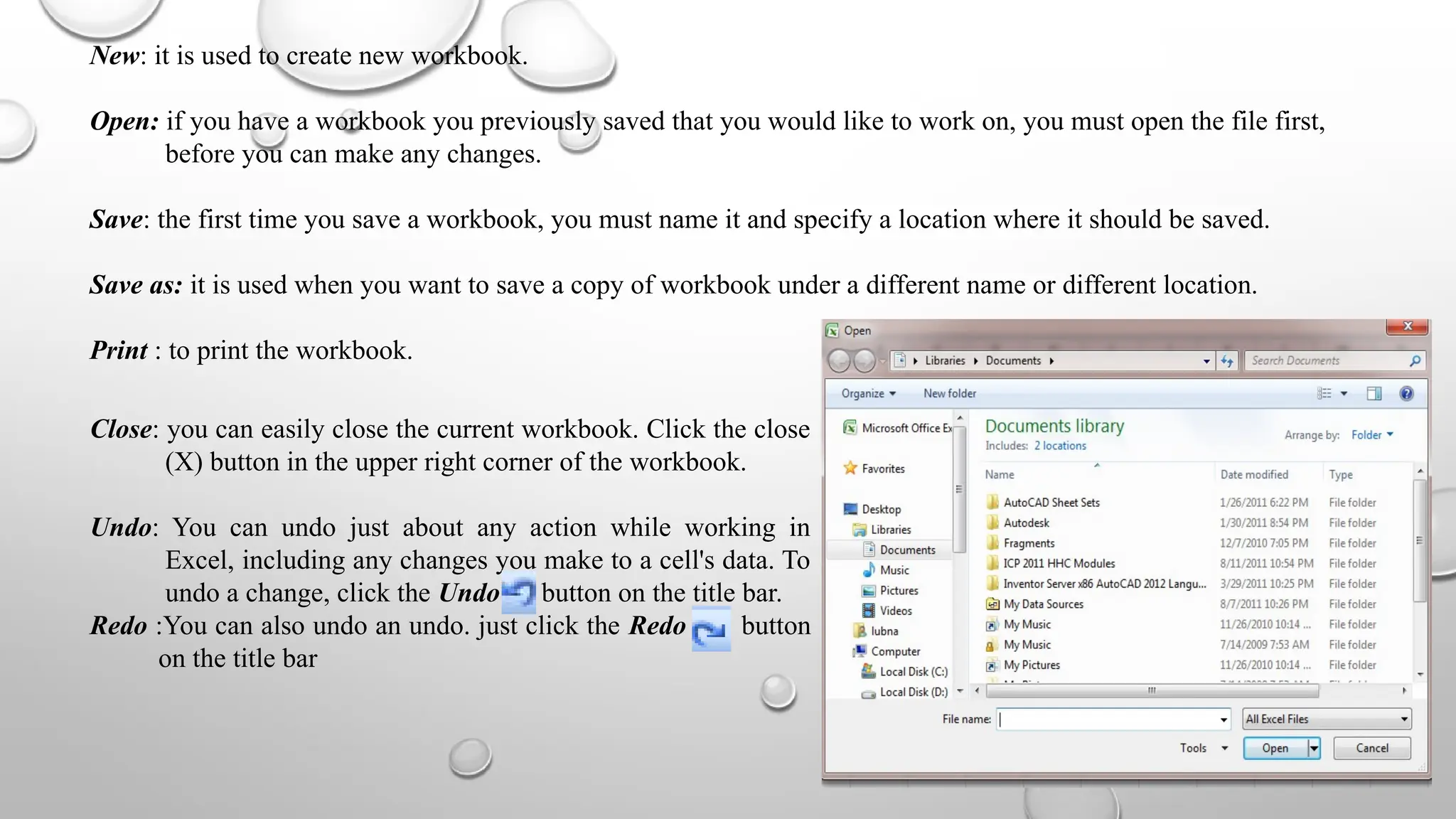
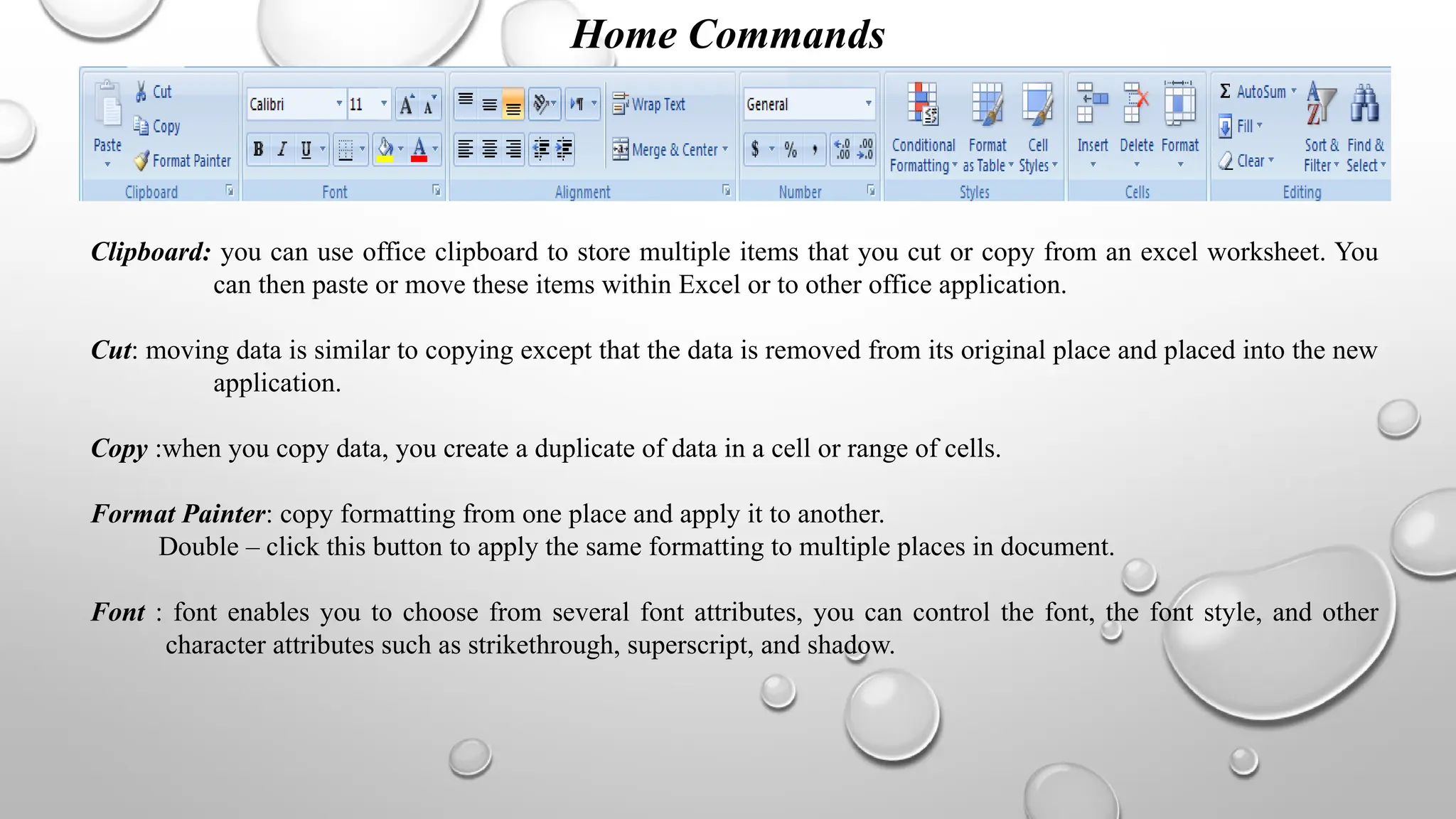
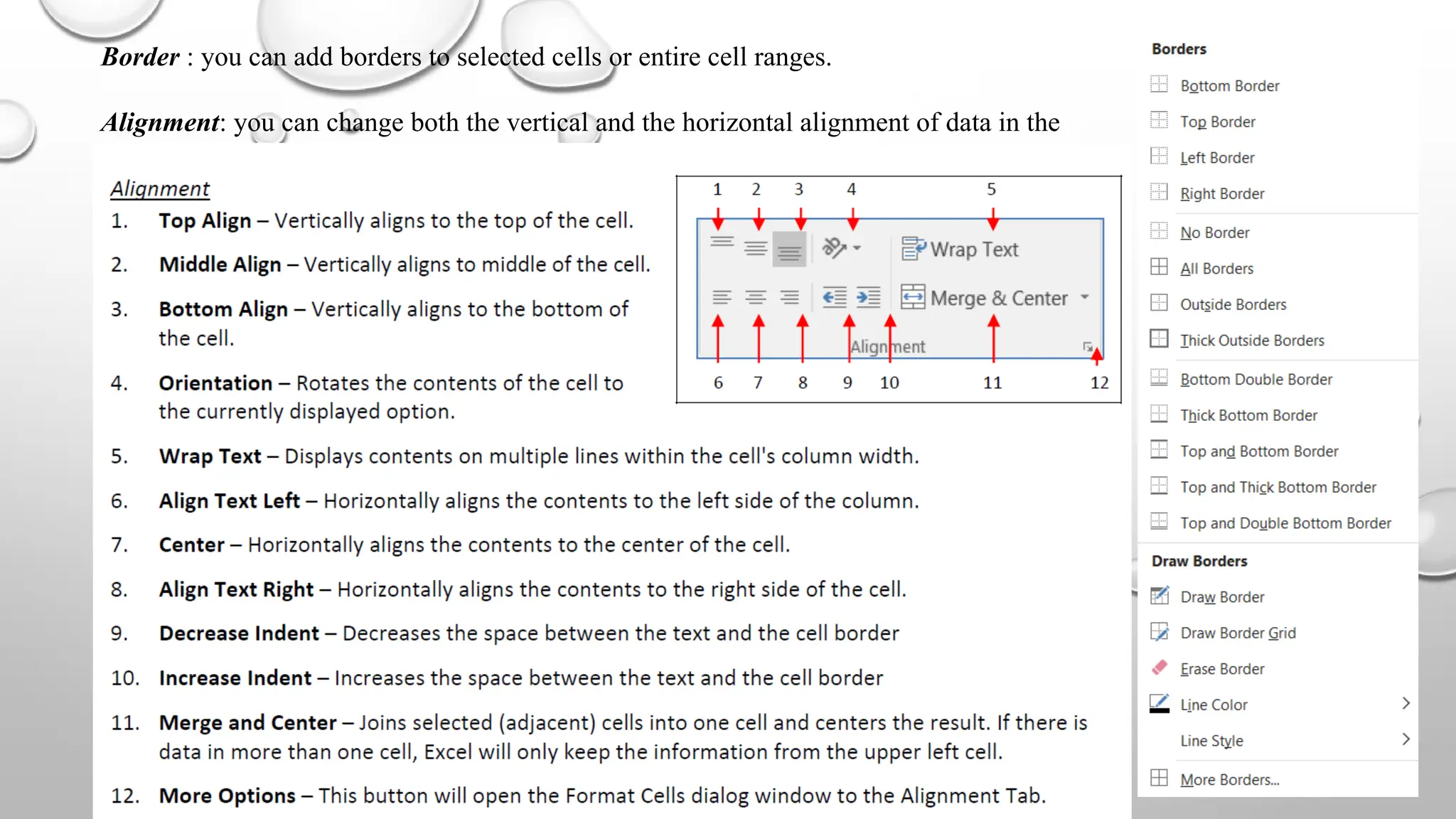
