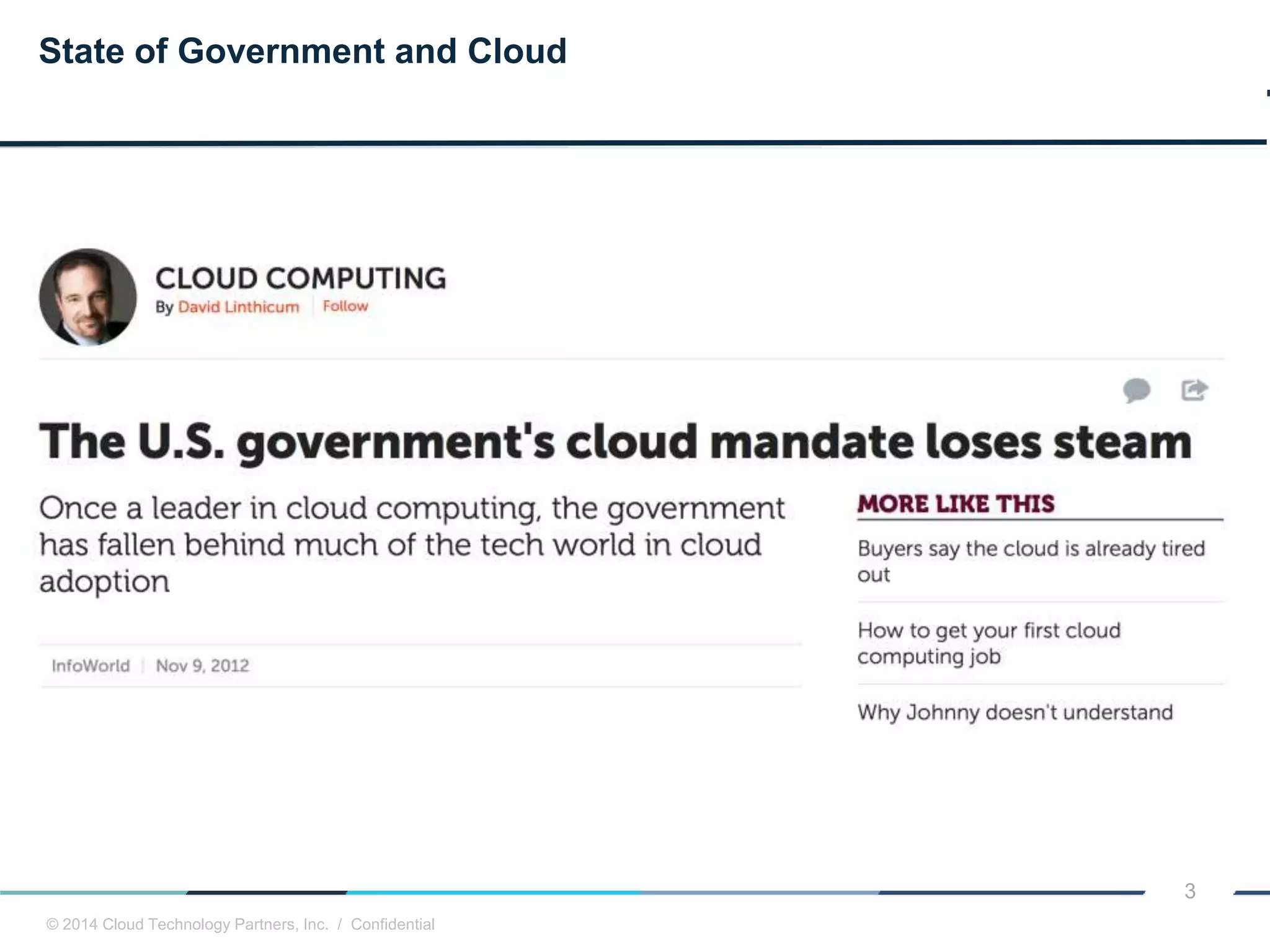
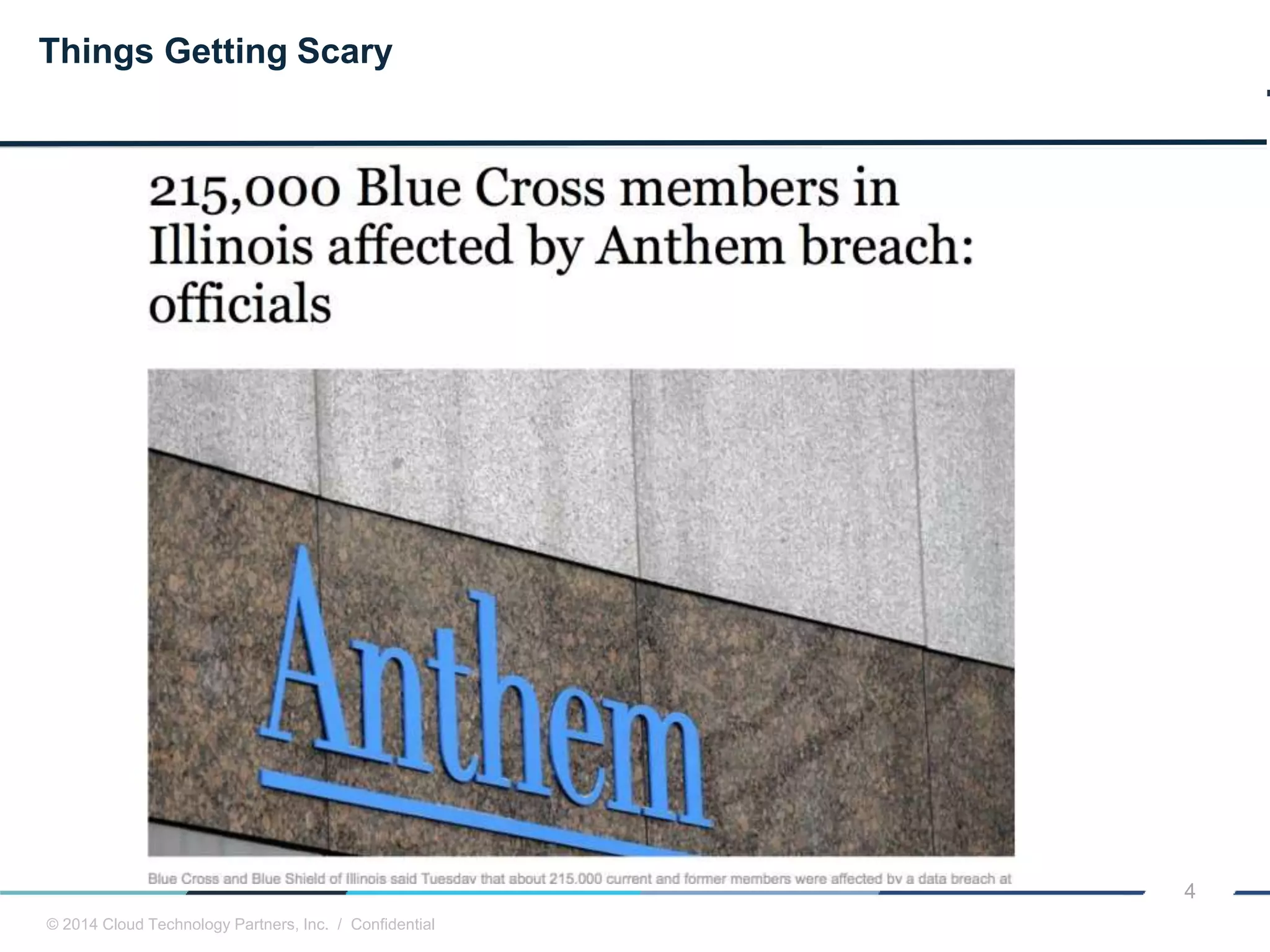
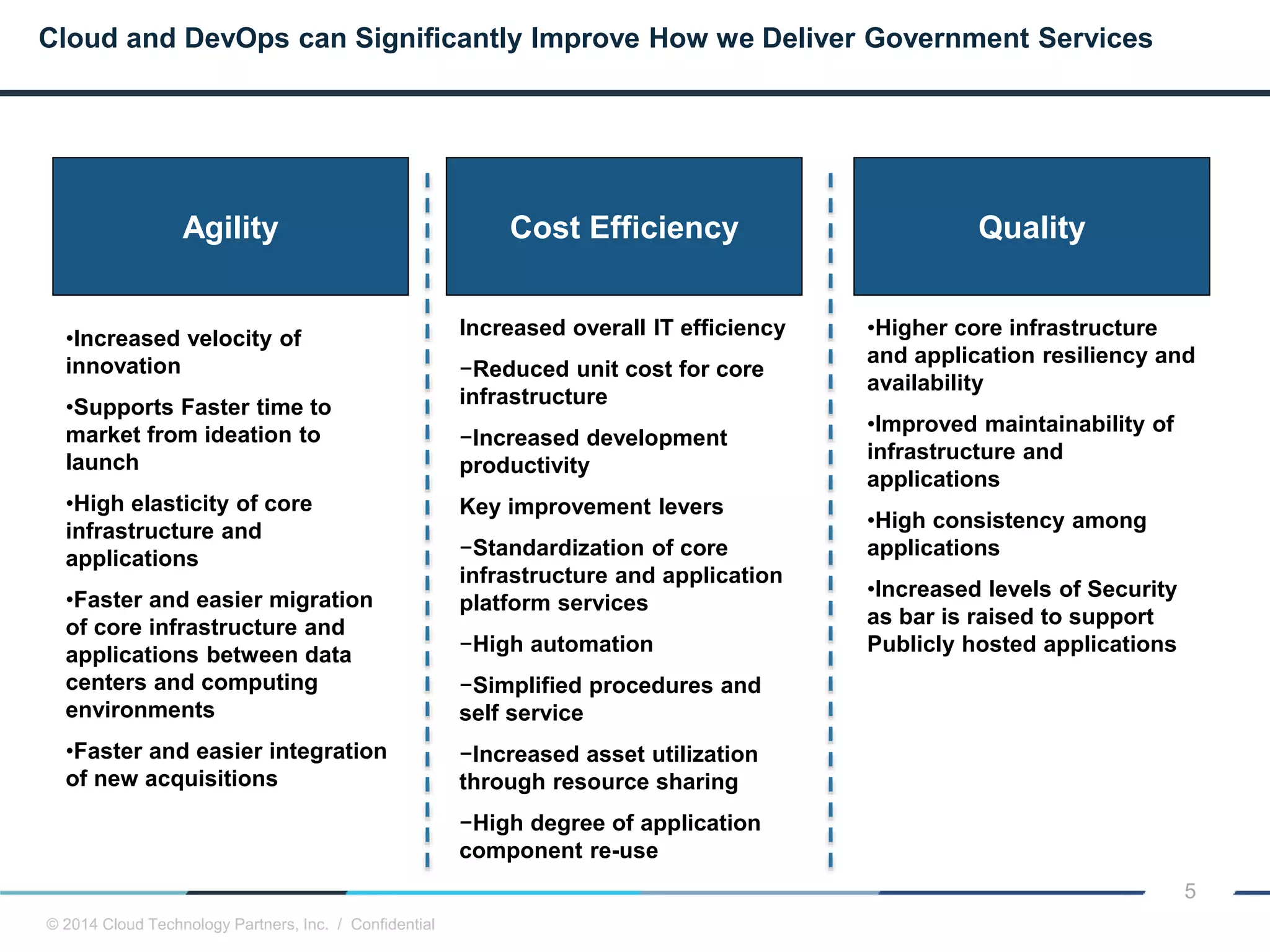
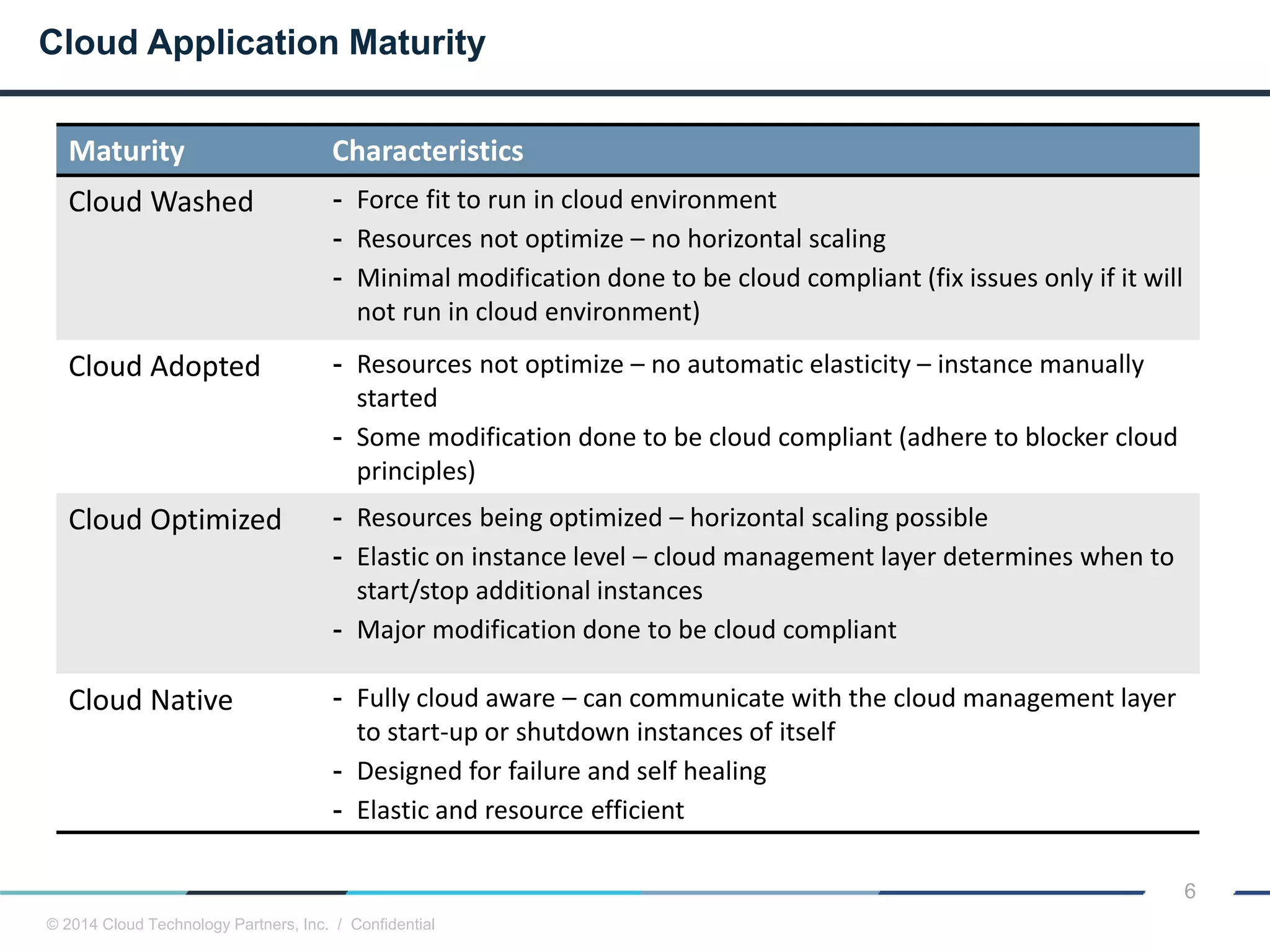
