The document provides a comprehensive guide on using Core Location and Map Kit for iPhone development, covering topics such as obtaining current location data, creating map interfaces, and handling various location technologies. It includes practical examples and code snippets for building applications that utilize location services, perform geocoding, and manage map annotations. Additionally, it discusses considerations when using third-party map providers and emphasizes adhering to their terms of service.









![Creating a CLLocationManager
locationManager = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init];
locationManager.delegate = self;
locationManager.desiredAccuracy =
kCLLocationAccuracyNearestTenMeters;
locationManager.distanceFilter = 10;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-11-2048.jpg)


![Delegate implementation
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager
didUpdateToLocation:(CLLocation *)newLocation
fromLocation:(CLLocation *)oldLocation {
! latLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%0.3f",
newLocation.coordinate.latitude];
! lngLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%0.3f",
newLocation.coordinate.longitude];
! altitudeLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%0.3f",
newLocation.altitude];
! courseLabel.text = (newLocation.course >= 0.0) ?
! ! [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%0.3f", newLocation.course] :
! ! @"N/A";
! speedLabel.text = (newLocation.speed >= 0.0) ?
! ! [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%0.3f", newLocation.speed]:
! ! @"N/A";
! timestampLabel.text = [timestampFormatter stringFromDate:newLocation.timestamp];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-14-2048.jpg)

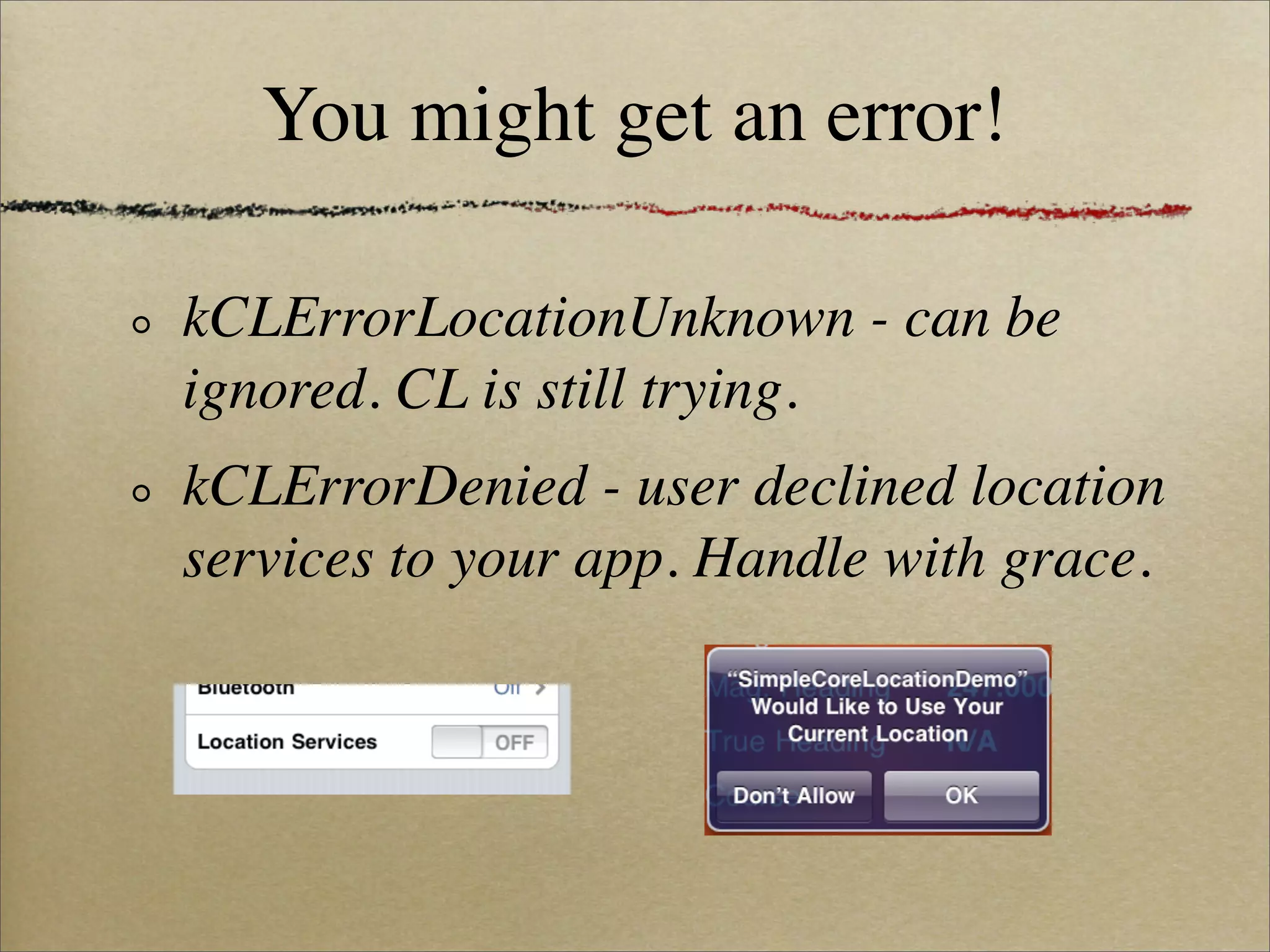
![Handling delegate errors
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager
didFailWithError:(NSError *)error {
! if ([error code] == kCLErrorDenied) {
! ! userDeclinedLocationPrivilegesHUD.hidden = NO;
! }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-17-2048.jpg)
![Other CL points of interest
-[CLLocation getDistanceFrom:]
CLHeading properties:
magneticHeading
trueHeading](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-19-2048.jpg)









