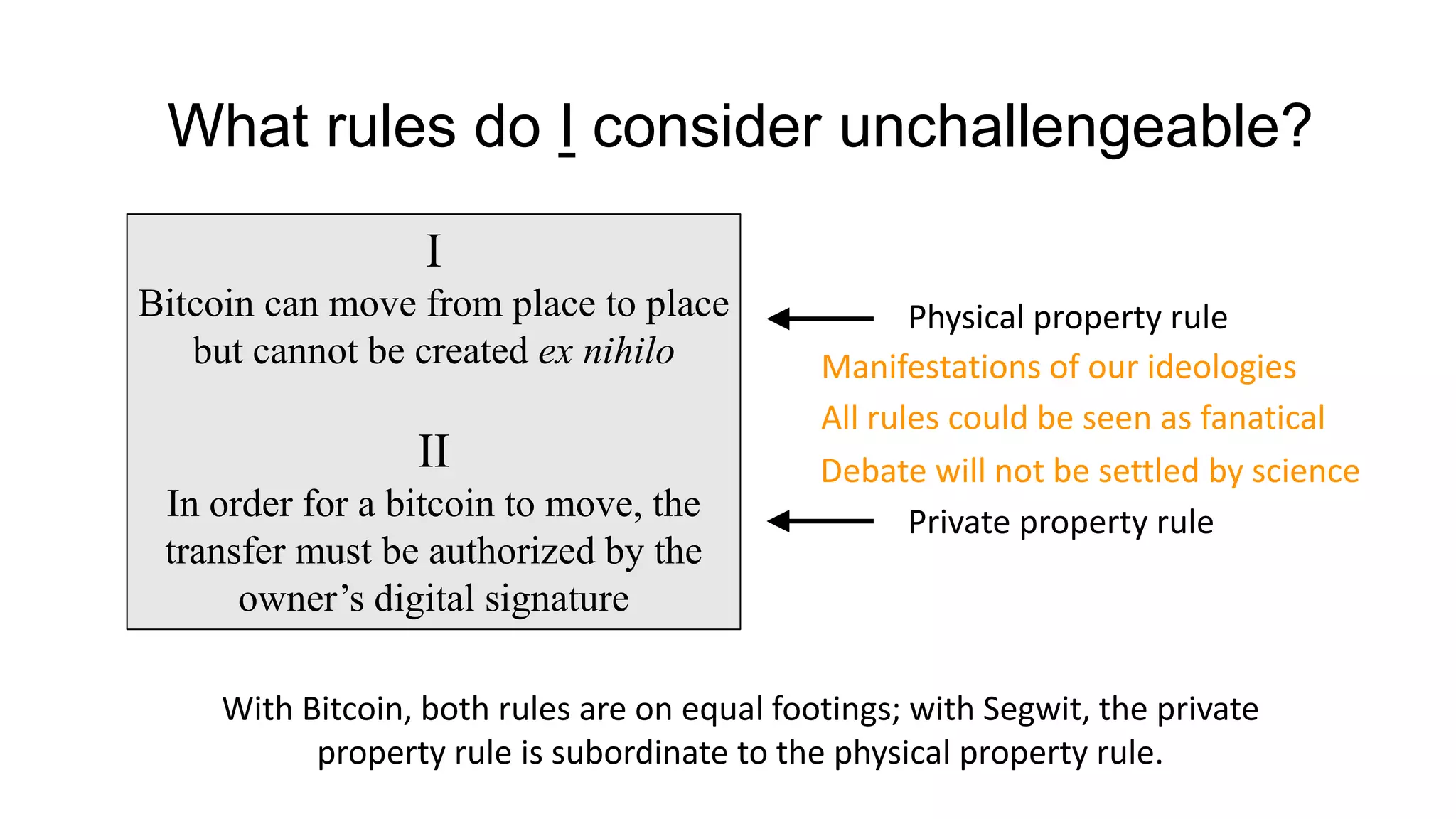
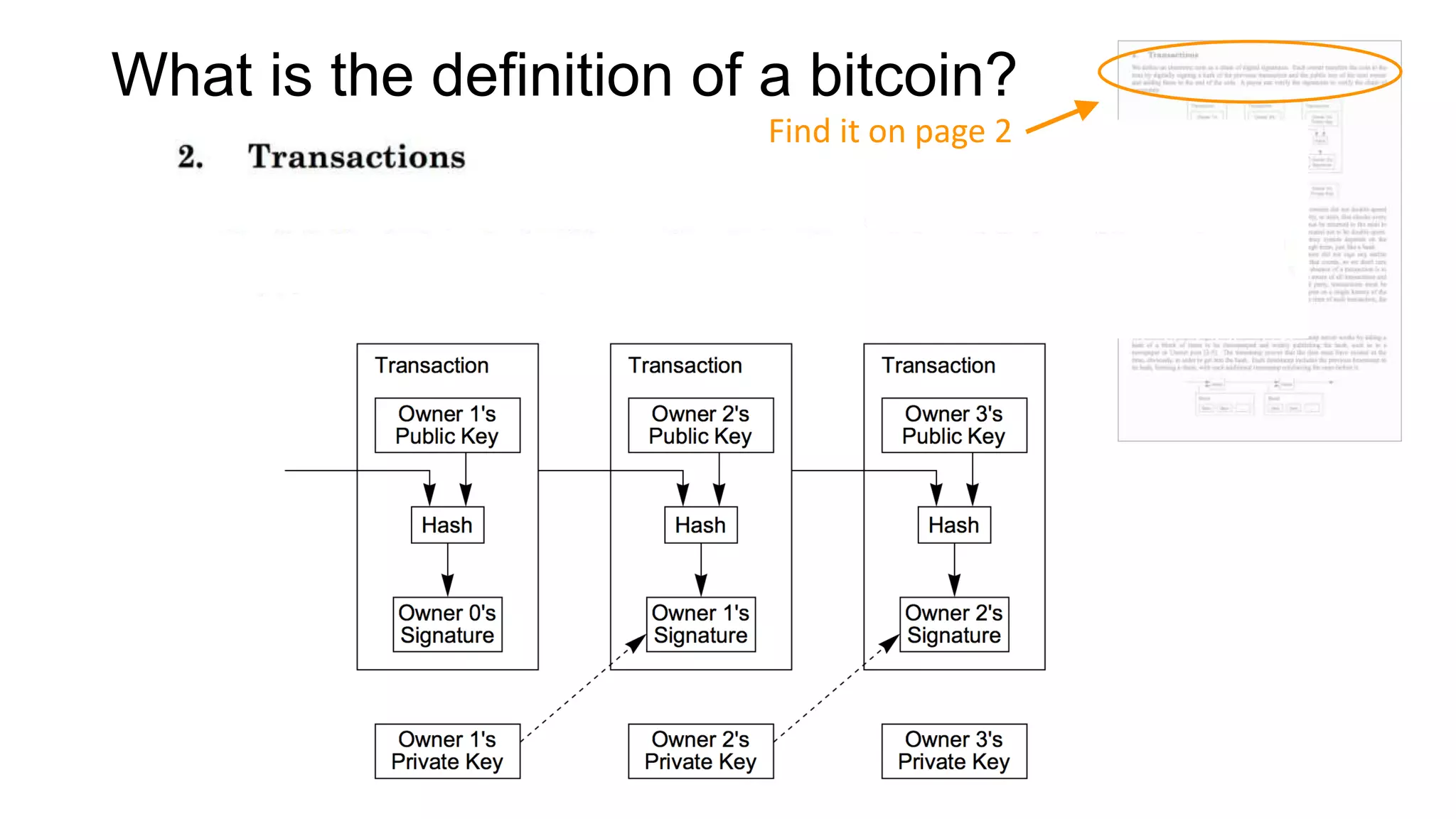
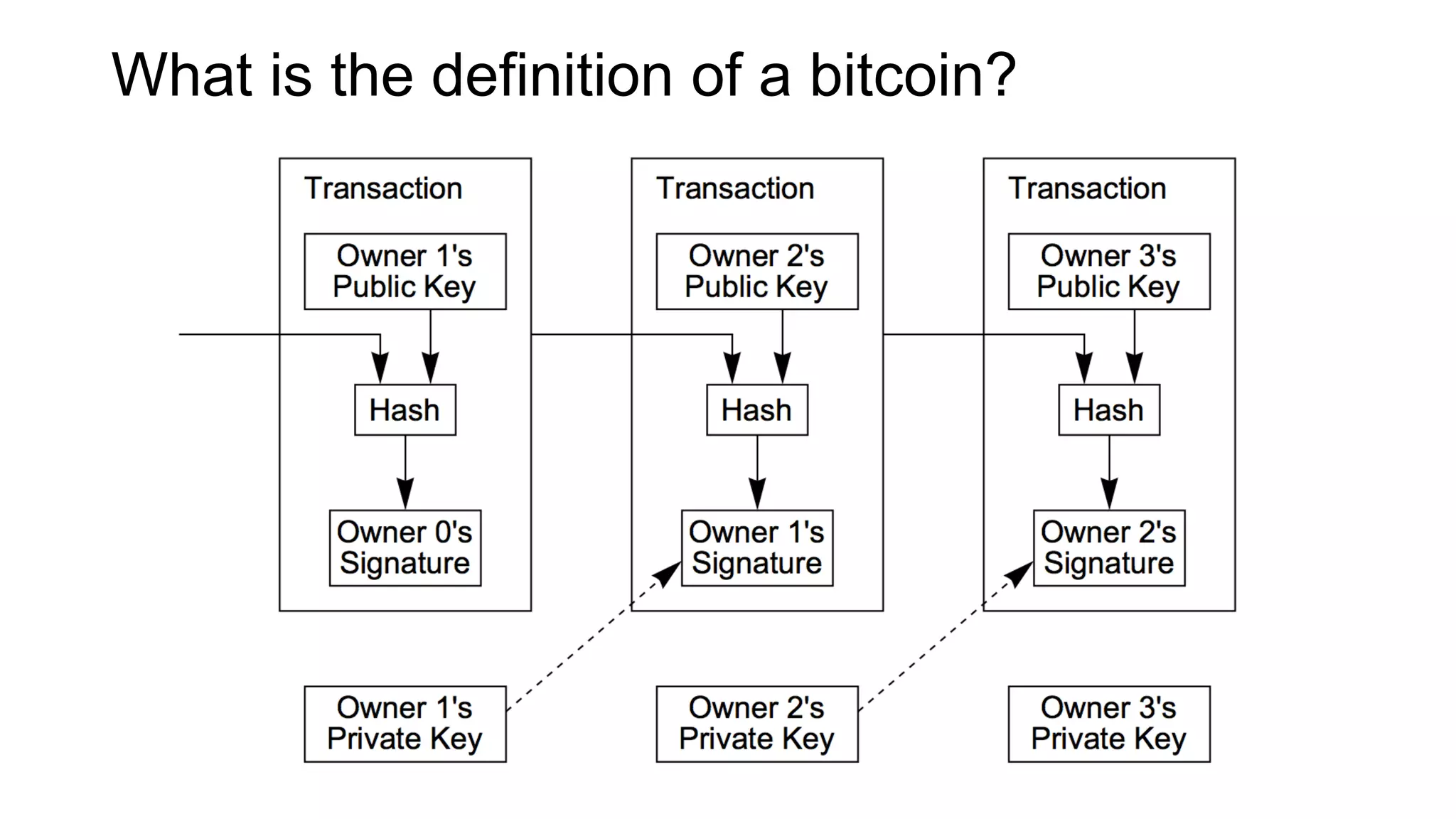
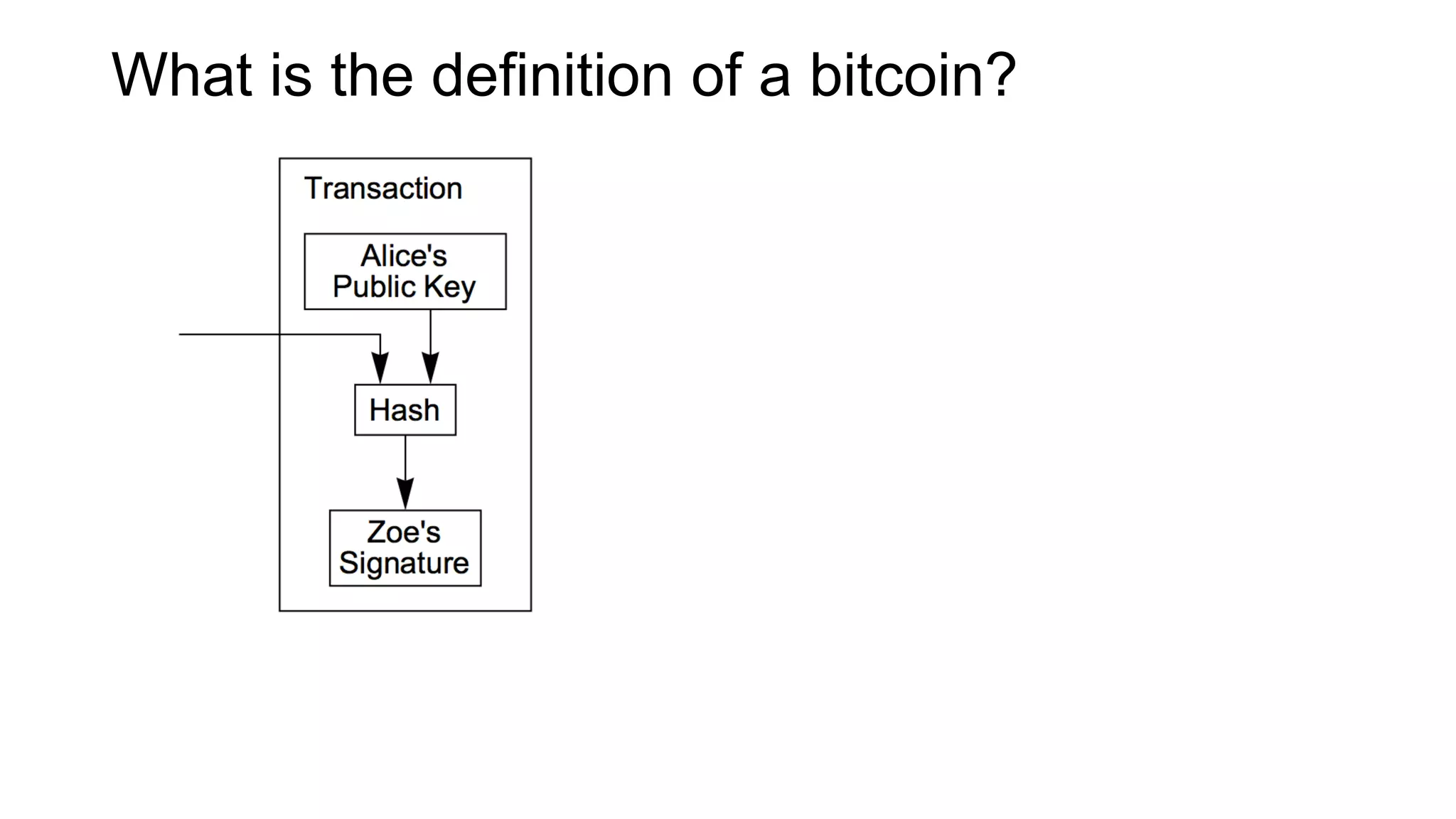