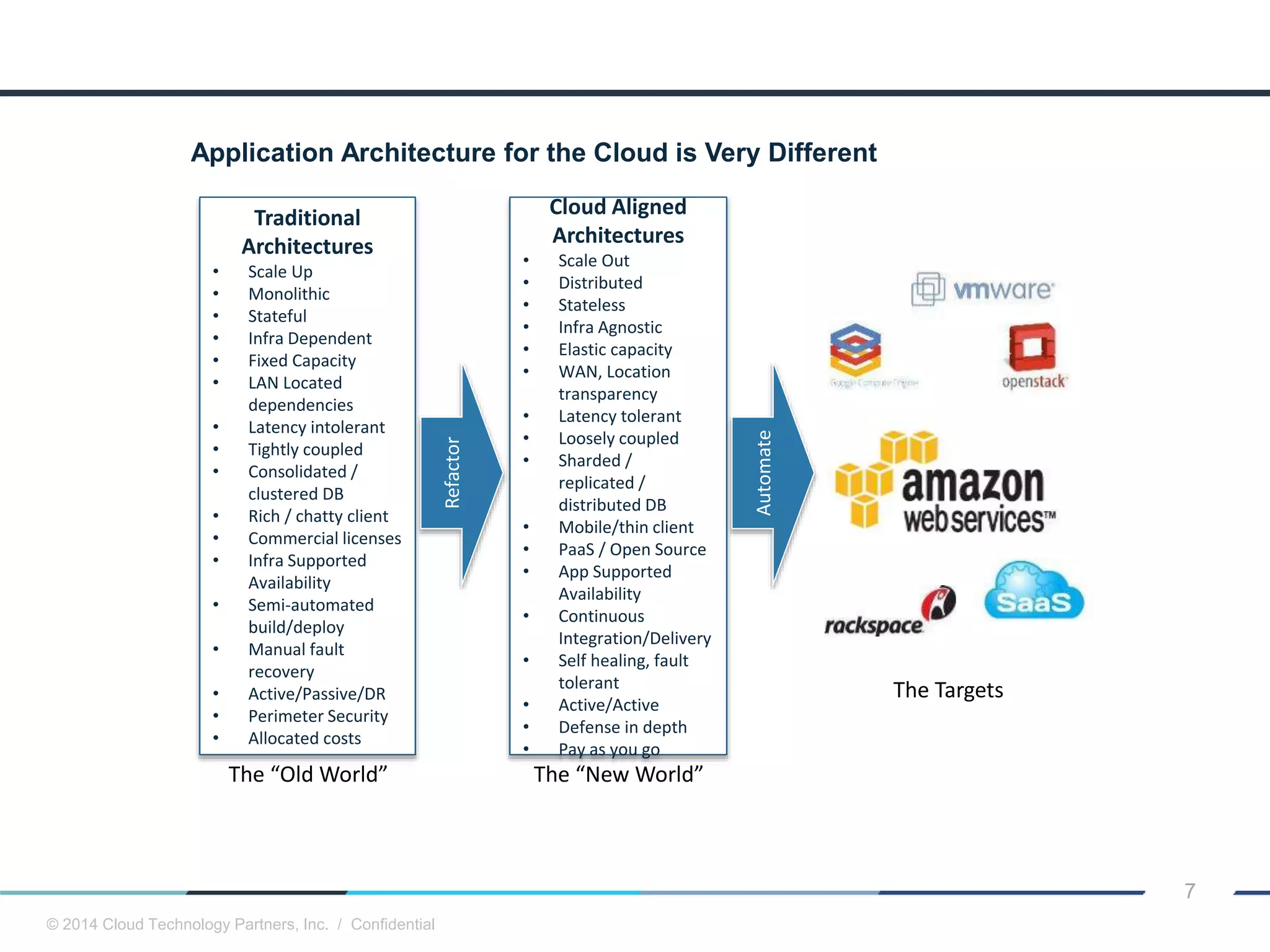
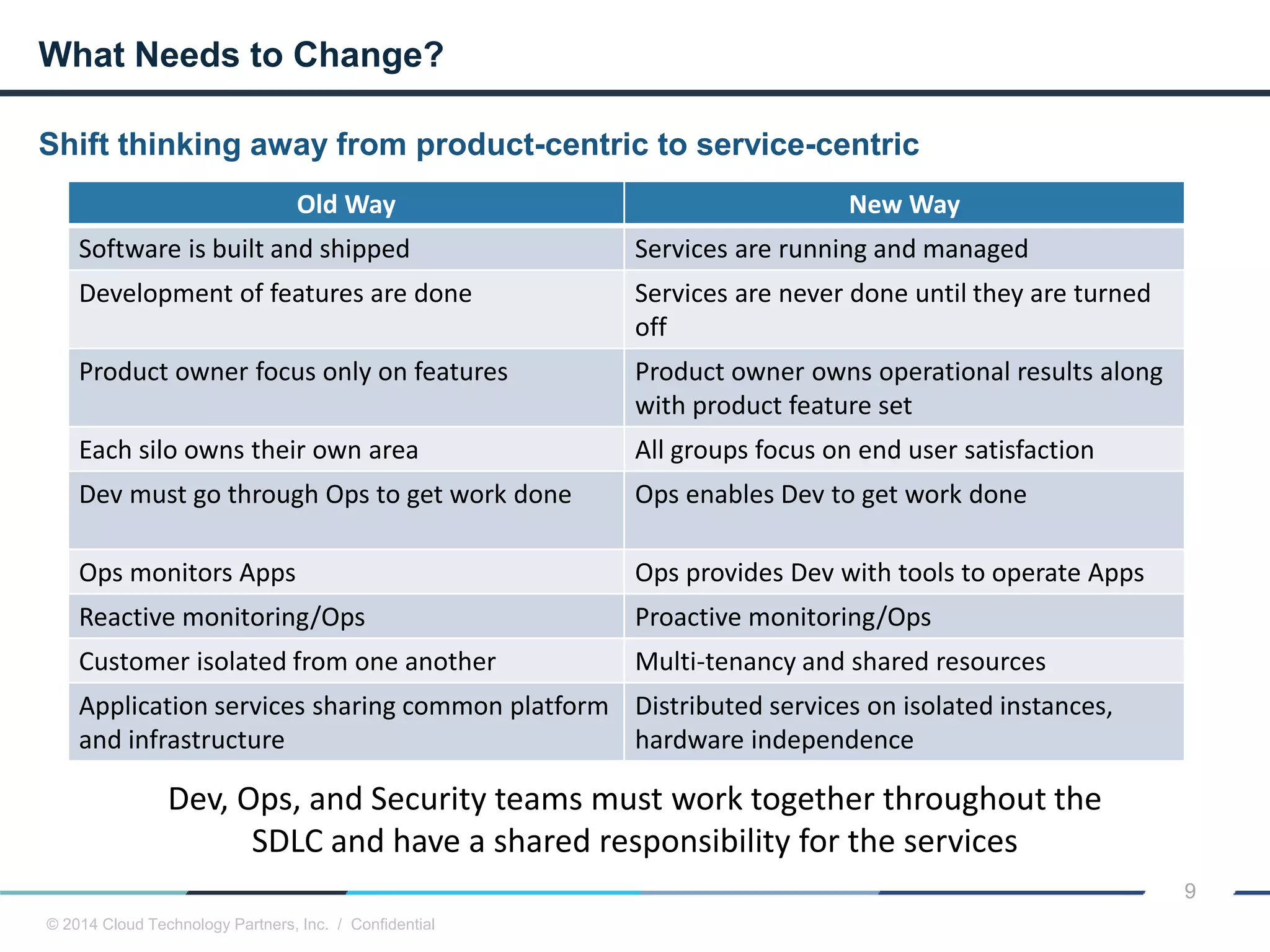
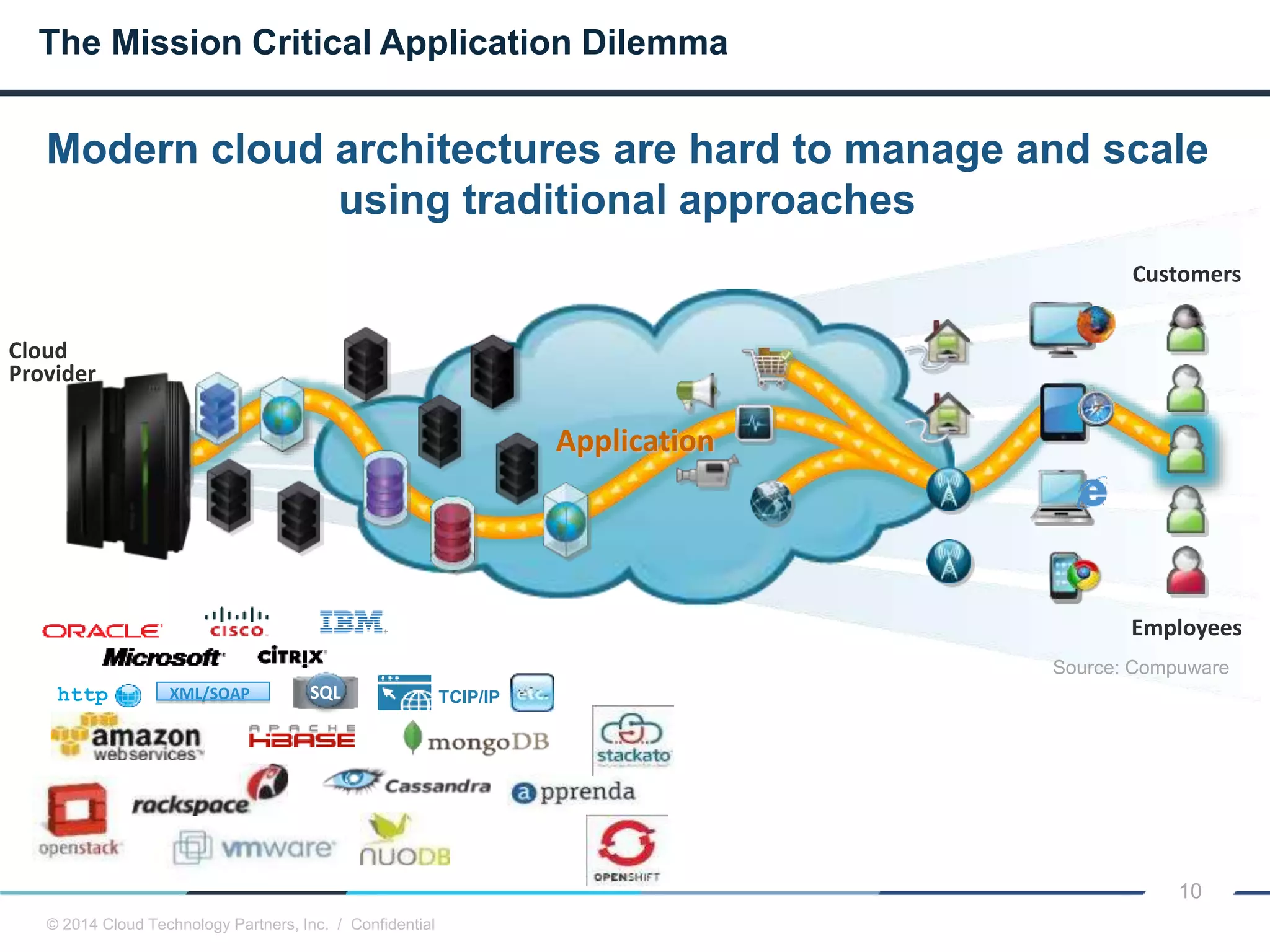
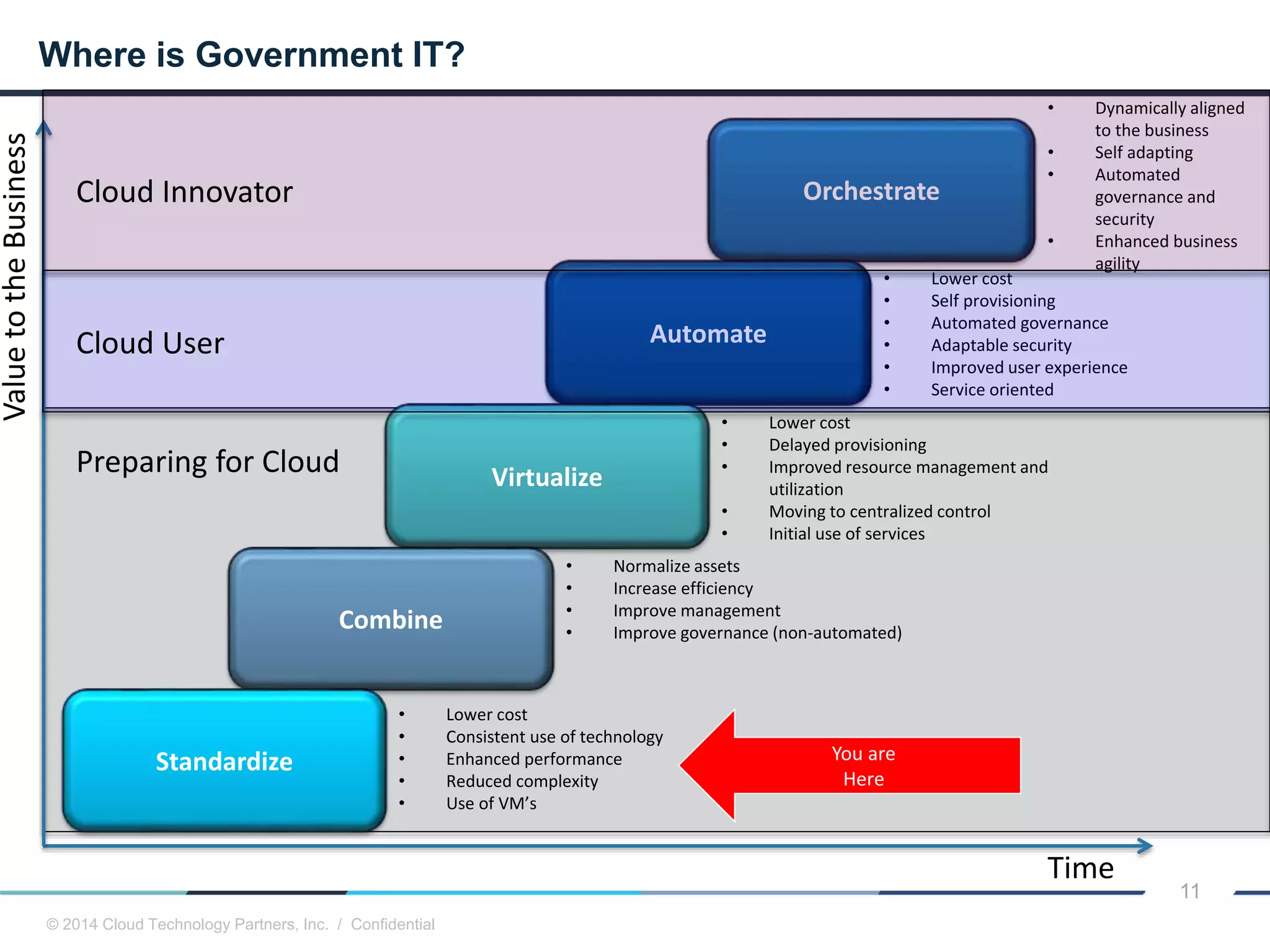
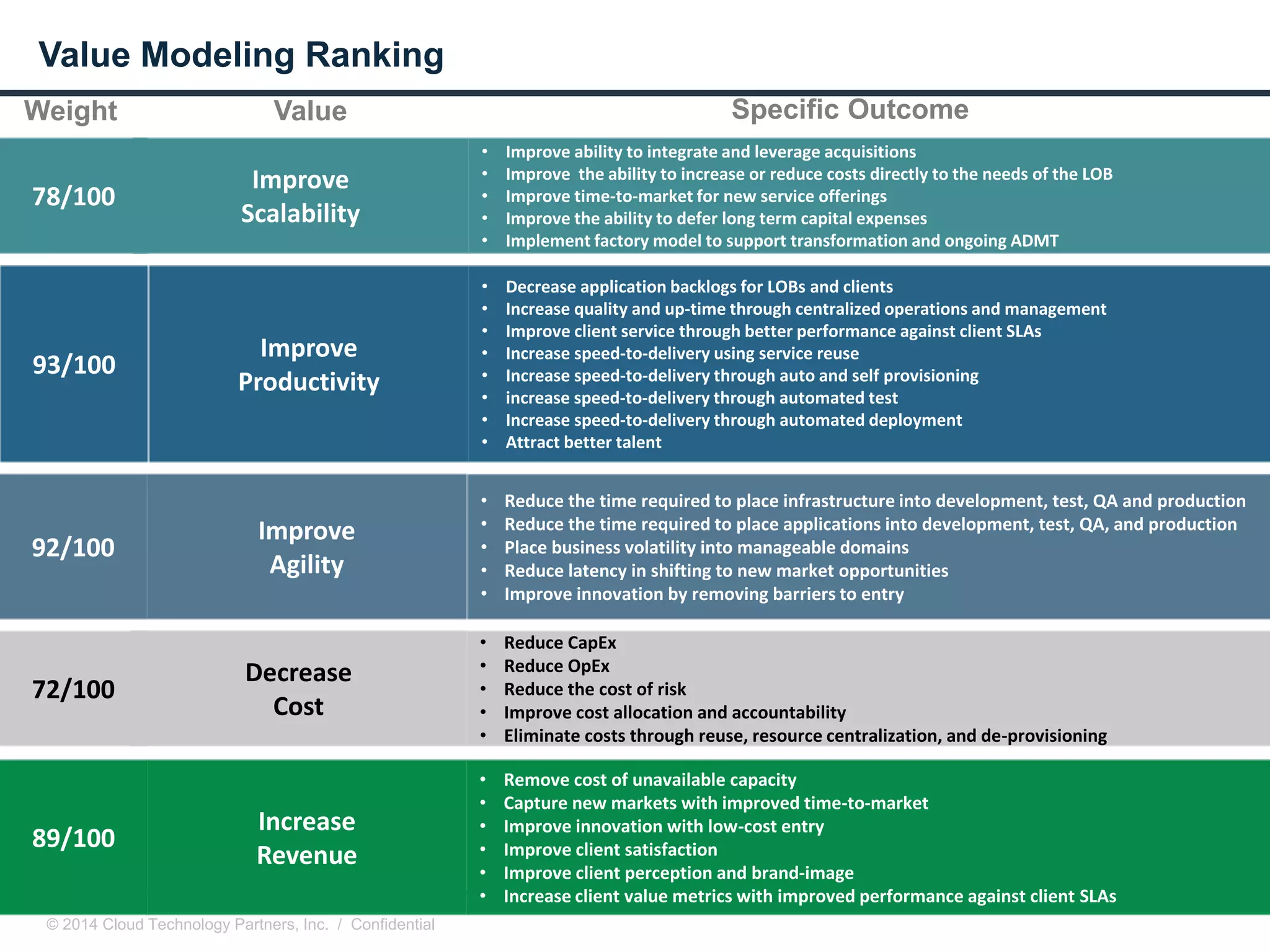