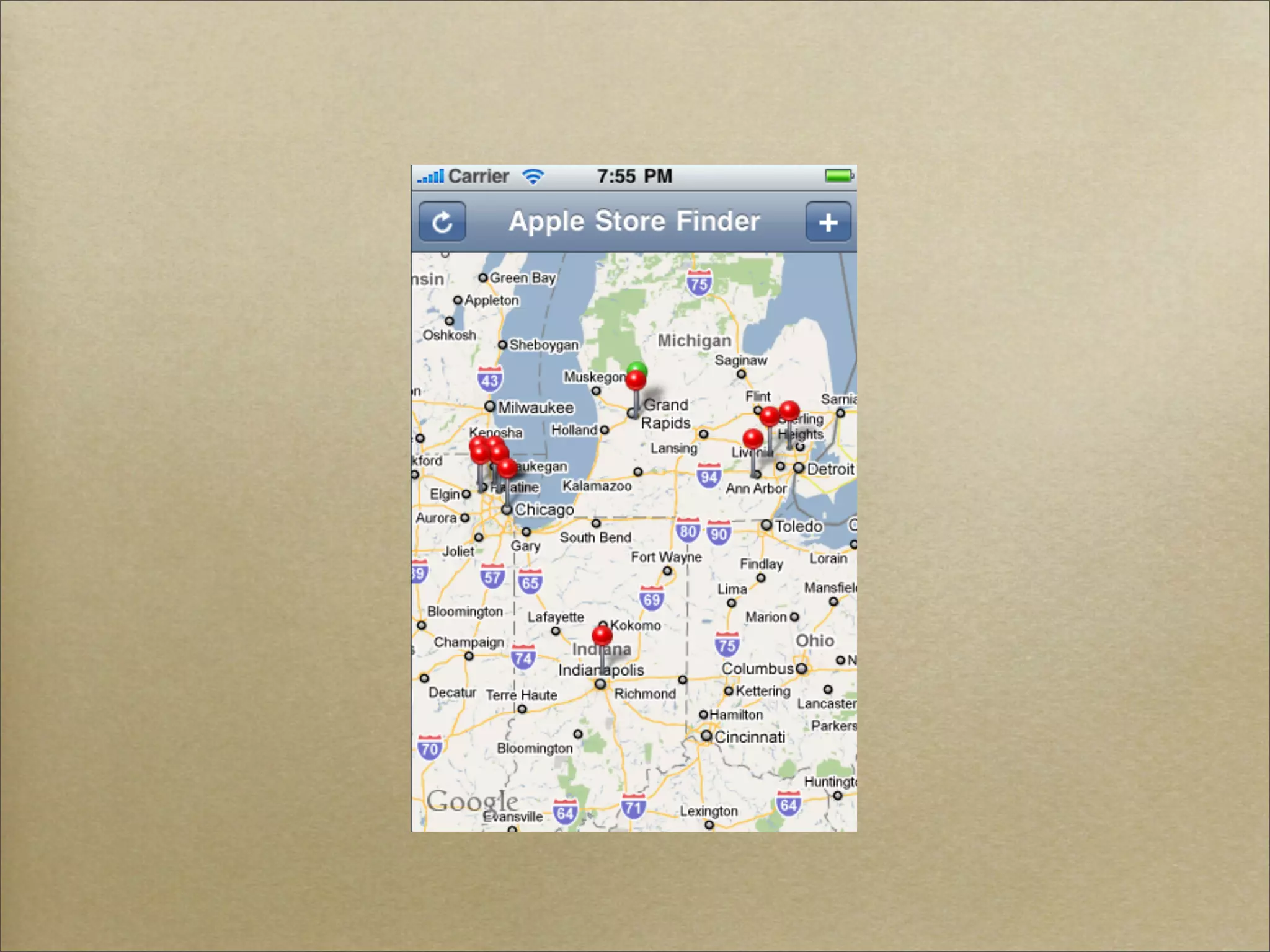
![Adding annotations to map
-(IBAction) plusButtonTapped: (id) sender {
! // todo: bounds check
! NSDictionary *poiDict = [poiArray objectAtIndex:nextPoiIndex++];
! CLLocationCoordinate2D poiCoordinate;
! poiCoordinate.latitude = [[poiDict valueForKey:@"latitude"] doubleValue];
! poiCoordinate.longitude = [[poiDict valueForKey:@"longitude"] doubleValue];
! MyMapAnnotation *poiAnnotation = [[MyMapAnnotation alloc]
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! initWithCoordinate:poiCoordinate
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! title:[poiDict valueForKey:@"name"]
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! color:MKPinAnnotationColorRed! ];
! [mapView addAnnotation:poiAnnotation];
! [self adjustMapZoom];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-29-2048.jpg)
![Zooming MKMapView, pt. 1
-(void) adjustMapZoom {
! if ([mapView.annotations count] == 1) {
! ! // if only one point, zoom smartly around it
! ! [mapView setRegion:MKCoordinateRegionMakeWithDistance
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ([[mapView.annotations objectAtIndex:0] coordinate],
! ! ! ! ! ! ! 2000, // 2 km lat span
! ! ! ! ! ! ! 2000) // 2 km lng span
! ! ! ! animated: YES];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-30-2048.jpg)
![Zooming MKMapView, pt. 2
! else {
! ! // find a region encompassing all annotations
! ! CLLocationDegrees maxLatitude = -180;
! ! CLLocationDegrees minLatitude = 180;
! ! CLLocationDegrees maxLongitude = -180;