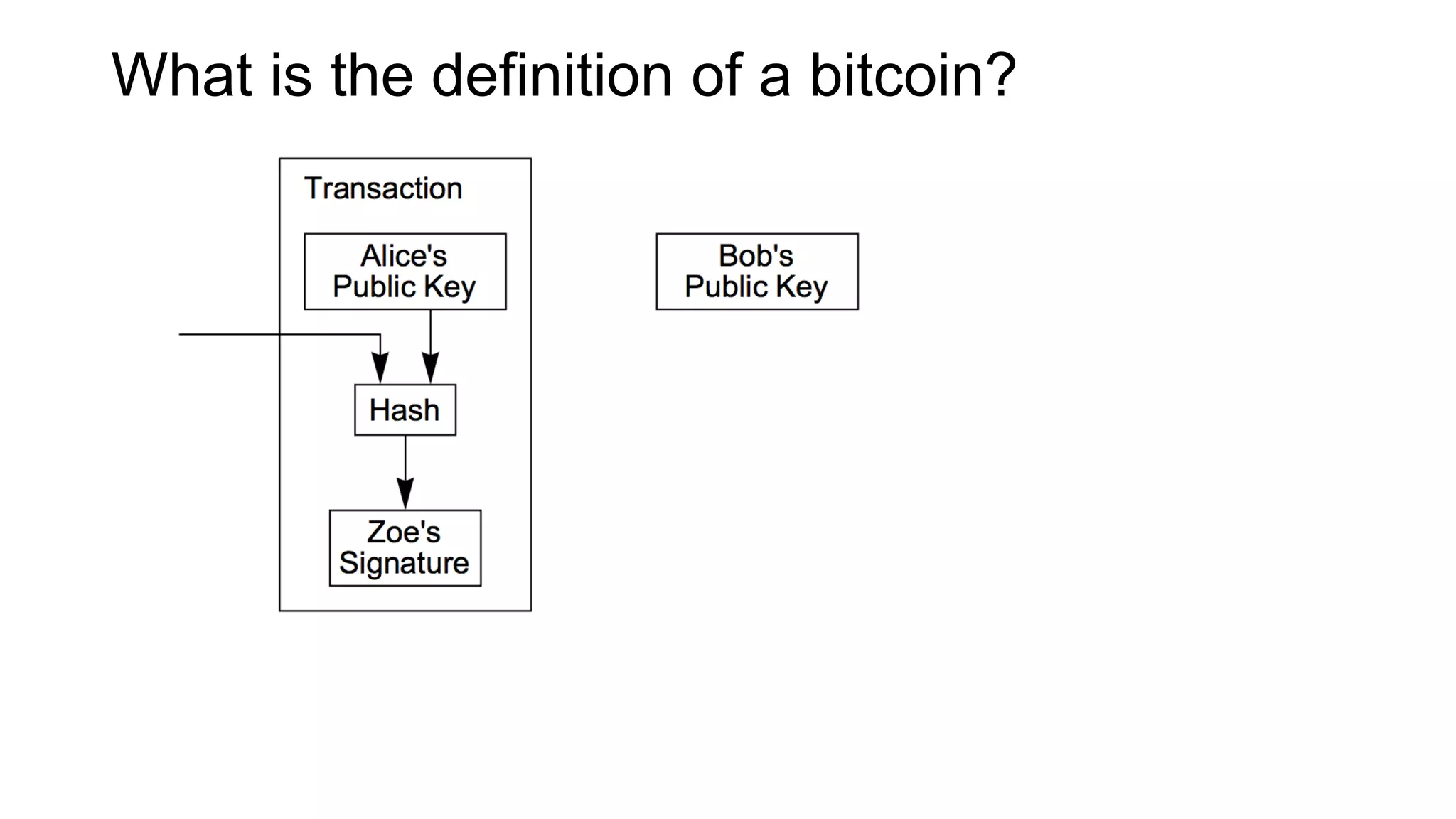
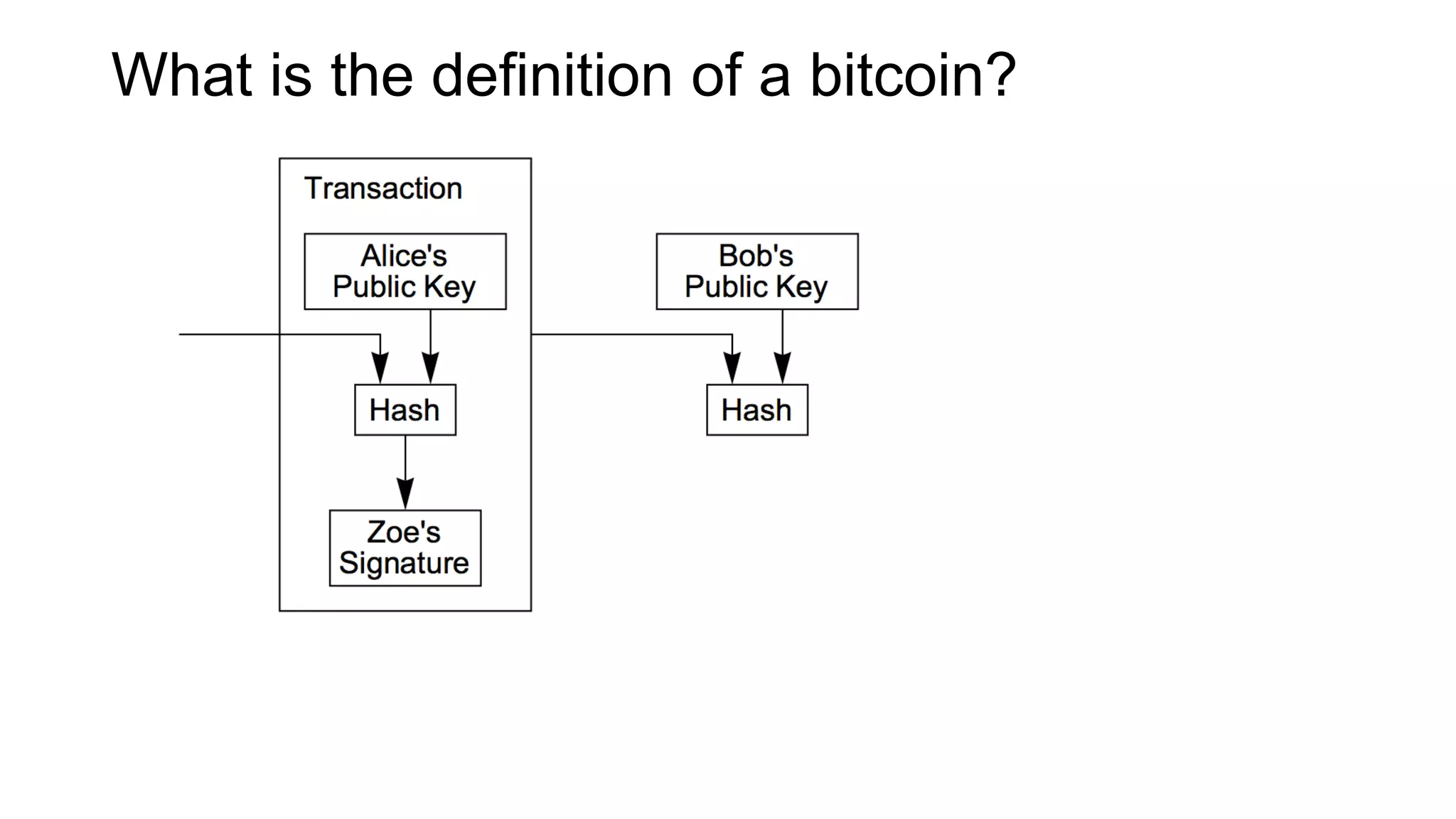
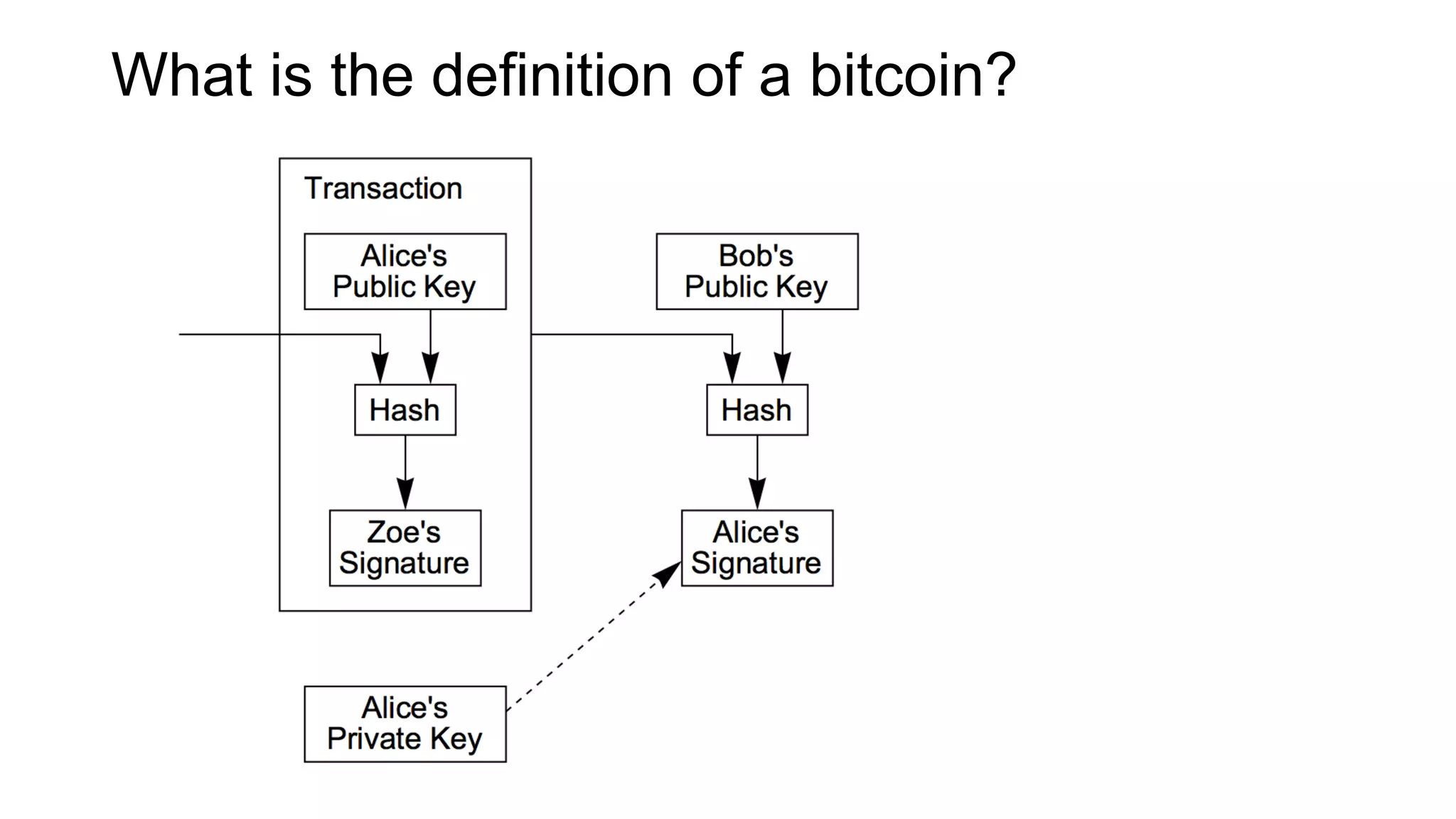
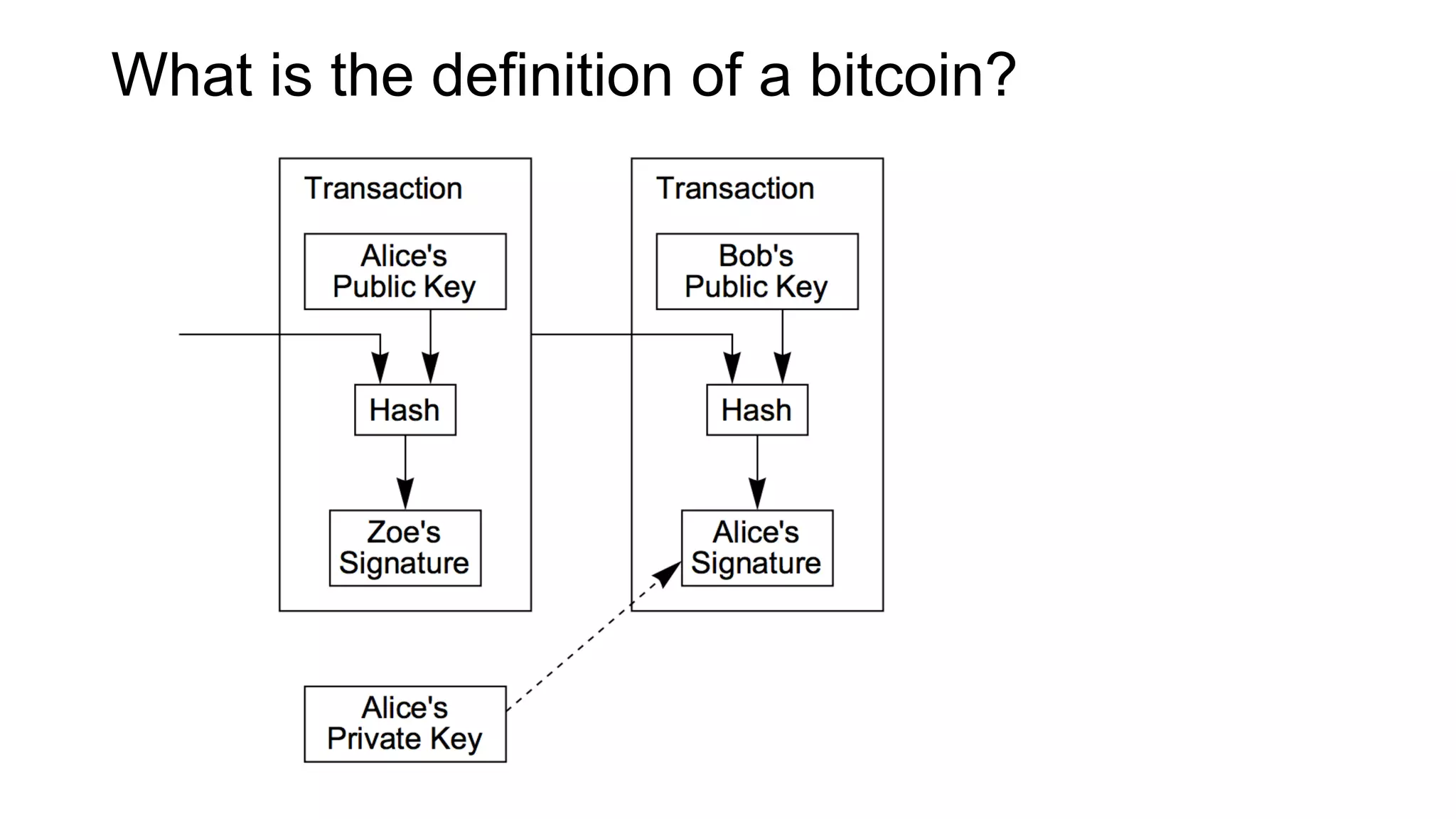