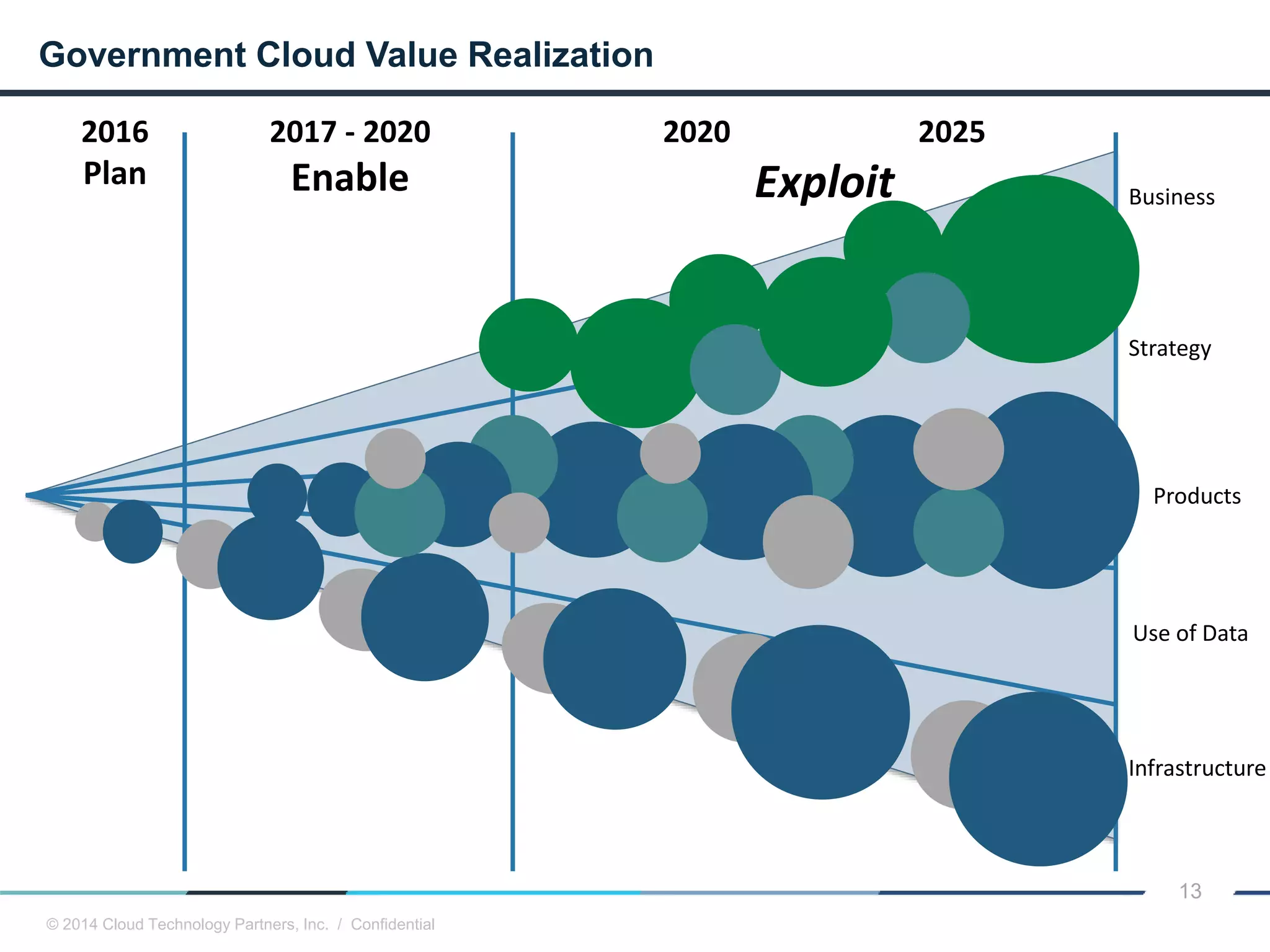
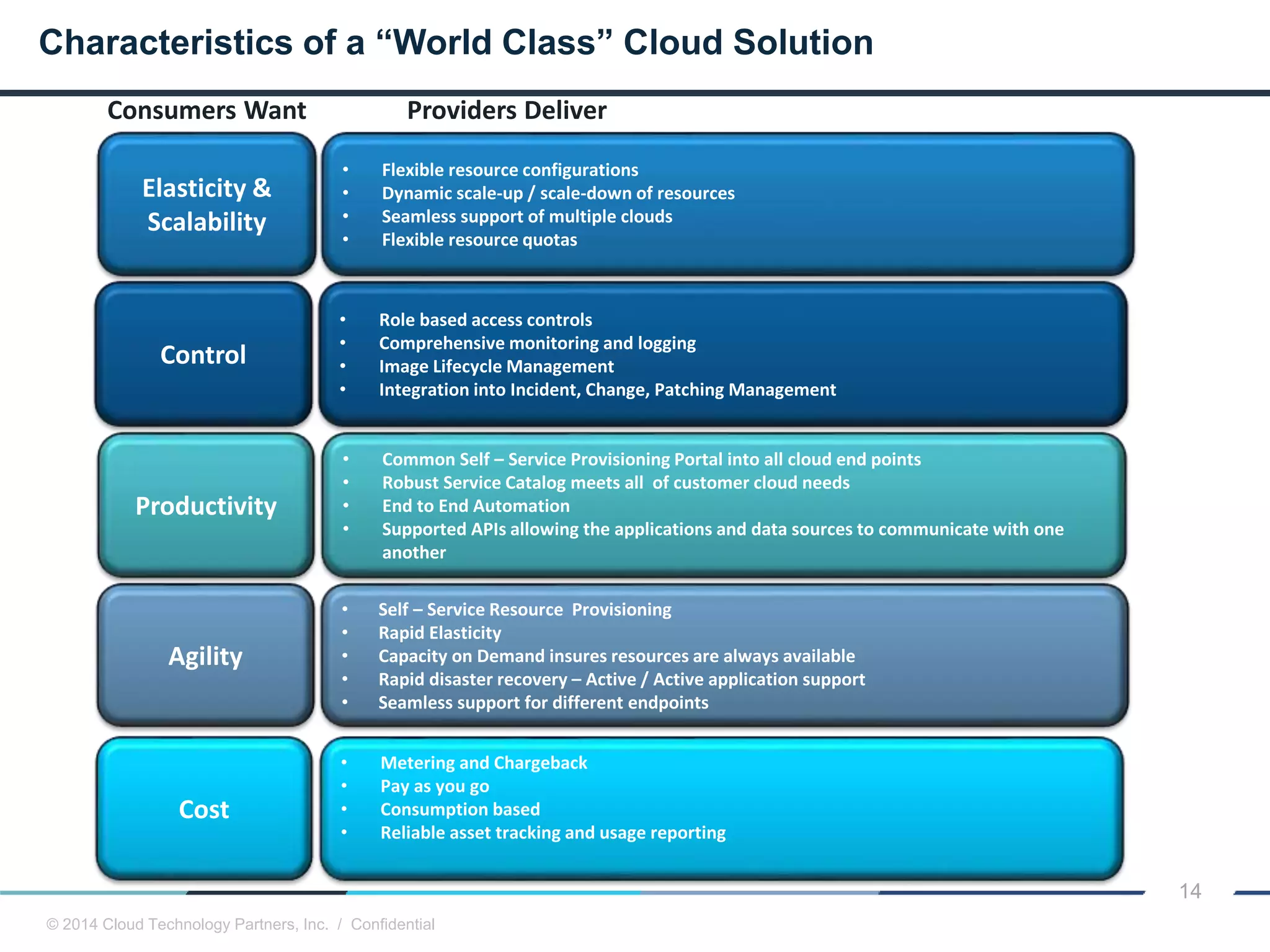
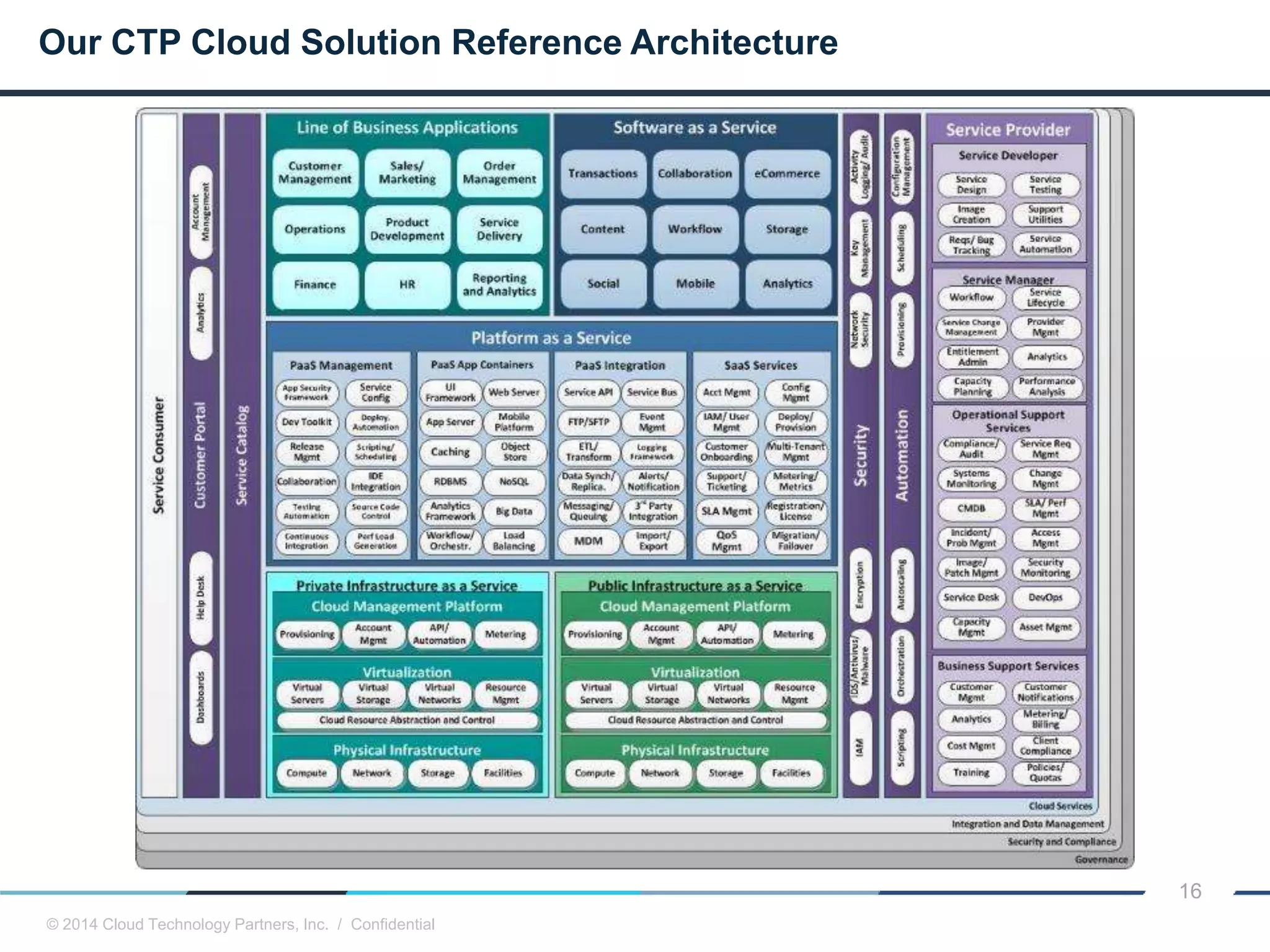
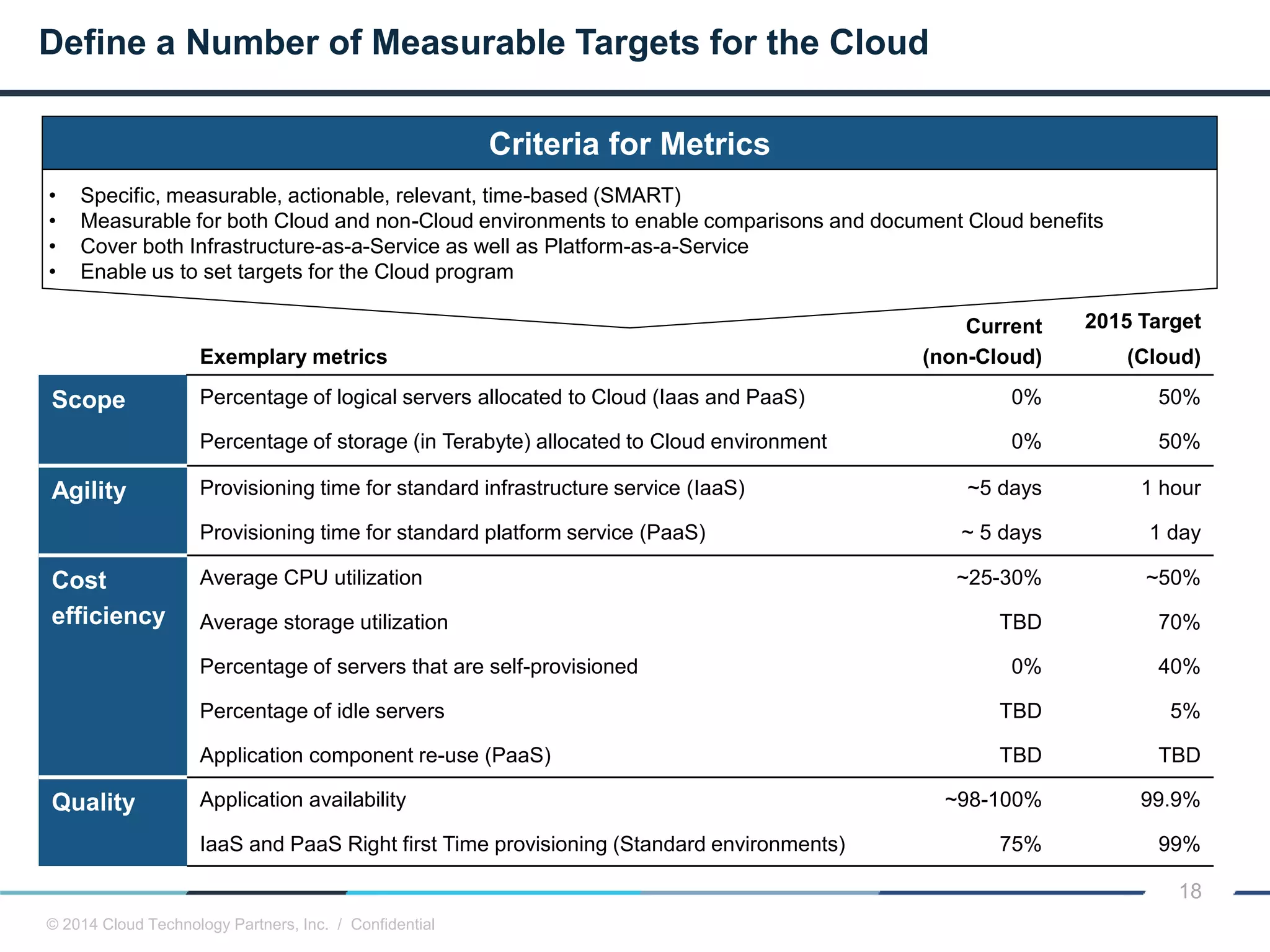
