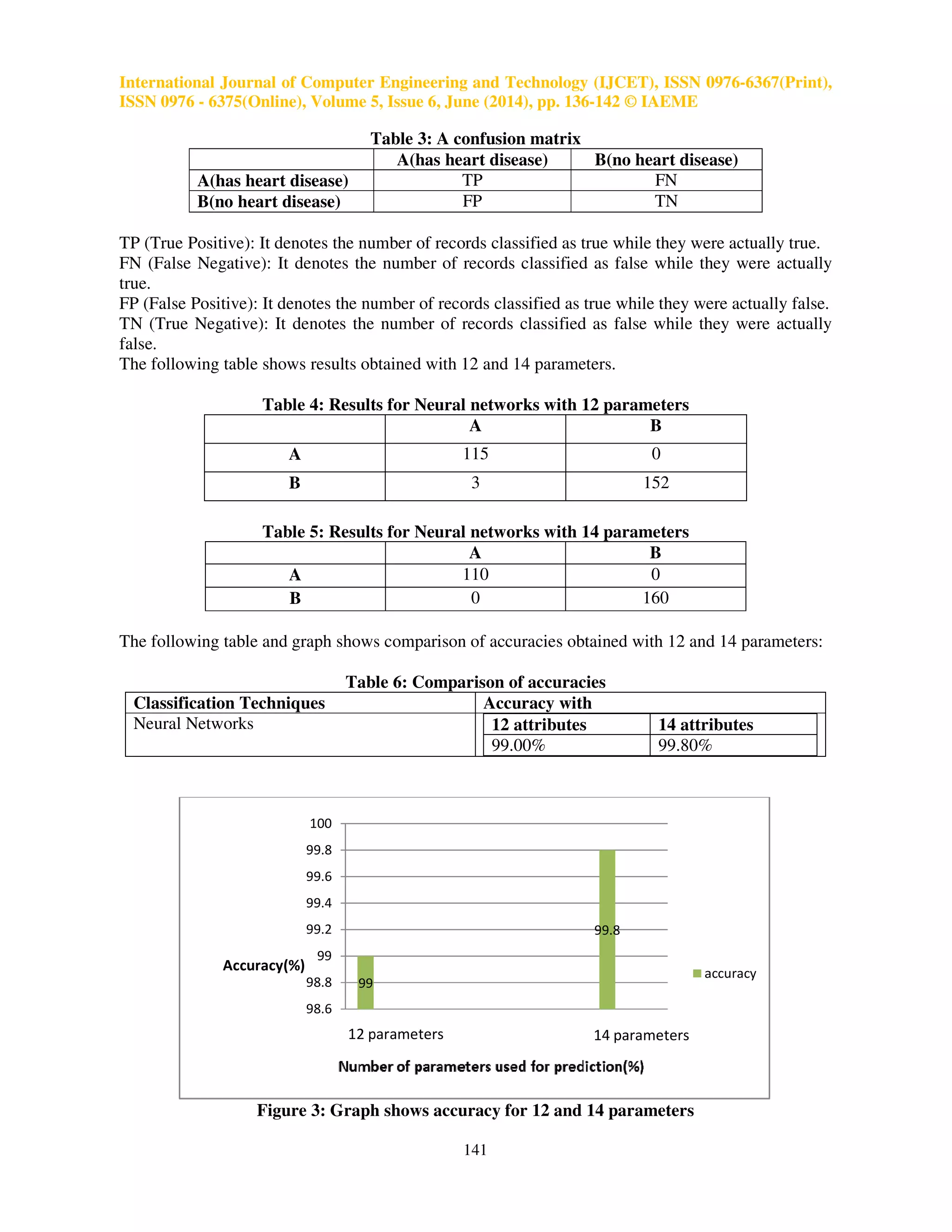
This paper presents an artificial neural network (ANN) based approach for predicting heart disease using a multilayer perceptron neural network with a backpropagation algorithm. The study highlights the significance of data mining in healthcare, showing that the developed system achieved an accuracy of 99.8% with 14 input attributes, which include key factors like smoking and family history. The results indicate that this method can enhance early detection and diagnosis of heart disease, contributing to improved patient outcomes.