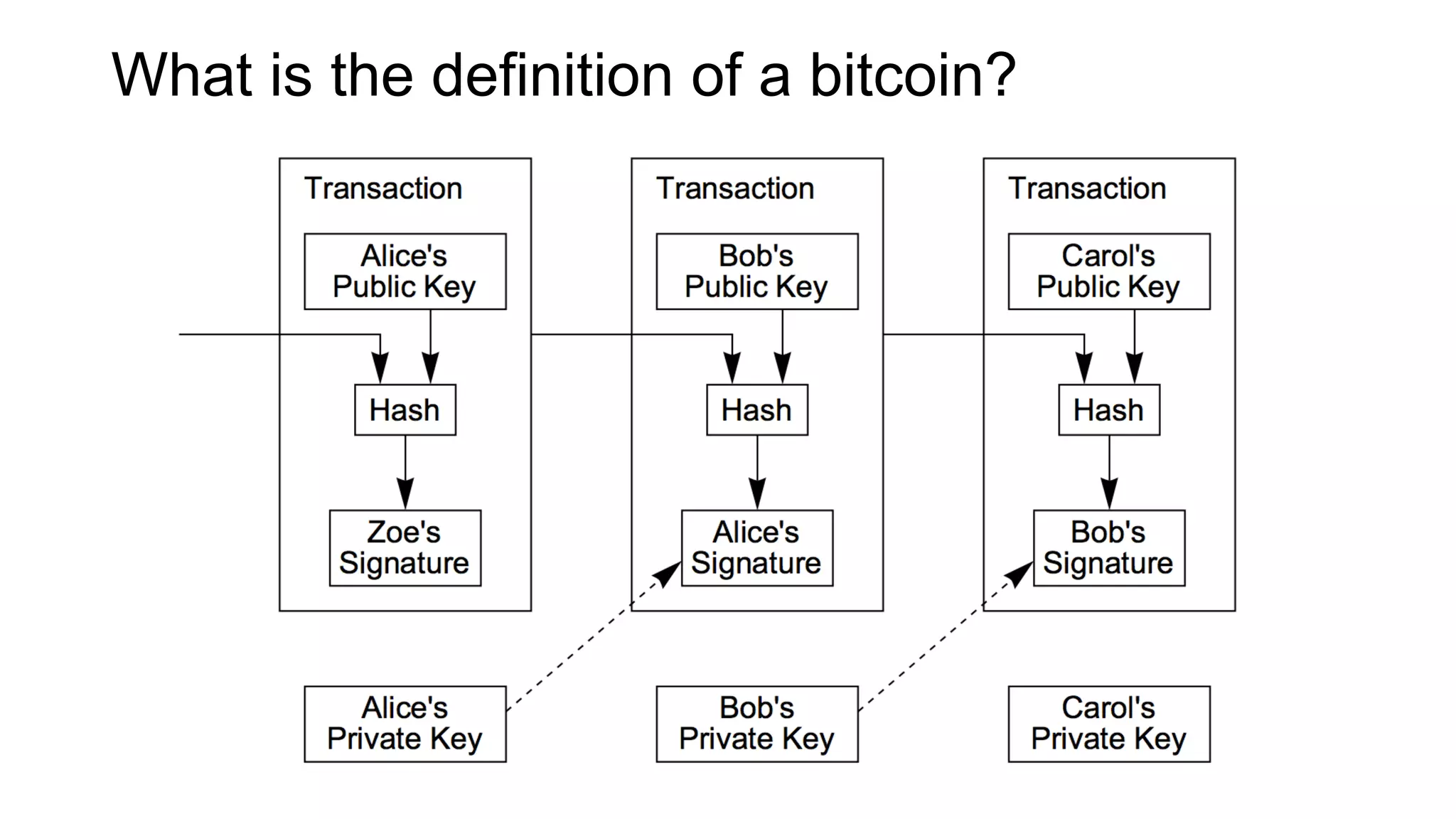
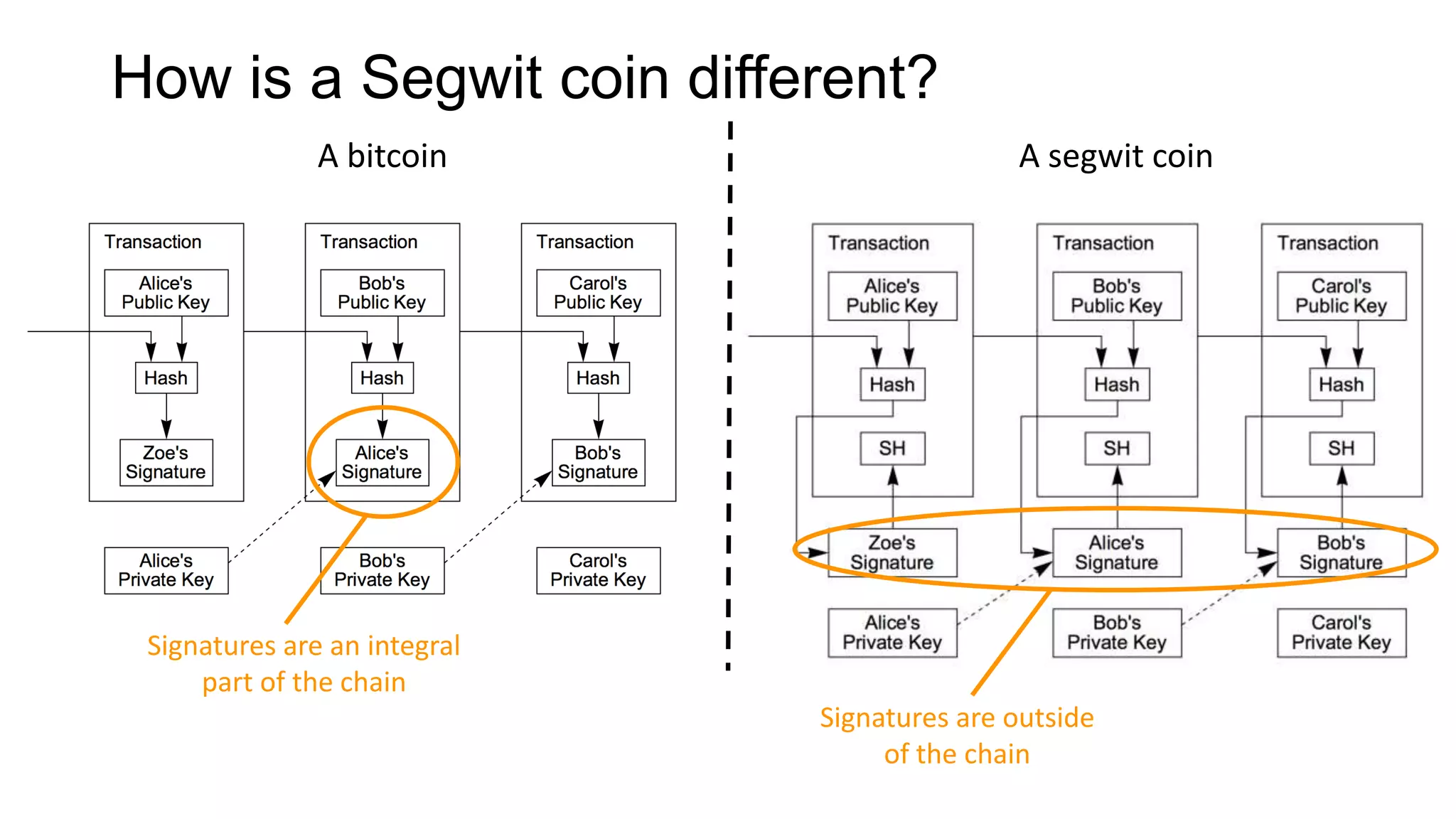
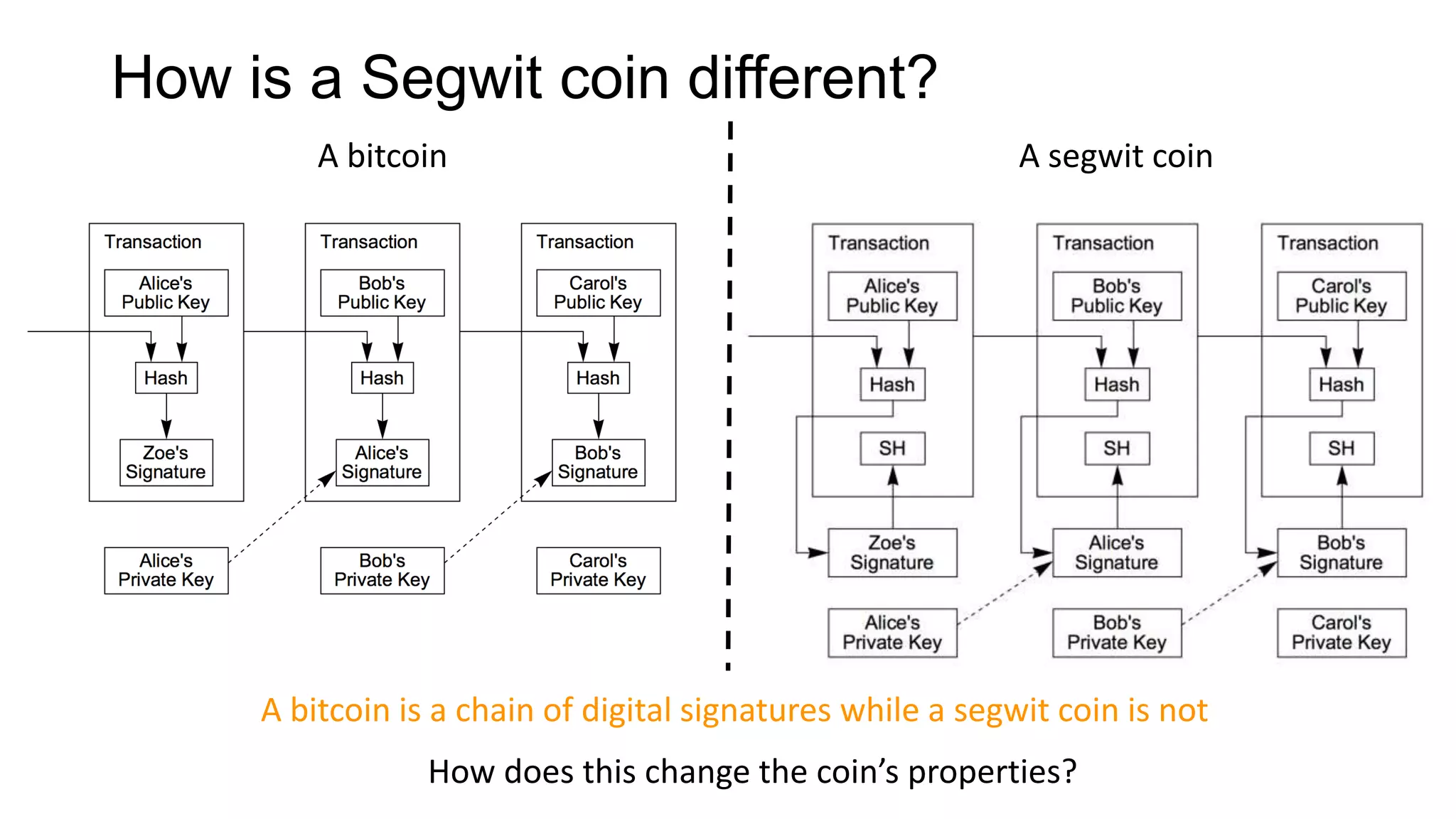
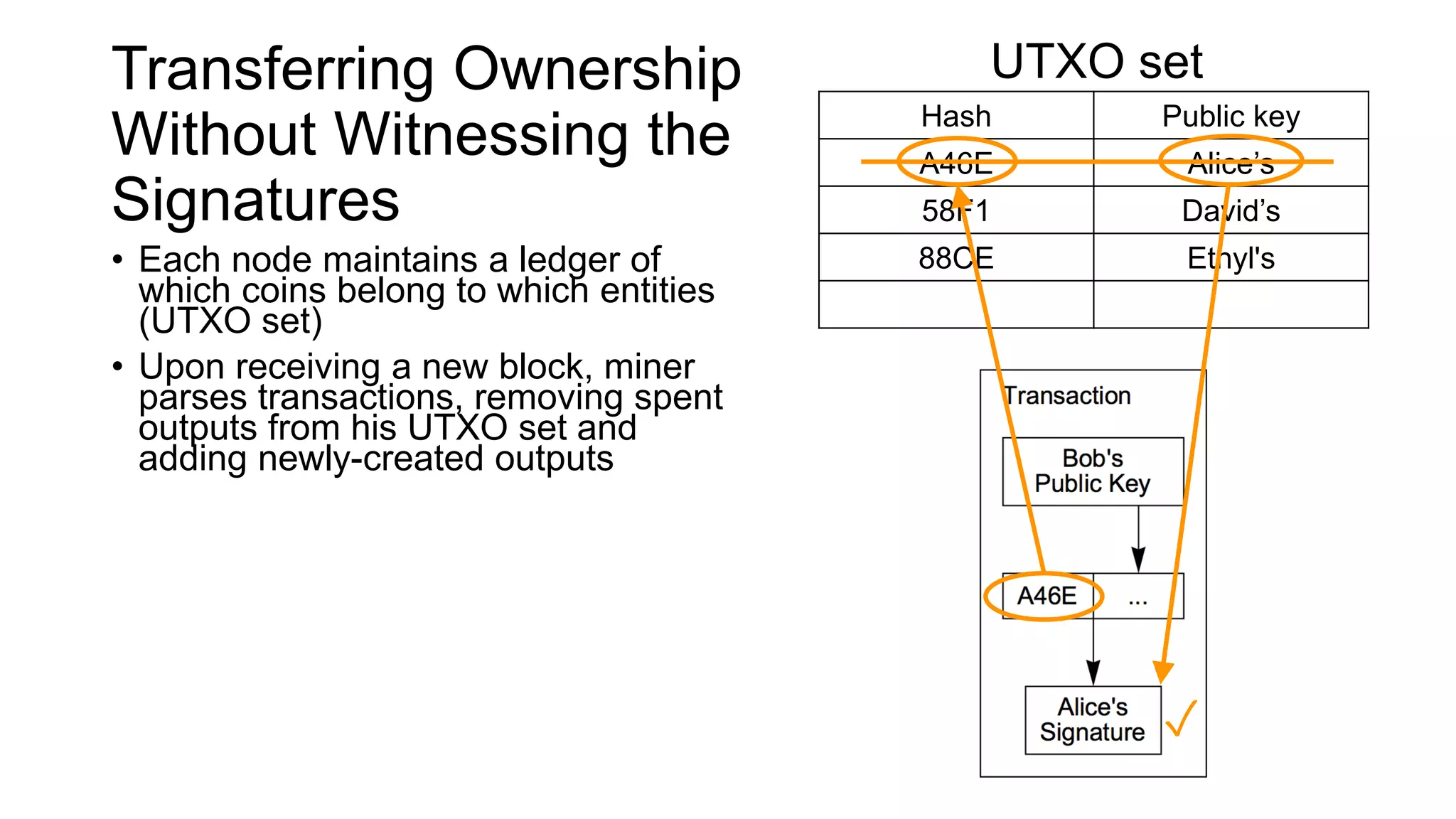
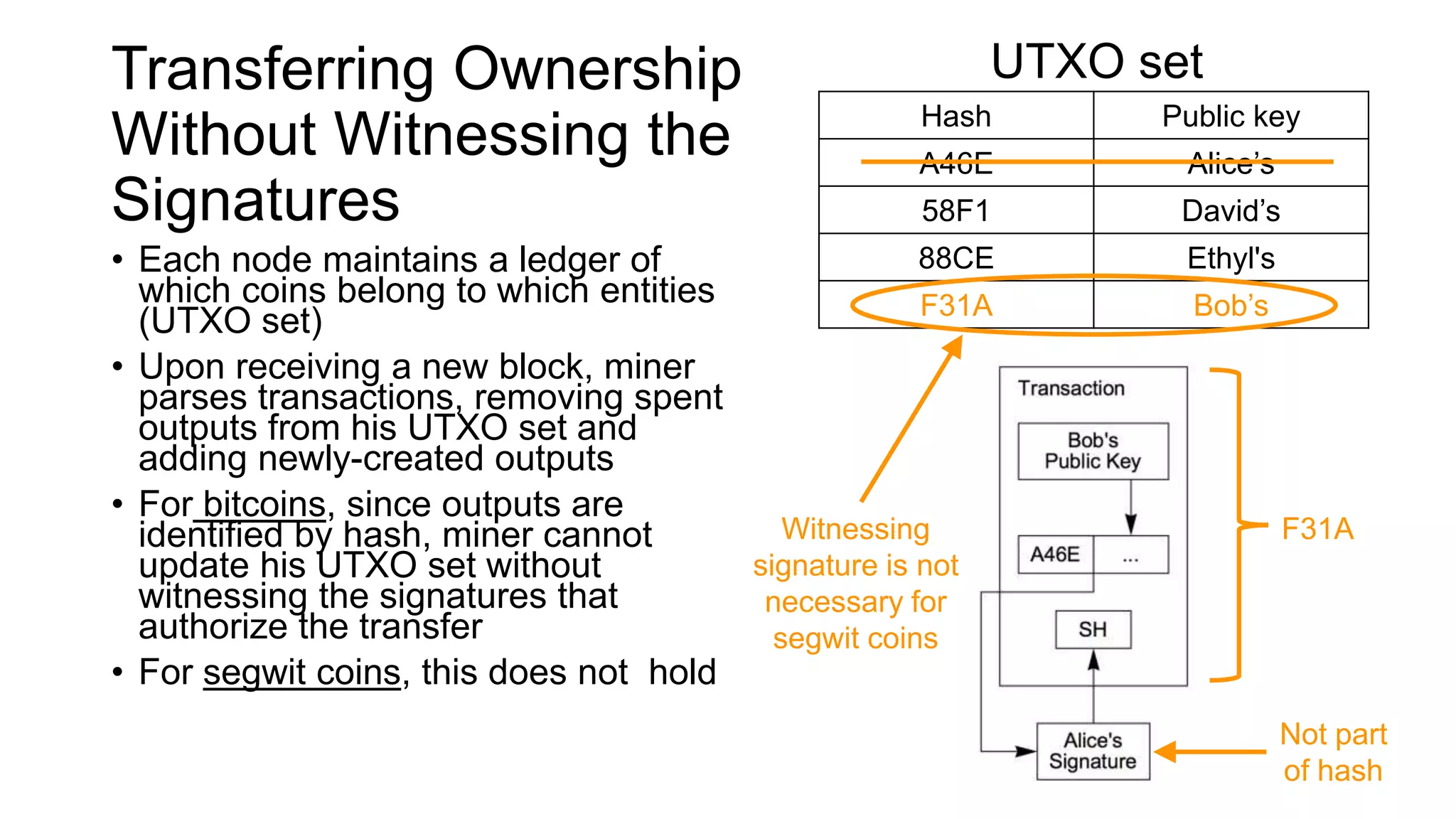
