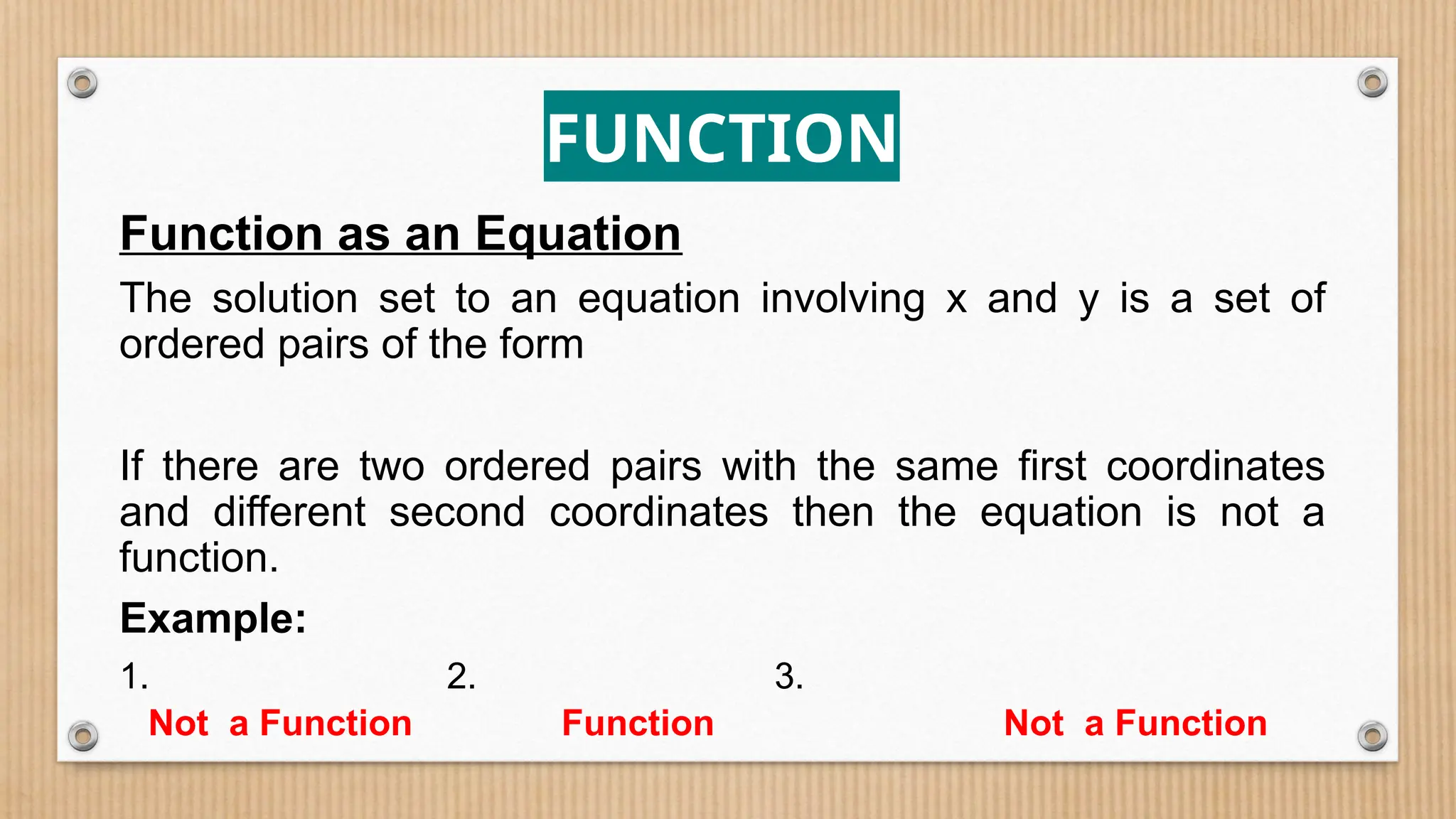
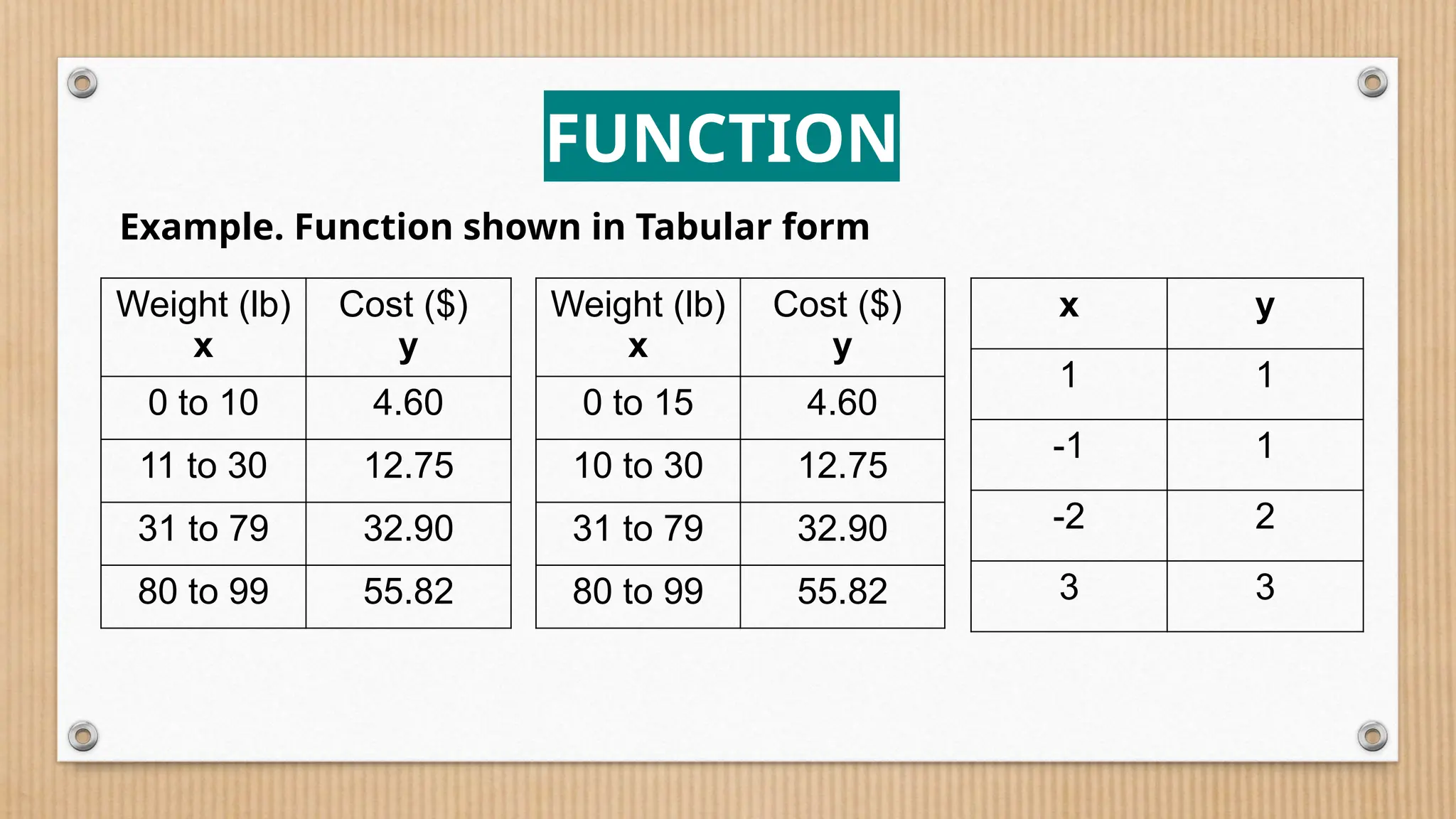