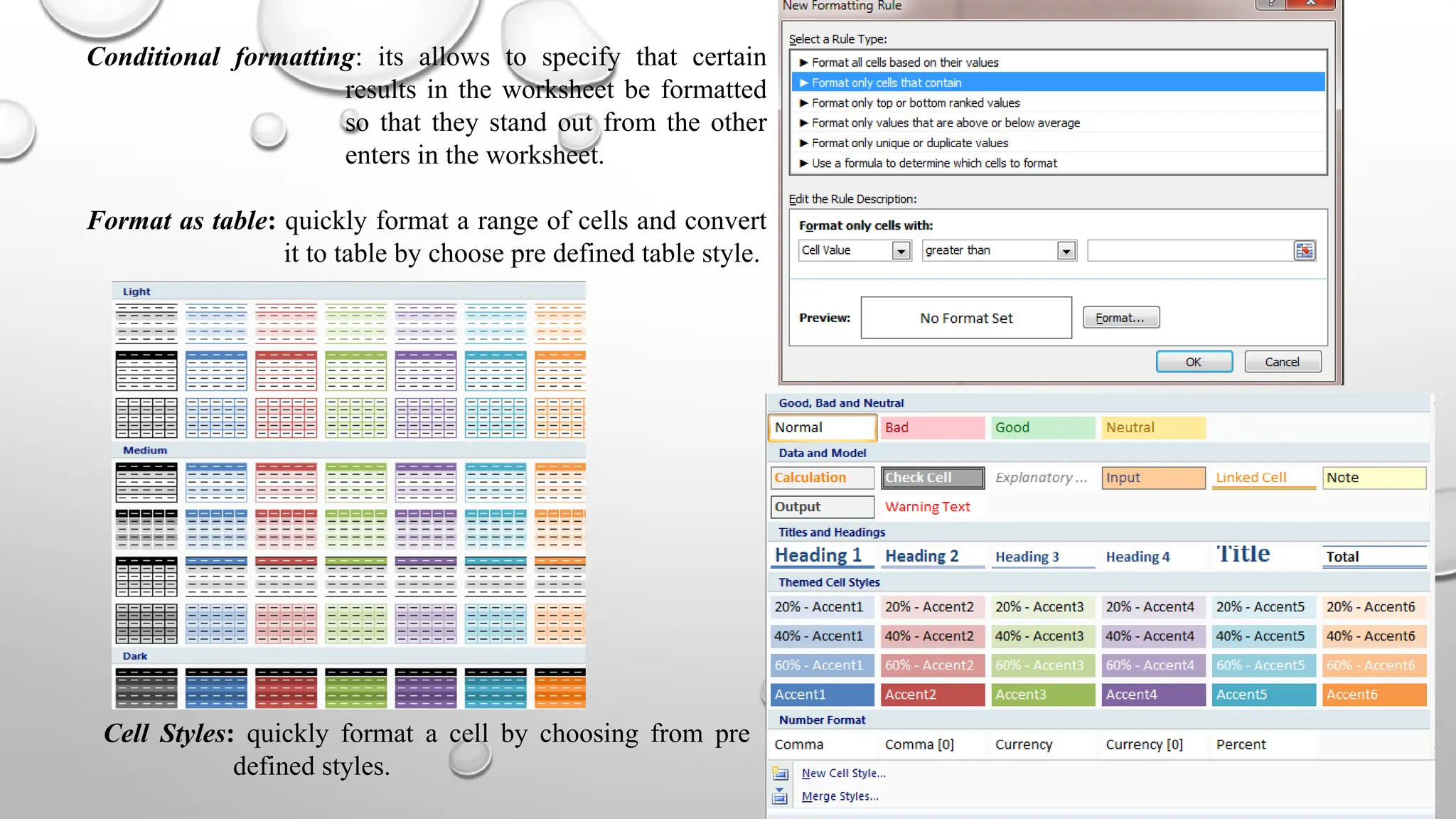
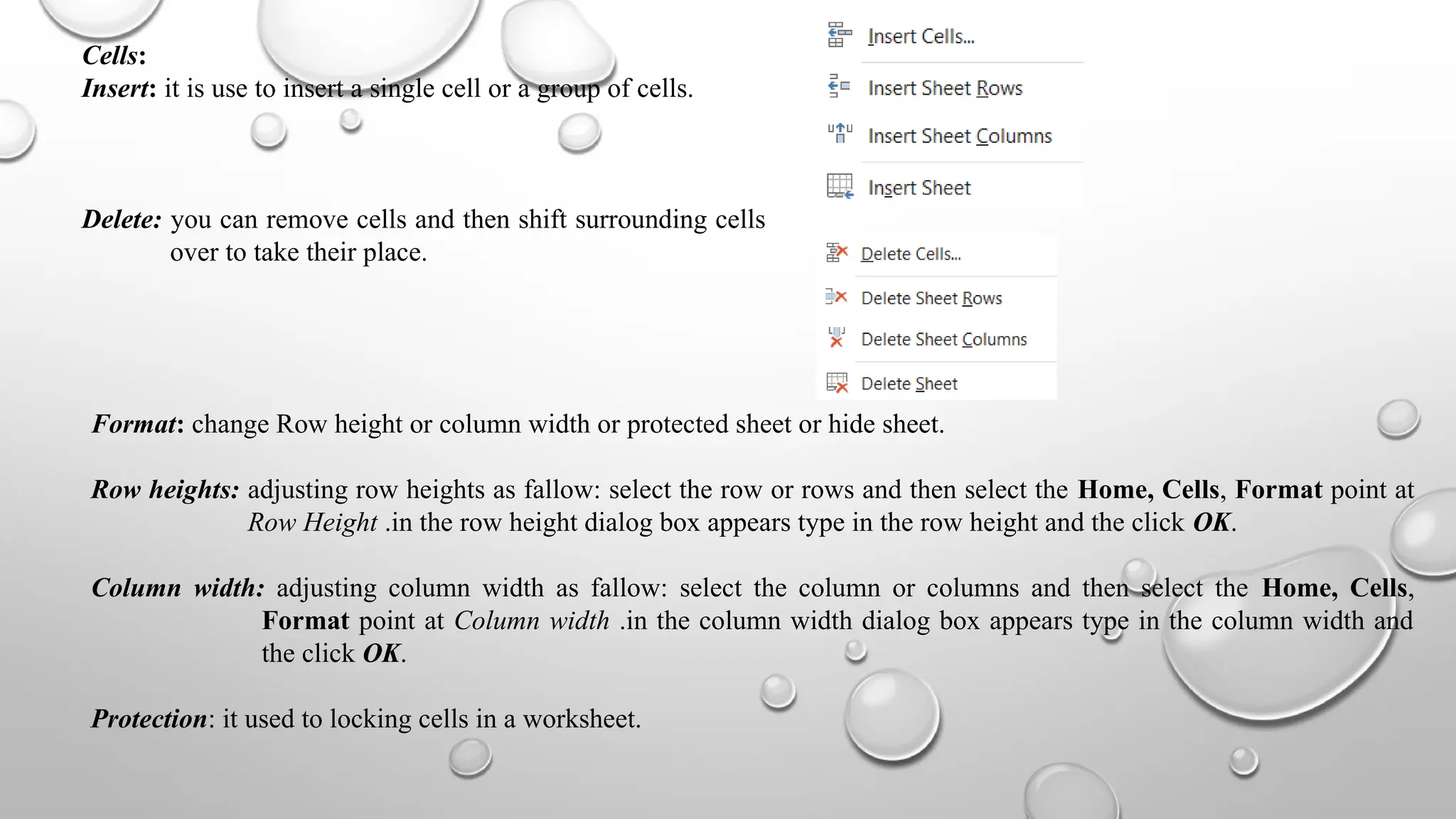
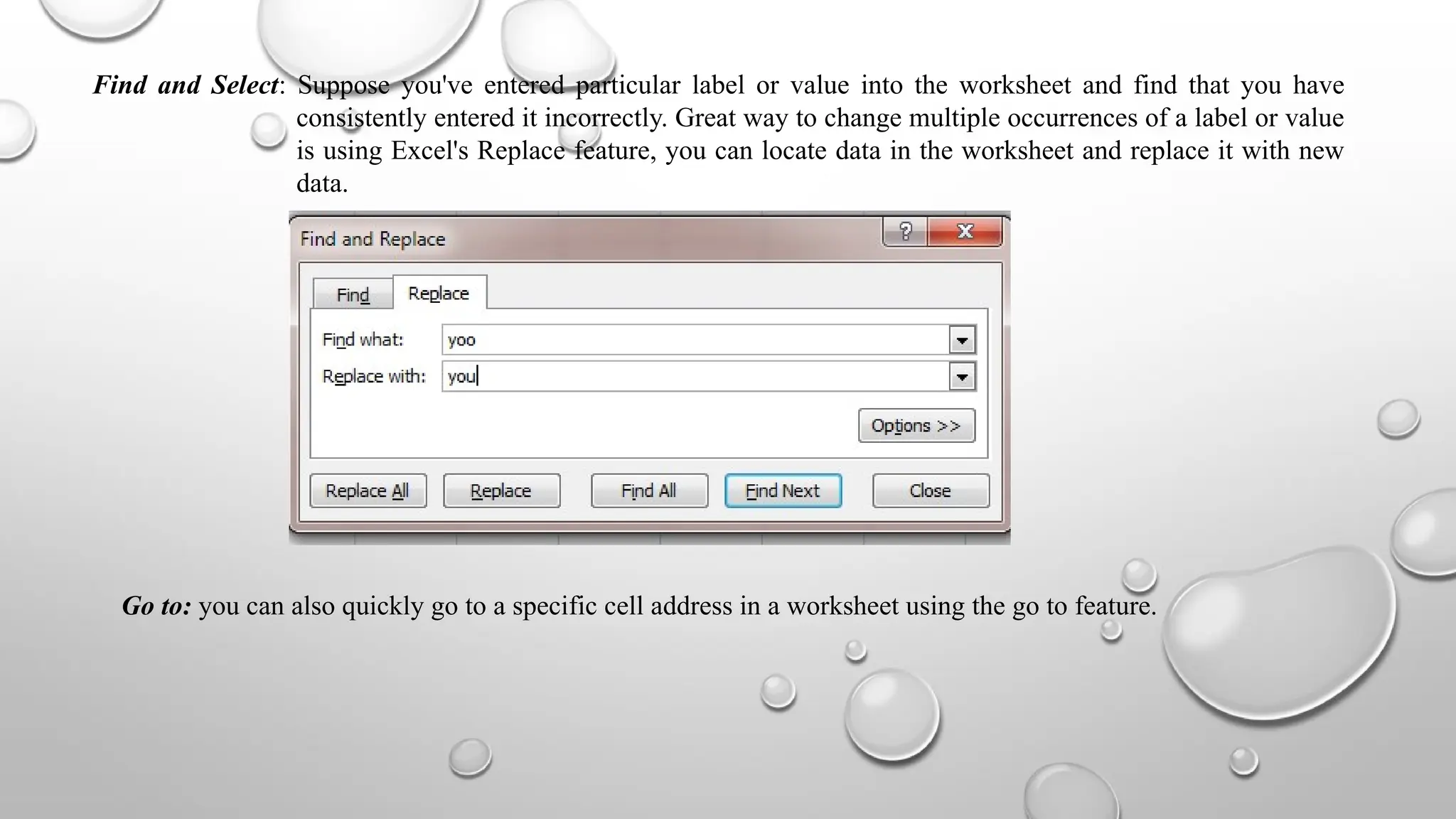