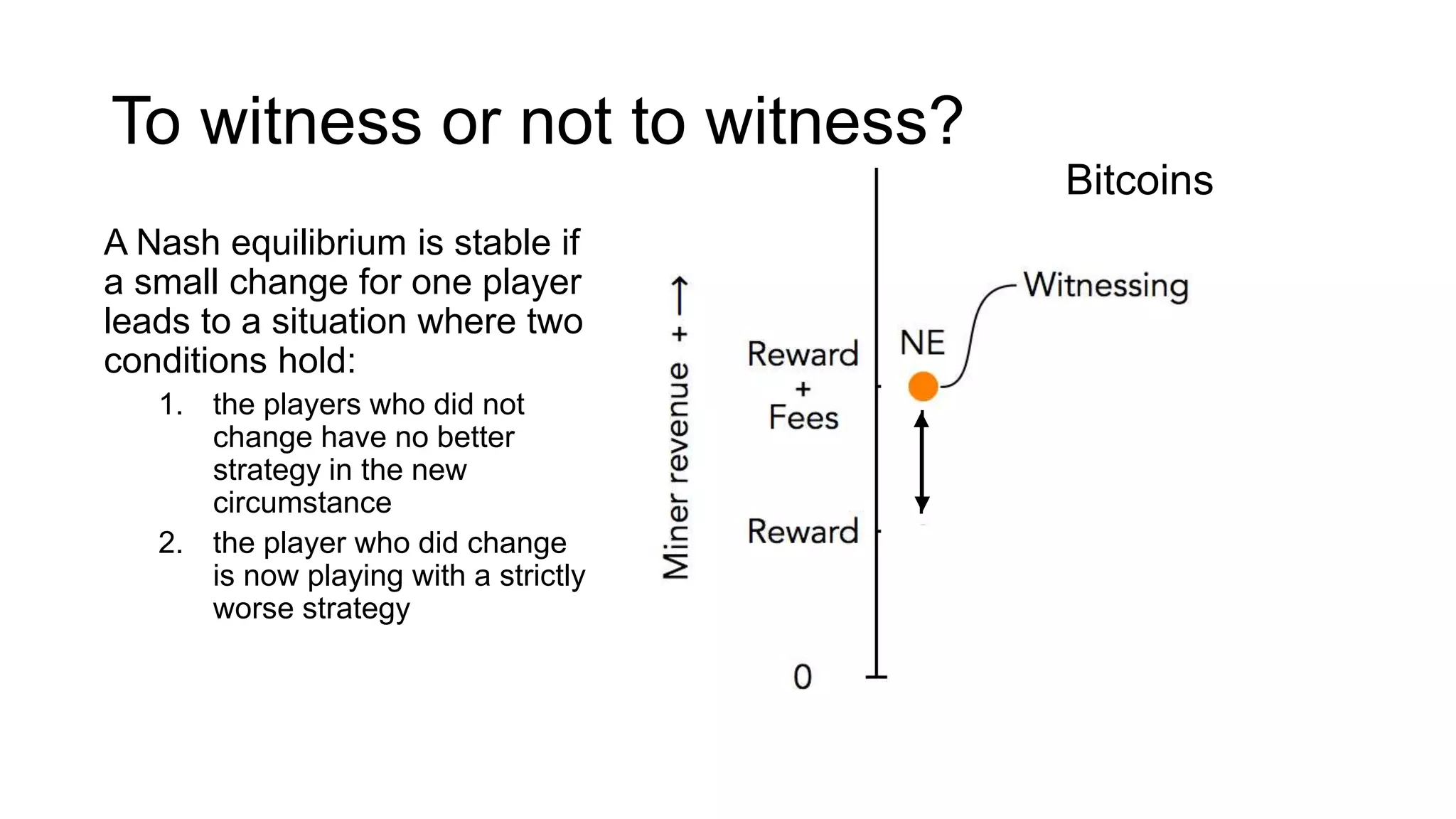
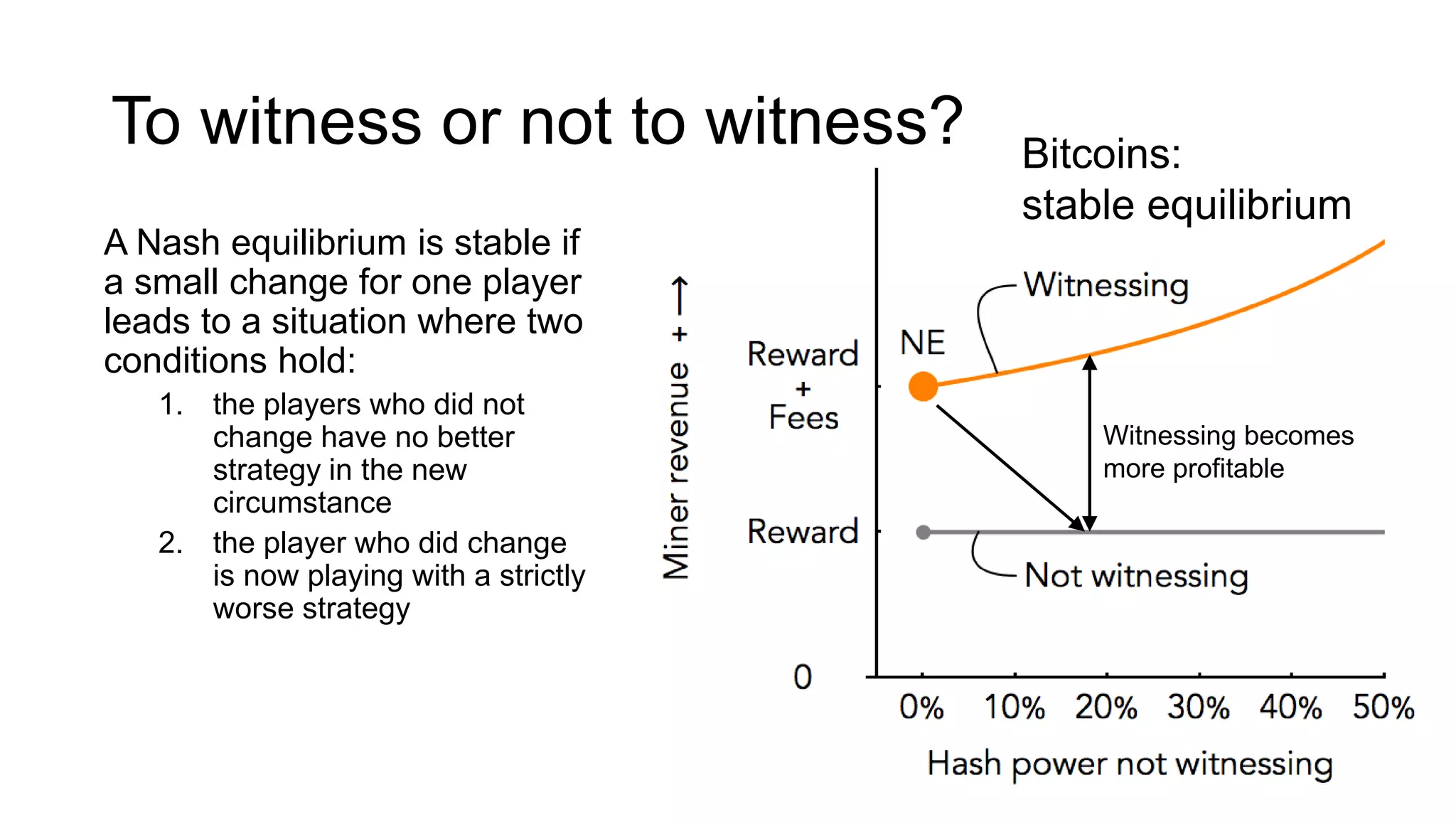
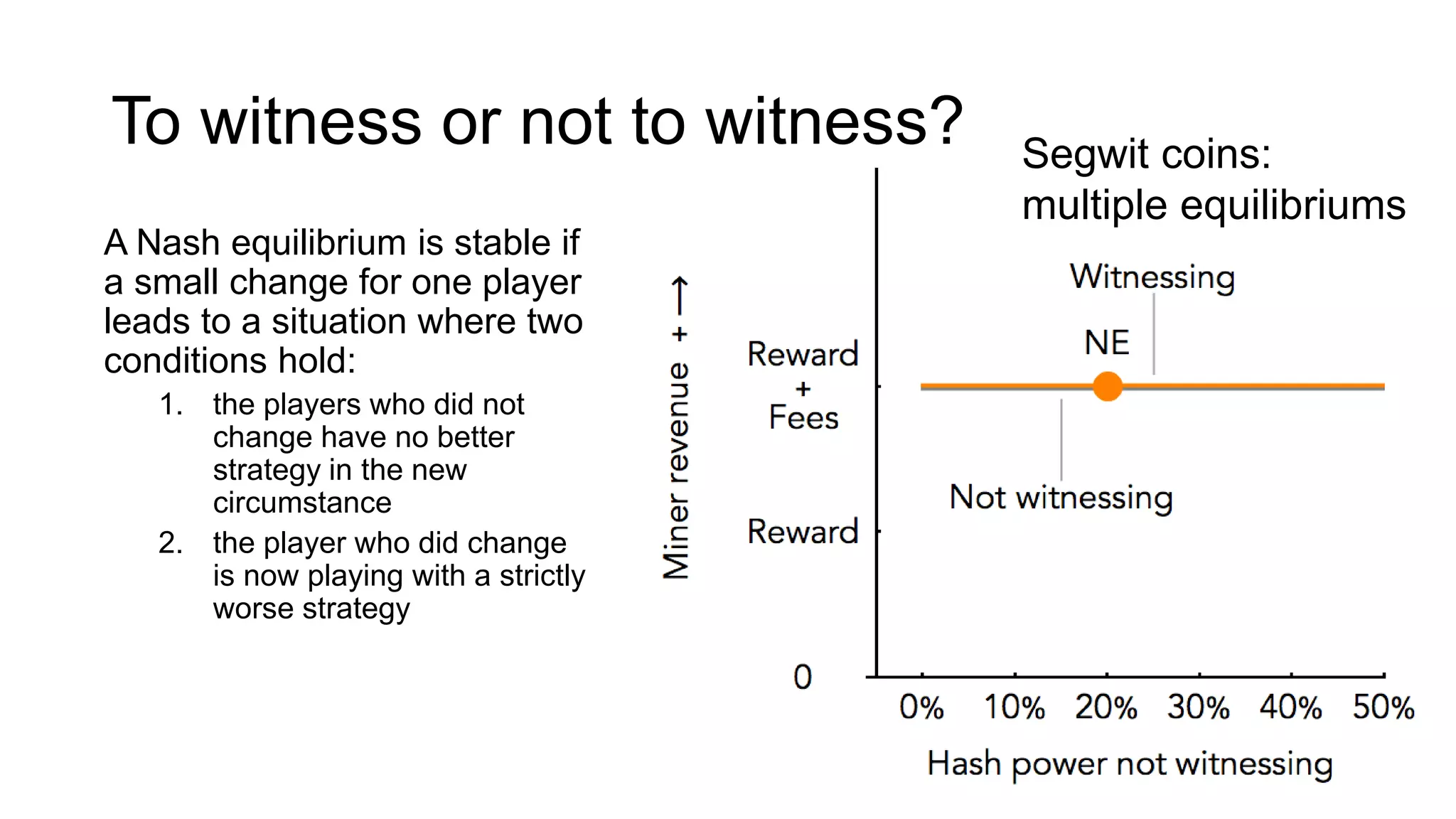
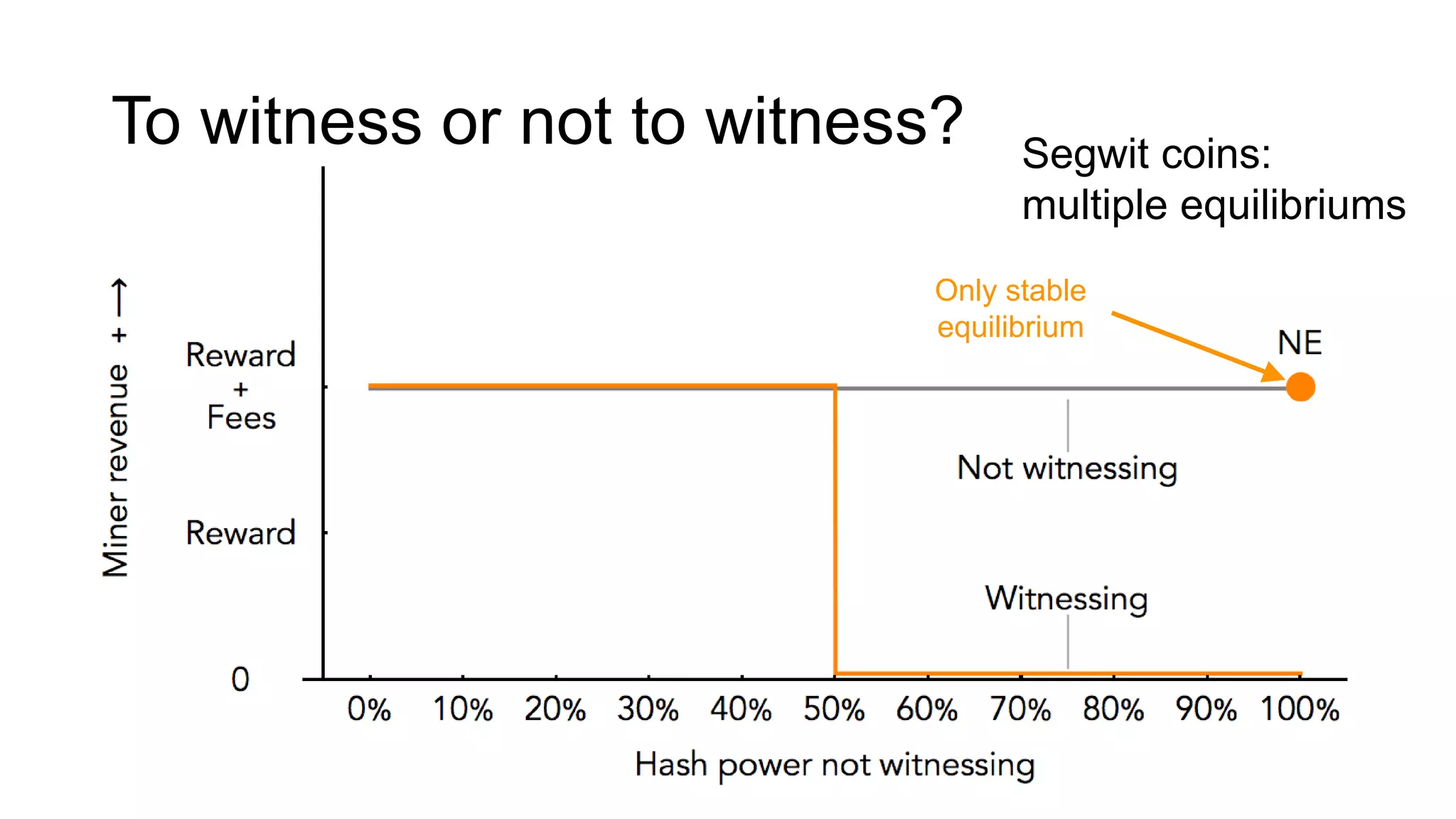