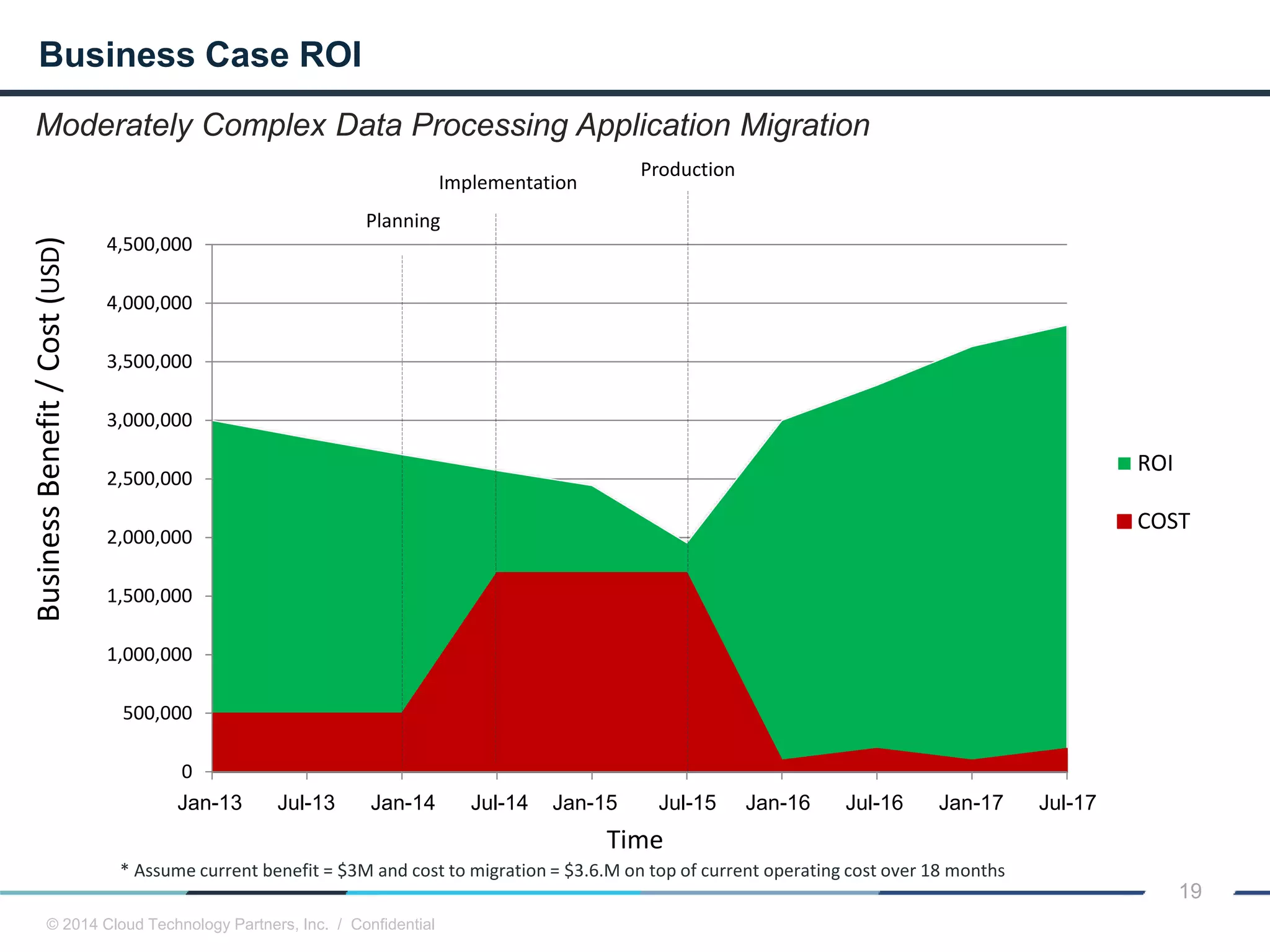
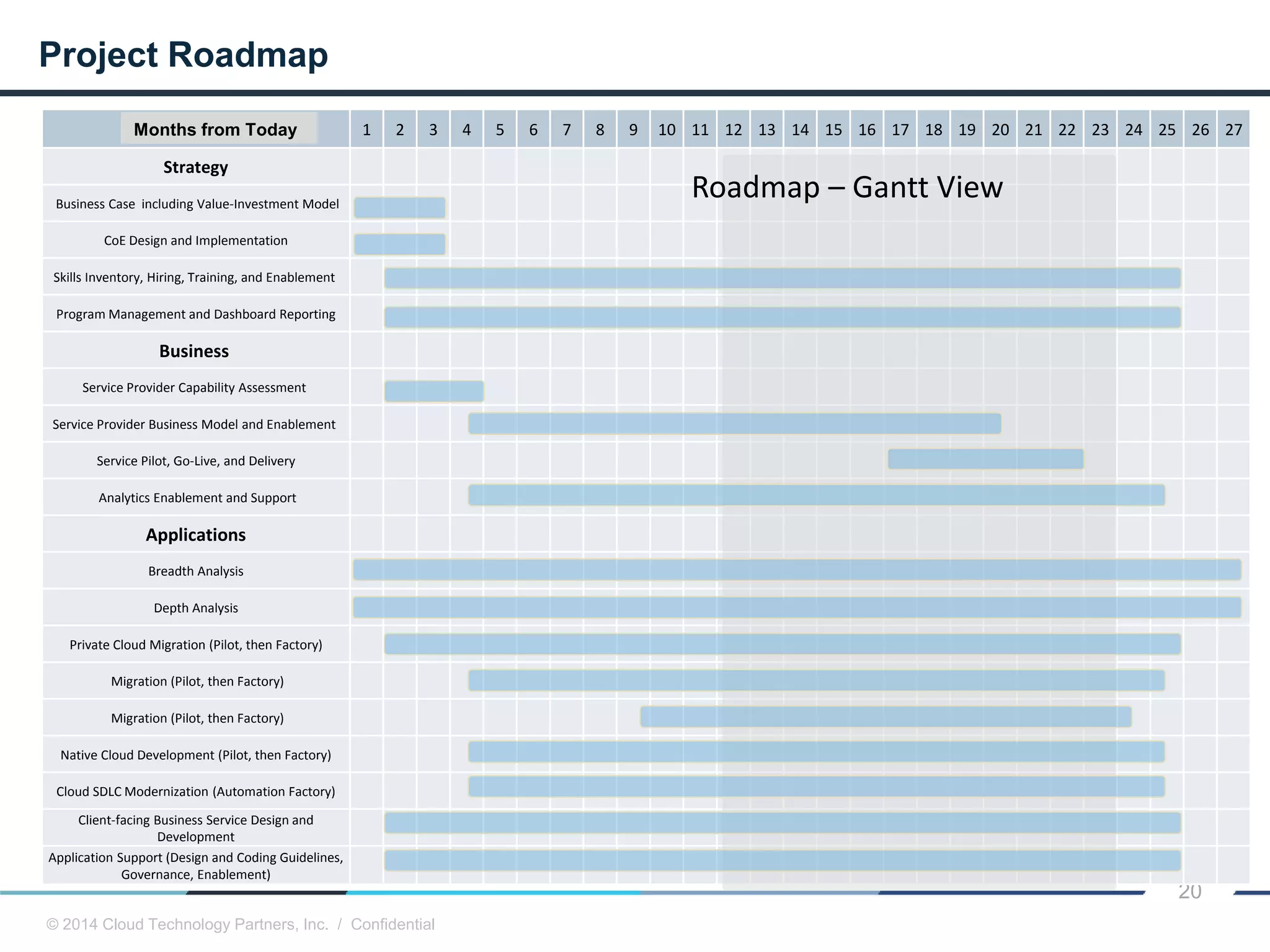
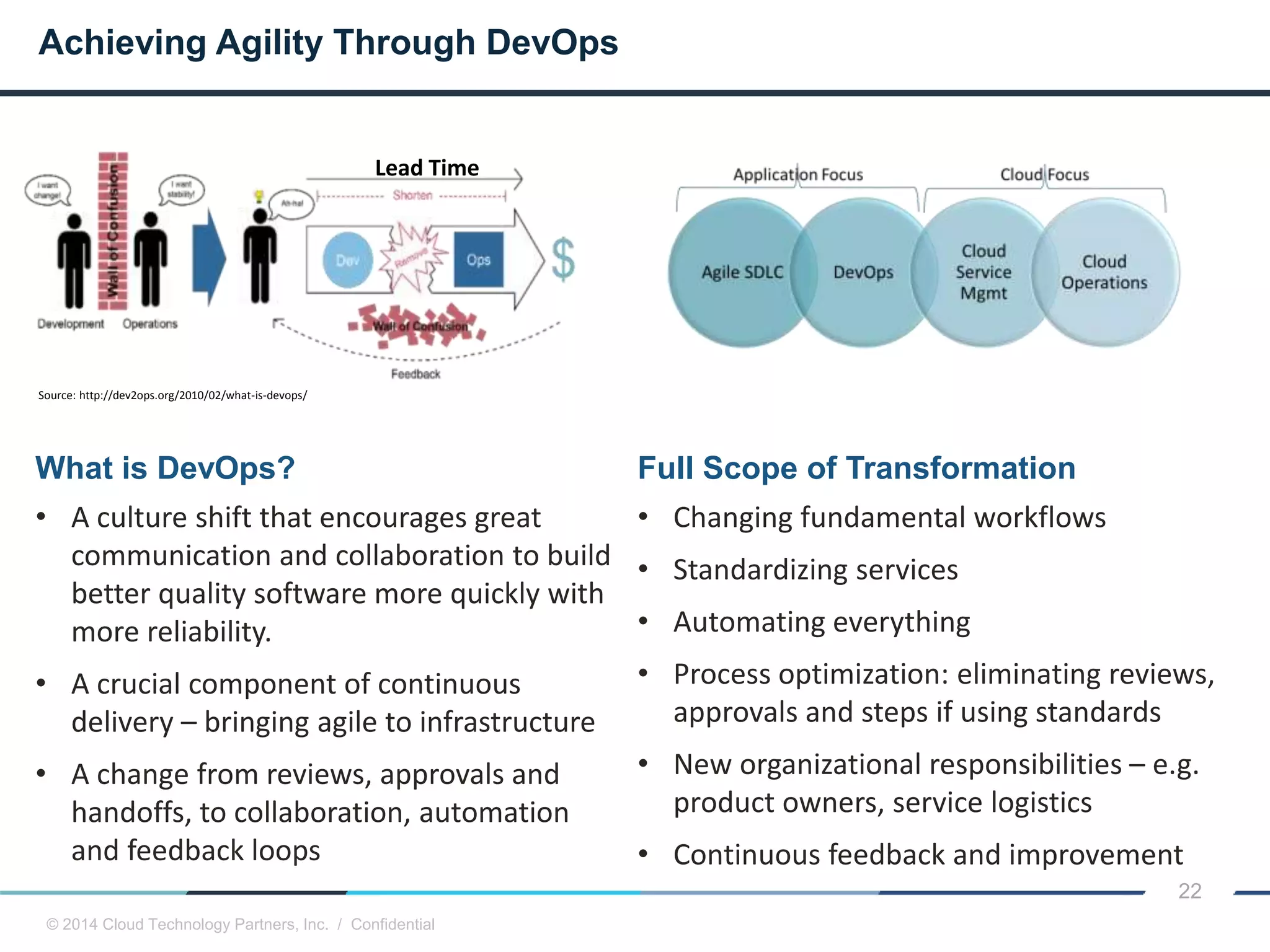
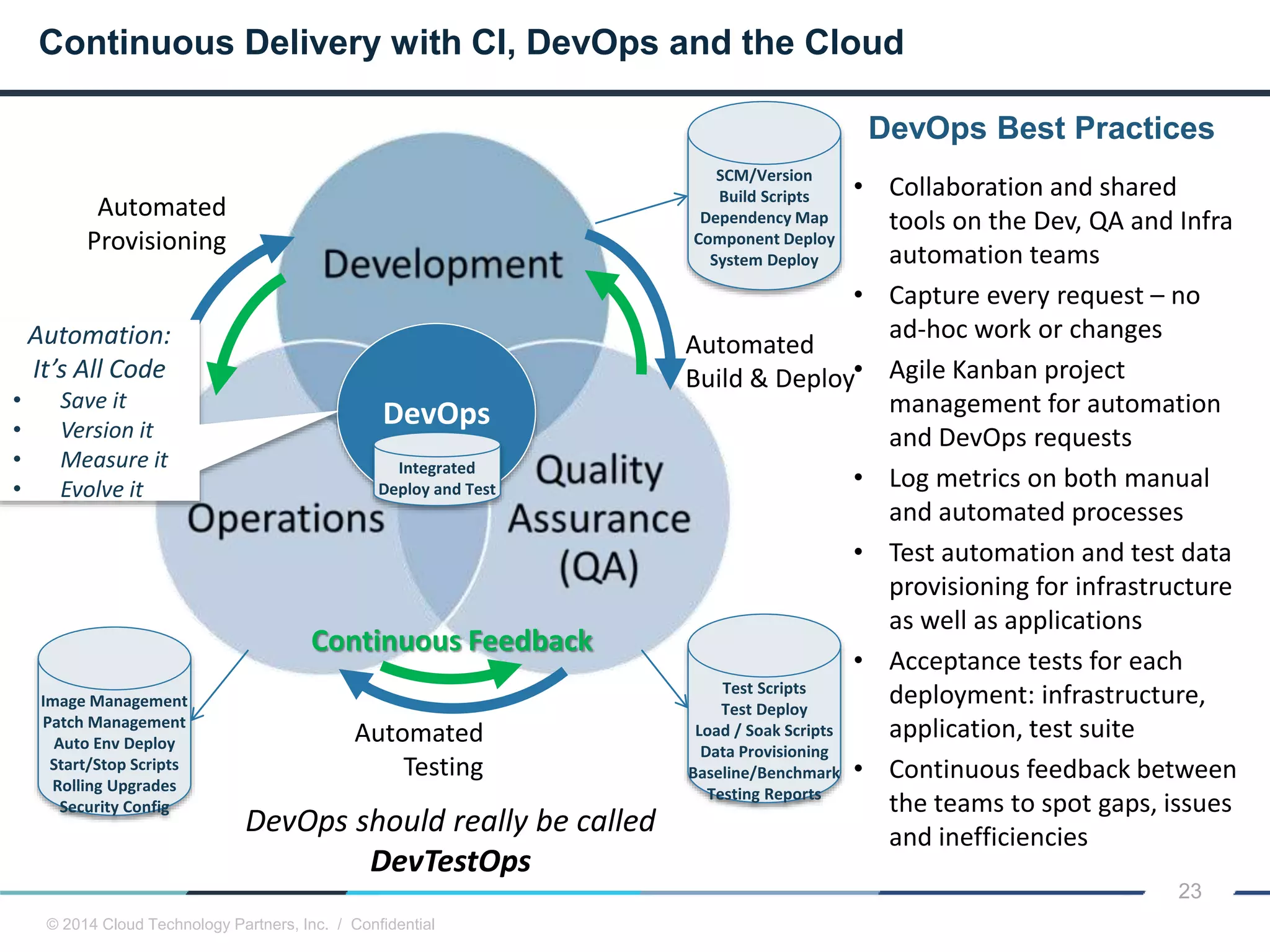
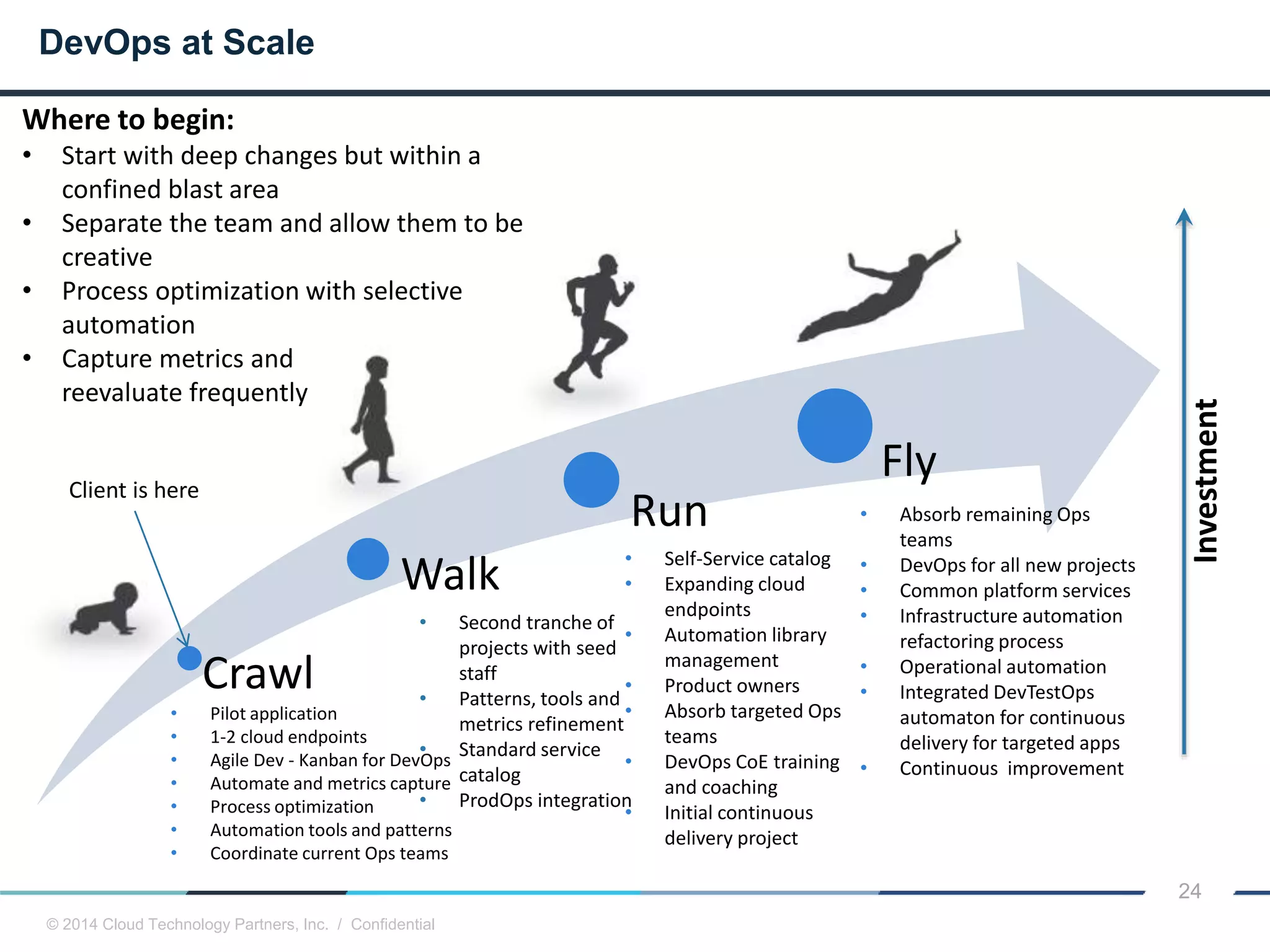