! ! CLLocationDegrees minLongitude = 180;
! !
! ! for (id<MKAnnotation> annotation in [mapView annotations]) {
! ! ! if ([annotation coordinate].latitude > maxLatitude) {
! ! ! ! maxLatitude = [annotation coordinate].latitude;
! ! ! }
! ! ! if ([annotation coordinate].latitude < minLatitude) {
! ! ! ! minLatitude = [annotation coordinate].latitude;
! ! ! }
! ! ! if ([annotation coordinate].longitude > maxLongitude) {
! ! ! ! maxLongitude = [annotation coordinate].longitude;
! ! ! }
! ! ! if ([annotation coordinate].longitude < minLongitude) {
! ! ! ! minLongitude = [annotation coordinate].longitude;
! ! ! }
! ! }
! !
! ! CLLocation *maxPoint = [[[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:maxLatitude
! ! ! ! ! ! longitude:maxLongitude] autorelease];
! ! CLLocation *minPoint = [[[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:minLatitude
! ! ! ! ! ! longitude:minLongitude] autorelease];
! ! CLLocationDistance distance = [maxPoint getDistanceFrom:minPoint];
! ! MKCoordinateRegion region;
! ! region.center.latitude = (maxPoint.coordinate.latitude + minPoint.coordinate.latitude) / 2.0;
! ! region.center.longitude = (maxPoint.coordinate.longitude + minPoint.coordinate.longitude) / 2.0;
! ! region.span.latitudeDelta = (distance / METERS_PER_DEGREE_LATITUDE) * 1.10;
! ! region.span.longitudeDelta = 0.0;
! ! MKCoordinateRegion adjustedRegion = [mapView regionThatFits:region];
! ! [mapView setRegion:adjustedRegion animated:YES];
! }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-31-2048.jpg)