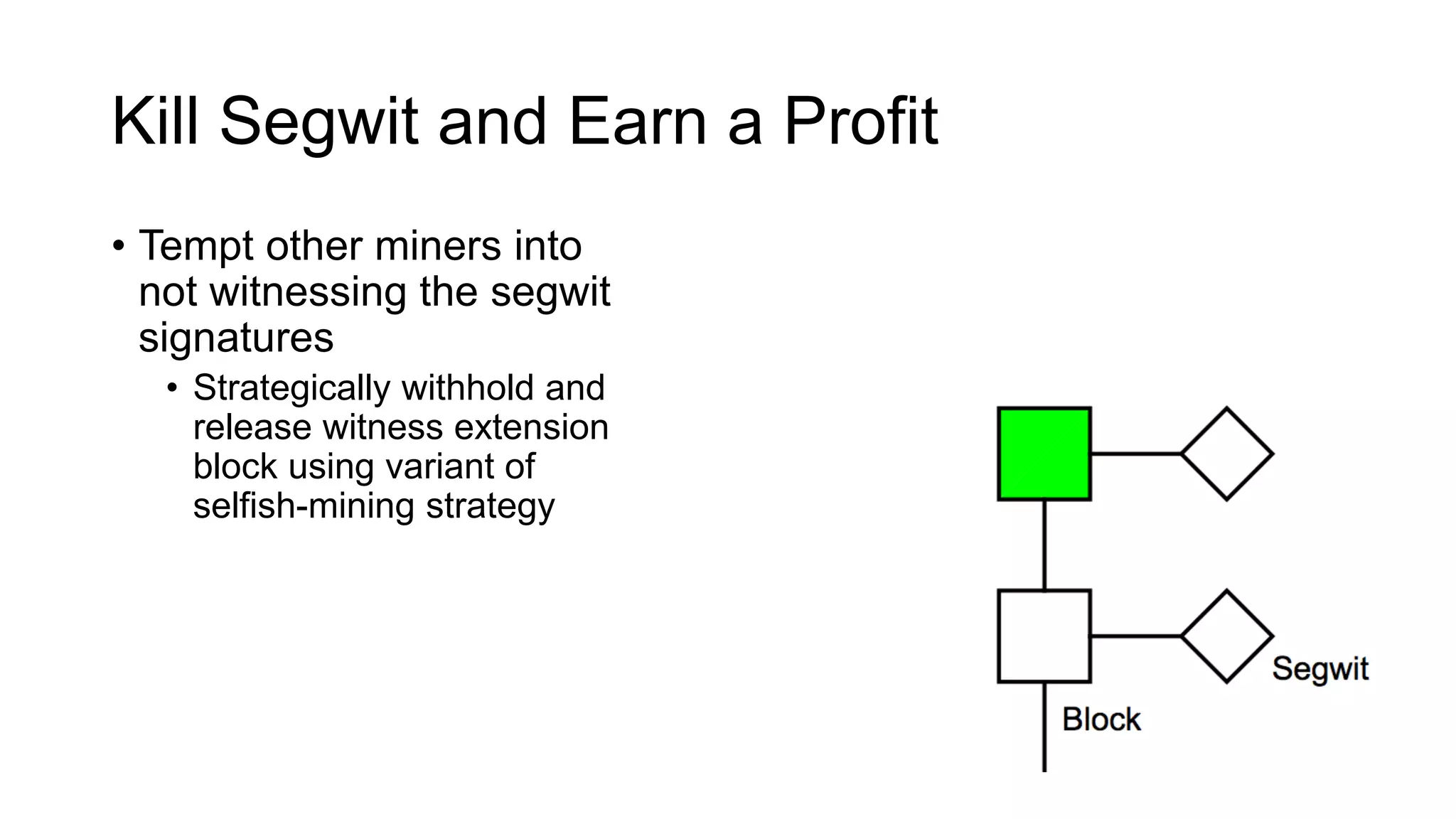
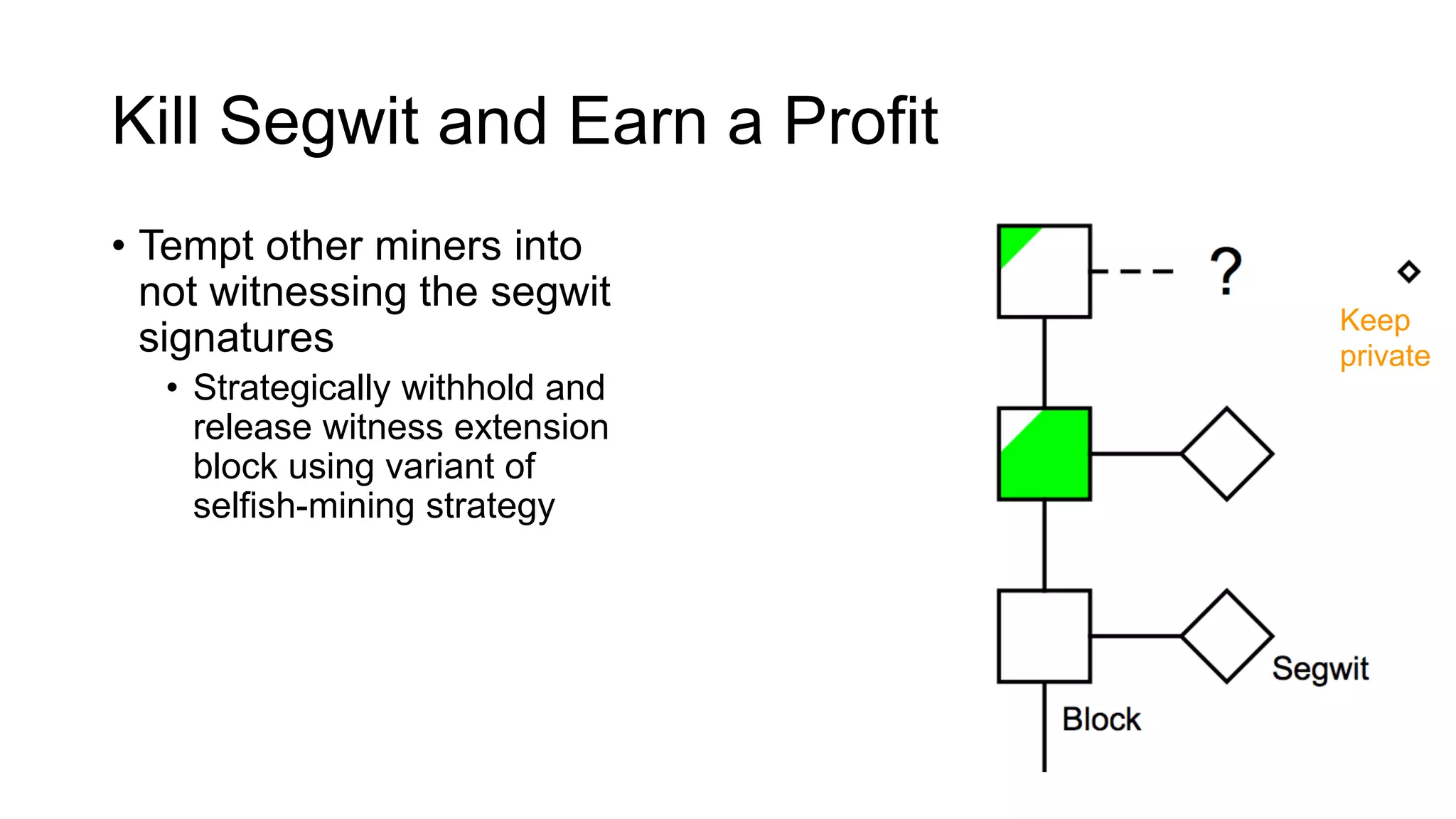
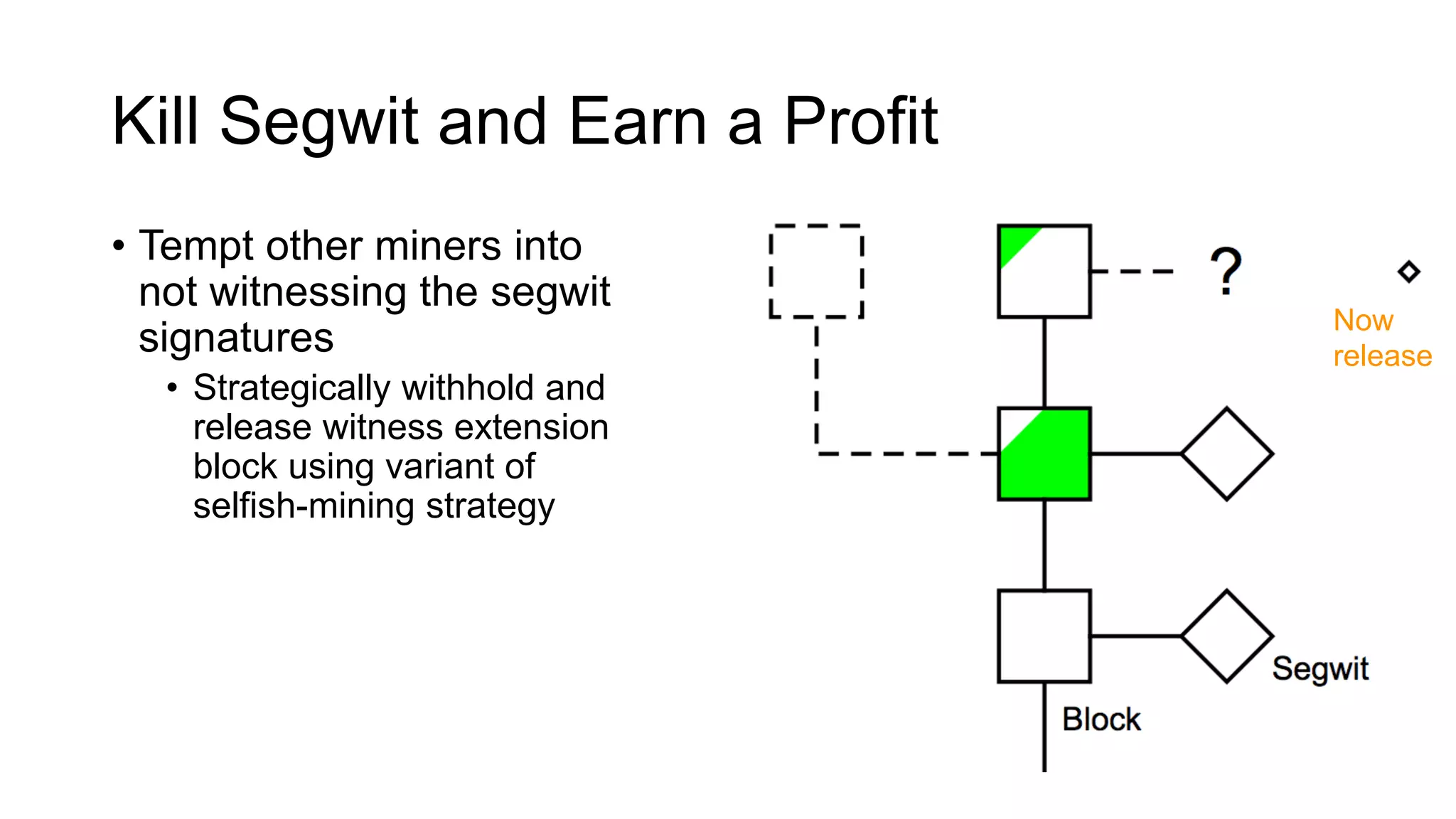
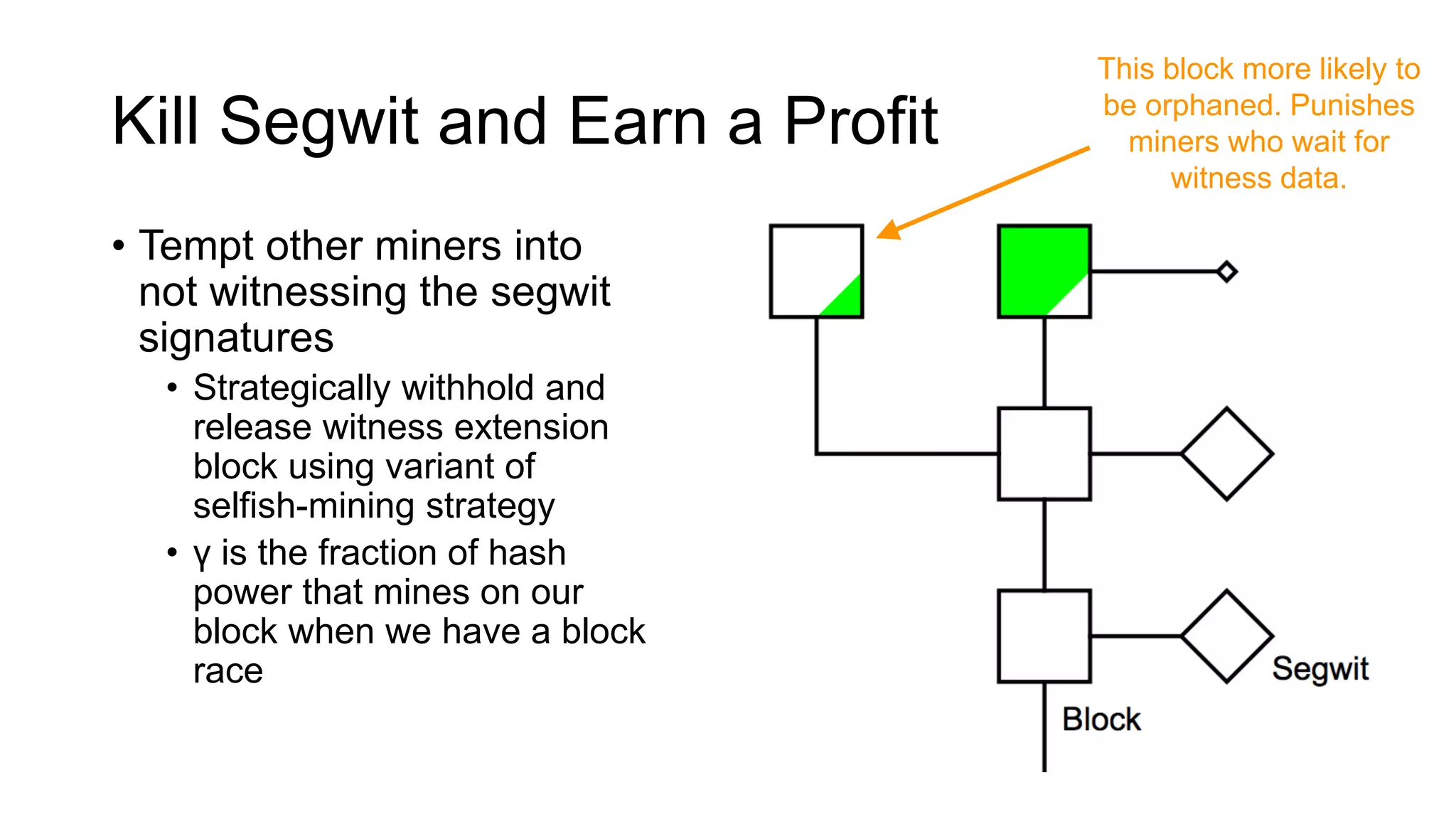
