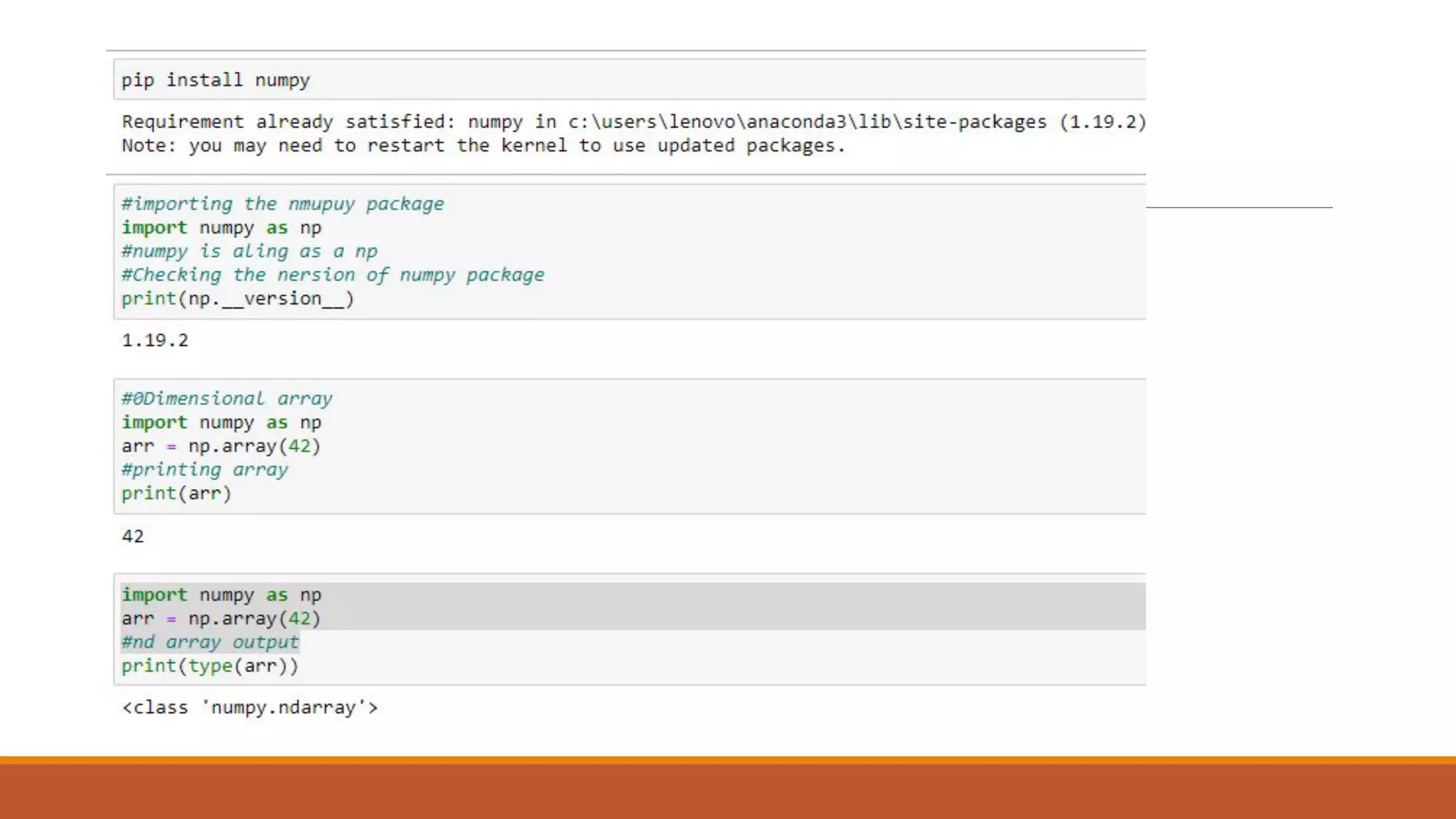
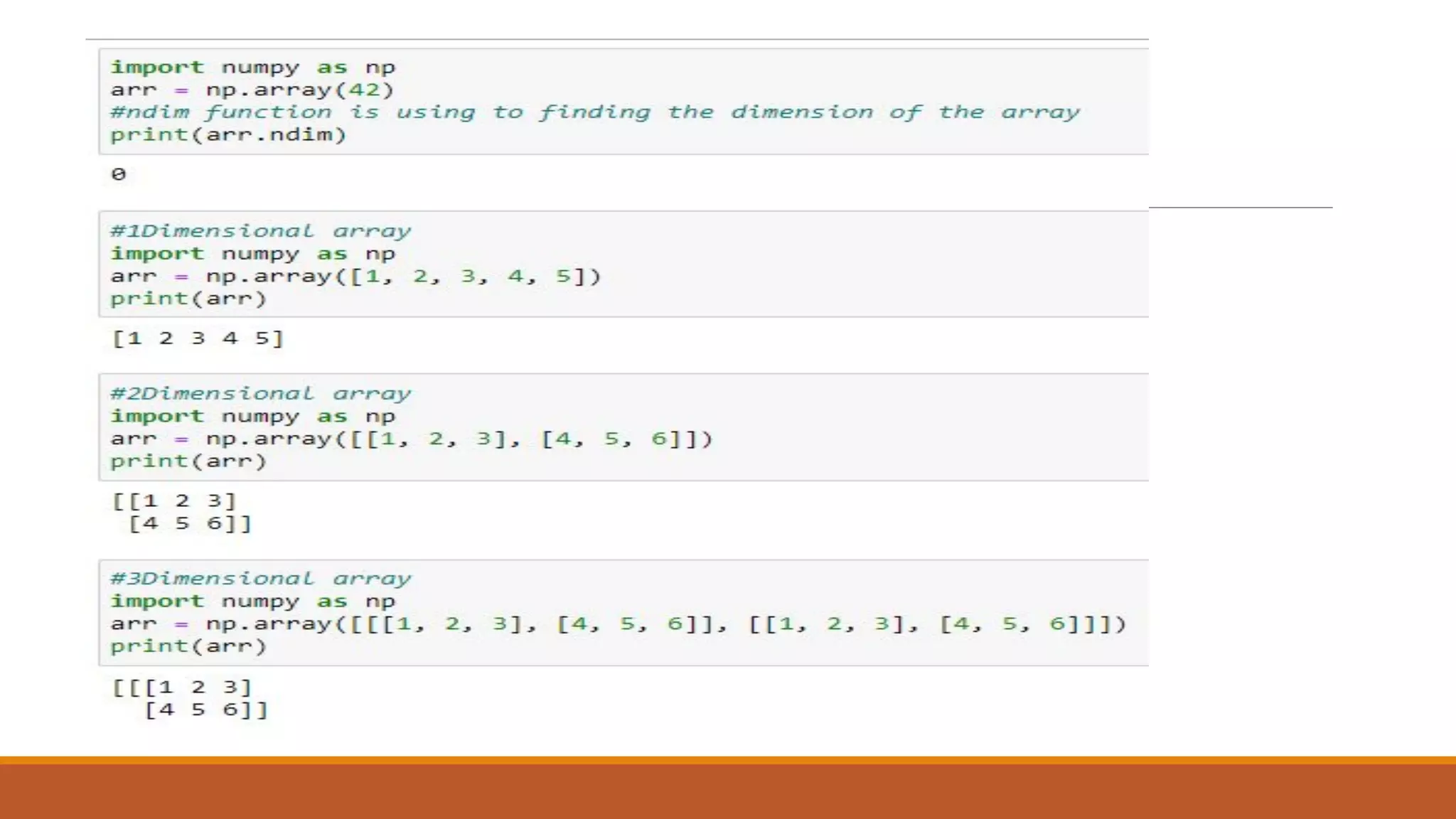
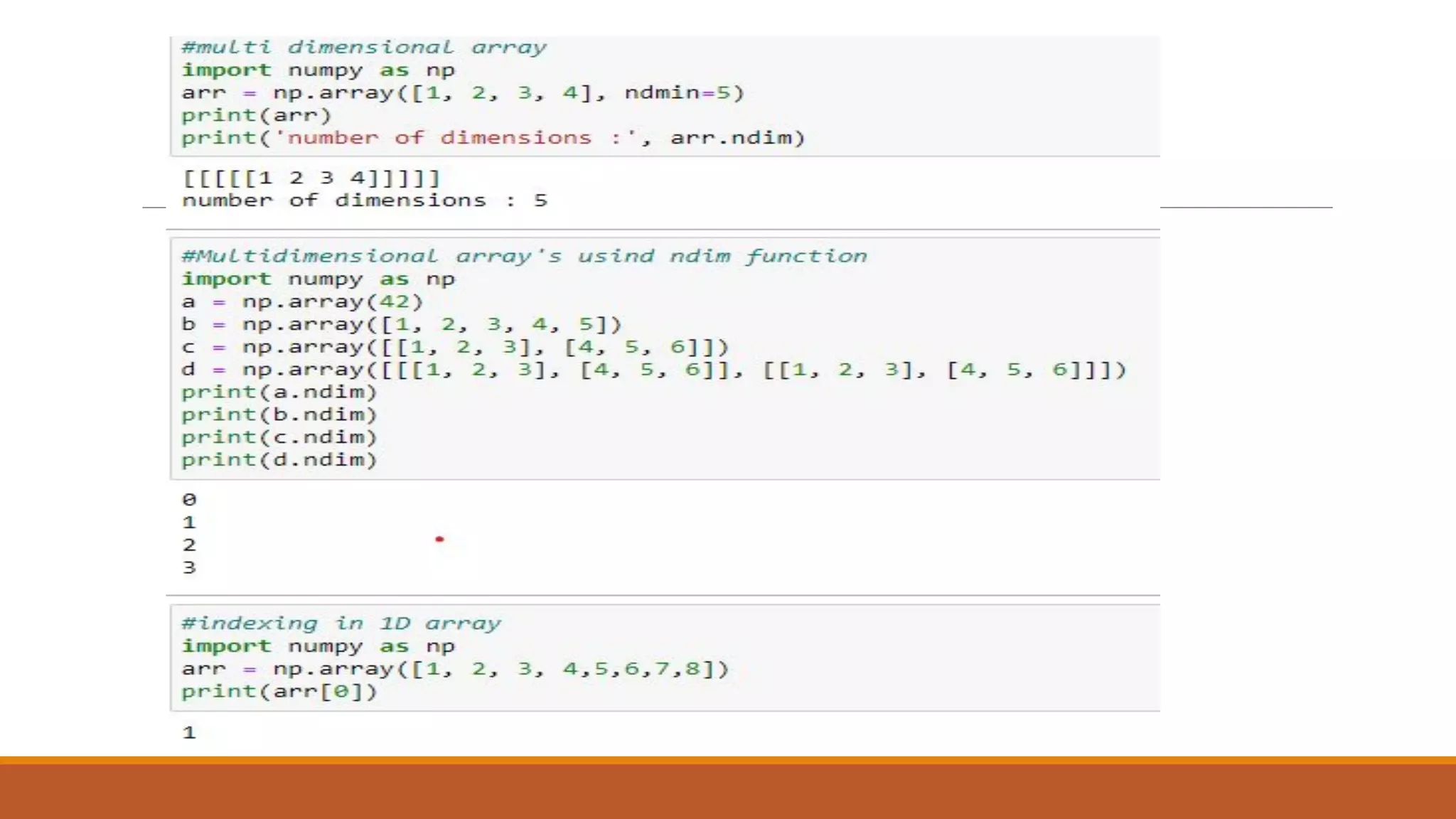
NumPy is a numerical Python package that provides a multidimensional array object and tools to work with these arrays. It allows fast operations on arrays of numeric data and is used for scientific computing and mathematics. NumPy arrays can be initialized from nested Python lists and accessed using square brackets. Common operations include indexing, slicing, reshaping arrays, and performing mathematical operations element-wise or on whole arrays.



