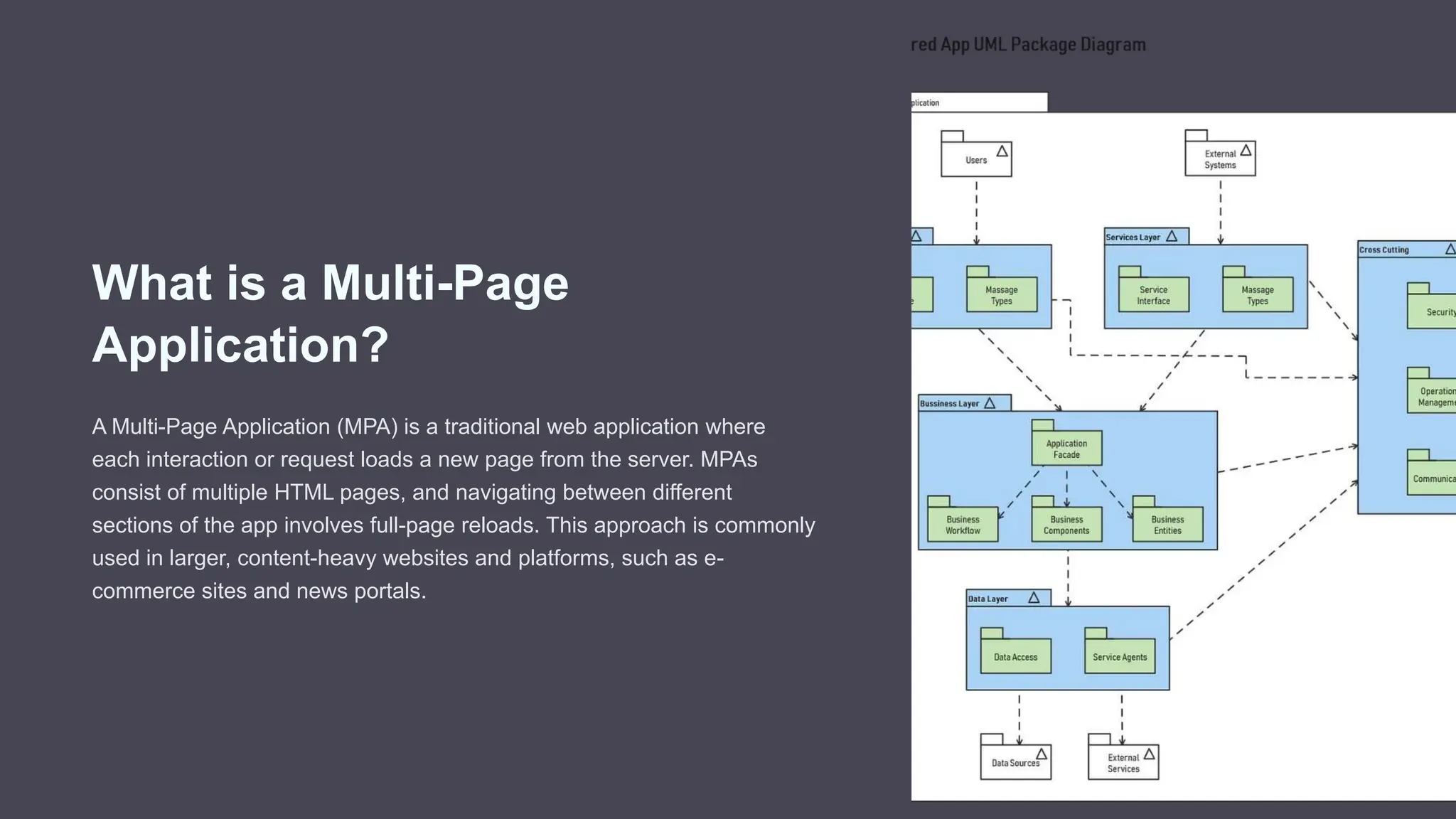
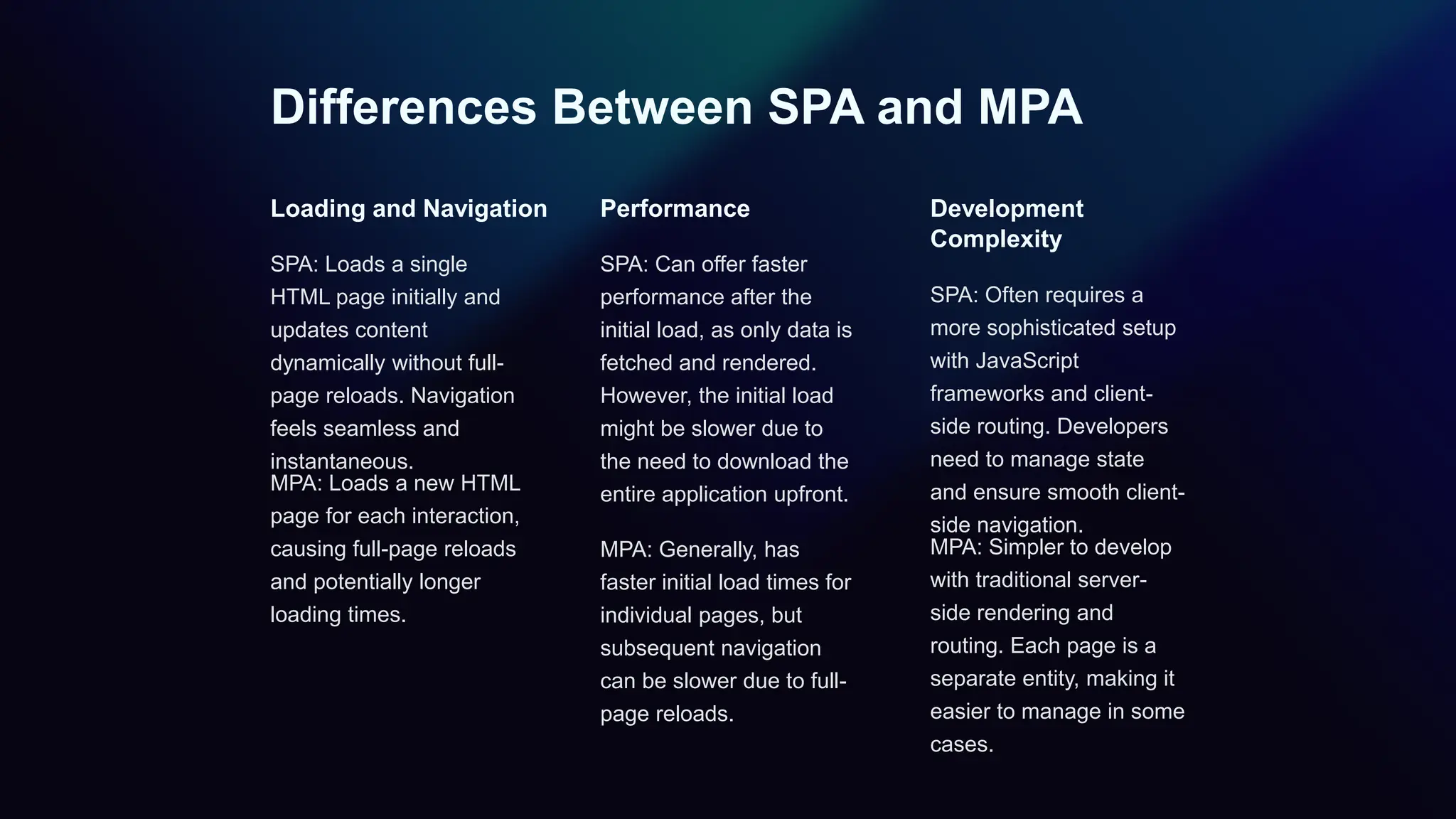
The document outlines the differences between single-page applications (SPAs) and multi-page applications (MPAs), focusing on their key characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks. SPAs offer a more dynamic user experience with faster interactions, while MPAs are more SEO-friendly and simpler to develop, but may have slower navigation. Ultimately, the choice between SPA and MPA depends on specific project requirements and goals.