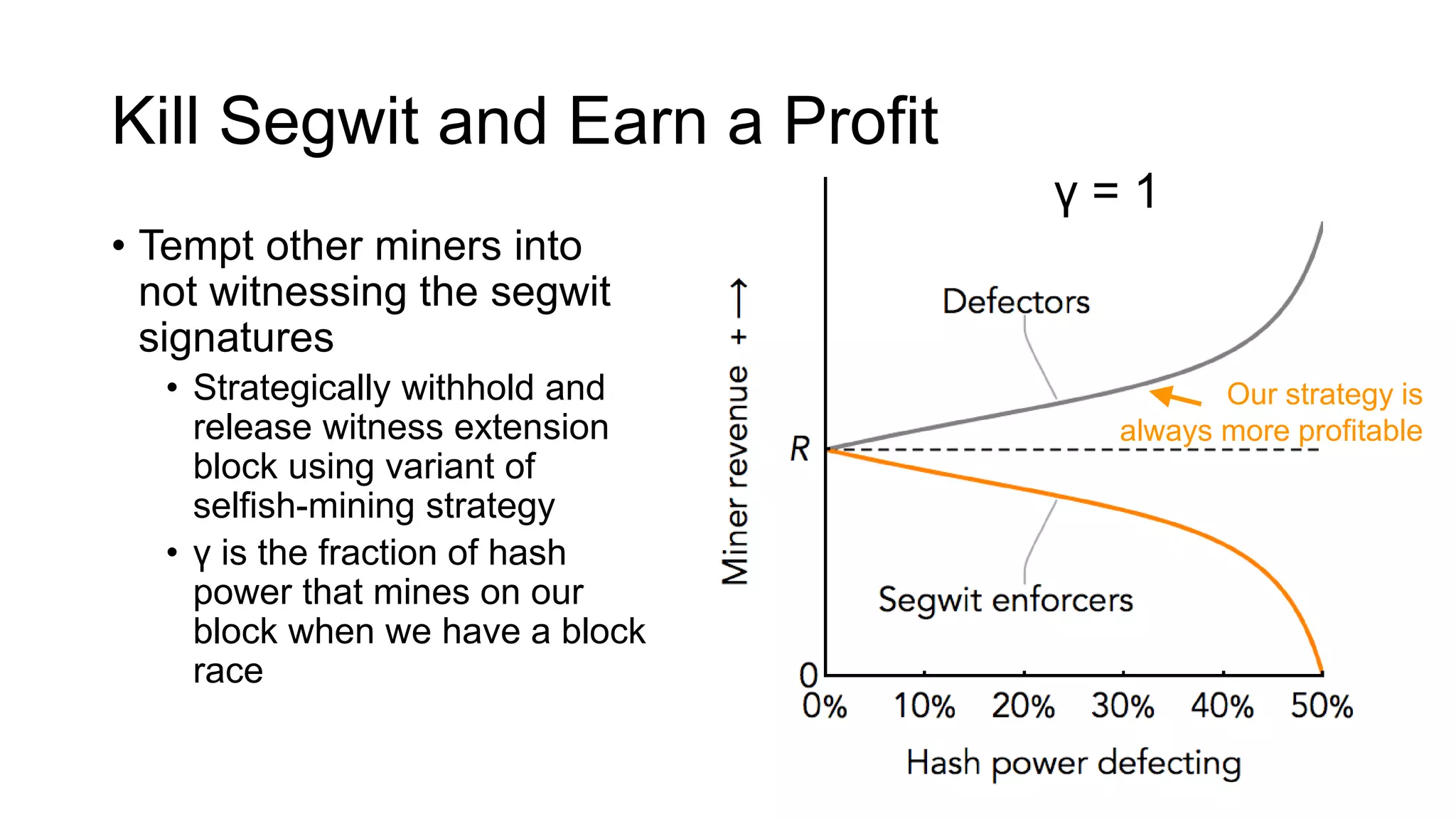
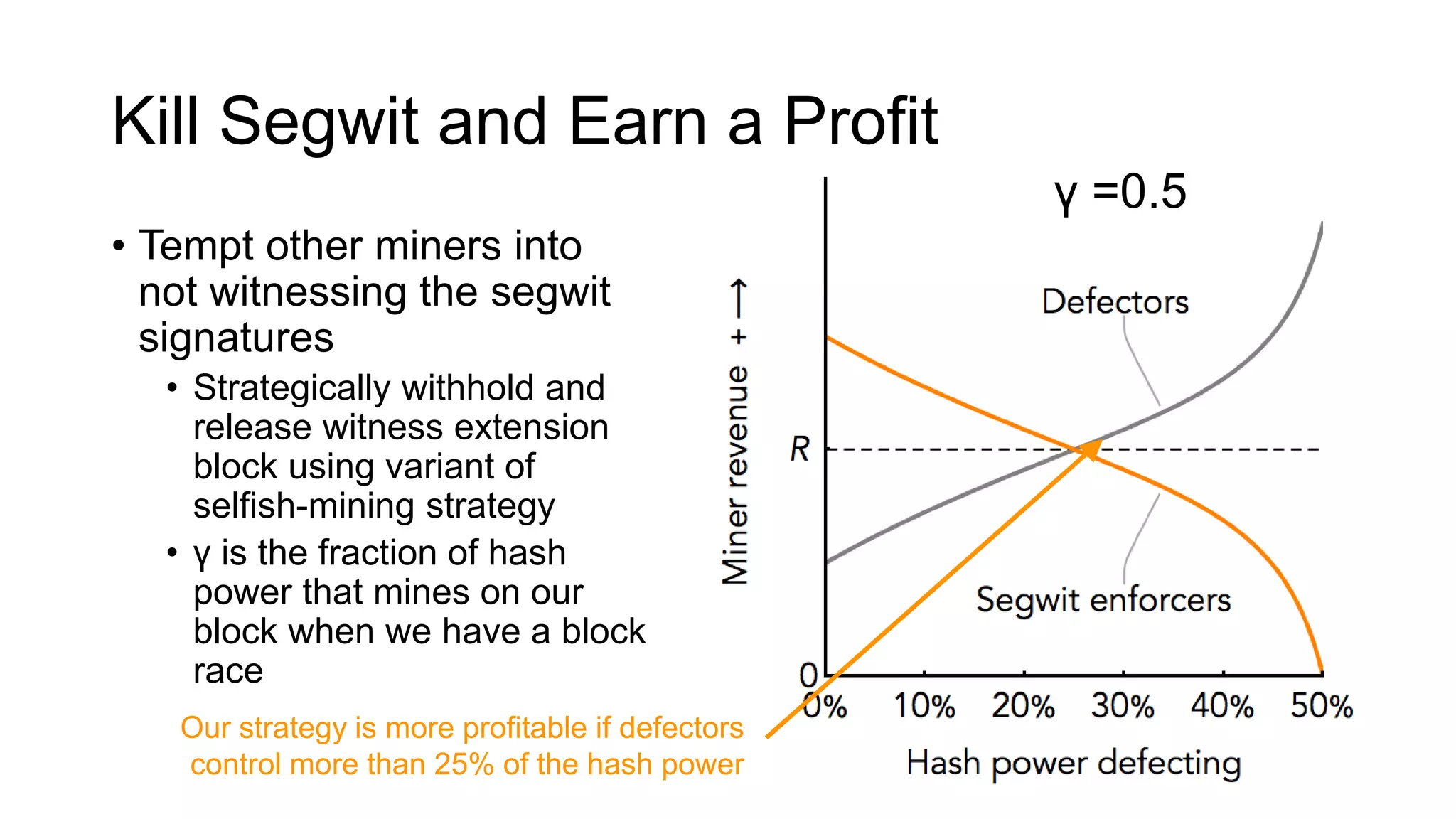
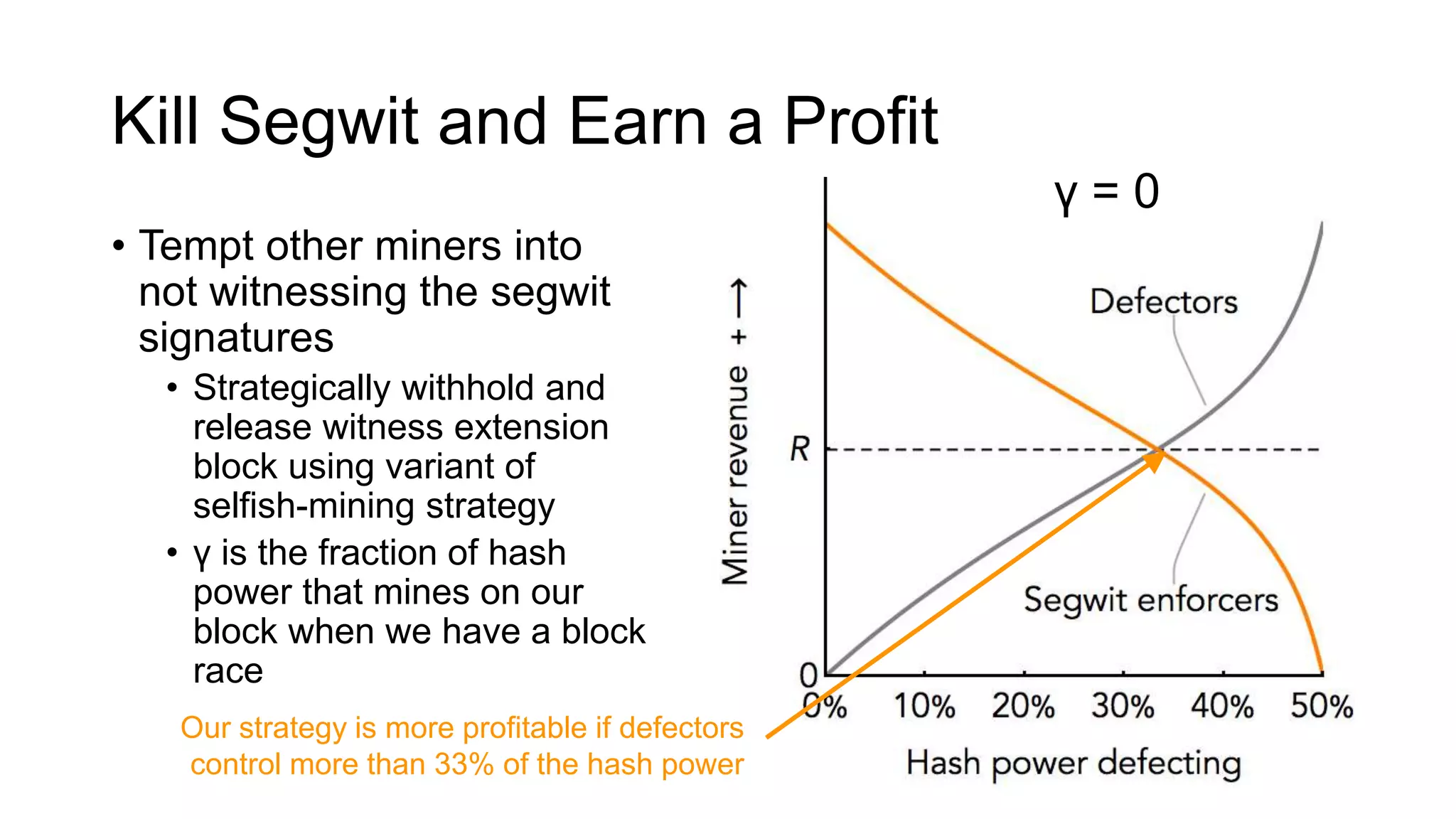
1. Segwit coins have a different definition than bitcoins which results in different properties. Unlike bitcoins, the digital signatures that authorize transactions are not an integral part of the blockchain for segwit coins.