![#Import numpy package
import numpy as np
a= np.array([12,78,456,90,10])
print(a)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acfrogaabslw3zcrlj0i-to2fpkpa9qthydknnla3vk282mnxalgja7apkd15-tw9ztqi98dah5iok2eyngvyyu1dotwkxfvjaor-221020082358-88281bc8/75/ACFrOgAabSLW3ZCRLJ0i-To_2fPk_pA9QThyDKNNlA3VK282MnXaLGJa7APKD15-TW9zT_QI98dAH5IOk2eYNgVYyu1dOTWKxFVJaorlNte-3MHkwdssPWXbcgzAPTlMuiQ4_Kkpyf9vaMj3LhdE-pdf-4-2048.jpg)

![Updating array values
We can update the array values with the help of index.
a=[1,2,3,4,5]
a[1]=44
print(a)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acfrogaabslw3zcrlj0i-to2fpkpa9qthydknnla3vk282mnxalgja7apkd15-tw9ztqi98dah5iok2eyngvyyu1dotwkxfvjaor-221020082358-88281bc8/75/ACFrOgAabSLW3ZCRLJ0i-To_2fPk_pA9QThyDKNNlA3VK282MnXaLGJa7APKD15-TW9zT_QI98dAH5IOk2eYNgVYyu1dOTWKxFVJaorlNte-3MHkwdssPWXbcgzAPTlMuiQ4_Kkpyf9vaMj3LhdE-pdf-10-2048.jpg)
![reshape()
#To declare rows and columns of an array
import numpy as np
a=np.arange(15).reshape(5,3)
print(a)
#Accessing Array elements
a[1,1]
a[3,2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acfrogaabslw3zcrlj0i-to2fpkpa9qthydknnla3vk282mnxalgja7apkd15-tw9ztqi98dah5iok2eyngvyyu1dotwkxfvjaor-221020082358-88281bc8/75/ACFrOgAabSLW3ZCRLJ0i-To_2fPk_pA9QThyDKNNlA3VK282MnXaLGJa7APKD15-TW9zT_QI98dAH5IOk2eYNgVYyu1dOTWKxFVJaorlNte-3MHkwdssPWXbcgzAPTlMuiQ4_Kkpyf9vaMj3LhdE-pdf-11-2048.jpg)