![International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET), ISSN 0976-6367(Print),
ISSN 0976 - 6375(Online), Volume 5, Issue 6, June (2014), pp. 136-142 © IAEME
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING
TECHNOLOGY (IJCET)
ISSN 0976 – 6367(Print)
ISSN 0976 – 6375(Online)
Volume 5, Issue 6, June (2014), pp. 136-142
© IAEME: www.iaeme.com/IJCET.asp
Journal Impact Factor (2014): 8.5328 (Calculated by GISI)
www.jifactor.com
136
IJCET
© I A E M E
ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK BASED DATA MINING APPROACH
FOR HUMAN HEART DISEASE PREDICTION
Shikha Dixit, Appu Kuttan. K.K
Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal, India
1. INTRODUCTION
Human heart can be described as a compound body organ contains muscles together with
biological nerves. Human heart pumps nearly 5 litre of blood in the body providing the human body
with renewed material [6]. If operation of heart is not proper, it will affect the other body parts of
human such as brain, kidney etc. various study revealed that heart disease have emerged as the
number one killer in world. About 25 per cent of deaths in the age group of 25-69 years occur
because of heart disease. There are number of factors, which increase the risk of heart disease such
as smoking, cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity and low physical exercise etc. The World
Health Organisation (WHO) has estimated that 12 million deaths occur worldwide, every year due to
heart diseases. WHO estimated by 2030, almost 23.6 million people will die due to Heart
disease.Cardiovascular disease includes coronary heart disease (CHD), cerebrovascular disease
(stroke), Hypertensive heart disease, congenital heart disease, peripheral artery disease, rheumatic
heart disease, inflammatory heart disease [5].
Heart disease prediction can help in reduction of deaths due to heart problems. Diagnosis is
usually based on signs, symptoms and physical examination of a patient. Heart diagnosis is not
always possible at every medical centre and due to lack of advance heart diagnosis equipment
usually physicians goes through intuition and experience to diagnosis the patient. Consequently
medical errors and indivisible results are reasons for computer based diagnosis system [7]. Health
care industry today generates large amount of complex data about patients, hospitals resources,
disease diagnosis, electronic patient records, medical devices etc. The large amounts of data act as a
key source to be processed and analysed for knowledge extraction that act as support for cost-savings
and decision making [3]. Now a days, computer method intelligent data processing are available and
applied for this purpose and thus expert medical system can be created. One of the promising method
is Data mining and Artificial neural network which is highly effective tool used in classification task
as well as to solve many important problem, such as signal enhancement, identification and
prediction of signals and factors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/50120140506016-140924011335-phpapp02/75/50120140506016-1-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET), ISSN 0976-6367(Print),
ISSN 0976 - 6375(Online), Volume 5, Issue 6, June (2014), pp. 136-142 © IAEME
137
2. ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK
Artificial Neural network (ANN) are originally modelled as a computational model [4] to
mimic the way of brain works. Brain is made from small functional units called neurons. Each
neuron connected to several other neurons by dendrites and exons. Dendrites receive the signal from
other neurons and act as a input to the neuron. Similar way artificial neural network built from
several computational units which are sometimes called neurons. These units are connected links and
each links have a weight associate with it. Each unit computes the weighted some of the input values
and transfer function transforms a final valve that act as a unit output valve. Before using any ANN
model it must be trained with representative data [8]. The ANNcan be classified in two main groups
according to the way they learn,
I. Supervised learning:
It is a simple model, in which the networks compute a response to each input
and then compare it with target value. If the computed response differs from
target value, the weights of the network are adapted according to a learning
rule.
E.g.: Single-layer perceptron, Multi-layer perceptron.
II. Unsupervised learning:
These networks learn by identifying special features in the problems they are
exposed to.
e.g.: Self-organizing feature maps.
• Neural network has following properties:
• Nonlinearity
• Learning ability
• Input-output mapping
• Adaptivity
• Evidential response
• Fault tolerance
• Neurological analogy
In medical field, decision making is done by neural network because they provide more
accurate results.