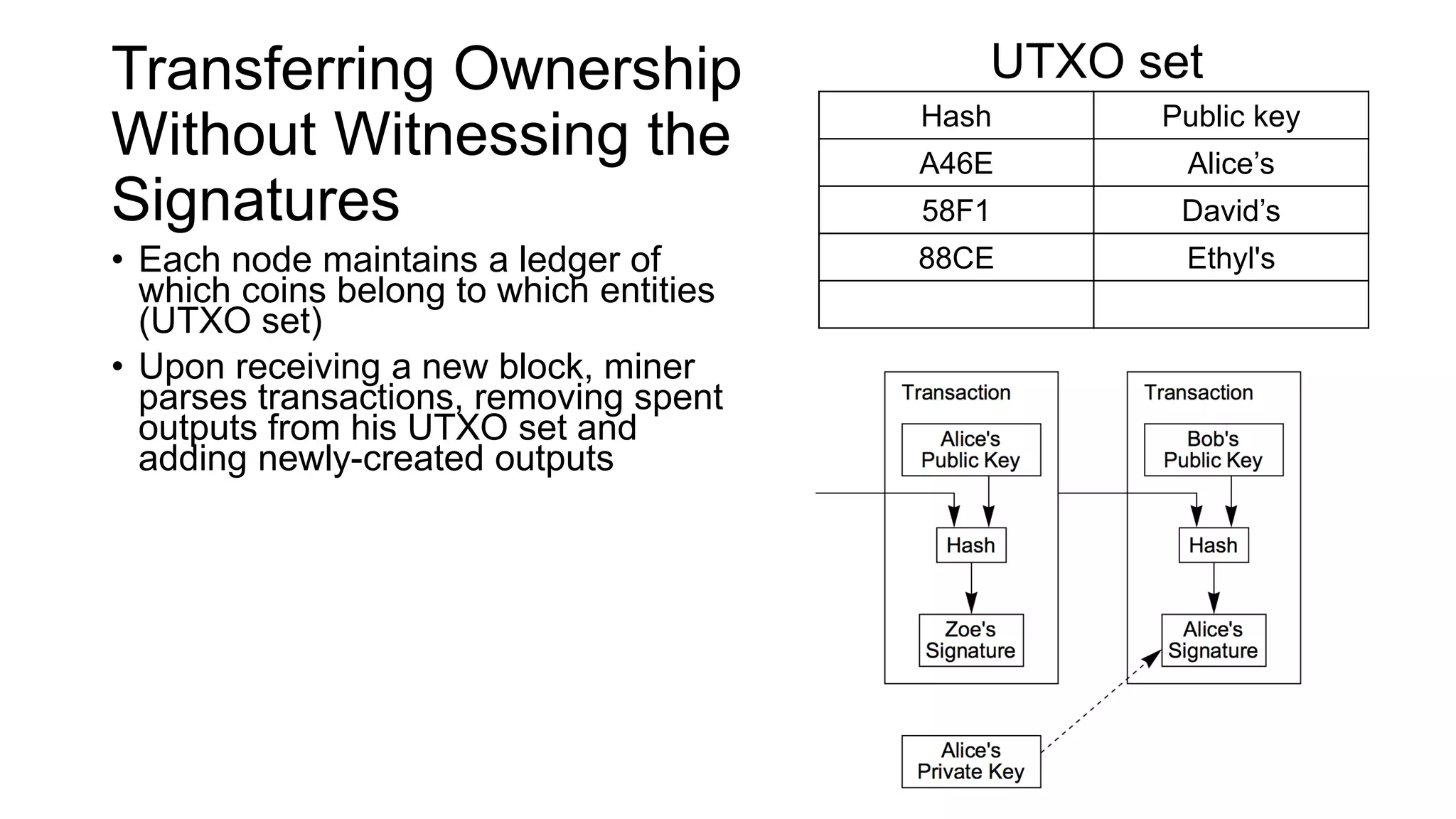
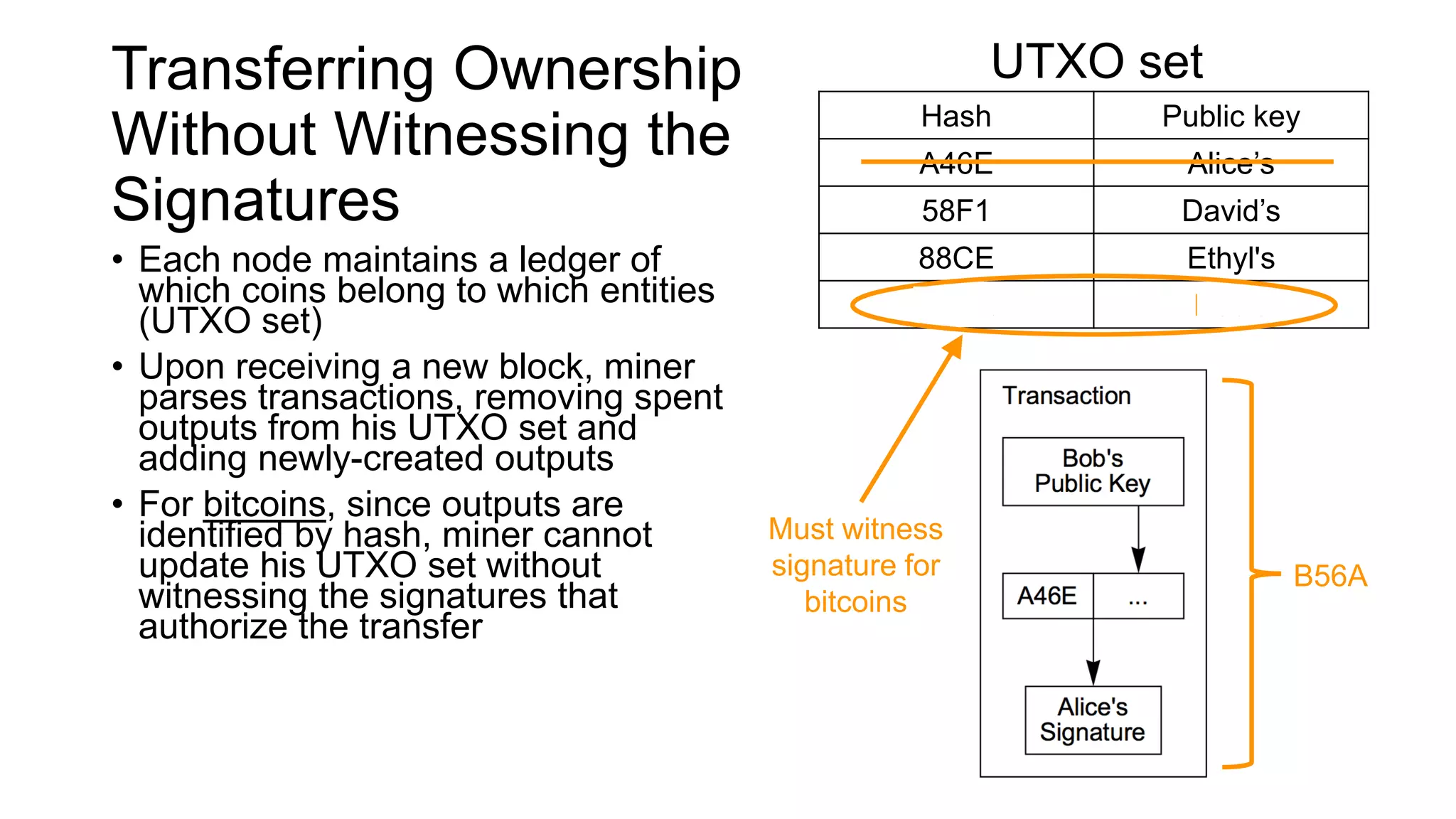
2. Miners can update their ledger of coin ownership (UTXO set) without witnessing the previous owners' digital signatures for segwit coins, but they cannot do this for bitcoins.
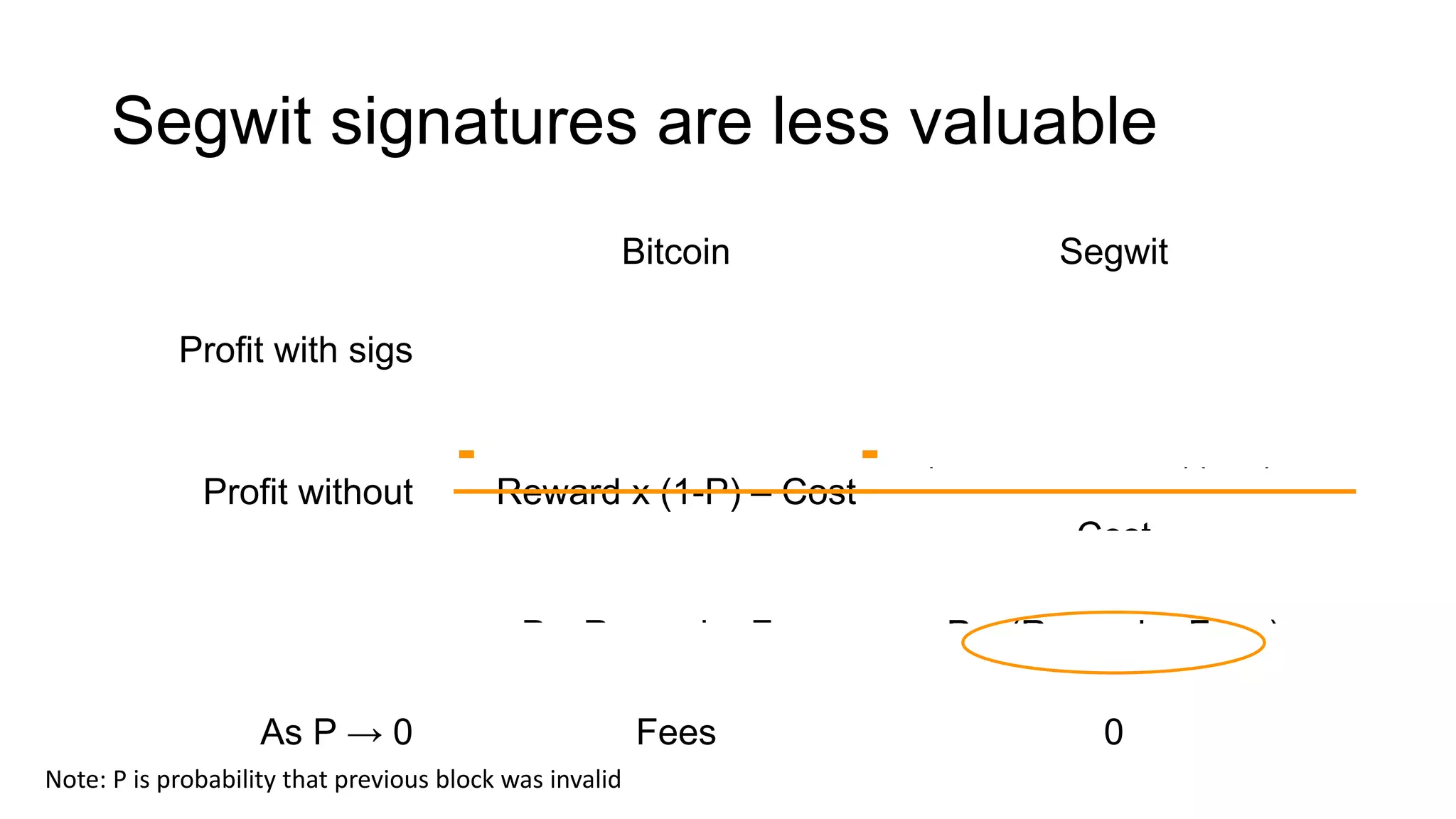
3. The previous owners' digital signatures have less value and importance to miners for segwit coins than for bitcoins because miners do not require them to claim transaction fees.