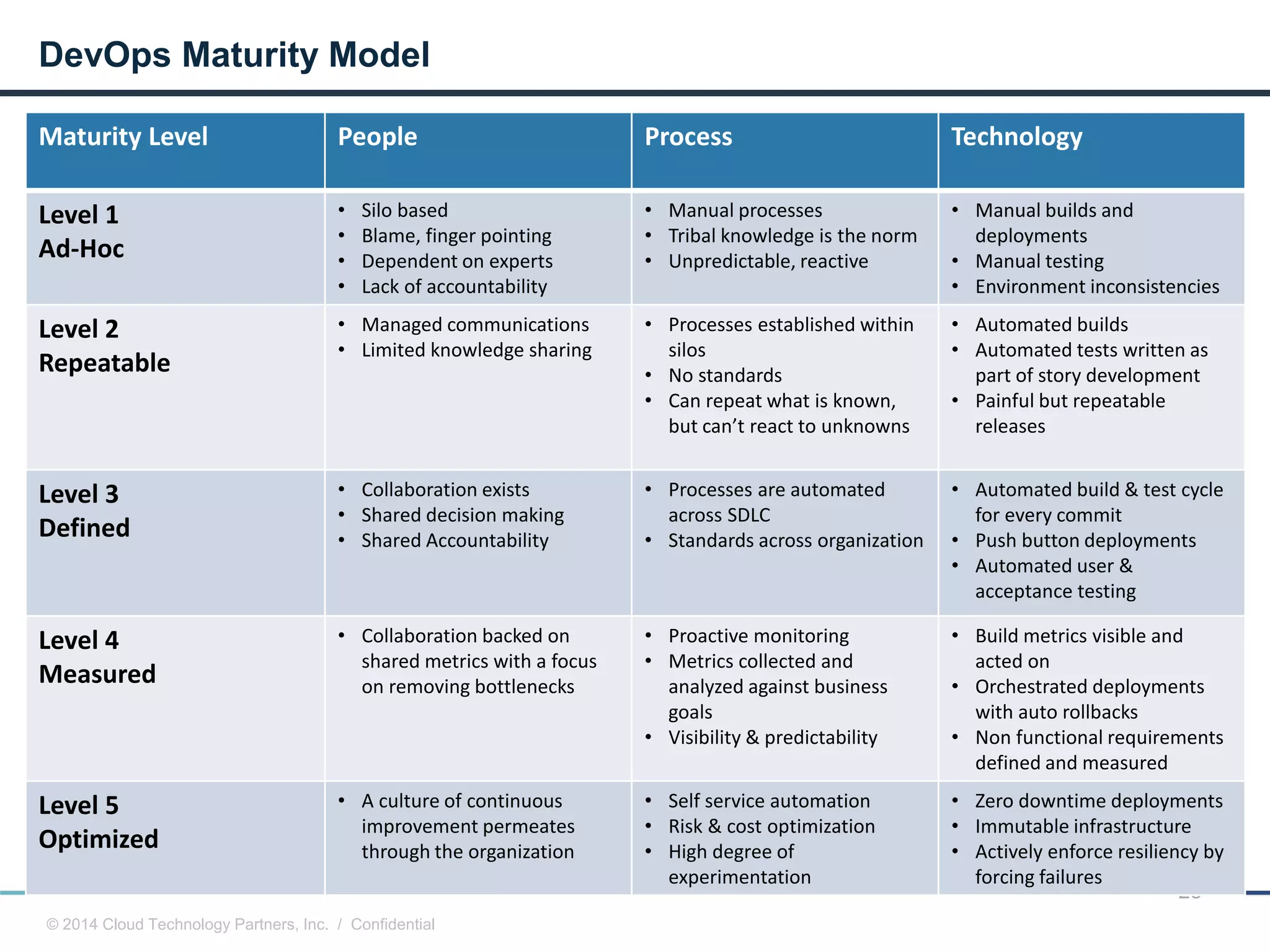
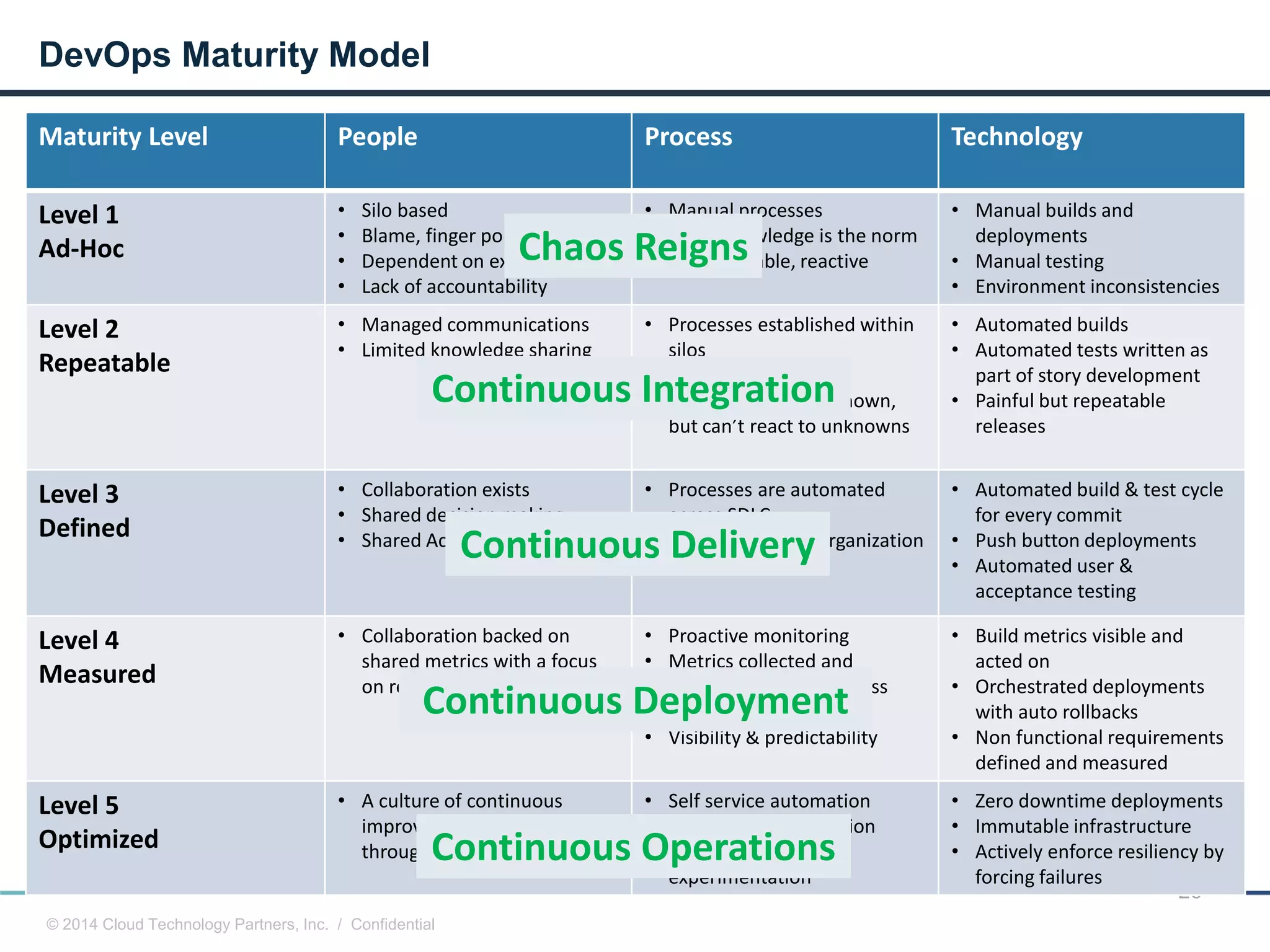
The document discusses how cloud computing and DevOps can improve how government services are delivered. It argues that cloud and DevOps can increase agility, reduce costs, and improve quality by enabling faster innovation, elastic infrastructure, standardized platforms, increased automation, and higher availability and security. It then provides examples of cloud application maturity levels and how traditional application architectures need to change to be optimized for the cloud. Finally, it proposes metrics that governments can use to measure improvements in scope, agility, cost efficiency, and quality when adopting cloud technologies.