3. NEURAL NETWORK FOR HEART DISEASE PREDICTION
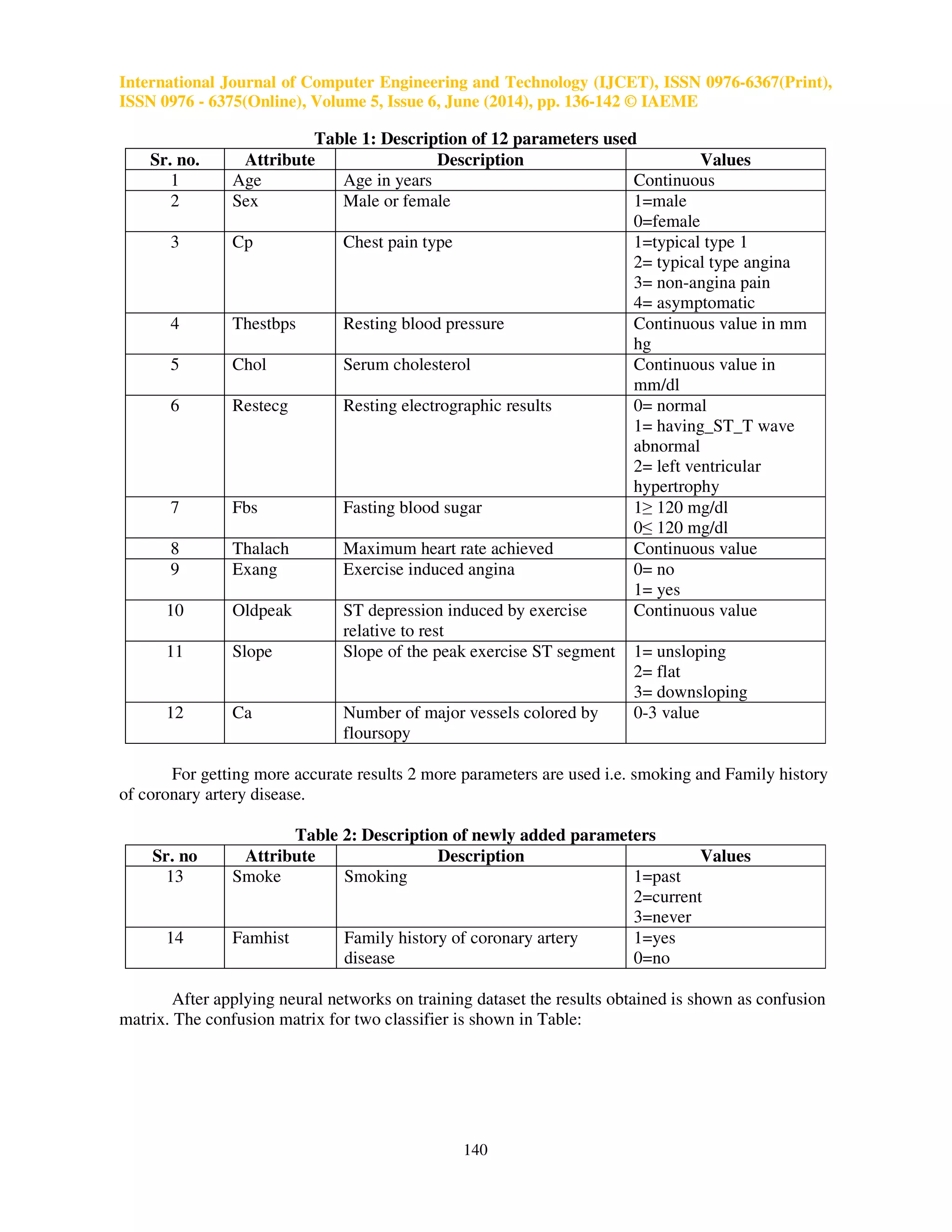
In this study, decision support system is developed for predicting heart disease of a patient.
The prediction is done based on historical heart disease database. The system uses medical terms
such as sex, blood pressure and cholesterol like 12 input attributes are used(web). To get more
appropriate results, two more attributes ie. Smoking and family history of coronary artery disease, as
these are considered as most prominent attributes for heart disease. For this, the technique of
Multilayer Perception Neural Network (MLPNN) with Backpropagation algorithm (BP) is used.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/50120140506016-140924011335-phpapp02/75/50120140506016-2-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Computer Engineering and Technology (IJCET), ISSN 0976-6367(Print),
ISSN 0976 - 6375(Online), Volume 5, Issue 6, June (2014), pp. 136-142 © IAEME
3.1 Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network(MLPNN)
138
In Artificial Neural Network the most important model is MLPNN because of its multilayer
infrastructure.
Figure 1: Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network
The MLPNN consists of one input layer, one output layer and one or more hidden layers.
Each layer consists of one or more nodes, represented by small circles. The lines between nodes
indicate flow of information from one node to another node. The input layer receives the signal from
external nodes. The output of input layer is given to hidden layer, through weighted connection links.
It performs computations and transmits the result to output layer through weighted links. The output
of hidden layer is forwarded to output layer. This output layer performs computations and produce
final result[1].