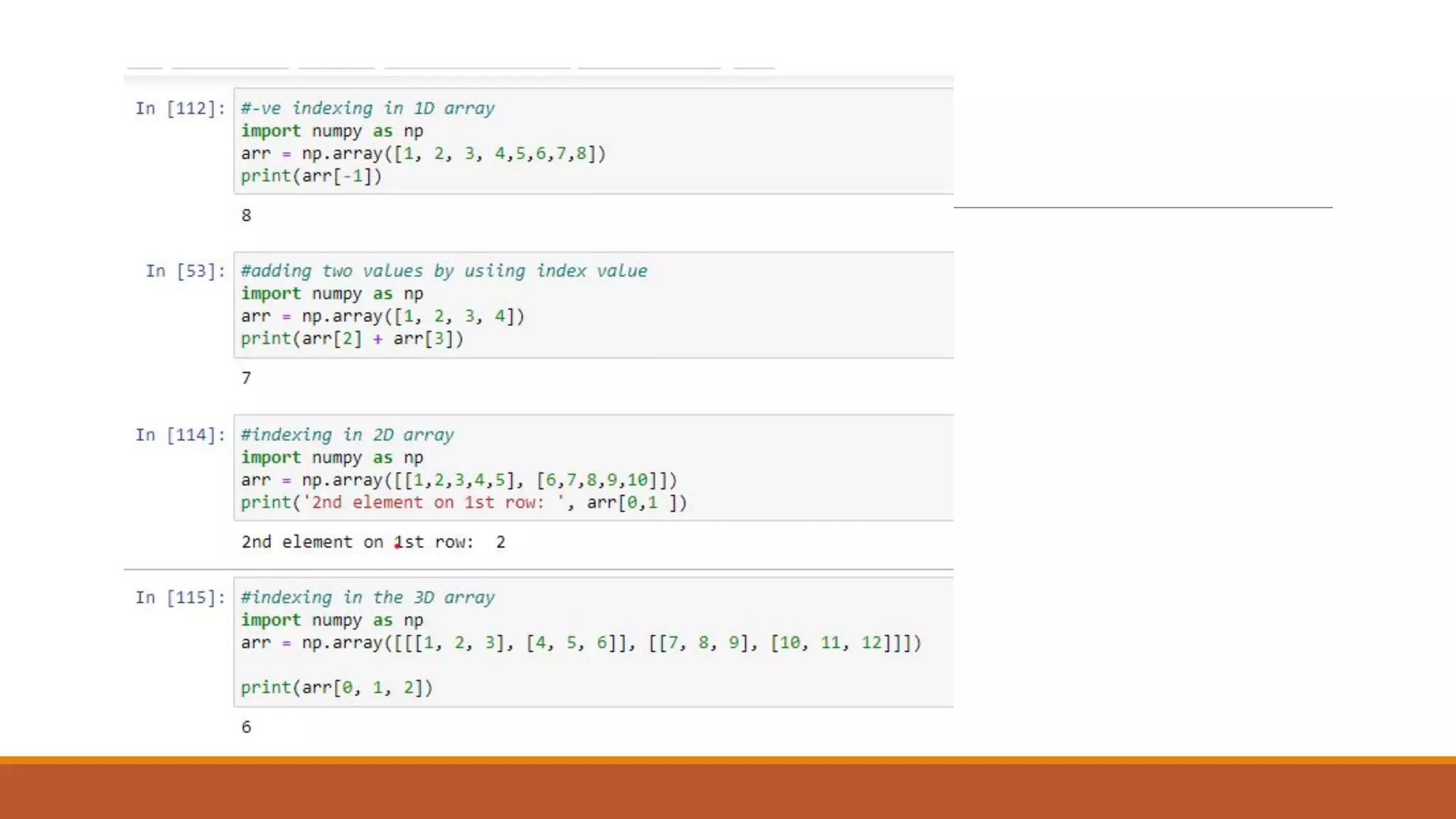
![Indexing
import numpy as np
# NumPy array with elements from 1 to 9
x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
# Index values can be negative.
arr = x[ np. array([1, 3, -3])]
print(arr)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acfrogaabslw3zcrlj0i-to2fpkpa9qthydknnla3vk282mnxalgja7apkd15-tw9ztqi98dah5iok2eyngvyyu1dotwkxfvjaor-221020082358-88281bc8/75/ACFrOgAabSLW3ZCRLJ0i-To_2fPk_pA9QThyDKNNlA3VK282MnXaLGJa7APKD15-TW9zT_QI98dAH5IOk2eYNgVYyu1dOTWKxFVJaorlNte-3MHkwdssPWXbcgzAPTlMuiQ4_Kkpyf9vaMj3LhdE-pdf-12-2048.jpg)
![Boolean Indexing
This indexing has some boolean expression as the index. Those elements are
returned which satisfy that Boolean expression. It is used for filtering the desired
element values
import numpy as np
a = np.array([10, 40, 80, 50, 100])
print(a[a>50])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acfrogaabslw3zcrlj0i-to2fpkpa9qthydknnla3vk282mnxalgja7apkd15-tw9ztqi98dah5iok2eyngvyyu1dotwkxfvjaor-221020082358-88281bc8/75/ACFrOgAabSLW3ZCRLJ0i-To_2fPk_pA9QThyDKNNlA3VK282MnXaLGJa7APKD15-TW9zT_QI98dAH5IOk2eYNgVYyu1dOTWKxFVJaorlNte-3MHkwdssPWXbcgzAPTlMuiQ4_Kkpyf9vaMj3LhdE-pdf-13-2048.jpg)
![Slicing
import numpy as np
# Arrange elements from 0 to 19
a = np.arange(20)
print("n Array is:n ",a)
# a[ start:stop:step]
print("n a[-8:17:1] = ",a[-8:17:1])
