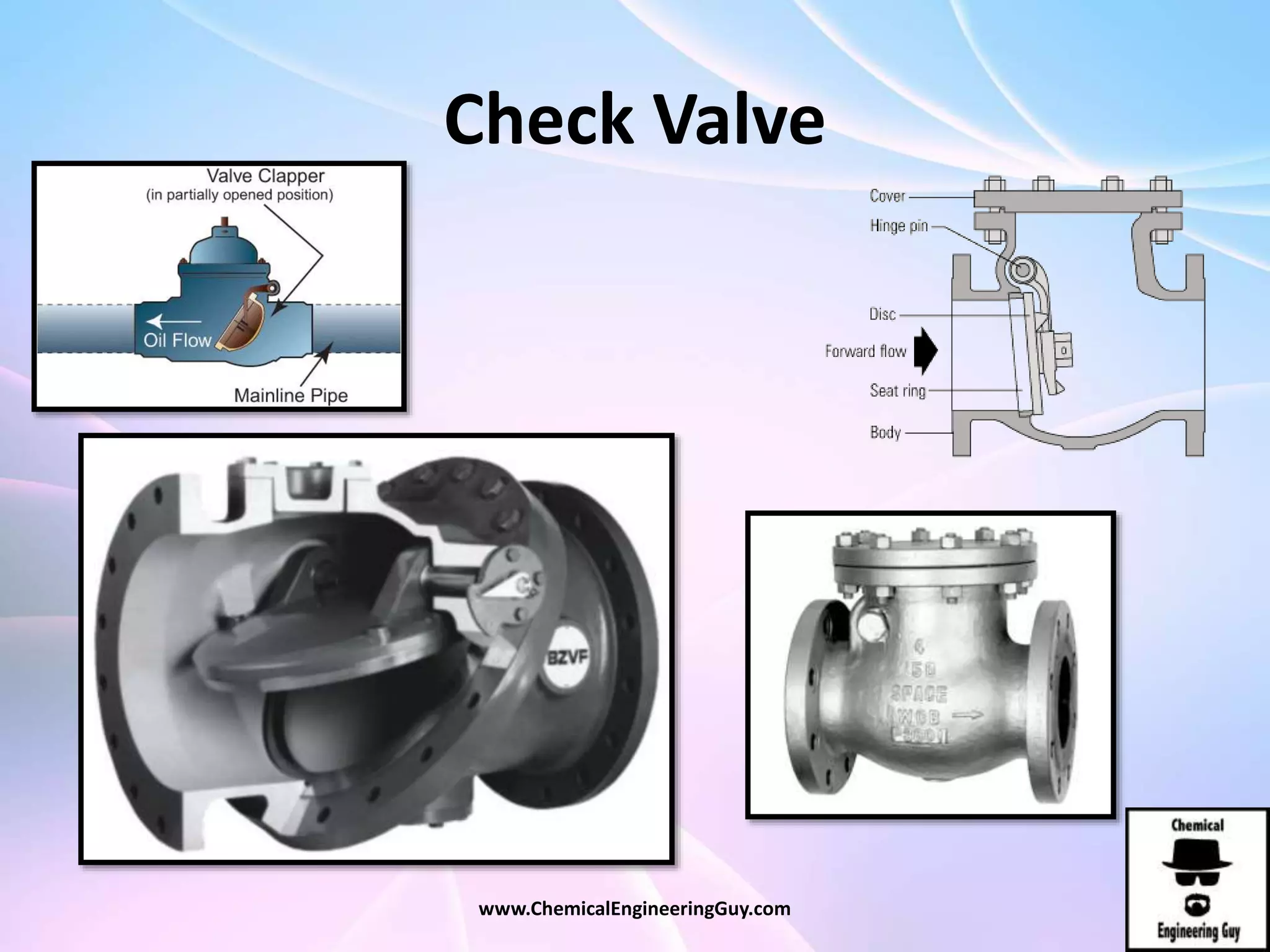
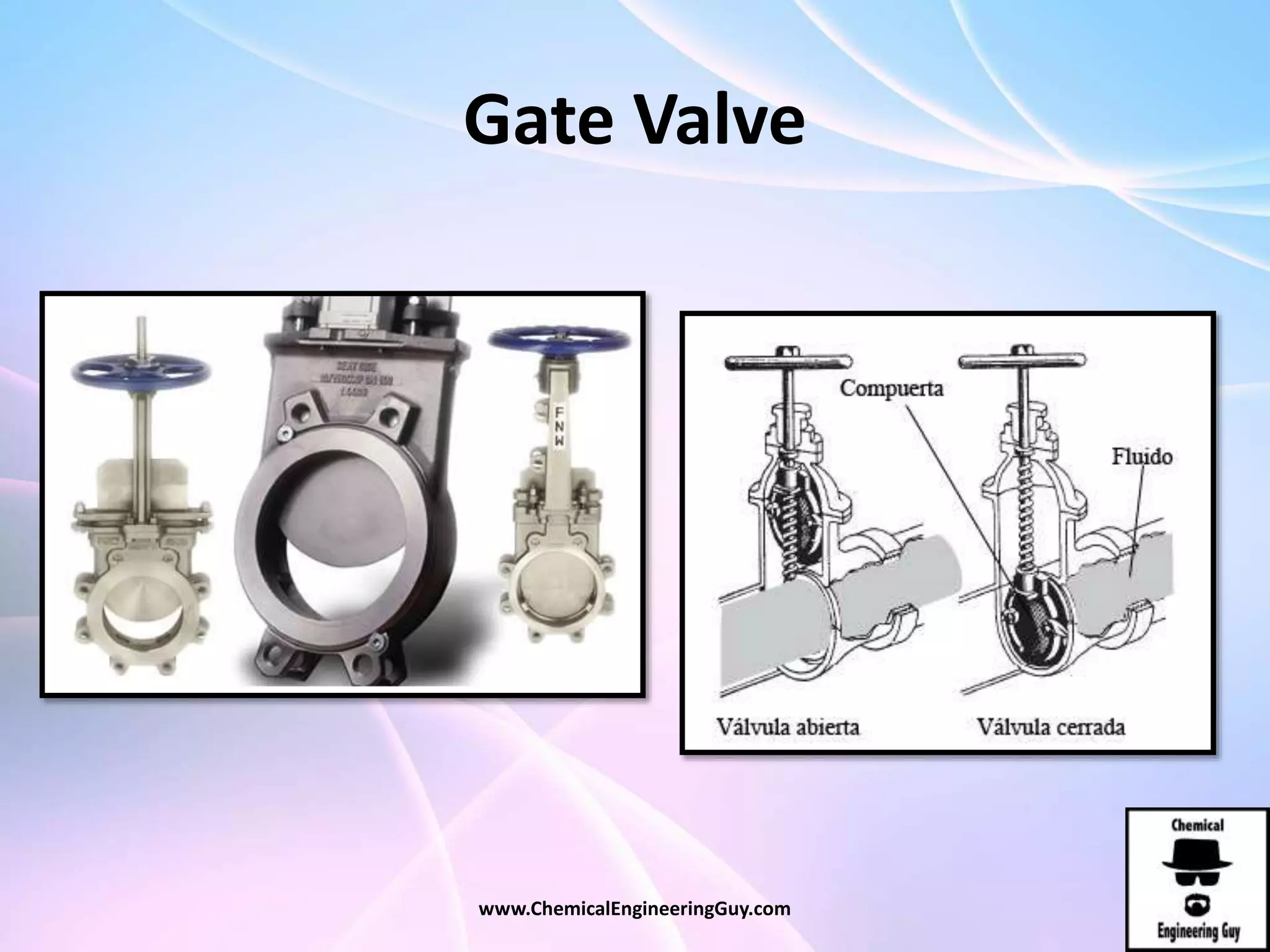
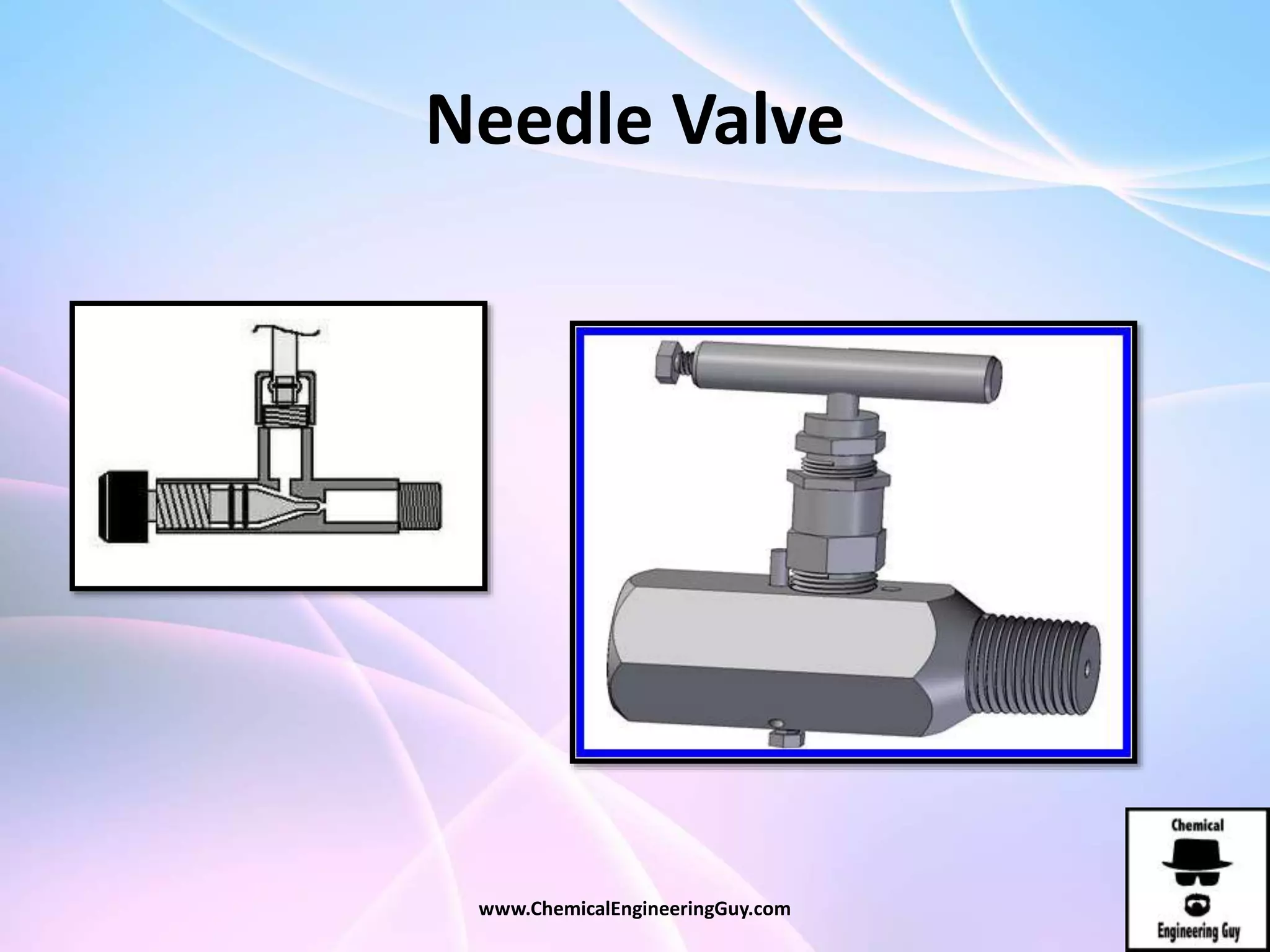
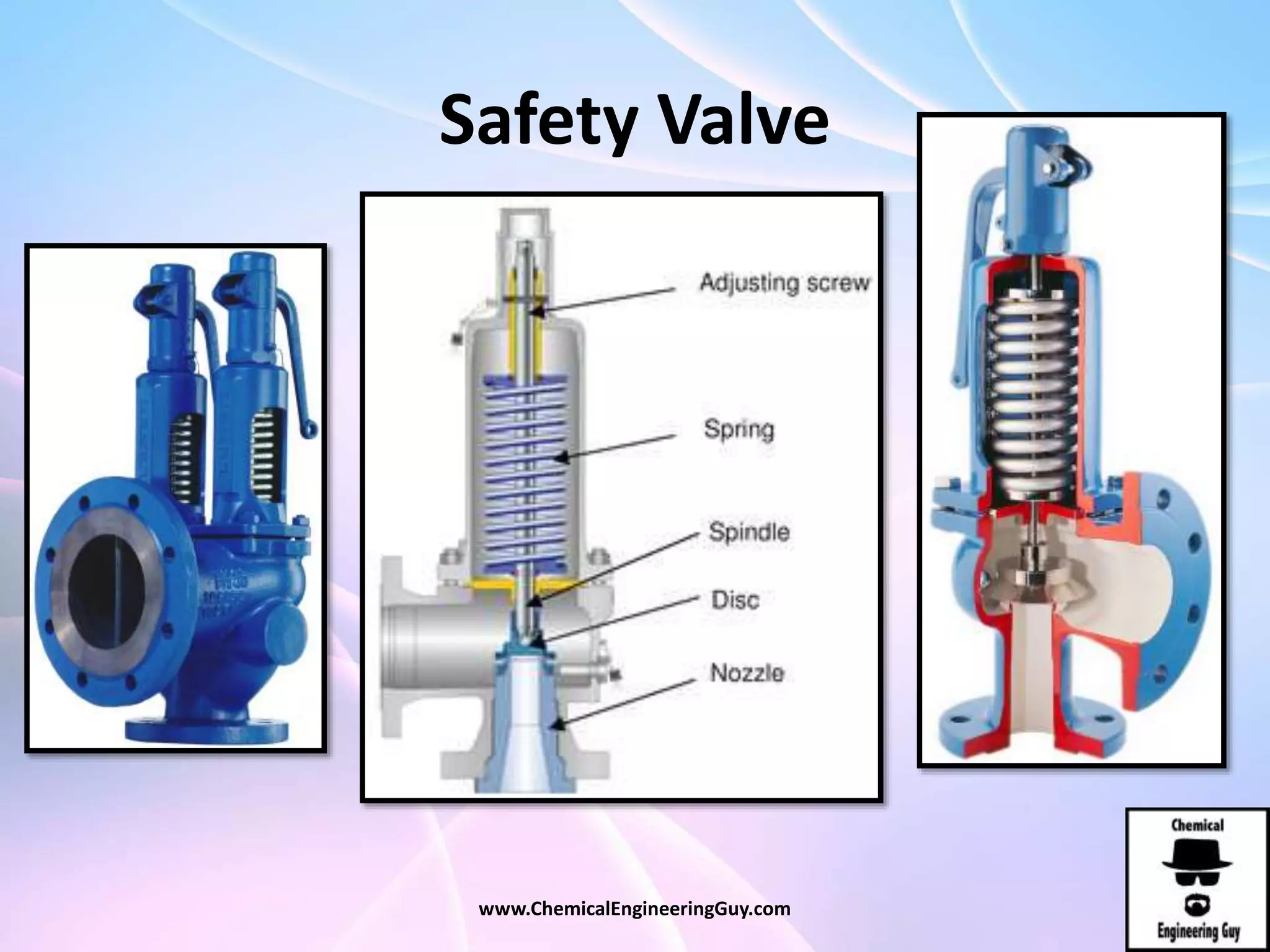
This document discusses piping, fittings, and valves used in fluid dynamics. It begins by defining common piping terminology and describing common piping materials like steel, copper, plastic, and ceramics. It then discusses factors for pipe selection like fluid type and operating conditions. Key aspects of piping design covered include material roughness, pipe sizing methods using schedules and BWG, and considerations for pipe expansion and supports. Common pipe fittings are also defined, including flanges, elbows, reducers, and flow measurement devices. Finally, the document outlines the purpose and types of valves used to control fluid flow, such as globe, ball, gate, and safety valves.