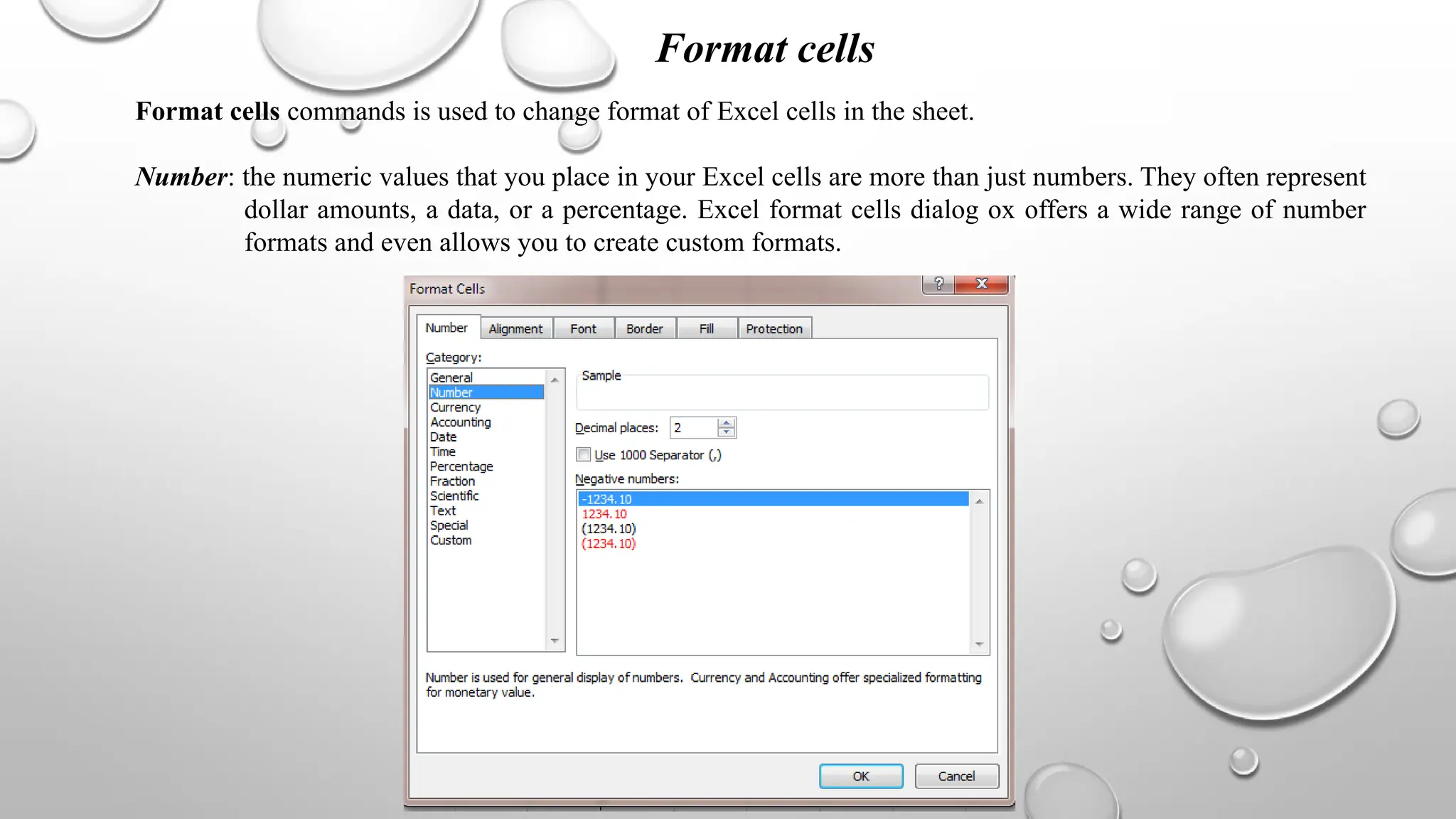
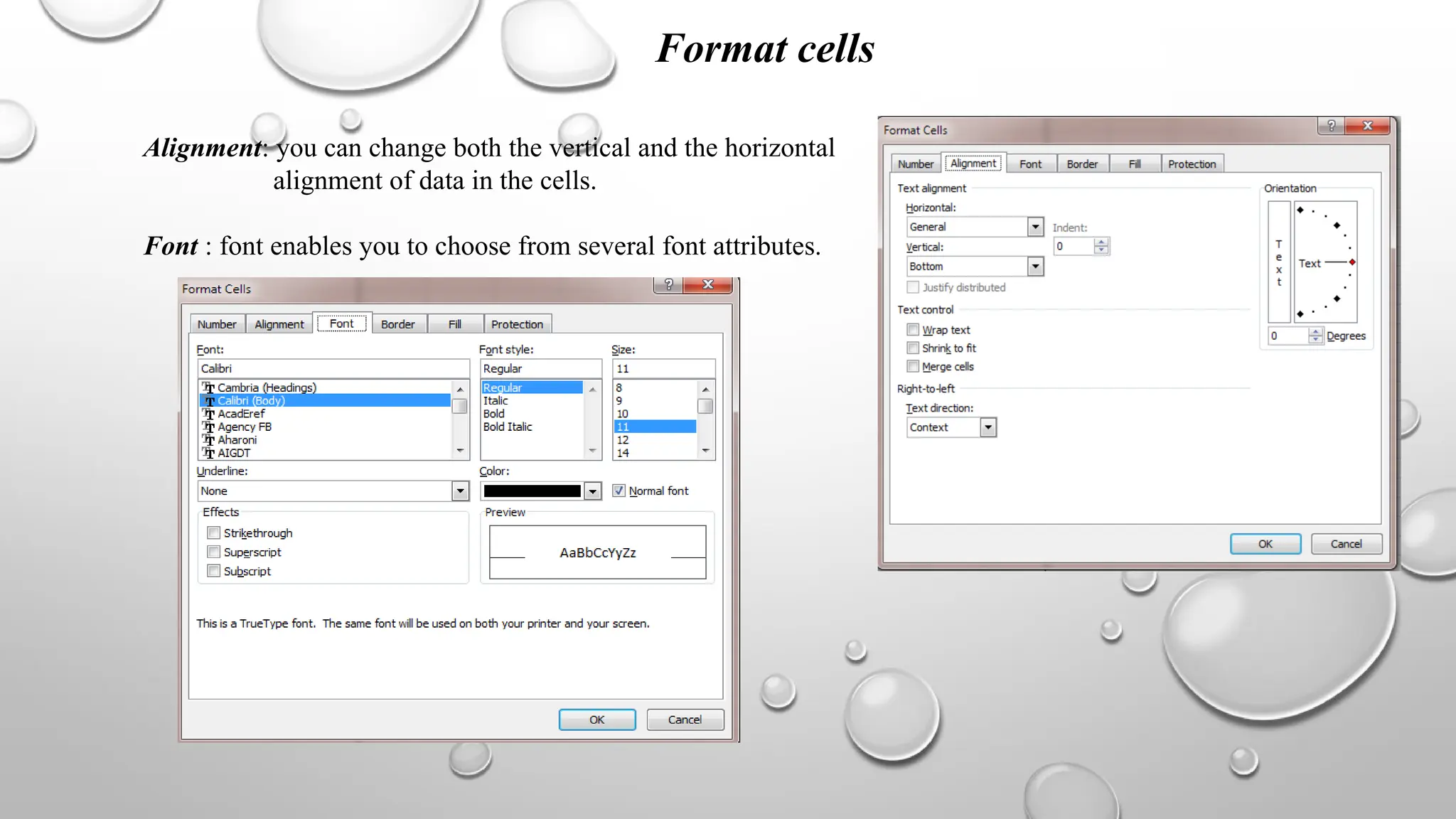