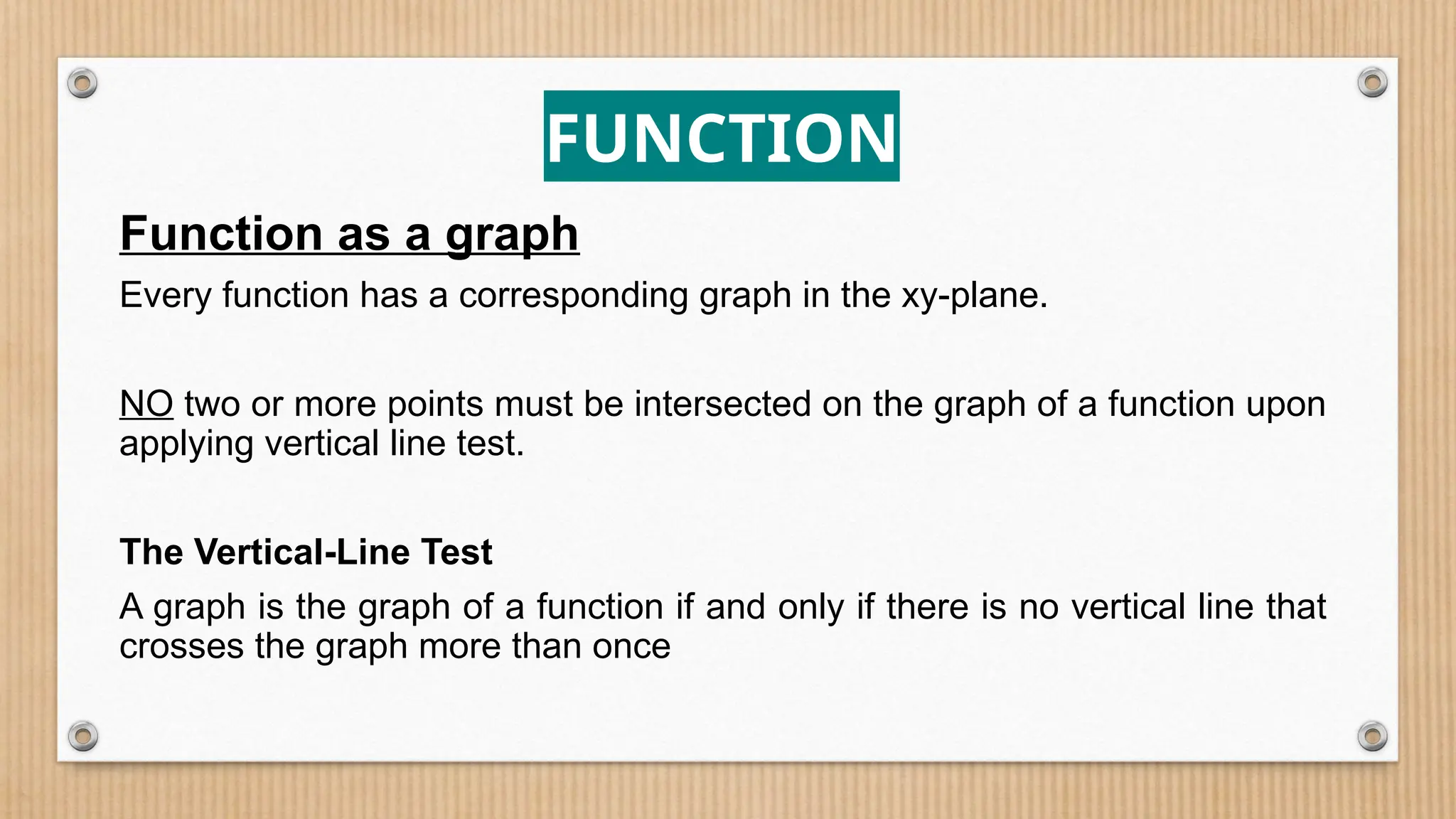
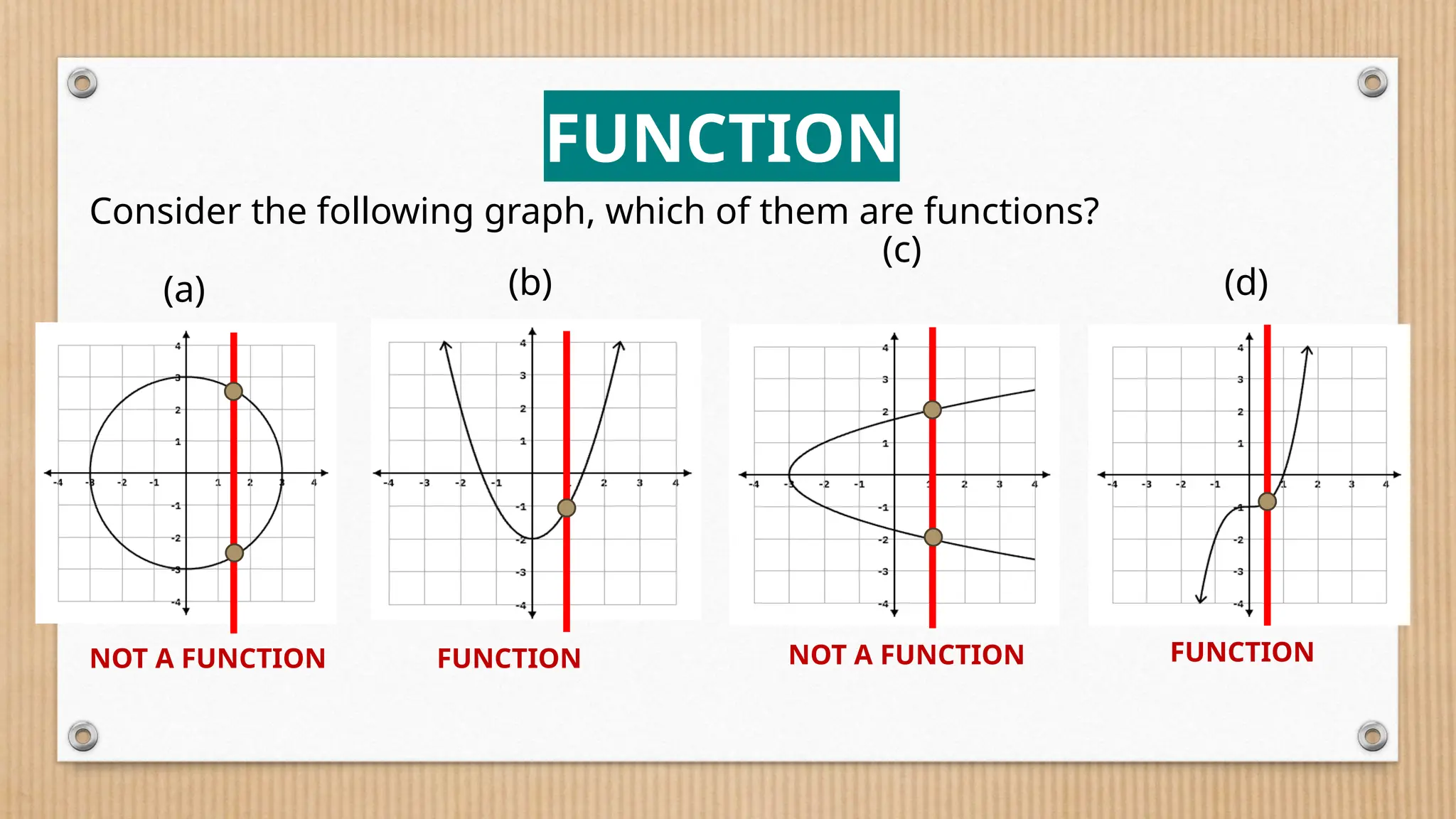
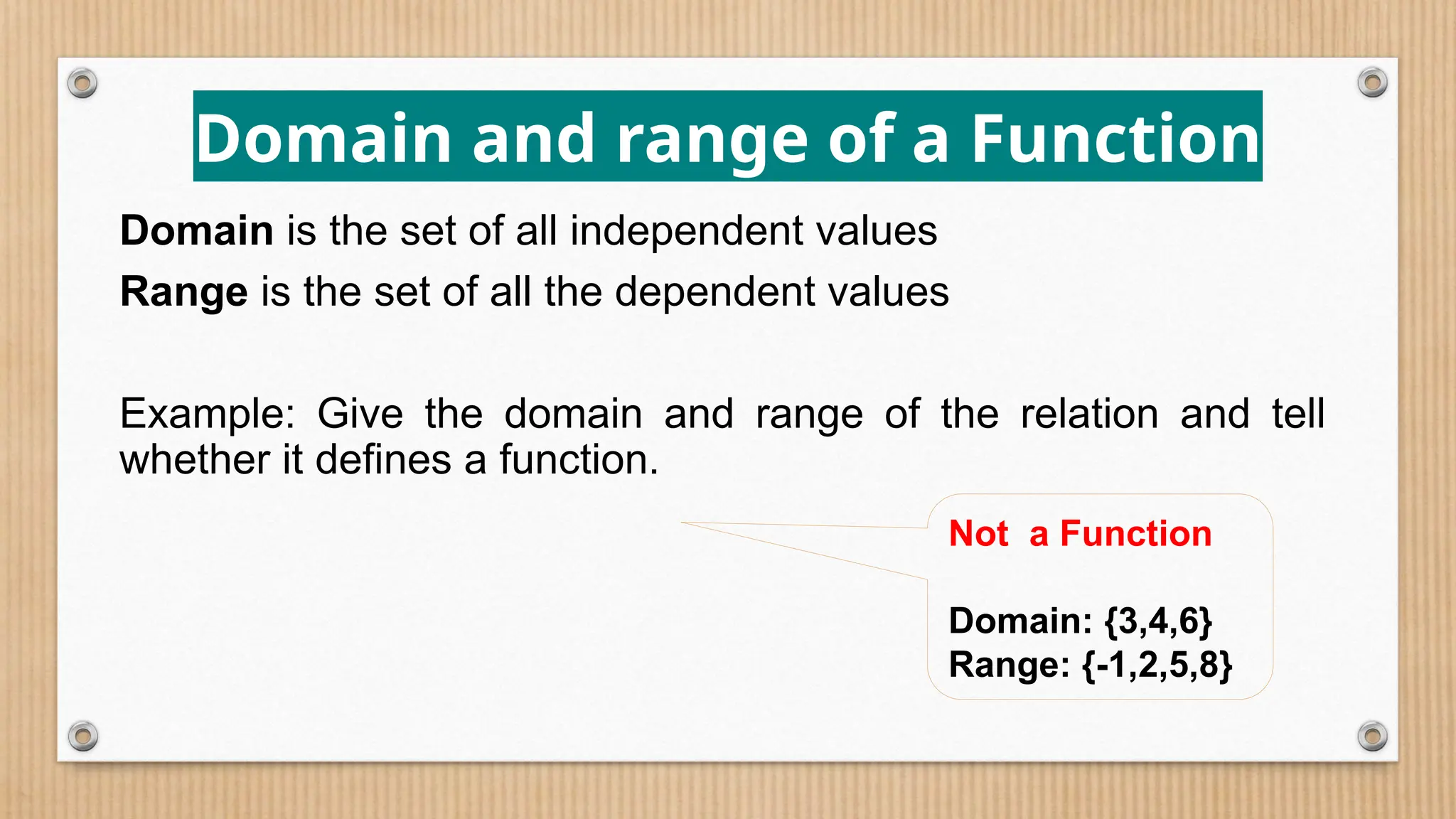