![Providing views for annotations
- (MKAnnotationView *)mapView:(MKMapView *)mapViewP
viewForAnnotation:(id <MKAnnotation>)annotation {
! MKPinAnnotationView *pinView = (MKPinAnnotationView*)
[mapViewP dequeueReusableAnnotationViewWithIdentifier:@"pin"];
! if (pinView) {
! ! pinView.annotation = annotation;
! } else {
! ! pinView = [[[MKPinAnnotationView alloc]
initWithAnnotation:annotation reuseIdentifier:@"pin"]
autorelease];
! }
!
! pinView.animatesDrop = YES;
! pinView.canShowCallout = YES;
! if ([annotation isKindOfClass:[MyMapAnnotation class]]) {
! ! MyMapAnnotation *myAnnotation = (MyMapAnnotation*) annotation;
! ! pinView.pinColor = myAnnotation.color;
! }
! return pinView;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-33-2048.jpg)




















![Send web service request
#define MQ_DIRECTIONS_REQUEST_FORMAT
@"http://www.mapquestapi.com/directions/v1/route?key=%@&from=%f,%f&to=%@,
%@&outFormat=xml"
-(void) addDrivingDistanceToPoiDict: (NSMutableDictionary*) poiDict {
! NSString *poiLat = [poiDict valueForKey: @"latitude"];
! NSString *poiLng = [poiDict valueForKey: @"longitude"];
! NSString *mqURLS = [NSString stringWithFormat:MQ_DIRECTIONS_REQUEST_FORMAT,
! ! ! ! ! ! MQ_APP_KEY,
! ! ! ! ! ! homeCoordinate.latitude, homeCoordinate.longitude,
! ! ! ! ! ! poiLat, poiLng];
! NSURL *mqURL = [NSURL URLWithString:mqURLS];
! NSURLRequest *mqURLRequest = [NSURLRequest requestWithURL:mqURL];
! NSURLResponse *mqURLResponse = nil;
! NSError *mqURLError = nil;
! NSData *routeData = [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:mqURLRequest
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! returningResponse:&mqURLResponse
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! error:&mqURLError];
! MQDirectionsParser *parser = [[MQDirectionsParser alloc] initWithXML:routeData];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-57-2048.jpg)

![Create an XML parser
-(id) initWithXML: (NSData*) xml {
! if (self = [super init]) {
! ! routeDict = [[NSMutableDictionary alloc] init];
! ! routeDistance = -1;
! !
! ! NSXMLParser *parser = [[NSXMLParser alloc] initWithData:xml];
! ! [parser setDelegate:self];
! ! [parser parse];
! }
! return self;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-59-2048.jpg)
![Notice interesting tags
- (void) parser:(NSXMLParser *)parser didStartElement:(NSString *)elementName
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! namespaceURI:(NSString *)namespaceURI
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! qualifiedName:(NSString *)qualifiedName
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! attributes:(NSDictionary *)attributeDict {
! // only care about "distance" and "narrative" tags
! if ([elementName isEqualToString:@"distance"] |
! ! [elementName isEqualToString:@"narrative"]) {
! ! currentCharacters = [[NSMutableString alloc] init];
! }
! if ([elementName isEqualToString:@"legs"]) {
! ! narrativeArray = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
! }
}
- (void)parser:(NSXMLParser *)parser foundCharacters:(NSString *)string {
! [currentCharacters appendString:string];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-60-2048.jpg)
![Retrieve values from tags
- (void)parser:(NSXMLParser *)parser didEndElement:(NSString *)elementName
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! namespaceURI:(NSString *)namespaceURI
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! qualifiedName:(NSString *)qName {
! if ([elementName isEqualToString:@"distance"]) {
! ! // if this is first distance, not part of a leg, then it's the whole trip
! ! if (routeDistance == -1) {
! ! ! routeDistance = [currentCharacters doubleValue];
! ! }
! }
! if ([elementName isEqualToString:@"narrative"]) {
! ! [narrativeArray addObject:currentCharacters];
! }
!
! [currentCharacters release];
! currentCharacters = nil;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-61-2048.jpg)



![Interesting MapQuest TOS
01. (d) Traffic information shall not be (i) used for Real-Time Navigation; (ii)
used in conjunction with in-car or stand alone portable navigation devices; or (iii)
used for the primary purpose of Your page or application. For the purposes of
this Agreement, “Real-Time Navigation” shall mean using a sensor to determine
location and providing contemporaneous turn-by-turn directions as the user
moves through the route.
RESTRICTIONS. Except as expressly authorized by MapQuest, You shall not:
▪ derive results from the Service based on sensor-derived location data or information or input
in the form of coordinate data, provided that a coordinate location or location derived by a
single sensor, including without limitation a sensor incorporated into, connected to or in
communication with any mobile device or system, may be used solely as an origin or
destination in deriving a map or direction;
▪ […]
▪ use the Service with products, systems or applications capable of navigation, positioning,
tracking or routing of a movable asset;
http://developer.mapquest.com/web/info/terms-of-
use-free](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-66-2048.jpg)