# The : operator means all elements till the end.
print("n a[10:] = ",a[10:])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acfrogaabslw3zcrlj0i-to2fpkpa9qthydknnla3vk282mnxalgja7apkd15-tw9ztqi98dah5iok2eyngvyyu1dotwkxfvjaor-221020082358-88281bc8/75/ACFrOgAabSLW3ZCRLJ0i-To_2fPk_pA9QThyDKNNlA3VK282MnXaLGJa7APKD15-TW9zT_QI98dAH5IOk2eYNgVYyu1dOTWKxFVJaorlNte-3MHkwdssPWXbcgzAPTlMuiQ4_Kkpyf9vaMj3LhdE-pdf-14-2048.jpg)
![Basic operations on single array
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1, 2, 5, 3])
# add 1 to every element
print ("Adding 1 to every element:", a+1)
# subtract 3 from each element
print ("Subtracting 3 from each element:", a-3)
# multiply each element by 10
print ("Multiplying each element by 10:", a*10)
# square each element
print ("Squaring each element:", a**2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acfrogaabslw3zcrlj0i-to2fpkpa9qthydknnla3vk282mnxalgja7apkd15-tw9ztqi98dah5iok2eyngvyyu1dotwkxfvjaor-221020082358-88281bc8/75/ACFrOgAabSLW3ZCRLJ0i-To_2fPk_pA9QThyDKNNlA3VK282MnXaLGJa7APKD15-TW9zT_QI98dAH5IOk2eYNgVYyu1dOTWKxFVJaorlNte-3MHkwdssPWXbcgzAPTlMuiQ4_Kkpyf9vaMj3LhdE-pdf-15-2048.jpg)
![Unary operators in numpy
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 5, 6], [4, 7, 2], [3, 1, 9]])
# maximum element of array
print ("Largest element is:", arr.max())
#print first columns in the array
print ("Row-wise maximum elements:", arr.max(axis = 1))
# minimum element of array
print ("Column-wise minimum elements:", arr.min(axis = 0))
# sum of array elements
print ("Sum of all array elements: “,arr.sum())](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acfrogaabslw3zcrlj0i-to2fpkpa9qthydknnla3vk282mnxalgja7apkd15-tw9ztqi98dah5iok2eyngvyyu1dotwkxfvjaor-221020082358-88281bc8/75/ACFrOgAabSLW3ZCRLJ0i-To_2fPk_pA9QThyDKNNlA3VK282MnXaLGJa7APKD15-TW9zT_QI98dAH5IOk2eYNgVYyu1dOTWKxFVJaorlNte-3MHkwdssPWXbcgzAPTlMuiQ4_Kkpyf9vaMj3LhdE-pdf-16-2048.jpg)
![Binary operators in NumPy
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b = np.array([[4, 3],[2, 1]])
# add arrays
print ("Array sum:n", a + b)
# multiply arrays (element wise multiplication)
print ("Array multiplication:n", a*b)
# matrix multiplication
print ("Matrix multiplication:n", a.dot(b))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acfrogaabslw3zcrlj0i-to2fpkpa9qthydknnla3vk282mnxalgja7apkd15-tw9ztqi98dah5iok2eyngvyyu1dotwkxfvjaor-221020082358-88281bc8/75/ACFrOgAabSLW3ZCRLJ0i-To_2fPk_pA9QThyDKNNlA3VK282MnXaLGJa7APKD15-TW9zT_QI98dAH5IOk2eYNgVYyu1dOTWKxFVJaorlNte-3MHkwdssPWXbcgzAPTlMuiQ4_Kkpyf9vaMj3LhdE-pdf-17-2048.jpg)