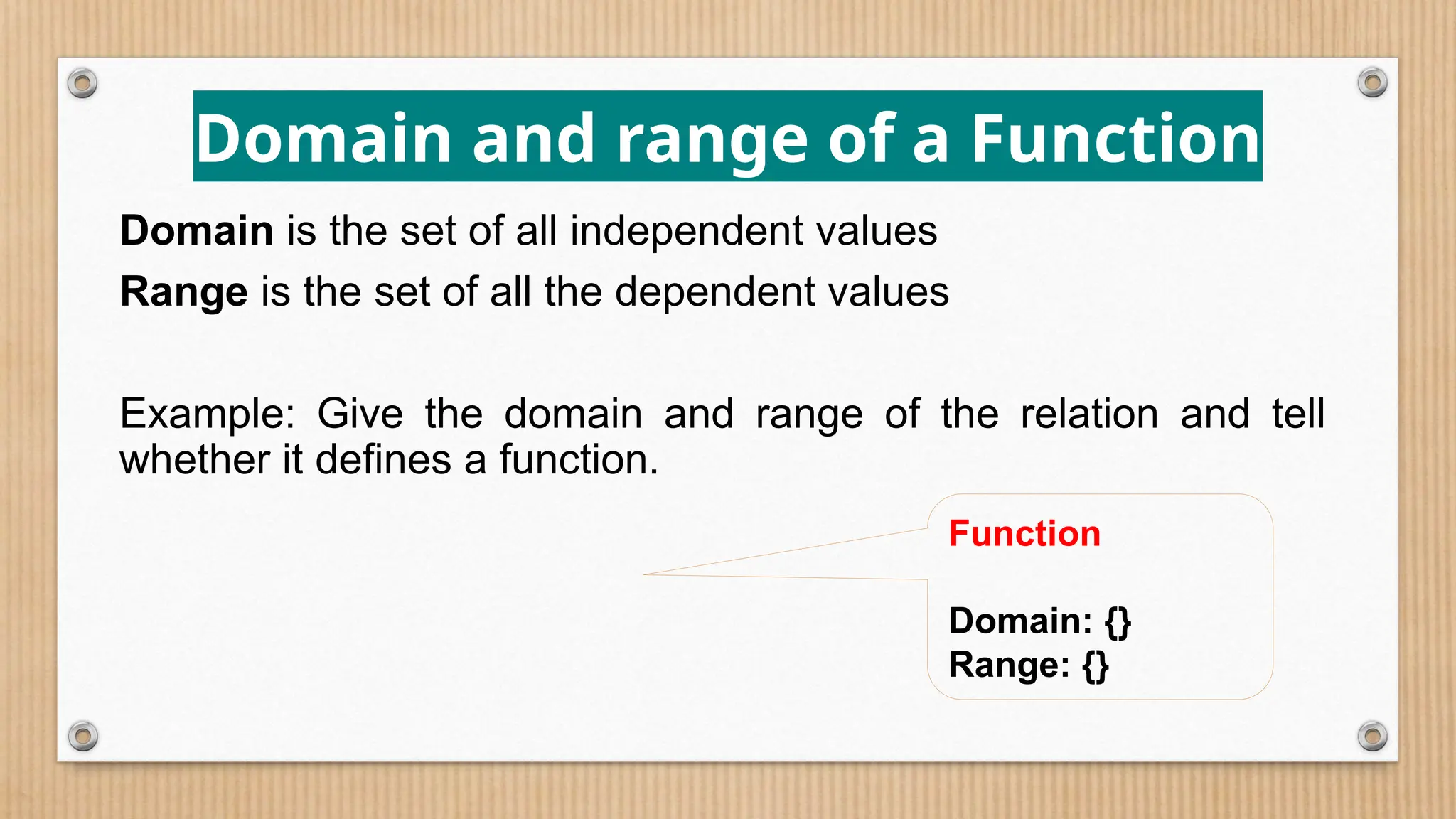
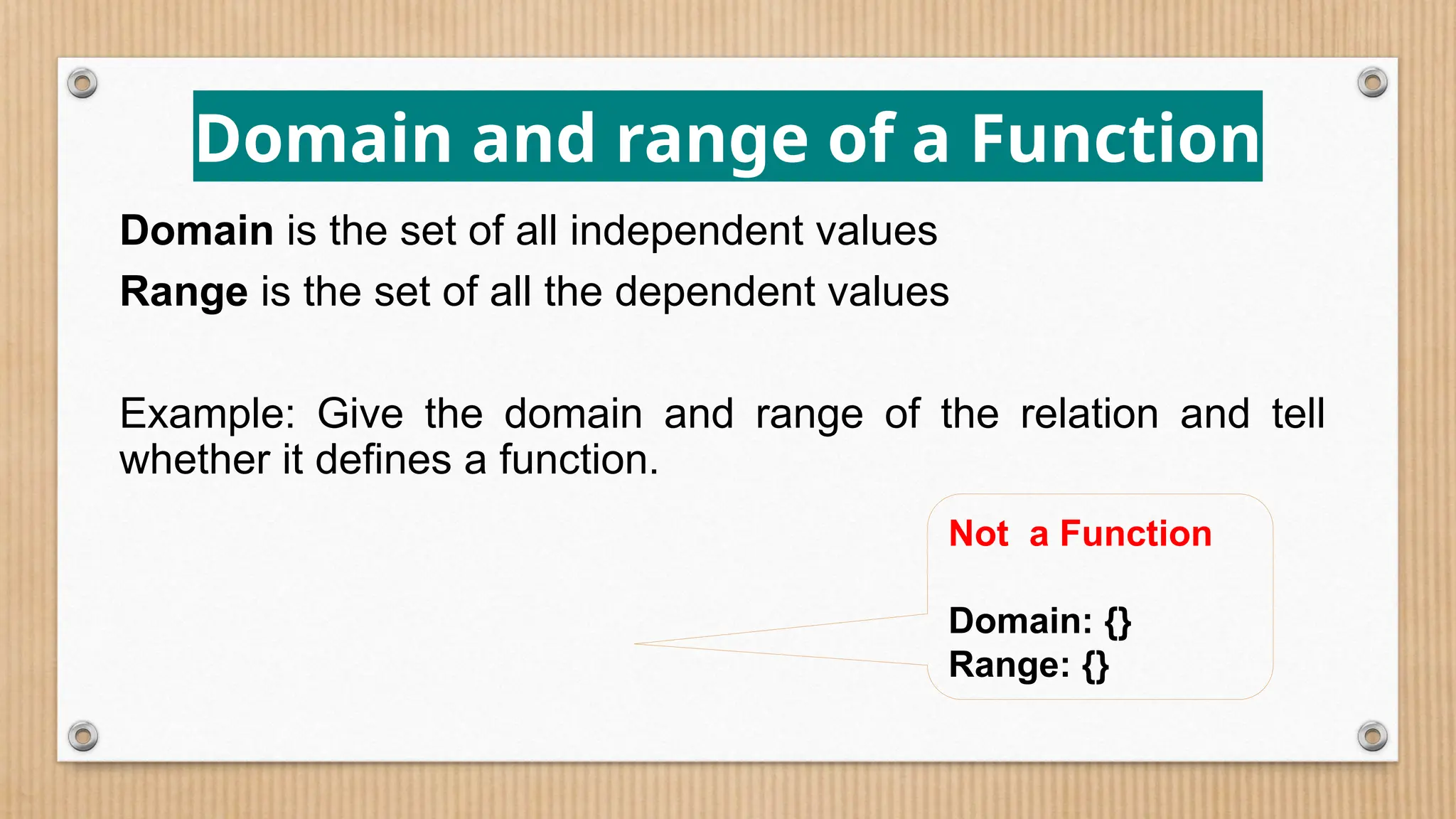