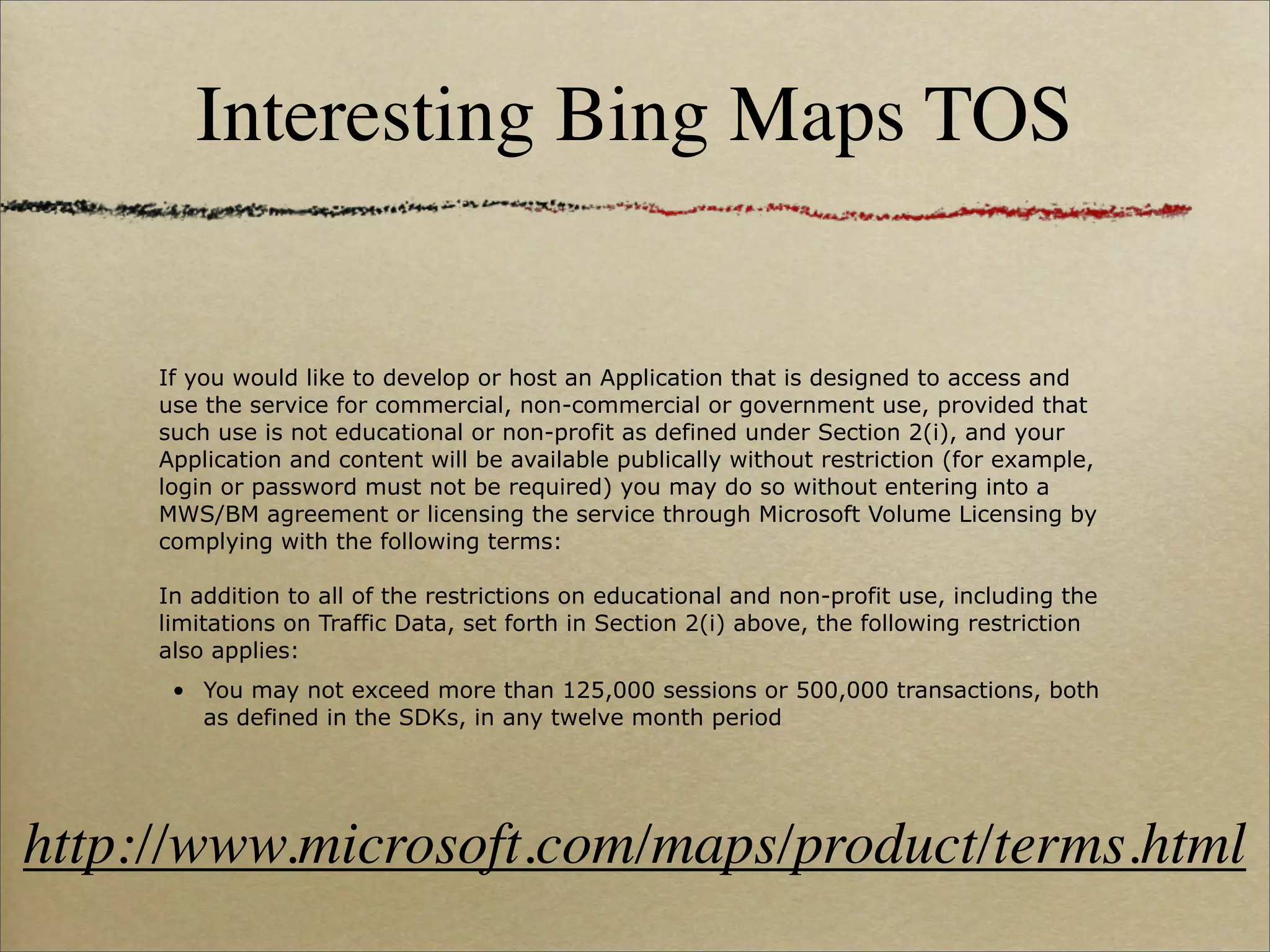
![More Bing Maps TOS
Restrictions on your use: We do have some restrictions on your use of the service. You may
not:
• copy, store, archive, or create a database of the content, except that geocodes may be
stored locally only for use with your Applications;
• exceed 50,000 geocoding transactions or requests in any 24 hour period;
• download more than 250 points of interest at any one time;
• use the service for business asset tracking, fleet management, or dispatch;
• present or alert an end user to individual maneuvers of a route in any way that is
synchronized with the end-user’s sensor-based position along the route, (e.g. “real-time”
navigation);
• […]
• integrate the Bing Maps Platform or any of its content with any other mapping platform;
http://www.microsoft.com/maps/product/terms.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-69-2048.jpg)






![Thanks!
http://www.subfurther.com/blog
@invalidname
invalidname [at] gmail [dot] com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adamson-bringing-your-own-maps-100426004904-phpapp02/75/Core-Location-and-Map-Kit-Bringing-Your-Own-Maps-Voices-That-Matter-iPhone-2010-77-2048.jpg)