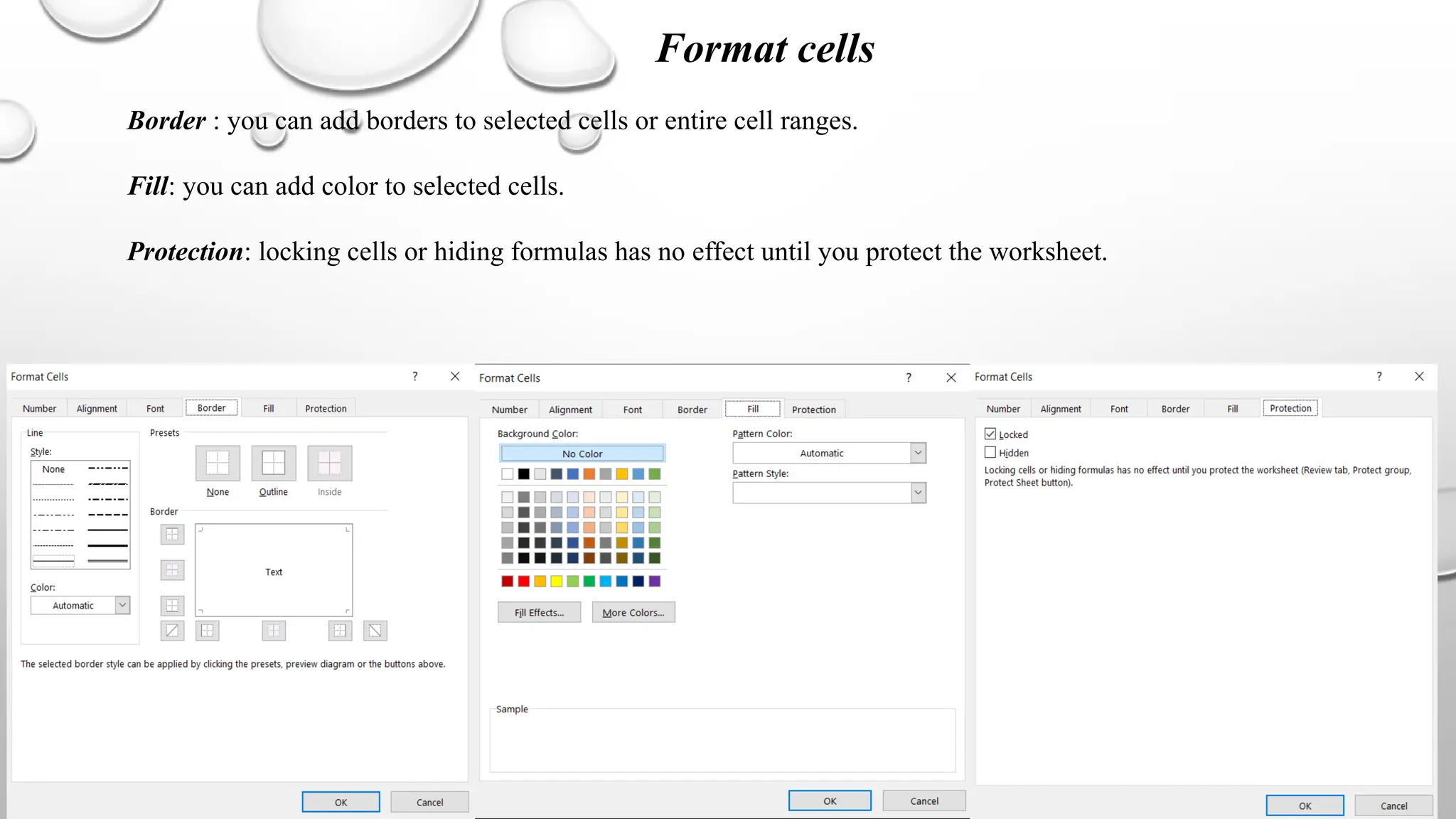
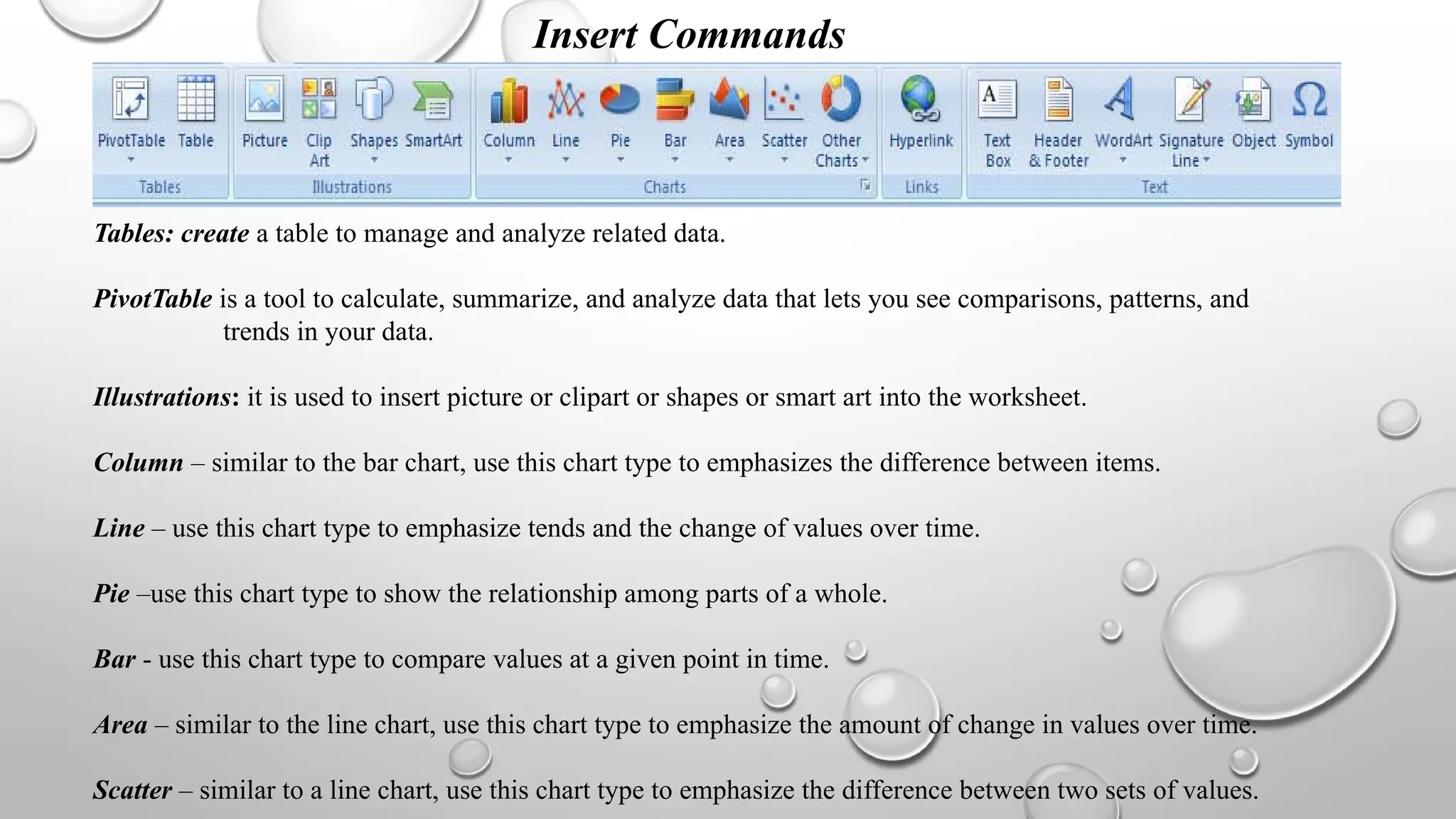
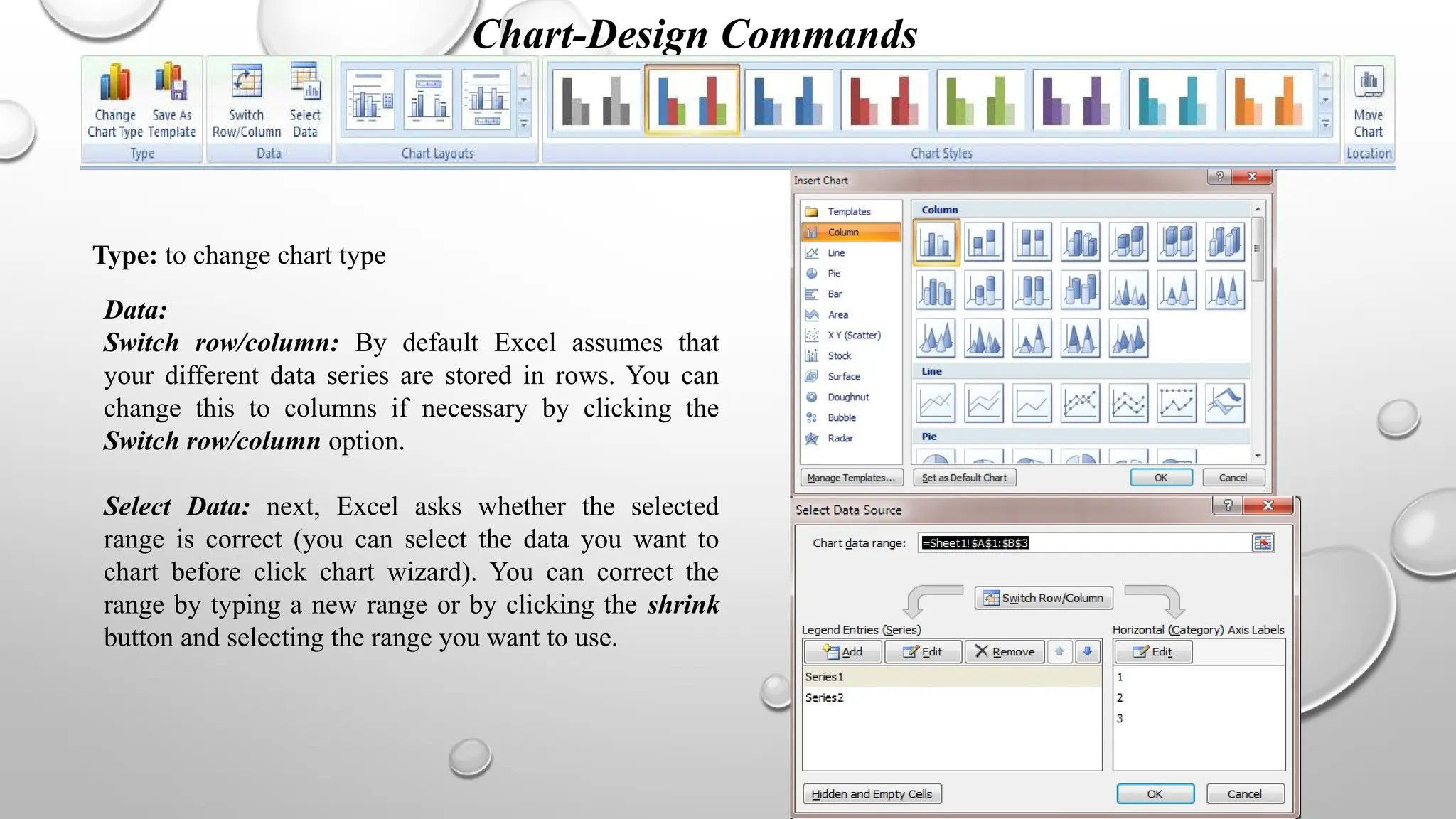
Microsoft Excel is an electronic spreadsheet program used for storing, manipulating, and charting numeric data, commonly utilized by researchers for analyzing mathematical and statistical information. The document outlines key features and commands of Excel, including creating, saving, and modifying workbooks, data formatting, and chart creation tools. Additionally, it covers editing functions, cell formatting, and the use of various commands for efficient data management.