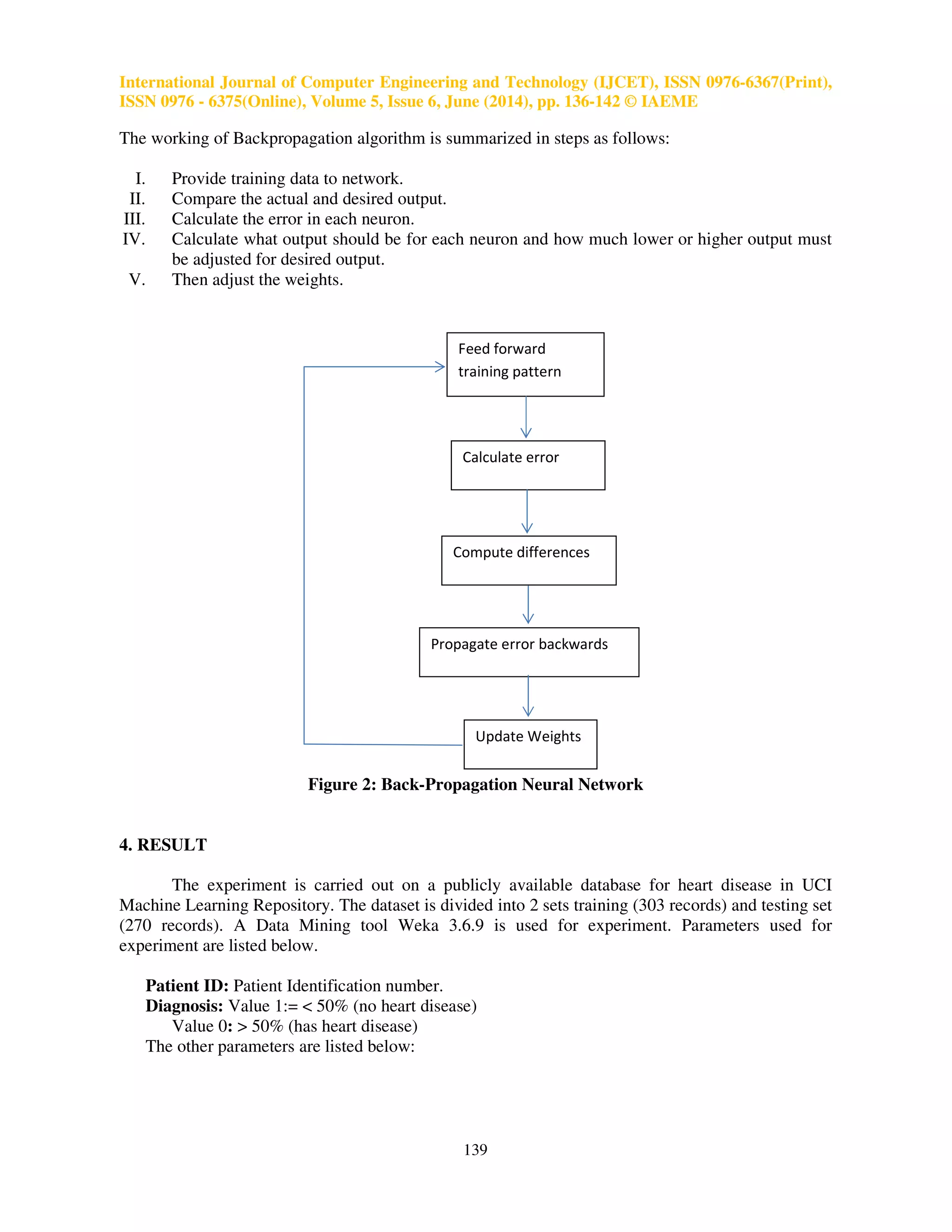
The working of Multilayer perceptron neural network is summarised in steps as mentioned below:
I. Input data is provided to input layer for processing, which produces a predicted output.
II. The predicted output is subtracted from actual output and error value is calculated.
III. The network then uses a Backpropagation algorithm which adjusts the weights.
IV. For weights adjusting it starts from weights between output layer nodes and last hidden layer
nodes and works backwards through network.
V. When back propagation is finished, the forwarding process starts again.
VI. The processes repeated until the error between predicted and actual ouput is minimized.
3.2 Backpropagation Network
The most widely used training algorithm for multilayer and feed forward network is
Backpropagation. The name given is back propagation because, it calculates the difference between
actual and predicted values from output nodes backward to nodes in previous layer. This is done to
improve weights during processing [2].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/50120140506016-140924011335-phpapp02/75/50120140506016-3-2048.jpg)