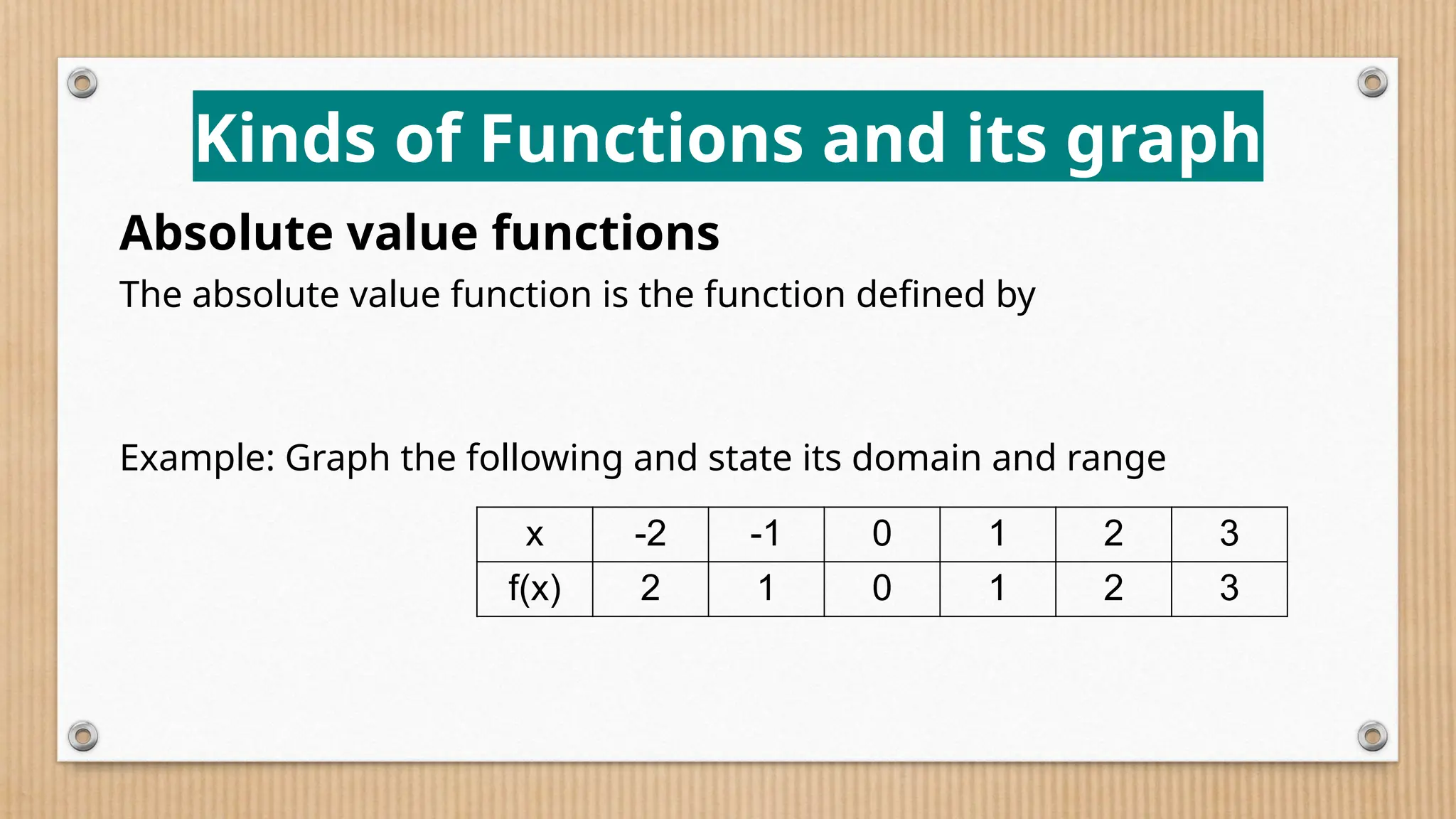
The document provides a comprehensive overview of functions, defining crucial components like domain, range, and types of functions including linear, absolute value, and quadratic functions. It explains the concept of functions as relations and describes how to determine if a relation is a function through examples and graphical representations. The document also emphasizes the importance of the vertical line test in identifying functions from their graphs.